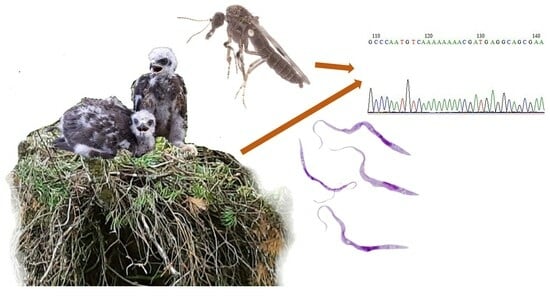
Trypanosomatids in Bloodsucking Diptera Insects (Ceratopogonidae and Simuliidae) Wild-Caught at Raptor Bird Nests in Temperate Forests
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Investigation of Nestlings
2.2. Insect Collection
2.3. Insect Identification
2.4. PCR-Based Screening and Statistics
2.5. Phylogenetic Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Species Composition of Culicoides Biting Midges
3.2. Biting Midge Infection with Trypanosomatids
3.3. Raptor Nestling Blood Analysis for the Presence of Trypanosoma Parasites
3.4. Phylogenetic Analysis
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kostygov, A.Y.; Karnkowska, A.; Votýpka, J.; Tashyreva, D.; Maciszewski, K.; Yurchenko, V.; Lukeš, J. Euglenozoa: Taxonomy, diversity and ecology, symbioses and viruses. Open Biol. 2021, 11, 200407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Podlipaev, S.A. Catalogue of the world fauna of Protozoa of the family Trypanosomatidae. Cat. World Fauna Protozoa Fam. Trypanos. 1990, 217, 178. [Google Scholar]
- Zídková, L.; Cepicka, I.; Szabová, J.; Svobodová, M. Biodiversity of avian trypanosomes. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2012, 12, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svobodová, M.; Dolnik, O.V.; Čepička, I.; Rádrová, J. Biting midges (Ceratopogonidae) as vectors of avian trypanosomes. Parasit. Vectors 2017, 10, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molyneux, D.H.; Cooper, J.E.; Smith, W.J. Studies on the pathology of an avian trypanosome (T. bouffardi) infection in experimentally infected canaries. Parasitology 1983, 87, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valkiūnas, G.; Iezhova, T.A.; Sehgal, R.N.M. Deforestation does not affect the prevalence of a common trypanosome in African birds. Acta Trop. 2016, 162, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svobodová, M.; Čepička, I.; Zídková, L.; Kassahun, A.; Votýpka, J.; Peške, L.; Hrazdilová, K.; Brzoňová, J.; Voříšek, P.; Weidinger, K. Blood parasites (Trypanosoma, Leucocytozoon, Haemoproteus) in the Eurasian sparrowhawk (Accipiter nisus): Diversity, incidence and persistence of infection at the individual level. Parasit. Vectors 2023, 16, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chagas, C.R.F.; Binkienė, R.; Ilgūnas, M.; Iezhova, T.; Valkiūnas, G. The buffy coat method: A tool for detection of blood parasites without staining procedures. Parasit. Vectors 2020, 13, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, J.R. Biology of the Trypanosomes of Birds; Lumsden, W.H.R., Evans, D.A., Eds.; Biology of the Kinetoplastida; Academic Press: London, UK; New York, NY, USA; San Francisco, CA, USA, 1976; pp. 131–174. [Google Scholar]
- Bernotienė, R.; Iezhova, T.A.; Bukauskaitė, D.; Chagas, C.R.F.; Kazak, M.; Valkiūnas, G. Development of Trypanosoma everetti in Culicoides biting midges. Acta Trop. 2020, 210, 105555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miltgen, F.; Landau, I. Culicoides nubeculosus, an experimental vector of a new trypanosome from psittaciforms: Trypanosoma bakeri n. sp. Ann. Parasitol. Hum. Comparée 1982, 57, 423–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molyneux, D.H. Vector relationships in the Trypanosomatidae. Adv. Parasitol. 1977, 15, 1–82. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Votýpka, J.; Svobodová, M. Trypanosoma avium: Experimental transmission from black flies to canaries. Parasitol. Res. 2004, 92, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svobodová, M.; Rádrová, J. Phlebotominae Sandflies—Potential Vectors of Avian Trypanosomes. Acta Protozool. 2017, 57, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seblova, V.; Sadlova, J.; Carpenter, S.; Volf, P. Speculations on biting midges and other bloodsucking arthropods as alternative vectors of Leishmania. Parasit. Vectors 2014, 7, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frolov, A.O.; Kostygov, A.Y.; Yurchenko, V. Development of monoxenous trypanosomatids and phytomonads in insects. Trends Parasitol. 2021, 37, 538–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, G.F. Development of trypanosomes of the T. avium complex in the invertebrate host. Can. J. Zool. 1970, 48, 945–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirkpatrick, C.E.; Terway-Thompson, C.A.; Iyengar, M.R. Biochemical characterization of some raptor trypanosomes. II. Enzyme studies, with a description of Trypanosoma bennetti n. sp. Can. J. Zool. 1986, 64, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pornpanom, P.; Salakij, C.; Prasopsom, P.; Lertwatcharasarakul, P.; Kasorndorkbua, C.; Santavakul, M. Morphological and molecular characterization of avian trypanosomes in raptors from Thailand. Parasitol. Res. 2019, 118, 2419–2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svobodová, M.; Weidinger, K.; Peške, L.; Volf, P.; Votýpka, J.; Voříšek, P. Trypanosomes and haemosporidia in the buzzard (Buteo buteo) and sparrowhawk (Accipiter nisus): Factors affecting the prevalence of parasites. Parasitol. Res. 2015, 114, 551–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Votýpka, J.; Oborník, M.; Volf, P.; Svobodová, M.; Lukeš, J. Trypanosoma avium of raptors (Falconiformes): Phylogeny and identification of vectors. Parasitology 2002, 125, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svobodová, M.; Zídková, L.; Čepička, I.; Oborník, M.; Lukeš, L.; Votýpka, J. Sergeia podlipaevi gen. nov., sp. nov. (Trypanosomatidae, Kinetoplastida), a parasite of biting midges (Ceratopogonidae, Diptera). Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2007, 57, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valkiūnas, G. Avian Malaria Parasites and Other Haemosporidia; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Dyce, A.L. The recognition of nulliparous and parous Culicoides (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae) without dissection. Aust. J. Entomol. 1969, 8, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathieu, B.; Cêtre-Sossah, C.; Garros, C.; Chavernac, D.; Balenghien, T.; Carpenter, S.; Setier-Rio, M.L.; Vignes-Lebbe, R.; Ung, V.; Candolfi, E.; et al. Development and validation of IIKC: An interactive identification key for Culicoides (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae) females from the Western Palaearctic region. Parasit. Vectors 2012, 5, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yankovsky, A.V. Key to the Identification of Black Flies (Diptera: Simuliidae) of Russia and Adjacent Territories; Institute of Zoology of Russian Academy of Sciences: Sankt Peterburg, Russia, 2002. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Sambrook, J.; Russell, D.W. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 3rd ed.; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Sehgal, R.N.M.; Iezhova, T.A.; Marzec, T.; Valkiūnas, G. Trypanosoma naviformis sp. nov. (Kinetoplastidae: Trypanosomatidae) from widespread African songbirds, the Olive sunbird (Cyanomitra olivacea) and Yellow-whiskered greenbul (Andropadus latirostris). Zootaxa 2015, 4034, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valkiūnas, G.; Iezhova, T.A.; Carlson, J.S.; Sehgal, R.N.M. Two new Trypanosoma species from African birds, with notes on the taxonomy of avian trypanosomes. J. Parasitol. 2011, 97, 924–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folmer, O.; Black, M.; Hoeh, W.; Lutz, R.; Vrijenhoek, R. DNA primers for amplification of mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit I from diverse metazoan invertebrates. Mol. Mar. Biol. Biotechnol. 1994, 3, 294–299. [Google Scholar]
- Darriba, D.; Taboada, G.L.; Doallo, R.; Posada, D. jModelTest 2: More models, new heuristics and parallel computing. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guindon, S.; Gascuel, O. A simple, fast, and accurate algorithm to estimate large phylogenies by maximum likelihood. Syst. Biol. 2003, 52, 696–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronquist, F.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models. Bioinformatics 2003, 19, 1572–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, G.F. On the specificity and transmission of some avian trypanosomes. Can. J. Zool. 1961, 39, 17–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Černý, O.; Votýpka, J.; Svobodová, M. Spatial feeding preferences of ornithophilic mosquitoes, blackflies and biting midges. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2011, 25, 104–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molyneux, D.H. Trypanosoma everetti sp. nov. a trypanosome from the black-rumped waxbill Estrilda t. troglodytes Lichtenstein. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 1973, 67, 219–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukeš, J.; Tesařová, M.; Yurchenko, V.; Votýpka, J. Characterization of a new cosmopolitan genus of trypanosomatid parasites, Obscuromonas gen. nov. (Blastocrithidiinae subfam. nov.). Eur. J. Protistol. 2021, 79, 125778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Votýpka, J.; Petrželková, K.J.; Brzoňová, J.; Jirků, M.; Modrý, D.; Lukeš, J. How monoxenous trypanosomatids revealed hidden feeding habits of their tsetse fly hosts. Folia Parasitol. 2021, 68, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmittner, S.M.; McGhee, R.B. Host specificity of various species of Crithidia Leger. J. Parasitol. 1970, 56, 684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostygov, A.Y.; Grybchuk-Ieremenko, A.; Malysheva, M.N.; Frolov, A.O.; Yurchenko, V. Molecular revision of the genus Wallaceina. Protist 2014, 165, 594–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoener, E.; Uebleis, S.S.; Cuk, C.; Nawratil, M.; Obwaller, A.G.; Zechmeister, T.; Lebl, K.; Rádrová, J.; Zittra, C.; Votýpka, J.; et al. Trypanosomatid parasites in Austrian mosquitoes. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0196052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svobodová, M.; Volf, P.; Votýpka, J. Trypanosomatids in ornithophilic bloodsucking Diptera. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2015, 29, 444–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunantaraporn, S.; Hortiwakul, T.; Kraivichian, K.; Siriyasatien, P.; Brownell, N. Molecular identification of host blood meals and detection of blood parasites in Culicoides Latreille (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae) collected from Phatthalung province, Southern Thailand. Insects 2022, 13, 912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganyukova, A.I.; Zolotarev, A.V.; Frolov, A.O. Geographical distribution and host range of monoxenous trypanosomatid Crithidia brevicula (Frolov et Malysheva, 1989) in the northern regions of Eurasia. Protistology 2020, 2, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drobelis, E. Birds of Prey of Lithuanian Forests; Spauda: Vilnius, Lithuania, 2004. [Google Scholar]

| Insect Species | Bird Nest | No of Individuals | No of Positive Insects | Detected Kinetoplastids |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Culicoides (Oecacta) festivipennis | Buteo buteo | 178 | 1 | Crithidia brevicula |
| 1 | Crithidia sp. | |||
| 5 | Trypanosoma mixed infection | |||
| 4 | T. bennetti group Hap 5 | |||
| Clanga pomarina | 221 | 38 | Trypanosoma mixed infection | |
| 1 | T. bennetti group Hap 2 | |||
| 21 | T. bennetti group Hap 5 | |||
| C. (O.) kibunensis | B. buteo | 93 | 10 | Trypanosoma mixed infection |
| 1 | C. brevicula | |||
| 1 | Obscuromonas sp. | |||
| C. pomarina | 67 | 7 | Trypanosoma mixed infection | |
| 2 | Trypanosoma sp. | |||
| 2 | T. bennetti group Hap 1 | |||
| 1 | T. bennetti group Hap 3 | |||
| 3 | T. bennetti group Hap 5 | |||
| 1 | T. bennetti group Hap 6 | |||
| C. (O.) pictipennis | B. buteo | 599 | 22 | Trypanosoma mixed infection |
| 2 | C. brevicula | |||
| 1 | Trypanosoma avium | |||
| 4 | T. bennetti group Hap 4 | |||
| 3 | T. bennetti group Hap 5 | |||
| C. pomarina | 21 | 1 | Trypanosoma mixed infection | |
| 2 | T. bennetti group Hap 5 | |||
| C. (Avaritia) obsoletus | B. buteo | 3 | 0 | |
| C. pomarina | 4 | 0 | ||
| C. (Culicoides) impunctatus | B. buteo | 23 | 0 | |
| C. (C.) newsteadi | B. buteo | 2 | 0 | |
| C. (C.) punctatus | B. buteo | 3 | 0 | |
| C. pomarina | 9 | 1 | Trypanosoma mixed infection | |
| C. (Silvaticulicoides) archayi | B. buteo | 1 | 0 | |
| C. (S.) pallidicornis | B. buteo | 1 | 0 | |
| C. pomarina | 2 | 0 | ||
| C. (Wirthomyia) reconditus | B. buteo | 1 | 0 | |
| C. (W.) segnis | B. buteo | 5 | 0 | |
| C. pomarina | 15 | 1 | T. avium | |
| 1 | T. bennetti group Hap 1 | |||
| 1 | T. bennetti group Hap 5 | |||
| Simulium (Eusimulium) angustipes | C. pomarina | 2 | 0 | |
| S. (Nevermannia) vernum | B. buteo | 1 | 1 | T. avium |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kazak, M.; Bernotienė, R.; Treinys, R.; Bukauskaitė, D. Trypanosomatids in Bloodsucking Diptera Insects (Ceratopogonidae and Simuliidae) Wild-Caught at Raptor Bird Nests in Temperate Forests. Diversity 2023, 15, 692. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15050692
Kazak M, Bernotienė R, Treinys R, Bukauskaitė D. Trypanosomatids in Bloodsucking Diptera Insects (Ceratopogonidae and Simuliidae) Wild-Caught at Raptor Bird Nests in Temperate Forests. Diversity. 2023; 15(5):692. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15050692
Chicago/Turabian StyleKazak, Margarita, Rasa Bernotienė, Rimgaudas Treinys, and Dovilė Bukauskaitė. 2023. "Trypanosomatids in Bloodsucking Diptera Insects (Ceratopogonidae and Simuliidae) Wild-Caught at Raptor Bird Nests in Temperate Forests" Diversity 15, no. 5: 692. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15050692
APA StyleKazak, M., Bernotienė, R., Treinys, R., & Bukauskaitė, D. (2023). Trypanosomatids in Bloodsucking Diptera Insects (Ceratopogonidae and Simuliidae) Wild-Caught at Raptor Bird Nests in Temperate Forests. Diversity, 15(5), 692. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15050692