Targeting HSP90 with Ganetespib to Induce CDK1 Degradation and Promote Cell Death in Hepatoblastoma
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Lines
2.2. Western Blot Assay
2.3. Cell Viability Assay
2.4. RNA Expression Analysis
2.5. Proliferation Assay
2.6. Colony Formation Assay
2.7. Spheroid Assay
2.8. Live and Dead Staining
2.9. Cell Cycle Analysis
2.10. Apoptosis Assay
2.11. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Ganetespib Is the Most Effective HSP90 Inhibitor for Impeding HB Viability
3.2. Ganetespib Significantly Suppresses HB Growth Potential
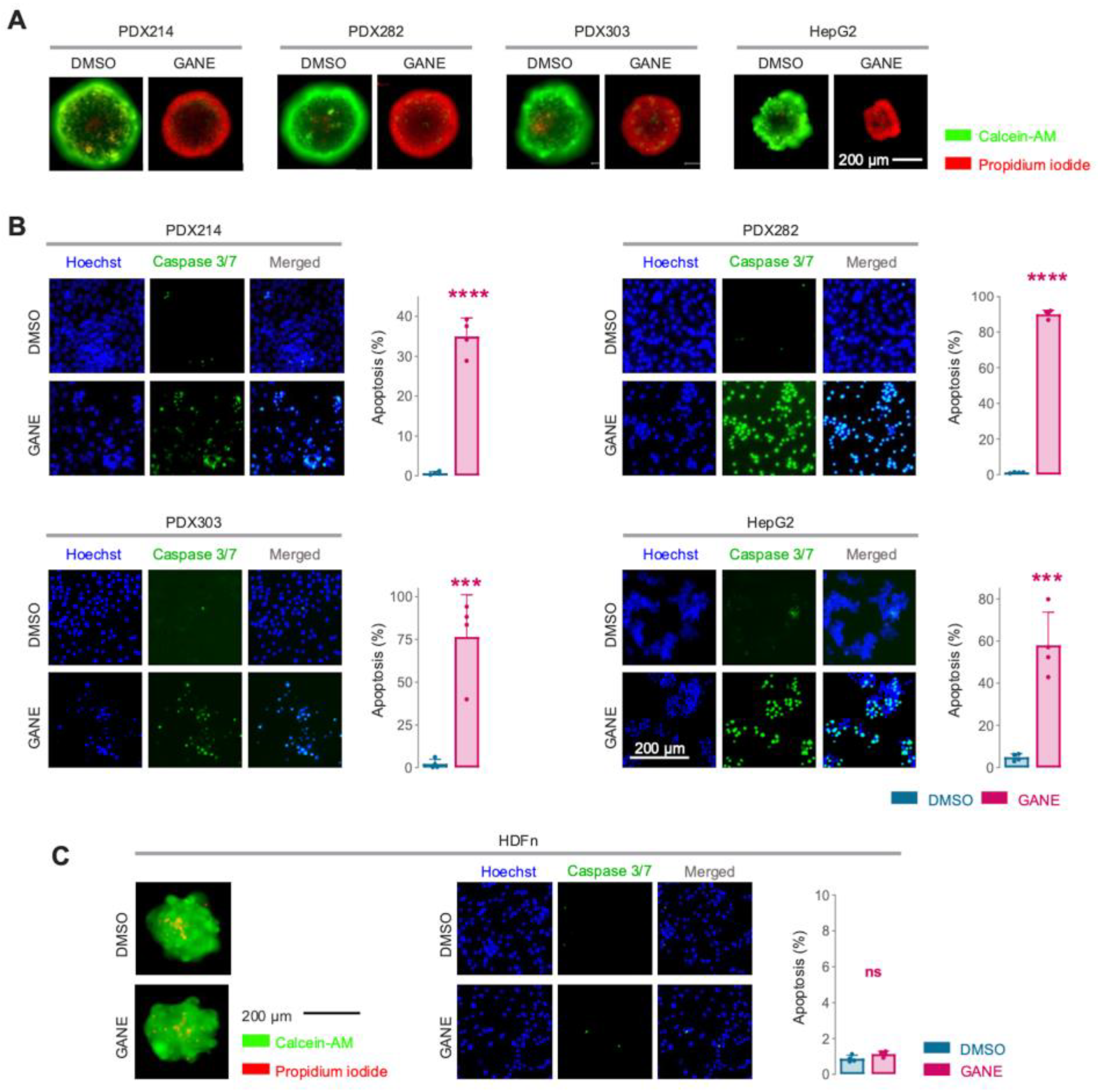
3.3. Ganetespib Triggers Tumor Cell Death in HB Models
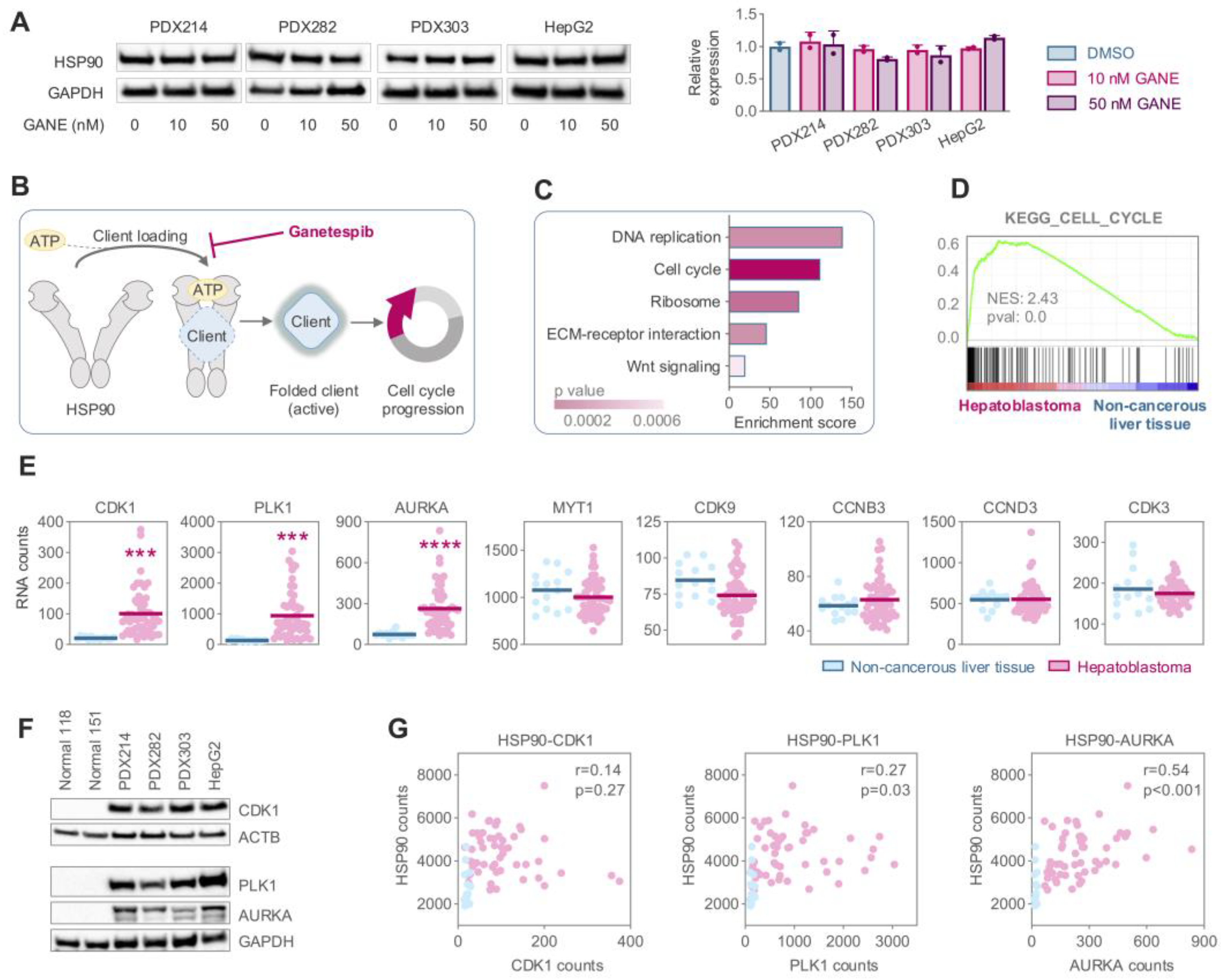
3.4. Elevated Expression of the HSP90 Client CDK1 Drives Hyperactivation of Cell Cycle Mechanisms in HB
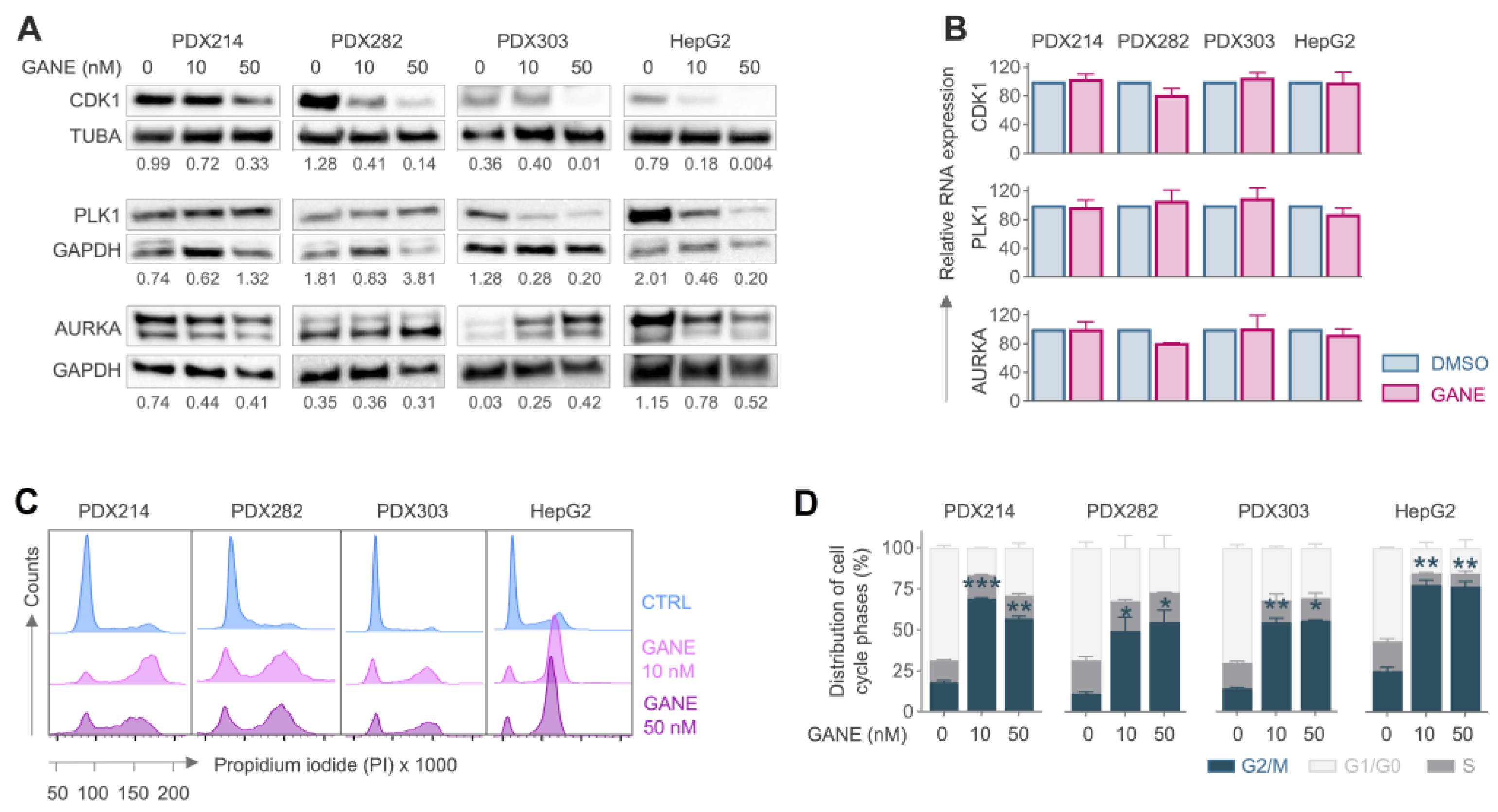
3.5. Ganetespib-Induced Inhibition CDK1 Leads to G2/M Arrest
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HB | Hepatoblastoma |
| HSP90 | Heat shock protein 90 |
| CDK1 | Cyclin-dependent kinase 1 |
| AUC | Area under the curve |
| TWS | Therapeutic window scores |
| GSEA | Gene set enrichment analysis |
References
- Spector, L.G.; Birch, J. The epidemiology of hepatoblastoma. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2012, 59, 776–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, T.C.; Zai, H.Y.; Jiang, W.; Zhu, Q.; Jiang, B.; Yao, L.; Li, X.Y.; Wang, Z.M. Survival and analysis of prognostic factors for hepatoblastoma: Based on SEER database. Ann. Transl. Med. 2019, 7, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perilongo, G.; Maibach, R.; Shafford, E.; Brugieres, L.; Brock, P.; Morland, B.; de Camargo, B.; Zsiros, J.; Roebuck, D.; Zimmermann, A.; et al. Cisplatin versus cisplatin plus doxorubicin for standard-risk hepatoblastoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 1662–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zsiros, J.; Brugieres, L.; Brock, P.; Roebuck, D.; Maibach, R.; Zimmermann, A.; Childs, M.; Pariente, D.; Laithier, V.; Otte, J.B.; et al. Dose-dense cisplatin-based chemotherapy and surgery for children with high-risk hepatoblastoma (SIOPEL-4): A prospective, single-arm, feasibility study. Lancet Oncol. 2013, 14, 834–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, C.; Santos, R.X.; Cardoso, S.; Correia, S.; Oliveira, P.J.; Santos, M.S.; Moreira, P.I. Doxorubicin: The good, the bad and the ugly effect. Curr. Med. Chem. 2009, 16, 3267–3285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsang, R.Y.; Al-Fayea, T.; Au, H.J. Cisplatin overdose: Toxicities and management. Drug Saf. 2009, 32, 1109–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eichenmüller, M.; Trippel, F.; Kreuder, M.; Beck, A.; Schwarzmayr, T.; Häberle, B.; Cairo, S.; Leuschner, I.; von Schweinitz, D.; Strom, T.M.; et al. The genomic landscape of hepatoblastoma and their progenies with HCC-like features. J. Hepatol. 2014, 61, 1312–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, T.Z.; Pilet, J.; Morcrette, G.; Roehrig, A.; Monteiro, B.J.E.; Molina, L.; Bayard, Q.; Trepo, E.; Meunier, L.; Caruso, S.; et al. Integrated Genomic Analysis Identifies Driver Genes and Cisplatin-Resistant Progenitor Phenotype in Pediatric Liver Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2021, 11, 2524–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagae, G.; Yamamoto, S.; Fujita, M.; Fujita, T.; Nonaka, A.; Umeda, T.; Fukuda, S.; Tatsuno, K.; Maejima, K.; Hayashi, A.; et al. Genetic and epigenetic basis of hepatoblastoma diversity. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, A.; Denkhaus, D.; Albrecht, S.; Leuschner, I.; von Schweinitz, D.; Pietsch, T. Childhood hepatoblastomas frequently carry a mutated degradation targeting box of the beta-catenin gene. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 269–273. [Google Scholar]
- Giardiello, F.M.; Petersen, G.M.; Brensinger, J.D.; Luce, M.C.; Cayouette, M.C.; Bacon, J.; Booker, S.V.; Hamilton, S.R. Hepatoblastoma and APC gene mutation in familial adenomatous polyposis. Gut 1996, 39, 867–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, H.V.; Koval, A.; Katanaev, V.L. Targeting the Wnt signalling pathway in cancer: Prospects and perils. Swiss Med. Wkly. 2019, 149, w20129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cairo, S.; Armengol, C.; Maibach, R.; Haberle, B.; Becker, K.; Carrillo-Reixach, J.; Guettier, C.; Vokuhl, C.; Schmid, I.; Buendia, M.A.; et al. A combined clinical and biological risk classification improves prediction of outcome in hepatoblastoma patients. Eur. J. Cancer 2020, 141, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schopf, F.H.; Biebl, M.M.; Buchner, J. The HSP90 chaperone machinery. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2017, 18, 345–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D. Hallmarks of Cancer: New Dimensions. Cancer Discov. 2022, 12, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitesell, L.; Lindquist, S.L. HSP90 and the chaperoning of cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2005, 5, 761–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascale, R.M.; Simile, M.M.; Calvisi, D.F.; Frau, M.; Muroni, M.R.; Seddaiu, M.A.; Daino, L.; Muntoni, M.D.; De Miglio, M.R.; Thorgeirsson, S.S.; et al. Role of HSP90, CDC37, and CRM1 as modulators of P16(INK4A) activity in rat liver carcinogenesis and human liver cancer. Hepatology 2005, 42, 1310–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.O.; Park, S.G.; Yoo, J.H.; Park, Y.M.; Kim, H.J.; Jang, K.T.; Cho, J.W.; Yoo, B.C.; Jung, G.H.; Park, C.K. Expression of heat shock proteins (HSP27, HSP60, HSP70, HSP90, GRP78, GRP94) in hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinomas and dysplastic nodules. World J. Gastroenterol. 2005, 11, 2072–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurley, E.H.; Tao, J.; Liu, S.; Krutsenko, Y.; Singh, S.; Monga, S.P. Inhibition of Heat Shock Factor 1 Signaling Decreases Hepatoblastoma Growth via Induction of Apoptosis. Am. J. Pathol. 2023, 193, 148–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kissoondoyal, A.; DeSousa, E.; Quaglietta, P.R.; Indersie, E.; Cairo, S.; Malkin, D.; Luques, L.; Baertschiger, R.M. Reduction in cell viability of hepatoblastoma cells following inhibtion of Hsp90. Cancer Res. 2023, 83 (Suppl. S7), 3540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modi, S.; Stopeck, A.; Linden, H.; Solit, D.; Chandarlapaty, S.; Rosen, N.; D’Andrea, G.; Dickler, M.; Moynahan, M.E.; Sugarman, S.; et al. HSP90 inhibition is effective in breast cancer: A phase II trial of tanespimycin (17-AAG) plus trastuzumab in patients with HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer progressing on trastuzumab. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 5132–5139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoy, S.M. Pimitespib: First Approval. Drugs 2022, 82, 1413–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, L.; Wadlow, R.C.; Blaszkowsky, L.S.; Wolpin, B.M.; Abrams, T.A.; McCleary, N.J.; Sheehan, S.; Sundaram, E.; Karol, M.D.; Chen, J.; et al. A phase I and pharmacokinetic study of ganetespib (STA-9090) in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Investig. New Drugs 2015, 33, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, S.; Hotes, A.; Schmid, T.; Cairo, S.; Indersie, E.; Pisano, C.; Hiyama, E.; Hishiki, T.; Vokuhl, C.; Branchereau, S.; et al. Drug prioritization identifies panobinostat as a tailored treatment element for patients with metastatic hepatoblastoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2024, 43, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eichenmüller, M.; Gruner, I.; Hagl, B.; Häberle, B.; Müller-Höcker, J.; von Schweinitz, D.; Kappler, R. Blocking the hedgehog pathway inhibits hepatoblastoma growth. Hepatology 2009, 49, 482–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfaffl, M.W. A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, e45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, S.; Razizadeh, N.; Indersie, E.; Branchereau, S.; Cairo, S.; Kappler, R. Targeting G9a/DNMT1 methyltransferase activity impedes IGF2-mediated survival in hepatoblastoma. Hepatol. Commun. 2024, 8, e0378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zsiros, J.; Maibach, R.; Shafford, E.; Brugieres, L.; Brock, P.; Czauderna, P.; Roebuck, D.; Childs, M.; Zimmermann, A.; Laithier, V.; et al. Successful treatment of childhood high-risk hepatoblastoma with dose-intensive multiagent chemotherapy and surgery: Final results of the SIOPEL-3HR study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 2584–2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrows, F.; Zhang, H.; Kamal, A. Hsp90 activation and cell cycle regulation. Cell Cycle 2004, 3, 1530–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echeverria, P.C.; Bernthaler, A.; Dupuis, P.; Mayer, B.; Picard, D. An interaction network predicted from public data as a discovery tool: Application to the Hsp90 molecular chaperone machine. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e26044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kats, D.; Ricker, C.A.; Berlow, N.E.; Noblet, B.; Nicolle, D.; Mevel, K.; Branchereau, S.; Judde, J.G.; Stiverson, C.D.; Stiverson, C.L.; et al. Volasertib preclinical activity in high-risk hepatoblastoma. Oncotarget 2019, 10, 6403–6417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Zhang, H.; He, B.; Liu, Z.; Wu, X.; Liu, Y.; Xu, X.; Gou, X.; Wang, H.; Yang, Q. Heat shock protein 90 inhibitors induce cell differentiation via the ubiquitin-dependent aurora kinase A degradation in a MPLW515L mouse model of primary myelofibrosis. Hematol. Oncol. 2023, 41, 474–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Kalsbeek, R.J.; Hudson, M.M.; Mulder, R.L.; Ehrhardt, M.; Green, D.M.; Mulrooney, D.A.; Hakkert, J.; den Hartogh, J.; Nijenhuis, A.; van Santen, H.M.; et al. A joint international consensus statement for measuring quality of survival for patients with childhood cancer. Nat. Med. 2023, 29, 1340–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, S.; Joshi, A.; Sato, N.; Lee, S.; Lee, M.J.; Trepel, J.B.; Neckers, L. An update on the status of HSP90 inhibitors in cancer clinical trials. Cell Stress Chaperones 2024, 29, 519–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saber, S.; Hasan, A.M.; Mohammed, O.A.; Saleh, L.A.; Hashish, A.A.; Alamri, M.M.S.; Al-Ameer, A.Y.; Alfaifi, J.; Senbel, A.; Aboregela, A.M.; et al. Ganetespib (STA-9090) augments sorafenib efficacy via necroptosis induction in hepatocellular carcinoma: Implications from preclinical data for a novel therapeutic approach. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 164, 114918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, J.W.; Raju, R.N.; Gordon, G.A.; El-Hariry, I.; Teofilivici, F.; Vukovic, V.M.; Bradley, R.; Karol, M.D.; Chen, Y.; Guo, W.; et al. A first in human, safety, pharmacokinetics, and clinical activity phase I study of once weekly administration of the Hsp90 inhibitor ganetespib (STA-9090) in patients with solid malignancies. BMC Cancer 2013, 13, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Gholami, A.M.; Kuster, B. Systematic identification of the HSP90 candidate regulated proteome. Mol. Cell Proteom. 2012, 11, M111.016675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Workman, P.; Burrows, F.; Neckers, L.; Rosen, N. Drugging the cancer chaperone HSP90: Combinatorial therapeutic exploitation of oncogene addiction and tumor stress. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2007, 1113, 202–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, N.; Gupta, S.; Sharma, S.; Soni, A.; Bagabir, S.A.; Bhattacharyya, M.; Mukherjee, A.; Almalki, A.H.; Alkhanani, M.F.; Haque, S.; et al. CDK1 and HSP90AA1 Appear as the Novel Regulatory Genes in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Bioinformatics Approach. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Guo, X.; Yuan, Q.; Nian, S.; Kang, P.; Xu, Z.; Li, L.; Ye, Y. Systematic Pan-Cancer Analysis Identifies CDK1 as an Immunological and Prognostic Biomarker. J. Oncol. 2022, 2022, 8115474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; He, F.; Zhang, Z.; Xiang, Z.; Hu, D. CDK1 serves as a potential prognostic biomarker and target for lung cancer. J. Int. Med. Res. 2020, 48, 300060519897508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunada, S.; Saito, H.; Zhang, D.; Xu, Z.; Miki, Y. CDK1 inhibitor controls G2/M phase transition and reverses DNA damage sensitivity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2021, 550, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Lu, Z.; Shi, X.; Liu, L.; Zhang, P.; Golemis, E.A.; Tu, Z. HSP90 inhibition downregulates DNA replication and repair genes via E2F1 repression. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 297, 100996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, Z.; Wang, L.; Zheng, Y.; Liang, N.; Wang, X.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, C.; Zhu, T.; Liu, C. PADI3 plays an antitumor role via the Hsp90/CKS1 pathway in colon cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2019, 19, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Zhou, X.; He, Y.; Ke, X.; Wen, Y.; Zou, F.; Chen, X. Hyperthermia enhances 17-DMAG efficacy in hepatocellular carcinoma cells with aggravated DNA damage and impaired G2/M transition. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jung, L.A.; Demir, S.; Hotes, A.; Hiyama, E.; Hishiki, T.; Indersie, E.; Branchereau, S.; Cairo, S.; Kappler, R. Targeting HSP90 with Ganetespib to Induce CDK1 Degradation and Promote Cell Death in Hepatoblastoma. Cancers 2025, 17, 1341. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17081341
Jung LA, Demir S, Hotes A, Hiyama E, Hishiki T, Indersie E, Branchereau S, Cairo S, Kappler R. Targeting HSP90 with Ganetespib to Induce CDK1 Degradation and Promote Cell Death in Hepatoblastoma. Cancers. 2025; 17(8):1341. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17081341
Chicago/Turabian StyleJung, Lea Amelie, Salih Demir, Alina Hotes, Eiso Hiyama, Tomoro Hishiki, Emilie Indersie, Sophie Branchereau, Stefano Cairo, and Roland Kappler. 2025. "Targeting HSP90 with Ganetespib to Induce CDK1 Degradation and Promote Cell Death in Hepatoblastoma" Cancers 17, no. 8: 1341. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17081341
APA StyleJung, L. A., Demir, S., Hotes, A., Hiyama, E., Hishiki, T., Indersie, E., Branchereau, S., Cairo, S., & Kappler, R. (2025). Targeting HSP90 with Ganetespib to Induce CDK1 Degradation and Promote Cell Death in Hepatoblastoma. Cancers, 17(8), 1341. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17081341







