Drug Combinations Targeting FAK and MEK Overcomes Tumor Heterogeneity in Glioblastoma
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Compound and Drug Combination Screening
2.3. Cell Viability Assay
2.4. Cellular Imaging and Quantification
2.5. Quantification of Tumor Area in IHC Stained Sections
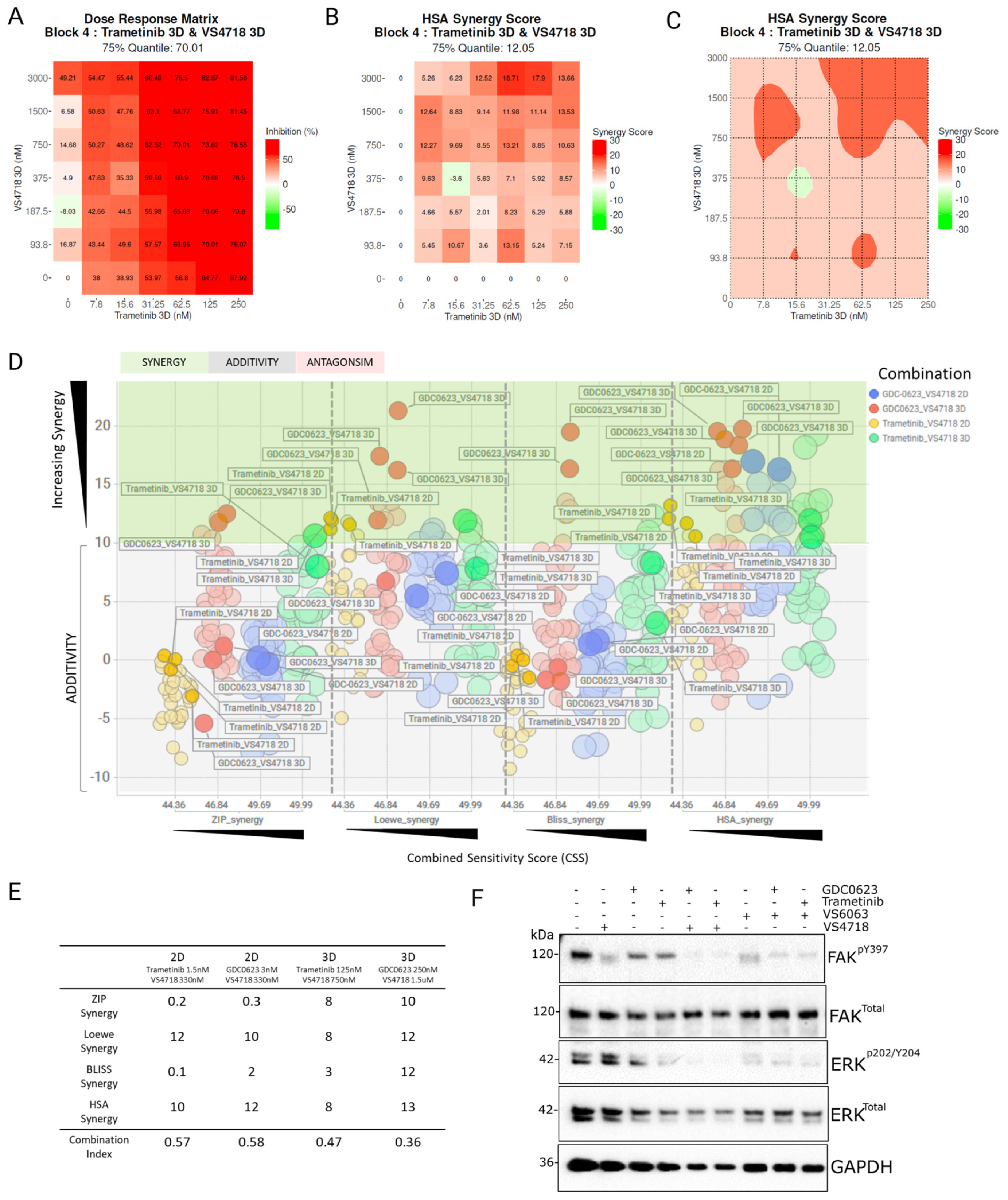
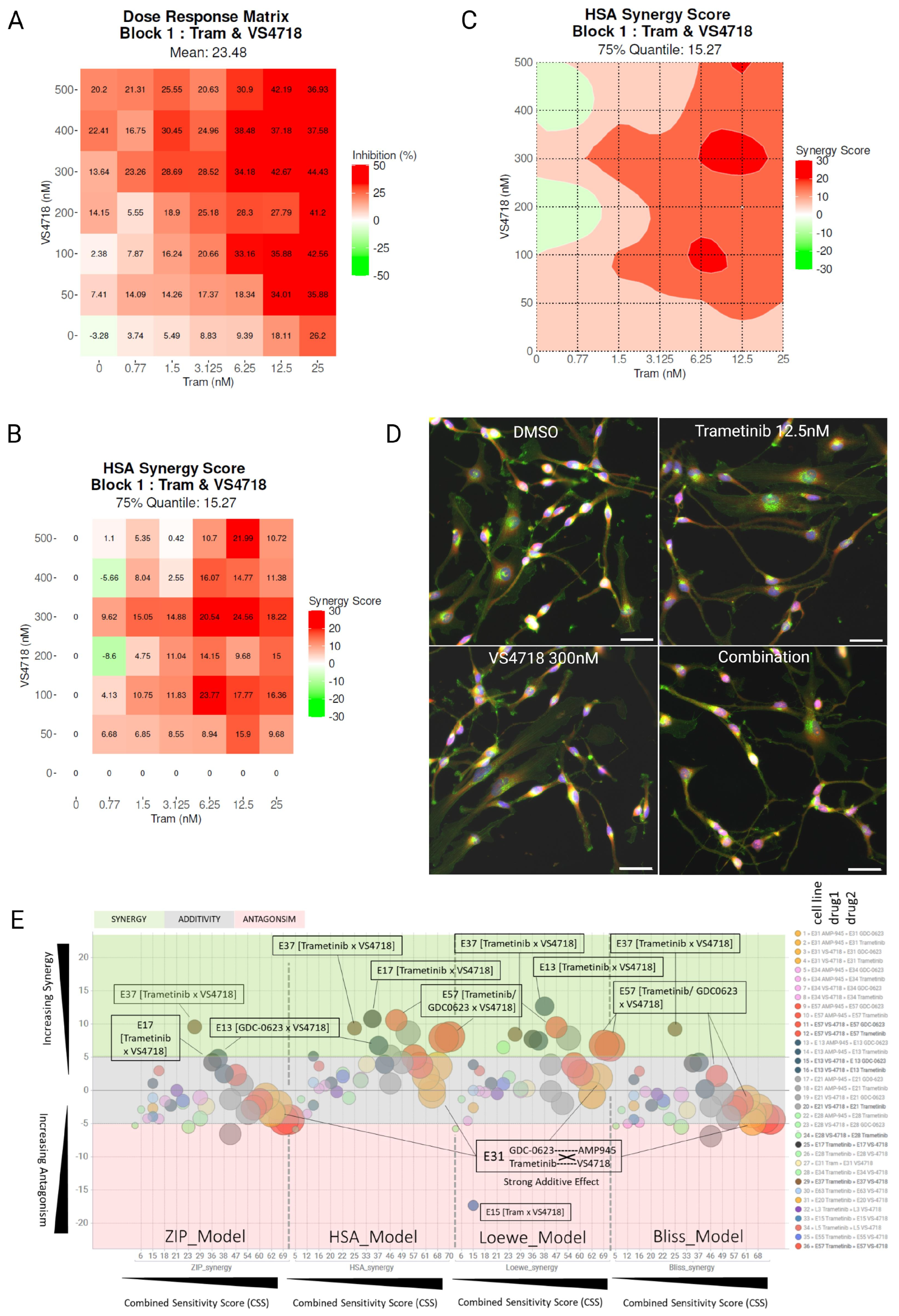
2.6. Synergy Calculation
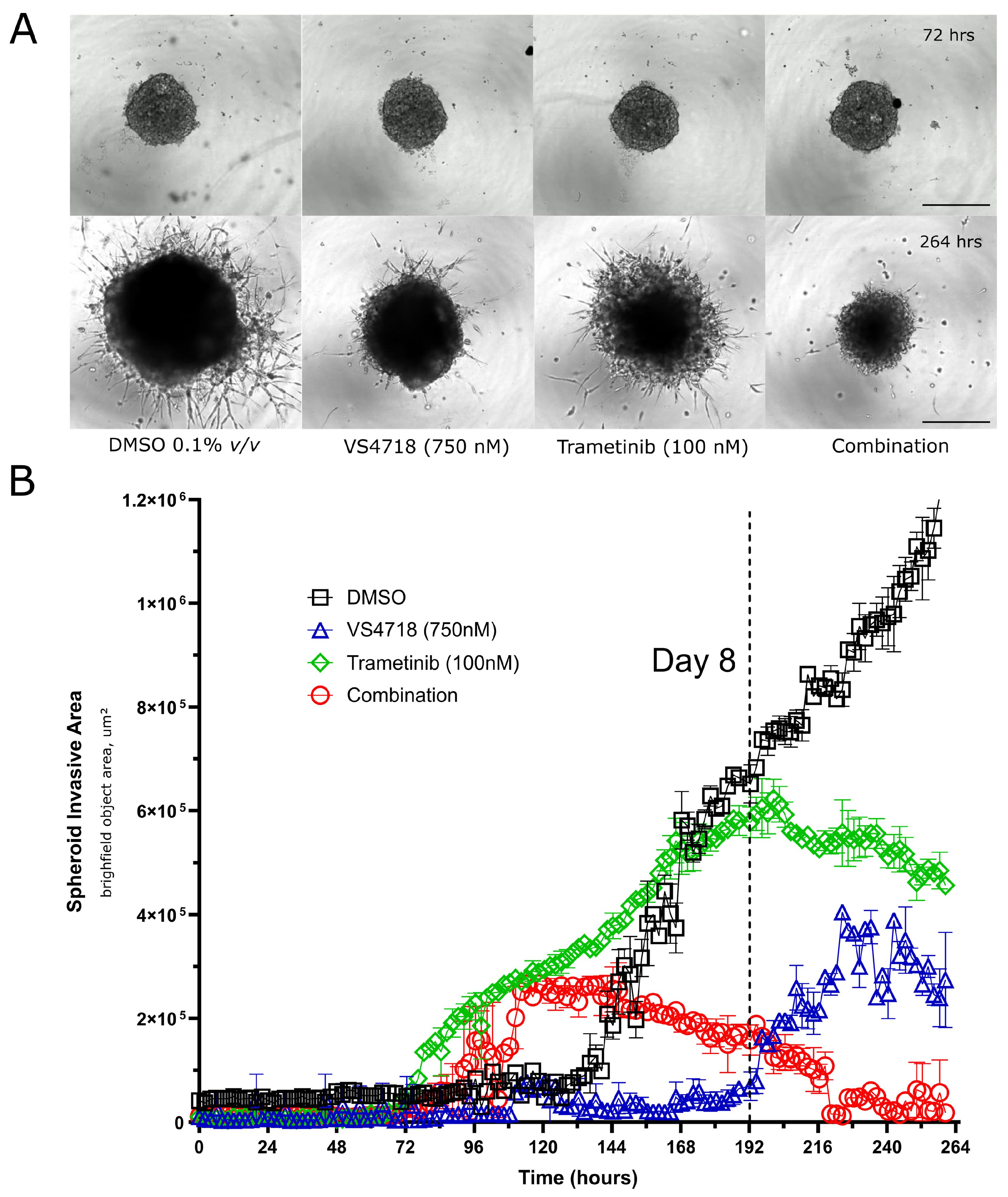
2.7. Three-Dimensional Spheroid Invasion Assay
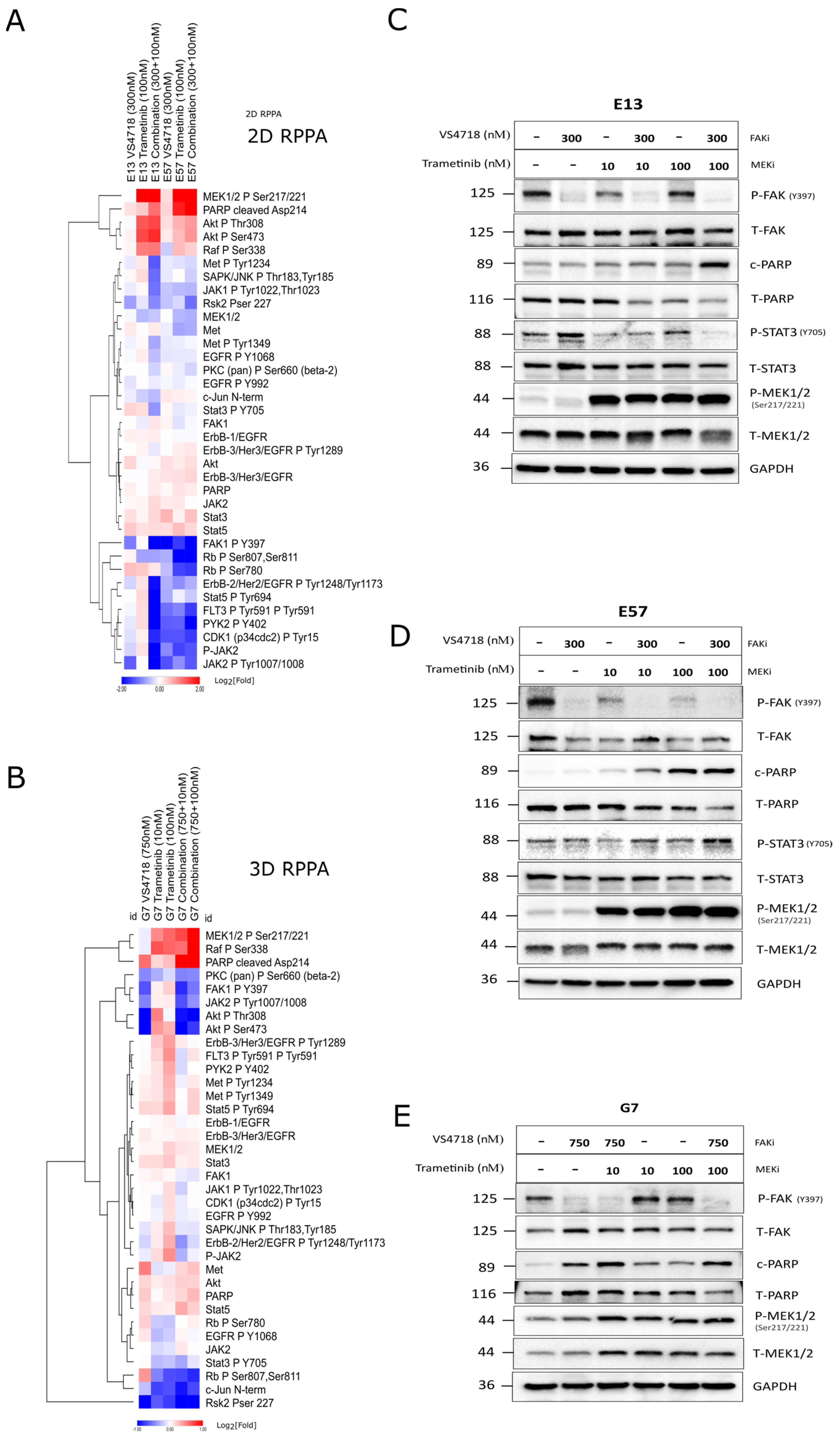
2.8. Western Blotting
2.9. Animal Studies
2.10. Immunohistochemistry
2.11. Reverse-Phase Protein Array
3. Results
3.1. Chemogenomic Screening to Identify Synergistic Combinations with Loss of FAK Kinase Activity
3.2. Identifying Synergistic Combinations Between MEK and FAK Inhibitors
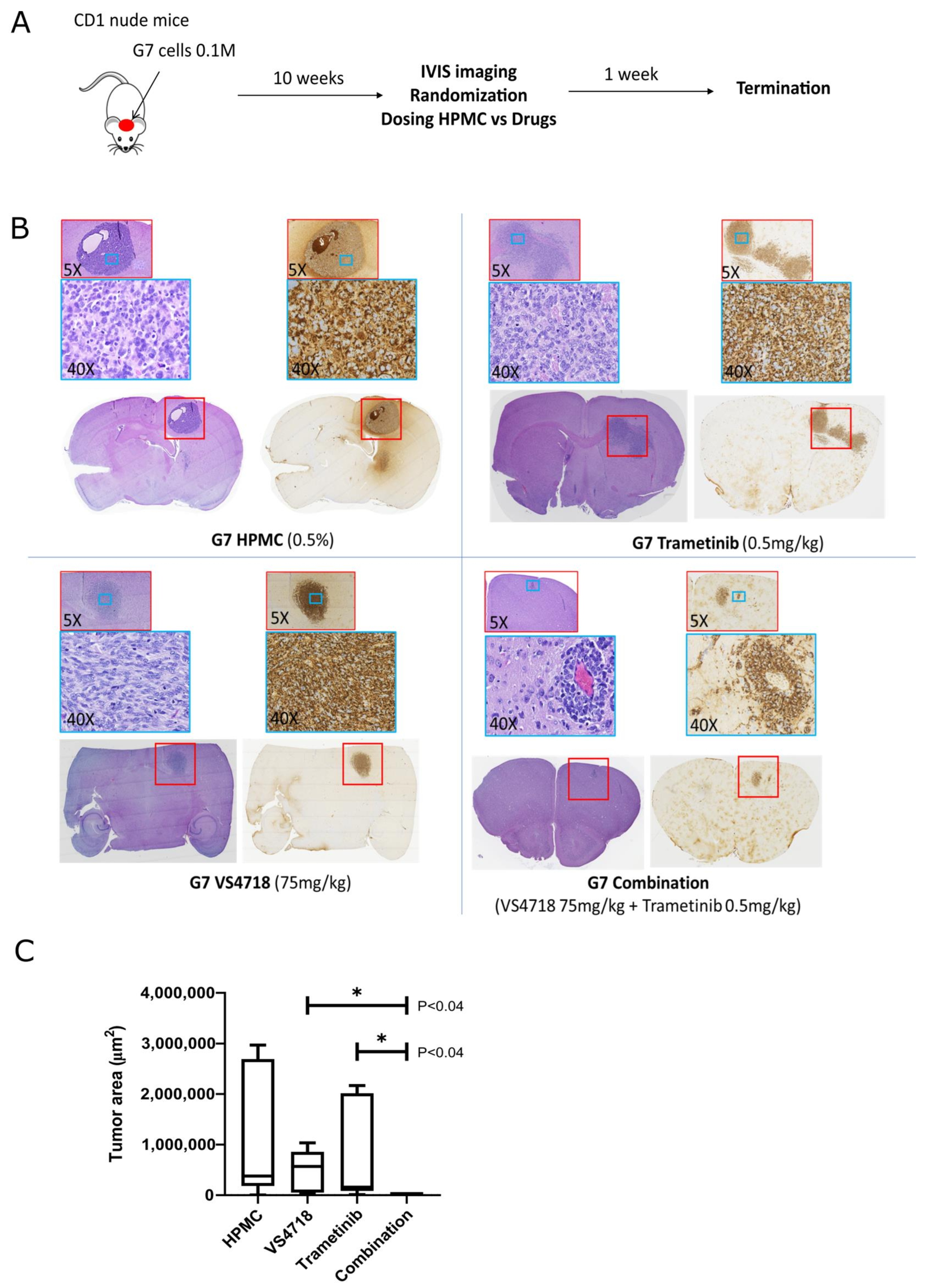
3.3. FAK+MEK Drug Combination In Vivo: Investigation with Mouse Glioma Model
3.4. FAK and MEK Inhibitor Profiling Across Patient-Derived Human Glioma Stem Cells
3.5. FAK and MEK Inhibitor Combinations Inhibit 3D GBM Spheroid Growth and Invasion
3.6. FAK+MEK Inhibitor Combination Profiling by Reverse-Phase Protein Array (RPPA)
3.7. In Vivo Activity
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stupp, R.; Mason, W.P.; van den Bent, M.J.; Weller, M.; Fisher, B.; Taphoorn, M.J.; Belanger, K.; Brandes, A.A.; Marosi, C.; Bogdahn, U.; et al. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lathia, J.D.; Mack, S.C.; Mulkearns-Hubert, E.E.; Valentim, C.L.; Rich, J.N. Cancer stem cells in glioblastoma. Genes Dev. 2015, 29, 1203–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietras, A.; Katz, A.M.; Ekstrom, E.J.; Wee, B.; Halliday, J.J.; Pitter, K.L.; Werbeck, J.L.; Amankulor, N.M.; Huse, J.T.; Holland, E.C. Osteopontin-CD44 signaling in the glioma perivascular niche enhances cancer stem cell phenotypes and promotes aggressive tumor growth. Cell Stem Cell 2014, 14, 357–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, F.C.; Yaffe, M.B. Kicking Genomic Profiling to the Curb: How Re-wiring the Phosphoproteome Can Explain Treatment Resistance in Glioma. Cancer Cell 2016, 29, 435–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Shin, Y.S.; Xue, M.; Matsutani, T.; Masui, K.; Yang, H.; Ikegami, S.; Gu, Y.; Herrmann, K.; Johnson, D.; et al. Single-Cell Phosphoproteomics Resolves Adaptive Signaling Dynamics and Informs Targeted Combination Therapy in Glioblastoma. Cancer Cell 2016, 29, 563–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, C.W.; Verhaak, R.G.; McKenna, A.; Campos, B.; Noushmehr, H.; Salama, S.R.; Zheng, S.; Chakravarty, D.; Sanborn, J.Z.; Berman, S.H.; et al. The somatic genomic landscape of glioblastoma. Cell 2013, 155, 462–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verhaak, R.G.; Hoadley, K.A.; Purdom, E.; Wang, V.; Qi, Y.; Wilkerson, M.D.; Miller, C.R.; Ding, L.; Golub, T.; Mesirov, J.P.; et al. Integrated genomic analysis identifies clinically relevant subtypes of glioblastoma characterized by abnormalities in PDGFRA, IDH1, EGFR, and NF1. Cancer Cell 2010, 17, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, S.; Louis, D.N.; Curry, W.T.; Batchelor, T.T.; Dietrich, J. Diagnostic and therapeutic avenues for glioblastoma: No longer a dead end? Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 10, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbato, M.I.; Nashed, J.; Bradford, D.; Ren, Y.; Khasar, S.; Miller, C.P.; Zolnik, B.S.; Zhao, H.; Li, Y.; Bi, Y.; et al. FDA Approval Summary: Dabrafenib in Combination with Trametinib for BRAFV600E Mutation-Positive Low-Grade Glioma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2024, 30, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paraiso, K.H.; Fedorenko, I.V.; Cantini, L.P.; Munko, A.C.; Hall, M.; Sondak, V.K.; Messina, J.L.; Flaherty, K.T.; Smalley, K.S. Recovery of phospho-ERK activity allows melanoma cells to escape from BRAF inhibitor therapy. Br. J. Cancer 2010, 102, 1724–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, A.J.; Arnone, M.R.; Bleam, M.R.; Moss, K.G.; Yang, J.; Fedorowicz, K.E.; Smitheman, K.N.; Erhardt, J.A.; Hughes-Earle, A.; Kane-Carson, L.S.; et al. Dabrafenib; preclinical characterization, increased efficacy when combined with trametinib, while BRAF/MEK tool combination reduced skin lesions. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e67583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flaherty, K.T.; Infante, J.R.; Daud, A.; Gonzalez, R.; Kefford, R.F.; Sosman, J.; Hamid, O.; Schuchter, L.; Cebon, J.; Ibrahim, N.; et al. Combined BRAF and MEK inhibition in melanoma with BRAF V600 mutations. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 1694–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subbiah, V.; Kreitman, R.J.; Wainberg, Z.A.; Gazzah, A.; Lassen, U.; Stein, A.; Wen, P.Y.; Dietrich, S.; de Jonge, M.J.A.; Blay, J.Y.; et al. Dabrafenib plus trametinib in BRAFV600E-mutated rare cancers: The phase 2 ROAR trial. Nat. Med. 2023, 29, 1103–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Nunno, V.; Gatto, L.; Tosoni, A.; Bartolini, S.; Franceschi, E. Implications of BRAF V600E mutation in gliomas: Molecular considerations, prognostic value and treatment evolution. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 1067252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johanssen, T.; McVeigh, L.; Erridge, S.; Higgins, G.; Straehla, J.; Frame, M.; Aittokallio, T.; Carragher, N.O.; Ebner, D. Glioblastoma and the search for non-hypothesis driven combination therapeutics in academia. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 1075559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaaks, P.; Coker, E.A.; Vis, D.J.; Edwards, O.; Carpenter, E.F.; Leto, S.M.; Dwane, L.; Sassi, F.; Lightfoot, H.; Barthorpe, S.; et al. Effective drug combinations in breast, colon and pancreatic cancer cells. Nature 2022, 603, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellert-Miklaszewska, A.; Poleszak, K.; Pasierbinska, M.; Kaminska, B. Integrin Signaling in Glioma Pathogenesis: From Biology to Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malric, L.; Monferran, S.; Gilhodes, J.; Boyrie, S.; Dahan, P.; Skuli, N.; Sesen, J.; Filleron, T.; Kowalski-Chauvel, A.; Cohen-Jonathan Moyal, E.; et al. Interest of integrins targeting in glioblastoma according to tumor heterogeneity and cancer stem cell paradigm: An update. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 86947–86968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducassou, A.; Uro-Coste, E.; Verrelle, P.; Filleron, T.; Benouaich-Amiel, A.; Lubrano, V.; Sol, J.C.; Delisle, M.B.; Favre, G.; Ken, S.; et al. alphavbeta3 Integrin and Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 (FGFR1): Prognostic factors in a phase I-II clinical trial associating continuous administration of Tipifarnib with radiotherapy for patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma. Eur. J. Cancer 2013, 49, 2161–2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Erfani, S.; Liu, Z.; Jia, C.; Chen, Y.; Xu, B.; Deng, X.; Alfaro, J.E.; Chen, L.; Napier, D.; et al. CD151-alpha3beta1 integrin complexes are prognostic markers of glioblastoma and cooperate with EGFR to drive tumor cell motility and invasion. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 29675–29693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz Rivera, J.; Velez Crespo, G.; Inyushin, M.; Kucheryavykh, Y.; Kucheryavykh, L. Pyk2/FAK Signaling Is Upregulated in Recurrent Glioblastoma Tumors in a C57BL/6/GL261 Glioma Implantation Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reardon, D.A.; Nabors, L.B.; Stupp, R.; Mikkelsen, T. Cilengitide: An integrin-targeting arginine-glycine-aspartic acid peptide with promising activity for glioblastoma multiforme. Expert. Opin. Investig. Drugs 2008, 17, 1225–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stupp, R.; Hegi, M.E.; Gorlia, T.; Erridge, S.C.; Perry, J.; Hong, Y.K.; Aldape, K.D.; Lhermitte, B.; Pietsch, T.; Grujicic, D.; et al. Cilengitide combined with standard treatment for patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma with methylated MGMT promoter (CENTRIC EORTC 26071-22072 study): A multicentre, randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 1100–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ram, R.; Lorente, G.; Nikolich, K.; Urfer, R.; Foehr, E.; Nagavarapu, U. Discoidin domain receptor-1a (DDR1a) promotes glioma cell invasion and adhesion in association with matrix metalloproteinase-2. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2006, 76, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mooney, K.L.; Choy, W.; Sidhu, S.; Pelargos, P.; Bui, T.T.; Voth, B.; Barnette, N.; Yang, I. The role of CD44 in glioblastoma multiforme. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2016, 34, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLean, G.W.; Carragher, N.O.; Avizienyte, E.; Evans, J.; Brunton, V.G.; Frame, M.C. The role of focal-adhesion kinase in cancer—A new therapeutic opportunity. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2005, 5, 505–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westhoff, M.A.; Serrels, B.; Fincham, V.J.; Frame, M.C.; Carragher, N.O. SRC-mediated phosphorylation of focal adhesion kinase couples actin and adhesion dynamics to survival signaling. Mol. Cell Biol. 2004, 24, 8113–8133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulzmaier, F.J.; Jean, C.; Schlaepfer, D.D. FAK in cancer: Mechanistic findings and clinical applications. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2014, 14, 598–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storch, K.; Sagerer, A.; Cordes, N. Cytotoxic and radiosensitizing effects of FAK targeting in human glioblastoma cells in vitro. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 33, 2009–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, L.J.; Skirzynska, A.; Chin, A.A.; Arnold, A.E.; Kushida, M.; Dirks, P.B.; Shoichet, M.S. Engineered In Vitro Tumor Model Recapitulates Molecular Signatures of Invasion in Glioblastoma. ACS Mater. Au 2023, 3, 514–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Rivera, J.; Nunez, R.; Kucheryavykh, Y.; Kucheryavykh, L. The PYK2 inhibitor PF-562271 enhances the effect of temozolomide on tumor growth in a C57Bl/6-Gl261 mouse glioma model. J. Neurooncol 2023, 161, 593–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gangoso, E.; Southgate, B.; Bradley, L.; Rus, S.; Galvez-Cancino, F.; McGivern, N.; Guc, E.; Kapourani, C.A.; Byron, A.; Ferguson, K.M.; et al. Glioblastomas acquire myeloid-affiliated transcriptional programs via epigenetic immunoediting to elicit immune evasion. Cell 2021, 184, 2454–2470.e26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollard, S.M.; Yoshikawa, K.; Clarke, I.D.; Danovi, D.; Stricker, S.; Russell, R.; Bayani, J.; Head, R.; Lee, M.; Bernstein, M.; et al. Glioma stem cell lines expanded in adherent culture have tumor-specific phenotypes and are suitable for chemical and genetic screens. Cell Stem Cell 2009, 4, 568–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Athanasiadis, P.; Ravikumar, B.; Elliott, R.J.R.; Dawson, J.C.; Carragher, N.O.; Clemons, P.A.; Johanssen, T.; Ebner, D.; Aittokallio, T. Chemogenomic library design strategies for precision oncology, applied to phenotypic profiling of glioblastoma patient cells. iScience 2023, 26, 107209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Wang, W.; Aldahdooh, J.; Malyutina, A.; Shadbahr, T.; Tanoli, Z.; Pessia, A.; Tang, J. SynergyFinder Plus: Toward Better Interpretation and Annotation of Drug Combination Screening Datasets. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2022, 20, 587–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, B.; Wennerberg, K.; Aittokallio, T.; Tang, J. Searching for Drug Synergy in Complex Dose-Response Landscapes Using an Interaction Potency Model. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2015, 13, 504–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Wennerberg, K.; Aittokallio, T. What is synergy? The Saariselka agreement revisited. Front. Pharmacol. 2015, 6, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malyutina, A.; Majumder, M.M.; Wang, W.; Pessia, A.; Heckman, C.A.; Tang, J. Drug combination sensitivity scoring facilitates the discovery of synergistic and efficacious drug combinations in cancer. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2019, 15, e1006752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, C.I.; Al-Ali, H.; Andrews, D.M.; Asquith, C.R.M.; Axtman, A.D.; Dikic, I.; Ebner, D.; Ettmayer, P.; Fischer, C.; Frederiksen, M.; et al. The Kinase Chemogenomic Set (KCGS): An Open Science Resource for Kinase Vulnerability Identification. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webber, P.J.; Park, C.; Qui, M.; Ramalingam, S.S.; Khuri, F.R.; Fu, H.; Du, Y. Combination of heat shock protein 90 and focal adhesion kinase inhibitors synergistically inhibits the growth of non-small cell lung cancer cells. Oncoscience 2015, 2, 765–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, J.C.; Serrels, A.; Stupack, D.G.; Schlaepfer, D.D.; Frame, M.C. Targeting FAK in anticancer combination therapies. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2021, 21, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradis, J.S.; Acosta, M.; Saddawi-Konefka, R.; Kishore, A.; Gomes, F.; Arang, N.; Tiago, M.; Coma, S.; Lubrano, S.; Wu, X.; et al. Synthetic Lethal Screens Reveal Cotargeting FAK and MEK as a Multimodal Precision Therapy for GNAQ-Driven Uveal Melanoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 3190–3200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarin, M.; Nemati, F.; Decaudin, D.; Canbezdi, C.; Marande, B.; Silva, L.; Derrien, H.; Jochemsen, A.G.; Gardrat, S.; Piperno-Neumann, S.; et al. FAK Inhibitor-Based Combinations with MEK or PKC Inhibitors Trigger Synergistic Antitumor Effects in Uveal Melanoma. Cancers 2023, 15, 2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, J.; Burns, C.J.; Devlin, M.; Kruger, N.; Lickliter, J.; Sullivan, M.; Tong, W. Abstract CT511: A phase 1 trial of AMP945, a potent and selective focal adhesion kinase inhibitor, in healthy volunteers. Cancer Res. 2022, 82 (Suppl. S12), CT511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golubovskaya, V.M.; Huang, G.; Ho, B.; Yemma, M.; Morrison, C.D.; Lee, J.; Eliceiri, B.P.; Cance, W.G. Pharmacologic blockade of FAK autophosphorylation decreases human glioblastoma tumor growth and synergizes with temozolomide. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2013, 12, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvasaravanan, K.D.; Wiederspohn, N.; Hadzalic, A.; Strobel, H.; Payer, C.; Schuster, A.; Karpel-Massler, G.; Siegelin, M.D.; Halatsch, M.E.; Debatin, K.M.; et al. The limitations of targeting MEK signalling in Glioblastoma therapy. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camidge, D.R.; Pachter, J.; Koustenis, A.; Patrick, G.; Spigel, D.R. Abstract P048: A phase 2 study of VS-6766 (dual RAF/MEK inhibitor) RAMP 202, as a single agent and in combination with defactinib (FAK inhibitor) in recurrent KRAS-mutant (KRAS-MT) non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Mol. Cancer Ther. 2021, 20 (Suppl. S12), P048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Wei, C.; Chung, M.; Li, H.; Guo, Z.; Long, M.; Li, Y.; Wang, W.; Aimaier, R.; Li, Q.; et al. Concurrent inhibition of FAK/SRC and MEK overcomes MEK inhibitor resistance in Neurofibromatosis Type I related malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 910505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak, G.; Soria, J.C.; Blagden, S.P.; Plummer, R.; Fleming, R.A.; Nebot, N.; Zhang, J.; Mazumdar, J.; Rogan, D.; Gazzah, A.; et al. A phase Ib dose-finding, pharmacokinetic study of the focal adhesion kinase inhibitor GSK2256098 and trametinib in patients with advanced solid tumours. Br. J. Cancer 2019, 120, 975–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aung, K.L.; McWhirter, E.; Welch, S.; Wang, L.; Lovell, S.; Stayner, L.A.; Ali, S.; Malpage, A.; Makepeace, B.; Ramachandran, M.; et al. A phase II trial of GSK2256098 and trametinib in patients with advanced pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2022, 13, 3216–3226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Grochot, R.; Shinde, R.; Lima, J.; Krebs, M.; Rahman, R.; Little, M.; Tunariu, N.; Curcean, A.; Badham, H.; et al. Phase I study of the combination of the dual RAF/MEK inhibitor VS-6766 and the FAK inhibitor defactinib: Results of efficacy in low grade serous ovarian cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, S728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulzmaier, F.J.; Young-Robbins, S.; Jiang, P.; Geerts, D.; Prechtl, A.M.; Matter, M.L.; Kesari, S.; Ramos, J.W. RSK2 activity mediates glioblastoma invasiveness and is a potential target for new therapeutics. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 79869–79884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, G.X.; Yang, W.S.; Jin, L.; Matter, M.L.; Ramos, J.W. RSK2 drives cell motility by serine phosphorylation of LARG and activation of Rho GTPases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E190–E199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koutsougianni, F.; Alexopoulou, D.; Uvez, A.; Lamprianidou, A.; Sereti, E.; Tsimplouli, C.; Ilkay Armutak, E.; Dimas, K. P90 ribosomal S6 kinases: A bona fide target for novel targeted anticancer therapies? Biochem. Pharmacol. 2023, 210, 115488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Xia, Y.; Hawke, D.; Halle, M.; Tremblay, M.L.; Gao, X.; Zhou, X.Z.; Aldape, K.; Cobb, M.H.; Xie, K.; et al. FAK phosphorylation by ERK primes ras-induced tyrosine dephosphorylation of FAK mediated by PIN1 and PTP-PEST. Mol. Cell 2009, 35, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawson, J.C.; Carragher, N.O. Quantitative phenotypic and pathway profiling guides rational drug combination strategies. Front. Pharmacol. 2014, 5, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, J.C.; Munro, A.; Macleod, K.; Muir, M.; Timpson, P.; Williams, R.J.; Frame, M.; Brunton, V.G.; Carragher, N.O. Pathway profiling of a novel SRC inhibitor, AZD0424, in combination with MEK inhibitors for cancer treatment. Mol. Oncol. 2022, 16, 1072–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirata, E.; Girotti, M.R.; Viros, A.; Hooper, S.; Spencer-Dene, B.; Matsuda, M.; Larkin, J.; Marais, R.; Sahai, E. Intravital imaging reveals how BRAF inhibition generates drug-tolerant microenvironments with high integrin beta1/FAK signaling. Cancer Cell 2015, 27, 574–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinde, R.; Terbuch, A.; Little, M.; Caldwell, R.; Kurup, R.; Riisnaes, R.; Crespo, M.; Ruddle, R.; Gurel, B.; Stewart, A.; et al. Abstract CT143: Phase I study of the combination of a RAF-MEK inhibitor CH5126766 and FAK inhibitor defactinib in an intermittent dosing schedule with expansions in KRAS mutant cancers. Cancer Res. 2020, 80 (Suppl. S16), CT143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glading, A.; Bodnar, R.J.; Reynolds, I.J.; Shiraha, H.; Satish, L.; Potter, D.A.; Blair, H.C.; Wells, A. Epidermal growth factor activates m-calpain (calpain II), at least in part, by extracellular signal-regulated kinase-mediated phosphorylation. Mol. Cell Biol. 2004, 24, 2499–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carragher, N.O.; Westhoff, M.A.; Fincham, V.J.; Schaller, M.D.; Frame, M.C. A novel role for FAK as a protease-targeting adaptor protein: Regulation by p42 ERK and Src. Curr. Biol. 2003, 13, 1442–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.N.; Ring, K.L.; Nieuwenhuysen, E.V.; Fabbro, M.; Aghajanian, C.; Oaknin, A.; Colombo, N.; Santin, A.; Clamp, A.R.; Moore, K.N.; et al. Initial efficacy and safety results from ENGOT-ov60/GOG-3052/RAMP 201: A phase 2 study of avutometinib (VS-6766) ± defactinib in recurrent low-grade serous ovarian cancer (LGSOC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41 (Suppl. S16), 5515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaidhyanathan, S.; Mittapalli, R.K.; Sarkaria, J.N.; Elmquist, W.F. Factors influencing the CNS distribution of a novel MEK-1/2 inhibitor: Implications for combination therapy for melanoma brain metastases. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2014, 42, 1292–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Sauvage, M.A.; Torrini, C.; Nieblas-Bedolla, E.; Summers, E.J.; Sullivan, E.; Zhang, B.S.; Batchelor, E.; Marion, B.; Yamazawa, E.; Markson, S.C.; et al. The ERK inhibitor LY3214996 augments anti-PD-1 immunotherapy in preclinical mouse models of BRAFV600E melanoma brain metastasis. Neuro-Oncology 2024, 26, 889–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gampa, G.; Kim, M.; Cook-Rostie, N.; Laramy, J.K.; Sarkaria, J.N.; Paradiso, L.; DePalatis, L.; Elmquist, W.F. Brain Distribution of a Novel MEK Inhibitor E6201: Implications in the Treatment of Melanoma Brain Metastases. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2018, 46, 658–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pickering, A.J.; Lamson, N.G.; Marand, M.H.; Hwang, W.; Straehla, J.P.; Hammond, P.T. Layer-by-Layer Polymer Functionalization Improves Nanoparticle Penetration and Glioblastoma Targeting in the Brain. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 24154–24169, Erratum in: ACS Nano 2024, 18, 8555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lamson, N.G.; Pickering, A.J.; Wyckoff, J.; Ganesh, P.; Calle, E.A.; Straehla, J.P.; Hammond, P.T. Trafficking through the blood-brain barrier is directed by core and outer surface components of layer-by-layer nanoparticles. Bioeng. Transl. Med. 2024, 9, e10636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, A.; Hynynen, K. Drug delivery across the blood-brain barrier using focused ultrasound. Expert. Opin. Drug Deliv. 2014, 11, 711–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loftus, A.E.P.; Romano, M.S.; Phuong, A.N.; McKinnel, B.J.; Muir, M.T.; Furqan, M.; Dawson, J.C.; Avalle, L.; Douglas, A.T.; Mort, R.L.; et al. An ILK/STAT3 pathway controls glioblastoma stem cell plasticity. Dev. Cell 2024, 59, 3197–3212.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, J.C.; Joughin, B.A.; Prota, A.E.; Mühlethaler, T.; Jonas, O.H.; Whitman, M.A.; Varmeh, S.; Chen, S.; Balk, S.P.; Steinmetz, M.O.; et al. VISAGE Reveals a Targetable Mitotic Spindle Vulnerability in Cancer Cells. Cell Syst. 2019, 9, 74–92.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Furqan, M.; Elliott, R.J.R.; Nagle, P.W.K.; Dawson, J.C.; Masalmeh, R.; Garcia, V.A.; Munro, A.F.; Drake, C.; Morrison, G.M.; Pollard, S.M.; et al. Drug Combinations Targeting FAK and MEK Overcomes Tumor Heterogeneity in Glioblastoma. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 549. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17050549
Furqan M, Elliott RJR, Nagle PWK, Dawson JC, Masalmeh R, Garcia VA, Munro AF, Drake C, Morrison GM, Pollard SM, et al. Drug Combinations Targeting FAK and MEK Overcomes Tumor Heterogeneity in Glioblastoma. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(5):549. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17050549
Chicago/Turabian StyleFurqan, Muhammad, Richard J. R. Elliott, Peter W. K. Nagle, John C. Dawson, Roza Masalmeh, Virginia Alvarez Garcia, Alison F. Munro, Camilla Drake, Gillian M. Morrison, Steven M. Pollard, and et al. 2025. "Drug Combinations Targeting FAK and MEK Overcomes Tumor Heterogeneity in Glioblastoma" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 5: 549. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17050549
APA StyleFurqan, M., Elliott, R. J. R., Nagle, P. W. K., Dawson, J. C., Masalmeh, R., Garcia, V. A., Munro, A. F., Drake, C., Morrison, G. M., Pollard, S. M., Ebner, D., Brunton, V. G., Frame, M. C., & Carragher, N. O. (2025). Drug Combinations Targeting FAK and MEK Overcomes Tumor Heterogeneity in Glioblastoma. Pharmaceutics, 17(5), 549. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17050549





