Measurable Residual Disease Analysis by Flow Cytometry: Assay Validation and Characterization of 385 Consecutive Cases of Acute Myeloid Leukemia
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Patients and Methods
2.1. Patients
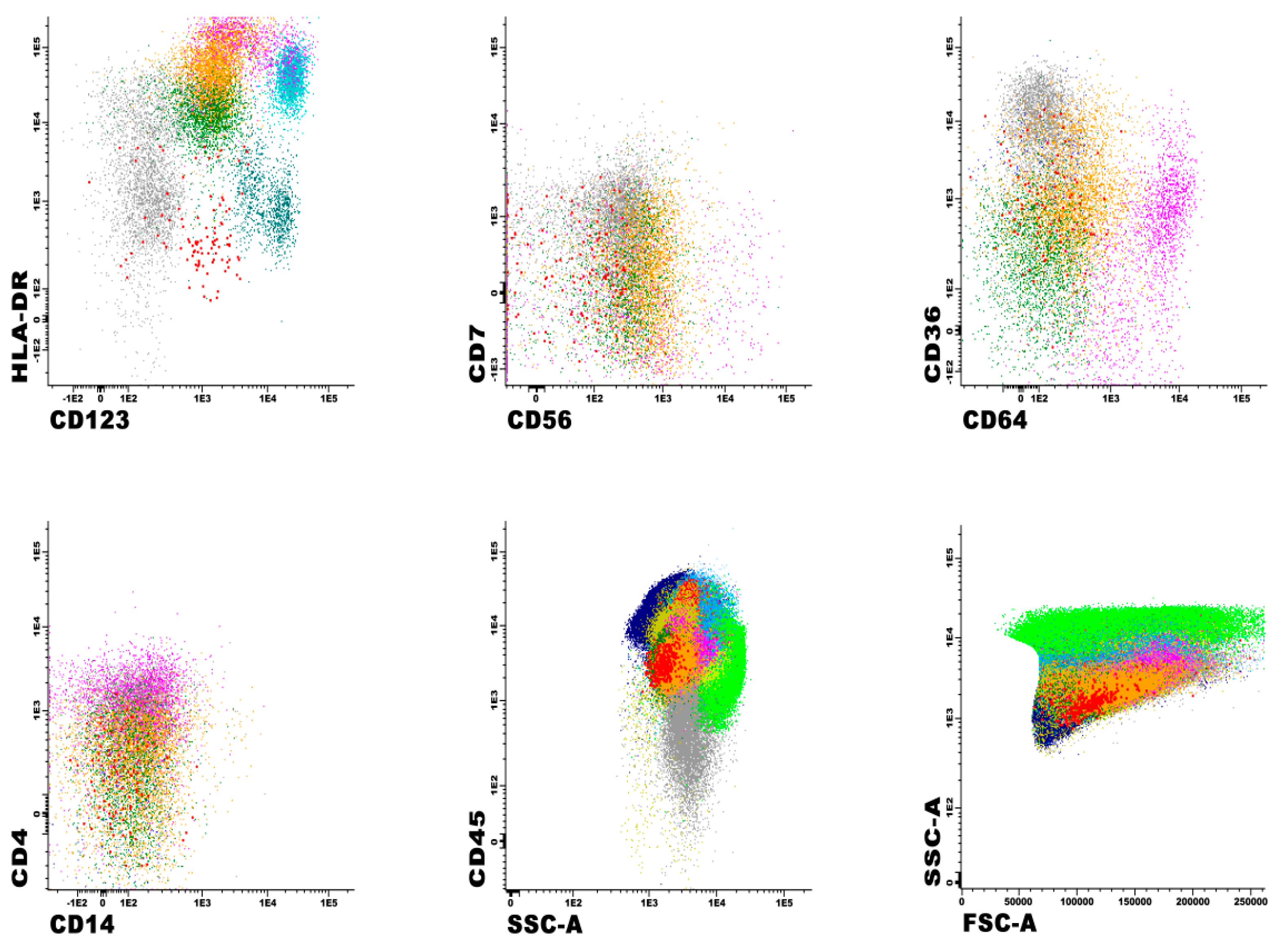
2.2. Morphology and Flow Cytometry
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. AML MRD Flow Cytometry Assay Design and Performance
3.3. Immunophenotypic Findings in Patients with Positive AML MRD Flow Cytometry Analyses
3.4. Correlation with Morphology and Other Ancillary Testing Findings
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Solary, E.; Gujral, S. Acute myeloid leukaemia. In WHO Classification of Tumours (5th Edition) Haematolymphoid Tumours Part A; WHO Classification of Tumours Editorial Board, Ed.; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 2024; pp. 110–168. [Google Scholar]
- Döhner, H.; Wei, A.H.; Appelbaum, F.R.; Craddock, C.; DiNardo, C.D.; Dombret, H.; Ebert, B.L.; Fenaux, P.; Godley, L.A.; Hasserjian, R.P.; et al. Diagnosis and management of AML in adults: 2022 recommendations from an international expert panel on behalf of the ELN. Blood 2022, 140, 1345–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Comprehenisve Cancer Network. Acute Myeloid Leukemia (Version 1.2025). Available online: https://www.nccn.org/login?ReturnURL=https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/PDF/aml.pdf (accessed on 10 January 2025).
- Short, N.J.; Rytting, M.E.; Cortes, J.E. Acute myeloid leukaemia. Lancet 2018, 392, 593–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Chaer, F.; Hourigan, C.S.; Zeidan, A.M. How I treat AML incorporating the updated classifications and guidelines. Blood 2023, 141, 2813–2823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Short, N.J.; Zhou, S.; Fu, C.; Berry, D.A.; Walter, R.B.; Freeman, S.D.; Hourigan, C.S.; Huang, X.; Nogueras Gonzalez, G.; Hwang, H.; et al. Association of Measurable Residual Disease With Survival Outcomes in Patients With Acute Myeloid Leukemia: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Oncol. 2020, 6, 1890–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernasconi, P.; Borsani, O. Eradication of Measurable Residual Disease in AML: A Challenging Clinical Goal. Cancers 2021, 13, 3170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, N.; Gui, G.; Dumezy, F.; Roumier, C.; Andrew, G.; Green, S.; Jenkins, M.; Adams, A.; Khan, N.; Craddock, C.; et al. Pre-emptive detection and evolution of relapse in acute myeloid leukemia by flow cytometric measurable residual disease surveillance. Leukemia 2024, 38, 1667–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckley, S.A.; Wood, B.L.; Othus, M.; Hourigan, C.S.; Ustun, C.; Linden, M.A.; DeFor, T.E.; Malagola, M.; Anthias, C.; Valkova, V.; et al. Minimal residual disease prior to allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation in acute myeloid leukemia: A meta-analysis. Haematologica 2017, 102, 865–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Petrova-Drus, K.; Roshal, M. Optimal Measurable Residual Disease Testing for Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Surg. Pathol. Clin. 2019, 12, 671–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godwin, C.D.; Zhou, Y.; Othus, M.; Asmuth, M.M.; Shaw, C.M.; Gardner, K.M.; Wood, B.L.; Walter, R.B.; Estey, E.H. Acute myeloid leukemia measurable residual disease detection by flow cytometry in peripheral blood vs bone marrow. Blood 2021, 137, 569–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loghavi, S.; DiNardo, C.D.; Furudate, K.; Takahashi, K.; Tanaka, T.; Short, N.J.; Kadia, T.; Konopleva, M.; Kanagal-Shamanna, R.; Farnoud, N.R.; et al. Flow cytometric immunophenotypic alterations of persistent clonal haematopoiesis in remission bone marrows of patients with NPM1-mutated acute myeloid leukaemia. Br. J. Haematol. 2021, 192, 1054–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeijlemaker, W.; Grob, T.; Meijer, R.; Hanekamp, D.; Kelder, A.; Carbaat-Ham, J.C.; Oussoren-Brockhoff, Y.J.M.; Snel, A.N.; Veldhuizen, D.; Scholten, W.J.; et al. CD34+CD38− leukemic stem cell frequency to predict outcome in acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 2019, 33, 1102–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanekamp, D.; Snel, A.N.; Kelder, A.; Scholten, W.J.; Khan, N.; Metzner, M.; Irno-Consalvo, M.; Sugita, M.; de Jong, A.; Oude Alink, S.; et al. Applicability and reproducibility of acute myeloid leukaemia stem cell assessment in a multi-centre setting. Br. J. Haematol. 2020, 190, 891–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aitken, M.J.L.; Ravandi, F.; Patel, K.P.; Short, N.J. Prognostic and therapeutic implications of measurable residual disease in acute myeloid leukemia. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 14, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pratz, K.W.; Jonas, B.A.; Pullarkat, V.; Recher, C.; Schuh, A.C.; Thirman, M.J.; Garcia, J.S.; DiNardo, C.D.; Vorobyev, V.; Fracchiolla, N.S.; et al. Measurable Residual Disease Response and Prognosis in Treatment-Naïve Acute Myeloid Leukemia With Venetoclax and Azacitidine. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 855–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roboz, G.J.; Ravandi, F.; Wei, A.H.; Dombret, H.; Thol, F.; Voso, M.T.; Schuh, A.C.; Porkka, K.; La Torre, I.; Skikne, B.; et al. Oral azacitidine prolongs survival of patients with AML in remission independently of measurable residual disease status. Blood 2022, 139, 2145–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Short, N.J.; Ravandi, F. How close are we to incorporating measurable residual disease into clinical practice for acute myeloid leukemia? Haematologica 2019, 104, 1532–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Chaer, F.; Perissinotti, A.J.; Loghavi, S.; Zeidan, A.M. Pre-emptive therapeutic decisions based on measurable residual disease status in acute myeloid leukemia: Ready for prime time? Leukemia 2025, 39, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modvig, S.; Hallböök, H.; Madsen, H.O.; Siitonen, S.; Rosthøj, S.; Tierens, A.; Juvonen, V.; Osnes, L.T.N.; Vålerhaugen, H.; Hultdin, M.; et al. Value of flow cytometry for MRD-based relapse prediction in B-cell precursor ALL in a multicenter setting. Leukemia 2021, 35, 1894–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuurhuis, G.J.; Heuser, M.; Freeman, S.; Béné, M.C.; Buccisano, F.; Cloos, J.; Grimwade, D.; Haferlach, T.; Hills, R.K.; Hourigan, C.S.; et al. Minimal/measurable residual disease in AML: A consensus document from the European LeukemiaNet MRD Working Party. Blood 2018, 131, 1275–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tettero, J.M.; Freeman, S.; Buecklein, V.; Venditti, A.; Maurillo, L.; Kern, W.; Walter, R.B.; Wood, B.L.; Roumier, C.; Philippé, J.; et al. Technical Aspects of Flow Cytometry-based Measurable Residual Disease Quantification in Acute Myeloid Leukemia: Experience of the European LeukemiaNet MRD Working Party. Hemasphere 2022, 6, e676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heuser, M.; Freeman, S.D.; Ossenkoppele, G.J.; Buccisano, F.; Hourigan, C.S.; Ngai, L.L.; Tettero, J.M.; Bachas, C.; Baer, C.; Béné, M.C.; et al. 2021 Update on MRD in acute myeloid leukemia: A consensus document from the European LeukemiaNet MRD Working Party. Blood 2021, 138, 2753–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). Validation for Assays Performed by Flow Cytometry; CLSI: Wayne, PA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Jevremovic, D.; Shi, M.; Horna, P.; Otteson, G.E.; Timm, M.M.; Bennett, S.A.; Baughn, L.B.; Greipp, P.T.; Gonsalves, W.I.; Kapoor, P.; et al. FDA IDE validation of multiple myeloma MRD test by flow cytometry. Am. J. Hematol. 2024, 99, 2399–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jevremovic, D.; Nanaa, A.; Geyer, S.M.; Timm, M.; Azouz, H.; Hengel, C.; Reberg, A.; He, R.; Viswanatha, D.; Salama, M.E.; et al. Abnormal CD13/HLA-DR Expression Pattern on Myeloblasts Predicts Development of Myeloid Neoplasia in Patients With Clonal Cytopenia of Undetermined Significance. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2022, 158, 530–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spears, M.D.; Harrington, A.M.; Kroft, S.H.; Olteanu, H. Immunophenotypic stability of T-cell large granular lymphocytic leukaemia by flow cytometry. Br. J. Haematol. 2010, 151, 97–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughan, J.; Harrington, A.M.; Hari, P.N.; Kroft, S.H.; Olteanu, H. Immunophenotypic stability of Sézary cells by flow cytometry: Usefulness of flow cytometry in assessing response to and guiding alemtuzumab therapy. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2012, 137, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olteanu, H.; Harrington, A.M.; Kroft, S.H. Immunophenotypic stability of CD200 expression in plasma cell myeloma. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2012, 137, 1013–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrington, A.; Olteanu, H.; Kroft, S. The specificity of immunophenotypic alterations in blasts in nonacute myeloid disorders. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2010, 134, 749–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seegmiller, A.C.; Kroft, S.H.; Karandikar, N.J.; McKenna, R.W. Characterization of immunophenotypic aberrancies in 200 cases of B acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2009, 132, 940–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jevremovic, D.; Timm, M.M.; Reichard, K.K.; Morice, W.G.; Hanson, C.A.; Viswanatha, D.S.; Howard, M.T.; Nguyen, P.L. Loss of blast heterogeneity in myelodysplastic syndrome and other chronic myeloid neoplasms. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2014, 142, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, R.B.; Buckley, S.A.; Pagel, J.M.; Wood, B.L.; Storer, B.E.; Sandmaier, B.M.; Fang, M.; Gyurkocza, B.; Delaney, C.; Radich, J.P.; et al. Significance of minimal residual disease before myeloablative allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation for AML in first and second complete remission. Blood 2013, 122, 1813–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tettero, J.M.; Dakappagari, N.; Heidinga, M.E.; Oussoren-Brockhoff, Y.; Hanekamp, D.; Pahuja, A.; Burns, K.; Kaur, P.; Alfonso, Z.; van der Velden, V.H.J.; et al. Analytical assay validation for acute myeloid leukemia measurable residual disease assessment by multiparametric flow cytometry. Cytom. B Clin. Cytom. 2023, 104, 426–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buccisano, F.; Palmieri, R.; Piciocchi, A.; Arena, V.; Maurillo, L.; Del Principe, M.I.; Paterno, G.; Irno-Consalvo, M.A.; Ottone, T.; Divona, M.; et al. Clinical relevance of an objective flow cytometry approach based on limit of detection and limit of quantification for measurable residual disease assessment in acute myeloid leukemia. A post-hoc analysis of the GIMEMA AML1310 trial. Haematologica 2022, 107, 2823–2833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Arbolí, E.; Othus, M.; Freeman, S.D.; Buccisano, F.; Ngai, L.L.; Thomas, I.; Palmieri, R.; Cloos, J.; Johnson, S.; Meddi, E.; et al. Optimal prognostic threshold for measurable residual disease positivity by multiparameter flow cytometry in acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Leukemia 2024, 38, 2266–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mannelli, F.; Piccini, M.; Bencini, S.; Gianfaldoni, G.; Peruzzi, B.; Caporale, R.; Scappini, B.; Fasano, L.; Quinti, E.; Ciolli, G.; et al. Effect of age and treatment on predictive value of measurable residual disease: Implications for clinical management of adult patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Haematologica 2024, 109, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shopsowitz, K.; Lofroth, J.; Chan, G.; Kim, J.; Rana, M.; Brinkman, R.; Weng, A.; Medvedev, N.; Wang, X. MAGIC-DR: An interpretable machine-learning guided approach for acute myeloid leukemia measurable residual disease analysis. Cytom. B Clin. Cytom. 2024, 106, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seheult, J.N.; Shi, M.; Olteanu, H.; Otteson, G.E.; Timm, M.M.; Weybright, J.W.; Horna, P. Machine Learning Enhancement of Flow Cytometry Data Accelerates the Identification of Minimal Residual Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Blood 2023, 14, 4339–4340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
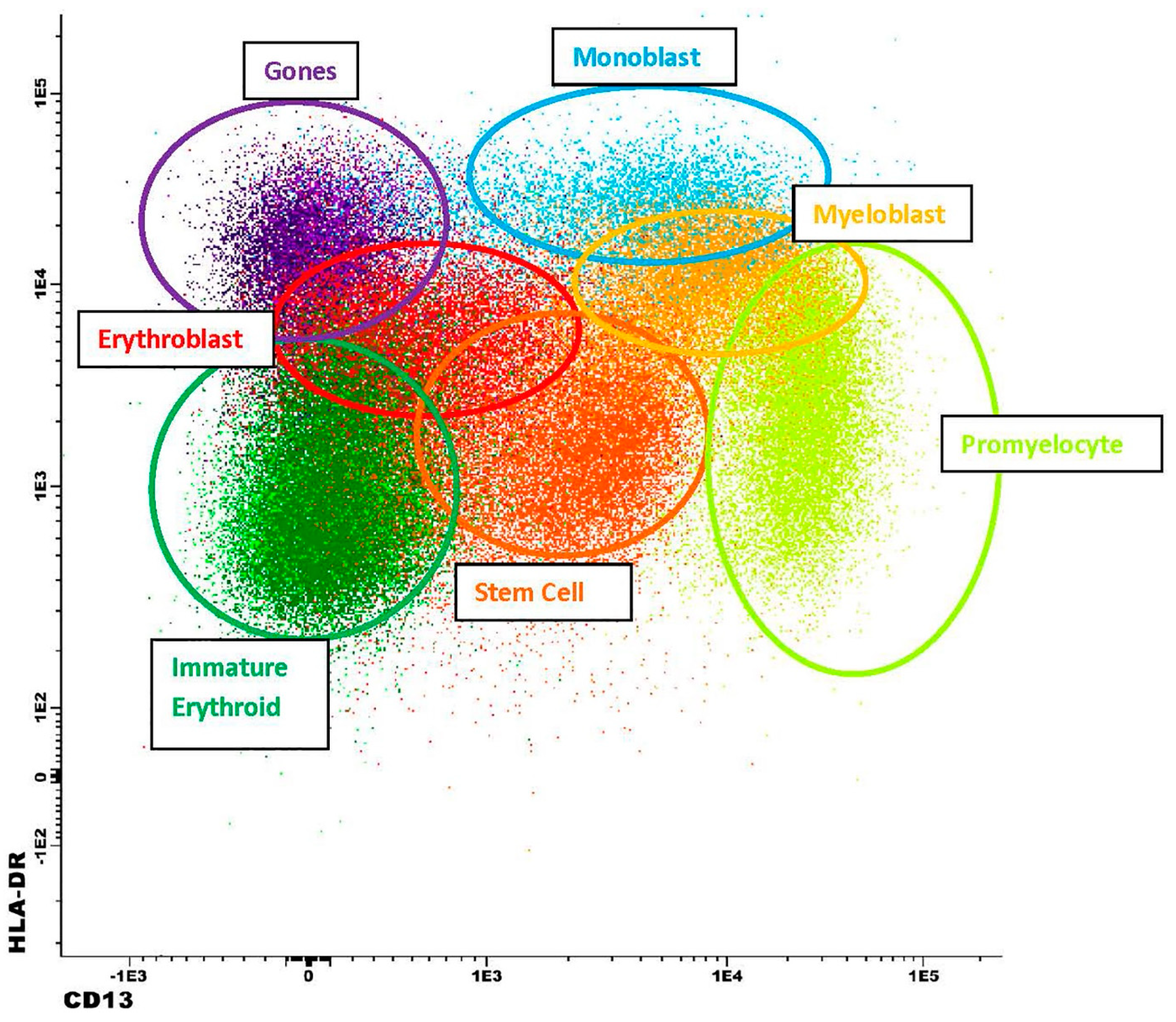
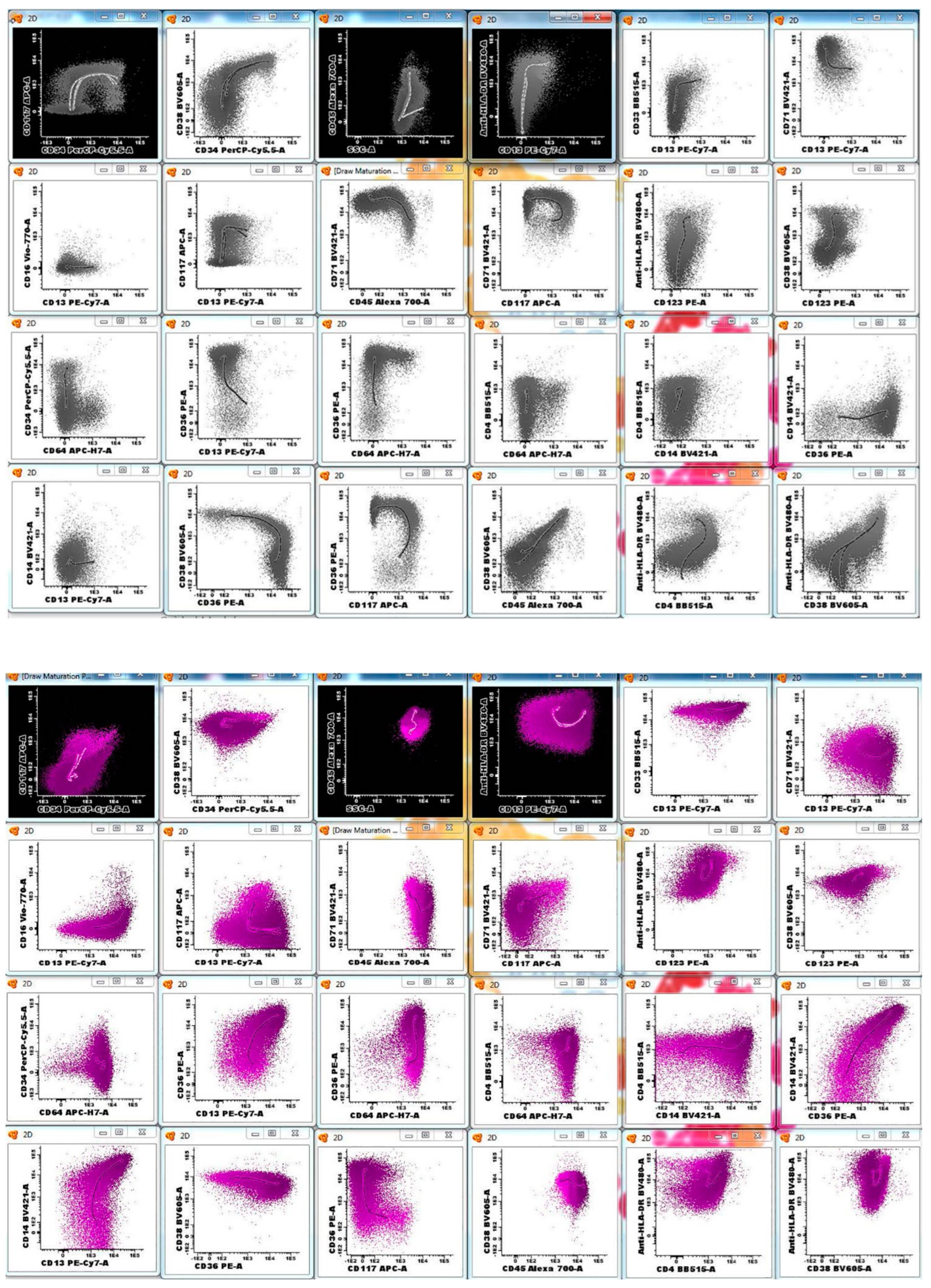
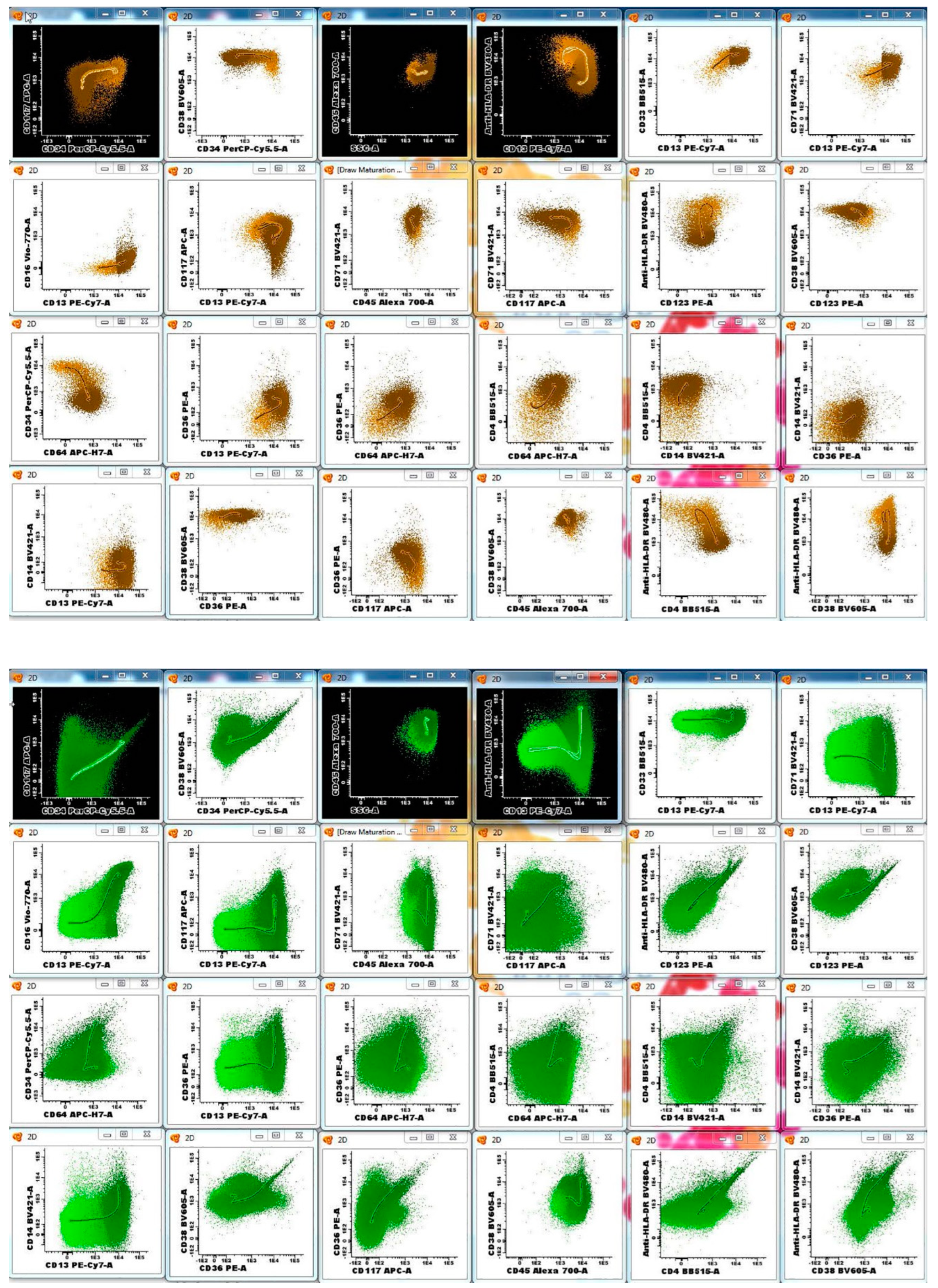
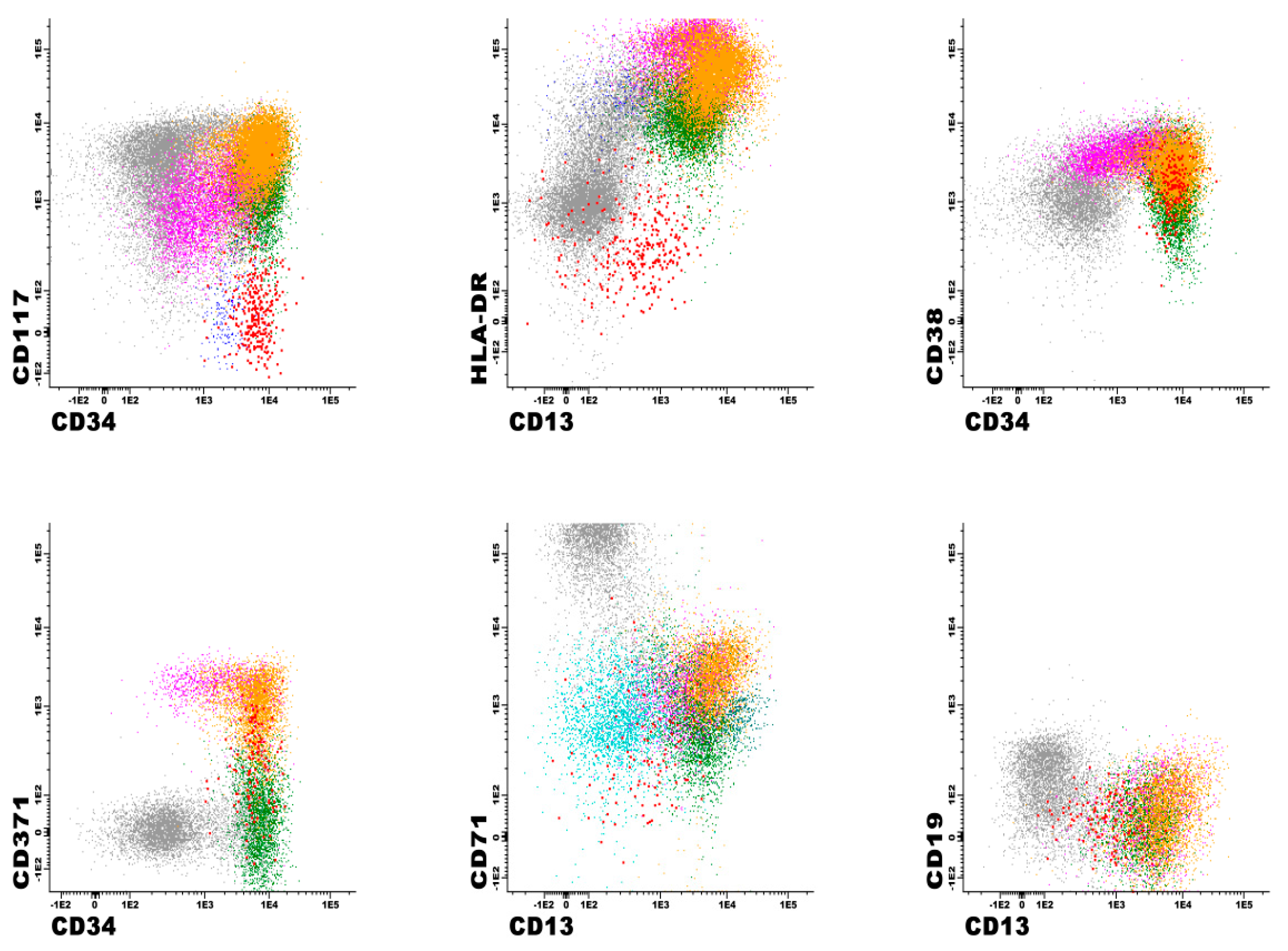

| FITC | PE | PerCP or PerCP-Cy5.5 | PE-Cy7 | APC | APC-H7 | V450 | V500 | APC-R700 | BV605 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tube 1 | Antibody | CD33 BB515 | CD123 | CD34 | CD13 | CD117 | CD16 APC-Vio770 | CD71 BV421 | HLA-DR BV480 | CD45 APC-AF700 | CD38 BV605 |
| Catalog# | 564588 | 306006 | 347213 | 338432 | 341106 | 130-113-393 | 562995 | 566113 | 560566 | 562665 | |
| Vendor | BD Horizon | BioLegend | BD | BD | BD | Miltenyi Biotec | BD Horizon | BD Horizon | BD Pharmingen | BD Horizon | |
| Tube 2 | Antibody | CD4 BB515 | CD36 | CD34 | CD13 | CD117 | CD64 APC-Fire750 | CD14 BV421 | HLA-DR BV480 | CD45 APC-AF700 | CD38 BV605 |
| Catalog# | 564419 | 555455 | 347213 | 338432 | 341106 | 305036 | 659450 | 566113 | 560566 | 562665 | |
| Vendor | BD Horizon | BD Pharmingen | BD | BD | BD | BioLegend | BD Horizon | BD Horizon | BD Pharmingen | BD Horizon | |
| Tube 3 | Antibody | CD7 BB515 | CD19 | CD34 | CD13 | CD117 | CD371 APC-Vio770 | CD56 BV421 | HLA-DR BV480 | CD45 APC-AF700 | CD15 BV605 |
| Catalog# | 565211 | 340720 | 347213 | 338432 | 341106 | 130-106-485 | 562751 | 566113 | 560566 | 562980 | |
| Vendor | BD Horizon | BD | BD | BD | BD | Miltenyi Biotec | BD Horizon | BD Horizon | BD Pharmingen | BD Horizon |
| AML Subtype | Count | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| AML, myelodysplasia-related | 33/126 | 26% |
| AML with NPM1 mutation | 31/126 | 25% |
| AML with biallelic TP53 inactivation | 11/126 | 9% |
| AML post cytotoxic therapy | 10/126 | 8% |
| AML with CEBPA mutation | 4/126 | 3% |
| AML with CBFB::MYH11 fusion | 4/126 | 3% |
| AML with KMT2A rearrangement | 4/126 | 3% |
| AML with RUNX1::RUNX1T1 | 3/126 | 3% |
| AML, transformation from a prior chronic myeloid neoplasm | 3/126 | 3% |
| AML with DEK::NUP214 fusion | 2/126 | 2% |
| AML with NUP98 rearrangement | 2/126 | 2% |
| Myeloid sarcoma | 2/126 | 2% |
| Mixed phenotype acute leukemia, B/myeloid | 2/126 | 2% |
| Mixed phenotype acute leukemia, T/myeloid | 1/126 | 1% |
| AML defined by differentiation | 12/126 | 11% |
| AML with maturation | 4/126 | 3% |
| Acute monocytic leukemia | 2/126 | 2% |
| Acute myelomonocytic leukemia | 6/126 | 5% |
| Stem Cells | Myeloblasts | Monoblasts | Erythroids (Immature) | Erythroids (Maturing) | Basophils | PDCs | Promyelocytes | Hematogones (“Mature”) | Hematogones (“Immature”) | Plasma Cells | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD34 | + | + | +/− | + | − | − | − | − | − | + | − |
| CD117 | + | + | + | + | + | − | − | + | − | − | − |
| HLA-DR | dim | + | bright | dim | dim | − | + | + | + | + | dim |
| CD13 | dim | + | + | − | − | + | − | bright | − | − | − |
| CD45 | dim | dim | dim | dim | dim | + | + | dim | dim | dim | dim |
| CD38 | −/dim | + | + | dim | bright | + | + | bright | bright | bright | |
| CD123 | dim | dim | + | − | − | bright | bright | − | +/− | +/− | − |
| CD71 | − | dim | dim | dim | bright | − | − | dim | − | − | − |
| CD33 | dim | + | + | − | − | + | − | + | − | − | − |
| CD16 | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| CD36 | − | − | − | dim | bright | + | + | − | − | − | − |
| CD64 | − | − | dim | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| CD14 | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| CD4 | − | − | dim | − | − | − | + | − | − | − | − |
| CD371 | − | + | + | − | − | dim | +/− | + | − | − | − |
| CD56 | − | − | − | − | − | − | +/− | − | − | − | +/− |
| CD15 | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | +/− | − | − | − |
| CD7 | − | − | − | − | − | − | +/− | − | − | − | − |
| CD19 | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | + | + | +/− |
| B Cells | T Cells | NK Cells | Mature Monocytes | Promonocytes | Mast Cells | Eosinophils | |||||
| CD34 | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | ||||
| CD117 | − | − | − | − | +/− | bright | − | ||||
| HLA-DR | bright | +/− | − | + | bright | dim | + | ||||
| CD13 | − | − | − | + | + | −/dim | + | ||||
| CD45 | + | + | + | + | + | dim | + | ||||
| CD38 | +/− | − | + | + | + | − | + | ||||
| CD123 | − | − | − | dim | + | − | − | ||||
| CD71 | − | − | − | − | − | dim | + | ||||
| CD33 | − | − | − | + | + | + | + | ||||
| CD16 | − | − | + | +/− | − | − | − | ||||
| CD36 | − | − | − | + | − | − | dim | ||||
| CD64 | − | − | − | + | + | − | − | ||||
| CD14 | − | − | − | + | − | − | − | ||||
| CD4 | − | +/− | − | dim | dim | dim | − | ||||
| CD371 | − | − | − | + | + | + | + | ||||
| CD56 | − | +/− | + | − | − | − | − | ||||
| CD15 | − | − | − | +/− | +/− | − | − | ||||
| CD7 | − | + | + | − | − | − | − | ||||
| CD19 | + | − | − | − | − | − | − | ||||
| Aberrant Antigen Expression | Abnormal | Dim/Negative | Bright |
|---|---|---|---|
| CD36 (positive) | 51/77 (66%) | ||
| CD13 | 45/77 (58%) | 41/77 (53%) | 4/77 (5%) |
| CD371 | 43/77 (56%) | 41/77 (53%) | 2/77 (3%) |
| CD34 (negative) | 39/77 (51%) | 33/77 (43%) | 6/77 (8%) |
| CD56 (positive) | 35/77 (46%) | ||
| HLA-DR | 35/77 (46%) | 30/77 (39%) | 5/77 (7%) |
| CD123 | 32/77 (42%) | 31/77 (41%) | 1/77 (1%) |
| CD7 (positive) | 30/77 (39%) | ||
| CD117 | 30/77 (39%) | 29/77 (38%) | 1/77 (1%) |
| CD38 | 27/77 (36%) | 25/77 (33%) | 2/77 (3%) |
| CD33 | 25/77 (33%) | 13/77 (17%) | 12/77 (16%) |
| CD15 (positive) | 17/77 (21%) | ||
| CD64 (positive) | 14/77 (18%) | ||
| CD4 (positive) | 13/77 (17%) | ||
| CD19 (positive) | 6/77 (8%) | ||
| CD45 (positive) | 5/77 (7%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jum’ah, H.A.; Otteson, G.E.; Timm, M.M.; Weybright, M.J.; Shi, M.; Horna, P.; Jevremovic, D.; Reichard, K.K.; Olteanu, H. Measurable Residual Disease Analysis by Flow Cytometry: Assay Validation and Characterization of 385 Consecutive Cases of Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Cancers 2025, 17, 1155. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17071155
Jum’ah HA, Otteson GE, Timm MM, Weybright MJ, Shi M, Horna P, Jevremovic D, Reichard KK, Olteanu H. Measurable Residual Disease Analysis by Flow Cytometry: Assay Validation and Characterization of 385 Consecutive Cases of Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Cancers. 2025; 17(7):1155. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17071155
Chicago/Turabian StyleJum’ah, Husam A., Gregory E. Otteson, Michael M. Timm, Matthew J. Weybright, Min Shi, Pedro Horna, Dragan Jevremovic, Kaaren K. Reichard, and Horatiu Olteanu. 2025. "Measurable Residual Disease Analysis by Flow Cytometry: Assay Validation and Characterization of 385 Consecutive Cases of Acute Myeloid Leukemia" Cancers 17, no. 7: 1155. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17071155
APA StyleJum’ah, H. A., Otteson, G. E., Timm, M. M., Weybright, M. J., Shi, M., Horna, P., Jevremovic, D., Reichard, K. K., & Olteanu, H. (2025). Measurable Residual Disease Analysis by Flow Cytometry: Assay Validation and Characterization of 385 Consecutive Cases of Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Cancers, 17(7), 1155. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17071155







