Trypsin Inhibitor from Soybean Whey Wastewater: Isolation, Purification and Stability
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Preparation of the Soybean Whey
2.3. Isolation and Purification of the STI from the Soybean Whey
2.3.1. Isolation and Purification of the STI Using the Isoelectric Point Method
2.3.2. Isolation and Purification of the STI via Ammonium Sulfate Salting Out
2.3.3. Isolation and Purification of the Trypsin Inhibitors via Gel Filtration Chromatography
2.4. Analytical Method
2.4.1. Determination of the Protein Concentration
2.4.2. Determination of the Trypsin Inhibitory Activity [15,31]
Reagent Preparation
Determination of the Trypsin Inhibitory Activity
2.4.3. Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate-Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE)
2.4.4. Circular Dichroism (CD) Spectroscopy
2.4.5. Examination of the STI Stability [15,32]
The Effect of Temperature on the STI Inhibitory Activity
The Effect of pH on the STI Inhibitory Activity
The Effect of Pepsin Treatment on the STI Inhibitory Activity
2.5. Statistics
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Analysis of the Soybean Whey
3.2. Isolation and Purification of STI
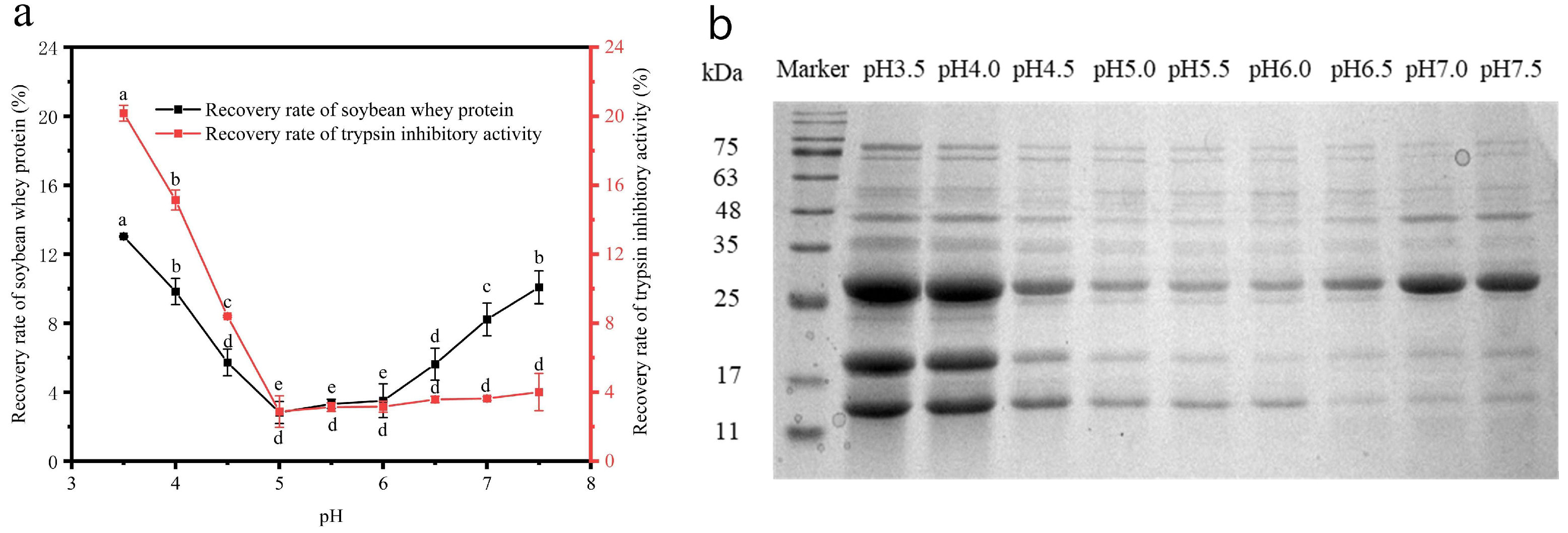
3.2.1. The Effect of pH on the Isolation and Purification of STI
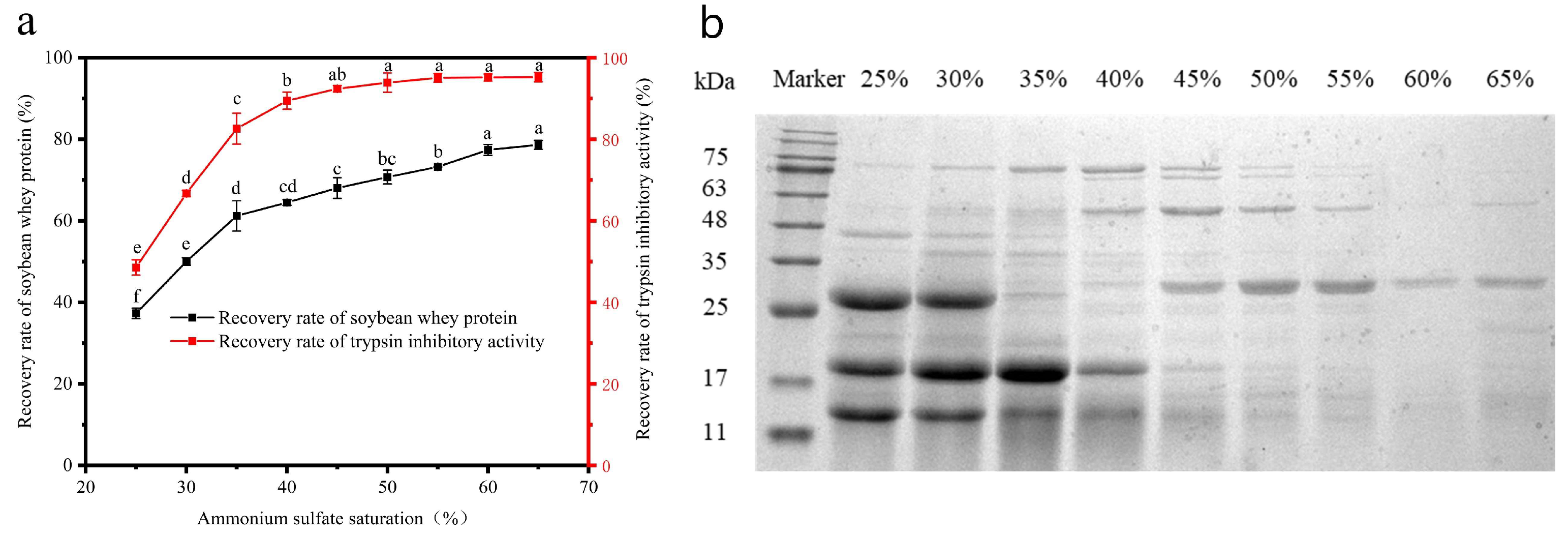
3.2.2. The Effect of Ammonium Sulfate Saturation on STI Isolation and Purification
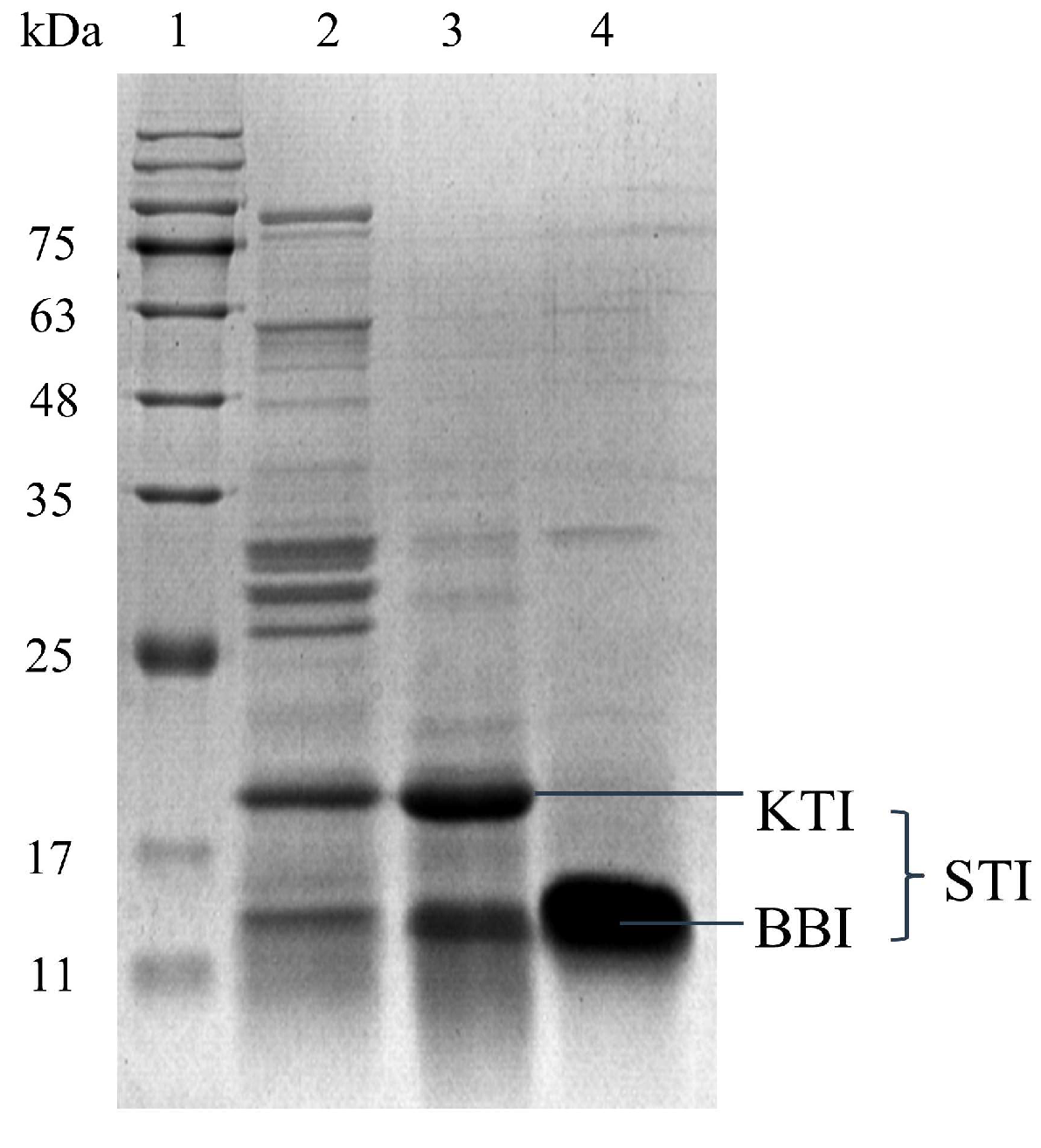
3.2.3. The Effect of Gel Filtration Chromatography on STI Isolation and Purification
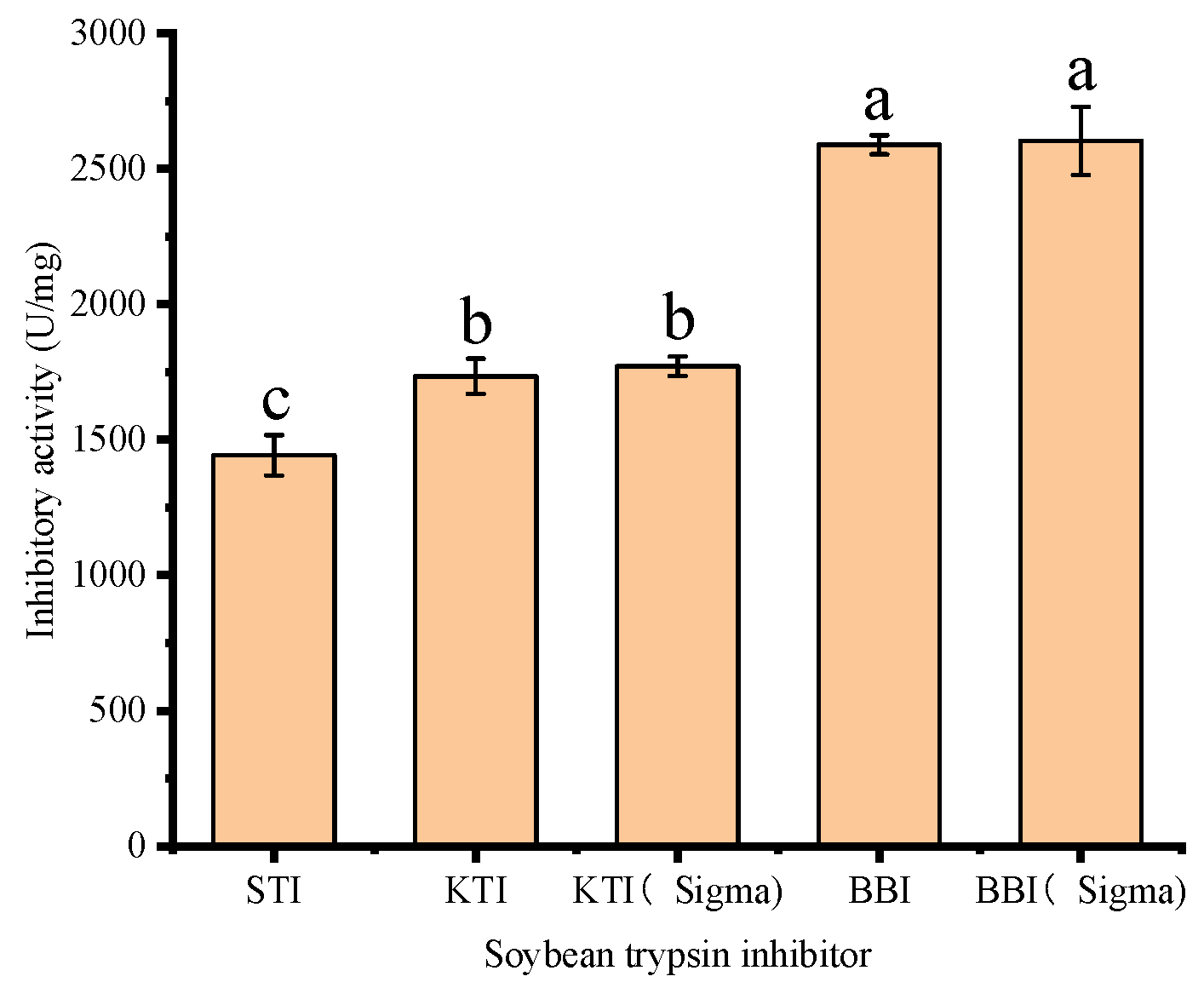
3.3. Analysis of the STI Activity
3.4. Stability Analysis of STI
3.4.1. The Effect of Temperature on the STI Activity
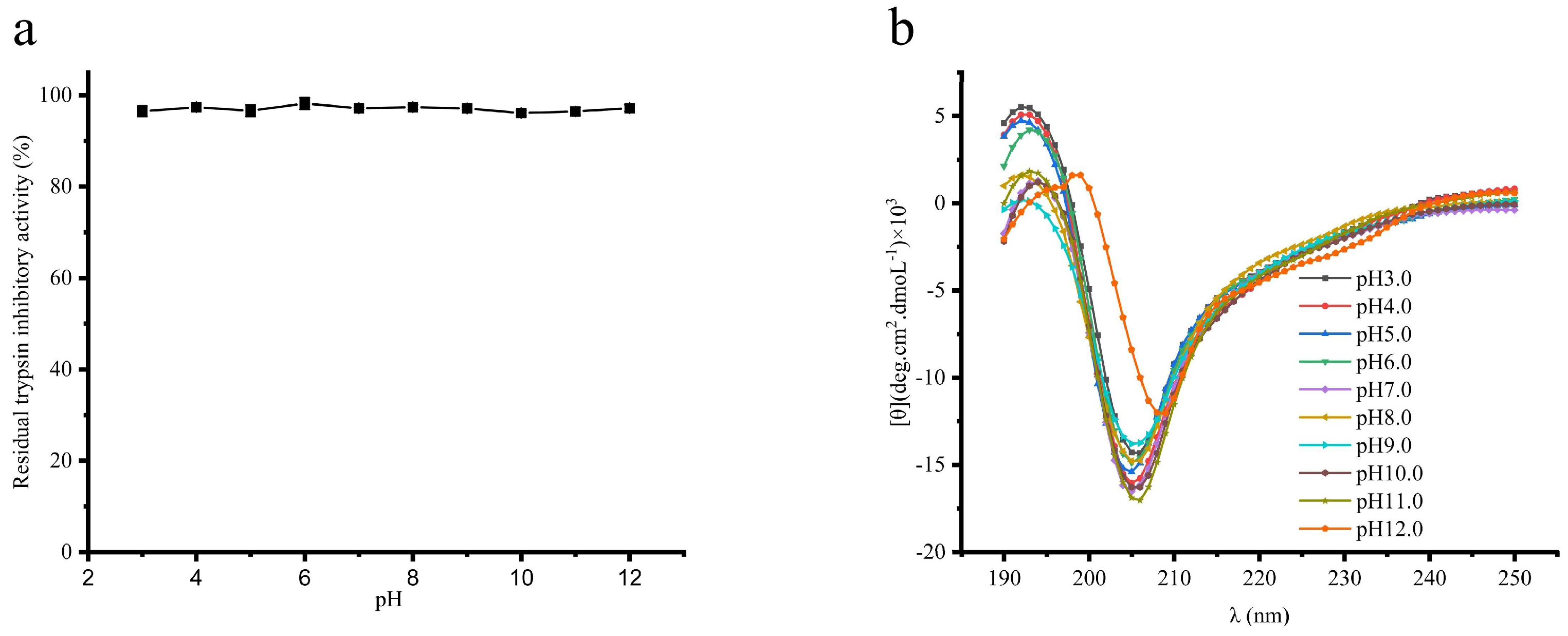
3.4.2. The Effect of pH on the STI Activity
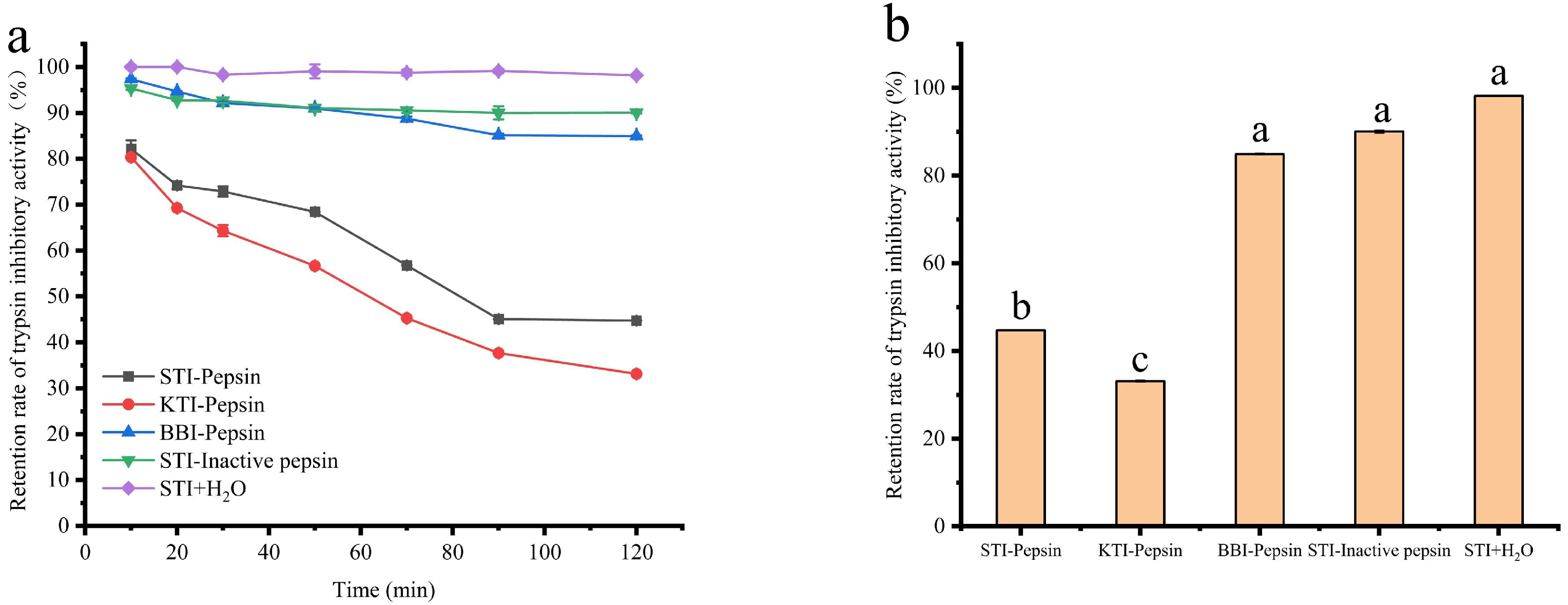
3.4.3. The Effect of Pepsin on the STI Activity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tang, C.-H. Emulsifying properties of soy proteins: A critical review with emphasis on the role of conformational flexibility. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 2636–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chua, J.-Y.; Liu, S.-Q. Soy whey: More than just wastewater from tofu and soy protein isolate industry. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 91, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Dong, D.; Hua, Y.; Chen, Y.; Kong, X.; Zhang, C. Soybean Whey Protein/Chitosan Complex Behavior and Selective Recovery of Kunitz Trypsin Inhibitor. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 7279–7286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Hua, Y.; Chen, Y.; Kong, X.; Zhang, C.; Yu, X. An advance for removing antinutritional protease inhibitors: Soybean whey purification of Bowman-Birk chymotrypsin inhibitor by combination of two oppositely charged polysaccharides. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 164, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belén, F.; Sánchez, J.; Hernández, E.; Auleda, J.; Raventós, M. One option for the management of wastewater from tofu production: Freeze concentration in a falling-film system. J. Food Eng. 2012, 110, 364–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Serventi, L. Sustainability of dairy and soy processing: A review on wastewater recycling. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 237, 117821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Xintong, J.; Youshuang, Z.; Yuran, Z.; Jing, G. Precipitation of proteins from soybean whey wastewater by successive foaming and defoaming. Chem. Eng. Process. 2018, 128, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiPietro, C.M.; Liener, I.E. Heat inactivation of the Kunitz and Bowman-Birk soybean protease inhibitors. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1989, 37, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Rani, A.; Shuaib, M.; Mittal, P. Comparative Assessment of Trypsin Inhibitor vis-à-vis Kunitz Trypsin Inhibitor and Bowman-Birk Inhibitor Activities in Soybean. Food Anal. Methods 2018, 11, 2431–2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liener, I.E. Implications of antinutritional components in soybean foods. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 1994, 34, 31–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, G.; Guo, W.; Zheng, J.; Zhao, M.; Sun, W. Effect of interaction between tea polyphenols with soymilk protein on inactivation of soybean trypsin inhibitor. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 111, 106177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, C.; Song, X.; Zhao, L.; Pan, S.; Qin, G. Purification and Characterization of Bowman-Birk Trypsin Inhibitor from Soybean. J. Food Nutr. Res. 2014, 2, 546–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kårlund, A.; Paukkonen, I.; Gómez-Gallego, C.; Kolehmainen, M. Intestinal Exposure to Food-Derived Protease Inhibitors: Digestion Physiology- and Gut Health-Related Effects. Healthcare 2021, 9, 1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieto-Veloza, A.; Wang, Z.; Zhong, Q.; D’Souza, D.; Krishnan, H.B.; Dia, V.P. Lunasin protease inhibitor concentrate decreases pro-inflammatory cytokines and improves histopathological markers in dextran sodium sulfate-induced ulcerative colitis. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2022, 11, 1508–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Huang, L.; Luo, Z.; Tamer, T.M. Stability of trypsin inhibitor isolated from potato fruit juice against pH and heating treatment and in vitro gastrointestinal digestion. Food Chem. 2020, 328, 127152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz-Huerta, E.; Fernández-Tomé, S.; Arques, M.C.; Amigo, L.; Recio, I.; Clemente, A.; Hernández-Ledesma, B. The protective role of the Bowman-Birk protease inhibitor in soybean lunasin digestion: The effect of released peptides on colon cancer growth. Food Funct. 2015, 6, 2626–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fang, E.F.; Wong, J.H.; Ng, T.B. Thermostable Kunitz trypsin inhibitor with cytokine inducing, antitumor and HIV-1 reverse transcriptase inhibitory activities from Korean large black soybeans. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2010, 109, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patriota, L.L.D.S.; Ramos, D.D.B.M.; e Silva, M.G.; dos Santos, A.C.L.A.; Silva, Y.A.; Marinho, A.D.O.; Coelho, L.C.B.B.; Paiva, P.M.G.; Pontual, E.V.; Mendes, R.L.; et al. The trypsin inhibitor from Moringa oleifera flowers (MoFTI) inhibits acute inflammation in mice by reducing cytokine and nitric oxide levels. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2021, 143, 474–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, A.R. The Bowman-Birk inhibitor from soybeans as an anticarcinogenic agent. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1998, 68, 1406–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chua, J.-Y.; Lu, Y.; Liu, S.-Q. Biotransformation of soy whey into soy alcoholic beverage by four commercial strains of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2017, 262, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xiao, L.; Tian, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Fang, Y.; Li, W. Structural Characterization, Rheological Properties and Protection of Oxidative Damage of an Exopolysaccharide from Leuconostoc citreum 1.2461 Fermented in Soybean Whey. Foods 2022, 11, 2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, X.; Wang, Q.; Lin, B.; Sun, M.; Zheng, Q.; Huang, J.; Lai, G. Structural characterization of a soluble polysaccharide SSPS1 from soy whey and its immunoregulatory activity in macrophages. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 217, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Li, Z.; Yu, B.; Wang, S.; Shen, Y.; Cong, H. Recent advances on protein separation and purification methods. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 284, 102254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duong-Ly, K.C.; Gabelli, S.B. Salting out of Proteins Using Ammonium Sulfate Precipitation. Methods Enzym. 2014, 541, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, S.; Dong, Y.; Xu, Y.; Yin, J.; Geng, L.; Xiu, Z. One-step salting-out extraction of bacteriophage from its infection broth of Acinetobacter baumannii. J. Chromatogr. A 2022, 1679, 463407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong-Ly, K.C.; Gabelli, S.B. Gel Filtration Chromatography (Size Exclusion Chromatography) of Proteins. Methods Enzym. 2014, 541, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novák, P.; Havlíček, V. Protein Extraction and Precipitation. In Proteomic Profiling and Analytical Chemistry, 2nd ed.; Ciborowski, P., Silberring, J., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohebrad, B.; Rezaee, A.; Sohrabi, B. Effect of isoelectric point on cheese whey wastewater treatment using a microbial electrochemical system. Bioelectrochemistry 2019, 130, 107200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Yang, M.; Ma, S.; Huang, J. Isolation, purification, and characterization of the globulin from wheat germ. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 57, 1708–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.; Hao, M.; Ma, S.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, J.; Ding, Q.; Sun, S.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, W. Identification of peptides with antioxidant, anti-lipoxygenase, anti-xanthine oxidase and anti-tyrosinase activities from velvet antler blood. LWT 2022, 168, 113889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Seegers, S.; Cao, W.; Wanasundara, J.; Chen, J.; Silva, A.E.; Ross, K.; Franco, A.L.; Vrijenhoek, T.; Bhowmik, P.; et al. An International Collaborative Study on Trypsin Inhibitor Assay for Legumes, Cereals, and Related Products. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2021, 98, 375–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herwade, A.P.; Kasar, S.S.; Rane, N.R.; Ahmed, S.; Maras, J.S.; Pawar, P.K. Characterization of a Bowman–Birk type trypsin inhibitor purified from seeds of Solanum surattense. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osman, M.A.; Reid, P.M.; Weber, C.W. Thermal inactivation of tepary bean (Phaseolus acutifolius), soybean and lima bean protease inhibitors: Effect of acidic and basic pH. Food Chem. 2002, 78, 419–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roychaudhuri, R.; Sarath, G.; Zeece, M.; Markwell, J. Reversible denaturation of the soybean Kunitz trypsin inhibitor. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2003, 412, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, C.; Kong, X.; Hua, Y. Heat-induced inactivation mechanisms of Kunitz trypsin inhibitor and Bowman-Birk inhibitor in soymilk processing. Food Chem. 2014, 154, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klomklao, S.; Benjakul, S.; Kishimura, H.; Chaijan, M. Extraction, purification and properties of trypsin inhibitor from Thai mung bean (Vigna radiata (L.) R. Wilczek). Food Chem. 2011, 129, 1348–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjakul, S.; Visessanguan, W.; Thummaratwasik, P. ISOLATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF TRYPSIN INHIBITORS FROM SOME THAI LEGUME SEEDS. J. Food Biochem. 2000, 24, 107–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, L.P.; Oliveira, J.T.; Rocha-Bezerra, L.C.; Sousa, D.O.; Costa, H.P.; Araujo, N.M.; Carvalho, A.F.; Tabosa, P.M.; Monteiro-Moreira, A.C.; Lobo, M.D.; et al. A trypsin inhibitor purified from Cassia leiandra seeds has insecticidal activity against Aedes aegypti. Process Biochem. 2017, 57, 228–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Temperature (°C) | α-Helix | β-Sheet | β-Turn | Random Coil |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NO heating | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 39.23 ± 0.58 | 15.30 ± 0.50 | 45.30 ± 0.98 |
| 40 | 0.20 ± 0.16 | 39.27 ± 1.25 | 15.53 ± 0.12 | 44.97 ± 1.48 |
| 50 | 0.27 ± 0.09 | 39.33 ± 1.32 | 15.03 ± 0.52 | 45.30 ±1.87 |
| 60 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 40.17 ± 1.27 | 14.20 ± 1.44 | 45.63 ± 1.37 |
| 70 | 0.33 ± 0.34 | 40.87 ± 1.45 | 15.10 ± 0.78 | 43.70 ± 1.93 |
| 80 | 0.07 ± 0.09 | 41.33 ± 1.52 | 15.30 ± 0.50 | 43.33 ± 1.92 |
| 90 | 0.43 ± 0.61 | 41.07 ± 0.41 | 15.20 ± 0.22 | 43.33 ± 1.08 |
| 100 | 0.13 ± 0.19 | 41.73 ± 0.52 | 15.17 ± 0.12 | 42.97 ± 0.52 |
| pH | α-Helix | β-Sheet | β-Turn | Random Coil |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3.0 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 40.17 ± 0.95 a | 15.03 ± 0.31 ab | 44.67 ± 0.84 b |
| 4.0 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 40.13 ± 1.67 a | 15.03 ± 0.42 ab | 44.83 ± 2.07 ab |
| 5.0 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 39.57 ± 0.94 a | 14.60 ± 0.29 b | 45.83 ± 1.91 ab |
| 6.0 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 39.67 ± 0.46 a | 14.93 ± 0.17 ab | 45.40 ± 0.62 ab |
| 7.0 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 39.76 ± 0.59 a | 15.10 ± 0.22 ab | 45.10 ± 0.85 ab |
| 8.0 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 38.33 ± 1.43 ab | 14.77 ± 0.58 ab | 46.87 ± 2.04 ab |
| 9.0 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 38.60 ± 1.53 ab | 15.00 ± 0.14 ab | 46.40 ± 1.67 ab |
| 10.0 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 37.23 ± 0.21 b | 14.90 ± 0.36 ab | 47.90 ± 0.45 a |
| 11.0 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 36.90 ± 1.19 b | 15.50 ± 0.49 ab | 48.60 ± 1.43 a |
| 12.0 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 35.50 ± 0.92 b | 15.60 ± 0.64 a | 48.90 ± 1.56 a |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ying, Z.; Li, W.; Li, H.; Liu, X. Trypsin Inhibitor from Soybean Whey Wastewater: Isolation, Purification and Stability. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 10084. https://doi.org/10.3390/app121910084
Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Ying Z, Li W, Li H, Liu X. Trypsin Inhibitor from Soybean Whey Wastewater: Isolation, Purification and Stability. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(19):10084. https://doi.org/10.3390/app121910084
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yihao, Yinxiao Zhang, Zhiwei Ying, Wenhui Li, He Li, and Xinqi Liu. 2022. "Trypsin Inhibitor from Soybean Whey Wastewater: Isolation, Purification and Stability" Applied Sciences 12, no. 19: 10084. https://doi.org/10.3390/app121910084
APA StyleZhang, Y., Zhang, Y., Ying, Z., Li, W., Li, H., & Liu, X. (2022). Trypsin Inhibitor from Soybean Whey Wastewater: Isolation, Purification and Stability. Applied Sciences, 12(19), 10084. https://doi.org/10.3390/app121910084









