Methodologies to Evaluate the Hair Follicle-Targeted Drug Delivery Provided by Nanoparticles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Skin Models
3. Methods Involving the Quantification of Nano-Entrapped Drugs
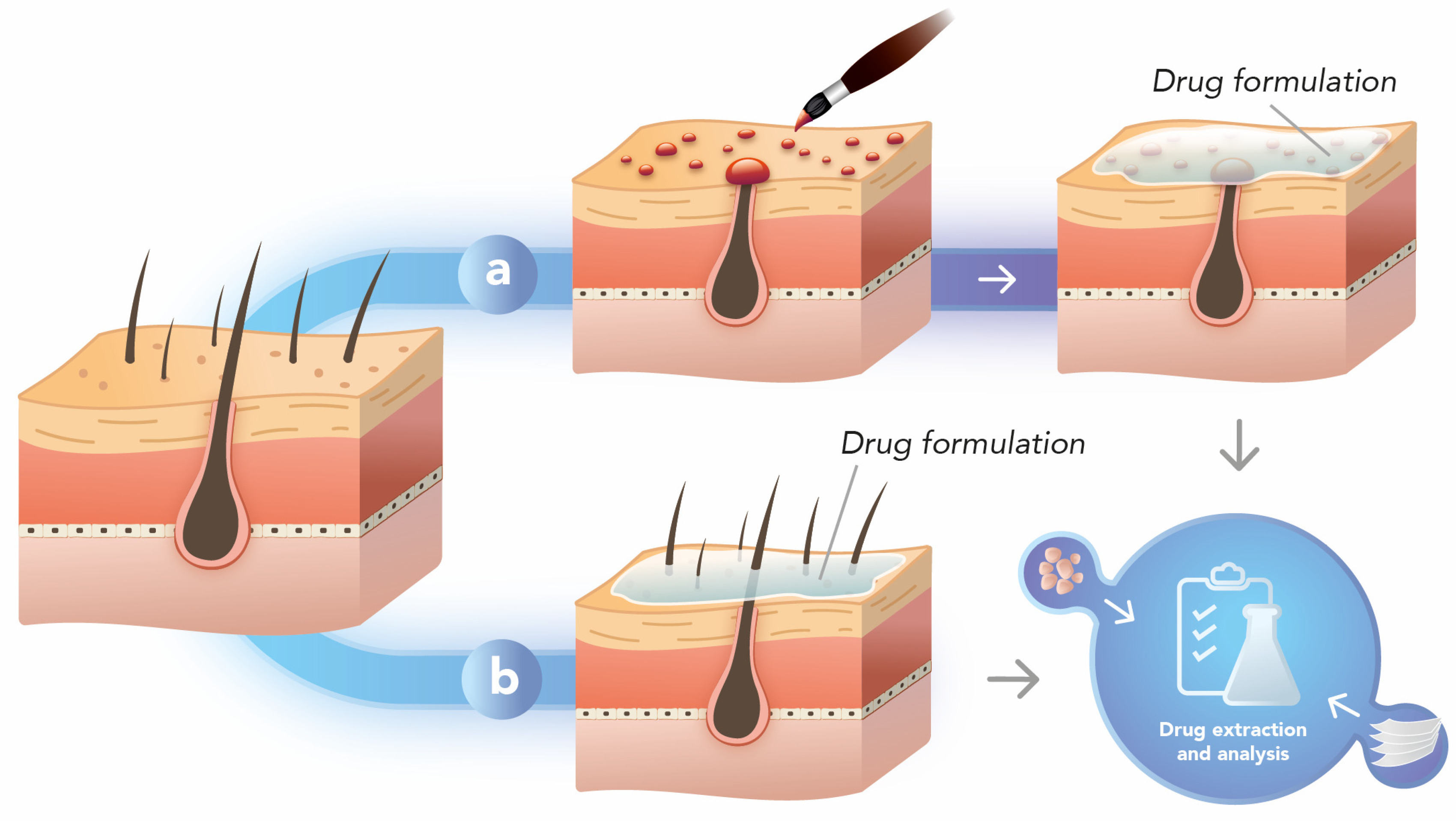
3.1. Differential Stripping
3.2. Hair Follicle Occlusion
3.3. Punch Test
4. Qualitative Methods
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tapfumaneyi, P.; Imran, M.; Mohammed, Y.; Roberts, M.S. Recent Advances and Future Prospective of Topical and Transdermal Delivery Systems. Front. Drug Deliv. 2022, 2, 957732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iliopoulos, F.; Sil, B.C.; Evans, C.L. The Role of Excipients in Promoting Topical and Transdermal Delivery: Current Limitations and Future Perspectives. Front. Drug Deliv. 2022, 2, 1049848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stacey, S.K.; Mceleney, M. Topical Corticosteroids: Choice and Application. Am. Fam. Physician 2021, 103, 337–343. [Google Scholar]
- Benson, H.A.E.; Grice, J.E.; Mohammed, Y.; Namjoshi, S.; Roberts, M.S. Topical and Transdermal Drug Delivery: From Simple Potions to Smart Technologies. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2019, 16, 444–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.Q.; Yang, X.; Wu, X.F.; Fan, Y. Bin Enhancing Permeation of Drug Molecules Across the Skin via Delivery in Nanocarriers: Novel Strategies for Effective Transdermal Applications. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 646554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tampucci, S.; Paganini, V.; Burgalassi, S.; Chetoni, P.; Monti, D. Nanostructured Drug Delivery Systems for Targeting 5-α-Reductase Inhibitors to the Hair Follicle. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polak-Witka, K.; Rudnicka, L.; Blume-Peytavi, U.; Vogt, A. The Role of the Microbiome in Scalp Hair Follicle Biology and Disease. Exp. Dermatol. 2020, 29, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gu, Y.; Bian, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, Q.; Gao, J. Hair Follicle-Targeting Drug Delivery Strategies for the Management of Hair Follicle-Associated Disorders. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 17, 333–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, M.R.; Schmidt-Ullrich, R.; Paus, R. The Hair Follicle as a Dynamic Miniorgan. Curr. Biol. 2009, 19, R132–R142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Sullivan, J.D.B.; Nicu, C.; Picard, M.; Chéret, J.; Bedogni, B.; Tobin, D.J.; Paus, R. The Biology of Human Hair Greying. Biol. Rev. 2021, 96, 107–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogt, A.; Constantinou, A.; Rancan, F.; Ghoreschi, K.; Blume-Peytavi, U.; Combadiere, B. A Niche in the Spotlight: Could External Factors Critically Disturb Hair Follicle Homeostasis and Contribute to Inflammatory Hair Follicle Diseases? Exp. Dermatol. 2020, 29, 1080–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houschyar, K.S.; Borrelli, M.R.; Tapking, C.; Popp, D.; Puladi, B.; Ooms, M.; Chelliah, M.P.; Rein, S.; Pförringer, D.; Thor, D.; et al. Molecular Mechanisms of Hair Growth and Regeneration: Current Understanding and Novel Paradigms. Dermatology 2020, 236, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, S.; Zhu, Z.; Sun, X.; Fu, X. Functional Hair Follicle Regeneration: An Updated Review. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 2021, 6, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.; Zhu, L.; He, J. Morphogenesis, Growth Cycle and Molecular Regulation of Hair Follicles. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 899095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruela, A.L.M.; Perissinato, A.G.; Lino, M.E.d.S.; Mudrik, P.S.; Pereira, G.R. Evaluation of Skin Absorption of Drugs from Topical and Transdermal Formulations. Braz. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 52, 527–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Feng, X.; Meng, S. Site-Specific Drug Delivery in the Skin for the Localized Treatment of Skin Diseases. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2019, 16, 847–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, M.; Stracke, F.; Hansen, S.; Schaefer, U.F. Nanoparticles and Their Interactions with the Dermal Barrier. Dermato -Endocrinol. 2009, 1, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Costa, C.; Cavaco-Paulo, A.; Matamá, T. Mapping Hair Follicle-Targeted Delivery by Particle Systems: What Has Science Accomplished so Far? Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 610, 121273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabat, R.; Jemec, G.B.E.; Matusiak, Ł.; Kimball, A.B.; Prens, E.; Wolk, K. Hidradenitis Suppurativa. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2020, 6, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amat-Samaranch, V.; Agut-Busquet, E.; Vilarrasa, E.; Puig, L. New Perspectives on the Treatment of Hidradenitis Suppurativa. Ther. Adv. Chronic Dis. 2021, 12, 20406223211055920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinde, U.A.; Parmar, S.J.; Easwaran, S. Metronidazole-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers to improve skin deposition and retention in the treatment of rosacea. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2019, 45, 1039–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, M.N.; Tolentino, S.; Pires, F.Q.; Anjos, J.L.V.; Alonso, A.; Gratieri, T.; Cunha-Filho, M.; Gelfuso, G.M. Nanostructured Lipid Carriers for Hair Follicle-Targeted Delivery of Clindamycin and Rifampicin to Hidradenitis Suppurativa Treatment. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2021, 197, 111448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira-Nunes, R.; Cunha-Filho, M.; Gratieri, T.; Gelfuso, G.M. Follicular-Targeted Delivery of Spironolactone Provided by Polymeric Nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2021, 208, 112101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbalho, G.N.; Matos, B.N.; Brito, G.F.d.S.; Miranda, T.d.C.; Alencar-Silva, T.; Sodré, F.F.; Gelfuso, G.M.; Cunha-Filho, M.; Carvalho, J.L.; da Silva, J.K.D.R.; et al. Skin Regenerative Potential of Cupuaçu Seed Extract (Theobroma Grandiflorum), a Native Fruit from the Amazon: Development of a Topical Formulation Based on Chitosan-Coated Nanocapsules. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, P.M.; Alencar-Silva, T.; Pires, F.Q.; Cunha-Filho, M.; Gratieri, T.; Carvalho, J.L.; Gelfuso, G.M. Nanostructured Lipid Carriers Loaded with an Association of Minoxidil and Latanoprost for Targeted Topical Therapy of Alopecia. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2022, 172, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolentino, S.; Pereira, M.N.; Cunha-Filho, M.; Gratieri, T.; Gelfuso, G.M. Targeted Clindamycin Delivery to Pilosebaceous Units by Chitosan or Hyaluronic Acid Nanoparticles for Improved Topical Treatment of Acne Vulgaris. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 253, 117295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lymberopoulos, A.; Demopoulou, C.; Kyriazi, M.; Katsarou, M.; Demertzis, N.; Hatziandoniou, S.; Maswadeh, H.; Papaioanou, G.; Demetzos, C.; Maibach, H.; et al. Liposome Percutaneous Penetration in Vivo. Toxicol. Res. Appl. 2017, 1, 2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verma, D.D.; Verma, S.; Blume, G.; Fahr, A. Liposomes Increase Skin Penetration of Entrapped and Non-Entrapped Hydrophilic Substances into Human Skin: A Skin Penetration and Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy Study. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2003, 55, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutradhar, K.B.; Amin, L. Nanoemulsions: Increasing Possibilities in Drug Delivery. Eur. J. Nanomed. 2013, 5, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Mattos, C.B.; Argenta, D.F.; Melchiades, G.d.L.; Cordeiro, M.N.S.; Tonini, M.L.; Moraes, M.H.; Weber, T.B.; Roman, S.S.; Nunes, R.J.; Teixeira, H.F.; et al. Nanoemulsions Containing a Synthetic Chalcone as an Alternative for Treating Cutaneous Leshmaniasis: Optimization Using a Full Factorial Design. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 5529–5542. [Google Scholar]
- Cheruvu, H.S.; Liu, X.; Grice, J.E.; Roberts, M.S. Modeling Percutaneous Absorption for Successful Drug Discovery and Development. Expert. Opin. Drug Discov. 2020, 15, 1181–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopf, N.B.; Champmartin, C.; Schenk, L.; Berthet, A.; Chedik, L.; Du Plessis, J.L.; Franken, A.; Frasch, F.; Gaskin, S.; Johanson, G.; et al. Reflections on the OECD Guidelines for in Vitro Skin Absorption Studies. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2020, 117, 104752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souto, E.B.; Fangueiro, J.F.; Fernandes, A.R.; Cano, A.; Sanchez-Lopez, E.; Garcia, M.L.; Severino, P.; Paganelli, M.O.; Chaud, M.V.; Silva, A.M. Physicochemical and Biopharmaceutical Aspects Influencing Skin Permeation and Role of SLN and NLC for Skin Drug Delivery. Heliyon 2022, 8, e08938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patzelt, A.; Lademann, J. Recent Advances in Follicular Drug Delivery of Nanoparticles. Expert Opin Drug Deliv 2020, 17, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Mahrooqi, J.H.; Khutoryanskiy, V.V.; Williams, A.C. Thiolated and PEGylated Silica Nanoparticle Delivery to Hair Follicles. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 593, 120130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.; Cho, H.-E.; Moon, S.H.; Ahn, H.-J.; Bae, S.; Cho, H.-D.; An, S. Transdermal Delivery Systems in Cosmetics. Biomed. Dermatol. 2020, 4, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carolina Oliveira dos Santos, L.; Spagnol, C.M.; Guillot, A.J.; Melero, A.; Corrêa, M.A. Caffeic Acid Skin Absorption: Delivery of Microparticles to Hair Follicles. Saudi Pharm. J. 2019, 27, 791–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brammann, C.; Bornemann, C.; Kannewurf, R.; Müller-Goymann, C.C. Solid Lipid Microparticles for Hair Follicle Targeting of Adapalene and Benzoyl Peroxide—Release through Targeted Erosion. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 60, 101990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patzelt, A.; Richter, H.; Knorr, F.; Schäfer, U.; Lehr, C.M.; Dähne, L.; Sterry, W.; Lademann, J. Selective Follicular Targeting by Modification of the Particle Sizes. J. Control. Release 2011, 150, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Griffin, P.; Price, G.J.; Guy, R.H. Preparation and in Vitro Evaluation of Topical Formulations Based on Polystyrene-Poly-2-Hydroxyl Methacrylate Nanoparticle. Mol. Pharm. 2009, 6, 1449–1456. [Google Scholar]
- Wosicka, H.; Cal, K. Targeting to the Hair Follicles: Current Status and Potential. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2010, 57, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, C.L.; Aljuffali, I.A.; Li, Y.C.; Fang, J.Y. Delivery and Targeting of Nanoparticles into Hair Follicles. Ther. Deliv. 2014, 5, 991–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, S.K.; Verma, A.; Jain, A.; Hurkat, P. Transfollicular Drug Delivery: Current Perspectives. Res. Rep. Transdermal Drug Deliv. 2016, 5, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, X.; He, H. A Review of Cosmetic Skin Delivery. J. Cosmet Dermatol. 2021, 20, 2020–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaefer, U.F.; Hansen, S.; Schneider, M.; Contreras, J.L.; Lehr, C.-M. Models for Skin Absorption and Skin Toxicity Testing; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Chambers, E.S.; Vukmanovic-Stejic, M. Skin Barrier Immunity and Ageing. Immunology 2020, 160, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lademann, J.; Richter, H.; Meinke, M.; Sterry, W.; Patzelt, A. Which Skin Model Is the Most Appropriate for the Investigation of Topically Applied Substances into the Hair Follicles? Skin Pharmacol. Physiol. 2010, 23, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flaten, G.E.; Palac, Z.; Engesland, A.; Filipović-Grčić, J.; Vanić, Ž.; Škalko-Basnet, N. In Vitro Skin Models as a Tool in Optimization of Drug Formulation. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 75, 10–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Todo, H. Transdermal Permeation of Drugs in Various Animal Species. Pharmaceutics 2017, 9, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nicoli, S.; Padula, C.; Aversa, V.; Vietti, B.; Wertz, P.W.; Millet, A.; Falson, F.; Govoni, P.; Santi, P. Characterization of Rabbit Ear Skin as a Skin Model for in Vitro Transdermal Permeation Experiments: Histology, Lipid Composition and Permeability. Skin Pharmacol. Physiol. 2008, 21, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobi, U.; Kaiser, M.; Toll, R.; Mangelsdorf, S.; Audring, H.; Otberg, N.; Sterry, W.; Lademann, J. Porcine Ear Skin: An In Vitro Model for Human Skin. Ski. Res. Technol. 2007, 13, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquet, F.; Grandclaude, M.-C.; Ferrari, E.; Champmartin, C. Capacity of an in Vitro Rat Skin Model to Predict Human Dermal Absorption: Influences of Aging and Anatomical Site. Toxicol. Vitr. 2019, 61, 104623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbero, A.M.; Frasch, H.F. Pig and Guinea Pig Skin as Surrogates for Human in Vitro Penetration Studies: A Quantitative Review. Toxicol. Vitr. 2009, 23, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.C.J.; Edwards, G.A.; Martin, D.J.; Huang, H.; Crichton, M.L.; Kendall, M.A.F. Allometric Scaling of Skin Thickness, Elasticity, Viscoelasticity to Mass for Micro-Medical Device Translation: From Mice, Rats, Rabbits, Pigs to Humans. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mangelsdorf, S.; Vergou, T.; Sterry, W.; Lademann, J.; Patzelt, A. Comparative Study of Hair Follicle Morphology in Eight Mammalian Species and Humans. Ski. Res. Technol. 2014, 20, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Ravenzwaay, B.; Leibold, E. A Comparison between in Vitro Rat and Human and in Vivo Rat Skin Absorption Studies. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2004, 23, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez, F.; Ruifernández, J.M. Distribution of Human Hair in Follicular Units A Mathematical Model for Estimating the Donor Size in Follicular Unit Transplantation. Dermatol. Surg. 1999, 25, 294–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araújo, R.; Fernandes, M.; Cavaco-Paulo, A.; Gomes, A. Biology of Human Hair: Know Your Hair to Control It. Adv. Biochem. Eng. Biotechnol. 2011, 125, 121–143. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gallagher, S.; Kruger, U.; Josyula, K.; Rahul; Gong, A.; Song, A.; Sweet, R.; Makled, B.; Parsey, C.; Norfleet, J.; et al. Thermally Damaged Porcine Skin Is Not a Surrogate Mechanical Model of Human Skin. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 4565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Q.; Yuan, R.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, T.; Shi, R.; Zhang, M.; Li, Y.; Fei, K.; Feng, R.; et al. A Single-Cell Transcriptome Atlas of Pig Skin Characterizes Anatomical Positional Heterogeneity. eLife 2023, 12, e86504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotnichenko, A.S.; Gilevich, I.V.; Melkonyan, K.I.; Yutskevich, Y.A.; Rusinova, T.V.; Karakulev, A.V.; Bogdanov, S.B.; Aladina, V.A.; Belich, Y.A.; Gumenyuk, S.E.; et al. Comparative Morphological Characteristics of the Results of Implantation of Decellularized and Recellularized Porcine Skin Scaffolds. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2021, 170, 378–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, F.K.H.; Delgado-Charro, M.B.; Bolhuis, A. Evaluation of an Explanted Porcine Skin Model to Investigate Infection with the Dermatophyte Trichophyton Rubrum. Mycopathologia 2020, 185, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, J.H.; Jeong, H.; Lee, N.; Hur, S.; Lee, N.; Han, J.J.; Jang, H.W.; Choi, W.K.; Nam, K.T.; Lim, K.M. Ex Vivo Live Full-Thickness Porcine Skin Model as a Versatile in Vitro Testing Method for Skin Barrier Research. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ta, Q.; Ting, J.; Harwood, S.; Browning, N.; Simm, A.; Ross, K.; Olier, I.; Al-Kassas, R. Chitosan Nanoparticles for Enhancing Drugs and Cosmetic Components Penetration through the Skin. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 160, 105765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, W.; Schönnagel, B.; Fleischer, L.-G. A Note on Integumental (1→3)(1→6)β-d-Glucan Permeation, Using the Porcine Ear Skin Model. Blackwell Publ. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2006, 5, 130–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praça, F.S.G.; Medina, W.S.G.; Eloy, J.O.; Petrilli, R.; Campos, P.M.; Ascenso, A.; Bentley, M.V.L.B. Evaluation of Critical Parameters for in Vitro Skin Permeation and Penetration Studies Using Animal Skin Models. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 111, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Neupane, R.; Boddu, S.H.S.; Renukuntla, J.; Babu, R.J.; Tiwari, A.K. Alternatives to Biological Skin in Permeation Studies: Current Trends and Possibilities. Pharmaceutics 2020, 1, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ranamukhaarachchi, S.A.; Lehnert, S.; Ranamukhaarachchi, S.L.; Sprenger, L.; Schneider, T.; Mansoor, I.; Rai, K.; Häfeli, U.O.; Stoeber, B. A micromechanical comparison of human and porcine skin before and after preservation by freezing for medical device development. Sci. Rep. 2016, 25, 32074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schmook, F.P.; Meingassner, J.G.; Billich, A. Comparison of Human Skin or Epidermis Models with Human and Animal Skin in In-Vitro Percutaneous Absorption. Int. J. Pharm. 2001, 215, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, C.; Chow, A.Y.K.; Downie, R.H.; Buttar, H.S. Percutaneous Absorption of Hexachlorophene in Rats, Guinea Pigs and Pigs. Toxicology 1978, 9, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, K.; Bhatia, A.; Tsen, F.; Chen, M.; Wong, A.K.; Woodley, D.T.; Li, W. Identification of the Critical Therapeutic Entity in Secreted Hsp90α That Promotes Wound Healing in Newly Re-Standardized Healthy and Diabetic Pig Models. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e113956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khiao In, M.; Richardson, K.C.; Loewa, A.; Hedtrich, S.; Kaessmeyer, S.; Plendl, J. Histological and Functional Comparisons of Four Anatomical Regions of Porcine Skin with Human Abdominal Skin. J. Vet. Med. Ser. C Anat. Histol. Embryol. 2019, 48, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patzelt, A.; Richter, H.; Buettemeyer, R.; Huber, H.J.R.; Blume-Peytavi, U.; Sterry, W.; Lademann, J. Differential Stripping Demonstrates a Significant Reduction of the Hair Follicle Reservoir In Vitro Compared to In Vivo. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2008, 70, 234–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, G.A.; Maibach, H.I. The Pig as an Experimental Animal Model of Percutaneous Permeation in Man: Qualitative and Quantitative Observations-An Overview. Ski. Pharmacol. Appl. Ski. Physiol. 2000, 13, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, B.; Matamá, T.; Gomes, A.; Cavaco-Paulo, A. Cyclosporin A-Loaded Poly(d,l-Lactide) Nanoparticles: A Promising Tool for Treating Alopecia. Nanomedicine 2020, 15, 1459–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matos, B.N.; Reis, T.A.; Gratieri, T.; Gelfuso, G.M. Chitosan Nanoparticles for Targeting and Sustaining Minoxidil Sulphate Delivery to Hair Follicles. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 75, 225–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ushirobira, C.Y.; Afiune, L.A.F.; Pereira, M.N.; Cunha-Filho, M.; Gelfuso, G.M.; Gratieri, T. Dutasteride Nanocapsules for Hair Follicle Targeting: Effect of Chitosan-Coating and Physical Stimulus. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 151, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.; Nagel, G.; Giulbudagian, M.; Calderón, M.; Patzelt, A.; Knorr, F.; Lademann, J. Temperature-Enhanced Follicular Penetration of Thermoresponsive Nanogels. Z. Phys. Chem. 2018, 232, 805–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolentino, S.; Pereira, M.N.; de Sousa, M.C.; Cunha-Filho, M.; Gelfuso, G.M.; Gratieri, T. The Influence of Sebaceous Content on the Performance of Nanosystems Designed for the Treatment of Follicular Diseases. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 59, 101895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahl, J.; Niedorf, F.; Wohlert, M.; Kietzmann, M. The In Vitro Use of the Hair Follicle Closure Technique to Study the Follicular and Percutaneous Permeation of Topically Applied Drugs. Altern. Lab. Anim. 2012, 40, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antônio, L.; Silva, D.; Fleury Taveira, S.; Lima, E.M.; Marreto, R.N. In Vitro Skin Penetration of Clobetasol from Lipid Nanoparticles: Drug Extraction and Quantitation in Different Skin Layers. Braz. J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 48, 811–817. [Google Scholar]
- Tiossi, R.F.J.; Da Costa, J.C.; Miranda, M.A.; Praça, F.S.G.; Vitória, M.; Bentley, L.B.; Bastos, J.K.; Mcchesney, J.D. A validated HPLC analytical method for the analysis of solasonine and solamargine in in vitro skin penetration studies. Quim. Nova 2012, 35, 2312–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferreira-Nunes, R.; Ferreira, L.A.; Gratieri, T.; Cunha-Filho, M.; Gelfuso, G.M. Stability-Indicating Analytical Method of Quantifying Spironolactone and Canrenone in Dermatological Formulations and Iontophoretic Skin Permeation Experiments. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2019, 33, e4656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolentino, S.; Gratieri, T.; Cunha-Filho, M.; Gelfuso, G.M. Curcumin Quantification in Skin and Mucosa: Optimization of Extraction and Chromatographic Method Validation. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2023, 1217, 123623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anjani, Q.K.; Bin Sabri, A.H.; Donnelly, R.F. Development and Validation of Simple and Sensitive HPLC-UV Method for Ethambutol Hydrochloride Detection Following Transdermal Application. Anal. Methods 2022, 14, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjani, Q.K.; Sabri, A.H.B.; McGuckin, M.B.; Li, H.; Hamid, K.A.; Donnelly, R.F. In Vitro Permeation Studies on Carvedilol Containing Dissolving Microarray Patches Quantified Using a Rapid and Simple HPLC-UV Analytical Method. AAPS PharmSciTech 2022, 23, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucca, L.G.; de Matos, S.P.; Weimer, P.; Teixeira, H.F.; Koester, L.S. Improved Skin Delivery and Validation of Novel Stability-Indicating HPLC Method for Ketoprofen Nanoemulsion. Arab. J. Chem. 2020, 13, 4505–4511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjani, Q.K.; Demartis, S.; Volpe-Zanutto, F.; Li, H.; Sabri, A.H.B.; Gavini, E.; Donnelly, R.F. Fluorescence-Coupled Techniques for Determining Rose Bengal in Dermatological Formulations and Their Application to Ex Vivo Skin Deposition Studies. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Dirbashi, O.; Kuroda, N.; Inuduka, S.; Menichini, F.; Nakashima, K. HPLC with Fluorescence Detection of Methamphetamine and Amphetamine in Segmentally Analyzed Human Hair. Analista 1999, 124, 493–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, P.M.; Sampaio, T.R.; França, L.C.F.; Gratieri, T.; Cunha-Filho, M.; Gelfuso, G.M. LC–MS Bioanalytical Method for Simultaneous Determination of Latanoprost and Minoxidil in the Skin. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2020, 187, 113373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pafili, A.; Meikopoulos, T.; Kontogiannidou, E.; Papageorgiou, S.; Demiri, E.; Meimari, D.; Fatouros, D.G.; Gika, H.; Theodoridis, G. Development and Validation of LC-MS/MS Method for the Determination of UV-Filters across Human Skin In Vitro. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2021, 1167, 122561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yang, Y.; Ashraf, M.; Cruz, C.N.; Lee, S.; Faustino, P.J. An Advanced Automation Platform Coupled with Mass Spectrometry for Investigating In Vitro Human Skin Permeation of UV Filters and Excipients in Sunscreen Products. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2022, 36, e9273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuzawa, T.; Nakano, M.; Oikawa, A.; Nakamura, Y.; Matsue, H. Three-Dimensional Epidermal Model from Human Hair Follicle-Derived Keratinocytes. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 1993, 123–137. [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, A.J.; Tawfik, S.S.; Baruah, K.P.; O’Toole, E.A.; O’Shaughnessy, R.F.L. Tape Strips in Dermatology Research. Br. J. Dermatol. 2021, 185, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zsikó, S.; Csányi, E.; Kovács, A.; Budai-Szűcs, M.; Gácsi, A.; Berkó, S. Methods to Evaluate Skin Penetration in Vitro. Sci. Pharm. 2019, 87, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Olesen, C.M.; Fuchs, C.S.K.; Philipsen, P.A.; Hædersdal, M.; Agner, T.; Clausen, M.L. Advancement through Epidermis Using Tape Stripping Technique and Reflectance Confocal Microscopy. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Teichmann, A.; Jacobi, U.; Ossadnik, M.; Richter, H.; Koch, S.; Sterry, W.; Rgen Lademann, J. Differential Stripping: Determination of the Amount of Topically Applied Substances Penetrated into the Hair Follicles. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2005, 125, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oliveira, A.C.S.; Oliveira, P.M.; Cunha-Filho, M.; Gratieri, T.; Gelfuso, G.M. Latanoprost Loaded in Polymeric Nanocapsules for Effective Topical Treatment of Alopecia. AAPS PharmSciTech 2020, 21, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, J.L.; Pires, F.Q.; Gross, I.P.; Alencar-Silva, T.; Gratieri, T.; Gelfuso, G.M.; Sá-Barreto, L.; Carvalho, J.L.; Cunha-Filho, M. Propranolol-Loaded Nanostructured Lipid Carriers for Topical Treatment of Infantile Hemangioma. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2023, 80, 104099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lademann, J.; Richter, H.; Teichmann, A.; Otberg, N.; Blume-Peytavi, U.; Luengo, J.; Weiß, B.; Schaefer, U.F.; Lehr, C.M.; Wepf, R.; et al. Nanoparticles—An Efficient Carrier for Drug Delivery into the Hair Follicles. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2007, 66, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teichmann, A.; Otberg, N.; Jacobi, U.; Sterry, W.; Lademann, J. Follicular Penetration: Development of a Method to Block the Follicles Selectively against the Penetration of Topically Applied Substances. Skin Pharmacol. Physiol. 2006, 19, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, A.L.; Lubda, M.; Akbarzadeh Taghavi, P.; Lademann, J.; Beckers, I.; Von Hagen, J.; Kolmar, H.; Patzelt, A. Solvent-Containing Closure Material Can Be Used to Prevent Follicular Penetration of Caffeine and Fluorescein Sodium Salt on Porcine Ear Skin. Skin Pharmacol. Physiol. 2020, 33, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trauer, S.; Patzelt, A.; Otberg, N.; Knorr, F.; Rozycki, C.; Balizs, G.; Büttemeyer, R.; Linscheid, M.; Liebsch, M.; Lademann, J. Permeation of Topically Applied Caffeine through Human Skin—A Comparison of In Vivo and In Vitro Data. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2009, 68, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blume-Peytavi, U.; Massoudy, L.; Patzelt, A.; Lademann, J.; Dietz, E.; Rasulev, U.; Garcia Bartels, N. Follicular and Percutaneous Penetration Pathways of Topically Applied Minoxidil Foam. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2010, 76, 450–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boakye, C.H.A.; Patel, K.; Singh, M. Doxorubicin Liposomes as an Investigative Model to Study the Skin Permeation of Nanocarriers. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 489, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Desai, P.R.; Shah, P.P.; Hayden, P.; Singh, M. Investigation of Follicular and Non-Follicular Pathways for Polyarginine and Oleic Acid-Modified Nanoparticles. Pharm. Res. 2013, 30, 1037–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lapteva, M.; Möller, M.; Gurny, R.; Kalia, Y.N. Self-Assembled Polymeric Nanocarriers for the Targeted Delivery of Retinoic Acid to the Hair Follicle. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 18651–18662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kandekar, S.G.; Del Río-Sancho, S.; Lapteva, M.; Kalia, Y.N. Selective Delivery of Adapalene to the Human Hair Follicle under Finite Dose Conditions Using Polymeric Micelle Nanocarriers. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 1099–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, R.S.; Agrawal, Y.K. Raman Spectroscopy: Recent Advancements, Techniques and Applications. Vib. Spectrosc. 2011, 57, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista, A.; Breunig, H.G.; Uchugonova, A.; Morgado, A.M.; König, K. Two-Photon Spectral Fluorescence Lifetime and Second-Harmonic Generation Imaging of the Porcine Cornea with a 12-Femtosecond Laser Microscope. J. Biomed. Opt. 2016, 21, 036002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramezanli, T.; Zhang, Z.; Michniak-Kohn, B.B. Development and Characterization of Polymeric Nanoparticle-Based Formulation of Adapalene for Topical Acne Therapy. Nanomedicine 2017, 13, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, A.D. Confocal Microscopy: Principles and Modern Practices. Curr. Protoc. Cytom. 2020, 92, e68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez-Román, R.; Naik, A.; Kalia, Y.N.; Fessi, H.; Guy, R.H. Visualization of Skin Penetration Using Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2004, 58, 301–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mateus, R.; Abdalghafor, H.; Oliveira, G.; Hadgraft, J.; Lane, M.E. A New Paradigm in Dermatopharmacokinetics-Confocal Raman Spectroscopy. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 444, 106–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franzen, L.; Anderski, J.; Windbergs, M. Quantitative Detection of Caffeine in Human Skin by Confocal Raman Spectroscopy—A Systematic in Vitro Validation Study. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2015, 95, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; An, Y.; Liao, Y. A Novel Peptide-Based Fluorescent Chemosensor for Cd(II) Ions and Its Applications in Bioimaging. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2019, 216, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Celli, A.; Zhu, H.; Elmahdy, A.; Cao, Y.; Hui, X.; Maibach, H. Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy to Estimate Nanoparticles’ Human Skin Penetration in Vitro. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 8035–8041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lapteva, M.; Santer, V.; Mondon, K.; Patmanidis, I.; Chiriano, G.; Scapozza, L.; Gurny, R.; Möller, M.; Kalia, Y.N. Targeted Cutaneous Delivery of Ciclosporin A Using Micellar Nanocarriers and the Possible Role of Inter-Cluster Regions as Molecular Transport Pathways. J. Control. Release 2014, 196, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahraman, E.; Özhan, G.; Özsoy, Y.; Güngör, S. Polymeric Micellar Nanocarriers of Benzoyl Peroxide as Potential Follicular Targeting Approach for Acne Treatment. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 146, 692–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caverzan, J.; de Jesus, M.B.; Durán, N. Nanostructured Lipid Carriers Loaded with 17-α-Estradiol Accumulate into Hair Follicles. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2020, 31, 1345–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, I.; Hida, Y.; Makino, K. Minoxidil-Encapsulated Poly(L-Lactide-Co -Glycolide) Nanoparticles with Hair Follicle Delivery Properties Prepared Using W/O/W Solvent Evaporation and Sonication. Biomed. Mater. Eng. 2018, 29, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.T. Cutaneous Drug Delivery: An Update. J. Investig. Dermatol. Symp. Proc. 2013, 16, S67–S69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Price, G.J.; Guy, R.H. Disposition of Nanoparticles and an Associated Lipophilic Permeant Following Topical Application to the Skin. Mol. Pharm. 2009, 6, 1441–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lohan, S.B.; Saeidpour, S.; Solik, A.; Schanzer, S.; Richter, H.; Dong, P.; Darvin, M.E.; Bodmeier, R.; Patzelt, A.; Zoubari, G.; et al. Investigation of the Cutaneous Penetration Behavior of Dexamethasone Loaded to Nano-Sized Lipid Particles by EPR Spectroscopy, and Confocal Raman and Laser Scanning Microscopy. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2017, 116, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grams, Y.Y.; Alaruikka, S.; Lashley, L.; Caussin, J.; Whitehead, L.; Bouwstra, J.A. Permeant Lipophilicity and Vehicle Composition Influence Accumulation of Dyes in Hair Follicles of Human Skin. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2003, 18, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, J.; Kang, H.S.; Park, W.S.; Han, S.H.; Kim, J.; Chang, I.S. Transdermal Delivery of Mixnoxidil with Block Copolymer Nanoparticles. J. Control. Release 2004, 97, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, W.Y.; Kim, S.; Lee, S.Y.; Lee, H.; Han, D.W.; Yang, S.Y.; Kim, K.S. Transdermal Delivery of Minoxidil Using HA-PLGA Nanoparticles for the Treatment in Alopecia. Biomater. Res. 2019, 23, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lapteva, M.; Mondon, K.; Möller, M.; Gurny, R.; Kalia, Y.N. Polymeric Micelle Nanocarriers for the Cutaneous Delivery of Tacrolimus: A Targeted Approach for the Treatment of Psoriasis. Mol. Pharm. 2014, 11, 2989–3001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitsutake, H.; Poppi, R.J.; Breitkreitz, M.C. Raman Imaging Spectroscopy: History, Fundamentals and Current Scenario of the Technique. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2019, 30, 2243–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saviello, D.; Trabace, M.; Alyami, A.; Mirabile, A.; Baglioni, P.; Giorgi, R.; Iacopino, D. Raman Spectroscopy and Surface Enhanced Raman Scattering (SERS) for the Analysis of Blue and Black Writing Inks: Identification of Dye Content and Degradation Processes. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binder, L.; SheikhRezaei, S.; Baierl, A.; Gruber, L.; Wolzt, M.; Valenta, C. Confocal Raman Spectroscopy: In Vivo Measurement of Physiological Skin Parameters—A Pilot Study. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2017, 88, 280–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Franzen, L.; Mathes, C.; Hansen, S.; Windbergs, M. Advanced Chemical Imaging and Comparison of Human and Porcine Hair Follicles for Drug Delivery by Confocal Raman Microscopy. J. Biomed. Opt. 2012, 18, 061210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, L.; Téllez S, C.A.; Sousa, M.P.J.; Azoia, N.G.; Cavaco-Paulo, A.M.; Martin, A.A.; Favero, P.P. In Vivo Confocal Raman Spectroscopy and Molecular Dynamics Analysis of Penetration of Retinyl Acetate into Stratum Corneum. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2017, 174, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alvarez-Figueroa, M.J.; Narváez-Araya, D.; Armijo-Escalona, N.; Carrasco-Flores, E.A.; González-Aramundiz, J.V. Design of Chitosan Nanocapsules with Compritol 888 ATO® for Imiquimod Transdermal Administration. Evaluation of Their Skin Absorption by Raman Microscopy. Pharm. Res. 2020, 37, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caspers, P.J.; Lucassen, G.W.; Puppels, G.J. Combined in Vivo Confocal Raman Spectroscopy and Confocal Microscopy of Human Skin. Biophys. J. 2003, 85, 572–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]




| Type | Technique | Skin Model | Findings | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quantitative methods | Differential stripping | Porcine | 30% more drug in hair follicles from nanoparticles compared to control solution. | [98] |
| Porcine | Doubled the minoxidil accumulation in the hair follicles. Drug are deposited in the hair follicles for up to 10 days. | [76,100] | ||
| Occlusion of the hair follicle | Porcine | Blocking hair follicles showed a significant difference between interfollicular and follicular penetration of topically applied caffeine. | [101] | |
| Human | Caffeine reached the receptor compartment of the diffusion cell with open hair follicles more quickly compared to closed hair follicles. | [103] | ||
| Human | In just 5 min, minoxidil was detected in blood samples when follicles remained open compared to 30 min with closed follicles. | [104] | ||
| Punch test | Human | The most significant follicular deposition of the drug in the follicles was obtained with the nanoformulation. | [108] | |
| Qualitative methods | Fluorescence microscopy | Porcine | PEG 5000 Da functionalized nanoparticles penetrated deeper into hair follicles compared to PEG 750 Da functionalized ones. | [35] |
| Confocal laser scanning microscopy | Human | The technique allowed seeing nanoparticles in the stratum corneum and hair follicles without penetrating the epidermis/dermis. | [117] | |
| Porcine | Micelle promotes threefold higher drug deposition than a commercial gel preparation. | [119] | ||
| Porcine | Nanostructured lipid carriers’ formulation accumulates less on top of the skin and more in the hair follicles. | [120] | ||
| Raman spectroscopy | Porcine | The drug was in the inner layers of the skin. | [135] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pereira, M.N.; Nogueira, L.L.; Cunha-Filho, M.; Gratieri, T.; Gelfuso, G.M. Methodologies to Evaluate the Hair Follicle-Targeted Drug Delivery Provided by Nanoparticles. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2002. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15072002
Pereira MN, Nogueira LL, Cunha-Filho M, Gratieri T, Gelfuso GM. Methodologies to Evaluate the Hair Follicle-Targeted Drug Delivery Provided by Nanoparticles. Pharmaceutics. 2023; 15(7):2002. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15072002
Chicago/Turabian StylePereira, Maíra N., Luma L. Nogueira, Marcilio Cunha-Filho, Tais Gratieri, and Guilherme M. Gelfuso. 2023. "Methodologies to Evaluate the Hair Follicle-Targeted Drug Delivery Provided by Nanoparticles" Pharmaceutics 15, no. 7: 2002. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15072002
APA StylePereira, M. N., Nogueira, L. L., Cunha-Filho, M., Gratieri, T., & Gelfuso, G. M. (2023). Methodologies to Evaluate the Hair Follicle-Targeted Drug Delivery Provided by Nanoparticles. Pharmaceutics, 15(7), 2002. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15072002






