Abstract
Logistics is becoming more cost competitive while customers and regulatory bodies pressure businesses to disclose their carbon footprints, creating interest in alternative fuels as a decarbonization strategy. This paper provides a thematic review of the role of alternative fuels in sustainable air, land, and sea logistics, their challenges, and potential mitigations. Through an extensive literature survey, we determined that biofuels, synthetic kerosene, natural gas, ammonia, alcohols, hydrogen, and electricity are the primary alternative fuels of interest in terms of environmental sustainability and techno-economic feasibility. In air logistics, synthetic kerosene from hydrogenated esters and fatty acids is the most promising route due to its high technical maturity, although it is limited by biomass sourcing. Electrical vehicles are favorable in road logistics due to cheaper green power and efficient vehicle designs, although they are constrained by recharging infrastructure deployment. In sea logistics, liquified natural gas is advantageous owing to its supply chain maturity, but it is limited by methane slip control and storage requirements. Overall, our examination indicates that alternative fuels will play a pivotal role in the logistics networks of the future.
1. Introduction
The increasing consumption of oil and gas, core fossil fuel energy sources, is taking its toll on the environment. The US Energy Information Administration estimates that fossil fuels still account for 80% of the global energy mix, with more than a third being petroleum-based [1]. The demand for fossil fuels remains strong, although sustainable sources, such as wind and solar, are gradually gaining traction [2,3,4].
Due to humanity’s over-reliance on these hydrocarbons, atmospheric CO2 emissions are increasing, leading to steadily increasing temperatures globally due to the greenhouse gas (GHG) effect [5]. The classification of such greenhouse gases is based on their “global warming potential”, which is based on normalizing their heat-capturing potential relative to a CO2 molecule [6]. Of these GHGs, CO2 is by far the largest contributor, with estimates ranging from 75 to 85% [7,8,9].
The global warming effect is compounded due to the rapid growth in the global population creating unsustainable demands on limited fossil fuel resources, and the effect of the global warming is being experienced more often with the passage of time [10].
Aside from global warming, atmospheric pollution can take the form of acid rain, caused primarily by SO2 and NOx, which has a devastating impact on both land and marine ecosystems [8]. Acid rain is largely attributed to the sulphur-rich bunker fuels traditionally used in sea-borne shipping, concentrating pollution particularly around ports, which has called for stringent regulations on SOx emissions from these fuels [8]. Another effect is smog, a phenomenon which combines smoke and fog, caused by NO2, which leads to breathing problems. Both acid rain and smog can extend over wide geographical areas, and they are not limited to the location of the polluting source, although their localized effects could also be problematic. For instance, localized NOx emissions are known to impact the lungs and evolve into emphysema if exposure is extended. Localized exposure to hydrocarbons, such as benzene (a carcinogen), could lead to cancer. NOx and volatile organic compounds (e.g., from unfiltered car exhausts) can react under sunlight to form ozone, which causes breathing issues, especially for the young and elderly. Engine exhausts also emit solid particulate matter which are thought to be carcinogens and are estimated to account for 12,000–24,000 premature deaths in the UK alone through respiratory and cardiovascular complications. Localized exposure to SO2 can lead to mild eye and throat irritation, although longer exposure levels could lead to respiratory problems, especially for those with pre-existing medical conditions. Potentially, the most serious is CO exposure, which can lead to cognitive impairment and ultimately death based on the exposure concentration and duration. Because of the detrimental impacts of exposure to such pollutants, the unprecedented rate of global warming, and the dwindling supplies of fossil fuel reserves, the pressure to pursue sustainable business practices has never been more justified [11].
Increasingly, customers are reducing their tolerance of unsustainable operating practices, and this has led to companies being exposed on a global scale as their unsustainable supply chain operations are brought to light, leaving their reputations destroyed [12]. Aside from customer pressure, regulations, non-governmental organizations, and activist action are forcing companies to act urgently in adopting more sustainable practices [13].
The purpose of this thematic literature review is to investigate the state of sustainable logistics with a particular focus on the role of alternative fuels. Following the introduction in Section 1, Section 2 presents the research methodology, followed by Section 3 and Section 4 which provide an overview of freight logistics and the link between the freight industry and environmental sustainability, respectively. Section 5 explores the importance of sustainable logistics and the various means to achieve greener logistics operations. Next, the use of alternative fuels in sustainable logistics is introduced in Section 6, with a brief overview, followed by a more detailed commentary on the prevalent alternative fuels classified under each mode of logistics in Section 7, Section 8 and Section 9. Section 10 covers challenges towards adoption of alternative fuels and potential mitigations addressed in the literature, and the final outcomes are restated in Section 11.
2. Methodology of the Study
This research begins by emphasizing the importance of sustainability in the logistics sector and examining the methods the industry employs to meet their sustainability targets. The primary focus is on the role of alternative fuels, exploring their characteristics and applications within freight logistics. Additionally, the research addresses the challenges hindering broader adoption of alternative fuels, aiming to highlight the complexity of those challenges. These challenges are categorized using the TECOP framework. Furthermore, the research explores potential solutions to these challenges, providing a basis for targeted research, manufacturing, and regulatory efforts to overcome them.
The scope of this study included papers from the past 20 years to ensure a relatively recent body of knowledge. The primary means of search included Google Scholar, with secondary sources obtained from Elicit. Additional exclusion criteria were applied, such as omitting sources focusing on the chemistry of specific fuel synthesis methods, as these are not aligned with the macro-level focus of the research. Sources, or sections of sources, covering rail transportation were excluded due to its lesser prominence compared to other transportation modes in global logistics, particularly in terms of freight value and usage frequency, as confirmed by the majority of the literature reviewed. Additionally, sources discussing cutting-edge alternative fuel production pathways were excluded, such as:
- Technologies still in the prototype stage with limited demonstration, such as the hydroprocessing of fermented sugars to produce synthesized iso-paraffins (HFS-SIP) and aqueous phase reforming (APR) with lignocellulosic sugars. These technologies require further de-risking and demonstration of scalability.
- Fuels or production pathways rarely mentioned in the identified literature, where most sources conclude that these fuels or pathways have not yet achieved significant commercial adoption.
Using the TECOP framework to categorize the challenges, it is important to establish a basis for allocation. A distinction is made between “technical” and “technological” challenges, where the former relates more directly to fuel characteristics, whereas the latter refers to the fuel production methods or the technologies used for fuel utilization, transportation, and storage infrastructure. Similarly, a distinction is made between “political” and “regulatory” challenges, where the former involves the interplay between stakeholders at multiple levels, whereas the latter pertains to governing authorities that provide testing and certification standards. When challenges could fall under multiple categories, we made independent judgements based on their closest association. For example, if a fuel degrades naturally over time, it is considered as an operational challenge due to its impacts on the maximum journey length and drivetrain performance (efficiency, emissions, corrosion, etc.), though it could also be categorized as a technical challenge in terms of improving fuel sustainability.
This literature review aims to identify the most credible alternative fuels across the three transportation modes, considering current adoption, future scale-up potential, existing barriers, and the complexity (in TECOP terms) of overcoming those barriers.
3. Logistics and the Role of Freight
Logistics is a broad term which generally encompasses the operational activities which transport, store, and handle raw materials from their source and through the value chain to their final point of consumption [8]. Its components center around the interactions with the supply chain, including forecasting, facility siting, and distribution chains on the supplier side, and customer service and returns handling on the consumer side, with warehousing in between [12]. The domain of logistics management includes planning, structuring, and controlling the movement of material from its origin to the consumer with efficiency [14]. Of note is the transportation component which is typically the largest contributor, both cost- and emissions-wise, although the latter element was not traditionally considered a significant factor [8]. According to the State of Logistics report by the Council of Supply Chain Management Professionals, transportation accounted for 63% of the total cost of the US logistics market in 2012, with 48% coming from trucking costs alone [15]. The rapid growth of commercial transportation has increased the significance of the sector to become the second largest source of CO2 emissions, having grown by almost 80% since 1990 [9].
The three primary forms of freight are land, air, and sea. Land freight consists of transportation via road or rail with road freight being predominant largely due to the established road infrastructure, ease of access, and flexible utilization [16]. Examples of freight classification in road logistics include truckload (e.g., full truckload vs. less-than-truckload) or vehicle size. The EU classifies light goods vehicles (LGVs) as those weighing less than 3.5 tons, medium goods vehicles (MGVs) weighing up to 15 tons, and heavy goods vehicles (HGVs) over 15 tons [16,17]. Rail freight is less common due to its reliance on fixed infrastructure and slower speeds compared to road transport, although the fixed infrastructure makes it a more reliable means of transport [16]. On the other hand, air freight is the fastest method, especially over long distances, although it is the most polluting form of transport [16]. It is usually reserved for items of high value or situations where shorter lead times justify the high fuel expense [16]. Sea freight, like rail, is slower but cheaper and it is traditionally used for shipping bulk volumes of low-value items [16]. It accounts for the largest volume in international trade. As supply chains become more efficient, companies are constantly seeking services that provide an optimal mix of speed and efficiency, generating short lead times with low variability [18].
Globalization has increased the distances between stages in the supply chain, from manufacturer to end-user, highlighting the importance of transportation in the logistics network [18,19]. The competition to adopt just-in-time inventory management promotes more frequent shipping with smaller batches, driven by changing consumer demands and advancements in freight transport technology [18]. This is particularly significant for high-value products with shorter shelf lives, generating high holding costs and placing emphasis on managing lead times [18]. For example, the US Federal Highway Administration predicts an increase in the value of freight from an average of USD 890 per ton in 2007 to USD 2145 per ton by 2040 [18]. However, these practices contribute to higher emissions, leading to both direct and indirect environmental impacts. Direct, or “first-order”, impacts are attributed to the method of freight transport, warehousing operations, and materials handling. Indirect, or “second-order”, impacts are more difficult to quantify as they include side-effects such as the displacement of endangered species due to freight infrastructure upgrades and maintenance [8]. To mitigate these effects, the focus on sustainable operations is expanding from a micro view of an entity’s carbon footprint to a macro view of the end-to-end supply chain [12].
4. Relationship between Logistics and Sustainability
The Council of Supply Chain Management Professionals estimates that logistics operations can account for up to 75% of an organization’s carbon footprint [12]. Of these logistics operations, transportation is by far the largest source of emissions, which means that an efficient logistics network should be optimized not just for operational costs but also for minimal emissions, through management of the type of freights, load sizes, and route selection [14]. Other issues associated with freight transport include noise pollution and increased number of accidents, although variations exist when comparing the different transportation modes [16].
Road freight is a considerable source of localized noise pollution [8]. Road freight also emits the highest amount of emissions, not due to inherent inefficiencies (as air freight is more polluting) but rather due to the fact that it accounts for the highest share of load size-transport distance (ton-km); 75% of freight in Europe and 70% in the US [12,16]. Road freight is estimated to account for 17 million barrels per day of oil consumption (20% of global capacity), which is expected to rise up to 22 million barrels per day by 2050 if no action is taken [20]. In 2015, road transport accounted for 75% of the energy demand, with 25% of that coming from road freight [21]. A 2015 statistic reported that road freight generates 7% of global emissions [20]. Of these emissions, HGVs account for 65% of sector emissions growth since 2000, coming mainly from the use of diesel [17]. Emissions from road freight are more harmful compared to sea and air logistics, since road freight occurs closer to human populations [17]. Although the popularity of electrified transport primarily stems from private consumers, there is significant potential to decarbonize road freight through alternative fuels and different drive trains [17].
In the context of sea freight, the International Maritime Organization (IMO) estimates that container ships, bulk freight carriers, and oil tankers account for 2.8%, or 1036 megatons of global emissions annually [17]. Emissions performance varies by ship type, fuel, and fuel efficiency, however global sea freight is estimated to emit roughly 1.4 megatons of particulate matter, 15% of NOx, and 13% of SOx emissions worldwide [17]. The cost of the fuel alone contributes to 60–80% of a ship’s operating cost [22]. Without intervention, GHG emissions from sea freight could increase by up to 250% by 2050 [17]. To address this, the IMO has introduced various measures, including emissions regulations and guidelines on ship energy efficiency management [23]. Approximately 30% of seaborne trade is solely based on hydrocarbon transport [22]. To meet the Paris Agreement goal of limiting emissions to below 2 °C above pre-industrial levels by 2050, it is predicted that sea freight emissions must be reduced by more than 80% compared to 2010 levels [24]. Despite this, sea freight is relatively carbon efficient, with emissions about one sixth of road freight or one one-hundredth of air freight, owing to the much higher load sizes of seaborne vessels [12].
It is reported that the aviation industry contributes about 2% of global emissions [17,25]. Aviation generates NOx which stimulates ozone creation in the upper atmosphere due to the vapor trails left behind by aircraft [17]. These contrails also promote the formation of cirrus clouds which impacts the earth’s radiation balance [26]. Emissions can also occur closer to the population during take-off and landing. Because of its global impact, it is estimated that aviation accounts for up to 5% of global warming [17]. Another study predicts that aviation claims 2.5% and 3.5% of global CO2 emissions and global warming effects, respectively [27]. It is predicted that air freight could account for as high as 4.7% of global CO2 emissions by 2050 [28].
The overview of land, air, and sea logistics highlights the critical role of sustainability in logistics. Sustainable logistics strategies not only reduce emissions but also lower operational costs and improve overall network efficiency [29]. For example, a study by Elhedhli and Merrick [19] demonstrated that incorporating an emissions penalty impacts the optimal supply chain configuration. Other benefits of sustainable logistics includes improved relationships with both internal and external stakeholders, decreased susceptibility to external risks and pressures, and a more motivated workforce [12]. But since businesses need to remain competitive, a cost-benefit analysis is usually conducted to balance carbon footprint and profits [8]. A 2008 survey of third-party logistics providers showed that the top three reasons for adopting a greener supply chain are ethical obligations, meeting environmentally-conscious customer expectations, and improving company image [30]. Another 2008 survey, exploring reasons for adopting a greener supply chain, found that the top three reasons were to enhance brand perceptions, meet customer expectations, and act as a competitive differentiator [8]. Thus, a green supply chain is deemed to be essential for both cost competitiveness and customer relationships [14].
5. Sustainable Logistics: Methods and Approaches
As indicated previously, the transportation cost is the largest cost component of logistics operations, significantly influencing the economics of manufacturing and distribution, and impacting a country’s economy [18]. The role of freight transport efficiency in providing a competitive edge is gaining prominence, prompting major players, such as the EU and China to invest heavily in transportation infrastructure [18]. However, such capital-intensive investments require high utilization to be cost-effective, which limits rail and sea freight to more industrial areas that typically carry low-value items [16]. In land, air, and sea logistics, fuel is a major part of the operating cost, accounting for approximately 38%, 33%, and 50% of these costs, respectively [17].
To control emissions, regulators have implemented policy changes. In the shipping industry, the International Convention for the Prevention of Pollution from Ships (MARPOL) has introduced regulations to control SOx and NOx emissions from marine operations since 2011 [24]. Recently, MARPOL has introduced a regulation to limit sulfur content in marine fuels to a maximum of 0.5% from 2020 onwards [22]. Their goal is to achieve a 70% reduction in sea freight carbon intensity and 50% in annual emissions by 2050 compared to 2008 levels [31]. Furthermore, the IMO has introduced emission control areas (ECAs) that require vessel operators to adhere to strict emissions limits within the boundaries of these areas [22]. In ECAs, the SOx limit is more stringent, being as low as 0.1% [22]. Hence, the future of logistics will require a careful balance in a globally competitive supply chain that is able to transport freight efficiently while minimizing environmental impact [18].
It is not that fuels are becoming more polluting, but that the greater demand placed on a global logistics system requires longer journeys with more and more goods being exchanged. Sustainable logistics is now being used as a differentiator in responsibly sourcing logistics suppliers by clients [12].
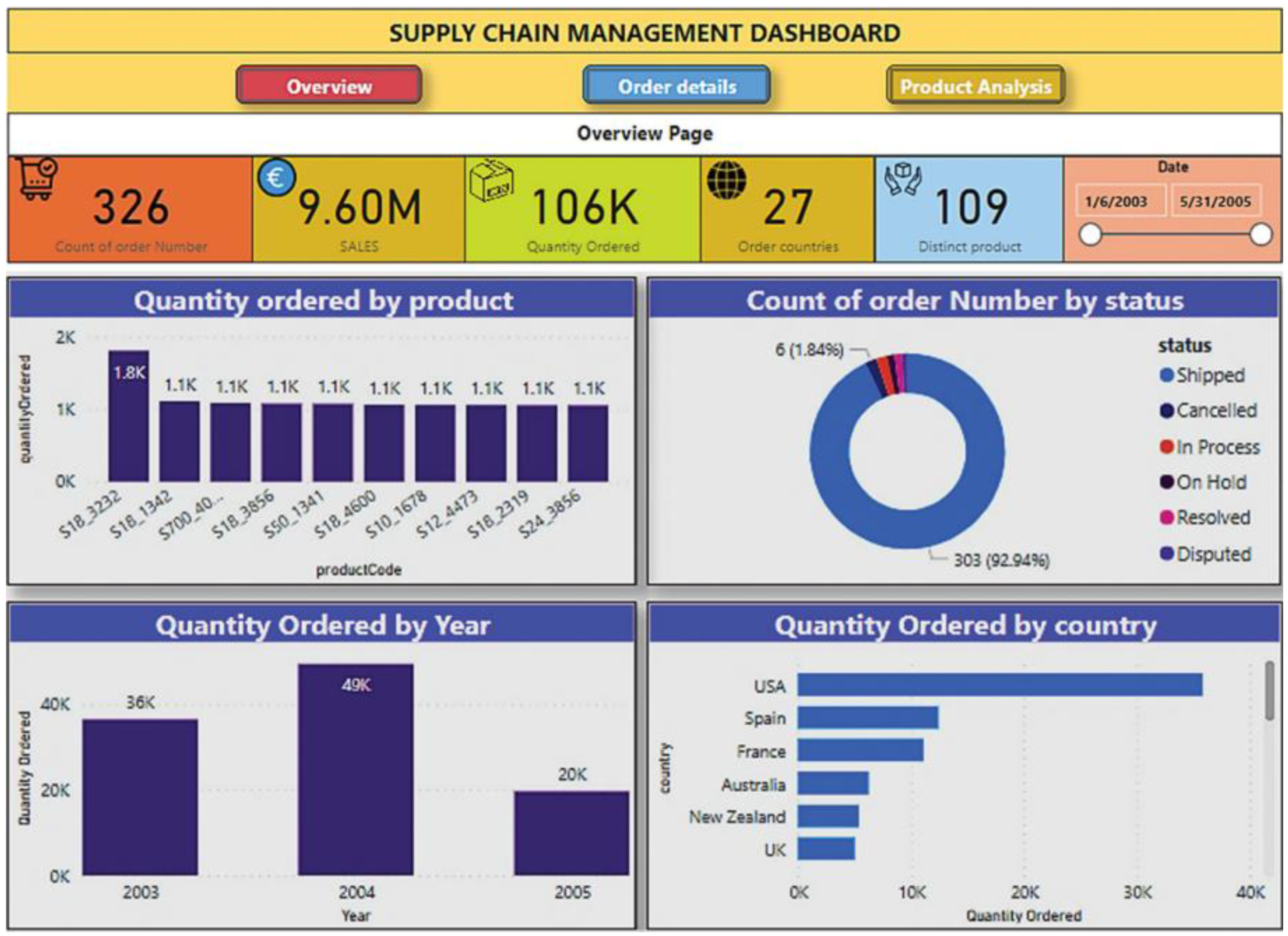
Companies can take multi-faceted approaches to implementing sustainable logistics such as reducing total freight shipping, improving city logistics, managing waste through reverse logistics, designing sustainable freight, practicing sustainable manufacturing, and integrating environmental strategies into operational, tactical, and strategic-level logistics decisions [8,14]. For example, companies are increasingly expected to adopt environmental reporting metrics as part of their corporate social responsibility agendas, particularly in the private sector, to provide transparency for customers and regulators [8]. The advent of Industry 4.0 has led to widespread adoption of business intelligence and data analytics, with tools like the dashboard in Figure 1 illustrating how analytics can be utilized to monitor a logistics supply chain.
Figure 1.
Example of a supply chain management business analytics dashboard. Reproduced under Creative Commons CC BY license from Ref. [32].
Such dashboards can be extended to adopt sustainability metrics. Sustainability reporting metrics include, but are not limited to, the average length of a road haul, average payload on a sea-borne vessel, energy efficiency over the distance travelled, and emissions normalized per unit of energy consumed [8]. The strategies applied by companies can also leverage technology, human resources, and operational processes.
Particularly in the private sector, companies are shifting to more fuel-efficient vehicles that use renewable energy to improve network efficiency. Logistics providers recognize the importance of modernizing their fleets to reduce their carbon footprint. DHL, for example, continuously updates its land and air fleets to be more sustainable [33]. It also extends to design modifications, as in the case of Norbert Dentressangle which adopted curved roofs on their trucks to minimize wind resistance, resulting in fuel savings of up to 8% [33]. The STEF group reduced their fleet emissions by improving aerodynamics with roof spoilers, using more sustainable tires, and installing energy efficient cooling systems [33]. By adopting roof deflectors, roof fairing, chassis skirts, and cab extenders, heavy duty trucks can reduce their fuel consumption by up to 10% [34]. In aviation, aircraft can be designed with reduced weight, more aerodynamic features, and efficient engines. Combined with improvements in air traffic control, such design innovations have led to fuel savings of 70% compared to the latter half of the 20th century [28]. At sea, ships can be designed with more efficient propulsion systems, improved hull designs, and waste heat recovery systems to enhance fuel efficiency [22]. Existing fleets can be retrofitted with exhaust scrubbers to selectively absorb particulate matter, but can be costly and may increase fuel consumption [22,23]. While companies can focus on each mode of freight separately, it is beneficial to consider a multimodal transportation network to utilize the benefits associated with each mode.
Achieving a balance between air, land, and sea, is crucial for optimizing costs and emissions when transporting goods. Many logistics providers report that leveraging multimodal transport improves sustainability performance. For example, DHL utilizes combinations of rail with air and sea with air, optimized through technology solutions [33].
Innovations in Information Technology (IT) and the Internet of Things (IoT) have enabled live monitoring of engine performance, fuel efficiency, optimal routing and re-routing, selective refueling as advised by a global positioning system (GPS), automatic engine cut-off during idling, and digital transactions [18]. Such applications of IT can shorten transportation routes, allow monitoring of driver and vehicle performance, and reduce human error in navigation, thereby decreasing emissions by eliminating unnecessary vehicle idling and routes [18]. Efficient routing technology can create routes with minimal in-between stops, minimal time spent at each stop, and avoiding congested paths that have higher likelihood of causing accidents [16]. This has successfully been applied at UPS, through an initiative called “Package Flow”, which aggregates orders on fewer routes and optimizes delivery sequence, generating savings of more than 100 million miles and more than 100,000 tons of emissions since 2003 [18]. The Federal Aviation Administration implemented their next generation traffic control system which manages air traffic around the US at a higher capacity while improving safety, accessibility, and environmental impacts [18]. An example of reduced idling is Walmart’s use of auxiliary power units in its land fleet, which cuts off engines after three minutes of inactivity, saving USD 23 million in fuel annually [18]. Several carriers have also adopted speed governors which apply a speed limit on their trucks that can increase driving range by up to 25% [18]. This has been applied by Schneider Electric, which applied a speed cap of 60 mph, leading to estimated savings of 3.75 million gallons of fuel and 83 megapounds of CO2 emissions annually [18]. However, these technologies come at a cost premium, requiring companies to perform cost-benefit analyses to determine which to adopt and explore alternative avenues [18].
A focus on packaging can also lead to sustainable logistics operations. Best practices include reducing package sizes and removing unnecessary packaging. Packaging can also be redesigned to be in the form of shapes that allow higher levels of stacking, or to use more sustainable material. For example, the packaging of HP’s LaserJet cartridges have shrunk by 45%, allowing an increase in the amount that can be loaded per pallet from 144 to 203 [18]. In terms of redesign, retailers such as Walmart and Costco have redesigned their milk cartons to resemble a rectangular prism, allowing easier stacking without crates [18]. Packaging also extends to the warehouse, where sustainable practices include energy efficient heating, cooling, and lighting, maximizing natural light, and minimizing waste generation [33]. Natural light also enhances workforce productivity and is relatively inexpensive to incorporate in warehouse design [35]. For example, a warehouse in Cleveland saved over USD 10,000 per year on utility bills by adopting fluorescent lighting, which can reduce lighting costs by 75% compared to incandescent bulbs while lasting longer [12]. Automated lighting systems based on motion detection have also been implemented [33]. Aside from using renewable energy to power a warehouse, using sustainable construction material sourced from a recycling plant has also seen common use amongst logistics service providers [33]. The use of reverse logistics is especially important in recycling and reusing packaging waste [33]. But once the cargoes are loaded, it is not necessary that the same company that sells the product also operates its own logistics fleet.
Companies are now collaborating to share shipping routes as a means of maximizing truck capacities and guaranteeing round trips [18]. This concept of pooling of a transport resource has allowed a company such as Macy’s to find shippers for 70 of its otherwise unutilized routes, leading to higher truck fill rates, fewer wasted miles, and an overall reduction in emissions [18]. Another example is Kraft Foods Inc., Chicago, IL, USA, which joined the SmartWay Transport Partnership in 2008 to consolidate its shipments and reduce the number of stops, yielding a 7% increase in miles per gallon compared to 2003 performance [12]. This concept can be combined with a higher order minimum and wider delivery windows, also benefiting the customer through fewer but larger shipments, hence reducing materials handling costs [18]. Materials handling can be minimized by opting for standardized containers [16]. To avoid empty routes in the first place, companies should consider locating their manufacturing and warehousing closer to their customers and/or suppliers, reducing transportation distances, fuel costs, and subsequently carbon emissions [18]. This approach also reduces risks in the supply chain and enhances responsiveness to changes in demand and supply [16].
On the human resources front, companies are implementing standardized training regimens for land-based logistics to share best practices in driving that can minimize emissions. These include driving at slow and fixed speeds, avoiding hard brakes and left-hand turns, using the GPS, proactively shutting off the engine during stops, and limiting reliance on air conditioning [18,33]. Employees can be incentivized, as in Schneider’s case who provided financial incentives to adhere to their 60 mph driving limits on their trucks [18]. Lower speeds can also be adopted in sea freight, since faster ships are correlated with higher emissions [22]. In the study by Grant et al. [16], a vessel on route from Hong-Kong to Rotterdam was expected to take 21 days at normal speed, increasing to 23 days if operating at lower speeds. Although operating ships at lower speeds can save on emissions, it introduces risks of higher engine vibrations and fouling of engine components, especially if operated below the optimal speed [36]. When considering incentives, they should be aligned amongst all entities in the supply chain to be effective, and hence can include environmental contract clauses, specific environmental key performance indicators (KPIs), or extending in-house training for free both upstream and downstream the supply chain [18]. In terms of downstream influence, companies can offer discounts on orders which maximize truckloads and penalties for expedited shipping [18]. In a study by Jørsfeldt et al. [29] on the sustainability practices of a Danish company outsourcing its logistics services, the company’s monitoring of its scope 3 emissions (indirect emissions from the supply chain via suppliers or customers) showed an increase in sustainable practices over time. Notably, transport emissions dropped while the amounts of goods transported increased. The application of environmental KPIs indicated that a third of the company’s entire emissions originated from transportation, with air freight accounting for 2% of shipping volume but 33% of its entire emissions, highlighting the powerful insights that can be gained from well-defined KPIs [29]. Unfortunately, most logistics KPIs do not consider environmental aspect, focusing instead on fuel consumption and efficient routing. Consequently, companies often need regulatory encouragement to adopt environmentally focused KPIs [18].
Sea freight, being a global operation, is managed by the UN’s IMO, which develops mandates to regulate seafaring emissions, as discussed previously. Additionally, governments are instituting carbon taxes to achieve their environmental goals. An example is the cap-and-trade system in the US, where companies have an emissions cap, face penalties if exceeded, and can sell unutilized portions of their quota to others [18]. In the US, all vehicles legally sold must be certified as meeting the emissions requirements set by the Environmental Protection Agency. In the EU, similar standards were introduced in 2008 which mandate biofuels constituting a minimum of 10% of road transport fuels by 2020 [18].
Fuel is a major cost component in all transport operations, and focusing on fuel savings has driven industry towards considering alternative fuels as widely reported in the extant literature. Alternative fuels have gained traction as innovations by companies seeking to enhance logistical competitiveness and comply with regulations, though they are typically considered as long-term solutions [16,17]. UPS has already deployed alternative fuels in its road freight operations which helped it increase fuel economy by up to 10%, with a 3% reduction in annual CO2 emissions [12]. FedEx operates more than 330 hybrid (diesel–electric) delivery trucks, improving their fuel economy by more than 40% and reducing emissions by 25% [12]. As of fiscal year 2023, FedEx operates more than 9000 vehicles on alternative fuels globally, with the majority (over 70%) running on electricity and almost a quarter (23%) on liquified petroleum gas (LPG), committing to running a carbon neutral fleet by 2040 [37].
6. A Brief Overview of Alternative Fuels
Conventional fuels are predominantly derived from fossil fuels, sourced from oil, coal, or natural gas, such as petrol for cars and kerosene for jet aircraft. Fuels which are not conventionally used in their form of transport, encompassing biodiesel, bioethanol, natural gas, biomethane, and hydrogen [38]. Any fuel sourced from biomass, such as biodiesel and bioethanol, is classified as a biofuel [38]. In the case of road transport, alternative fuels can be further categorized based on their compatibility with existing combustion engines and infrastructure or their requirement for electric drives via fuel cells or batteries [17]. For any fuel, a high energy density—both mass and volume based—is generally desirable to minimize mass and storage space requirements [17]. Although alternative fuels are used across various transport modes, their application in land, sea, and air transport poses varying complexities and unique challenges [17].
Alternative fuels are not inherently more environmentally sustainable compared to conventional fuels. In road transport, it is essential to consider the entire well-to-wheel lifecycle emissions, which include emissions from raw material extraction, conversion, transportation, storage, and combustion [17]. The sustainability of alternative fuels generated through electricity heavily depends on the source of that electricity. For example, producing hydrogen using electricity from a conventional gas power plant is less sustainable than using electricity from wind or solar farms [17]. Similarly, the feedstock source for biofuels production considerably influences its lifecycle emissions [17]. Considering these factors, companies and governments have explored alternative fuels to achieve self-sufficiency and diversify their energy portfolios. For instance, Brazil has become one of the world’s largest producers of bioethanol [25]. Additionally, energy producers have started to develop synthetic versions of conventional fuels, such as biodiesel from vegetable oils [25].
Biofuels are a category of fuels sourced from agricultural products, such as vegetable oils [8]. They can be in liquid form, like bioethanol and biodiesel, or gaseous form, such as biogas and hydrogen [8].
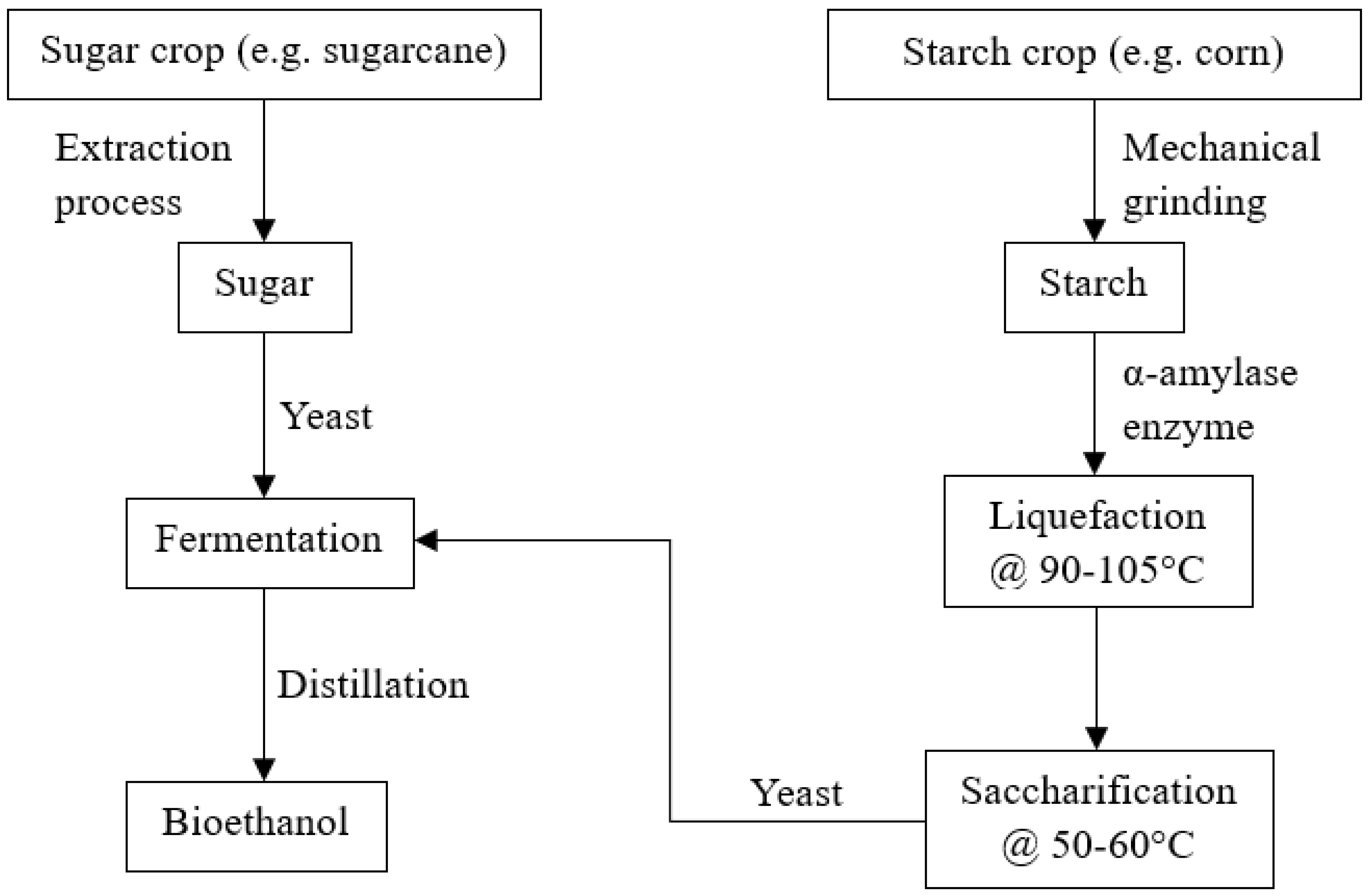
First generation biofuels are those derived from agricultural crops, such as grains, sugarcane, starchy material, vegetable oils, and animal fats [26,39]. For example, bioethanol can be produced through the fermentation of sugarcane or starchy material and biodiesel can be produced through transesterification of vegetable oils [26]. For instance, Figure 2 illustrates an example of the production of bioethanol through sugarcane where sugar can be extracted from sugar crop, followed by yeast fermentation and a final purification stage to produce bioethanol. Starch is extracted through a grinding process from corn, followed by enzymatic liquefaction and saccharification, concluding with yeast fermentation and distillation to separate the bioethanol in an alternative route.
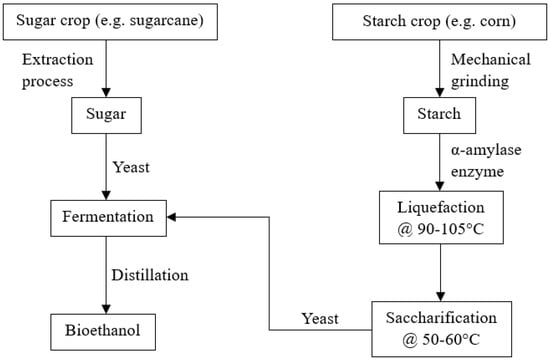
Figure 2.
Production pathway of first-generation bioethanol. Reproduced under Creative Commons CC BY license from Ref. [40].
Another process route, “biomass to liquids”, vaporizes the biomass at high temperatures to produce syngas (CO and H2) which is then used to make biofuels through the Fischer–Tropsch process [17]. Because biofuel production competes with food production as they share the same raw materials, additional generations of biofuels were developed. Second generation biofuels are sourced from forestry residues and agricultural waste (i.e., non-food crops), consisting of lignocellulosic material (i.e., woody biomass) [26,39]. Third-generation biofuels are produced by algae, which can be grown in controlled environments (zero competition for crops) and have a high yield of oils that resemble vegetable oils. These oils can undergo transesterification to produce biodiesel that can be used without any blending in conventional diesel engines [26,39]. Because algae can be grown in a variety of environments, they have the highest potential to be the foundation for large-scale future biofuels production [27]. This is because algal biofuels utilize sunlight, waste water, and atmospheric CO2 in their production process, hence they cancel out emissions produced during the combustion of the biofuel as opposed to fossil fuels which release sequestered CO2 from the earth into the environment [25,28].
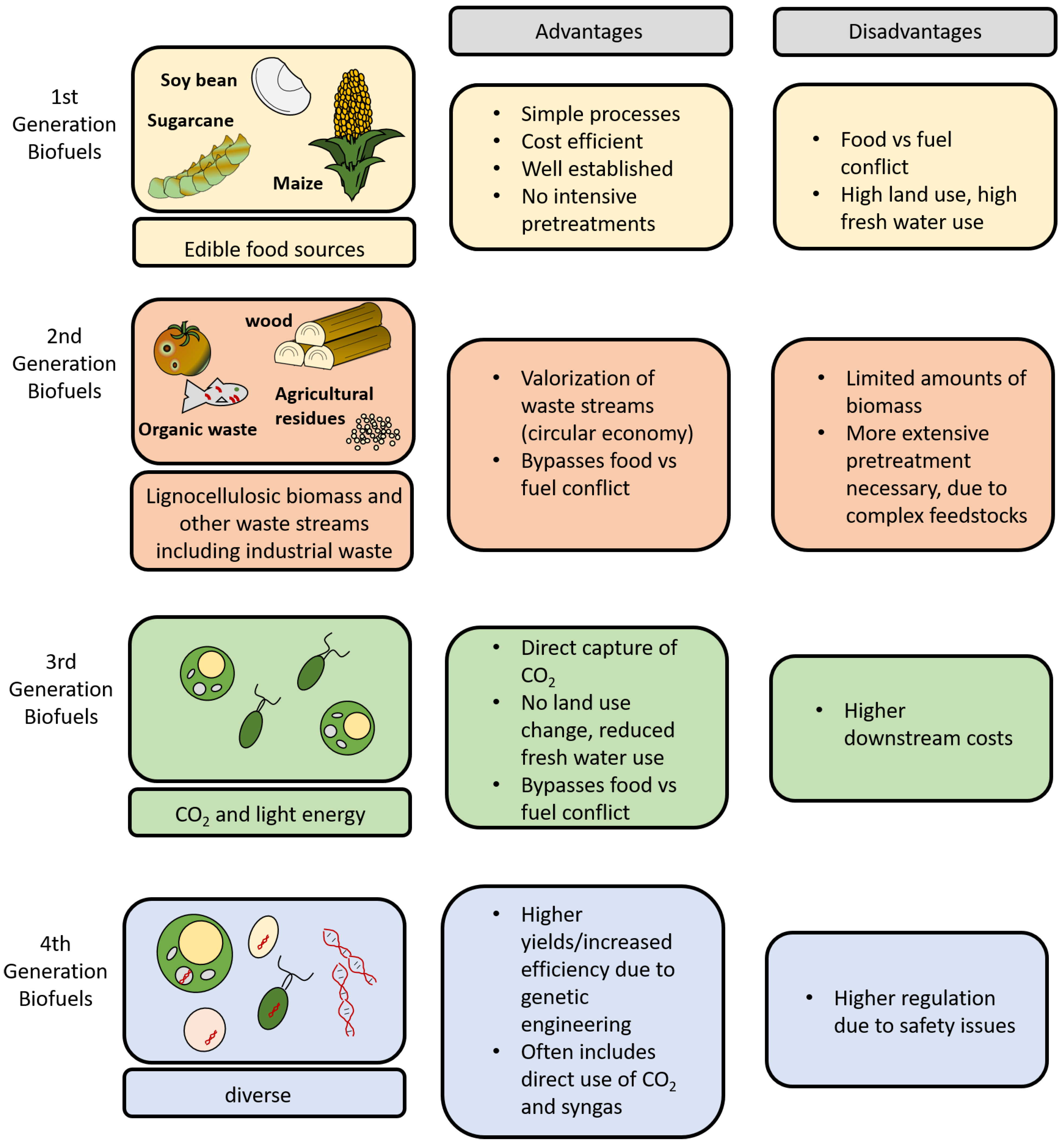
Studies have shown that third-generation biofuels can reduce lifecycle GHG emissions in the aviation sector by up to 76% [28]. Fourth-generation biofuels are based on the genetic engineering of both micro-organisms and their feedstock to push the yield boundaries further [41]. In addition, all generations, except the first, do not compete for food crops and land usage [26,28]. An overview of the biofuel generations, their respective biomass sources, advantages, and disadvantages is illustrated in Figure 3.
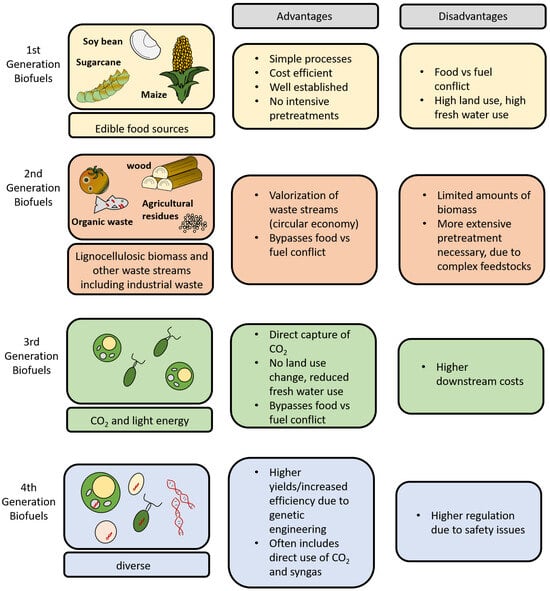
Figure 3.
Overview of biofuels generations, feed sources, advantages, and disadvantages. Reproduced under Creative Commons CC BY license from Ref. [42].
Bioethanol is typically produced from sugar (e.g., sugar beet), starchy material (e.g., corn), grains, and cellulosic waste (e.g., paper pulp) through fermentation [8,43]. Sugar beet and corn made up more than 80% of the global bioethanol market in 2007 [8]. Brazil has been using sugar cane to produce bioethanol since the 1930s and also offers vehicles that run exclusively on it [8]. The US and Brazil combined accounted for 85% of the global bioethanol market in 2016 [10]. Bioethanol can also be blended with conventional petrol to run in cars without retrofitting engines [8].
Similarly, biodiesel can be blended with conventional diesel as an additive [8]. Biodiesel is produced from vegetable oils, animal fats, and waste cooking oils, with the most common feedstocks being soybean, palm, and rapeseed oil [10]. The largest producers of biodiesel are the US, Australia, Malaysia, Indonesia, India, and Brazil [44].
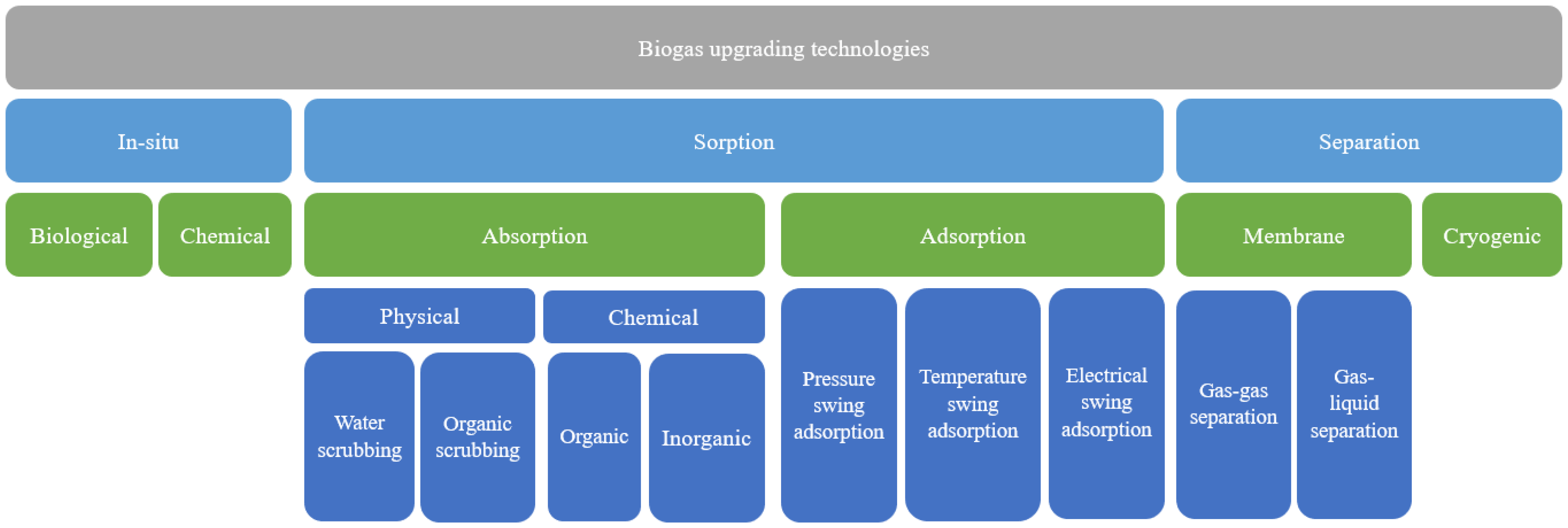
Biogas consists of a mixture of light gases (60–80% methane and 20–40% CO2, with trace H2S and nitrogen) which is produced through the biological digestion of organic waste, manure, and agricultural matter [10]. It can also be produced through anaerobic wastewater treatment of municipal sewage, and from municipal wastes such as sugar beet leaves [10]. Its production does not involve any combustion processes, and is cost effective since it can be produced on small scales [10]. In addition, biogas production is largely rural (due to the dependency on livestock) and hence has positive impacts on economic stimulation [17]. Biogas can further be upgraded to biomethane (consisting of 97% methane) through separation technologies [17]. An overview of the available biogas upgrading technologies is shown in Figure 4.
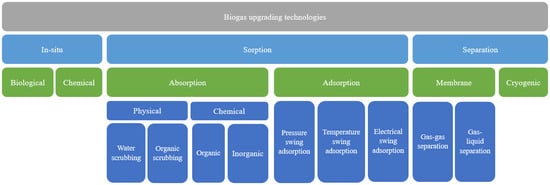
Figure 4.
Hierarchy of biogas upgrading processes. Reproduced under Creative Commons CC BY license from Ref. [45].
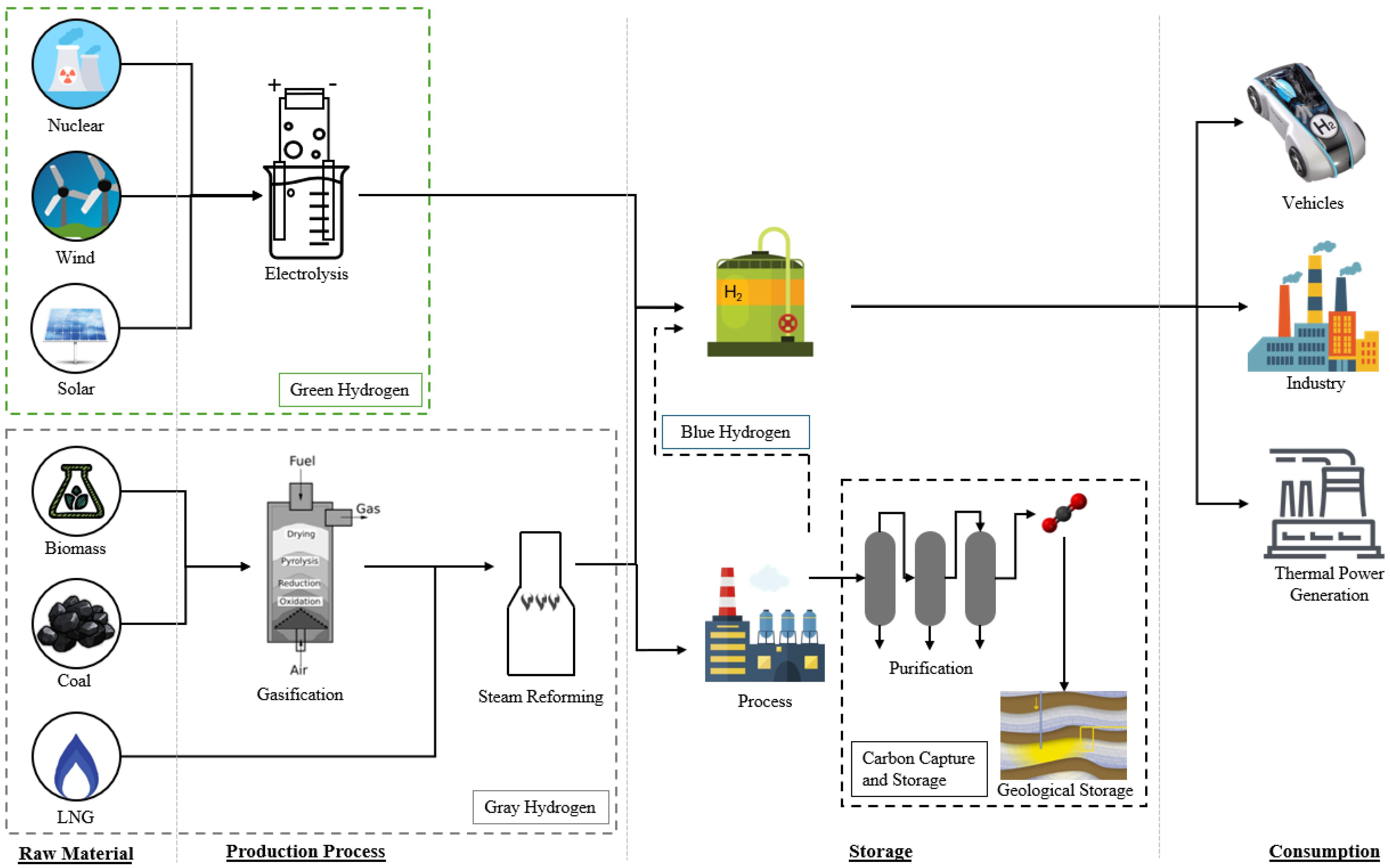
Hydrogen is the lightest of the alternative fuels and can be produced through a range of conversion technologies, including fossil fuels with or without carbon capture, electrolysis (ideally using renewable electricity), or biomass [17]. Hydrogen has essential uses in an industrial context (hydrogenation, hydrodesulphurization, steam and methane reforming, alcohol synthesis), in addition to applications in food processing and fertilizer manufacturing [46]. As a fuel, hydrogen has seen widespread use in rocket propulsion for space exploration [47]. In road transport, hydrogen is typically used in fuel cells, where it is electrochemically reduced into ions, generating water vapor as the only tailpipe emission while generating electricity for the motor [8]. It can be stored as a cryogenic liquid below its −253 °C boiling point (assuming atmospheric pressure) or as a gas under high pressure (700 bar) for use in fuel cells [17]. Hydrogen is also a key component in the production of other alternative fuels, such as methane, ammonia, and Fischer–Tropsch fuels [17]. Hydrogen is categorized by colors based on its production pathway: gray (produced from hydrocarbons), blue (gray with carbon capture), and green (zero emissions using renewable energy) [9,22,46]. A visual representation of the three aforementioned hydrogen production pathways is illustrated in Figure 5.
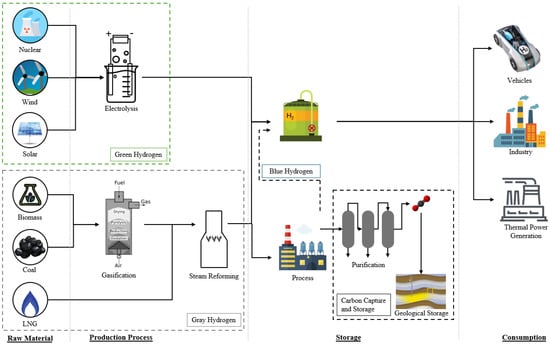
Figure 5.
Gray, blue, and green hydrogen production pathways, from storage to consumption. Adapted under Creative Commons CC BY license from Ref. [22].
Currently, more than 96% of global hydrogen production is gray through steam methane reforming of natural gas or coal gasification, both of which are much cheaper compared to current green hydrogen routes [4,17,22,46]. Most of the hydrogen produced is used in other industries, such as oil refining, rather than using the hydrogen itself as a fuel. For example, green hydrogen is typically combined with CO2 (e.g., from a concentrated point source or from direct air capture) and used to produce low carbon fuels, such as green methane, methanol, diesel, and jet fuel [17]. Green hydrogen can also be used in producing green ammonia, as ammonia is produced through the Haber–Bosch process utilizing nitrogen and hydrogen at high temperature and pressure [31]. Almost half of global hydrogen production is utilized towards ammonia production [47]. Green hydrogen production via water electrolysis is considered a potential solution to managing grid capacity by accepting surplus power to produce green fuels during off-peak hours [17].
The following section explores the use of alternative fuels in air, land, and sea logistics, followed by an overview of their challenges and potential solutions.
7. Alternative Fuels in Air Logistics
In the aviation industry, any new fuel must be a drop-in fuel to have any chance at mass adoption. Drop-in fuels can directly be blended with conventional fossil fuel-based kerosene without requiring hardware modifications to the plane or its surrounding infrastructure [25]. The importance of this is highlighted by the average expected life of commercial aircraft being 25–30 years, where a fleet overhaul would require upwards of a trillion dollars (assuming a replacement cost of USD 50 million per aircraft) [25]. The percentage of an alternative fuel, which could be blended with a conventional jet fuel, ranges up to 50% [26], as dictated by the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM, West Conshohocken, PA, USA).
Conventional jet fuel largely consists of kerosene, a hydrocarbon blend of linear, iso, and cyclic paraffins and aromatics. Such kerosene-based fuels are regulated through ASTM’s D1655 “Standard Specification for Aviation Turbine Fuels” [27]. The ASTM standard requires a jet fuel to meet several properties to be approved for use. This includes a high energy density (for fuel economy), high flash point (for safe handling), low freeze point (to remain liquid at cruising altitude), high thermal stability (to avoid thermal degradation during combustion), and a minimum aromatics content to provide a strong seal against fuel leakage [25]. The certification process considers chemical, physical, and combustion properties, in addition to safety aspects of handling, storage, and transportation [26]. Conventional kerosene meets the aforementioned required properties, but its specific composition is not fixed. For example, Jet A, which is used almost exclusively in North America, has a higher freeze point specification compared to Jet A-1, which is used in most other parts of the world and has a lower freeze point [17,27]. Jet B, a third variant, is used in colder climates, such as in the Nordic countries, due to its even lower freeze point [17]. In addition to fossil fuels, jet fuel specifications can also be met with sustainable aviation fuel (SAF) blends.
More than 280 million tons of aviation fuel is consumed annually, although less than 0.1% is considered to be from alternative fuels [48]. However, use of alternative fuels is slowly taking off in this sector. The first SAFs were approved for use in commercial aircraft in 2008, and by 2019, over 250 million flights on SAF had been conducted across 45 commercial airlines [27]. On a commercial scale, United Airlines conducted the world’s first flight using 100% SAF in 2021 [27]. There are several examples of multinational corporations showing interest in SAF production as well. For example, Fulcrum UK is aiming to commission its waste processing plant by 2028 in Chesire, aiming to produce 100 million liters of SAF annually based on the gasification of 600,000 tons of municipal waste per year through the Fischer Tropsch process [49]. According to the International Energy Agency’s prediction for a 2 °C temperature increase scenario, the world will require more than 150 million tons of SAF annually by 2060, despite the introduction of efficient aircraft and alternative transport modes [48].
Due to the rise in SAF usage, the ASTM developed the D7566 “Standard Specification for Aviation Turbine Fuel Containing Synthesized Hydrocarbons” to asses alternative fuel blends for Jet A/A-1 compliance [17]. So far, several alternative fuels have met ASTM approval for use as blending components, including synthetic paraffinic kerosene (SPK) from the hydro-processing of esters and fatty acids (HEFA–SPK), synthetic kerosene from Fischer–Tropsch Synthesis (FT–SPK), and synthetic kerosene from ethanol and isobutanol oligomerization (ATJ–SPK) [17]. The regulatory acceptance of alternative fuels has sparked innovations both in SAF scale-up and in alternatives to drop-in fuels, such as hydrogen and electricity.
For example, ENABLEH2 is a project focusing on exploring the feasibility of liquid hydrogen in civil aviation, from the perspectives of safety, infrastructure, economics, and public acceptance [17]. REWOFUEL is attempting to demonstrate a production pathway for SAF from wood waste in terms of fuel performance, reliability, and sustainability [50]. Bio4A is aiming to bring SAF production from lipids to a larger scale [51]. However, each fuel presents a different set of challenges and opportunities, making it important to quantify their current technological readiness for policymakers.
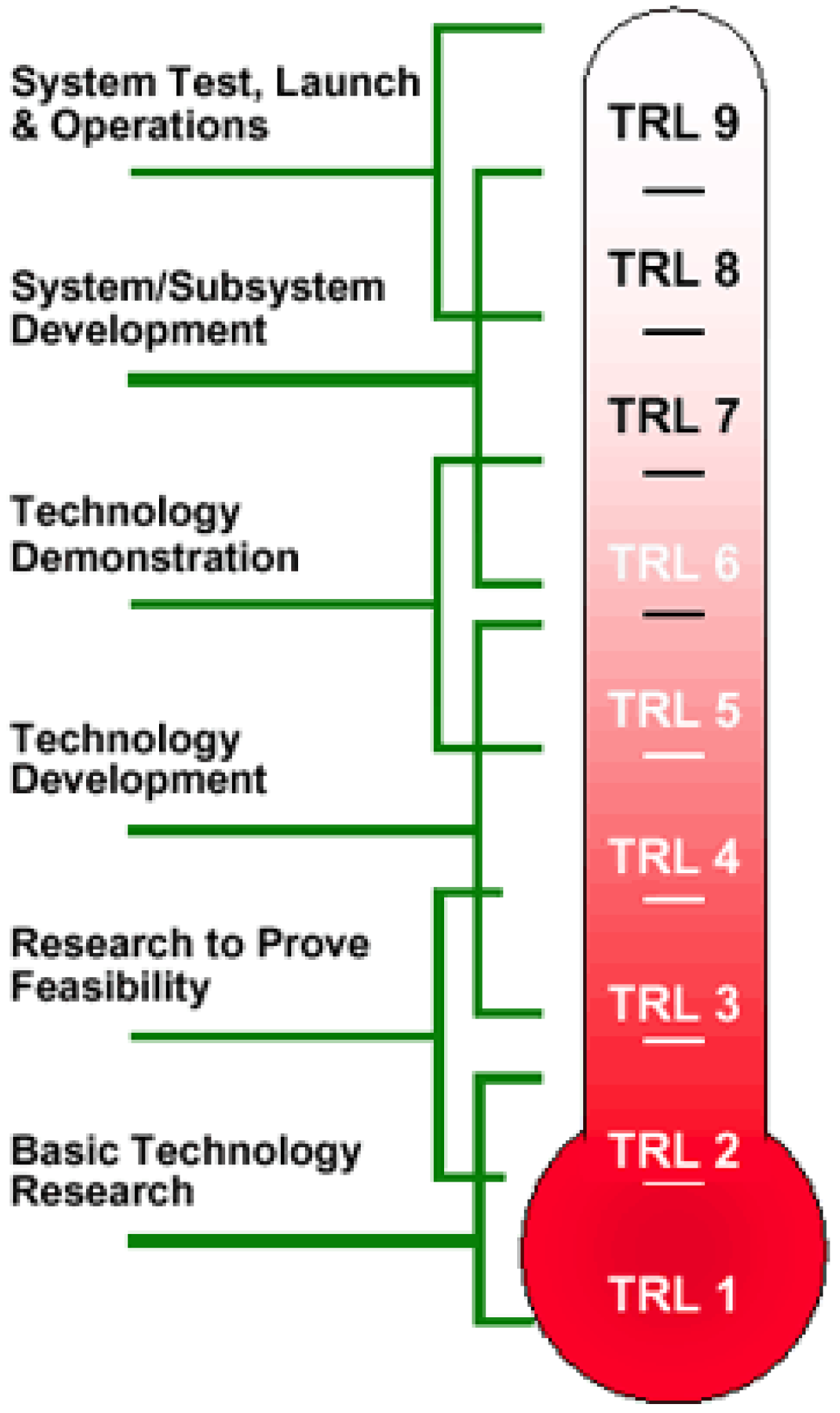
In 1974, a NASA scientist developed the technology readiness level (TRL) scale as a means of quantifying the relative maturity levels of different technologies under a common application or operational environment [52,53], which in the context of our study focuses on drop-in fuels. The modern version (Figure 6) is a nine-point scale, with 1 indicating that basic principles of a phenomenon are observed (fundamentals being established) whereas 9 indicates a technology has reached full-scale implementation in its final form [53].
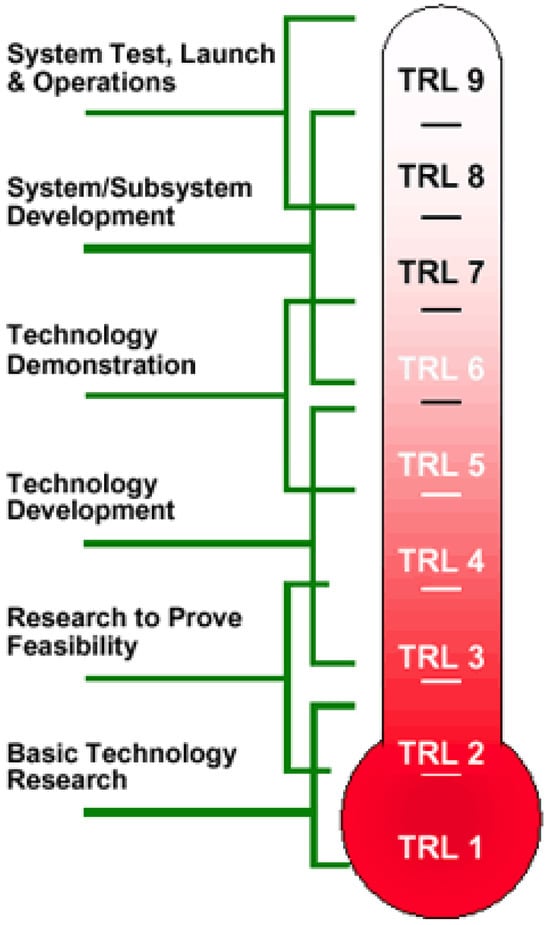
Figure 6.
Simplified representation of the TRL scale. Reproduced under Creative Commons CC BY license from Ref. [54].
Based on the study by Bauen et al. [48], different drop-in jet fuels can be assigned a TRL considering their current state of deployment. As of 2020, the highest TRL is allocated to HEFA–SPK (TRL 8), with the largest producer being Neste’s HEFA to SAF plant in Singapore, which recently doubled its capacity to 2.6 million tons of SAF [48,55].
7.1. Biofuels-Based Aviation Fuel
Collaborations across the industry in the EU have launched the Biofuels Flightpath Initiative to incorporate more than 2 million tons of biofuels annually into aviation fuel consumption from 2020 onwards [26]. Biofuels are already being used by several major airlines, including United Airlines [56], Lufthansa [57], and KLM [58]. More than 2000 commercial flights on biofuel blends have been completed since 2011 [28]. In 2015, Red Rock Biofuels announced an agreement to supply FedEx with around 3 million gallons of biokerosene annually for its airborne fleet [59]. The International Air Transport Association predicts that aviation fuel will consist of 30% biofuel by 2030 [28], indicating a clear future for biofuels in the aviation industry.
Although FT–SPK based on biomass gasification (“FT–BTL”, or biomass to liquids) can be categorized as a biofuel route, there are alternatives to the FT pathway. For example, biomass pyrolysis to generate an intermediate biocrude for further upgrading has been demonstrated on a commercial scale, primarily based on pyrolysis oil production [48]. The intermediate biocrude can be decoupled from the downstream facility that upgrades it into aviation fuel [48]. Although biomass pyrolysis is relatively mature at TRL 8, the final step of upgrading the biocrude into SAF has not been demonstrated on a large scale, bringing down the integrated pathway TRL to 6 [48]. Another biofuel is biodiesel, which, like alcohols, has similar characteristic issues and is not considered suitable for use in aviation engines [27]. An overview of SAF production pathways is illustrated in Figure 7.
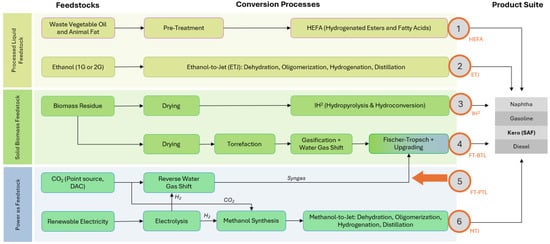
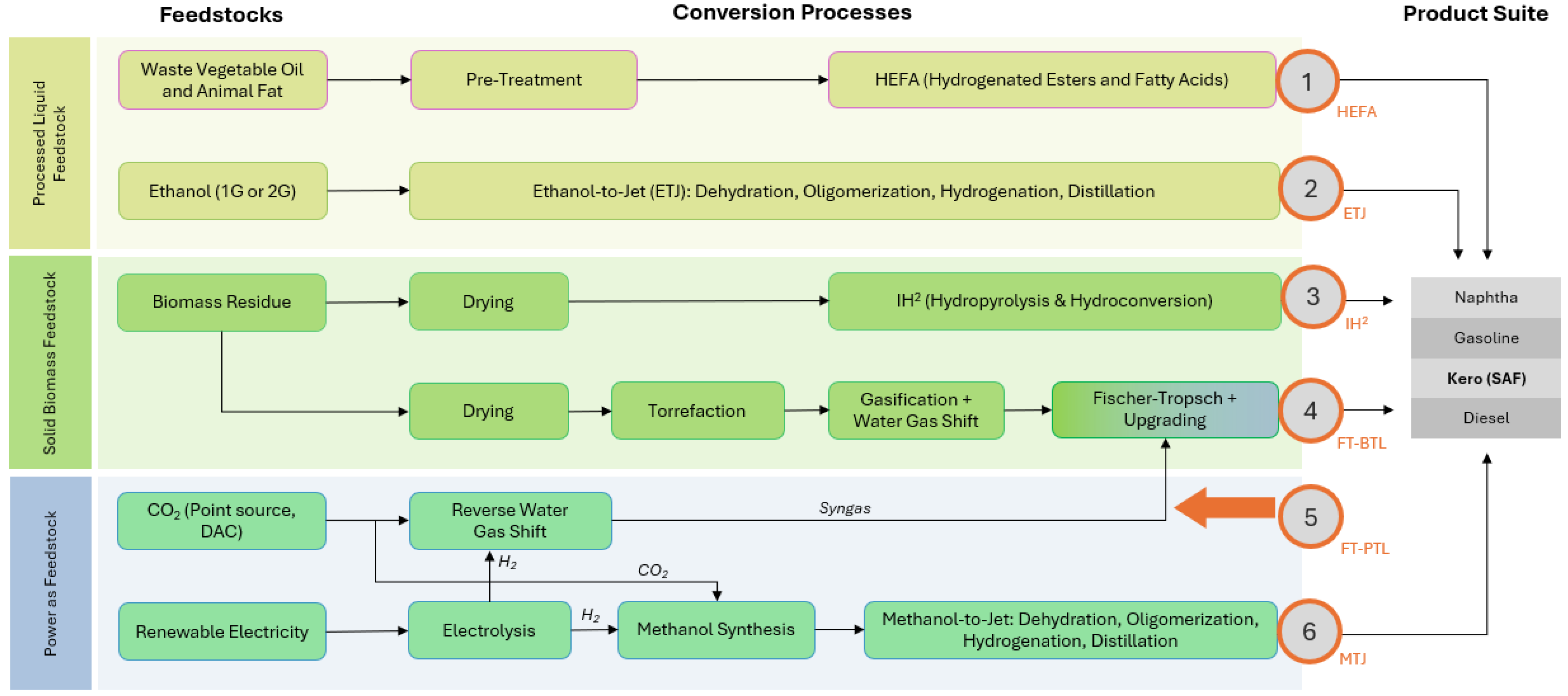
Figure 7.
SAF production pathways categorized by feedstocks and conversion processes.
In Figure 7, alcohol-to-jet technologies (ETJ and MTJ) contain multiple integrated reaction and conversion processes. The kerosene (SAF) fraction is highlighted in the product slate, but other valuable low-carbon byproducts are also produced to varying extents across the pathways.
7.2. Synthetic Paraffinic Kerosene in Air Transport
Synthetic kerosene derived from the Fischer–Tropsch process is currently approved for up to 50% blending with conventional kerosene [25]. The reason for this upper blend limit is due to the low aromatics content of FT–SPK, which could lead to swelling of piping seals that could lead to disastrous fuel leaks [25].
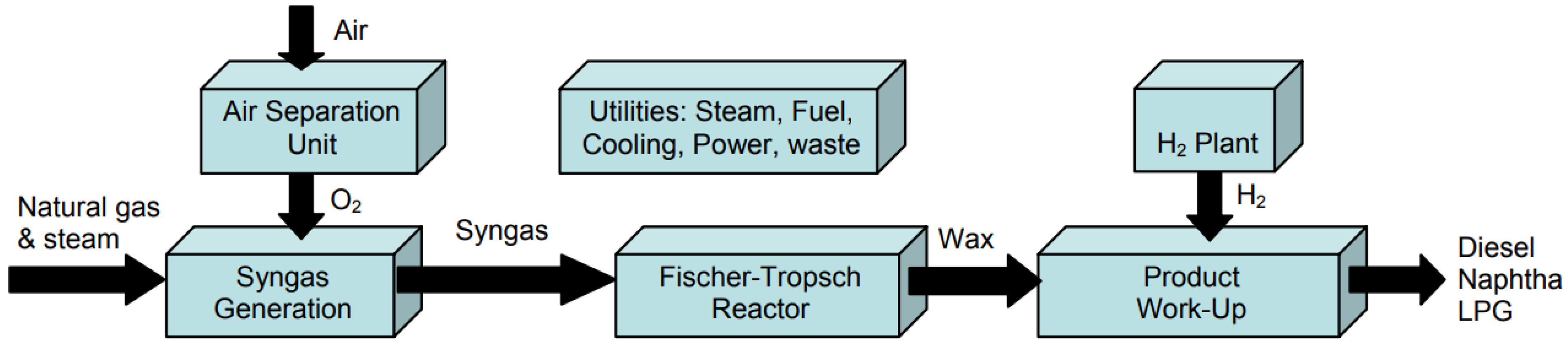
The Fischer–Tropsch process (Figure 8), which converts syngas to a synthetic crude for further upgrading and refining to SPK, was the first industrial process which received approval of its product for use in jet fuel under D7566 in 2009 [27].
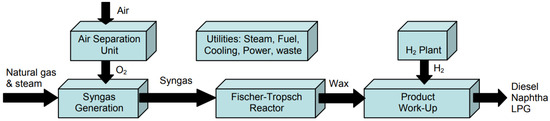
Figure 8.
Block flow diagram of the Fischer Tropsch process integrated in a gas-to-liquids plant. Reproduced under Creative Commons CC BY license from Ref. [60].
In the configuration illustrated in Figure 8, natural gas and excess steam are fed to an autothermal reformer, along with oxygen purified from an air separation unit, to generate the syngas (CO and H2 mixture). The syngas is fed into the Fischer–Tropsch reactor to produce a mixture of paraffinic hydrocarbons, which are processed downstream through isomerization, hydrocracking, and distillation processes to produce the value-added products.
Biomass gasification is an alternative route which uses biomass as the raw material to generate the syngas for the Fischer–Tropsch process (FT–BTL), reducing the carbon intensity of the SPK [28]. However, the latter process requires more pretreatment steps to condition the biomass (offsetting the reduction in lifecycle emissions), and has not been demonstrated at a commercial scale [27,48]. Although fossil fuel-based FT–SPK is mature (TRL 9), the biomass-based FT–SPK route is at approximately TRL 6-7 due to limited end-to-end integration of a biomass to biokerosene facility [48]. Another variant uses electrolyzed hydrogen (from green electricity) combined with CO2 from industrial waste streams (or biomass fermentation processes) as the syngas source (PTL “Power to Liquids” FTS). However, this route is mainly limited by the poor economies of scale with high capacity electrolysers and has not been demonstrated at scale (TRL 5-6) [48]. From a regulatory perspective, the ASTM does not specify blending restrictions on FT–SPK based on the raw material source [17].
Alcohols, as individual components, are usually not suited for use in aviation. For example, ethanol has a low flash point and is highly volatile, making handling dangerous and potentially causing losses through evaporation at cruising altitude [25]. Similarly, butanol has a high volatility with a flash point lower than Jet A [25]. Due to their low energy density, such alcohols are not used in aviation either as a pure or a blending component [28]. However, alcohols can be produced sustainably, such as through biomass fermentation, and therefore have the potential to be upgraded into synthetic aviation fuels that meet ASTM requirements.
Processes that convert alcohols to SPK are classified as alcohol-to-jet (ATJ). The benefit of ATJ–SPK is that alcohol production can be decoupled from the FT plant, allowing sustainable alcohol production in one region and transportation to the FT plant for conversion to SPK [48]. Similar to FT–SPK, ATJ–SPK is approved for blending up to 50% with conventional kerosene. However, ASTM currently only allows ethanol and iso-butanol as raw material in the ATJ–SPK process, while other alcohols are pending approval [27]. Combined with the regulatory approval bottleneck and the limited scale-up, ATJ–SPK is at a TRL of 6–7 [48].
HEFA–SPK is approved as a blending component by up to 50% with conventional kerosene [26]. There are a variety of commercial facilities that produce HEFA-based fuels at scale. Currently, HEFA–SPK is considered the most technologically mature alternative aviation fuel route when considering drop-in fuels (TRL 8), with the highest energy efficiency (76%) compared to the other routes [48]. Because of this, HEFA–SPK has powered more than 95% of all SAF-based flights to date [61]. It was the second route to achieve ASTM certification in 2011, following the approval of FT–SPK [27]. The pathway is based on the addition of hydrogen to vegetable oils and animal fats to saturate the olefins and aromatics into paraffinic chains that can be further refined into biokerosene [48].
7.3. Hydrogen-Based Propulsion in Air Transport
Hydrogen could potentially be used to power on-board auxiliary units in addition to providing energy for the propulsion mechanism, producing quieter, more efficient flights that eliminate NOx and only emit water vapor [48]. As a liquid, hydrogen can be used in fuel cells and could potentially replace on-board systems currently powered by batteries, such as controlling the emergency door mechanism on aircraft [48]. Boeing estimated that implementing hydrogen fuel cells to power auxiliary (non-propulsion) units on an aircraft could reduce fuel consumption by up to 40% relative to battery-powered auxiliary power units [48]. Hydrogen can also be combusted as a pressurized gas [27].
What makes hydrogen desirable as an aviation fuel is its 2.5 times higher energy density than kerosene on a mass basis [27]. However, it is crucial that hydrogen is produced via renewable energy sources, such as water electrolysis with renewable electricity or at least steam methane reforming with downstream carbon capture, to ensure it has overall lower lifecycle emissions compared to conventional kerosene [48].
7.4. Electric Propulsion and Fuel-Electric Hybrids in Air Transport
Fuel-electric hybrids have been successfully demonstrated in the aviation industry. For example, Boeing partnered with NASA to develop an electric hybrid, “Volt”, that selectively consumes the liquid fuel during high energy maneuvers (e.g., take-off and landing) while switching to the electric motor to power the dual-engines during steady-state cruising [48]. In such hybrid systems, a battery is used to independently power the engines during low thrust scenarios, or it could supplement the liquid fuel during high thrust requirements, enabling smaller engine designs with improved fuel efficiency [48].
Electric propulsion has the potential to fully eliminate CO2 and NOx emissions if implemented on a large scale. Because of increasing interest, policy makers are making long-term commitments to accelerate innovations in the field. For example, Norway committed to fully electrify all of its short-haul flights by 2040 [48]. As with hydrogen, the source of electricity matters when considering lifecycle emissions. Even though a battery powered plane would emit less emissions compared to one powered with conventional kerosene, more emissions would have been released upstream if the electricity for the battery was produced via a natural gas power plant compared to via solar or wind turbines.
8. Alternative Fuels in Land Logistics
Conventional liquid fuels in road transport include petrol and diesel, which are governed under ASTM EN228/EN590 standards in Europe, and D4814/975 in the US. Both fuels consist of a hydrocarbon mixture, with petrol primarily containing paraffins, olefins, and aromatics in the C4-C12 range, while diesel has heavier components, including naphthenes, in the C12-C20 range, resulting in a much higher boiling point than petrol [21]. For such fuels, compatibility with a vehicle’s engine is determined by its octane (petrol) and cetane (diesel) rating [34]. Spark ignition engines run on petrol and favor a high octane number to avoid premature ignition during the compression stroke, which can hinder fuel efficiency and damage the engine [34]. Diesel is used in compression ignition engines, where a higher cetane number is desirable for enhanced auto-ignition performance without a spark plug [34].
Diesel is the dominant fuel in the road logistics industry (making up half of global demand for diesel), as most HGVs travel long distances and hence use compression ignition engines as fuel efficiency matters [8,17]. Petrol-driven delivery vehicles are rarely used for LGVs due to their poor efficiency compared to diesel vehicles [17]. Although diesel engines release more CO2 compared to petrol engines of the same size (2.6 kgCO2/L diesel vs. 2.3 kgCO2/L petrol), the higher fuel efficiency of the diesel engine makes it overall a more sustainable option for long-distance heavy road freight applications [8]. Since road freight is the most commonly used method of freight transport, there is increasing interest in transitioning the industry to one that is fit for a sustainable future through the adoption of alternative fuels.
For example, Hyundai introduced its first batch of 50 hydrogen fuel cell-powered HGVs, the Hyundai H2 Xcient, to the Swiss market in 2020, the first of its kind in the European logistics market [62]. Expected in mid-2024, Daimler Truck is trialing five hydrogen fuel cell-powered HGVs in the German market covering long-haul routes, in collaboration with its customers such as Amazon, Air Products, and INEOS, showing clear interest in companies keen on green logistics [63]. Governments are also experimenting with market incentives, such as the National Hydrogen and Fuel Cell Technology Innovation Program deployed in Germany, providing financial support at the federal government level to accelerate the transition and market readiness of hydrogen as a robust alternative fuel [9]. But for these alternative fuels to compete with conventional petrol and diesel, they need competitive properties. Such properties include a high energy density (high fuel efficiency for long distances), competitive pricing relative to fossil fuels, lower lifecycle and end-user emissions, and a dependable refueling infrastructure [17]. Even though alternative fuels today may be more expensive per unit mass or volume, their higher efficiency drivetrains enable them to reduce their operating costs in the long-term [17].
8.1. Natural Gas Derivatives for Road Haulage
Although natural gas is a fossil fuel, it can be considered an alternative fuel since it is not commonly used compared to petrol and diesel. While it is a step up from petrol and diesel in terms of emissions, natural gas lifecycle emissions are still relatively high, and it is not considered a sustainable fuel. However, the natural gas itself could be sustainably sourced from biogas upgrading, yielding biomethane [8]. The advantages of methane-powered road haulage over conventional fuels is its lower CO2 emissions relative to petrol engines, although it is considered comparable to diesel engine emissions [8]. Today, natural gas powers more than 11 million vehicles and has an established infrastructure of more than 16,000 refueling stations worldwide [44]. Despite this, it is still only serving about 1.2% of global road haulage vehicles and is sometimes used as a secondary fuel in dual-fuel engines rather as a standalone fuel [17]. Its relative abundance keeps it competitively priced, and its widespread infrastructure establishes it as a viable transition fuel from today’s energy infrastructure to a more sustainable energy future.
There are several variants of natural gas in road transport. Compressed natural gas (CNG) is natural gas under high pressure (200–300 bar) suitable for LGVs for short-to-medium haul travel [21]. Natural gas can also be liquified under −161 °C into liquified natural gas (LNG), used more in HGVs for long-haul trips [21]. Another liquid form is LPG, consisting mainly of butane and propane in proportions which vary between countries and regions, ranging from 50% of each in Germany to a 90% propane-rich mixture in the UK [21]. In the study by Lizbetin et al. [64], a lab-controlled comparison of a variety of emissions from alternative fuels was conducted. The study found that CNG had the lowest CO emissions (0.0225 g/km) compared to petrol, diesel, LPG, E85 (mixture of 85% ethanol and 15% petrol), and biodiesel, as well as zero SO2 emissions. However, CNG had the highest NOx emissions (0.303 g/km). From a fuel efficiency perspective, CNG was found to be the most efficient (55 MJ/kg), while E85 was the least efficient (28.6 MJ/kg). In terms of CO2 emissions, both CNG (99.75 g/km) and LPG (211 g/km) were significantly outclassed by biodiesel (0.039 g/km), highlighting the unsustainable nature of natural gas fuels.
8.2. Biofuel Variants for Road Haulage
In the context of road freight, biofuel examples include biodiesel, bioethanol, biogas, and hydrotreated vegetable oil (also known as renewable diesel). Renewable diesel is produced through the hydrotreating of vegetable oils (HVO), whereas biodiesel is obtained through the transesterification of biomass [34]. The Fischer–Tropsch process (based on biomass gasification) can also be a pathway to biodiesel production [21]. Biodiesel is considered sulfur-free with lower CO and particular matter emissions compared to conventional diesel [8,10]. The downside of biodiesel from an emissions perspective is that it emits more NOx (0.079 g/km) compared to petrol (0.003 g/km) and conventional diesel (0.045 g/km). However, transitioning to lower sulfur biodiesel blends could enable the use of higher capacity NOx catalytic converters, which have the potential to further reduce NOx emissions from biodiesel [8,64].
Biofuels can be blended with conventional fuels, such as bioethanol with gasoline (e.g., E85), and biodiesel with conventional diesel, due to their similar characteristics [21]. Their attractiveness comes from their drop-in characteristics, as they are compatible with existing engine technology and refueling infrastructure [8]. However, there are blend limits up to which a normal engine would require modifications for compatibility due to the lower density and lubricity of the fuel blend (e.g., diesel engines can accept up to 15% biodiesel in the fuel mix without changes) [21,34].
Bioalcohols come into play when considering lighter liquid fuels. They typically have a high octane number and a low cetane number, making them more suitable for use in petrol engines than diesel engines [34]. They can be used in diesel engines after some engine modifications [34]. However, bioalcohols have a lower energy density than petrol, accelerate corrosion of the fuel system, and lead to inconsistent performance during transient conditions [34]. Hence, bioalcohols are typically mixed with additives, such as cetane enhancers, to improve compatibility with diesel engines and mitigate potential issues [34]. Both biomethanol and bioethanol reduce CO2 emissions in a petrol engine, however bioethanol has a higher energy density than biomethanol (hence it is more widely considered) and the energy density of both are lower than petrol, implying reduced mileage [34].
The lightest of the biofuels is biomethane, produced through the upgrading of biogas. Biogas is typically produced through anaerobic digestion of municipal waste or wastewater sludge [21]. Alternatively, landfill vapors can be directly upgraded to biogas. However, biomethane has a relatively low calorific value (36.1 MJ/kg) compared to every other alternative fuel, except for bioethanol (26.93 MJ/kg), and has a relatively high net positive production carbon footprint (excluding combustion emissions) [21]. Given the much higher energy density of competing gaseous alternative fuels such as CNG (56.69 MJ/kg) and LPG (49.68 MJ/kg), both of which have lower production emissions, biomethane has seen limited use [21].
8.3. Hydrogen-Based Propulsion for Road Haulage
The high energy density of hydrogen on a mass basis (higher heating value of 143 MJ/kg), along with its large flammability range, low ignition energy, and rapid flame front, has increased interest in hydrogen-powered road vehicles [34,46,47]. However, modern hydrogen mobility focuses on fuel cell, where hydrogen is stored in a compressed cylinder and is electrochemically converted to electricity for the motor [21]. This contrasts with battery electric vehicles, which store grid electricity on an onboard battery for discharge during use [21]. In contrast to onboard batteries, the highly compressed hydrogen (700 bar) enables a much higher energy density, extending the range and freight capacity of an HGV [17]. As with any alternative fuel, it is crucial to ensure that the hydrogen is produced sustainably and to consider any additional emissions generated during the design and manufacturing of fuel cell vehicles compared to conventional vehicles [21].
8.4. Electric and Plug-in Hybrids for Road Haulage
Electric vehicles are gaining more market share due to their sustainability performance and better efficiency compared to the combustion engine, while taking advantage of the increasing supply of renewable electricity [17]. It is predicted that electric vehicles and hybrids will reach a combined total of 220 million on the road by 2030 [21]. Electric hybrids are those which run in a dual-engine configuration, using the electric motor during load demand operation and switching to the combustion engine during higher duty requirements, such as acceleration or using the air conditioning at high settings [21]. These plug-in hybrids can be charged through electric charging points, while driving through regenerative braking (where the motor works in reverse as a generator), or by using surplus capacity of the combustion engine [21]. Electricity can also be generated onboard using an alternative fuel source, such as hydrogen, as discussed previously.
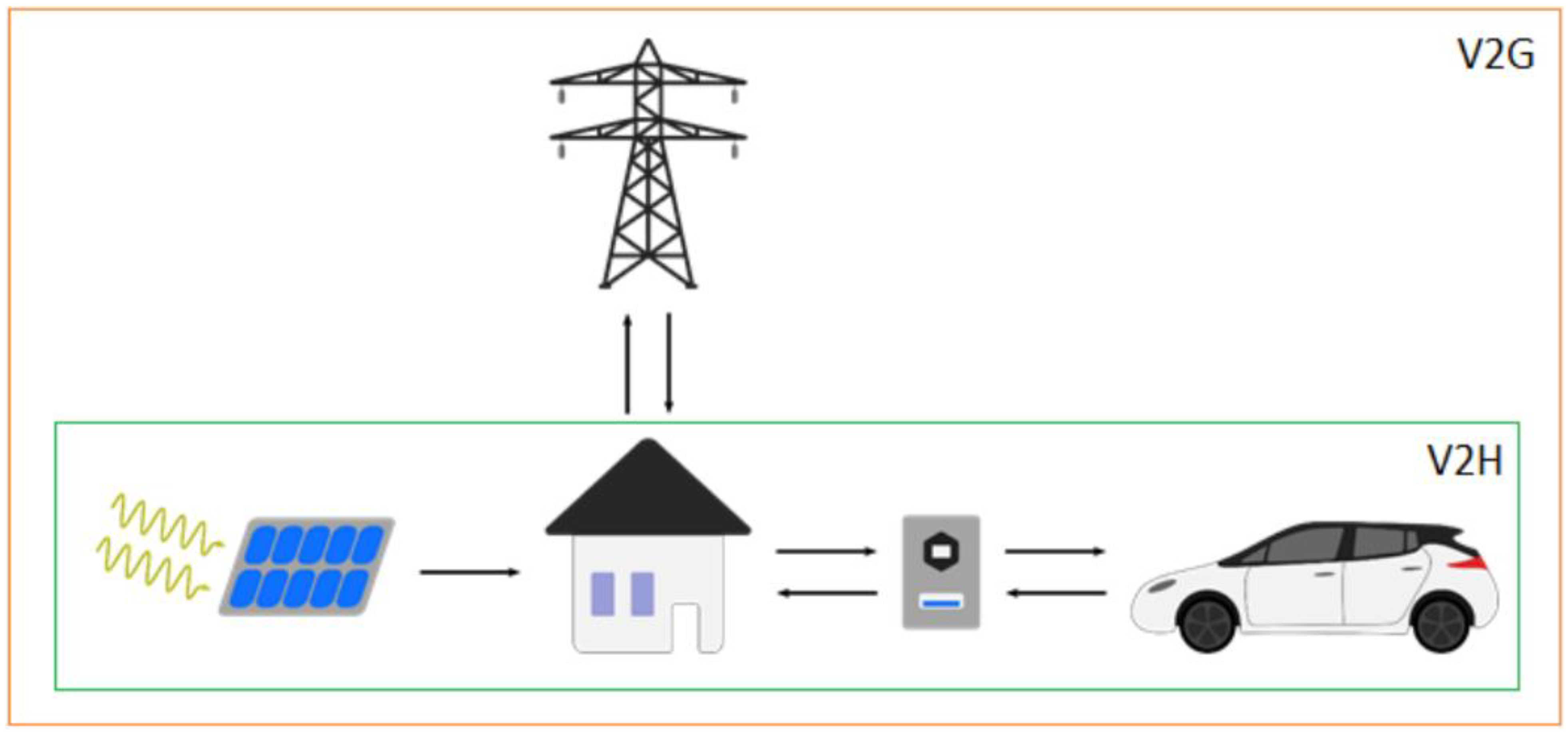
Some concerns have been raised about the impact of electric vehicle adoption on the power grid. To avoid excessive demand, research into vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technology (Figure 9) has been progressing.
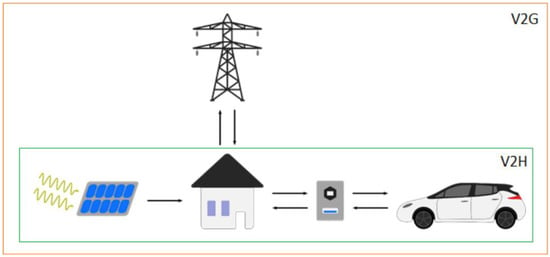
Figure 9.
Visual representation of the V2G and V2H systems, reproduced under Creative Commons CC BY license from Ref. [65].
This technology enables electric vehicles to deliver surplus power back to the grid, although it is still in its early stages with a high cost barrier and concerns about increased battery cycling, which reduces maintenance intervals [66]. In vehicle-to-home (V2H) systems, households generating surplus renewable power (e.g., via solar) can store it in their electric vehicles for later consumption, acting as a capacity buffer between the consumer and the grid. In V2G systems, electric vehicles can directly discharge surplus power back to the grid or adjust their charge or discharge rates, allowing for improved grid demand management.
Research also suggests the use of smart charging infrastructure, which allows charging points to selectively deliver electricity from the grid, smoothing the demand curve across the grid without causing fluctuations or risking overcapacity. However, this requires compatible infrastructure and users willing to extend the duration their vehicle is plugged in for [67].
Logistics providers are taking advantage of the benefits of electrified mobility by adopting LGVs and MGVs for urban freight transport, allowing for operational cost savings [17]. From an emissions perspective, electrified road freight produces zero tailpipe emissions and generates less noise pollution than their fossil fuel equivalents. The latter benefit makes them particularly well-suited for deployment in dense cities, where governments usually impose fees on polluting vehicles [8].
9. Alternative Fuels in Sea Logistics
Sea freight accounts for 80% of worldwide trade by volume and 70% by value [17]. As of 2017, this freight was transported aboard more than 90,000 vessels of varying sizes and carrying capacities [17]. Small (less than 500 ton) and medium (500–25,000 ton) vessels make up a combined 80% of the fleet of sea freight, whereas large (25,000–60,000 ton) and very large (more than 60,000 ton) vessels comprise the remainder [17]. Despite their small numbers, the latter two categories account for more than 82% of the total freight tonnage shipped worldwide [17]. The majority of fuel demand in the sea logistics sector, namely 70%, stems from bulk carriers, tankers, and container vessels of the aforementioned large and very large vessel types [17]. Refueling considerations are important for such charter vessels as they typically do not follow fixed paths and have to factor in inconsistent fueling patterns subject to fuel price and supply fluctuations [17]. Considering 2015 emissions from the sea logistics sector, 72% is estimated to be due to high sulfur heavy fuel oil, 26% from marine diesel oil, and the remainder from LNG [17].
Conventional marine fuels include marine gasoil (MGO), marine diesel oil (MDO), and heavy fuel oil (HFO) [22]. Variants of these fuel oils can be produced with low sulfur content, reaching as low as 0.5% total sulfur in MGO and 1% in HFO [22]. The sulfur content for such fuels is an aspect which is considered in IMO regulations.
IMO’s Energy Efficiency Design Index (EEDI) is an example of enforceable policy aimed at controlling emissions from the sea freight sector, although this applies to the design of newly built ships. Additionally, the IMO has also mandated a reduction in marine fuel sulfur content to a maximum of 0.5% globally and to 0.1% in specific ECAs from 2020 onwards [17]. Due to the long operating life of vessels, the complete replacement of the global fleet is not expected to meet EEDI targets until 2040 optimistically, which is why alternative fuels must be considered. In fact, most retrofitting operations on existing marine engines stem from replacing conventional engines with those that are dual-fuel compatible [17].
Similar to other sectors, alternative fuels need a defined set of properties to outcompete conventional marine fuels. These include a high energy density (to enable longer routes and not occupying valuable cargo space), competitive pricing, availability of bunkering infrastructure (to allow refueling at generic ports), and compatibility with existing marine propulsion, refueling, and fuel transport technology [17,22]. This is in addition to their assumed reduction in lifecycle emissions. The impact of alternative fuels on engine performance is also an important consideration, as a better environmental performance could come with trade-offs such as shorter maintenance intervals and higher repair costs [23].
Alternative marine fuels currently under consideration include alcohols (ethanol, methanol), ammonia, LPG, LNG, dimethyl ether, biofuels, and gaseous fuels such as hydrogen, propane, and CNG [22,31,68]. Al-Enazi et al. [22] concluded that ammonia and methanol appear to be the most promising options due to their widespread availability, presence in freight cargo, and compatibility with existing engine technology. In contrast, Xing et al. [31] suggest that LNG, LPG, and methanol have the most potential, considering their compatibility with existing engines and the slow progress in improving ship emissions capturing systems. These include sulfur scrubber systems which use a circulating solvent to selectively absorb sulfur from engine exhausts prior to release [17]. In terms of safety, Deniz and Zincir [23] evaluated alcohols as more hazardous due to their higher densities and lower auto-ignition temperatures compared to hydrogen and LNG, which increases the risk of localized fires in case of fuel leaks. Such concerns have not, however, impeded the pace of research in the field.
The EU FLAGSHIPS project contributes to the advancement of the field by deploying new (“Zulu”) and retrofitted (“FPS Waal”) vessels in 2024 which operate on hydrogen fuel cells [69]. Working on liquid hydrogen, the HySHIP project involves a European collaborative partnership to demonstrate operation of a liquid hydrogen-powered vessel for the transport of hydrogen cargoes along the Norwegian coast [70]. Another initiative is the ShipFC project which deploys a demonstration vessel (“Viking Energy”) with a 2 MW ammonia fuel cell-powered propulsion system, alongside parallel studies into technology transfer to three other vessel types [71]. These demonstration projects help drive innovations in the field and promote wider adoption of alternative fuels as a sustainable alternative for a cleaner future.
9.1. LNG as Marine Fuel
Because of its widespread presence in hydrocarbon freight, LNG boil-off from on-board storage has been used to power conventional ship engines since the 1970s [17]. LNG-fueled vessels have increased from 64 in 2015 to 118 in 2018, showing clear signs of a growing market [22]. LNG contains significantly less sulfur compared to conventional marine fuels and can reduce SOx and NOx emissions by 90% and 80%, respectively, when compared to HFO, resulting in an overall GHG emissions reduction of 20% [17]. Part of the growing demands for LNG as marine fuel are due to the increasing restrictions imposed by the IMO on sulfur content and the requirement of passage through ECAs (which are used by almost 70% of the global fleet) [22,72]. Its low sulfur content also avoids formation of sulfuric acid in the engines and can extend a ship’s maintenance cycle [22,23]. It also produces significantly less particulate matter emissions [17,72]. When compared to the lifecycle emissions of MDO, LNG generates about half as much emissions [22]. Due to its availability, LNG is expected to account for 80% of the marine fuel market by 2050 [22]. This is supported by a Monte Carlo-based analysis of the use of varying fuels and their effectiveness in meeting 400–500 ppm atmospheric CO2 levels by 2050 through a Global Energy Transition model [73]. Considering uncertainties in carbon capture technology adoption and fuel costs, the authors concluded that phasing out HFO within the next decade is necessary, while LNG emerged as a cost-effective replacement in the majority of scenarios, despite uncertainty in fuel cost [73].
However, LNG is still a fossil fuel and should ideally serve as a transition fuel until innovations enable the wide scale adoption of renewable alternatives. Although it reduces certain emissions, it increases CO and other hydrocarbon emissions [23]. Compared to MDO, LNG has a similar calorific value but half its density, requiring twice the storage space for a given duty requirement [23]. In one study, the mass consumption of LNG over a two-day voyage was recorded, showing that 38 tons of LNG required 84 m3 of storage space, whereas the same journey on HFO or MGO would have required 38 m3 [23]. In addition, engine modifications are still required in most cases as the majority of sea freight propulsion systems are based on conventional marine fuels [22]. LNG is unlikely to independently help reduce carbon emissions by 50% by 2050, as required by IMO [17].
9.2. Ammonia and Hydrogen-Based Marine Fuel
The majority of the world’s ammonia is produced using the Haber–Bosch process, which uses hydrogen and nitrogen as the reactants [22]. Although this conventionally uses gray hydrogen from steam methane reforming, green ammonia can also be produced if renewable electricity is used in the electrolysis of water to produce green hydrogen, which can then be used for the Haber–Bosch process [22]. The volumetric hydrogen density of liquid ammonia is 45% higher than that of liquid hydrogen, meaning that in a unit volume of liquid ammonia, there is more hydrogen compared to pure liquid hydrogen [4,22]. Ammonia can be stored under liquid conditions at higher temperatures compared to hydrogen (−33 °C at 1 bara) and can be used in multi-fuel engines in the presence of a pilot fuel [17]. Ammonia can also be blended, along with hydrogen, together with conventional marine fuels to improve combustion characteristics and reduce NOx emissions [22]. It can alternatively be used as a hydrogen source for on-board hydrogen fuel cells [17].
Hydrogen can be stored either as a compressed gas or as a cryogen liquid (at −252 °C at 1 bara) and can be used in fuel cells for marine propulsion [17]. The first large-scale freight implementation was announced in 2019 where Japan launched the world’s first hydrogen-powered carrier, the Suiso Frontier [22].
For marine engines, proton exchange membrane cells, molten carbonate cells, and solid oxide cells are deemed the most applicable based on an analytical hierarchy process study prioritizing safety, emissions, and cost, among other factors [74]. Specifically, molten carbonate and solid oxide cells are more suitable for long-distance freight due to their high energy densities compared to proton exchange membrane cells [31].
Compared to ammonia, hydrogen can be produced more efficiently (70% vs. 50%) and provides better fuel economy in a fuel cell compared to the multifuel configuration usage in the case of ammonia (60% vs. 40%) [17]. It largely mitigates CO2, CO, SOx, and particulate matter, although NOx emissions may increase depending on operating parameters [23].
However, whether as a compressed gas or a cryogenic liquid, hydrogen has a much lower density than HFO, which means it occupies additional cargo space if travel distance is not to be compromised [17]. Therefore, hydrogen is not considered a viable option for ships sensitive to changes in storage capacity, largely eliminating the application for most modern freight operations [31]. Furthermore, the higher calorific value compared to MDO result in faster flame speeds, leading to more wear and tear on the combustion chamber and a shorter maintenance cycle [23]. Despite these challenges, hydrogen can still be used as a blending component to partially decarbonize conventional marine fuels [22].
9.3. Alcohol-Based Marine Fuel
Alcohols, such as methanol and ethanol, lead to lower combustion emissions of NOx, SOx, and particulate matter in marine engines [23]. This makes them attractive to consider as alternatives for heavy operation in ECAs. For example, in a life cycle analysis of the well-to-wake emissions of methanol, methanol ranked similarly to LNG and HFO when considering CO2, but better than conventional marine fuels when comparing the other air contaminants [31]. Unlike with hydrogen, ammonia, and natural gas, ethanol is a liquid at atmospheric conditions, without requiring additional provisions for transportation and storage [31]. Demonstration projects have taken place to further understand the opportunities and limits of applying alcohols in marine freight.
Alcohols like methanol are typically used in multifuel engines, such as with MDO [31]. Examples include the two-stroke engine with a pilot fuel and the faster four-stroke dual (methanol and MDO) fuel engine as developed by prominent engine manufacturers Wärtsilä and MAN [31]. Research is also underway in further feasibility testing of methanol. An example is the Pilot Methanol project, which took place from 2013–2015 and involved the on-board conversion of the fuel system and all engines of a passenger ferry (“Stena Germanica”) to run on methanol and MGO [31]. Other research is occurring on a smaller scale. For example, one of the aspects of the LeanShips initiative is to conduct a lifecycle assessment of methanol in different vessel types, along with engine efficiency studies of a dual-fuel marine engine in methanol and MDO operation.
Other research avenues involve the use of methanol in onboard fuel cells. Examples include the Pa-X-ell MS MARIELLA project, which tested a 60 kW high temperature proton exchange membrane methanol cell to power auxiliary units, and the RiverCell project, which applied the same technology for a 250 kW cell in a river craft [75]. Based on the extant research, there is limited evidence of ethanol application in marine engines, and even methanol is not without its concerns.
Although both alcohols lead to reduced NOx and SOx emissions, they generate more CO2, CO, and harmful hydrocarbons [23]. In addition, the lower energy density compared to conventional marine fuels means that methanol and ethanol require twice the storage capacity as MDO for the same journey [23]. They also incur the costs of extra solvents needed to avoid separation of phases into an aqueous and an organic phase, losing mixture homogeneity required for optimal combustion performance [23]. Such challenges are explored further in Section 10.
9.4. Biofuel-Based Marine Fuel
Research indicates the potential for biofuels, such as HVO and FT-diesel, to be used in marine engines with limited retrofitting. Based on their physical and chemical properties, blends of conventional fuels with up to 10% biomethanol and 20% biodiesel are considered feasible [31], although some major engine manufacturers claim compatibility with pure biodiesel without requiring engine modifications [31]. If produced sustainably, biodiesel has the potential to be of great interest as an alternative fuel due to its combustion and emissions performance [31].
Another example is biomethane, which offers similar properties as LNG but with much lower lifecycle emissions [17]. Biomethane, which can be produced through the upgrading of biogas or through methanation (reacting captured CO2 and hydrogen utilizing renewable electricity), can be liquified and stored similar to conventional LNG [17].
9.5. Nuclear Energy as Marine Fuel
Nuclear fuel sources are considered renewable due to their low emissions compared to conventional fuels, and offer high energy density, which has led to their widespread use in military applications such as submarines [17]. However, nuclear fuels are sensitive topics due to their safety implications, and nuclear-fueled vessels have been barred from entering many commercial routes and ports worldwide [17]. Apart from its use in transportation logistics, nuclear energy presents distinct challenges not faced by other alternative fuel sources, including the management of depleted fuel rods and concerns about its perceived safety risks [76]. The proliferation of nuclear as an alternative fuel is not foreseen in the near future for commercial sea freight.
10. Challenges and Potential Solutions
Despite their numerous benefits, the adoption rate of alternative fuels is hindered by a variety of challenges that require different levels of incentives, ranging from financial to regulatory, to overcome. In the following section, the main challenges to the adoption of alternative fuels in each mode of logistics will be explored based on the extant literature, and potential mitigations are discussed wherever they are addressed in the literature.
10.1. Alternative Fuels in Air Logistics
In air logistics, the barriers to adoption of alternative fuels range from technological and technical aspects, such as maturity of the synthesis process, to regulatory reasons owing to limited incentives from governing bodies, especially when considering the complexity of the regulatory approval process [27]. Environmental concerns are also apparent, particularly for bio-derived fuels [27]. These challenges ultimately lead to poor economics that impede short-term adoption rates.
10.1.1. Technical/Technological Challenges
Based on the desirable aviation fuel characteristics previously described, any alternative fuel candidate which does not meet or exceed those fuel properties must clearly demonstrate other significant benefits to justify a global overhaul of the current aviation fuel infrastructure [25]. Alcohols are a prime example, as their low energy density would impede economic operation of aircraft. This is illustrated in Figure 10, which shows the lower energy density by mass and by volume of methanol relative to conventional jet fuel.
Figure 10.
Mass-based and volume-based energy densities of fuels. Reproduced under Creative Commons CC BY license from Ref. [17].
Even if their use was justified from a technical perspective, ethanol and butanol would require 78% and 23% more volume, respectively, to provide the equivalent energy content of conventional kerosene [25]. Furthermore, the lifecycle emissions of alcohol synthesis depend on the method of hydrogen product (or “color”), CO2 source, and the sustainability of the electrical grid, which could result in higher overall lifecycle emissions [77]. Even if alcohols were to be used in an ATJ process to produce synthetic kerosene, the ATJ route is challenged by the poor selectivity of jet fuel production [48] compared to other hydrocarbon fractions.
Similar challenges are faced by LNG, which has a lower energy density than conventional kerosene and brings added infrastructural complexities due to its cryogenic nature [25]. Pyrolysis oil also requires added pre-processing and dedicated transport infrastructure, in addition to its list of incompatibilities such as water and oxygen content, acidity, viscosity, and chemical instability [48]. Although no pyrolysis upgrading is established at an industrial scale, research is underway to increase its TRL and overcome these challenges [48].
Although HEFA–SPK is powering most SAF-based flights to date, it has not yet reached TRL 9 due to limited scale-up, which results in a cost premium [26]. Increasing investments in pilot and demonstration facilities serves to eliminate the residual technical risks in this route [78]. FT–SPK faces the opposite problem where the process is not optimized for smaller scale production when processing biomass feed, with poor catalyst selectivity and integration [48]. From a pathway viewpoint, the main issue with HEFA–SPK is in its feedstock, where the HEFA biomass competes for agricultural land which would otherwise be used for food production [26]. Changing land use to grow biomass feedstock to produce SPK could even lead to higher overall lifecycle emissions compared to conventional kerosene if emissions are not transparently accounted for [26]. Feedstock which does not compete with food crops, such as jatropha and algae, require further processing to satisfy fuel quality requirements, increasing the overall production cost [28]. Further challenges exist, for example with jatropha, such as poor yields, higher susceptibility to infections, and higher complexity of oil extraction [27].
Although hydrogen offers an advantage with its high mass-based energy density, it has an order of magnitude lower volume-based energy density compared to conventional kerosene [48]. Consequently, this would result in an overall heavier aircraft needed to store the liquid hydrogen onboard compared to conventional kerosene [77]. Retrofitting an aircraft to run on hydrogen would require a redesign to accommodate the heavily insulated storage tanks needed to keep hydrogen in its liquid form [48,77]. This requires new designs that significantly reduce storage tank mass to take advantage of hydrogen’s mass-based energy density advantage [77]. Other parts would also need to be redesigned, including the burners, turbine blades, fuel ducts, and cooling system, alongside a wider overhaul of the refueling infrastructure and associated supply chain [48]. Additional safety elements could be required due to its higher flammability range [27]. Maintenance regimes could also be impacted due to the introduction of the hydrogen embrittlement corrosion mechanism, as hydrogen could permeate certain materials leading to material defects over time [77]. Although hydrogen can be reliably produced through water electrolysis at efficiencies close to the theoretical limit (60–80%), it is likely that hydrogen will largely be supplied from steam methane reforming until electrolysis becomes more cost competitive [77]. The lifecycle emissions viewpoint should also consider the carbon intensity associated with producing the liquified hydrogen upstream the supply chain.
Similarly, battery-electric aircraft propulsion is limited by its lower energy density, reaching up to 1 MJ/kg compared to the 43 MJ/kg of conventional kerosene [48]. Hence, future developments are needed in improving battery energy density as well as improving the efficiency of onboard electric systems [48].
10.1.2. Environmental Challenges
For aviation, pathways which utilize biomass, such as making ethanol for ATJ–SPK or biomass pyrolysis, require careful consideration of lifecycle emissions. Biomass feedstock competes for land and water usage, and without proper management, lifecycle emissions could exceed those of fossil fuel route [25,27,77]. While 1–2.5 L of water are required to produce a liter of petroleum fuel, biofuel production could increase this amount due to the irrigation needs of the biomass feedstock [25]. Land can be permanently affected through the leaching of soil nutrients into freshwater reserves due to increased fertilizer consumption [25]. This can also impact local biodiversity by harming sensitive ecosystems [28]. Because of such environmental concerns, bio-based pathways are feedstock-constrained, as second and third-generation feedstock are scarcer than first generation [48]. Another issue is the variability in reporting lifecycle emissions due to the location sensitivity of the feedstock. For example, a study in Brazil reported an 85% reduction to a 60% increase in lifecycle emissions (compared to conventional kerosene) depending on where the jatropha crops were grown [77]. Biofuel production involves biomass growth and processing, which are steps not found in conventional kerosene production. The environmental impacts of these added steps introduce new risks to human health that would otherwise be avoided [77].
Based on the aforementioned concerns, adopting alternative fuels introduces the challenge of understanding both direct and indirect land use changes, requiring models that incorporate multiple sectors of the economy, including energy, agriculture, and forestry [25]. Utilizing crops that do not compete with agricultural land and that do not require excessive freshwater can be considered, although these could also be classified as invasive species, necessitating a balanced approach to their introduction and control. [25]. Furthermore, the literature suggests future reliance on second and third-generation feedstock to address food security issue [48]. Using second generation biomass, such as miscanthus, switchgrass, and poplar, in combination with bio-based FT–SPK or ATJ–SPK, could generate net negative emissions, essentially creating carbon sinks [77].
10.1.3. Commercial Challenges
The use of biomass to feed synthetic aviation fuel production processes incurs the opportunity cost of utilizing the same feedstock directly in more efficient heating applications and electricity generation [25]. Similarly, from an opportunity cost perspective, HEFA are more commonly used to produce renewable diesel for land transport rather than biokerosene, due to more favorable process selectivity [26].
For the ATJ route, using the alcohols as fuels directly in land transport is more attractive compared to using them to produce ATJ–SPK in terms of energy generation per unit capital cost [48]. Despite this, ATJ–SPK is considered 2–4 times cheaper relative to biomass-based kerosene production, and is less than half the cost of using ethanol itself as the fuel [77]. Considering FTS–SPK using the PTL approach (FT–PTL), the resultant product is considered too expensive with further economies of scale required, as mentioned earlier [48]. Furthermore, FTS–SPK via PTL requires a concentrated point-source of CO2, necessitating the facility’s proximity to an industrial supplier of CO2, thereby constraining location options [48]. This risk is amplified if direct air capture is considered as the CO2 source, which is ten times more expensive than a concentrated point-source [77]. Because of this, FTS–SPK via PTL is forecasted to be more expensive relative to biokerosene, and is especially susceptible to the availability of renewable electricity at scale [77].
As previously mentioned, biofuels are comparatively more expensive to produce than conventional kerosene, as most technologies have a relatively low TRL (except for HEFA–SPK) resulting in poor economies of scale [26]. Literature suggests that renewable kerosene is 2–5 times more expensive than regular kerosene [48]. This variability in cost estimation presents another commercial challenge, as the price is sensitive to the alternative jet fuel production method, plant capacity, and efficiency [78]. Companies are not incentivized to create a thriving market for biofuels trade due to limited compensation mechanisms for early adopters, especially considering the cost premium as an entry barrier [79].
Aside from drop-in fuels, liquid hydrogen for aviation is also considered 2–4.5 times more expensive relative to conventional kerosene, and this is conservatively assuming the price of hydrogen from a steam methane reforming process rather than a renewable one [77]. Furthermore, liquid hydrogen supply chains do not yet exist, and their deployment timeline is uncertain [77]. Similarly, LNG use in aviation would require significant expansion of the existing supply chain [25].
The cost of alternative jet fuel extends beyond the production process. Major cost components include the feedstock, which can contribute more than 30% to the fuel price per gallon, and the logistics, encompassing the transportation of feed to the plant and fuel to the blending facility or directly to the airport [78]. Considering such cost factors, it is vital that research leads the way in achieving economies of scale to reduce production costs [79]. Particularly for biomass, the market availability of second generation feedstocks is critical in lowering the production cost [78]. SAF production processes should also capitalize on any byproducts (refer to Figure 7) that could have their own market [79]. Scale up of alternative aviation fuel processes could be accelerated through partnerships between the aviation industry, conventional oil and gas players, and biofuels producers, offering synergy opportunities to reduce capital and operating costs and secure funding and regulatory support. An example includes collaborations to test renewable kerosene blends with conventional kerosene in existing plants, although this approach needs derisking from safety, reliability, and financial perspectives [78].
10.1.4. Operational Challenges
Although biodiesel could theoretically be used in an aircraft engine without modifications, its biological origin causes biodiesel to degrade naturally over time, generating microbial growth which affects its stability under long-term storage [28]. At cruising altitude, its high freeze point could be an issue, and its polar nature (from the oxygen atoms in the ester groups) tends to form emulsions with water that can plug up the fuel system [28]. Biodiesel also leaves deposits over time as it undergoes thermal stresses in the combustion compartment, which accumulate and degrade engine efficiency and safety over time. This was proven true even at blends as low as 1% biodiesel in conventional kerosene [25]. Upstream in the supply chain, storage considerations also apply to inventories of biofuels kept at the back end of the production plant. Additionally, storing raw biomass for the production facility requires an established logistics network to ensure maximum utilization of the plant [26].
Operationally, electric batteries are unlikely to replace kerosene as their low energy density limits trip distances significantly. It is expected that the range limit will be around 500 km even by 2050 [27]. Higher capacity batteries contribute to increasing the weight of the aircraft, and unlike liquid fuels, the weight of the battery stays consistent throughout the trip, rather than reducing as the fuel is consumed [27]. Electric batteries also pose new safety concerns, as they are susceptible to thermal runaway reactions if poorly designed and integrated [77]. Battery fires have occurred in electric aircraft, even in some commercial Boeing 787 planes, demonstrating that safety and reliability remain as challenges [77].
Similarly, liquid hydrogen poses safety concerns. The requirement for storage under insulated conditions introduces new handling methods, and direct exposure can lead to frostbite [77].
10.1.5. Political/Regulatory Challenges
As previously mentioned, alternative fuels in aviation must meet the ASTM standards for commercial use. The comprehensive approach set by the D4054 “Standard Practice for Qualification and Approval of New Aviation Turbine Fuels and Fuel Additives” requires navigating 4 tiers (Figure 11), from specifying the fuel at tier 1 to engine and auxiliary power unit testing at tier 4, before proceeding for approval under the D7566 standard [78].
Figure 11.
Aviation fuel evaluation process for fuels to be used above a 10 vol % blend. Reproduced under Creative Commons CC BY license from Ref. [80].
This entire process requires 3–5 years of work and costs at least $5 million but is typically from $20–$50 million [27,78]. Furthermore, proceeding from the initial tiers to the final tiers requires producing tens of cubic meters of fuel, which needs a functioning demonstration plant, adding a capital cost barrier to the process [81]. From a policy perspective, poor justification for the cost premiums of alternative aviation fuels is partially caused by lack of incentives, which limits the rate of investments in producing these fuels [26].
To ease the cost barrier for certification, ASTM introduced a fast track annex in 2020 as part of the D4054 revision, but limits any fuel certified under the fast track route to a maximum blend limit of 10% [27]. It is clear that further efforts are needed to further reduce both the certification costs and time [78]. Aside from the certification process, policy intervention in the form of taxes and mandates are required to help make the alternative fuels more affordable, both for the producer and the consumer [25]. In the US, this takes the form of tax exemptions and direct funding of SAF projects by the government [27]. For HEFA plants, policy intervention would contribute to making HEFA–SPK more competitive relative to the more common production of HEFA-diesel for land transport [48]. From a legislative perspective, countries should mandate the use of alternative fuels as part of their sustainability targets, as demonstrated by the EU’s ReFuelEU Aviation initiative, which specifies an increase of biofuels use at airports from 2% in 2025 to 63% in 2050 [27].
Specifically for liquid hydrogen, carriers and airports need to engage more with the public to address safety concerns, thereby garnering public support that can drive policymakers to incentivize further research and development for its application in aviation [77]. Since liquid hydrogen and battery electric systems are further from commercial adoption in aviation, policies should focus on funding research and development [27].
10.2. Alternative Fuels in Land Logistics
Similar to the previous section, the widespread adoption of alternative fuels in land logistics face various challenges that must be addressed to ensure a successful transition. Although similar alternative fuel production challenges are common across the three transportation modes—such as the land use issue with biofuels and the uncompetitive cost of green hydrogen—the importance of an established alternative fuels infrastructure is more prevalent in land logistics. This is largely due to the higher refueling demand for land-based journeys relative to air and sea freight, making it not only a question of adopting the required infrastructure but also scaling it appropriately. Literature also demonstrates that while alternative fuels tend to offset CO2 emissions, they can increase other environmental emissions and pose operational challenges, particularly for alcohols. A variety of legislative solutions have been proposed, but the literature emphasizes the difficulty of coordinating policies across stakeholders with competing interests.
10.2.1. Technical/Technological Challenges
As discussed previously, the biofuels issue was emphasized in literature, particularly second-generation biofuels, due to the high costs of production, transportation, and storage [21]. For instance, commercializing microalgal biodiesel requires optimization of microalgae harvesting and selecting appropriate microalgae species with high oil content, which can be technically challenging and costly.
For alcohols, technical challenges include material compatibility issues in the fuel system due to their corrosive properties, as well as cold start, part load, and transient operating issues caused by their low vapor pressure [34]. Furthermore, the lower energy content of alcohols compared to gasoline (Figure 10) is a significant concern [34]. Additionally, using alcohols in compression ignition engines requires modifications to the fuel, such as adding cetane-boosting additives or emulsifying the alcohol in diesel, which introduces an additional technical barrier to adoption [34].
In land logistics, literature highlights the importance of refueling infrastructure, especially considering its more frequent usage compared to other modes of transportation. In this context, more novel fuels such as hydrogen are challenged by the current lack of widespread refueling infrastructure [44]. Similarly, the infrastructure for producing and distributing natural gas as a vehicular fuel remains limited in many areas, particularly in developing countries, making it less reliable for logistics providers to consider overhauling their fleets for natural gas compatibility [44].
Hydrogen faces additional technological challenges of production and storage. However, methods of producing green hydrogen, such as water electrolysis, are still relatively inefficient compared to methods which utilize fossil fuels [82]. Furthermore, due to its low volume-based energy density, hydrogen storage poses challenges, requiring specialized storage methods such as compression, liquefaction, or the use of chemical hydrides and adsorption materials, which are still under research and development [34].
10.2.2. Environmental Challenges
Literature highlights the environmental challenges associated with the use of alcohols as alternative fuels. While alcohols can reduce CO2 emissions due to their lower carbon-to-hydrogen ratio compared to gasoline and diesel, they may increase emissions of other pollutants, such as aldehydes and ketones [34]. Additionally, the production of alcohols from renewable sources, such as bioethanol, can have environmental implications, including changes in land usage and competition with food production, as previously discussed. First-generation biofuels, made from edible crops, have been criticized for their potential competition with food production and resulting land use changes [44]. Second-generation biofuels, made from non-edible feedstocks, aim to address these concerns. While they can produce lower greenhouse gas emissions compared to fossil fuels, second-generation biofuels may still contribute to environmental impacts, including increased emissions of particulate matter, nitrous oxide, and nitrogen oxides [44]. These effects are highly dependent on the production method; for example, second-generation biodiesel and biogasoline produced via pyrolysis can result in negative carbon footprints, suggesting potential environmental benefits [21]. However, these fuels still have a considerable non-renewable energy footprint, underscoring the need for further optimization of production processes to reduce environmental implications.
Regarding hydrogen, the literature highlights that although hydrogen fuel cell vehicles emit zero tailpipe emissions, hydrogen production can have major environmental impacts [82]. Common production methods, like steam methane reforming and coal gasification, have significant carbon footprints and rely on non-renewable energy sources. Additionally, electrolysis using grid electricity can also have a high carbon footprint if the power is generated from conventional fossil fuel plants [82].
While natural gas and LPG have lower carbon content compared to gasoline or diesel, leading to reduced CO2 emissions, they still contribute to greenhouse gas emissions, as is the nature of a fossil fuel. Additionally, methane emissions from natural gas vehicles can be a concern, as methane is a potent greenhouse gas [34]. The extraction and processing of these fossil-based alternative fuels also have environmental impacts that need to be considered when assessing their overall sustainability. To address these challenges, solutions include the use of life cycle assessments to evaluate the overall environmental impact of fossil-based alternative fuels. However, it is clear that any fossil-based fuel serves only as a temporary solution in the long-term energy transition.
10.2.3. Commercial Challenges
The commercial challenges associated with alternative fuels in land logistics are significant and require careful consideration. A cost comparison of various alternative fuels highlights that hydrogen is the most expensive alternative fuel, followed by biodiesel, methanol, ethanol, compressed air, natural gas, propane, and electricity [82]. The high cost of hydrogen is attributed to the relatively high cost of production, as it requires a significant amount of energy relative to conventional fuels. Overall, literature highlights that the cost of alternative fuels is still higher than that of fossil fuel diesel and gasoline, which poses a challenge for their widespread adoption in the market [82].
A literature study by Tsolakis et al. [34] comparing the market share of alternative fuels in the automobile sector found that despite government incentives and investments to promote the use of natural gas in automotive applications, such programs were not well embraced in several countries, including Germany, the United States, and Japan. The absence of infrastructure is regarded as the primary cause of this low market penetration. Literature also indicates that the market share of electric cars, including plug-in hybrid electric vehicles and battery electric vehicles, remains very low, accounting for only a small percentage of total vehicle sales in most countries [34].
The high production costs of some alternative fuels, such as second-generation biofuels, can also pose a commercial barrier to their widespread adoption. Additionally, the transportation and storage costs of alternative fuels can be considerable, particularly for countries that lack rich biomass resources [44]. This highlights the need for government policies and incentives to promote the commercialization of new technologies and attract investments in alternative fuel production. However, incentivizing demand alone is unlikely to be effective without an incentivized market. In this context, public perception and acceptance of new technologies, such as hydrogen fuel cell vehicles, can be barriers to their widespread adoption despite incentives on the producer side [82]. Concerns regarding safety, potential hydrogen leakage, and the availability of refueling infrastructure may impact public confidence in hydrogen vehicles [82]. Therefore, public education and awareness campaigns should be considered to provide accurate information about the safety measures, technological advancements, and environmental benefits of such alternative fuels to foster greater acceptance [82].
Lastly, the competition between alternative fuels and conventional fossil fuels poses a major commercial challenge. The market share of diesel and gasoline vehicles remains dominant in many countries, with alternative fuels accounting for only a small percentage of total vehicle sales [34]. Government regulations, such as tax incentives, subsidies, and policies, can play a critical role in promoting the adoption of alternative fuels and providing a fair playing field in the market [34]. However, the effectiveness of these policies depends on various factors, including consumer preferences, infrastructure availability, and the overall cost-affordability of alternative fuels compared to traditional fossil fuels [34].
10.2.4. Operational Challenges
The operational challenges related to the alternative fuels in land logistics are diverse. For biofuels, the high viscosity of vegetable oils pose operating concerns in engines, which requires modifications to the engine and/or fuels to ensure adequate compatibility [21]. Additionally, literature emphasizes the need for efficient biofuel handling and storage to avoid the risk of blend separation, which can lead to performance issues in conventional internal combustion engines [21].
Challenges posed by gaseous fuels, such as hydrogen and natural gas, are also discussed in literature domain of land transportation. The low energy density of these fuels requires larger fuel tanks or more frequent refueling, which can impact the operational range and efficiency of vehicles [34]. This is in addition to the lack of widespread refueling infrastructure previously discussed for these fuels which can pose operational challenges, limiting the flexibility and convenience of using these alternative fuels in land-based logistics.
Electric vehicles also face challenges. Electric vehicles are considered to have relatively limited operating range and require regular charging, which limits long-distance travel [44]. Literature emphasizes the need for robust charging infrastructure and efficient charging management systems to ensure the smooth operation of electric vehicles, which is particularly important for a reliable transportation network [44].
The use of alcohols, such as ethanol and methanol, as alternative fuels also poses operational challenges. As previously discussed, their corrosive nature can lead to material compatibility issues in fuel systems, requiring modifications or the use of compatible materials [82]. Additionally, the challenge of cold start and transient operation of vehicles using alcohol fuels due to their low vapor pressure limits their applicable operating windows, which can affect operational performance and reliability [82].
Lastly, the operational challenges associated with the transition from conventional fossil fuels to alternative fuels were also observed in literature. Operationally, literature discusses the need for extensive training and education of personnel involved in the handling, storage, and distribution of alternative fuels to ensure safe and efficient operations [34]. It is important to establish standardized protocols and regulations for the production, transportation, and use of alternative fuels to maintain consistency and reliability in day-to-day operations [34]. Additionally, integrating alternative fuels into the existing supply chain and logistics networks might require considerable modifications and adaptations to ensure seamless operations and minimize disruptions during the transition period [34].
10.2.5. Political/Regulatory Challenges
The importance of government regulations and incentives to promote the adoption of alternative fuels is demonstrated in literature [21]. As already mentioned, the high costs of some alternative fuel technologies, such as advanced biofuels and fuel cell vehicles, can be an obstacle to their commercialization. Governments could play a crucial role in providing financial incentives, such as price controls, tax exemptions, and direct subsidies, to attract investments and support the development of these technologies [21]. Examples of US government policy include the GHG Emissions Standards and Fuel Efficient Standards for MGVs and HGVs, ratified in 2015 aiming for 20% and 24% reductions in land-based freight transportation emissions by 2024 and 2027 respectively [83]. In the EU, Regulation 2019/1242 [84] defines emissions targets for HGV manufacturers aiming for 15% and 30% emissions reductions from new HGVs in 2025 and 2030 respectively [85]. It also promotes the adoption of zero emissions vehicles and penalizes HGV manufacturers at a rate of €4250 per vehicle for every 1 g of CO2 per ton kilometer in exceedance from 2024 onwards [85]. This standard is part of a larger set classified as Euro VI standards which control all harmful vehicle emissions, covering both private and freight vehicles, and are expected to be superseded by a tighter set of limits in the future Euro VII standards [85].
Government policies are not limited to restrictions on conventional fuels; they have also had adapt with the advancement of alternative fuel vehicles. In the EU, the Renewable Energy Directive (RED) initiative sets targets that ramp up the incorporation of sustainable fuels in the transportation energy mix. For example, the RED obliges EU countries to achieve a minimum of at least 14% renewable energy consumption in their transportation sectors by 2030 [86]. It specifically advocates for the adoption of second (and later) generation biofuels by requiring a minimum of 3.5% “advanced biofuels” as part of the aforementioned renewable energy target [86]. Additionally, the Alternative Fuels Infrastructure Regulation (AFIR) promotes the establishment of refueling infrastructure for electric, hydrogen, and LNG vehicles [85]. Specific targets include the requirement of one dedicated HGV electric charger per 60 km along the trans-European transport network (TEN-T) by 2025, with the aim of total network coverage by 2030 [85]. It also requires a hydrogen refueling station per 200 km by 2030, with daily recharging capacities of 1 ton hydrogen at 700 bar [85]. Hydrogen also has dedicated standards, such as EU 79/2009 [87] and EU 406/2010 [88] on requirements for the approval of hydrogen-powered vehicles, among others, owing to the specific challenges posed by hydrogen as a fuel [89].
Due to their production methods, the biofuels industry is rife with political issues. Hence, government policies and regulations play a crucial role in the development of the biofuel industry [44]. For instance, blending mandates, tax incentives, and subsidies can boost the production and use of biofuels [44]. However, it is important to note that these policies can be influenced by competing interests, such as the food industry and environmental concerns, leading to political debates over natural resource usage [44]. This was exemplified in the media frenzy over perceptions of higher food prices, both in the US with the introduction of the Energy Policy Act in 2005, and in the EU with Directive 2003/30/EC [90,91]. Moreover, the effectiveness of biofuel policies can vary across regions, depending on factors such as resource availability, agricultural practices, and socio-economic conditions [44].
The success of the aforementioned policies depends on regional traits and national objectives, which can vary significantly across countries [21]. Furthermore, the lack of a comprehensive and robust refueling infrastructure is a significant obstacle for the widespread adoption of alternative fuels, such as hydrogen and natural gas [34]. The shift towards alternative fuels needs significant changes in the energy system, involving the development of infrastructure, new technologies, and market mechanisms [82]. Considering such infrastructural issues, governments need to invest in accelerating the development of refueling stations, transportation networks, and storage facilities to support the deployment of alternative fuel vehicles. This could include fiscal policy measures such as subsidies and grants to incentivize manufacturers, prompt innovation, and fund the transition to a new refueling infrastructure [83]. However, literature highlights that the allocation of resources and the coordination between different stakeholders, including government entities, fuel providers, and automotive manufacturers, can be politically challenging [34]. Additionally, political instability, changes in government priorities, and resistance from incumbent industries can create uncertainties and obstacles to the deployment of alternative fuels for land logistics [82]. Literature also highlights the need to make demonstration projects more effective by focusing on reducing the end-user cost and meeting customer needs rather than acting as public relations stunts to support political agendas [90].
Political challenges related to the international trade of alternative fuels and technologies were also identified. The need for harmonized standards and regulations across countries to facilitate the cross-border movement of alternative fuels and vehicles was discussed in literature [34], emphasizing the significance of international cooperation and sharing knowledge to quicken the development and deployment of alternative fuel technologies [34]. However, political tensions, trade disputes, and divergent national interests can impede the establishment of a global framework for alternative fuels [34]. This is reflected in the literature which demonstrates that fuel savings tests conducted in the lab and on a commercial scale vary considerably by region, owing to different vehicle standards, speeds, and size limits [90]. Therefore, governments need to engage in multilateral dialogues to address these challenges and promote a coordinated approach to the transition towards sustainable land logistics [34].
10.3. Alternative Fuels in Sea Logistics
The challenges faced by alternative fuels in marine logistics are shared with other modes of transport, with literature focusing more on the technical issues such as engine retrofitting requirements and ship design overhauls, as well as commercial issues related to the availability of alternative fuels at bunkering locations. Although alternative marine fuels pose a new set of environmental risks, they tend to be a step in the right direction in comparison to conventional marine fuels. However, further research is needed to study the lifecycle emissions of newer fuels like hydrogen and ammonia. The main operational risks identified are safety related. Literature emphasizes the importance of various policy interventions to incentivize further adoption and innovation of alternative marine fuels.
10.3.1. Technical/Technological Challenges
Although emissions capturing technologies with conventional marine fuels have been discussed in the extant literature, these technologies compromise onboard space availability and are not considered sustainable solutions [31]. Even though biofuels do not require extensive engine modifications to ensure compatibility with conventional marine propulsion systems, some level of modification is still necessary, covering both the engine and the fuel tank [22]. The organic vegetable oil composition of biodiesel increases its viscosity, leading to difficult pumping characteristics and engine fouling, which justifies the blending limit with MDO [22]. Other technical challenges with biodiesel include its lower volatility (higher vaporization rates), gum/wax formation in the engines, lower stability, and higher NOx emissions relative to conventional marine fuels [31]. Biodiesel has specific material requirements to avoid engine reliability issues due to its organic composition [31]. Biodiesel sourced specifically from first generation biomass has a higher tendency to plug fuel system filters, decreasing engine reliability [72]. Additional measures are required to prevent water contaminating the biodiesel reserve, as this creates an environment conducive to biological fouling mechanisms in the fuel system [72]. These compatibility challenges are exacerbated by the lack of incentives for engine manufacturers to create new models that are easily retrofitted for biodiesel compatibility [72]. The feedstock issue of using biofuels applies similarly to other modes of transport (i.e., competition for land and water use).
Several limitations of LNG were previously discussed, namely its density disadvantage, which requires 3–4 times higher storage volumes onboard to achieve the equivalent calorific value of MDO [72], as shown in Figure 12.
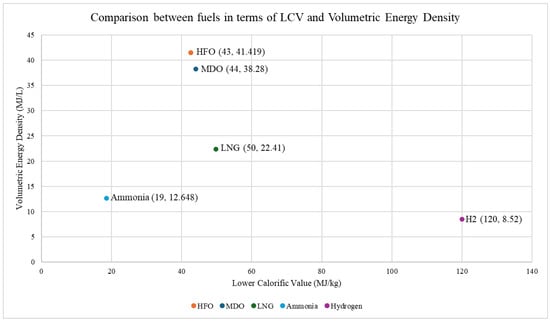
Figure 12.
Mass-based and volume-based energy densities of marine fuels. HFO = heavy fuel oil, MDO = marine diesel oil, LNG = liquified natural gas. Adapted under Creative Commons CC BY license from Ref. [92].
Although retrofitting diesel engines to run on LNG has been demonstrated, LNG use is primarily reserved for new ships that incorporate LNG as the main or secondary fuel during the design phase due to the extensive engine, fuel system, and storage space modifications [72]. Special requirements include cryogenic storage tanks with conditioning systems to keep the LNG liquified, fuel transfer piping, vapor space ventilation, and added safety barriers to handle the LNG at the bunkering station and in the engine room itself [23]. These requirements are needed due to the supercooled state of LNG, resulting in continuous evaporation during storage [22].
Similar challenges are faced with cryogenic hydrogen storage, and an economic solution is yet to be developed [22]. Hydrogen not only has a lower volume-based heating value, but also a lower density relative to conventional marine fuels, requiring larger storage space and engines [22,31]. Storage in insulated tanks means that energy losses are inevitable over time [23]. The high pressure storage requirements also reduces the inherent safety of the fuel onboard [22]. Compressed hydrogen requires 10–20 times more storage space (depending on the pressure) relative to conventional marine fuels, while cryogenic liquid hydrogen requires 4–5 times more storage space but necessitates additional insulation due to its low temperature [31]. Hydrogen use in an engine increases the chances of suboptimal combustion, leading to preignition or engine knocking, due to its low ignition energy and wide flammability limits [31]. This is to the extent that pure hydrogen ignition in compression engines perform poorly without pre-injection with a pilot fuel (such as MDO) to compensate [31].
The storage space dilemma applies further to the use of alcohols, as previously indicated. Both biomethanol and bioethanol require approximately twice the storage space since they have about half the density of conventional fuels [31]. Such alcohols are also known to cause corrosion issues due to material incompatibility [31]. Alcohols cannot directly replace conventional marine fuels due to their properties, such as lower cetane number, high heat of vaporization, and higher autoignition temperature [23]. They possess poorer lubrication properties [23].
Renewable energy sources and battery electric systems have not been discussed in the context of sea logistics due to their significant limitations. Onboard wind or solar power generation is highly dependent on weather conditions, temperature, wind speed and direction, barometric pressure, and solar irradiation [22]. Consequently, the inherent uncertainty of supply limits the viability of these forms of alternative fuels. Similar to other modes of transport, the low energy density of batteries restricts their application in international freight operations, although they can still be used to power auxiliary units [31].
Hence, it is clear that there are various technical issues in applying alternative fuels in marine logistics, but the area is not a dead end. Studies are ongoing to make the onboard and bunkering storage of cryogenic fuels, such as liquid hydrogen and LNG, more feasible [22]. Research is also required to overcome the climate-sensitive nature of renewable fuels, possibly through high-capacity energy storage solutions or expanding their use to power more onboard systems [22]. Engine compatibility issues can be mitigated for several of the aforementioned fuels through focused research and development, enabling the use of higher quantities of LNG and biofuels to advance the energy transition [31]. Such research avenues include improving the efficiency of dual-fuel engines [31].
10.3.2. Environmental Challenges
As discussed previously, biofuels result in higher NOx emissions, so they do not objectively improve all emissions characteristics during use. It is also evident that biofuels using first-generation biomass are not sustainable due to their impact on land use and water consumption. Even if first generation biofuels were used, it is not expected to be sufficient to meet the needs of the shipping industry in 2050 [31]. The literature suggests that there is not enough arable land available globally to meet the anticipated fuel demand [31]. This holds true even if second and third-generation biofuels are considered, as the biofuels production process still requires biomass feedstock and water [31]. Consequently, biofuels for marine logistics are not a reliable fuel option due to uncertainty in supply. Literature also questions the overall carbon neutrality of biofuels in general, owing to its dependency on the feedstock type and source [31].
Although operational emissions are generally reduced with LNG, the main issue with this alternative fuel is methane slip, where stored natural gas is released into the atmosphere [81]. This is a serious setback since methane has 28–34 times the global warming impact relative to an equivalent CO2 molecule [22]. This phenomenon dampens the perceived GHG benefits of using LNG versus conventional marine fuels by as much as 10% [72]. Despite the reduced NOx emissions claimed for alcohols, the use of pure methanol in modern engines is insufficient to satisfy IMO Tier 3 limits, which apply exclusively in ECAs [74]. For other fuels, such as hydrogen and ammonia, their use in marine logistics is relatively immature, resulting in inconsistent emissions data from studies [22]. Overall, the extant literature suggests that no single alternative fuel consistently abates GHG emissions across the supply chain. Newer fuels like hydrogen and battery electric tend to shift their emissions upstream. Although green methods for producing hydrogen, ammonia, and electricity exist, the current production volumes are insufficient to meet the demands of the marine logistics sector [93].
10.3.3. Commercial Challenges
Biofuels pose logistical challenges in meeting refueling demand at existing bunkering stations worldwide [22]. In addition, biofuels come at a cost premium compared to conventional marine fuels [22,31]. Similar challenges exist for LNG, as establishing a reliable supply chain is vital prior to its widespread adoption as a fuel [22]. It also incurs significant costs for engine retrofitting, LNG storage tanks, and associated safety requirements [22,23]. In particular, ship operators expect a positive return on investment within the useful operating life of their ships, which is challenging in the short term due to the capital expenditure required for ship modifications and the limited availability of LNG bunkering locations [22]. Biomethane (in liquid form) poses similar challenges to its fossil fuel LNG counterpart, with difficulties expected in transportation and storage [31]. The literature advises against building new ships and infrastructure to accommodate biomethane due to its limited availability compared to LNG, higher price, and tighter requirements [31]. Alternative fuels such as LNG, biomethane, and hydrogen, have unstable prices that vary by region owing to the current state of the supply chain [93]. The regional variations in natural gas prices over time are illustrated in Figure 13.
Figure 13.
Natural gas prices ($/MWh) from 1990–2022. Reproduced under Creative Commons CC BY license from Ref. [94].
For hydrogen to become a viable option, its cost must be reduced considerably, with apparent economies of scale benefits to justify bulk purchasing and storage [22]. Newer alternative fuels, such as ammonia and hydrogen, face poorly developed infrastructure and supply chains, leading to high costs of production, transportation, and storage [22]. The high-pressure, low temperature storage requirements for cryogenic hydrogen increase operating costs of transport and storage, while reducing onboard cargo space [31]. Alternatively, maintaining existing cargo space while storing a lower energy content of hydrogen reduces travel distances, making hydrogen a less competitive option compared to conventional fuels or LNG [31].
Alcohols, such as methanol, are also more expensive to produce. The literature suggests renewable methanol as being 1.5–4 times more expensive relative to methanol produced from fossil fuels [31]. Even when used in dual-fuel engines, high capital costs are incurred in converting existing engines for compatibility and adding the required safety elements in the engine room [23].
Consequently, it is apparent that feedstock limitations and production costs limit the reach of alternative fuels commercially in sea freight. However, these challenges present opportunities. For example, bunkering ports supplying LNG are likely to experience higher traffic and thus become more profitable, recouping their investment in the LNG supply chain [22]. Strategically, bunkering ports supplying biofuels can become profitable if located near ECAs, offering ship operators a convenient option to comply with emissions requirements in ECAs [72].
10.3.4. Operational Challenges
Although low-sulfur variants of conventional marine fuels can be produced, they require special precautions during engine transitioning to avoid impacting the engine’s operating life and causing technical issues [22]. For example, between 2009–2011, more than half of the marine engine propulsion incidents reported in California were due to using low-sulfur variants of conventional marine fuels in existing engines [22]. Other fuels pose safety risks during handling and onboard storage. For example, ammonia poses a high risk of catching fire due to its flammability range, and its vapors are toxic to humans, necessitating careful transportation and handling [31,47]. It also requires gaseous (hydrogen or methane) or conventional fuel additives to achieve sufficient ignition properties [47]. Similarly, methanol is acutely toxic to humans, requiring precautions to avoid inhalation, ingestion, or skin contact [31].
10.3.5. Political/Regulatory Challenges
As with other modes of transport, alternative fuels are unlikely to become competitive in marine logistics without established policy support. It is crucial to assess the impact of newly introduced local, regional, and international policies on the marine fuel market to evaluate their relative success or failure [22]. The literature suggests the need for global policy coordination, where multidisciplinary experts ensure consistency in the goals stated in such policies and their interrelationships [22]. Policy makers require strong collaboration across stakeholders, from researchers and fuel producers to ship designers and port managers, to pave the way for alternative fuels to become more technologically and economically feasible [22]. The literature suggests the use of mechanisms to distribute the risk across stakeholders in preventing withdrawal of support due to parties perceiving an uneven risk exposure relative to other stakeholders [22].
At a higher level, there are two paths for policy makers to contribute towards the adoption of alternative marine fuels: traditional measures and market-based measures. Traditional measures take the form of strict emissions requirements that require compliance to avoid incurring financial burdens. An example of this is the IMO’s introduction of the Energy Efficiency Design Index for Existing Ships, the Carbon Intensity Indicator, and the Enhanced Ship Energy Efficiency Management Plan, which took effect in 2023 [93]. Such measures are effective in reducing emissions in marine logistics as the transparency in emissions generation throughout the supply chain are apparent, encouraging the industry to adopt more sustainable alternatives [93]. The downside of traditional methods is that they encourage compliance with no motivation to innovate or improve performance beyond what is required by the regulatory limits [93]. Market-based methods, including examples such as the cap-and-trade system and the emissions offset schemes, could push for the adoption of innovative technologies [93]. Examples proposed in literature specific to marine logistics are the bunker levy, which taxes conventional marine fuel bunkering to fund emissions reduction measures; the GHG fund, similar to bunker levy but with voluntary contributions; and the establishment of a global maritime emissions trading scheme, which involves trading emissions allowances in an international market [93].
11. Results
This section highlights the outcome of the review in terms of the current state of sustainable logistics and highlights the leading alternative fuel candidates for each freight sector along with their primary barriers to further adoption.
11.1. State of Sustainable Logistics
As companies strives to enhance the efficiency of their transportation networks, they often adopt practices that negatively impact the environment. The literature highlights the importance of decarbonizing land logistics, given its significant contribution to global emissions. Over time, customers have become more environmentally conscious, demanding greater transparency in corporate sustainability efforts. This shift offers companies the opportunity to improve their reputation without necessarily increasing costs. Meanwhile, regulators are imposing tighter restrictions on freight emissions.
Aside from alternative fuels, strategies for adopting sustainable logistics include design elements such as fuel-efficient vehicle designs and IT innovations like optimized mapping routes. Other strategies involve using sustainable packaging materials and investing in human resources to spread awareness of best practices in driving. However, increasing interest in fuel conservation and efficiency has eventually shifted the spotlight onto alternative fuels as a potential avenue to be exploited to gain a competitive advantage.
11.2. Promising Alternative Fuels by Transportation Mode
The fuels addressed in this study, as outlined by the research methodology, include multigenerational biofuels, alcohols, hydrogen, ammonia, electricity, nuclear, biomethane, biogas, sustainably-sourced conventional fuels such as e-fuels (FT–PTL, green hydrogen), and biokerosene (ATJ–SPK and HEFA–SPK).
In air logistics, HEFA–SPK is considered the most promising option due to its proven use in SAF and higher technical maturity of its production pathway, giving it the greatest scale-up potential relative to the alternatives. However, all biomass-based fuels rely heavily on sustainable biomass sourcing, which remains a key challenge for this pathway. In land logistics, electric vehicles are viewed as the leading candidate, primarily due to the rapid scale-up of commercial recharging infrastructure and advancements in battery capacity and electric drivetrains. Nonetheless, the literature highlights that the cost of infrastructure upgrades needs to decrease to facilitate adoption, and long-haul freight vehicle designs are lagging behind the progress seen in electric passenger vehicles. In sea logistics, LNG is currently the most popular alternative fuel due to its use in international freighters and its superior emissions performance over conventional marine fuels. It is expected to continue as a transitional fuel with the introduction of stricter regulations. However, challenges related to storage, both onboard and onshore, as well as methane slip control, limit its broader adoption.
12. Conclusions
The purpose of this study was to conduct an in-depth literature review on the role of alternative fuels in sustainable logistics, focusing on the transportation component, which constitutes the largest cost in logistics. The review includes both fossil-based fuels, such as natural gas, LPG, and LNG, and non-fossil-based fuels typically characterized as alternative fuels. While there is a wealth of literature covering various aspects of alternative fuels—ranging from production pathway, synthesis methods, and performance characterization to economic viability, environmental impacts, and regulatory hurdles—this study contributes to the field by synthesizing and structuring the recent literature into a comprehensive format focused on the freight sector.
This review distils the macro-level characteristics of alternative fuels into a structured thematic review, rather than exploring specific characteristics in detail. It categorizes the challenges associated with alternative fuels using the TECOP framework, making the complex issues more accessible to stakeholders with a vested interest in overcoming these challenges, including policymakers, industry players, and researchers. Each set of alternative fuels presents its own unique challenges, many of which are shared across the three major modes of logistics, and those challenges are highlighted to direct future studies in exploiting those areas of opportunity. The extant literature consistently highlights the need for additional market incentives and regulatory interventions to sustain momentum in alternative fuels research and development among producers, engine and vehicle manufacturers, and researchers. Business-as-usual projections suggest that running future logistics networks at higher capacities will not effectively address the climate crisis. Instead, innovative solutions leveraging technological advancements to decarbonize freight transportation are crucial, with alternative fuels playing a vital role during and after the energy transition.
Author Contributions
A.A.A.-M.: conceptualization, methodology, writing—original draft, writing—review and editing, and project administration. K.E.: resources, supervision, and writing—review and editing. M.E.: writing—review and editing, and funding acquisition. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The APC was funded by the Supply Chain Innovation and Resilience Lab (SCIRL) at the University of Miami’s Miami Institute of Clean Energy (MinCE).
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study. Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Jacobson, M.Z.; Delucchi, M.A.; Bazouin, G.; Bauer, Z.A.F.; Heavey, C.C.; Fisher, E.; Morris, S.B.; Piekutowski, D.J.Y.; Vencill, T.A.; Yeskoo, T.W. 100% Clean and Renewable Wind, Water, and Sunlight (WWS) All-Sector Energy Roadmaps for the 50 United States. Energy Environ. Sci. 2015, 8, 2093–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smil, V. Energy Transitions: Global and National Perspectives. Available online: https://ourworldindata.org/grapher/global-energy-substitution (accessed on 28 May 2024).
- Energy Institute Statistical Review of World Energy. Available online: https://ourworldindata.org/grapher/global-energy-substitution (accessed on 28 May 2024).
- Ahmed, A.; Al-Amin, A.Q.; Ambrose, A.F.; Saidur, R. Hydrogen Fuel and Transport System: A Sustainable and Environmental Future. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 1369–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omer, A.M. Energy, Environment and Sustainable Development. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2008, 12, 2265–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyring, V.; Corbett, J.J.; Lee, D.S.; Winebrake, J.J. Brief Summary of the Impact of Ship Emissions on Atmospheric Composition, Climate, and Human Health; Health and Environment Sub-Group of the International Maritime Organization: London, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, M.W.; Peters, G.P.; Gasser, T.; Andrew, R.M.; Schwingshackl, C.; Gütschow, J.; Houghton, R.A.; Friedlingstein, P.; Pongratz, J.; Le Quéré, C. National Contributions to Climate Change Due to Historical Emissions of Carbon Dioxide, Methane and Nitrous Oxide. Available online: https://ourworldindata.org/grapher/ghg-emissions-by-gas (accessed on 28 May 2024).
- McKinnon, A.C.; Cullinane, S.; Browne, M.; Whiteing, A. (Eds.) Green Logistics: Improving the Environmental Sustainability of Logistics; Kogan Page: London, UK, 2010; ISBN 978-0-7494-5678-8. [Google Scholar]
- Aguilar, P.; Groß, B. Battery Electric Vehicles and Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles, an Analysis of Alternative Powertrains as a Mean to Decarbonise the Transport Sector. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2022, 53, 102624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhan, C.; Verma, L.; Singh, J. Alternative Fuels for Sustainable Development. In Environmental Concerns and Sustainable Development; Shukla, V., Kumar, N., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 317–331. ISBN 9789811358883. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.L. Don’t Tweak Your Supply Chain—Rethink It End to End. Available online: https://hbr.org/2010/10/dont-tweak-your-supply-chain-rethink-it-end-to-end (accessed on 21 February 2024).
- Dey, A.; LaGuardia, P.; Srinivasan, M. Building Sustainability in Logistics Operations: A Research Agenda. Manag. Res. Rev. 2011, 34, 1237–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassini, E.; Surti, C.; Searcy, C. A Literature Review and a Case Study of Sustainable Supply Chains with a Focus on Metrics. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2012, 140, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Berishy, N.; Rügge, I.; Scholz-Reiter, B. The Interrelation between Sustainability and Green Logistics. IFAC Proc. Vol. 2013, 46, 527–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SCDigest Editorial Staff. Supply Chain Graphic of the Week: US Logistics Cost Breakdown. Available online: https://www.scdigest.com/assets/newsviews/13-06-28-1.php?cid=7193ut (accessed on 3 June 2024).
- Grant, D.B.; Trautrims, A.; Wong, C.Y. Sustainable Logistics and Supply Chain Management: Principles and Practices for Sustainable Operations and Management, 2nd ed.; Kogan Page: New York, NY, USA, 2017; ISBN 978-0-7494-7827-8. [Google Scholar]
- Gray, N.; McDonagh, S.; O’Shea, R.; Smyth, B.; Murphy, J.D. Decarbonising Ships, Planes and Trucks: An Analysis of Suitable Low-Carbon Fuels for the Maritime, Aviation and Haulage Sectors. Adv. Appl. Energy 2021, 1, 100008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruamsook, K.; Thomchick, E.A. Sustainable Freight Transportation: A Review of Strategies; AgEcon Search: Tampa, FL, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Elhedhli, S.; Merrick, R. Green Supply Chain Network Design to Reduce Carbon Emissions. Transp. Res. D Transp. Environ. 2012, 17, 370–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Energy Agency The Future of Trucks: Implications for Energy and the Environment. Available online: https://iea.blob.core.windows.net/assets/a4710daf-9cd2-4bdc-b5cf-5141bf9020d1/TheFutureofTrucksImplicationsforEnergyandtheEnvironment.pdf (accessed on 21 February 2024).
- Navas-Anguita, Z.; García-Gusano, D.; Iribarren, D. A Review of Techno-Economic Data for Road Transportation Fuels. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 112, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Enazi, A.; Okonkwo, E.C.; Bicer, Y.; Al-Ansari, T. A Review of Cleaner Alternative Fuels for Maritime Transportation. Energy Rep. 2021, 7, 1962–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deniz, C.; Zincir, B. Environmental and Economical Assessment of Alternative Marine Fuels. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 113, 438–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldi, F.; Ahlgren, F.; Melino, F.; Gabrielii, C.; Andersson, K. Optimal Load Allocation of Complex Ship Power Plants. Energy Convers. Manag. 2016, 124, 344–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hileman, J.I.; Stratton, R.W. Alternative Jet Fuel Feasibility. Transp. Policy 2014, 34, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, S.; Braun-Unkhoff, M.; Naumann, C.; Riedel, U. Paths to Alternative Fuels for Aviation. CEAS Aeronaut. J. 2018, 9, 389–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera, E.; De Sousa, J.M.M. Use of Sustainable Fuels in Aviation—A Review. Energies 2022, 15, 2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, N.; Atmanli, A. Sustainable Alternative Fuels in Aviation. Energy 2017, 140, 1378–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jørsfeldt, L.M.; Hvolby, H.-H.; Nguyen, V.T. Implementing Environmental Sustainability in Logistics Operations: A Case Study. Strateg. Outsourcing Int. J. 2016, 9, 98–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieb, K.J.; Lieb, R.C. Environmental Sustainability in the Third-party Logistics (3PL) Industry. Int. J. Phys. Distrib. Logist. Manag. 2010, 40, 524–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, H.; Stuart, C.; Spence, S.; Chen, H. Alternative Fuel Options for Low Carbon Maritime Transportation: Pathways to 2050. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 297, 126651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabil, D.H.; Rahman, M.H.; Chowdhury, A.H.; Menezes, B.C. Managing Supply Chain Performance Using a Real Time Microsoft Power BI Dashboard by Action Design Research (ADR) Method. Cogent Eng. 2023, 10, 2257924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colicchia, C.; Marchet, G.; Melacini, M.; Perotti, S. Building Environmental Sustainability: Empirical Evidence from Logistics Service Providers. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 59, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsolakis, A.; Bogarra, M.; Herreros, J. Road Vehicle Technologies and Fuels. In Issues in Environmental Science and Technology; Harrison, R.M., Hester, R.E., Eds.; Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 2017; pp. 1–24. ISBN 978-1-78262-892-7. [Google Scholar]
- Bellona, S. Justifying Energy Efficiency as Oil Prices Tumble. Chron. High. Educ. 2009, 55, A14. [Google Scholar]
- Mersin, K.; Bayirhan, İ.; Gazioglu, C. Review of CO2 Emission and Reducing Methods in Maritime Transportation. Therm. Sci. 2019, 23, 2073–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FedEx 2024 ESG Report. Available online: https://www.fedex.com/content/dam/fedex/us-united-states/sustainability/gcrs/FedEx_2024_ESG_Report.pdf (accessed on 29 July 2024).
- Hosseini, S.E.; Wahid, M.A. Hydrogen Production from Renewable and Sustainable Energy Resources: Promising Green Energy Carrier for Clean Development. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 57, 850–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, J.K.; Saini, R.; Tewari, L. Lignocellulosic Agriculture Wastes as Biomass Feedstocks for Second-Generation Bioethanol Production: Concepts and Recent Developments. 3 Biotech 2015, 5, 337–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aruwajoye, G.; Kassim, A.; Saha, A.; Kana, E. Prospects for the Improvement of Bioethanol and Biohydrogen Production from Mixed Starch-Based Agricultural Wastes. Energies 2020, 13, 6609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Dhurandhar, R.; Chakrabortty, S.; Ghosh, A.K. Chapter 12—Downstream Process: Toward Cost/Energy Effectiveness. In Handbook of Biofuels; Sahay, S., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2022; pp. 249–260. ISBN 978-0-12-822810-4. [Google Scholar]
- Cavelius, P.; Engelhart-Straub, S.; Mehlmer, N.; Lercher, J.; Awad, D.; Brück, T. The Potential of Biofuels from First to Fourth Generation. PLoS Biol. 2023, 21, e3002063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietrzak, W.; Kawa-Rygielska, J. Simultaneous Saccharification and Ethanol Fermentation of Waste Wheat–Rye Bread at Very High Solids Loading: Effect of Enzymatic Liquefaction Conditions. Fuel 2015, 147, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Loo, B.P.Y. Alternative and Transitional Energy Sources for Urban Transportation. Curr. Sustain./Renew. Energy Rep. 2014, 1, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shonhiwa, C.; Makaka, G.; Mukumba, P.; Shambira, N. Biogas Valorisation to Biomethane for Commercialisation in South Africa: A Review. Energies 2023, 16, 5272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Jain, S.; Ps, V.; Tiwari, A.K.; Nouni, M.R.; Pandey, J.K.; Goel, S. Hydrogen: A Sustainable Fuel for Future of the Transport Sector. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 51, 623–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stančin, H.; Mikulčić, H.; Wang, X.; Duić, N. A Review on Alternative Fuels in Future Energy System. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 128, 109927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauen, A.; Bitossi, N.; German, L.; Harris, A.; Leow, K. Sustainable Aviation Fuels: Status, Challenges and Prospects of Drop-in Liquid Fuels, Hydrogen and Electrification in Aviation. Johns. Matthey Technol. Rev. 2020, 64, 263–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierra BioFuels Plant & Feedstock Processing Facility. Available online: https://fulcrumnorthpoint.com/the-plans/ (accessed on 25 September 2024).
- REWOFUEL-REsidual Soft WOod Conversion to High Characteristics Drop-in bioFUELs. Available online: https://www.rewofuel.eu/ (accessed on 22 February 2024).
- Bio4A. Advanced Sustainable Biofuels for Aviation. Available online: https://www.bio4a.eu/ (accessed on 22 February 2024).
- Banke, J. Technology Readiness Levels Demystified. Available online: https://www.nasa.gov/aeronautics/technology-readiness-levels-demystified/ (accessed on 24 February 2024).
- Directorate of Technology, Engineering, and Quality (TEC) Technology Readiness Levels Handbook for Space Applications (TEC-SHS/5551/MG/Ap). Available online: https://connectivity.esa.int/sites/default/files/TRL_Handbook.pdf (accessed on 24 February 2024).
- NASA/Airspace Systems (AS). NASA TRL Meter. Available online: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:NASA_TRL_Meter.png (accessed on 29 May 2024).
- Neste. Neste Celebrates the Opening of the Singapore Expansion and Establishes a Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF) Supply Chain to Changi Airport. Available online: https://www.neste.sg/releases-and-news/renewable-solutions/neste-celebrates-opening-singapore-expansion-and-establishes-sustainable-aviation-fuel-saf-supply (accessed on 24 February 2024).
- United. Our Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF) Program. Available online: https://www.united.com/en/us/fly/company/responsibility/sustainable-aviation-fuel.html (accessed on 23 February 2024).
- Lufthansa Group. Sustainable Aviation Fuel. Available online: https://www.lufthansagroup.com/en/responsibility/climate-environment/sustainable-aviation-fuel.html (accessed on 23 February 2024).
- KLM. KLM Further Expands Approach for Sustainable Aviation Fuel. Available online: https://klmf.ly/3tgT2fg (accessed on 23 February 2024).
- Bioenergy International Red Rock Biofuels Signs Biojet Fuel Off-Take Agreement with FedEx Express. Available online: https://bioenergyinternational.com/red-rock-biofuels-signs-biojet-fuel-off-take-agreement-with-fedex-express/ (accessed on 23 February 2024).
- Heimel, S.; Lowe, C. Technology Comparison of CO2 Capture for a Gas-to-Liquids Plant. Energy Procedia 2009, 1, 4039–4046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Basics of SAF Technology. Available online: https://skynrg.com/sustainable-aviation-fuel/technology-basics/ (accessed on 23 February 2024).
- Hyundai. Hyundai and Hydrospider to Build Industrial Hydrogen Ecosystem. Available online: https://www.hyundai.news/uk/articles/press-releases/hyundai-and-hydrospider-to-build-industrial-hydrogen-ecosystem.html#:~:text=Partnership%20is%20forged%20among%20Hyundai,clean%20transportation%20of%20the%20future (accessed on 24 February 2024).
- Daimler Truck AG. Fuel-Cell Technology: Daimler Truck Builds First Mercedes-Benz GenH2 Truck Customer-Trial Fleet. Available online: https://www.daimlertruck.com/en/newsroom/pressrelease/fuel-cell-technology-daimler-truck-builds-first-mercedes-benz-genh2-truck-customer-trial-fleet-52552943?basket_case=fuel-cell-technology-daimler-truck-builds-first-mercedes-benz-genh2-truck-customer-trial-fleet-52552943&cHash=87bc672a770d75159c2d92c56fe5ed81 (accessed on 24 February 2024).
- Lizbetin, J.; Bartuska, L.; Rakhmangulov, A. Comparative Analysis of Alternative Fuels Used in Road Transport. Komunikácie 2017, 19, 86–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Videgain Barranco, P.; Covrig, C.F. Case Study: Vehicle-to-Grid and/or Vehicle-to-Home Round Trip Efficiency; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Richardson, D.B. Electric Vehicles and the Electric Grid: A Review of Modeling Approaches, Impacts, and Renewable Energy Integration. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 19, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatne, Å.; Molinas, M.; Foosnas, J.A. Analysis of a Scenario of Large Scale Adoption of Electrical Vehicles in Nord-Trøndelag. Energy Procedia 2012, 20, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Banawan, A.A.; El Gohary, M.M.; Sadek, I.S. Environmental and Economical Benefits of Changing from Marine Diesel Oil to Natural-Gas Fuel for Short-Voyage High-Power Passenger Ships. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. 2010, 224, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raising the Readiness of Zero-Emission Waterborne Transport. Available online: https://flagships.eu/about/ (accessed on 25 February 2024).
- HySHIP–Hydrogen Cargo Vessel. Available online: https://maritimecleantech.no/project/hyship-hydrogen-cargo-vessel/ (accessed on 25 February 2024).
- ShipFC. About. Available online: https://shipfc.eu/about/ (accessed on 25 February 2024).
- Kołwzan, K.; Narewski, M. Alternative Fuels for Marine Applications. Latv. J. Chem. 2012, 51, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taljegard, M.; Brynolf, S.; Grahn, M.; Andersson, K.; Johnson, H. Cost-Effective Choices of Marine Fuels in a Carbon-Constrained World: Results from a Global Energy Model. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 12986–12993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inal, O.B.; Deniz, C. Assessment of Fuel Cell Types for Ships: Based on Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 265, 121734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tronstad, T.; Åstrand, H.H.; Haugom, G.P.; Langfeldt, L. Study on the Use of Fuel Cells in Shipping; European Maritime Safety Agency: Lisbon, Portugal, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Schuelke-Leech, B.-A.; Leech, T.C. The Viability of Nuclear Power as an Alternative to Renewables for Clean Energy for Climate Change Mitigation. In Renewable Energy for Mitigating Climate Change; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2021; ISBN 978-1-00-324012-9. [Google Scholar]
- Ansell, P.J. Review of Sustainable Energy Carriers for Aviation: Benefits, Challenges, and Future Viability. Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 2023, 141, 100919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alternative Aviation Fuels: Overview of Challenges, Opportunities, and Next Steps; USDOE Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy (EERE): Washington, DC, USA, 2017.
- Sustainable Alternative Fuels for Aviation (SUSTAF) Experts Group of the International Civil Aviation Organization. 2013. The Future of Trucks: The Challenges for the Development and Deployment of Sustainable Alternative Fuels in Aviation. Available online: https://www.icao.int/environmental-protection/GFAAF/Documents/ICAO%20SUSTAF%20experts%20group%20outcomes_release%20May2013.pdf (accessed on 16 March 2024).
- Heyne, J.; Rauch, B.; Le Clercq, P.; Colket, M. Sustainable Aviation Fuel Prescreening Tools and Procedures. Fuel 2021, 290, 120004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiaramonti, D. Sustainable Aviation Fuels: The Challenge of Decarbonization. Energy Procedia 2019, 158, 1202–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enoma, N.; Inikori, I.; Kwasi-Effah, C.C.; Charles, A.; Ovuru, P.D.; Aduwenye, B.K. A Comprehensive Review of Alternative Fuels for Automobiles: Benefits, Challenges and Future Direction. J. Sci. Technol. Res. 2022, 4, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abad, A.V. Selection of Low Carbon Technologies for Heavy Goods Vehicles. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Southampton, Southampton, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Regulation 2019/1242; Setting CO2 Emission Performance Standards for New Heavy-Duty Vehicles and Amending Regulations (EC) No 595/2009 and (EU) 2018/956 of the European Parliament and of the Council and Council Directive 96/53/EC. Publications Office of the European Union: Brussels, Belgium, 2019.
- Hashvitha, R. Sustainable Supply Chain Transportation. Master’s Thesis, Aalto University, Espoo, Finland, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. Biofuels. Available online: https://energy.ec.europa.eu/topics/renewable-energy/bioenergy/biofuels_en (accessed on 5 April 2024).
- EU 79/2009; On Type-Approval of Hydrogen-Powered Motor Vehicles, and Amending Directive 2007/46/EC. Publications Office of the European Union: Brussels, Belgium, 2009.
- EU 406/2010; Implementing Regulation (EC) No 79/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council on Type-Approval of Hydrogen-Powered Motor Vehicles. Publications Office of the European Union: Brussels, Belgium, 2010.
- Huertes Gara, P.; del Mar Llomparte Juame, M. Standards, Codes and Regulations of Hydrogen Refueling Stations and Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicles. Bachelor’s Thesis, Université de technologie de Belfort Montbéliard, Montbéliard, France, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Browne, D.; O’Mahony, M.; Caulfield, B. How Should Barriers to Alternative Fuels and Vehicles Be Classified and Potential Policies to Promote Innovative Technologies Be Evaluated? J. Clean. Prod. 2012, 35, 140–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 2003/30/EC; On the Promotion of the Use of Biofuels or Other Renewable Fuels for Transport. Publications Office of the European Union: Brussels, Belgium, 2003.
- Bertagna, S.; Kouznetsov, I.; Braidotti, L.; Marino, A.; Bucci, V. A Rational Approach to the Ecological Transition in the Cruise Market: Technologies and Design Compromises for the Fuel Switch. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wright, L.A. A Comparative Review of Alternative Fuels for the Maritime Sector: Economic, Technology, and Policy Challenges for Clean Energy Implementation. World 2021, 2, 456–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Energy Institute Based on S&P Global Platts Natural Gas Prices. Available online: https://ourworldindata.org/grapher/natural-gas-prices (accessed on 29 May 2024).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).