Applications of Green Carbon Dots in Personalized Diagnostics for Precision Medicine
Abstract
:1. Introduction
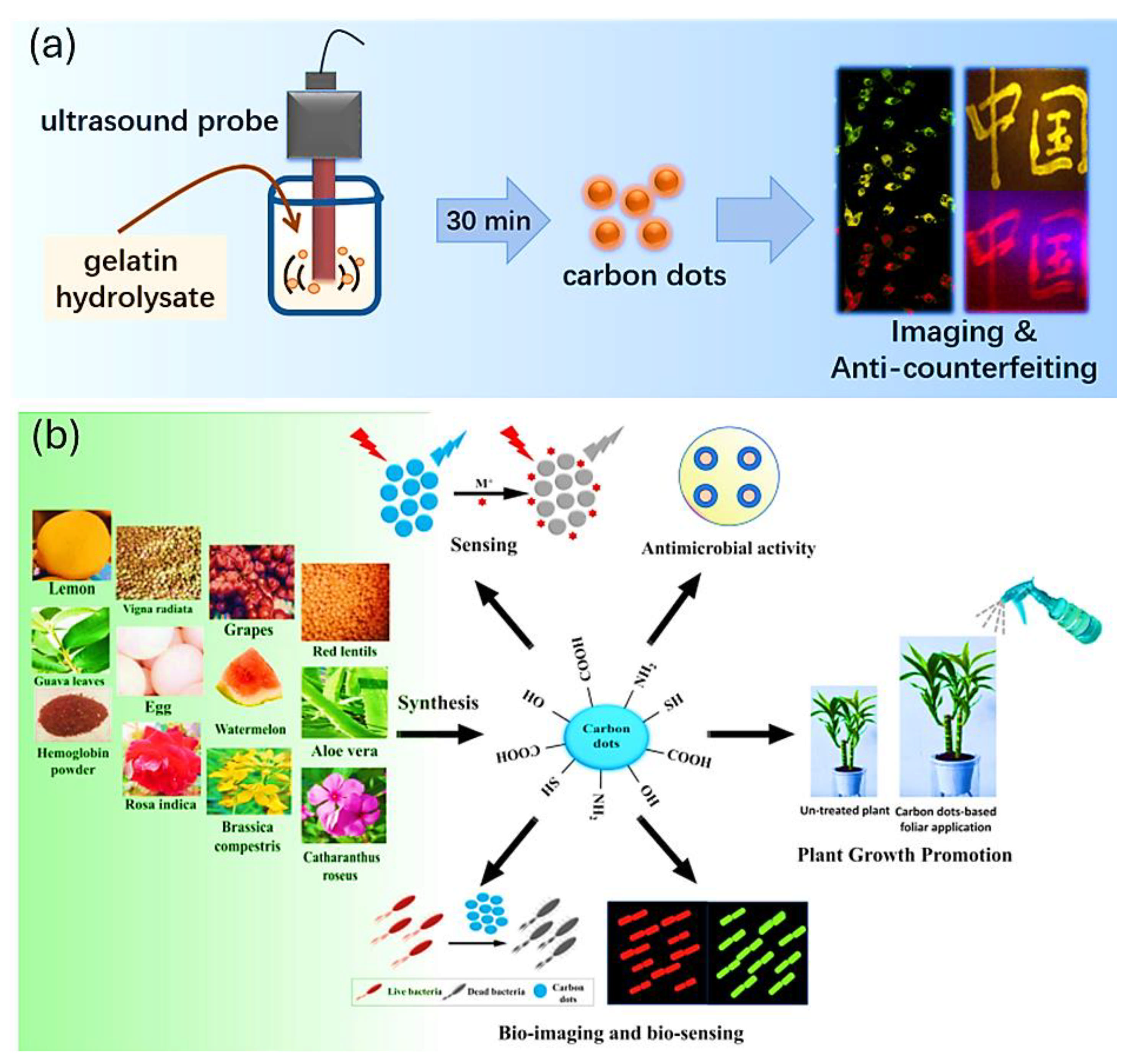
2. Fundamentals of Green Carbon Dots
Top-Down and Bottom-Up Approaches for Carbon Dots
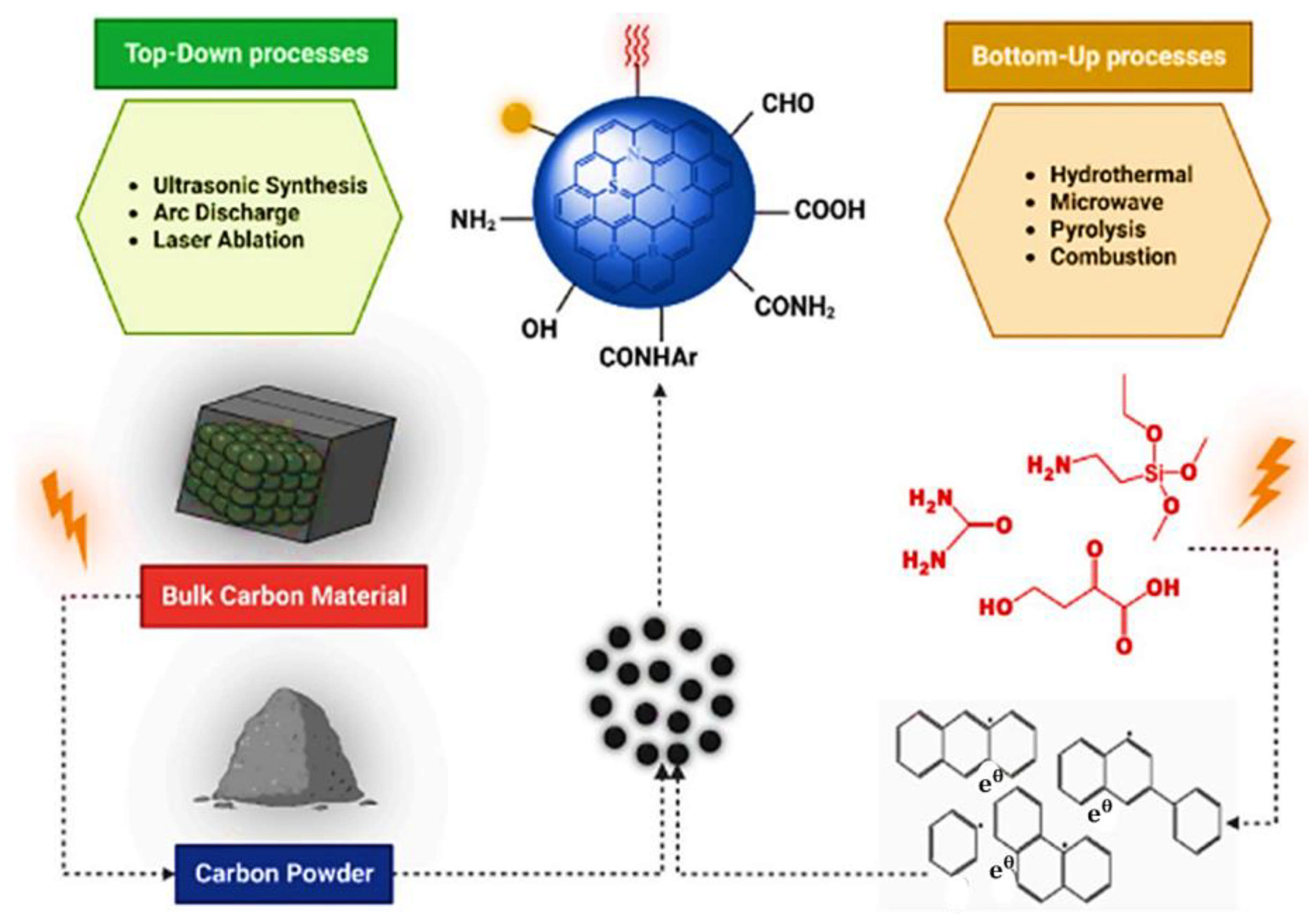
3. Role of Carbon Dots in Personalized Diagnostics
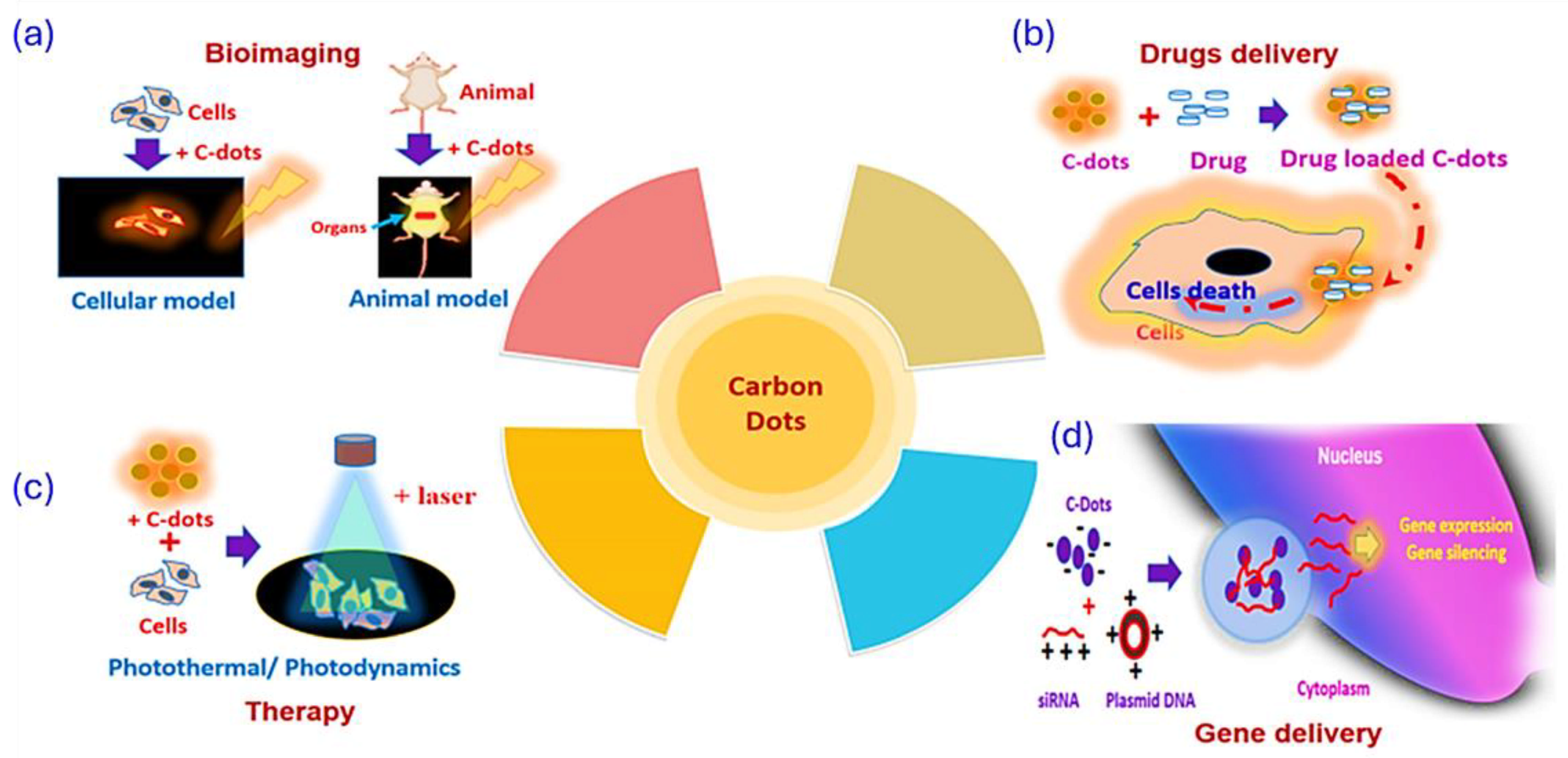
Photoluminescent Properties in Imaging-Based Diagnostics
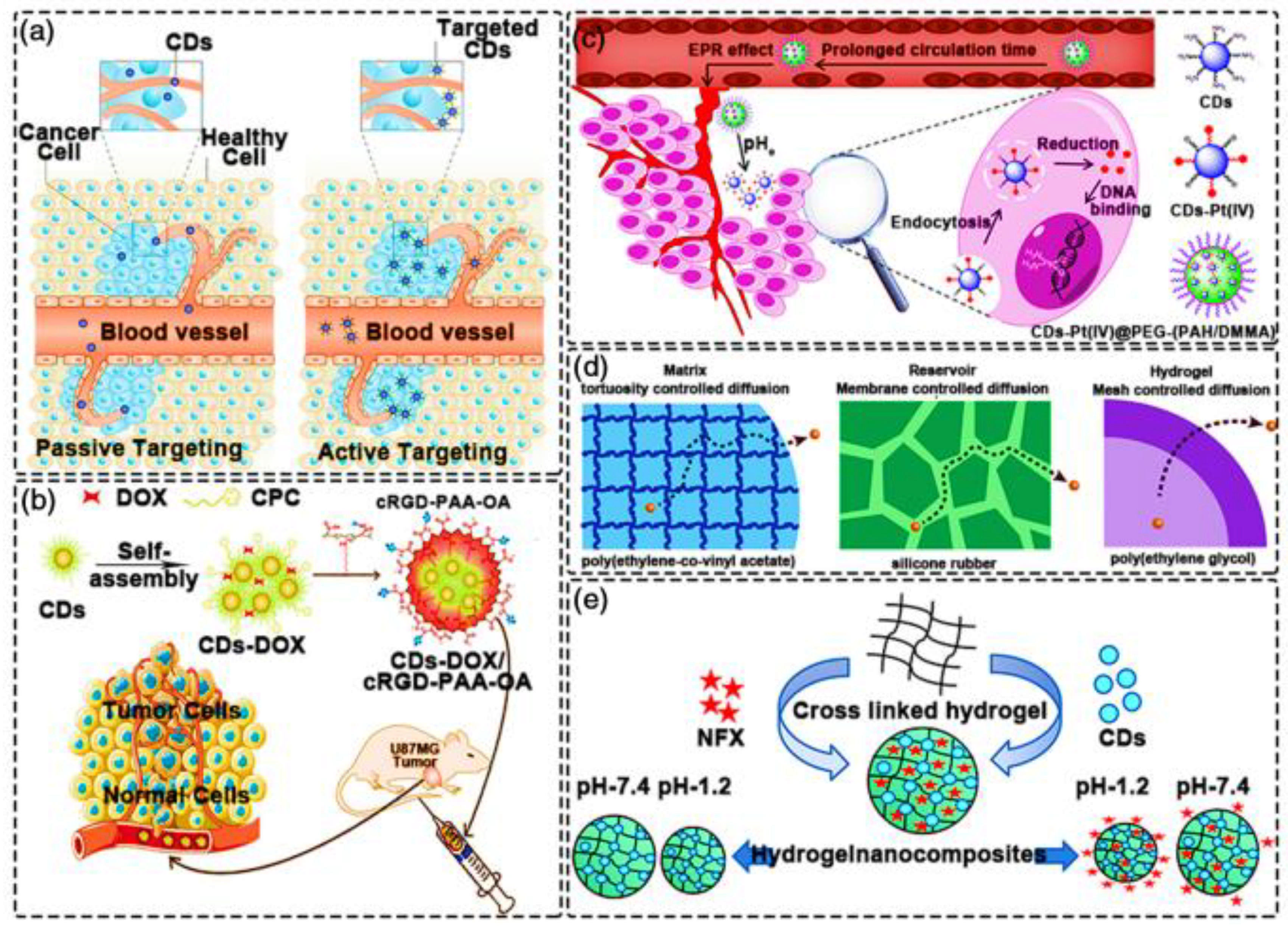
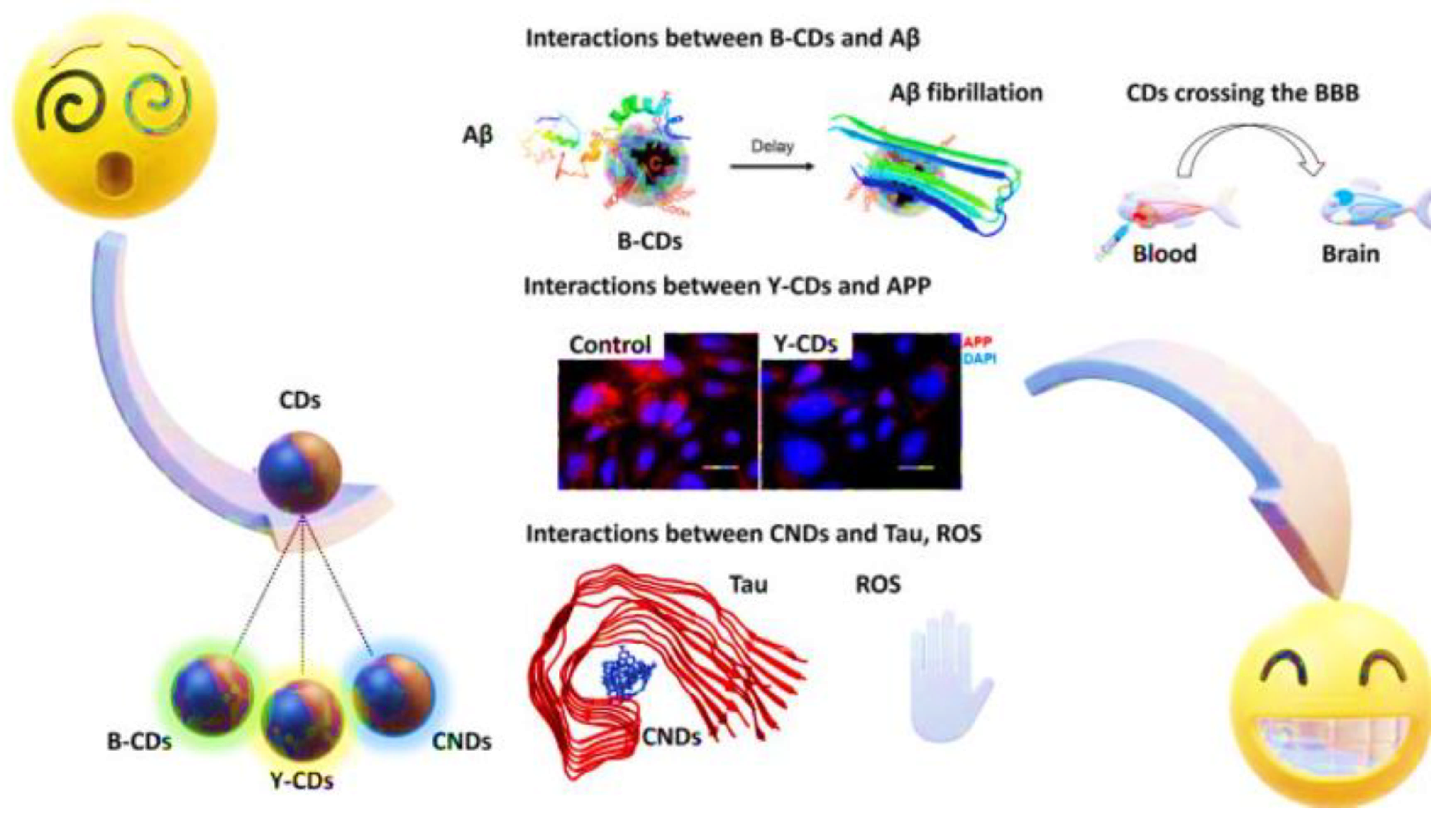
4. Applications of GCDs in Precision Medicine
4.1. Personalized Diagnostics for Cancer
Imaging for Precision Medicine
4.2. Therapy Selection and Monitoring
Drug Delivery Systems
5. Challenges in the Application of GCDs
5.1. Standardization and Scalability of Synthesis
5.2. Understanding and Minimizing Toxicity
5.3. Limited Targeting Precision and Delivery Efficiency
6. Future Directions for GCDs in Precision Medicine
6.1. Developing Targeted and Functionalized GCDs
6.1.1. Enhancing Biocompatibility and Safety Profiles
6.1.2. Advancing Bioinformatics Integration and Real-Time Monitoring Systems
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jangjou, A.; Zareshahrabadi, Z.; Abbasi, M.; Talaiekhozani, A.; Kamyab, H.; Chelliapan, S.; Vaez, A.; Golchin, A.; Tayebi, L.; Vafa, E.; et al. Time to Conquer Fungal Infectious Diseases: Employing Nanoparticles as Powerful and Versatile Antifungal Nanosystems Against a Wide Variety of Fungal Species. Sustainability 2022, 14, 12942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnaiah, P.; Atchudan, R.; Gangadaran, P.; Perumal, S.; Rajendran, R.L.; Sundramoorthy, A.K.; Kumar, R.S.; Ramalingam, S.; Ahn, B.-C.; Lee, S.W.; et al. A sustainable synthesis and applications of biomass waste-derived tunable fluorescent carbon dots: In vitro and in vivo fluorescent imaging. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2025, 458, 115944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moniruzzaman, M.; Kim, J. Synthesis and post-synthesis strategies for polychromatic carbon dots toward unique and tunable multicolor photoluminescence and associated emission mechanism. Nanoscale 2023, 15, 13858–13885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Lin, Q.; Song, J.; Shen, H.; Zhang, H.; Li, L.S.; Li, X.; Du, Z. Quantum-dot light-emitting diodes for outdoor displays with high stability at high brightness. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2020, 8, 1901145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Gao, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, Y.; Lin, Q.; Li, Z.; Chen, L.; Zeng, Z.; Li, X.; Jia, Y.; et al. Visible quantum dot light-emitting diodes with simultaneous high brightness and efficiency. Nat. Photonics 2019, 13, 192–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasari, B.L.; Nouri, J.M.; Brabazon, D.; Naher, S. Graphene and derivatives—Synthesis techniques, properties and their energy applications. Energy 2017, 140, 766–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, W.; Li, P.; Zia, M.; Bhuiyan, S.A.; Liu, Y.; Chen, D.; Tudi, M.; Gao, Y.; Yan, X.; Jia, Y.; et al. A Comparative Review on Carbon Nanomaterials and Their Impact on Plant Growth with the Lens of Green Chemistry Principles. Glob. Chall. 2024, 8, 2400008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biranje, A.; Azmi, N.; Tiwari, A.; Chaskar, A. Quantum dots based fluorescent probe for the selective detection of heavy metal ions. J. Fluoresc. 2021, 31, 1241–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F. Synthesis and Device Applications of Graphene Derivatives and Quantum Dots; Springer Nature: London, UK, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, A.U.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Ullah, M.W.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, D.; Kang, Z.; Mao, B. Advancements in the green synthesis of carbon dots for sustainable development. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2024, 41, e01004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, Y.; Cai, F.; Wang, D.; Wang, J.-X.; Chen, J.-F. Colloidal synthesis of semiconductor quantum dots toward large-scale production: A review. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 1790–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Li, X.; Fei, L.; Liu, W.; Liu, X.; Xu, H.; Liu, Y. A review on sustainable synthetic approaches toward photoluminescent quantum dots. Green Chem. 2022, 24, 675–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamba, R.; Yukta, Y.; Mondal, J.; Kumar, R.; Pani, B.; Singh, B. Carbon dots: Synthesis, characterizations, and recent advancements in biomedical, optoelectronics, sensing, and catalysis applications. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2024, 7, 2086–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatimuria, M.; Phukan, P.; Bag, S.; Ghosh, J.; Gavvala, K.; Pabbathi, A.; Das, J. Green carbon dots: Applications in development of electrochemical sensors, assessment of toxicity as well as anticancer properties. Catalysts 2023, 13, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdellatif, A.A.; Younis, M.A.; Alsharidah, M.; Al Rugaie, O.; Tawfeek, H.M. Biomedical applications of quantum dots: Overview, challenges, and clinical potential. Int. J. Nanomed. 2022, 17, 1951–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, Y.R.; Deshmukh, K.; Sadasivuni, K.K.; Pasha, S.K.K. Graphene quantum dot based materials for sensing, bio-imaging and energy storage applications: A review. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 23861–23898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, D.; Sarkar, K.; Devi, P.; Kim, K.-H.; Kumar, P. Current and future perspectives of carbon and graphene quantum dots: From synthesis to strategy for building optoelectronic and energy devices. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 135, 110391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gidwani, B.; Sahu, V.; Shukla, S.S.; Pandey, R.; Joshi, V.; Jain, V.K.; Vyas, A. Quantum dots: Prospectives, toxicity, advances and applications. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 61, 102308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wambu, E.W.; Huang, J. Chemistry of Graphene: Synthesis, Reactivity, Applications and Toxicities; BoD—Books on Demand: Norderstedt, Germany, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, H.; Peng, H.; He, H.; Feng, J.; Sun, Y.; He, H.; Li, L. Green and low-temperature synthesis of carbon dots for simple detection of kaempferol. J. Fluoresc. 2023, 33, 1971–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.T.; Yin, X.B. Carbon dots, unconventional preparation strategies, and applications beyond photoluminescence. Small 2019, 15, 1901803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.; Tiwari, P.; Mobin, S.M. Sustainable carbon-dots: Recent advances in green carbon dots for sensing and bioimaging. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 8904–8924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pho, Q.H.; Escriba-Gelonch, M.; Losic, D.; Rebrov, E.V.; Tran, N.N.; Hessel, V. Survey of synthesis processes for N-doped carbon dots assessed by green chemistry and circular and EcoScale metrics. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 4755–4770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.L.; Liu, Z.X.; Yuan, Y.H. Carbon dots: Materials, synthesis, properties and approaches to long-wavelength and multicolor emission. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 3794–3809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waskaas, M. Synthesis and Comparative Analysis of Carbon Dots: A Study on Continuous Flow, Microwave, and Furnace Methods. Master’s Thesis, The University of Bergen, Bergen, Norway, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, I.; Arora, R.; Dhiman, H.; Pahwa, R. Carbon quantum dots: Synthesis, characterization and biomedical applications. Turk. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 15, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adewuyi, A.O.; Awodumi, O.B. Renewable and non-renewable energy-growth-emissions linkages: Review of emerging trends with policy implications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 69, 275–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güney, T. Renewable energy, non-renewable energy and sustainable development. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. World Ecol. 2019, 26, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majhi, K.C.; Karfa, P.; Kumar, S.; Madhuri, R. Water as the green solvent in organic synthesis. Ind. Appl. Green Solvents 2019, 2, 182–201. [Google Scholar]
- Hessel, V.; Tran, N.N.; Asrami, M.R.; Tran, Q.D.; Long, N.V.D.; Escribà-Gelonch, M.; Tejada, J.O.; Linke, S.; Sundmacher, K. Sustainability of green solvents—Review and perspective. Green Chem. 2022, 24, 410–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maraveas, C. Production of sustainable and biodegradable polymers from agricultural waste. Polymers 2020, 12, 1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velvizhi, G.; Shanthakumar, S.; Das, B.; Pugazhendhi, A.; Priya, T.S.; Ashok, B.; Nanthagopal, K.; Vignesh, R.; Karthick, C. Biodegradable and non-biodegradable fraction of municipal solid waste for multifaceted applications through a closed loop integrated refinery platform: Paving a path towards circular economy. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 731, 138049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgakilas, V.; Perman, J.A.; Tucek, J.; Zboril, R. Broad family of carbon nanoallotropes: Classification, chemistry, and applications of fullerenes, carbon dots, nanotubes, graphene, nanodiamonds, and combined superstructures. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 4744–4822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Yang, M.; Duan, Y. Chemistry, biology, and medicine of fluorescent nanomaterials and related systems: New insights into biosensing, bioimaging, genomics, diagnostics, and therapy. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 6130–6178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phan, L.M.T.; Cho, S. Retracted: Fluorescent Carbon Dot-Supported Imaging-Based Biomedicine: A Comprehensive Review. Bioinorg. Chem. Appl. 2022, 2022, 9303703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paramasivam, G.; Palem, V.V.; Meenakshy, S.; Suresh, L.K.; Gangopadhyay, M.; Antherjanam, S.; Sundramoorthy, A.K. Advances on Carbon Nanomaterials and Their Applications in Medical Diagnosis and Drug Delivery. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2024, 241, 114032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahana, S.; Gautam, A.; Singh, R.; Chandel, S. A recent update on development, synthesis methods, properties and application of natural products derived carbon dots. Nat. Prod. Bioprospect. 2023, 13, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, S.; Daniel, S. Green synthesis of zero-dimensional carbon nanostructures in energy storage applications—A review. Energy Storage 2024, 6, e500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juengst, E.; McGowan, M.L.; Fishman, J.R.; Settersten, R.A., Jr. From “personalized” to “precision” medicine: The ethical and social implications of rhetorical reform in genomic medicine. Hastings Cent. Rep. 2016, 46, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- YahyaAlmakrami, I.; Al Omorat, T.; GhannamShreaf, M.M.; Al-Yami, S.A.S.; Alyami, K.A. Tailoring Treatment to the Individual: A Critical Examination of Precision Medicine and Personalized Healthcare Through the Lens of Genetics, Lifestyle, and Environmental Factors. Chelonian Res. Found. 2023, 18, 550–564. [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborty, R.; Vilya, K.; Pradhan, M.; Nayak, A.K. Recent advancement of biomass-derived porous carbon based materials for energy and environmental remediation applications. J. Mater. Chem. A 2022, 10, 6965–7005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, B.; Wang, A. Fabrication and Applications of Carbon/Clay Mineral Nanocomposites. In Nanomaterials from Clay Minerals; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 537–587. [Google Scholar]
- Unnikrishnan, B.; Wu, R.-S.; Wei, S.-C.; Huang, C.-C.; Chang, H.-T. Fluorescent carbon dots for selective labeling of subcellular organelles. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 11248–11261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, G.B.; Singh, P.; Biswas, K. Potentialities of Bio-Functionalized Carbon Nanotubes for Different Anti-Cancerous Activities. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2024, 34, 2325–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, Q.; Li, J.; Tian, Y.; Kang, Y.; Ren, G.; Liu, W.; Wang, H.; Wang, B.; Yan, L.; et al. Targeted delivery of doxorubicin using transferrin-conjugated carbon dots for cancer therapy. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2021, 4, 7280–7289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minervini, G.; Panniello, A.; Dibenedetto, C.N.; Madonia, A.; Fanizza, E.; Curri, M.L.; Striccoli, M. Exploring Carbon Dots: Green Nanomaterials for Unconventional Lasing. Small 2024, 20, 2403653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, H.H.; Shati, A.A.; Alfaifi, M.Y.; Elbehairi, S.E.I.; Sasidharan, S. The future of plant based green carbon dots as cancer Nanomedicine: From current progress to future perspectives and beyond. J. Adv. Res. 2024, 67, 133–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Chen, Q.; He, H.; Jiang, H.; Hu, J.; Liu, Y.; Yao, L.; Mao, H.; Li, J.; Li, B.; et al. Carbon dots-based materials and their applications in regenerative medicine. MedComm–Biomater. Appl. 2024, 3, e98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genc, M.T.; Yanalak, G.; Aksoy, I.; Aslan, E.; Patır, I.H. Green carbon dots (GCDs) for photocatalytic hydrogen evolution and antibacterial applications. ChemistrySelect 2021, 6, 7317–7322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakkakula, J.; Kalra, P.; Mallick, G.; Mittal, H.; Uddin, I. Revolutionizing cancer treatment: Enhancing photodynamic therapy with cyclodextrin nanoparticles and synergistic combination therapies. Mater. Today Sustain. 2024, 28, 100958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Xiong, M.; Zhang, J.; He, C.; Ma, X.; Zhang, H.; Kuang, Y.; Yang, M.; Huang, Q. Carbon dots based on natural resources: Synthesis and applications in sensors. Microchem. J. 2021, 160, 105604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thota, S.P.; Kurdekar, A.; Vadlani, P.V.; Kumar, B.S. Green Synthesis of Highly Fluorescent Carbon Dots from Groundnut Shell Biomass for Bioimaging Applications. J. Fluoresc. 2024, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juntree, N.; Sangjan, A.; Pongchaikul, P.; Arjfuk, P.; Wanmolee, W.; Khemthong, P.; Srifa, A.; Posoknistakul, P.; Laosiripojana, N.; Wu, K.C.; et al. Unveiling role of carbon dots for non-invasive and ultra-sensitive glucose detection in biofluids for personal preventive care testing. Green Anal. Chem. 2024, 11, 100165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yu, L.; He, M.; Chen, C.; Yu, Z.; Jiang, S.; Wang, Y.; Li, L.; Li, B.; Wang, G.; et al. Review on carbon dots: Synthesis and application in biology field. BMEMat 2023, 1, e12045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etefa, H.F.; Tessema, A.A.; Dejene, F.B. Carbon dots for future prospects: Synthesis, characterizations and recent applications: A review (2019–2023). C 2024, 10, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wang, C.; Liu, C.; Chen, S. Facile access to fabricate carbon dots and perspective of large-scale applications. Small 2023, 19, 2206671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usman, M.; Cheng, S. Recent Trends and Advancements in Green Synthesis of Biomass-Derived Carbon Dots. Eng 2024, 5, 2223–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Rani, N.; Kumar, S.; Kumar, P.; Mohan, B.; Pallavi; Bhankar, V.; Kataria, N.; Kumar, R.; Kumar, K. Assessing the biomass-based carbon dots and their composites for photocatalytic treatment of wastewater. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 413, 137474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varadharajan, S.; Vasanthan, K.S.; Mathur, V.; Hariperumal, N.; Mazumder, N. Green synthesis and multifaceted applications: Challenges and innovations in carbon dot nanocomposites. Discov. Nano 2024, 19, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Sun, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, H.; Long, B.; Xie, D.; Chen, J.; Wang, K. Rapid and green fabrication of carbon dots for cellular imaging and anti-counterfeiting applications. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 3232–3237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanwal, A.; Bibi, N.; Hyder, S.; Muhammad, A.; Ren, H.; Liu, J.; Lei, Z. Recent advances in green carbon dots (2015–2022): Synthesis, metal ion sensing, and biological applications. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2022, 13, 1068–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Bai, Y.; Han, Z.; He, W.; Guo, Z. Photoluminescence imaging of Zn2+ in living systems. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 4517–4546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.; Wen, Z.; Zhang, P.; Chen, Y.; Wang, H.; Jin, H.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Y.; Wang, S.; Pan, S. Color-Tunable Perovskite Nanomaterials with Intense Circularly Polarized Luminescence and Tailorable Compositions. Small 2024, 20, 2311013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, H.S.; Choi, J.; Jeong, S.; Nam, S.; Kim, J.; Song, J.K. Fluorophore-Dependent Optical Properties of Multicolor Carbon Dots for Bioimaging and Optoelectronic Devices. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2023, 6, 17120–17129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Lin, F.; Hu, M.; Li, C.; Xu, T.; Chen, C.; Guo, X. Carbon dots with tunable emission, controllable size and their application for sensing hypochlorous acid. J. Lumin. 2014, 151, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Adolfsson, K.H.; Xu, Y.; Fang, H.; Hakkarainen, M.; Wu, M. Carbon dot/polymer nanocomposites: From green synthesis to energy, environmental and biomedical applications. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2021, 29, e00304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, H.H.; Bardakci, F.; Akgöl, S.; Kusat, K.; Adnan, M.; Alam, M.J.; Gupta, R.; Sahreen, S.; Chen, Y.; Gopinath, S.C.; et al. Green carbon dots: Synthesis, characterization, properties and biomedical applications. J. Funct. Biomater. 2023, 14, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nocito, G.; Calabrese, G.; Forte, S.; Petralia, S.; Puglisi, C.; Campolo, M.; Esposito, E.; Conoci, S. Carbon dots as promising tools for cancer diagnosis and therapy. Cancers 2021, 13, 1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Ruan, S.; Liu, S.; Sun, T.; Qu, D.; Zhao, H.; Xie, Z.; Gao, H.; Jing, X.; Sun, Z. Self-targeting fluorescent carbon dots for diagnosis of brain cancer cells. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 11455–11461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Xia, X.; Liang, Z.; Zuo, T.; Xu, G.; Wei, F.; Yang, J.; Hu, Q.; Zhao, Z.; Tang, B.Z.; et al. Self-Assembled DNA Nanospheres Driven by Carbon Dots for MicroRNAs Imaging in Tumor via Logic Circuit. Small 2024, 20, 2310728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnanasegaran, G.; Shabo, G.; Buscombe, J.R. Ischaemic and Inflammatory Biomarkers in Cardiovascular Disease. In Integrating Cardiology for Nuclear Medicine Physicians: A Guide to Nuclear Medicine Physicians; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 77–85. [Google Scholar]
- Théroux, P. Acute Coronary Syndromes: A Companion to Braunwald’s Heart Disease E-Book; Elsevier Health Sciences: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Radhakrishnan, K.; Suriyaprakash, R.; Balamurugan, S.; Kumar, J.V.; Albeshr, M.F.; Mythili, R.; Srinivasan, P.; Nunna, G.P.; Ko, T.J. Fluorometric detection of copper and imidacloprid using nitrogen-doped graphitic carbon dots: A promising method for environmental monitoring. Luminescence 2024, 39, e4849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Wu, S.; Chen, W.; Duan, X.; Sun, X.; Li, S.; Mai, Z.; Wu, W.; Zeng, G.; Liu, H.; et al. Designing intelligent nanomaterials to achieve highly sensitive diagnoses and multimodality therapy of bladder cancer. Small Methods 2023, 7, 2201313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratre, P.; Nazeer, N.; Kumari, R.; Thareja, S.; Jain, B.; Tiwari, R.; Kamthan, A.; Srivastava, R.K.; Mishra, P.K. Carbon-based fluorescent nano-biosensors for the detection of cell-free circulating MicroRNAs. Biosensors 2023, 13, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratre, P.; Jain, B.; Kumari, R.; Thareja, S.; Tiwari, R.; Srivastava, R.K.; Goryacheva, I.Y.; Mishra, P.K. Bioanalytical applications of graphene quantum dots for circulating cell-free nucleic acids: A review. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 39586–39602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, J.; Hussain, C.M. Early detection of cancer utilizing biosensors based on “Green Graphene”: An innovative and sustainable methodology for advancing cancer diagnosis. Trends Anal. Chem. 2023, 167, 117254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asghar, Z.; Ahmad, F.; Khan, M.I.; Shanableh, A.; Lashari, M.H. Advancements in Gadolinium-Doped Carbon Quantum Dots for Dual-Modal Bioimaging: Synthesis and Applications. MatSci Express 2025, 2, 77–92. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, S.; Zhang, R.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, X.; Wu, X.; Li, B. Synthesis, applications in therapeutics, and bioimaging of traditional Chinese medicine-derived carbon dots. Carbon Lett. 2024, 34, 545–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y. Carbon Dots for Nanomedicine: C-Dots and C-Dots Nanotec describe how carbon dots can aid high-performance drug delivery in the future treatment of human diseases. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. News 2022, 42, 50–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herlem, G.; Picaud, F.; Girardet, C.; Micheau, O. Carbon nanotubes: Synthesis, characterization, and applications in drug-delivery systems. In Nanocarriers for Drug Delivery; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 469–529. [Google Scholar]
- Riley, R.; June, C.H.; Langer, R.; Mitchell, M.J. Delivery technologies for cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2019, 18, 175–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, A.; Yuan, Y.; Xu, H.; Lei, J.; Yan, C. Structural basis of human monocarboxylate transporter 1 inhibition by anti-cancer drug candidates. Cell 2021, 184, 370–383.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Teng, X.; Wang, Y.; Si, S.; Ju, J.; Pan, W.; Wang, J.; Sun, X.; Wang, W. Carbon dots based fluorescence methods for the detections of pesticides and veterinary drugs: Response mechanism, selectivity improvement and application. Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 144, 116430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.-K.; Zhang, L.-L.; Yang, Z.-Y.; Guo, X.-H.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Luo, J.-K.; Tang, T.; Wang, Y. Herbal medicine derived carbon dots: Synthesis and applications in therapeutics, bioimaging and sensing. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 19, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Sigdel, G.; Mintz, K.J.; Seven, E.S.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, C.; Leblanc, R.M. Carbon Dots: A future Blood-Brain Barrier Penetrating Nanomedicine and Drug Nanocarrier. Int. J. Nanomed. 2021, 16, 5003–5016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrese, G.; De Luca, G.; Nocito, G.; Rizzo, M.G.; Lombardo, S.P.; Chisari, G.; Forte, S.; Sciuto, E.L.; Conoci, S. Carbon dots: An innovative tool for drug delivery in brain tumors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.M.; Thomas, M.Z.; Magdy, T.; Eisenmann, E.D.; Uddin, M.E.; DiGiacomo, D.F.; Pan, A.; Keiser, M.; Otter, M.; Xia, S.H.; et al. Targeting OCT3 Attenuates Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiac Injury. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2020168118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, F.; Gao, J.; Xu, Z.; Li, T.; Gao, A.; Sun, F.; Wang, F.; Wang, W.; Geng, Y.; Zhang, F.; et al. Overcoming immune resistance by sequential prodrug nanovesicles for promoting chemoimmunotherapy of cancer. Nano Today 2021, 36, 101025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhao, Z.; Qiu, N.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, G.; Jiang, H.; Piao, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Tang, J.; Shen, Y. Co-delivery of IOX1 and doxorubicin for antibody-independent cancer chemo-immunotherapy. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnstone, T.C.; Suntharalingam, K.; Lippard, S.J. The next generation of platinum drugs: Targeted Pt (II) agents, nanoparticle delivery, and Pt (IV) prodrugs. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 3436–3486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaft, J.E.; Rimner, A.; Weder, W.; Azzoli, C.G.; Kris, M.G.; Cascone, T. Evolution of systemic therapy for stages I–III non-metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 18, 547–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.M.; Gupta, S.; Kitchlu, A.; Meraz-Munoz, A.; North, S.A.; Alimohamed, N.S.; Blais, N.; Sridhar, S.S. Defining cisplatin eligibility in patients with muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2021, 18, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenkrans, Z.T.; Sun, T.; Jiang, D.; Chen, W.; Barnhart, T.E.; Zhang, Z.; Ferreira, C.A.; Wang, X.; Engle, J.W.; Huang, P.; et al. Selenium-Doped Carbon Quantum Dots Act as Broad-Spectrum Antioxidants for Acute Kidney Injury Management. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 2000420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.N.Q.; Tran, N.N.; Escribà-Gelonch, M.; Serra, C.A.; Fisk, I.; McClements, D.J.; Hessel, V. Microfluidic encapsulation for controlled release and its potential for nanofertilisers. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 11979–12012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Zhang, N.; Tian, J.; Xin, G.; Liu, L.; Sun, X.; Li, B. Advanced approaches for improving bioavailability and controlled release of anthocyanins. J. Control. Release 2022, 341, 285–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Cai, H.; Waterhouse, G.I.N.; Qu, X.; Yang, B.; Lu, S. Carbon dots in bioimaging, biosensing and therapeutics: A comprehensive review. Small Sci. 2022, 2, 2200012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Liu, X.; Yang, S.; Tan, H.; Yang, L.-P.; Wang, L.-L. Guanidinium-Functionalized Carbon Dots: An Efficient Antibacterial Agent Against Multidrug-Resistant ESKAPE Pathogens. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 65955–65969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Germain, N.; Samb, R.; Côté, É.; Toulouse-Fournier, A.; Robitaille, J.; Turcotte, S.; Morin, M.; Audet, M.; Bert, L.; Rivard, J.; et al. Impact of a geriatric emergency management nurse on thirty-day emergency department revisits: A retrospective propensity score matched case-control study. medRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Xu, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, T. Insight Into the Synthetic Strategies of Carbon Dots and Its Structure-Property Interplay for Next-Generation Technologies. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 496, 153914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, M.J.; Billingsley, M.M.; Haley, R.M.; Wechsler, M.E.; Peppas, N.A.; Langer, R. Engineering precision nanoparticles for drug delivery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 101–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Ukidve, A.; Kim, J.; Mitragotri, S. Targeting strategies for tissue-specific drug delivery. Cell 2020, 181, 151–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Deng, Y.; Jiang, X.; Bai, Y.; Qian, C.; Shi, H.; Wang, J. Advances in Carbon Dot Based Enhancement of Photodynamic Therapy of Tumors. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2024, 7, 8149–8162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhari, K.G.; Patil, P.O.; Nangare, S.N.; Khan, M.G.; Bari, S.B.; Khan, Z.G. Exploring the Significance of Carbon Quantum Dots and Graphene Quantum Dots in Sarcosine Sensing: A Key Biomarker for Prognosticating Prostate Cancer. ChemistrySelect 2024, 9, e202401643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, D.; Shende, P. Integration of Internet of Things with Quantum Dots: A State-of-the-Art of Medicine. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2021, 27, 2068–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horstmann, C.; Davenport, V.; Zhang, M.; Peters, A.; Kim, K. Transcriptome profile alterations with carbon nanotubes, quantum dots, and silver nanoparticles: A review. Genes 2021, 12, 794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J. Develop the Disease Specific Bioinformatics Platforms with Integrated Bioinformatics Data. Ph.D. Thesis, Indiana University-Purdue University Indianapolis, Indianapolis, IN, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, W. Bioinformatics in the Age of Big Data: Leveraging Computational Tools for Biological Discoveries. Comput. Mol. Biol. 2024, 14, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, R.; Oliveira, J.; Sousa, M. Bioinformatics and computational tools for next-generation sequencing analysis in clinical genetics. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, G.O.; Sharker, S.M.; Ryu, J.H. Emerging biomedical applications of carbon dot and polymer composite materials. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 10565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Property | Green Carbon Dots (GCDs) | Quantum Dots (QDs) | Graphene Derivatives |
|---|---|---|---|
| Efficacy | Tunable photoluminescence, High biocompatibility, Easy functionalization [2,3] | Superior brightness, Narrow emission spectra, High stability [4,5] | Excellent electrical conductivity, High mechanical strength, Large surface area [6] |
| Safety | Low toxicity, Biodegradable, Eco-friendly synthesis [7] | High toxicity (heavy metal-based), Biocompatibility issues [8] | Moderate toxicity, Environmental concerns [9] |
| Cost-Effectiveness | Low-cost synthesis and scalable production [10] | High production costs, Limited scalability [11] | Moderate cost, Energy-intensive synthesis [12] |
| Applications |
|
| Electronics, Energy storage, and Sensors [16] |
| Limitations |
|
| Toxicity in biological systems, High energy consumption [19] |
| Parameter | Green Synthesis of Carbon Dots | Conventional Methods | Comparison | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Energy Consumption | ||||
| Reaction Temperature | 100–200 °C (low-temperature processes) | 300–800 °C (high-temperature pyrolysis) | ~50–70% lower energy input | [20,21] |
| Energy Input (per gram) | 0.5–1.5 kWh/g | 2–5 kWh/g | ~60–75% lower energy consumption | [22,23] |
| Duration of Synthesis | 1–4 h | 6–12 h | ~50–70% shorter synthesis time | [24,25,26] |
| Environmental Impact | ||||
| Raw Materials | Renewable (e.g., biomass, waste) | Non-renewable (e.g., fossil fuels) | 100% renewable vs. non-renewable | [27,28] |
| Solvent Use | Water or mild solvents | Toxic organic solvents | Non-toxic vs. toxic solvents | [29,30] |
| Waste Generation | Minimal (biodegradable by-products) | Significant (hazardous waste) | ~80–90% less waste | [31,32] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Etefa, H.F.; Dejene, F.B. Applications of Green Carbon Dots in Personalized Diagnostics for Precision Medicine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2846. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26072846
Etefa HF, Dejene FB. Applications of Green Carbon Dots in Personalized Diagnostics for Precision Medicine. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(7):2846. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26072846
Chicago/Turabian StyleEtefa, Habtamu F., and Francis B. Dejene. 2025. "Applications of Green Carbon Dots in Personalized Diagnostics for Precision Medicine" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 7: 2846. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26072846
APA StyleEtefa, H. F., & Dejene, F. B. (2025). Applications of Green Carbon Dots in Personalized Diagnostics for Precision Medicine. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(7), 2846. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26072846






