Retrospectively Quantified T2 Improves Detection of Clinically Significant Peripheral Zone Prostate Cancer
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
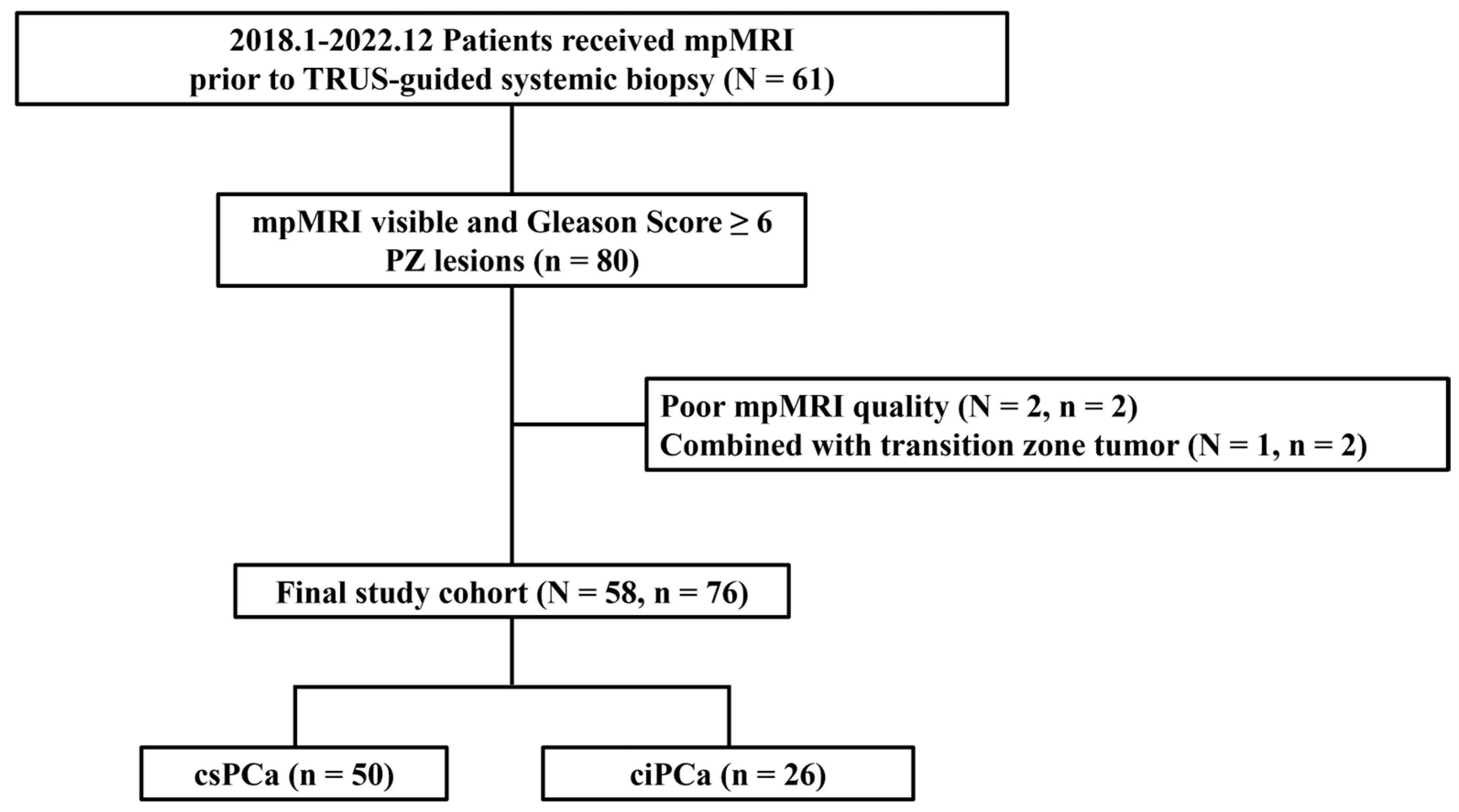
2.1. Patient Population and Data Acquisition
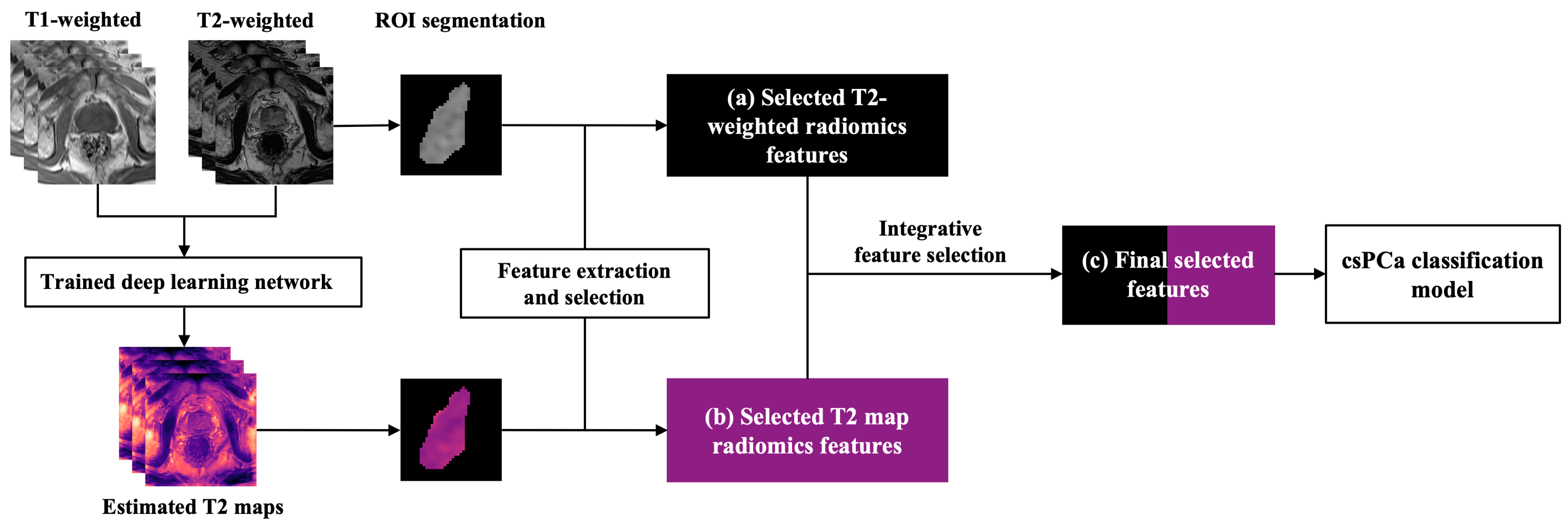
2.2. Data Generation and Preprocessing
2.3. Radiomics Analysis
2.3.1. Feature Extraction
2.3.2. Model Development
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
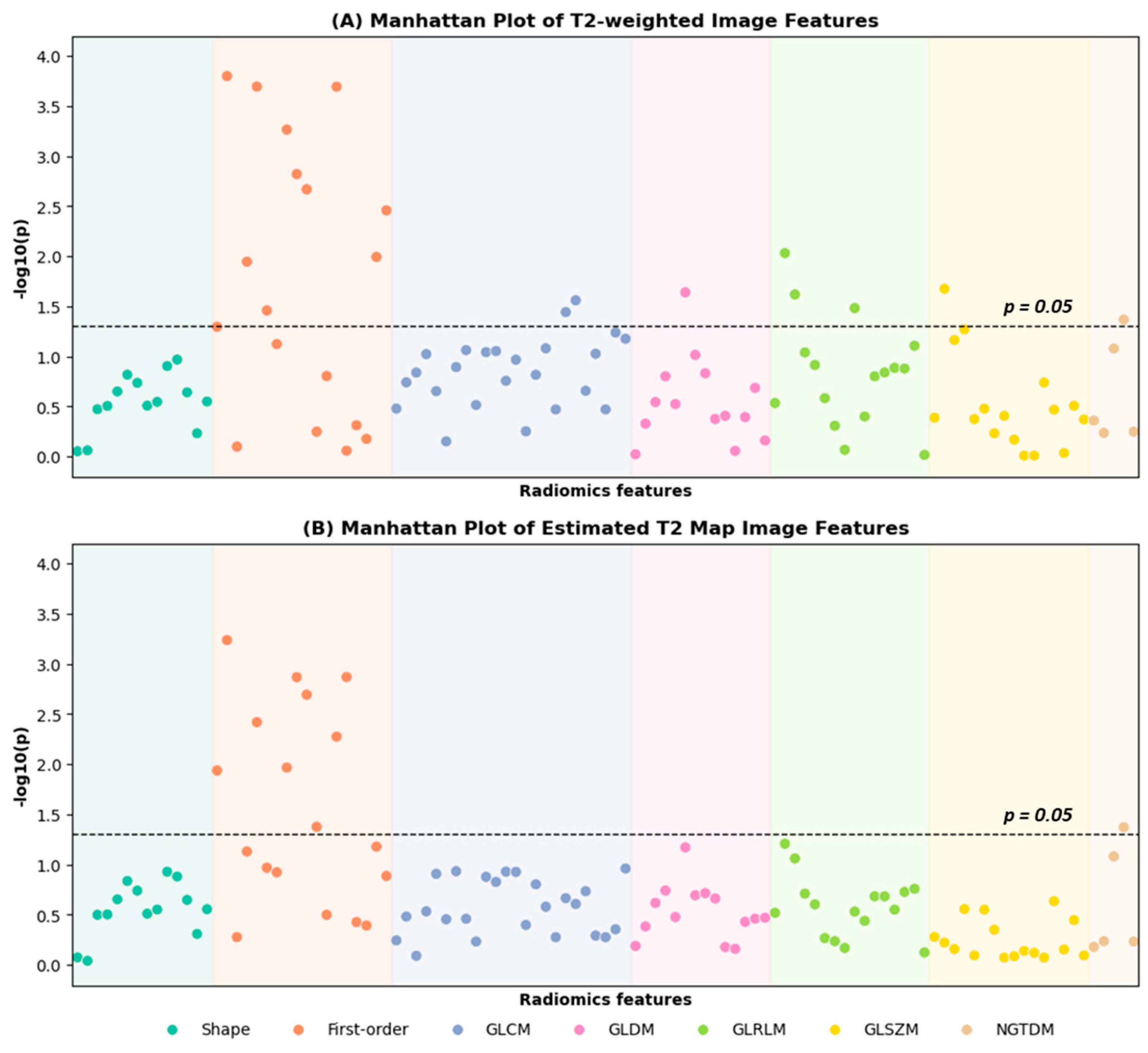
3.1. Radiomics Feature Selection of T2-Weighted Images and Estimated T2 Maps
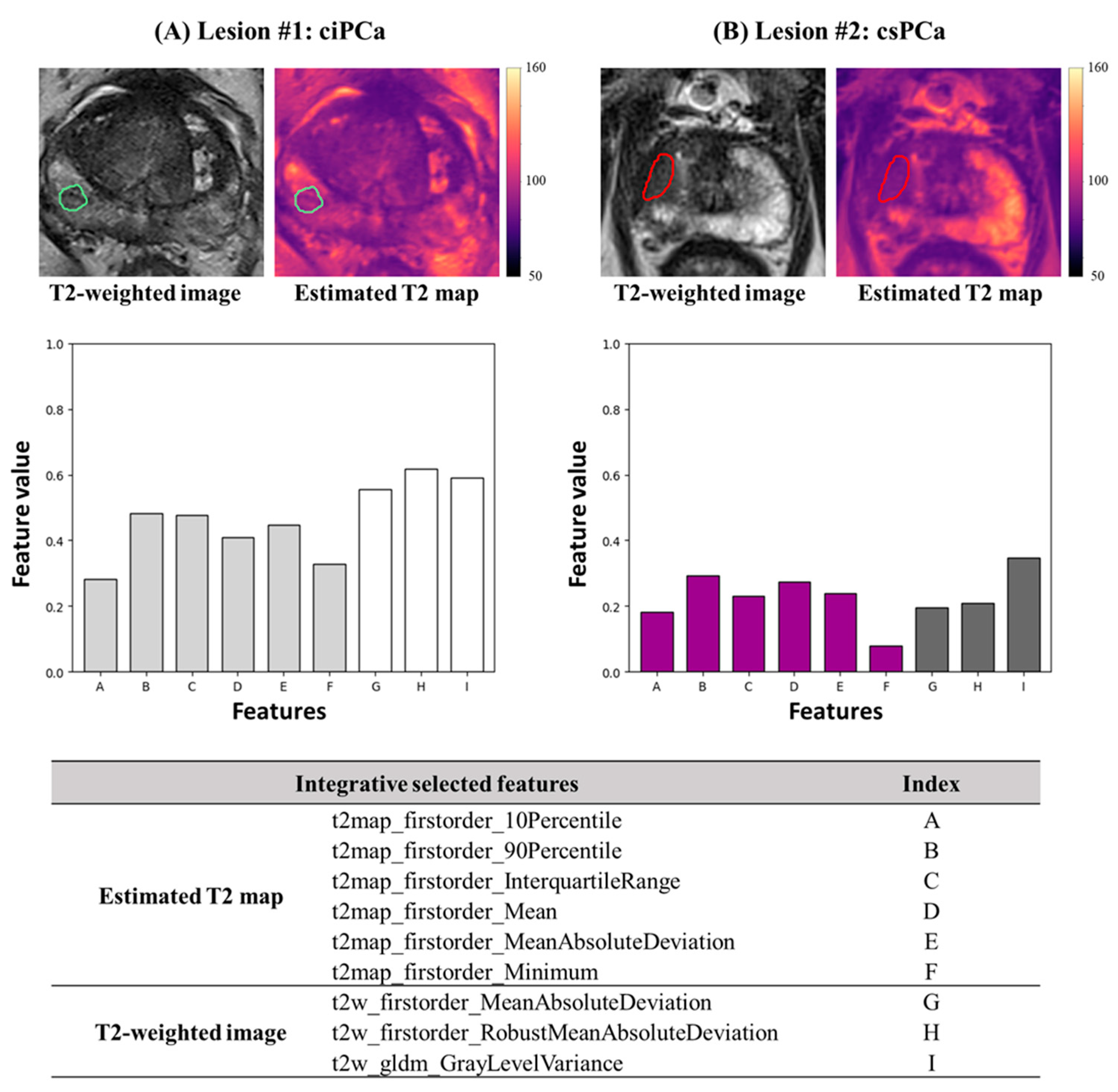
3.2. Integrative Model Construction
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Giaquinto, A.N.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2024. CA. Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 12–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Cancer Society. Cancer Facts & Figures 2024. Atlanta Am. Cancer Soc. 2024. [Google Scholar]
- EAU Guidelines. Edn. Presented at the EAU Annual Congress Paris 2024; EAU Guidelines Office: Arnhem, The Netherlands, 2024; ISBN 978-94-92671-23-3. [Google Scholar]
- Stephan, C.; Rittenhouse, H.; Hu, X.; Cammann, H.; Jung, K. Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) Screening and New Biomarkers for Prostate Cancer (PCa). EJIFCC 2014, 25, 55–78. [Google Scholar]
- Descotes, J.-L. Diagnosis of Prostate Cancer. Asian J. Urol. 2019, 6, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loeb, S.; Vellekoop, A.; Ahmed, H.U.; Catto, J.; Emberton, M.; Nam, R.; Rosario, D.J.; Scattoni, V.; Lotan, Y. Systematic Review of Complications of Prostate Biopsy. Eur. Urol. 2013, 64, 876–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, N.E.; Mendhiratta, N.; Taneja, S.S. Patterns of Repeat Prostate Biopsy in Contemporary Clinical Practice. J. Urol. 2015, 193, 1178–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkbey, B.; Rosenkrantz, A.B.; Haider, M.A.; Padhani, A.R.; Villeirs, G.; Macura, K.J.; Tempany, C.M.; Choyke, P.L.; Cornud, F.; Margolis, D.J.; et al. Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System Version 2.1: 2019 Update of Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System Version 2. Eur. Urol. 2019, 76, 340–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, H.U.; El-Shater Bosaily, A.; Brown, L.C.; Gabe, R.; Kaplan, R.; Parmar, M.K.; Collaco-Moraes, Y.; Ward, K.; Hindley, R.G.; Freeman, A.; et al. Diagnostic Accuracy of Multi-Parametric MRI and TRUS Biopsy in Prostate Cancer (PROMIS): A Paired Validating Confirmatory Study. Lancet 2017, 389, 815–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.E.; van Leeuwen, P.J.; Moses, D.; Shnier, R.; Brenner, P.; Delprado, W.; Pulbrook, M.; Böhm, M.; Haynes, A.M.; Hayen, A.; et al. The Diagnostic Performance of Multiparametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging to Detect Significant Prostate Cancer. J. Urol. 2016, 195, 1428–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yakar, D.; Debats, O.A.; Bomers, J.G.R.; Schouten, M.G.; Vos, P.C.; van Lin, E.; Fütterer, J.J.; Barentsz, J.O. Predictive Value of MRI in the Localization, Staging, Volume Estimation, Assessment of Aggressiveness, and Guidance of Radiotherapy and Biopsies in Prostate Cancer. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2012, 35, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fütterer, J.J.; Briganti, A.; De Visschere, P.; Emberton, M.; Giannarini, G.; Kirkham, A.; Taneja, S.S.; Thoeny, H.; Villeirs, G.; Villers, A. Can Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer Be Detected with Multiparametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging? A Systematic Review of the Literature. Eur. Urol. 2015, 68, 1045–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenkrantz, A.B.; Ginocchio, L.A.; Cornfeld, D.; Froemming, A.T.; Gupta, R.T.; Turkbey, B.; Westphalen, A.C.; Babb, J.S.; Margolis, D.J. Interobserver Reproducibility of the PI-RADS Version 2 Lexicon: A Multicenter Study of Six Experienced Prostate Radiologists. Radiology 2016, 280, 793–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greer, M.D.; Shih, J.H.; Lay, N.; Barrett, T.; Bittencourt, L.; Borofsky, S.; Kabakus, I.; Law, Y.M.; Marko, J.; Shebel, H.; et al. Interreader Variability of Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System Version 2 in Detecting and Assessing Prostate Cancer Lesions at Prostate MRI. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2019, 212, 1197–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillies, R.J.; Kinahan, P.E.; Hricak, H. Radiomics: Images Are More than Pictures, They Are Data. Radiology 2016, 278, 563–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambin, P.; Leijenaar, R.T.H.; Deist, T.M.; Peerlings, J.; de Jong, E.E.C.; van Timmeren, J.; Sanduleanu, S.; Larue, R.T.H.M.; Even, A.J.G.; Jochems, A.; et al. Radiomics: The Bridge between Medical Imaging and Personalized Medicine. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 749–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.; Li, M.; Gu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, S.; Wei, C.; Wu, J.; Li, X.; Zhao, W.; Shen, J. Prostate Cancer Differentiation and Aggressiveness: Assessment With a Radiomic-Based Model vs. PI-RADS V2. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2019, 49, 875–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toivonen, J.; Montoya Perez, I.; Movahedi, P.; Merisaari, H.; Pesola, M.; Taimen, P.; Boström, P.J.; Pohjankukka, J.; Kiviniemi, A.; Pahikkala, T.; et al. Radiomics and Machine Learning of Multisequence Multiparametric Prostate MRI: Towards Improved Non-Invasive Prostate Cancer Characterization. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0217702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, X.; Li, M.; Dong, D.; Feng, Z.; Zhang, P.; Ke, Z.; You, H.; Han, F.; Ma, H.; Tian, J.; et al. Multi-Parametric MRI-Based Radiomics Signature for Discriminating between Clinically Significant and Insignificant Prostate Cancer: Cross-Validation of a Machine Learning Method. Eur. J. Radiol. 2019, 115, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hectors, S.J.; Cherny, M.; Yadav, K.K.; Beksaç, A.T.; Thulasidass, H.; Lewis, S.; Davicioni, E.; Wang, P.; Tewari, A.K.; Taouli, B. Radiomics Features Measured with Multiparametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging Predict Prostate Cancer Aggressiveness. J. Urol. 2019, 202, 498–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Turkbey, B.; Sénégas, J.; Remmele, S.; Xu, S.; Kruecker, J.; Bernardo, M.; Wood, B.J.; Pinto, P.A.; Choyke, P.L. Accelerated T2 Mapping for Characterization of Prostate Cancer. Magn. Reson. Med. 2011, 65, 1400–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang Dinh, A.; Souchon, R.; Melodelima, C.; Bratan, F.; Mège-Lechevallier, F.; Colombel, M.; Rouvière, O. Characterization of Prostate Cancer Using T2 Mapping at 3T: A Multi-Scanner Study. Diagn. Interv. Imaging 2015, 96, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, A.; O’Connor, G.; Lo, W.C.; Jiang, Y.; Margevicius, S.; Schluchter, M.; Ponsky, L.E.; Gulani, V. Targeted Biopsy Validation of Peripheral Zone Prostate Cancer Characterization With Magnetic Resonance Fingerprinting and Diffusion Mapping. Investig. Radiol. 2019, 54, 485–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hepp, T.; Kalmbach, L.; Kolb, M.; Martirosian, P.; Hilbert, T.; Thaiss, W.M.; Notohamiprodjo, M.; Bedke, J.; Nikolaou, K.; Stenzl, A.; et al. T2 Mapping for the Characterization of Prostate Lesions. World J. Urol. 2022, 40, 1455–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, A.; Devaraj, A.; Mathew, M.; Szasz, T.; Antic, T.; Karczmar, G.S.; Oto, A. Performance of T2 Maps in the Detection of Prostate Cancer. Acad. Radiol. 2019, 26, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langer, D.L.; van der Kwast, T.H.; Evans, A.J.; Plotkin, A.; Trachtenberg, J.; Wilson, B.C.; Haider, M.A. Prostate Tissue Composition and MR Measurements: Investigating the Relationships between ADC, T2, Ktrans, ve, and Corresponding Histologic Features. Radiology 2010, 255, 485–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Wang, L.; Daskivich, T.; Qiu, S.; Han, F.; D’Agnolo, A.; Saouaf, R.; Christodoulou, A.G.; Kim, H.; Li, D.; et al. Retrospective T2 Quantification from Conventional Weighted MRI of the Prostate Based on Deep Learning. Front. Radiol. 2023, 3, 1223377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, D.N.; Nguyen, C.; Sirohi, D.; Falahatian, V.; Saouaf, R.; Luthringer, D.; Li, D.; Kim, H.L. Use of Cylindrical Coordinates to Localize Prostate Cancers on MRI and Prostatectomy Pathology. Urol. Oncol. Semin. Orig. Investig. 2017, 35, 673.e15–673.e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yushkevich, P.A.; Piven, J.; Hazlett, H.C.; Smith, R.G.; Ho, S.; Gee, J.C.; Gerig, G. User-Guided 3D Active Contour Segmentation of Anatomical Structures: Significantly Improved Efficiency and Reliability. NeuroImage 2006, 31, 1116–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwanenburg, A.; Vallières, M.; Abdalah, M.A.; Aerts, H.J.W.L.; Andrearczyk, V.; Apte, A.; Ashrafinia, S.; Bakas, S.; Beukinga, R.J.; Boellaard, R.; et al. The Image Biomarker Standardization Initiative: Standardized Quantitative Radiomics for High-Throughput Image-Based Phenotyping. Radiology 2020, 295, 328–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Griethuysen, J.J.; Fedorov, A.; Parmar, C.; Hosny, A.; Aucoin, N.; Narayan, V.; Beets-Tan, R.G.; Fillion-Robin, J.-C.; Pieper, S.; Aerts, H.J. Computational Radiomics System to Decode the Radiographic Phenotype. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, e104–e107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Hou, Y.; Yan, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, M.; Yao, Y.; Yang, G. FeAture Explorer (FAE): A Tool for Developing and Comparing Radiomics Models. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0237587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeLong, E.R.; DeLong, D.M.; Clarke-Pearson, D.L. Comparing the Areas under Two or More Correlated Receiver Operating Characteristic Curves: A Nonparametric Approach. Biometrics 1988, 44, 837–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sunoqrot, M.R.S.; Nketiah, G.A.; Selnæs, K.M.; Bathen, T.F.; Elschot, M. Automated Reference Tissue Normalization of T2-Weighted MR Images of the Prostate Using Object Recognition. Magn. Reson. Mater. Phys. Biol. Med. 2021, 34, 309–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sørland, K.I.; Sunoqrot, M.R.S.; Sandsmark, E.; Langørgen, S.; Bertilsson, H.; Trimble, C.G.; Lin, G.; Selnæs, K.M.; Goa, P.E.; Bathen, T.F.; et al. Pseudo-T2 Mapping for Normalization of T2-Weighted Prostate MRI. Magn. Reson. Mater. Phys. Biol. Med. 2022, 35, 573–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klingebiel, M.; Schimmöller, L.; Weiland, E.; Franiel, T.; Jannusch, K.; Kirchner, J.; Hilbert, T.; Strecker, R.; Arsov, C.; Wittsack, H.-J.; et al. Value of T2 Mapping MRI for Prostate Cancer Detection and Classification. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2022, 56, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonekamp, D.; Kohl, S.; Wiesenfarth, M.; Schelb, P.; Radtke, J.P.; Götz, M.; Kickingereder, P.; Yaqubi, K.; Hitthaler, B.; Gählert, N.; et al. Radiomic Machine Learning for Characterization of Prostate Lesions with MRI: Comparison to ADC Values. Radiology 2018, 289, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itou, Y.; Nakanishi, K.; Narumi, Y.; Nishizawa, Y.; Tsukuma, H. Clinical Utility of Apparent Diffusion Coefficient (ADC) Values in Patients with Prostate Cancer: Can ADC Values Contribute to Assess the Aggressiveness of Prostate Cancer? J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2011, 33, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wibmer, A.; Hricak, H.; Gondo, T.; Matsumoto, K.; Veeraraghavan, H.; Fehr, D.; Zheng, J.; Goldman, D.; Moskowitz, C.; Fine, S.; et al. Haralick Texture Analysis of Prostate MRI: Utility for Differentiating Non-Cancerous Prostate from Prostate Cancer and Differentiating Prostate Cancers with Different Gleason Scores. Eur. Radiol. 2015, 25, 2840–2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignati, A.; Mazzetti, S.; Giannini, V.; Russo, F.; Bollito, E.; Porpiglia, F.; Stasi, M.; Regge, D. Texture Features on T2-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging: New Potential Biomarkers for Prostate Cancer Aggressiveness. Phys. Med. Biol. 2015, 60, 2685–2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegde, J.V.; Mulkern, R.V.; Panych, L.P.; Fennessy, F.M.; Fedorov, A.; Maier, S.E.; Tempany, C.M. Multiparametric MRI of Prostate Cancer: An Update on State-of-the-Art Techniques and Their Performance in Detecting and Localizing Prostate Cancer. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2013, 37, 1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ginsburg, S.B.; Algohary, A.; Pahwa, S.; Gulani, V.; Ponsky, L.; Aronen, H.J.; Boström, P.J.; Böhm, M.; Haynes, A.-M.; Brenner, P.; et al. Radiomic Features for Prostate Cancer Detection on MRI Differ Between the Transition and Peripheral Zones: Preliminary Findings from a Multi-Institutional Study. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2017, 46, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| T1w (FLASH) | T2w (TSE) | DWI (EPI) | DCE (GRE) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TE (ms) | 2.03 | 132 | 95 | 1.07 |
| TR (ms) | 277 | 4000 | 6500 | 3.02 |
| Flip angle (°) | 65 | 158 | 90 | 10 |
| # Slices | 45 | 30 | 29 | 31 |
| Thickness (mm) | 6 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| Resolution (mm2) | 1.125 × 1.125 | 0.63 × 0.63 | 0.781 × 0.781 | 1.250 × 1.250 |
| FOV (mm2) | 360 × 247.5 | 160 × 160 | 200 × 200 | 160 × 160 |
| Temporal Resolution (s) | / | / | / | 20 |
| b-value (s/mm2) | / | / | 50, 800, 1400 | / |
| Scan time (min) | 0.5 | 4.5 | 6.4 | 8.2 |
| Characteristics | (Total Patients N = 58, Total Lesions n = 76) |
|---|---|
| Age (yr), median {IQR} | 69 {63.5–73} |
| PSA (ng/mL), median {IQR} | 6.2 {5.1–7.3} |
| PSAD (ng/mL^2), median {IQR} | 0.16 {0.09–0.25} |
| Prostate volume (cc), median {IQR} | 41.78 {26.77–58.36} |
| Gleason Score, n {%} | |
| 3 + 3 | 26 {34.2} |
| 3 + 4 | 34 {44.7} |
| 4 + 3 | 7 {9.2} |
| ≥4 + 4 | 9 {11.8} |
| PI-RADS, n {%} | |
| 1 | 0 {0} |
| 2 | 0 {0} |
| 3 | 6 {7.9} |
| 4 | 47 {61.8} |
| 5 | 23 {30.3} |
| T2-Weighted Features | csPCa | ciPCa | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| firstorder_90Percentile | 0.44 ± 0.14 | 0.58 ± 0.15 | <0.001 *** |
| firstorder_MeanAbsoluteDeviation | 0.32 ± 0.17 | 0.48 ± 0.18 | <0.001 *** |
| firstorder_RobustMeanAbsoluteDeviation | 0.31 ± 0.18 | 0.49 ± 0.21 | <0.001 *** |
| firstorder_Mean | 0.46 ± 0.15 | 0.58 ± 0.17 | <0.01 ** |
| gldm_GrayLevelVariance | 0.30 ± 0.19 | 0.41 ± 0.19 | 0.02 * |
| ngtdm_Contrast | 0.20 ± 0.17 | 0.29 ± 0.16 | 0.04 * |
| Estimated T2 Map Features | csPCa | ciPCa | p-Value |
| firstorder_90Percentile | 0.40 ± 0.15 | 0.53 ± 0.16 | <0.001 *** |
| firstorder_InterquartileRange | 0.25 ± 0.15 | 0.36 ± 0.14 | <0.01 ** |
| firstorder_Mean | 0.38 ± 0.15 | 0.51 ± 0.16 | <0.01 ** |
| firstorder_10Percentile | 0.32 ± 0.16 | 0.43 ± 0.19 | 0.01 * |
| firstorder_MeanAbsoluteDeviation | 0.29 ± 0.16 | 0.38 ± 0.13 | 0.01 * |
| firstorder_Minimum | 0.31 ± 0.23 | 0.43 ± 0.22 | 0.04 * |
| AUC | 95% CIs | ACC | SEN | SPE | PPV | NPV | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T2-weighted image | 0.700 | [0.568–0.831] | 0.737 | 0.800 | 0.615 | 0.800 | 0.615 | / |
| Estimated T2 map | 0.763 | [0.649–0.877] | 0.711 | 0.640 | 0.846 | 0.890 | 0.550 | 0.260 |
| T2 weighted + Estimated T2 map | 0.803 | [0.694–0.913] | 0.803 | 0.780 | 0.846 | 0.907 | 0.667 | 0.043 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, H.; Wang, L.; Daskivich, T.; Qiu, S.; Lee, H.-L.; Gao, C.; Saouaf, R.; Lo, E.; D’Agnolo, A.; Kim, H.; et al. Retrospectively Quantified T2 Improves Detection of Clinically Significant Peripheral Zone Prostate Cancer. Cancers 2025, 17, 381. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17030381
Sun H, Wang L, Daskivich T, Qiu S, Lee H-L, Gao C, Saouaf R, Lo E, D’Agnolo A, Kim H, et al. Retrospectively Quantified T2 Improves Detection of Clinically Significant Peripheral Zone Prostate Cancer. Cancers. 2025; 17(3):381. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17030381
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Haoran, Lixia Wang, Timothy Daskivich, Shihan Qiu, Hsu-Lei Lee, Chang Gao, Rola Saouaf, Eric Lo, Alessandro D’Agnolo, Hyung Kim, and et al. 2025. "Retrospectively Quantified T2 Improves Detection of Clinically Significant Peripheral Zone Prostate Cancer" Cancers 17, no. 3: 381. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17030381
APA StyleSun, H., Wang, L., Daskivich, T., Qiu, S., Lee, H.-L., Gao, C., Saouaf, R., Lo, E., D’Agnolo, A., Kim, H., Li, D., & Xie, Y. (2025). Retrospectively Quantified T2 Improves Detection of Clinically Significant Peripheral Zone Prostate Cancer. Cancers, 17(3), 381. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17030381






