Abstract
This article provides a comprehensive overview of state-of-the-art techniques for detecting and diagnosing stator winding inter-turn short faults (ITSFs) in permanent-magnet synchronous motors (PMSMs) for electric vehicles (EVs). The review focuses on the following three main categories of diagnostic approaches: motor model-based, signal processing-based, and artificial intelligence (AI)-based fault detection and diagnosis methods. Motor model-based methods utilize motor state estimation and motor parameter estimation as the primary strategies for ITSF diagnosis. Signal processing-based techniques extract fault signatures from motor measured data across time, frequency, or time-frequency domains. In contrast, AI-based methods automatically extract higher-order fault signatures from large volumes of preprocessed data, thereby enhancing the effectiveness of fault diagnosis. The strengths and limitations of each approach are thoroughly examined, providing valuable insights into the advancements in ITSF detection and diagnosis techniques for PMSMs in EV applications. The emphasis is placed on the application of signal processing methods and deep learning techniques in the diagnosis of ITSF in PMSMs in EV applications.
1. Introduction
Electric vehicles (EVs) are attracting more and more attention in transportation due to enhanced performance, safety, and reduced environmental impacts. In particular, permanent magnet synchronous motors (PMSM) are applied widely as traction motors in EVs because of their high efficiency and power density. The healthy operation of the traction motor is crucial for the proper functioning of an EV. Since EV motors run in a harsh environment and complicated operating conditions, the stator winding insulation exhibits a higher failure rate []. This fault can lead to a catastrophic accident; therefore, timely identification and diagnosis of insulation faults for traction PMSMs are extremely important to ensure the safe operation of EVs.
It is reported that inter-turn short faults (ITSF) account for 21% of all motor faults [], which can lead to reduced motor efficiency and power output and even catastrophic failure. The majority of ITSFs originate in winding faults, which are caused by insulation malfunctions [], but rapidly evolve into more severe failures that substantially impact motors. On the one hand, short-circuit paths in the motor can lead to a decline in its performance. These paths allow currents to bypass the normal winding segments [], leading to reduced output power and efficiency. For PMSMs, this type of fault can generate a magnetic field with a higher intensity than the coercivity of the magnets, leading to permanent demagnetization and machine damage. On the other hand, ITSFs cause excessive temperature rises in the motor. Excessive heat can accelerate the aging and embrittlement of insulation materials, potentially leading to burnouts and exacerbating the short-circuit phenomenon []. Furthermore, ITSFs increase motor noise and vibration. The presence of short-circuit paths introduces additional electromagnetic forces and vibrational forces in the motor, resulting in abnormal sounds and vibrations []. This not only adds to the noise pollution in the working environment but also risks loosening and damaging other components, further exacerbating the development of faults.
The impacts and losses caused by stator winding short circuits in electric motors are extremely severe []. Therefore, timely diagnosis and repair of these faults are crucial to ensure the safe operation and prolongation of the motor’s lifespan.
By conducting regular motor inspections, tests, and maintenance, as well as implementing appropriate insulation protection measures, the occurrence of stator winding short-circuit faults can be minimized. This comprehensive approach not only enhances the reliability of electric motors but also ensures their optimal performance and extends their lifespan []. Many approaches have been proposed to diagnosis and detect ITSFs, and these methods can be categorized into three types, as follows: model-based fault diagnosis methods; signal processing-based fault diagnosis methods; and artificial intelligence-based fault diagnosis methods. The concept of ITSF diagnosis is visually represented in Figure 1.
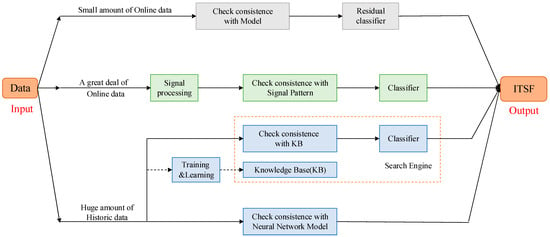
Figure 1.
Data flow of ITSF diagnosis.
Figure 1 illustrates the upper section, which outlines model-based fault diagnosis methods that rely on a limited amount of online data for fault detection and diagnosis purposes. Parametric mathematical models can be derived, either through fundamental principles or by utilizing system identification techniques. The data-processing engine takes input–output data from the system and uses it to compare the measured data with the predictions of the model. This process produces residuals, which represent the differences between the observed and predicted values. Following that, a residual classifier or classifier is utilized to assess the residuals and detect the occurrence of faults. This classifier plays a crucial role in determining the potential type of fault that might be present in the system. Ideally, a well-designed model-based fault diagnosis method is primarily sensitive to system faults, while being relatively insensitive to disturbances or deviations in the system inputs. This ensures that it can accurately identify and diagnose actual faults in the system without being significantly affected by external factors or non-fault-related changes in the system inputs.
The middle section of Figure 1 presents the block diagram representing signal-based fault diagnosis methods. Signal-based fault diagnosis methods revolve around the association between faults and signal patterns. These techniques capitalize on the fact that faults in a system tend to have a direct impact on output variables. Consequently, most signal-based fault diagnosis methods leverage sampled signals of these output variables instead of relying on intricate dynamic input–output models of the system. By scrutinizing these signals, these methods can adeptly detect and diagnose faults, eliminating the necessity for comprehensive system modeling. This characteristic proves to be advantageous in complex industrial processes or machine systems, where obtaining precise input–output models is often unattainable and estimating their parameters is difficult.
In cases where a process is too excessively intricate to be accurately modeled analytically and traditional signal analysis approaches do not provide definitive diagnoses, artificial intelligence-based fault diagnosis methods come into play. These methods typically involve utilizing extensive historical data to train models and make accurate predictions regarding system faults. This leads to artificial intelligence AI -based fault diagnosis methods, as depicted in the bottom section of Figure 1. Such methods rely on mining implicit knowledge from extensive historical data using machine learning techniques. Once knowledge is derived from historical data, it is utilized to create a knowledge base that represents the implicit dependencies among system variables. Subsequently, the consistency between recent data and the knowledge base is examined. Finally, a classifier is employed to make the ultimate decision based on the available information. In recent years, deep neural networks have emerged as the most popular intelligent approach. Neural networks possess advantages such as learning complex features, strong robustness, handling large-scale and high-dimensional data, and generalization capabilities in diagnosing ITSFs in PMSMs. Leveraging the powerful capabilities of neural networks can improve the accuracy and efficiency of motor fault diagnosis, ensuring the safe operation of motors. The above three approaches for PMSM ITSF diagnosis are comprehensively reviewed in the following sections.
2. Motor Model-Based Approach to Fault Diagnosis
The model-based fault diagnosis method is one of the fault diagnosis methods proposed decades ago. It requires a more accurate mathematical model of the PMSMs, and its advantage is that the internal state of the system and the influence of the fault on the machine can be unveiled. The framework of model-based diagnosis is shown in Figure 2.
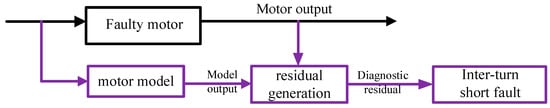
Figure 2.
Framework of model-based diagnostic approach.
With a loss in generality, the system model can be expressed in a general state–space model []:
where the subscript represents the time indicator, is a state vector, is the input, represents modeling errors, measurement noise, and external interference, indicates the possible faults to be detected, is a system parameter.
Examining changes in state variables and model parameter outputs provides a means to assess the presence of faults, as faults typically result in observable variations in these quantities. Based on (1), the model-based fault diagnosis method utilizes input data to generate estimates for outputs, parameters, and states. These estimates are obtained through the implementation of the method. As shown in Figure 2, fault diagnosis will be conducted by examining the resulting residuals between these estimates and their expected values. The model-based fault diagnosis approach can be classified into two main categories: state estimation and parameter estimation.
2.1. State Estimation Method
The method of state estimation is the process of comparing the system state estimated by the state observer with the actual signal detected by the system and using the generated residual signal as the basis for fault diagnosis. In addition, the state estimation method can also obtain the fault severity and fault location by analyzing and evaluating the fault residual signal.
Due to its simplicity, traceability, and robustness, the Kalman filter (KF) has been proven to be the optimal solution for state estimation in linear dynamic systems. The state observer of KF is:
where and are respectively the state and input control, is noise measurement, is an external disturbance vector. , and are, respectively, the state transition matrix, control input matrix and state observation matrix.
The health model of the Kalman filter is used to estimate the residual voltage drop of the rotor reference DQ axis under an ITSF []. This observer avoids the use of voltage sensors but does not reduce the diagnostic accuracy of the ITSF. Ali performed KF observations on the current and voltage signals respectively [], using the residual signal as the fault detection index; this method was robust against different fault resistances. However, linear KF cannot be used for systems with significant nonlinearity. Since most systems are nonlinear, suboptimal state estimation techniques can be employed. The extended Kalman filter (EKF) is one of these suboptimal techniques [], where the measurement and system model equations are linearized, enabling the application of the linear Kalman filter algorithm. Nonetheless, the linearization in EKF may introduce instability to the method, particularly when dealing with extremely nonlinear systems. To overcome the limitations of EKF, the unscented Kalman filter (UKF) was proposed in []. The UKF employs a set of sigma points to estimate the propagation of the mean and covariance matrix []. EKF and UKF were used to detect the percentage and location of faults []. Another difference in the method is that the ratio of short-circuit turns is used as the state estimator.
The ITSF diagnosis method based on the Luenberger state observer and current second-order harmonics was established in []. The advantage of this method is the ability to assess the severity of failures, as well as the efficiency with which failures can be detected at an early stage and under various operating conditions. A high-order sliding mode observer was used to estimate the rotor flux and three-phase stator current in the fault state []. By comparing the measured and estimated values of stator three-phase currents, a fault detection method was designed. This comparison produces a set of residuals that are sensitive to failure. The analysis of these residual signals can be used to detect the damage of the stator windings. An equivalent model of the single-phase interturn fault motor served as the observer [], where the error between the measured current and the estimated current were corrected as the core of the fault severity estimator. A sufficiently accurate model is established to determine the variation of different variables in the motor under this fault condition, and then the residual generated by the sliding mode observer is used to detect the ITSF. In another study, a PMSM model of single-phase short-circuit fault is established, and a sliding mode observer is developed to extract voltage disturbance information from the derived equivalent control signal to detect interturn faults []. However, the Luenberger observer is sensitive to changes in motor parameters.
Table 1 compares the advantages and disadvantages of the existing state estimation methods. The state estimation method has the advantages of early fault detection, non-invasiveness, real-time and multiple fault detection. However, it also has disadvantages such as a dependence on sensors, difficulty in parameter modeling, complex data processing, and false positives and false negatives.

Table 1.
Summary of existing state estimation methods for ITSF diagnosis.
2.2. Parameter Estimation Method
The principle of the parameter estimation method is to select the key parameters of the system for online identification and compare the estimated value with the parameters under the normal system to achieve fault diagnosis. Since some parameters of the machine are changed because of ITSFs, the fault diagnosis can be carried out by identifying these parameters online. When ITSFs occur, the stator three-phase winding is asymmetrical, so that the stator resistance value of the motor changes. An ITSF is judged by identifying the three-phase stator resistance change, but judging only the parameter change is not enough to accurately judge the fault, because the winding temperature rise and other factors also cause the same impact, and the parameter estimation method ca not be limited to identifying the parameters. It is also necessary to further distinguish between parameter changes due to faults and parameter changes due to factors such as temperature rise.
Since ITSFs result in asymmetrical stator winding, the parameters of PMSMs, such as resistance, back electromotive force (BEMF), self and mutual inductance and impedance, have a substantial impact on the sensitivity of the system, leading to undesirable changes. The occurrence and severity of faults can be diagnosed by observing these parameters during operation [].
On the other hand, due to a counter-magnetic field generated at the short-circuited turns of the faulty phase, the ITSF directly affects the magnetic flux distribution. As a result, electrical parameters such as self and mutual inductance can change dramatically. In one study, the disparity in inductance increment between normal and faulty motors was employed for ITSF diagnosis []. A modeling method for the analysis and modeling of the magnetic characteristics of motors based on fault impedance was proposed. Based on the established model, analysis was conducted on the input phase current, fault/cycle current, magnetic flux distribution, BEMF, torque density, and motor performance. In addition, the input impedance served as the indicator for evaluating ITSFs []. In another study, different modes of impedance change were observed as a result of the impacts of ITSFs []. In order to investigate ITSFs, a dynamic model of PMSM was established using a theoretical method []. Additionally, a magnetic permeability network was utilized for the study of ITSFs [].
An open-loop BEMF estimation method based on physical principle is proposed [], which is suitable for any anti-electromotive force waveform of PMSMs. The non-stationary and nonlinear behavior of machine performance measurement will limit the use of many methods, but this method is not limited by buffering, and can determine the intensity and index of fault phase in real time. By evaluating the reconfiguration of the BEMF coefficient as a function of the ITSF of a typical progressive failure of the motor [], this BEMF signal is extremely sensitive to the failure mode and appropriately insensitive to other external factors.
The HF signal injection method for fault detection is insensitive to the machine’s working condition, ensuring fault sensitivity under light load and low speed []. However, when the PMSM operates with high fundamental frequency, conventional methods can easily detect the distinct fault signatures induced by ITSF.
By estimating the parameters of the motor, potential faults can be detected early, and more comprehensive and accurate information can be provided to diagnose faults. In addition, the parameter estimation method has strong real-time and adaptability, and can dynamically diagnose the fault during the operation of the motor. The pros and cons of each parameter estimation method are summarized as shown in the Table 2.

Table 2.
Summary of existing parameter estimation methods for ITSF diagnosis.
However, the parameter estimation method also has some of the following shortcomings:
- In the process of parameter estimation, a large amount of sensor data needs to be obtained, and complex calculations and analysis are carried out, which requires significant hardware and algorithms;
- The parameter estimation method is subject to the accuracy of the motor model and the satisfaction of the assumptions. If the model is not accurate or the assumptions are not valid, it may lead to the deviation of the parameter estimation results;
- The parameter estimation method is sensitive to noise and interference, which may affect the stability and accuracy of the system;
- Parameter estimation methods usually require a long training time and a large amount of sample data, which may have certain limitations for fault diagnosis scenarios with high real-time requirements.
3. Signal Processing-Based Diagnostic Methods
The fault diagnosis method of ITSF based on signal processing is to analyze physical quantities, such as stator current, stator voltage, vibration or noise, power, magnetic flux, impedance, torque, temperature, speed, acceleration, etc., and use the analysis methods in the time domain, frequency domain and time-frequency domain to extract the fault signatures from the sampled signal.
As shown in Figure 3, the diagnostic framework based on signal processing shows that the causes of motor turn-to-turn short-circuit faults include aging or damaged insulation, strong voltage impulses, foreign matter entering the windings, gear or bearing faults, overload or overheating, etc. The signals extracted in the motor with these problems are abnormal, and this is the most important part of the method; the selection of appropriate signal processing methods can efficiently extract fault features. Sometimes, it is also important to consider some prior knowledge to enhance diagnostic accuracy.
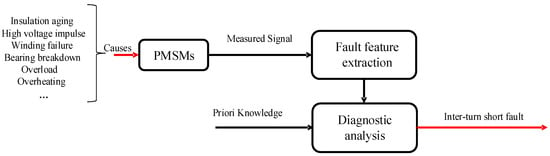
Figure 3.
Diagnostic framework based on signal processing.
3.1. Signal Processing Methods
Signal processing techniques facilitate the extraction of distinctive features associated with a particular type of failure. Categorically, these methods can be classified into three groups: time-domain techniques, frequency-domain techniques, and time-frequency domain techniques. These are shown in Figure 4.
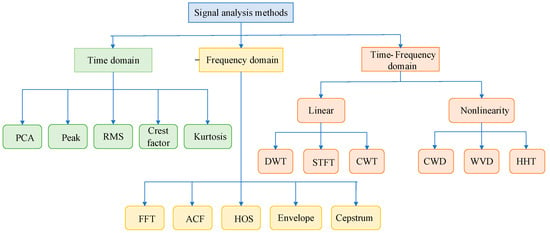
Figure 4.
Classification of signal processing methods. (PCA—principal components analysis, peak—principal components analysis, RMS—root mean square, STFT—short-time Fourier transform, CWT—continuous wavelet transform, DWT—discrete wavelet transformation, WVD—Wigner–Ville distribution, HHT—Hilbert–Huang transform, CWD—Choi–Williams distribution, FFT—fast Fourier transform, ACF—autocorrelation function, HOS—higher order spectra).
Statistical analysis plays a central role in the time-domain approach. These methods utilize specific signal parameters for analysis and assessment such as principal component analysis [], peak [], root mean square or mean [], peak factor [], and kurtosis []. Compared with the frequency domain and time-frequency domain methods, the accuracy and feasibility of using the time-domain method for the diagnosis of ITSF are low; thus, the time-domain method has seldom been applied to diagnose motor faults in recent years, and only some of them are combined with other intelligent methods.
Currently, the frequency-domain and time-frequency domain methods are extensively utilized in the diagnosis of PMSMs, representing the most prevalent approaches in this field. FFT is widely employed for the frequency-domain analysis of stator current or mechanical vibrations, making it one of the most commonly used methods in this context. The technique known as motor current signature analysis (MCSA) refers to the analysis of the amplitudes of components in the current spectrum [,,]. The extended Park’s vector approach(EPVA) method, is used in the analysis of stator phase currents [,]. Due to the limitations of FFTs, such as the need for signal stationarity and long measurement times, there has been a growing preference for advanced signal processing methods based on higher order statistics (HOS) in recent years. These HOS-based techniques offer improved performance and have gained in popularity in various applications []. Spectral envelope [] and cepstrum analysis [] play a significant role in PMSM diagnostics, especially when it comes to situations where detecting mechanical damage. and vibration processing is not possible due to the limitations of the frequency method and information on the moment of failure cannot be obtained.
Time-frequency domain methods, such as STFT, CWT and HHT, are increasingly being used for fault diagnosis. However, it is important to understand their limitations in order to properly apply these methods.
STFT segments the signal into time intervals using a window of a specific type and length, and then applies Fourier transform (FT) to analyze each segment [,,]. It is crucial to choose the appropriate window size that matches the frequency characteristics of the fault, which may not be known in advance. Hence, there is a trade-off between temporal and frequency resolution, where a longer window yields an improved frequency resolution while a shorter window provides an enhanced temporal resolution. STFT is particularly well-suited for low-dynamic non-stationary signals, where a longer window can approximate stationarity and yield better results.
For high-dynamic PMSM drives, multi-resolution signal processing methods, like wavelet transform, can provide improved outcomes. CWT offers uniform resolution in both the temporal and frequency domains [,,,]. However, its application requires that suitable parameters be determined, particularly with respect to the basic wavelet function, which governs consistent resolution across the complete frequency range. One drawback of wavelet analysis is its non-adaptive nature. On the other hand, DWT extracts a specific frequency range through continuous high-frequency and low-frequency filtering, based on the targeted damage component [,,]. Consequently, CWT has a significantly longer computation time compared to DWT, making it favorable for detecting slow-moving failures.
To summarize, time-frequency domain methods have their limitations, and choosing the appropriate method depends on the dynamic characteristics and specific requirements of the system under consideration. Understanding these limitations helps when selecting the most suitable approach for effective fault diagnosis.
Nonlinear time-frequency distribution methods, such as WVD [,,,] or CWD [,], are employed for fault diagnosis. Unlike linear methods that break down the signal into its constituent components, nonlinear time-frequency distribution decomposes the signal into the frequency and time domains based on energy distribution. The Cohen class encompasses various distributions with distinct characteristics obtained through a specified kernel function. These distributions also offer high resolution since they utilize the entire signal within each frequency range to obtain energy. However, these approaches encounter challenges arising from the interplay between pairs of time-frequency components, which can result in pronounced cross-terms and negative power signal values in certain frequency bands. The presence of aliasing issues can also arise when applying WVD to discrete signals.
WVD is used to detect whether there are short circuits between turns and coils of the motor, and to track the evolution of high and low frequencies of the analyzed signal []. WVD adds time information of PMSM on the basis of FFT, and can track high-frequency and quantitative defects well with sufficient time resolution. However, the cross term inherent in WVD can mean problems, mainly in the case of fewer early turns of the short circuit, CWD is needed [].
Another transformation used for analyzing time-frequency energy is HHT [,]. It was originally designed for pure sinusoidal signals with a zero-reference level but has been modified for non-stationary signals. HHT employs the empirical mode decomposition (EMD) method to decompose the input time-domain signal into a finite number of pure oscillation functions called intrinsic mode functions (IMFs), followed by the application of Hilbert transform (HT). This transformation provides information in both the time and frequency domains, resembling the Fourier transform. Unlike the Fourier transform, HHT adapts to the signal characteristics and does not require prior knowledge of fault frequencies. Additionally, it eliminates unwanted frequencies and focuses on the specific characteristic frequencies of the faults. Consequently, HHT has been widely utilized in transient signal analysis.
To sum up, nonlinear time-frequency distribution methods, such as WVD and CWD, provide high-resolution results but may encounter challenges like severe cross-terms and aliasing. On the other hand, HHT, employing EMD and HT, offers adaptability, locality, and the ability to identify characteristic fault frequencies without distortion caused by frequency component interactions. As a result, HHT has found significant applications in transient signal analysis in recent years. The advantages and disadvantages of existing signal processing methods are outlined in Table 3.

Table 3.
Summary of existing signal processing methods for ITSF diagnosis.
3.2. Application of Signal Processing Methods
With a relatively mature signal processing method, it is necessary to consider another equally important factor, the choice of signal. In these analyzable signals, current and voltage measurements are non-intrusive and easy to capture directly from the PMSMs’ own current/voltage sensor. Conversely, other signals are intrusive, requiring additional sensors to obtain the required signals. Therefore, current and voltage are the two non-intrusive signals most frequently selected. The following will be a detailed introduction to the diagnosis methods of current, voltage, vibration, and magnetic flux.
3.2.1. Diagnostic Method Based on Stator Current Signal
MCSA is one of the most commonly used techniques to monitor the operating state of PMSMs. By defining different failure modes under steady-state and transient conditions, it is applied to the short-circuit fault detection of PMSMs.
The influence of ITSF faults on the stator current and electromagnetic torque of axial flux PMSMs was studied. Results of the study showed that the stator current harmonics caused by the short-circuit fault have a pattern as shown in (3) []:
where is the number of pole pairs, and is an integer number.
In ITSF fault detection for PMSMs, various methods have been used to analyze the motor currents. These methods offer advantages such as ease of implementation and independence from the winding topology. One common approach is the frequency analysis of motor currents using single-component discrete Fourier transforms [], which can be easily implemented in motor drive systems without requiring excessive instruction cycles. This method can detect certain fault features such as the third harmonic of the phase current and the second harmonic of the Q-axis current [].
Studies have shown that the occurrence of ITSF faults induces the 9th current harmonics in the fault phase, and these harmonics remain unchanged regardless of the fault level []. Additionally, ITSF faults excite second-order harmonics in the q-axis current, which can be utilized for detection [,]. The root mean square value of the fault phase current increases with higher fault levels [,]. Various methods, such as MCSA and EPVA, have been proposed for ITSF fault detection, focusing on fault components, such as the second harmonic component of the q-axis current, and utilizing the park transform of the stator current [].
Alam obtained the phase current data of the four-phase motor, using Parker transform to determine the fault characteristics [], and determined the fault type by analyzing its amplitude. Fonseca performed a spatial complex transformation of the switching signal and the current signal [], used the transformed signal as the fault indication signal, and verified it on an 8-6 pole switched reluctance motor model. K.-H. Kim proposed a method to monitor the second-order harmonic component of a Q-axis current through harmonic analysis [], aiming at the detection problem of short-circuit faults in the stator windings of PMSMs. The scheme does not require any additional hardware; as long as the steady-state condition is met, the fault can be effectively detected during operation.
To summarize, ITSF fault detection methods for PMSMs often involve motor current characterization using frequency analysis or time-frequency analysis techniques. These approaches offer different advantages in terms of implementation ease and response time. Additionally, wavelet transform has been used to analyze transient states and study the influence of transient voltage on the stator current.
3.2.2. Diagnostic Method Based on Stator Voltage Signal
The diagnostic methods for ITSF in PMSM based on stator voltage and stator current aim to extract characteristic signals that can identify these faults. By analyzing and processing the stator voltage, the presence of ITSF can be determined.
The severity of an ITSF is assessed based on various indicators derived from the phase voltage or DQ-axis voltage. For example, the amplitude of the negative sequence component of the phase voltage is used as an indicator [], while changes in the amplitude and phase of the DQ-axis voltage are employed to detect ITSFs []. Harmonics at twice the angular velocity frequency of the DQ-axis voltage are utilized to detect ITSFs, as described in [,].
One advantage of the methods relying on driver voltage and winding current is their applicability to general-purpose PMSM drives. However, a disadvantage is that the frequency characteristics of the current and voltage can be affected by motor speed, torque, and the control algorithm of the driver.
Another fault indicator used is the imbalance of the reference phase voltage, which is regulated by the controller to compensate for the asymmetric fault effect. New metrics and analysis techniques have been proposed to improve the detection and troubleshooting of ITSFs based on changes in the reference voltage [,].
It should be noted that voltage characterization faces challenges related to sensing through low-pass filters and isolation elements. Detecting fault features with limited-resolution ADCs in three-phase systems can be challenging due to the typically small fault signatures compared to the output voltage. Symmetrical component analysis is commonly employed for ITSF detection, with zero-sequence voltage components (ZSVC) [] used as indicators in star-connected systems; zero-sequence current components (ZSCC) [] are preferred in delta-connected windings.
The PMSM ITSF diagnosis methods based on stator voltage offer the advantages of non-intrusiveness and cost-saving since no additional hardware overhead is required. However, their diagnostic accuracy can be influenced by harmonics, load variations, operating speed, and motor temperature in the drive system. Consequently, fault diagnosis accuracy may fluctuate significantly under various operational states of the motor.
3.2.3. Diagnostic Method Based on Vibration Signals
ITSFs lead to an increase in the magnetic pull force, which in turn increases the magnetic stress acting on the stator. The magnetic stress is proportional to the square of the magnetic flux density. Therefore, any change in the magnetic flux density is reflected in the vibration signal of the motor. By analyzing the vibration signal using FFT or arbitrary time-frequency analysis methods, fault-signature signals can be extracted for fault detection and separation. The spectrum analysis method, based on vibration signals, is used to detect the vibration frequency of the motor for fault diagnosis. It is very similar to stator current spectroscopy. Different types of faults will produce vibrations of different frequencies, and the fault of the motor can be diagnosed through vibration signal spectrum analysis, and even the fault location of the motor can be located.
A fault diagnosis model for ITSFs based on vibration-current fusion was proposed, and the correlation characteristics between current square and shaft radial vibrations were analyzed using Pearson’s correlation coefficient [].
A weak correlation between the square of the excitation current and the vibration signal during the early defect was amplified in study [], and the co-gain residuals were further calculated by combining the residuals between the measured and predicted excitation currents; an early warning signal was issued when the co-gain residuals exceed the threshold. In another study, the air gap magnetic flux density and total force density were used to diagnose the frequency index of the ITSF of the synchronous generator in the winding field [].
Classical continuous wavelet transform is used to analyze the vibration signal. Although the use of vibrations in fault detection is a current diagnostic technique for electrical machines, the exploitation of the harmonic components requires significant calculation time. The continuous wavelet transform of the vibration signal in the event of an ITSF shows its limitations.
3.2.4. Fault Localization Method Based on Characteristics of the Motor Magnetic Field
In no-load conditions, a stray flux can detect faults more effectively than stator current []. What is more, the stray magnetic communication signal can provide information about the location of the fault [].
An analytical model for computing BEMF in the air-gap search coil was developed []. This model utilizes geometric and circuit parameters, rotor speed, three-phase currents, and the magnetization coefficient as inputs. By combining the measured BEMF data with the model data, demagnetization faults can be identified. The accuracy of this method largely depends on a precise motor model. A technique for detecting ITSF using the stray magnetic field of a small-sized tunnel reluctance sensor was introduced in [], which allows for easier installation and replacement of the motor stator outside the yoke while the PMSM remains operational. It enables accurate detection of the location of the ITSF. A partition analysis model was developed for PMSMs under demagnetization faults, and used to investigate the impacts of the quantity and placement of permanent magnets on motor performance [].
Moreover, a stator detection coil system was proposed and its ability to detect ITSFs in PMSMs was verified []. The relationship between fault severity and the amplitude of the detection signal was also investigated. To address location-related issues, a dual probe coil system was proposed to effectively detect faults without signal-size dependence. Power-density spectrum analysis of the probe coil signal after stator turn short-circuit faults revealed clear fault characteristics, particularly when the number of faults was small [].
In addition, there are a variety of motor ITSF diagnosis methods, such as the partial discharge method [], instantaneous power decomposition method [], negative sequence impedance method [], torque harmonic component method [], etc., which have been applied to a certain extent.
3.3. Fault Feature Extraction of Non-Stationary Information
Traditional fault diagnosis methods for PMSMs are applicable to the fault diagnosis of EV traction motors under certain operating scenarios such as constant speed cruising. However, under variable operating conditions, such as acceleration and deceleration, these methods may not work. Due to the complex and variable operating conditions of EV motors, signals obtained for diagnosis are often non-stationary. Analyzing signals solely in the time domain or frequency domain cannot capture the signal’s time-frequency non-stationary characteristics. For non-stationary signal processing, methods such as time-frequency domain analysis and order tracking are primarily used. Discrete wavelet transform was employed to extract non-stationary current fault features in motors []. An early ITSF diagnosis method based on the Goerges phenomenon for extracting magnetic flux features was developed []. A dynamic Bayesian network-based method was used to diagnose non-stationary and intermittent faults in motor systems []. The use of short-frequency Fourier transform (SFFT) for motor fault diagnosis in non-stationary states was shown to enhance computational efficiency []. An adaptive window short-time esprit (AWSTE) method for diagnosing rotor faults in transiently operating motors was developed []. An instantaneous frequency estimation order tracking method was proposed to extract instantaneous frequencies related to bearing faults for identifying bearing fault types [].
4. Artificial Intelligence-Based Fault Diagnosis Methods
The application of artificial intelligence (AI) methods in machine fault diagnosis is an emerging and promising field. With the help of technologies, such as machine learning, pattern recognition and deep learning, AI methods can realize real-time diagnosis and accurate prediction of motor faults by learning features and patterns from a large amount of sampled data. AI methods have developed rapidly in the past decade, as shown in Figure 5, from the original qualitative methods based on symbolic reasoning to quantitative methods based on machine learning algorithms [].
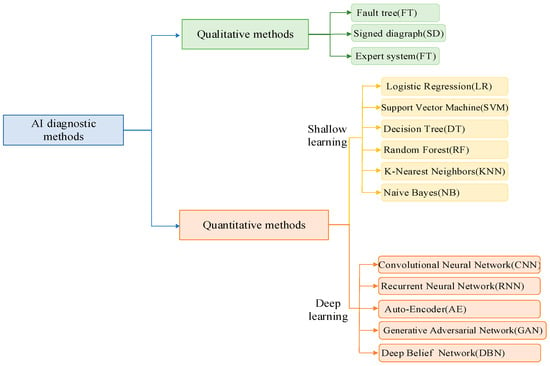
Figure 5.
AI-based ITSF diagnosis methods.
Qualitative methods include fault tree (FT), signature diagram (SD) and expert system (ES). FT is a logistic causal tree that propagates the main event (failure) from the bottom to the top event (symptom). It is used in [] for fault diagnosis with high accuracy. SG is a directed arc graph from the Cause node to the Result node, and these arcs are represented by positive or negative signs. In fault diagnosis, it can be used to detect the amount of abnormal states []. ES is usually a tailor-made system that encompasses depth but expertise in a narrow area. The expert system is actually a rule-based system that presents a person’s expertise in the form of a set of rules. The combination of expert systems with other diagnostic methods can make motor diagnostics more efficient []. These qualitative methods are more based on the experience accumulated in actual motor fault diagnosis, to make a judgment on whether the fault is faulty. Accuracy is difficult to guarantee, and it is generally necessary to combine other diagnostic methods to improve the accuracy.
Today, due to the exponential growth in computing power, computational intelligence has become the most attractive AI technology. Machine learning is a powerful approach for extracting insights from vast amounts of empirical data, albeit at the cost of significant computational resources. Applying machine learning to detect and diagnose faults from data is simple and does not require explicit models. Shallow neural networks mainly include logistic regression [], support vector machines (SVM) [], random forest [], the k-nearest neighbor algorithm [], and naive Bayes [], which can adaptively learn features without necessitating the creation of a precise mathematical model, thereby reducing the uncertainty and intricacy associated with human involvement. Nevertheless, conventional shallow neural networks have limitations, including gradient vanishing, overfitting, susceptibility to local minima, and the requirement for substantial prior information, all of which diminish the efficacy of fault diagnosis. The method of deep learning can solve these problems easily. It brings the following advantages to motor fault diagnosis: (1) processing larger amounts of data; (2) faster diagnosis; (3) greater robustness; (4) more advanced automatic feature learning; and (5) end-to-end learning (predictions are made directly from raw input data).
An essential aspect of EV motor fault diagnosis is the analysis of extensive real-time data streams. With the development of networked technologies, such as the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) and cyber–physical systems, it is easier to obtain large amounts of operational-status data flow in real time. For example, large-scale data-processing technologies, such as cloud computing and digital twins, have made AI’s fault diagnosis methods more mature, making it easy to carry out real-time fault prediction and diagnosis. AI approaches can ensure the normal functioning of the motor and avoid impacting vehicle performance through a series of measures during real-time fault diagnosis. Initially, the neural network autonomously acquires profound abstract features from extensive input data in a hierarchical manner. Subsequently, the network is trained based on the correlation between feature attributes and fault patterns. Ultimately, the trained network is employed for diagnosing faults in new monitoring data. Some deep hierarchical networks can even directly process source data as input for real-time monitoring [].
A deep learning algorithm utilizing efficient convolutional neural networks (ECNNs) was designed to run on edge-computing nodes for real-time motor fault diagnosis and dynamic control []. A new three-phase architecture utilizing deep learning was proposed for real-time monitoring []. The model is end-to-end adaptable and processes data sequentially. A real-time fault diagnostic method using data collected from multiple sensors was also developed []. The method is based on a multi-sensor convolutional neural network (MS-CNN) that incorporates feature extraction, sensor selection, and fault diagnosis into an end-to-end model. A compact adaptive 1D CNN classifier was used for real-time fault diagnosis [] that can obtain source data directly as input and effectively learn the optimal features through appropriate training. A dual-flow feature fusion convolutional neural network (TSFFCNN) was proposed for real-time fault diagnosis utilizing a dual-channel network model constructed with 1D-CNN and 2D-CNN [].
4.1. Application of Convolutional Neural Network (CNN)
CNNs possess local receptive fields and weight-sharing properties, leading to a decreased number of network parameters and mitigating overfitting to some extent. Therefore, it is the neural network most commonly considered in the field of motor fault diagnosis. In Figure 6, the specific steps of CNN for motor fault diagnosis are shown on the left, and include:
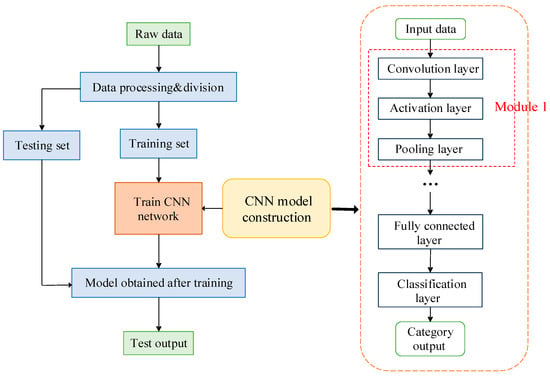
Figure 6.
CNN-based diagnostic framework and CNN model structure.
- Capturing the time domain or frequency domain signal of the motor in normal and abnormal conditions using sensors;
- Preprocessing the signal and divide the signal into a training set and a test set;
- Using the received data to determine the model construction of CNN;
- Initializing the parameters of the CNN network, train it using the labeled training set through supervised learning, and iteratively update the network parameters until the maximum number of iterations is achieved;
- Using the trained CNN model to troubleshoot the test set.
On the right side of Figure 6 is the model construction of CNN. The preprocessed data first enters the convolutional layer for preliminary feature extraction, and the activation function is used to perform nonlinear transformation of the output after the convolution operation. The purpose of the activation function is to introduce nonlinearity so that the model can learn more complex feature representations. Commonly used activation functions include ReLU, sigmoid, and tanh. The sigmoid function and tanh function are saturated nonlinear functions, which are mostly used in traditional CNNs, while the unsaturated nonlinear function ReLU can effectively improve CNN network performance []; therefore, among the current diagnostic methods, the ReLU activation function is the most widely used. Features are transformed nonlinearly into a pooling layer, which is used to reduce the size of the feature map and help to extract the most important features. It does this by performing an aggregation operation, such as maximum pooling or average pooling, within a local area. In some cases, you the activation layer can be omitted and the output of the convolutional layer can be connected directly to the pooling layer. This usually occurs in the early layers of the network, or during some specific tasks. However, in most cases, the use of activation functions can increase the nonlinearity of the model and improve the expressiveness and performance of the model.
The convolutional layer, activation layer, and pooling layer form a module, which is equivalent to a specific feature extraction of the signal. Therefore, the operation of the above modules will be repeated, and the features will become more and more accurate with each convolution operation. However, too many convolutions will lead to data overfitting; therefore the appropriate number of convolutions is very important, and experiments have proved that the effect is generally best using 6–7 convolutions.
The extracted features will enter the fully connected layer, which flattens the input high-dimensional feature vectors into one-dimensional vectors, performs matrix multiplication operations with the weight matrix, and then obtains the final classification output result through the nonlinear transformation of the activation function. In the latest CNN architectures, such as ResNet, Inception, etc., the use of the fully connected layer has been reduced or even completely removed. This is because the fully connected layer has a large number of parameters, which can lead to overfitting and the layer cannot handle variable-sized inputs. Instead, these architectures typically use global average pooling or other techniques to convert convolutional feature maps into fixed-length vectors that can then be used directly for classification or regression tasks. This reduces model complexity, reduces the number of parameters, and improves the generalization ability of the model.
The fundamental role of CNN is to extract advanced features from the input signal through convolution operations. These networks lack predefined architectures, parameter selection methods, or specific rules governing the quantity of convolutional layers. The architecture of a CNN should be viewed as the evolution of features that are refined with each additional convolutional layer. When introducing the application of CNNs in the diagnostic process, the initial layer can be perceived as filtering out fundamental features such as maximum or minimum values. The following convolution operation enables the detection of more complex features, such as the range between the minimum and maximum values. Hence, the configuration of the network will rely on the nature of the input data and the tasks carried out by the CNN. To identify intricate features, a framework comprising multiple layer sets is employed. The network’s capability to recognize features is connected to the mechanism, through which it develops generalized abilities.
Motor fault detection can benefit from the consideration of local correlation in early data, as demonstrated in []. CNN models that utilize the original current signal exhibit higher accuracy and shorter training times when classifying ITSF levels []. Proper adjustments to the form and size of input signals can enhance diagnostic effectiveness during classification and in the assessment of injury severity []. Moreover, novel feature extraction techniques using FOP-CNN can be applied to signals from vibration sensors and thermocouples, expanding the scope of time-series applications [].
In the context of fault diagnosis, sequence data can be converted into grayscale images and classified using EWT and deep CNN models, resulting in satisfactory diagnostic results []. N-LSTM, a multiscale convolutional neural network combined with long short-term memory, allows for the direct processing of raw data without preprocessing []. By utilizing multiscale convolutional neural networks, fault information from multiple components and time scales of vibrational signals can be effectively learned []. Additionally, the CNN model structure incorporating global average pooling techniques and support vector machines enables the extraction of representative features and fault classification [].
A diagnostic framework known as DTS-CNN is built upon the features of motor vibration signals []. It introduces an offset before the convolutional layer, which captures the correlations between signals at various time intervals within periodic mechanical signals. This approach overcomes the limitations of standard neural networks, making it particularly suitable for modern PMSMs operating in non-stationary environments. Another study demonstrates the conversion of time series data into two-dimensional images, leveraging the feature extraction capabilities of CNN for failure-mode classification and severity recognition []. The superior accuracy of CNN in extracting features from such two-dimensional images is verified.
Table 4 presents a summary of the strengths and weaknesses of existing CNN methods. In summary, motor fault detection methods benefit from considering local correlations in early data and utilizing the original current signal. Adjusting the form and size of input signals can improve diagnostic effectiveness.

Table 4.
Summary of existing CNN for ITSF diagnosis.
The parameter-sharing feature of CNN improves its processing ability for high-dimensional input data. For 2-D image data, parameter sharing can capture similar feature patterns at different locations, thereby improving the generalization ability of the model.
4.2. Application of Recurrent Neural Network (RNN)
RNN is a neural network model that is good at processing time series, and has the characteristics of fast convergence, high accuracy, and high stability. When it comes to defect diagnosis, RNNs are particularly well-suited for complex devices or systems.
A typical RNN has the problem of vanishing gradients or exploding gradients, which makes it unusable with information from the past; therefore, a long short-term memory neural network (LSTM) is proposed to solve this problem, as it solves the gradient problem and has advantages in processing data with strong correlation with time series. LSTM is widely used in the field of fault diagnosis.
Figure 7 shows the core memory block of LSTM, which mainly contains three gates (forget gate, input gate, output gate) and a memory unit (cell).
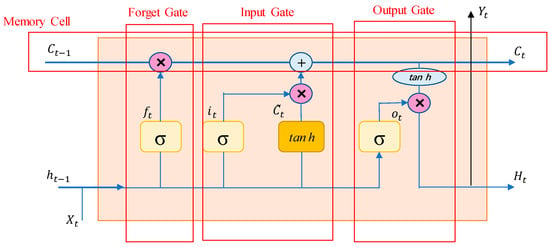
Figure 7.
Memory block of LSTM.
The forgetting gate controls whether to retain previous memory information to the current moment in order to filter out unimportant information. The gradient vanishing problem in traditional RNNs is avoided, allowing the network to better capture long-term dependencies:
where , are each gate’s input weights and bias respectively ( can be ,, or ), and are nonlinear functions and “” means matrix multiplication. is the last output and is the latest input.
The memory gate controls how the current input is combined with the previous memory to update the memory state at the current moment through (4). With the ability to selectively update memories, the memory state can be flexibly adjusted based on the importance of the current input. It can effectively deal with the noise and redundant information in the sequence data and improve the robustness and generalization ability of the model:
The output gate via (5)–(7) controls how the memory state of the current moment is output to the next moment or used for final prediction. It has the ability to selectively output memories and can flexibly adjust the output information according to the needs of the current task. It provides a mechanism to balance memory and forgotten information and improves the model’s attention to important information in the sequence data.
The memory unit is capable of storing the input of the current moment, the memory of the past moment, and the output of the previous moment, and combines this information to form a new memory state . The memory information is further processed through (10) to become the output .
Since the special LSTM in RNN is more often used for motor fault diagnosis, we built a fault diagnosis framework based on LSTM. As shown in Figure 8, the core is the choice of the number of layers of LSTM cells. If the data volume is small or the data characteristics are simple, the shallower LSTM network may be sufficient, while for larger or more complex datasets, the number of layers of LSTM cells needs to be increased. LSTM networks require more computing resources and longer training times. Therefore, it is necessary to judge the suitability of the number of layers of LSTM units through a performance evaluation of the verification set and the test set, and according to the accuracy and generalization ability of the model. Sometimes increasing the number of layers does not necessarily lead to significant performance improvements and may even lead to overfitting.
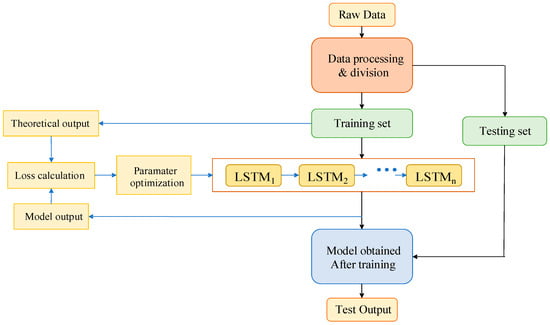
Figure 8.
LSTM-based diagnostic framework.
To estimate the ITSF of PMSMs, a medium network is employed within an encoder–decoder structure featuring an attention mechanism []. In this approach, the encoder employs a bidirectional LSTM, which consists of two LSTMs working in opposite directions to extract both forward and backward dependencies. The network obtains inputs such as raw values of negative sequence current, positive sequence current (calculated from the stator three-phase current), and rotational speed. However, the fault indicator, despite indicating fault severity and achieving high estimation accuracy, is not utilized for automatic fault detection and classification.
The LSTM method is used for predicting output variables, and the fault state is diagnosed by comparing true and predicted probability distributions. Model training utilizes 128 monitoring variables, with wind speed and active power selected as input variables for temperature and pressure predictions. This method achieves 92% accuracy in detecting generator winding faults, surpassing other advanced methods [].
Building upon the LSTM network, the EMD signal-processing tool is employed to extract representative features, enabling the detection of various stator short-circuit faults, even in the presence of a single short turn, with an accuracy of approximately 95% [].
Compared to LSTMs, features extracted by CNN, exhibit greater robustness, achieving an accuracy rate of 98% (compared to LSTMs’ 88% accuracy) []. This can be attributed to the fact that CNNs can be stacked into deep models, which has proven to be a robust method. Additionally, CNNs resemble feedforward neural networks with stacked multi-layer perceptrons, minimizing the need for data pre-processing. On the other hand, LSTMs leverage their internal memory to process inputs for arbitrary sequences.
The output of a CNN is considered a feature map [], serving as the input for LSTM and GRU models for classification. Experimental results demonstrate that the mixed 1DCNN-LSTM and mixed 1DCNN-GRU models provide better early diagnosis effectiveness. Among various LSTM variants, the one-way variant of the LSTM neural network proves to be the best classifier for low-severity ITSFs, offering the highest test accuracy of 99.08% with the fewest trainable parameters [].
A hybrid structure combining a two-dimensional convolutional neural network (2DCNN) and long short-term memory/gated recurrent unit (LSTM/GRU), referred to as FDS, is proposed as a relatively lightweight planar diagnostic structure. Its applicability in fault diagnosis and in the severity evaluation of industrial drive systems under frequency conversion and load change conditions was experimentally demonstrated in [].
In another study [], a motor defect detection method based on LSTM was proposed. Real-time prediction of the three-phase current value at the next sampling moment was employed, capturing the three-phase current value and phase angle information from previous sampling data for real-time motor observation. The benefits and drawbacks of existing RNN methods are compiled in Table 5.

Table 5.
Summary of existing RNN for ITSF diagnosis.
RNNs can effectively store and transmit contextual information through structures such as memory recurrent units (LSTMs) or gated recurrent units (GRUs). In the process of motor fault diagnosis, contextual information is very important in order to understand the current state, judge anomalies, and predict fault development trends. The memory mechanism of the RNN allows the model to make better use of previous information for troubleshooting.
However, RNNs also have some limitations and challenges, such as gradient vanishing and explosion problems, low computational efficiency, and possible difficulties in processing long sequences. In addition, choosing the appropriate RNN structure and hyperparameter settings is also an important factor affecting its performance.
4.3. Application of Self-Encoding Network (AE)
The shallow network includes the original autoencoder network and its evolved sparse autoencoder network and denoising autoencoder network. In practice, they are often stacked in deeply stacked AE. Due to their advantages, stacked auto-coding networks are popular. The ability to understand the attributes of data is a concern for many experts and scholars. A deep sparse autoencoder network was used to detect ITSF defects in PMSMs. Negative sequence current and torque signals made up the sample. To increase the sample size and create a training set, a generative adversarial network (GAN) was used. In the classification test, the sparse autoencoder network generated by sample training was used, and the experiment showed that the classification accuracy reached 99.4% [].
Variables such as the type, activation function and depth of the autoencoder [], the sparsity of the sparse autoencoder, the number of features and the pooling strategy were studied, and the optimal solution for the detection of turn-to-turn faults was found by combining the channel selection of the ITSF detection, the timespan of the input signal and the signal sampling frequency, and the overall recognition accuracy reached 99.5%.
AE is unique in that it can learn low-dimensional representations of the input data, which can be used for data reconstruction and visualization. By compressing the original data into a lower-dimensional space and then performing decoding operations, samples that are similar to the original data can be reconstructed. This helps to better understand the structure, distribution, and characteristics of the data, and can help to identify and visualize failure modes.
However, AE also has some limitations, such as the potential for difficulty in modeling complex patterns, potential overfitting problems, and limited use of label information. In addition, when designing an autoencoder, choosing the right architecture, loss function, and hyperparameter settings can also have an impact on its performance.
4.4. Application of Generative Adversarial Network (GAN)
CGAN is used to enhance the joint features of ITSF and enrich the training set, thus overcoming the shortcomings of insufficient network training based on deep learning. At the same time, the noise injection strategy is introduced to expand the diversity of fault samples and enhance the sparse representation of the network. Finally, the OSAE is optimized to achieve the purpose of efficient and accurate diagnosis of ITSF faults.
The negative sequence current and torque characteristic signals of PMSMs are collected, and the sample data are extended by using the generative adversarial network and the network. A variety of training sets are constructed, and the sparse autoencoder network is combined to achieve efficient and accurate fault feature classification and identification. Experimental results showed that the accuracy of the method can reach 99% [].
What makes GANs unique is that new sample data can be synthesized by generating models. In motor fault diagnosis, if the annotated fault data are relatively small, the use of GAN can generate more synthetic data to increase the size and diversity of the training set. This helps to improve the generalization ability of the model and allows for effective data augmentation and sample generation when real failure data are lacking.
However, GANs still face some challenges in the field of motor fault diagnosis, such as training stability, mode diversity, and the quality of the generated samples.
4.5. Challenges and Future Work
While deep learning algorithms have yielded promising results in solving the feature extraction problem, they often require expertise in constructing neural network structures and selecting appropriate hyperparameters to achieve the desired outcomes. However, diagnosing faults using deep learning is generally considered less complex due to its reliance on supervised learning, which involves matching input data to corresponding outputs. Consequently, there is a need to explore more intelligent systems capable of detecting failures solely based on raw data, eliminating the requirement for feature extraction expertise or optimal hyperparameter selection.
5. Prospects for the Development of Diagnostic Technology
The following are some viewpoints on the future development prospects of ITSF diagnosis technology:
- Promoting continuous development and innovation in sensor technology, including vibration sensors, temperature sensors, current sensors, etc., enables the acquisition of more precise and diverse motor operation data, facilitating the design and optimization of feature extraction and diagnostic algorithms for PMSMs;
- Investigating future research prospects for identifying EV motor faults through an AI-based onboard diagnostic system poses a formidable challenge;
- Integrating multiple data sources (such as vibration, sound, current, etc.) for data fusion and comprehensive analysis can enhance the diagnostic accuracy of ITSF. Through the amalgamation of data from various sensors, a more thorough and dependable fault signature can be derived, thereby enhancing the robustness and reliability of diagnostics;
- Detecting faults in EV motors during operation in real-time without employing complex signal decomposition methods remains a challenging task;
- Diagnosing hybrid simultaneous faults in EV motors is also a focus of research;
- Monitoring the motor’s condition and providing early warning of failures when EVs operate under complex conditions is of paramount importance.
Figure 9 shows the breakthrough points in the field of EV motor fault diagnosis.
Figure 9.
Future trends in EV motor fault diagnosis.
6. Conclusions
This paper provides a comprehensive review of the state-of-the-art techniques for detecting and diagnosing stator ITSFs in the PMSMs used in electric vehicles EVs. The existing diagnostic techniques were classified into the following three categories: motor model-based; signal processing; and AI. The capabilities and limitations of these technologies were thoroughly discussed. Model-based motor fault diagnosis methods exhibit high accuracy and interpretability; however, limitations exist, particularly under conditions in which there are complex faults or inaccurate models. Signal processing-based approaches offer advantages, such as broad applicability and precise diagnostic outcomes, but are also constrained by a reliance on feature extraction and their susceptibility to noise interference. In contrast, AI-based diagnostic methods boast characteristics such as high precision, automatic processing, and strong adaptability, making them the most promising method for development in current times. Finally, the research prospects and future challenges of EV motor fault diagnosis were discussed.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, W.L. and B.J.; investigation, Y.J. and J.Z.; resources, J.Y.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.J.; writing—review and editing, W.L. and J.Y.; visualization, Y.J. and J.Z.; supervision, W.L.; project administration, B.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Defense Basic Scientific Research Program of China under Grant JCKY2021606B014.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Upadhyay, A.; Alaküla, M.; Márquez-Fernández, F.J. Characterization of Onboard Condition Monitoring Techniques for Stator Insulation Systems in Electric Vehicles—A Review. In Proceedings of the IECON 2019—45th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Lisbon, Portugal, 14–17 October 2019; Volume 1, pp. 3179–3186. [Google Scholar]
- Xian, R.; Wang, L.; Zhang, B.; Li, J.; Xian, R.; Li, J. Identification Method of Interturn Short Circuit Fault for Distribution Transformer Based on Power Loss Variation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2003, 20, 2444–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faiz, J.; Nejadi-Koti, H.; Valipour, Z. Comprehensive Review on Inter-turn Fault Indexes in Permanent Magnet Motors. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2017, 11, 142–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yang, J.; Ye, H.; Zhou, W. A Review of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Fault Diagnosis. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Conference and Expo Transportation Electrification Asia-Pacific (ITEC Asia-Pacific), Beijing, China, 31 August–3 September 2014; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.; Guo, C.; Xie, Z.; Ni, F.; Liu, H. A Signal-Based Fault Detection and Tolerance Control Method of Current Sensor for PMSM Drive. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 65, 9646–9657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Xu, Z.; Cheng, M.; Wang, W.; Hu, Y. Comprehensive Diagnosis and Tolerance Strategies for Electrical Faults and Sensor Faults in Dual Three-Phase PMSM Drives. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 34, 6669–6684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlowska-Kowalska, T.; Wolkiewicz, M.; Pietrzak, P.; Skowron, M.; Ewert, P.; Tarchala, G.; Krzysztofiak, M.; Kowalski, C.T. Fault Diagnosis and Fault-Tolerant Control of PMSM Drives–State of the Art and Future Challenges. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 59979–60024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akrad, A.; Hilairet, M.; Diallo, D. Design of a Fault-Tolerant Controller Based on Observers for a PMSM Drive. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2011, 58, 1416–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Gao, Z. From Model, Signal to Knowledge: A Data-Driven Perspective of Fault Detection and Diagnosis. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2013, 9, 2226–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansouri, B.; Idrissi, H.J.; Venon, A. Inter-Turn Short-Circuit Failure of PMSM Indicator Based on Kalman Filtering in Operational Behavior. In Proceedings of the Annual Conference of the PHM Society, Scottsdale, AZ, USA, 21–26 September 2019; Volume 11. [Google Scholar]
- Namdar, A.; Samet, H.; Allahbakhshi, M.; Tajdinian, M.; Ghanbari, T. A Robust Stator Inter-Turn Fault Detection in Induction Motor Utilizing Kalman Filter-Based Algorithm. Measurement 2022, 187, 110181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Park, H.J.; Lee, D.; Lee, S.; Choi, J.-H. A Novel Kalman Filter-Based Prognostics Framework for Performance Degradation of Quadcopter Motors. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2023, 73, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.-C.; Cheng, T.-H. Motor-Efficiency Estimation and Control of Multirotors Comprising a Cooperative Transportation System. IEEE Access. 2023, 11, 36566–36578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, A.; Tahavori, M.; Midtiby, H.S. Model-Based Fault Diagnosis Algorithms for Robotic Systems. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 2250–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Sayed, W.; Abd El Geliel, M.; Lotfy, A. Fault Diagnosis of PMSG Stator Inter-Turn Fault Using Extended Kalman Filter and Unscented Kalman Filter. Energies 2020, 13, 2972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudi, A.; Jlassi, I.; Cardoso, A.J.M.; Yahia, K.; Sahraoui, M. Inter-Turn Short-Circuit Faults Diagnosis in Synchronous Reluctance Machines, Using the Luenberger State Observer and Current’s Second-Order Harmonic. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021, 69, 8420–8429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guezmil, A.; Berriri, H.; Pusca, R.; Sakly, A.; Romary, R.; Mimouni, M.F. Detecting Inter-Turn Short-Circuit Fault in Induction Machine Using High-Order Sliding Mode Observer: Simulation and Experimental Verification. J. Control Autom. Electr. Syst. 2017, 28, 532–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouakoura, M.; Naït-Saïd, M.-S.; Nait-Said, N. Incipient Inter-Turn Short Circuit Fault Estimation Based on a Faulty Model Observer and Ann-Method for Induction Motor Drives. Recent Adv. Electr. Electron. Eng. Former. Recent Pat. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2019, 12, 374–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasilios, I.C. Detection of PMSM Inter-Turn Short-Circuit Based on a Fault-Related Disturbance Observer. Int. J. Simul. Syst. Sci. Technol. 2020, 21, 31.1–31.7. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Dou, M.; Dai, Z.; Zhao, D.; Zhang, Z. Modeling and Fault Diagnosis of Inter-Turn Short Circuit for Five-Phase PMSM Based on Particle Swarm Optimization. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition (APEC), Long Beach, CA, USA, 20–24 March 2016; pp. 3134–3139. [Google Scholar]
- Haddad, R.Z.; Strangas, E.G. Detection of Static Eccentricity and Turn-to-Turn Short Circuit Faults in Permanent Magnet Synchronous AC Machines. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 10th International Symposium on Diagnostics for Electrical Machines, Power Electronics and Drives (SDEMPED), Guarda, Portugal, 1–4 September 2015; pp. 277–283. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.-K.; Jeong, C.-L.; Lee, S.-T.; Hur, J. Early Detection Technique for Stator Winding Inter-Turn Fault in BLDC Motor Using Input Impedance. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2014, 51, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Zafarani, M.; Akin, B.; Fedigan, S.E. Analysis and Detection of Inter-Turn Short-Circuit Fault through Extended Self-Commissioning. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2016, 53, 2730–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leboeuf, N.; Boileau, T.; Nahid-Mobarakeh, B.; Takorabet, N.; Meibody-Tabar, F.; Clerc, G. Estimating Permanent-Magnet Motor Parameters under Inter-Turn Fault Conditions. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2012, 48, 963–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leboeuf, N.; Boileau, T.; Nahid-Mobarakeh, B.; Takorabet, N.; Meibody-Tabar, F.; Clerc, G. Inductance Calculations in Permanent-Magnet Motors under Fault Conditions. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2012, 48, 2605–2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarikhani, A.; Mohammed, O.A. Inter-Turn Fault Detection in PM Synchronous Machines by Physics-Based Back Electromotive Force Estimation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2013, 60, 3472–3484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quattrocchi, G.; Berri, P.; Dalla, M.V.; Maggiore, P. Diagnostics of Electro-Mechanical Actuators Based Upon the Back-EMF Reconstruction. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, Online, 2–4 September 2020; Volume 1024, p. 012096. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, J. Winding Condition Monitoring for Inverter-Fed PMSM Using High-Frequency Current Injection. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2021, 57, 5818–5828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, K.K.; Joshi, S.H.; Kumar, R. A State-Space Model for Induction Machine Stator Inter-Turn Fault and Its Evaluation at Low Severities by PCA. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Asia-Pacific Conference on Computer Science and Data Engineering (CSDE), Brisbane, Australia, 8–10 December 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Li, Z.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, K.; Xu, Y. Motor Current Time-varying Quadratic Phase Coupling Analysis and its Application in Traction Motor Fault Detection under Varying-speed Condition. IEEE Sens. J. 2024, 24, 12877–12886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai , B.; Hao, K.; Wang, Z.; Yang, C.; Kong, X.; Liu, Z.; Ji, R.; Liu, Y. Data-driven early fault diagnostic methodology of permanent magnet synchronous motor. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 177, 115000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, C.; Melero, M.; Cabanas, M.; Cano, J.; Orcajo, G.; Pedrayes, F. Finite Element Model for the Study of Inter-Turn Short Circuits in Induction Motors. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE International Symposium on Diagnostics for Electric Machines, Power Electronics and Drives, Cracow, Poland, 6–8 September 2007; pp. 415–419. [Google Scholar]
- Ghanbari, T.; Mehraban, A.; Farjah, E. Inter-Turn Fault Detection of Induction Motors Using a Method Based on Spectrogram of Motor Currents. Measurement 2022, 205, 112180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejia-Barron, A.; Tapia-Tinoco, G.; Razo-Hernandez, J.R.; Valtierra-Rodriguez, M.; Granados-Lieberman, D. A Neural Network-Based Model for MCSA of Inter-Turn Short-Circuit Faults in Induction Motors and Its Power Hardware in the Loop Simulation. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2021, 93, 107234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zouzou, S.; Sahraoui, M.; Ghoggal, A.; Guedidi, S. Detection of Inter-Turn Short-Circuit and Broken Rotor Bars in Induction Motors Using the Partial Relative Indexes: Application on the MCSA. In Proceedings of the The XIX International Conference on Electrical Machines-ICEM 2010, Rome, Italy, 6–8 September 2010; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Prasob, K.; Kumar, N.P.; Isha, T. Inter-Turn Short Circuit Fault Analysis of PWM Inverter Fed Three-Phase Induction Motor Using Finite Element Method. In Proceedings of the 2017 international conference on circuit, power and computing technologies (ICCPCT), Kollam, India, 20–21 April 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Sahraoui, M.; Ghoggal, A.; Guedidi, S.; Zouzou, S.E. Detection of Inter-Turn Short-Circuit in Induction Motors Using Park–Hilbert Method. Int. J. Syst. Assur. Eng. Manag. 2014, 5, 337–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyftakis, K.N.; Marques-Cardoso, A.J. Reliable Detection of Very Low Severity Level Stator Inter-Turn Faults in Induction Motors. In Proceedings of the IECON 2019-45th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Lisbon, Portugal, 14–17 October 2019; Volume 1, pp. 1290–1295. [Google Scholar]
- Rebouças Filho, P.P.; Nascimento, N.M.; Sousa, I.R.; Medeiros, C.M.; de Albuquerque, V.H.C. A Reliable Approach for Detection of Incipient Faults of Short-Circuits in Induction Generators Using Machine Learning. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2018, 71, 440–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaparoli, I.O.; Rabelo Baccarini, L.M.; Lamim Filho, P.C.M.; Batista, F.B. Transient Envelope Current Analysis for Inter-Turn Short-Circuit Detection in Induction Motor Stator. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2020, 42, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seera, M.; Lim, C.P.; Ishak, D.; Singh, H. Fault Detection and Diagnosis of Induction Motors Using Motor Current Signature Analysis and a Hybrid FMM–CART Model. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2011, 23, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, W.; Yun, S.-H.; Lim, Y.-S.; Cheong, S.; Bae, J.; Park, Y.-H. Fault Diagnosis of Inter-Turn Short Circuit in Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors with Current Signal Imaging and Semi-Supervised Learning. In Proceedings of the IECON 2022–48th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Brussels, Belgium, 17–20 October 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Jeong, H.; Moon, S.; Lee, J.; Kim, S.W. Inter-Turn Short Fault Diagnosis of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machines Using Negative Sequence Components. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Industrial Technology (ICIT), Taipei, Taiwan, 14–17 March 2016; pp. 170–174. [Google Scholar]
- Ehya, H.; Nysveen, A. Pattern Recognition of Interturn Short Circuit Fault in a Synchronous Generator Using Magnetic Flux. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2021, 57, 3573–3581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, S.; Das, S.; Purkait, P.; Chakravorti, S. Application of Wavelet Transform to Discriminate Induction Motor Stator Winding Short Circuit Faults from Incipient Insulation Failures. In Proceedings of the 2012 1st International Conference on Power and Energy in NERIST (ICPEN), Nirjuli, Arunachal Pradesh, India, 28–29 December 2012; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Hammond, D.N.A.; Frimpong, E.A.; Ohene, J.Y. Detection of Inter-Turn Faults in Transformers Using Continuous Wavelet Transform and Convolutional Neural Network. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE PES/IAS PowerAfrica, Nairobi, Kenya, 25–28 August 2020; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Hossein, S.; Abedi, M. Detection of the Stator Inter-Turn Fault Using the Energy Feature of the Wavelet Coefficients Obtained through Continuous Wavelet Transform. Sci. Iran. Trans. Comput. Sci. Eng. Electr. Eng. 2023, 30, 536–550. [Google Scholar]
- Das, S.; Koley, C.; Purkait, P.; Chakravorti, S. Wavelet Aided SVM Classifier for Stator Inter-Turn Fault Monitoring in Induction Motors. In Proceedings of the IEEE PES general meeting, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 25–29 July 2010; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Cherif, H.; Menacer, A.; Romary, R.; Pusca, R. Dispersion Field Analysis Using Discrete Wavelet Transform for Inter-Turn Stator Fault Detection in Induction Motors. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 11th International Symposium on Diagnostics for Electrical Machines, Power Electronics and Drives (SDEMPED), Tinos, Greece, 29 August–1 September 2017; pp. 104–109. [Google Scholar]
- Bessam, B.; Menacer, A.; Boumehraz, M.; Cherif, H. Wavelet Transform and Neural Network Techniques for Inter-Turn Short Circuit Diagnosis and Location in Induction Motor. Int. J. Syst. Assur. Eng. Manag. 2017, 8, 478–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roshanfekr, R.; Jalilian, A. Wavelet-Based Index to Discriminate between Minor Inter-Turn Short-Circuit and Resistive Asymmetrical Faults in Stator Windings of Doubly Fed Induction Generators: A Simulation Study. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2016, 10, 374–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DOĞAN, Z.; SELÇUK, R. A Diagnosis of Stator Winding Fault Based on Empirical Mode Decomposition in PMSMs. Balk. J. Electr. Comput. Eng. 2020, 8, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Caballero-Peña, J.A.; Rosero-Garcìa, J. Decentralized Inter-Turn Fault Diagnosis of Induction Motors Based on Wireless Sensor Networks. Dyna 2021, 88, 237–246. [Google Scholar]
- Climente-Alarcón, V.; Antonino-Daviu, J.; Riera-Guasp, M.; Puche, R.; Escobar-Moreira, L.; Jover-Rodriguez, P.; Arkkio, A. Diagnosis of Stator Short-Circuits through Wigner-Ville Transient-Based Analysis. In Proceedings of the 2009 35th Annual Conference of IEEE Industrial Electronics, Porto, Portugal, 3–5 November 2009; pp. 1097–1102. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Liang, S.; Li, W.; Liang, H.; Wang, C. Faults and Diagnosis Methods of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors: A Review. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faiz, J.; Mazaheri-Tehrani, E. Demagnetization Modeling and Fault Diagnosing Techniques in Permanent Magnet Machines under Stationary and Nonstationary Conditions: An Overview. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2016, 53, 2772–2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Prieto, M.D.; Romeral, L.; Chen, Z.; Blaabjerg, F.; Liu, X. Detection of Partial Demagnetization Fault in PMSMs Operating under Nonstationary Conditions. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2016, 52, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-K.; Hur, J. Detection of Inter-Turn and Dynamic Eccentricity Faults Using Stator Current Frequency Pattern in IPM-Type BLDC Motors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 63, 1771–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urresty, J.-C.; Riba, J.-R.; Saavedra, H.; Romeral, L. Detection of Inter-Turns Short Circuits in Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors Operating under Transient Conditions by Means of the Zero Sequence Voltage. In Proceedings of the 2011 14th European Conference on Power Electronics and Applications, Birmingham, UK, 30 August–1 September 2011; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Ogidi, O.O.; Barendse, P.S.; Khan, M.A. The Detection of Interturn Short Circuit Faults in Axial-Flux Permanent Magnet Machine with Concentrated Windings. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE), Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–24 September 2015; pp. 1810–1817. [Google Scholar]
- Mirchevska, B.; Pek, C.; Werling, M.; Althoff, M.; Boedecker, J. High-Level Decision Making for Safe and Reasonable Autonomous Lane Changing Using Reinforcement Learning. In Proceedings of the 2018 21st International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC), Maui, HI, USA, 4–7 November 2018; pp. 2156–2162. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S.; Bi, Z.; Sun, Z.; Aggarwal, A.; Huang, X.; Wu, L.; Niu, F. Detection of Stator Winding Faults in PMSMs Based on Second Harmonics of Phase Instantaneous Reactive Powers. Energies 2022, 15, 3248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, F.; Wang, Z.; Yang, J. Analysis of Stator Winding Inter-Turn Short Circuit Fault of PMSM for Electric Vehicle Based on Finite Element Simulation. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Conference and Expo Transportation Electrification Asia-Pacific (ITEC Asia-Pacific), Beijing, China, 31 August–3 September 2014; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.-H.; Gu, B.-G.; Jung, I.-S. Online Fault-Detecting Scheme of an Inverter-Fed Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor under Stator Winding Shorted Turn and Inverter Switch Open. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2011, 5, 529–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Hu, Y.; Zhu, Z.Q. Current harmonics and unbalance suppression of dual three-phase PMSM based on adaptive linear neuron controller. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2023, 38, 2353–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liang, Y. A Comparative Study on Inter-Tern Short Circuit Fault of PMSM Using Finite Element Analysis and Experiment. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Advanced Mechatronic Systems (ICAMechS), Beijing, China, 22–24 August 2015; pp. 290–294. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, Z.; Liang, Y. Evaluating the Stator Winding Inter-Tern Short Circuit Fault of Permanent Magnet Motor Using FEA Combined with Experiment. In Proceedings of the 2014 17th International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS), Hangzhou, China, 22–25 October 2014; pp. 1034–1038. [Google Scholar]
- Nejad, M.S.; Taghipour, M. Inter-Turn Stator Winding Fault Diagnosis and Determination of Fault Percent in PMSM. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE Applied Power Electronics Colloquium (IAPEC), Johor Bahru, Malaysia, 18–19 April 2011; pp. 128–131. [Google Scholar]
- Alam, M.; Shah, V.; Payami, S. Online Fault Diagnosis of Static and Dynamic Eccentricity in Switched Reluctance Motors Using Parks Vector Algorithm. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Power Electronics, Machines and Drives (PEMD 2020), Online, 15–17 December 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Fonseca, D.; Cardoso, A.J.M. On-Line Inter-Turn Short-Circuit Fault Diagnosis in Switched Reluctance Motors. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Electric Machines & Drives Conference (IEMDC), San Diego, CA, USA, 12–15 May 2019; pp. 198–202. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.-H. Simple Online Fault Detecting Scheme for Short-Circuited Turn in a PMSM through Current Harmonic Monitoring. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2010, 58, 2565–2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.; Moon, S.; Kim, S.W. An Early Stage Interturn Fault Diagnosis of PMSMs by Using Negative-Sequence Components. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 5701–5708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, R.Z.; Lopez, C.A.; Foster, S.N.; Strangas, E.G. A Voltage-Based Approach for Fault Detection and Separation in Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2017, 53, 5305–5314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, B.-G.; Choi, J.-H.; Jung, I.-S. Development and Analysis of Interturn Short Fault Model of PMSMs with Series and Parallel Winding Connections. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2013, 29, 2016–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boileau, T.; Leboeuf, N.; Nahid-Mobarakeh, B.; Meibody-Tabar, F. Synchronous Demodulation of Control Voltages for Stator Interturn Fault Detection in PMSM. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2013, 28, 5647–5654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, T.S.; Bastos, R.R.; Cardoso Filho, B.J. Synchronous-frame modeling and dq current control of an unbalanced nine-phase induction motor due to open phases. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2020, 56, 2097–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şahin, İ.; Keysan, O. Model Predictive Controller Utilized as an Observer for Inter-Turn Short Circuit Detection in Induction Motors. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2020, 36, 1449–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Xiong, J.; Wu, Y.; Cheng, M. An Improved High Frequency Voltage Injection Method for Inter-Turn Short-Circuit Fault Detection in PMSMs. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrification 2022, 9, 3228–3239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zou, J. An Inter-Turn Short-Circuits Fault Detection Strategy Considering Inverter Nonlinearity and Current Measurement Errors for Sensorless Control of SPMSM. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021, 69, 11709–11722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Li, J. Diagnosis of Inter-Turn Short Circuit of Synchronous Generator Rotor Winding Based on Volterra Kernel Identification. Energies 2018, 11, 2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.-T.; Hur, J.; Kang, G.-H. Inter-Turn Fault Analysis of IPM Type BLDC Motor Using Fault Impedance Modeling. In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Power Electronics-ECCE Asia, Jeju, Republic of Korea, 30 May–3 June 2011; pp. 2216–2224. [Google Scholar]
- Goktas, T.; Zafarani, M.; Lee, K.W.; Akin, B.; Sculley, T. Comprehensive Analysis of Magnet Defect Fault Monitoring Through Leakage Flux. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2017, 53, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da, Y.; Shi, X.; Krishnamurthy, M. A New Approach to Fault Diagnostics for Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machines Using Electromagnetic Signature Analysis. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2013, 28, 4104–4112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bisschop, J.; Sergeant, P.; Dupre, L. Demagnetization Fault Detection in Axial Flux PM Machines by Using Sensing Coils and an Analytical Model. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Electromagnetic Field Computation (CEFC), Miami, Fl, USA, 13–16 November 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Miao, W.; Xu, Q.; Cao, L.; Liu, C.; Pong, P.W.T. Inter-Turn Short-Circuit Fault Detection Approach for Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machines Through Stray Magnetic Field Sensing. IEEE Sens. J. 2019, 19, 7884–7895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Gao, B.; Xu, X.; Si, J.; Hu, Y. Automatic Demagnetization Fault Location of Direct-Drive Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Using Knowledge Graph. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2024, 73, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arellano-Padilla, J.; Sumner, M.; Gerada, C. Winding Condition Monitoring Scheme for a Permanent Magnet Machine Using High-Frequency Injection. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2011, 5, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Moon, S.; Jeong, H.; Kim, S.W. Robust Diagnosis Method Based on Parameter Estimation for an Interturn Short-Circuit Fault in Multipole PMSM under High-Speed Operation. Sensors 2015, 15, 29452–29466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Castro, B.A.; Binotto, A.; Ardila-Rey, J.A.; Fraga, J.R.C.P.; Smith, C.; Andreoli, A.L. New Algorithm Applied to Transformers’ Failures Detection Based on Karhunen-Loève Transform. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2023, 19, 10883–10891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; Zhang, B.; Li, C.; Lin, J.; Zhang, D. Feature mode decomposition: New decomposition theory for rotating machinery fault diagnosis. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2022, 70, 1949–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berzoy, A.; Eldeeb, H.H.; Mohammed, O.A. On-Line Detection of Stator Faults in DTC-Driven IM Using SC Impedance Matrix off-Diagonal Term. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2019, 55, 5906–5915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, D.; Song, D. Model-Based Robust Fault Diagnosis of Incipient ITSC for PMSM in Elevator Traction System. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2023, 72, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hmida, M.A.; Braham, A. Fault Detection of VFD-Fed Induction Motor under Transient Conditions Using Harmonic Wavelet Transform. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2020, 69, 8207–8215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyftakis, K.N. A Comparative Investigation of Interturn Faults in Induction Motors Suggesting a Novel Transient Diagnostic Method Based on the Goerges Phenomenon. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2021, 58, 304–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, B.; Liu, Y.; Xie, M. A Dynamic-Bayesian-Network-Based Fault Diagnosis Methodology Considering Transient and Intermittent Faults. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2016, 14, 276–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burriel-Valencia, J.; Puche-Panadero, R.; Martinez-Roman, J.; Sapena-Bano, A.; Pineda-Sanchez, M. Short-Frequency Fourier Transform for Fault Diagnosis of Induction Machines Working in Transient Regime. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2017, 66, 432–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Wang, K.; Chen, L. Broken Rotor Bars Detection in Inverter-Fed Induction Motors under Continuous Switching of Different Speed Modes. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2023, 71, 975–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Yan, L.; Zhao, D. Instantaneous Frequency Estimation-Based Order Tracking for Bearing Fault Diagnosis Under Strong Noise. IEEE Sens. J. 2023, 23, 30940–30949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, V.T.; Yang, B.-S.; Oh, M.-S.; Tan, A.C.C. Fault Diagnosis of Induction Motor Based on Decision Trees and Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference. Expert Syst. Appl. 2009, 36, 1840–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Xiao, D. Sensor Location Strategy in Large-Scale Systems for Fault Detection Applications. J. Comput. 2008, 3, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kafeel, A.; Aziz, S.; Awais, M.; Khan, M.A.; Afaq, K.; Idris, S.A.; Alshazly, H.; Mostafa, S.M. An Expert System for Rotating Machine Fault Detection Using Vibration Signal Analysis. Sensors 2021, 21, 7587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poręba, J.; Baranowski, J. Functional Logistic Regression for Motor Fault Classification Using Acoustic Data in Frequency Domain. Energies 2022, 15, 5535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bensaoucha, S.; Brik, Y.; Moreau, S.; Bessedik, S.A.; Ameur, A. Induction Machine Stator Short-Circuit Fault Detection Using Support Vector Machine. COMPEL -Int. J. Comput. Math. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2021, 40, 373–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiroz, J.C.; Mariun, N.; Mehrjou, M.R.; Izadi, M.; Misron, N.; Radzi, M.A.M. Fault Detection of Broken Rotor Bar in LS-PMSM Using Random Forests. Measurement 2018, 116, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanta, S.; Bera, J.; Sarkar, G. KNN Based Fault Diagnosis System for Induction Motor. In Proceedings of the 2016 2nd International Conference on Control, Instrumentation, Energy & Communication (CIEC), Kolkata, India, 28–30 January 2016; pp. 304–308. [Google Scholar]
- Saini, M.K.; Aggarwal, A. Detection and Diagnosis of Induction Motor Bearing Faults Using Multiwavelet Transform and Naive Bayes Classifier. Int. Trans. Electr. Energy Syst. 2018, 28, e2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Wang, J.; Lu, S.; Zhou, M.; Peng, X. A Review of Real-Time Fault Diagnosis Methods for Industrial Smart Manufacturing. Processes 2023, 11, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, K.; Lu, J.; Zhu, Q.; Wang, X.; De Silva, C.W.; Xia, M.; Lu, S. Edge Solution for Real-Time Motor Fault Diagnosis Based on Efficient Convolutional Neural Network. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2023, 72, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, O.D.; Martinez-Soltero, G.; Alvarez, J.G.; Alanis, A.Y. Real-Time Neural Classifiers for Sensor Faults in Three Phase Induction Motors. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 19657–19668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, H.; Jia, P.; Wang, X.; Wang, L. Real-Time Fault Diagnosis for Hydraulic System Based on Multi-Sensor Convolutional Neural Network. Sensors 2024, 24, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eren, L.; Ince, T.; Kiranyaz, S. A Generic Intelligent Bearing Fault Diagnosis System Using Compact Adaptive 1D CNN Classifier. J. Signal Process. Syst. 2019, 91, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, F.; Zhang, W.; Xue, F.; Li, D.; Xie, S.; Fleischer, J. A Novel Intelligent Fault Diagnosis Method of Rolling Bearing Based on Two-Stream Feature Fusion Convolutional Neural Network. Measurement 2021, 176, 109226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, V.; Hinton, G.E. Rectified Linear Units Improve Restricted Boltzmann Machines. In Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML-10), Haifa, Israel, 21–24 June 2010; pp. 807–814. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, T.; Alekhya, P.; Seshadrinath, J. Incipient Inter-Turn Fault Diagnosis in Induction Motors Using CNN and LSTM Based Methods. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Industry Applications Society Annual Meeting (IAS), Portland, OR, USA, 23–27 September 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Maraaba, L.S.; Milhem, A.S.; Nemer, I.A.; Al-Duwaish, H.; Abido, M.A. Convolutional Neural Network-Based Inter-Turn Fault Diagnosis in LSPMSMs. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 81960–81970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skowron, M.; Orlowska-Kowalska, T.; Wolkiewicz, M.; Kowalski, C.T. Convolutional Neural Network-Based Stator Current Data-Driven Incipient Stator Fault Diagnosis of Inverter-Fed Induction Motor. Energies 2020, 13, 1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piedad, E.J.; Chen, Y.-T.; Chang, H.-C.; Kuo, C.-C. Frequency Occurrence Plot-Based Convolutional Neural Network for Motor Fault Diagnosis. Electronics 2020, 9, 1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsueh, Y.-M.; Ittangihal, V.R.; Wu, W.-B.; Chang, H.-C.; Kuo, C.-C. Fault Diagnosis System for Induction Motors by CNN Using Empirical Wavelet Transform. Symmetry 2019, 11, 1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, B.; Gao, D. Bearing Fault Diagnosis Base on Multi-Scale CNN and LSTM Model. J. Intell. Manuf. 2021, 32, 971–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, D.; Wang, H.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, W.; Zuo, M.J.; Chen, J. Multibranch and Multiscale CNN for Fault Diagnosis of Wheelset Bearings under Strong Noise and Variable Load Condition. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2020, 16, 4949–4960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, W.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, M.; Wang, R.; Guan, C.; Wang, Q. A Novel Deep Learning Method for Intelligent Fault Diagnosis of Rotating Machinery Based on Improved CNN-SVM and Multichannel Data Fusion. Sensors 2019, 19, 1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Meng, G.; Yang, B.; Sun, C.; Chen, X. Dislocated Time Series Convolutional Neural Architecture: An Intelligent Fault Diagnosis Approach for Electric Machine. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2017, 13, 1310–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husari, F.; Seshadrinath, J. Incipient Interturn Fault Detection and Severity Evaluation in Electric Drive System Using Hybrid HCNN-SVM Based Model. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2022, 18, 1823–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Jeong, H.; Koo, G.; Ban, J.; Kim, S.W. Attention Recurrent Neural Network-Based Severity Estimation Method for Interturn Short-Circuit Fault in Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 68, 3445–3453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Ma, X. A Hybrid LSTM-KLD Approach to Condition Monitoring of Operational Wind Turbines. Renew. Energy 2022, 181, 554–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alipoor, G.; Mirbagheri, S.J.; Moosavi, S.M.M.; Cruz, S.M. Incipient Detection of Stator Inter-Turn Short-Circuit Faults in a Doubly-Fed Induction Generator Using Deep Learning. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2023, 17, 256–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husari, F.; Seshadrinath, J. Sensitive Inter-Tum Fault Identifcation in Induction Motors Using Deep Learning Based Methods. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Power Electronics, Smart Grid and Renewable Energy (PESGRE2020), Cochin, India, 2–4 January 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Husari, F.; Seshadrinath, J. Early Stator Fault Detection and Condition Identification in Induction Motor Using Novel Deep Network. IEEE Trans. Artif. Intell. 2021, 3, 809–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, K.K.; Joshi, S.; Kumar, R. A LSTM-Based Neural Strategy for Diagnosis of Stator Inter-Turn Faults with Low Severity Level for Induction Motors. In Proceedings of the 2022 25th International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS), Chiang Mai, Thailand, 29 November–2 December 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Husari, F.; Seshadrinath, J. Stator Turn Fault Diagnosis and Severity Assessment in Converter Fed Induction Motor Using Flat Diagnosis Structure Based on Deep Learning Approach. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2022, 11, 5649–5657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Qiu, J.; Shi, C. Fault Detection of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Based on Deep Learning Method. In Proceedings of the 2018 21st International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS), Jeju, Republic of Korea, 7–10 October 2018; pp. 699–703. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J. Diagnosis of Inter-Turn Short Circuit of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Based on Deep Learning and Small Fault Samples. Neurocomputing 2021, 442, 348–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, L.; Hu, J.; Zhao, G.; Chen, K.; Wang, S.X.; He, J. Method of Inter-Turn Fault Detection for next-Generation Smart Transformers Based on Deep Learning Algorithm. High Volt. 2019, 4, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, J.; Wang, S.; Li, S.; Tang, D. Application of Deep Learning in Interturn Short Circuit Fault Diagnosis of PMSM. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics and Automation (ICMA), Tianjin, China, 4–7 August 2019; pp. 993–997. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).