Abstract
The hydroprocessing of gasoline on modified alumina catalysts makes it possible to obtain high-octane products. The implementation and development of the process have largely become possible due to the development of modified alumina catalysts that do not contain noble metals and exhibit special catalytic properties. This article discusses topical issues of petrochemistry, namely the creation of catalysts with improved characteristics for the production of high-octane gasoline with low sulfur content. New catalytic systems based on alumina and other carriers modified with transition metals, lanthanum and phosphorus were synthesized. By physico-chemical methods of analysis TPD of ammonia, TEM and XRD, we studied the acid–base and structural characteristics of the developed catalysts. The activity of the developed catalysts in the studied process of hydrotreating gasoline fractions depends on the structure and condition of the active centers. The process of hydrotreating straight-run gasoline in the presence of synthesized catalysts was carried out on a laboratory flow unit. It was shown that, during the hydrotreating of straight-run gasoline on the NiO-MoO3-La-P-HZSM-HY-Al2O3 catalyst, the octane number in the final product increased to 88.6, and the sulfur content decreased from 0.0088 to 0.001%. It was found that the minimum sulfur content in the gasoline hydrotreating product of 0.0005% was achieved on the catalyst CoO-WO3-La-P-HZSM-HY-Al2O3, which is significantly lower than for other studied catalytic systems. The obtained results of the sulfur content in the hydrotreating products fully comply with the Euro-5 standard. Thus, the efficiency of hydrotreating the gasoline fractions studied in this work was mainly determined by the nature of the carriers and modifiers used for the synthesis of catalysts and the technological parameters of the process. The synthesized catalysts showed high activity and selectivity, resulting in high-octane gasoline with a low sulfur content that meets international quality standards.
1. Introduction
The intensive use of light oil as a raw material for the production of valuable petrochemical products is becoming increasingly important against the background of the gradual depletion of hydrocarbon resources and the weighting of oil fractions. The creation of new effective catalysts and technologies for processing petroleum fractions in order to obtain high-quality low-sulfur motor fuels that meet international standards remains an insufficiently studied area of scientific research. The market offers catalysts that differ in chemical composition, dispersion, granule diameter and strength properties and in cost. Manufacturers face the problem of choosing the right catalyst to increase the efficiency of oil refining. In this context, one of the most relevant areas of petrochemistry and catalysis is associated with the development of new modified catalytic compositions with improved properties, including activity, selectivity, stability, dispersion and sulfidability, or the more effective integration of active additives used for hydrotreating, hydroisomerization and hydrodesulfurization processes used on an industrial scale.
Advanced catalytic formulations with improved properties during hydrotreatment must meet increasingly stringent environmental requirements for the sulfur content in fuels for internal combustion engines. An important priority in the technologies of oil refineries for the production of high-quality gasoline, widely used in modern automobile engines, is the process of hydrotreating with zeolite-containing catalysts.
To obtain high-octane commercial gasoline and medium distillate fuel suitable for cold and Arctic climatic conditions, deep hydrotreating and hydroisomerization on solid catalysts that do not contain noble metals are increasingly used in oil refining [1,2,3,4,5]. The optimal catalysts for the hydrotreating process today are bimetallic catalysts based on molybdenum and tungsten sulfides, enriched with nickel, cobalt, zinc and rare earth elements and, as a rule, deposited on an inorganic oxide carrier. One way to improve the characteristics of the catalyst may be to replace the carrier with mesoporous carbon or polymer material, which significantly reduce the interaction of the active phase with the carrier; however, at the same time, the adjustable pore size ensures the best diffusion of reagent molecules [6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14].
The authors of [5] provide an overview of technologies for producing high-octane gasoline that meet European standards for environmental requirements. Various methods have been developed to remove sulfur-containing compounds from petroleum products. For ZSM-5 zeolites, the modification of Zn or Ga significantly increases the selectivity for aromatic compounds due to changes in the reaction pathways. Modifiers stimulate dehydrogenation reactions, leading to the formation of aromatic compounds [6]. In [8], zeolites X and Y were studied for the adsorption of sulfur compounds, due to their tunable selectivity with respect to polar molecules and pore size. Zeolites have shown good sulfur adsorption ability, good regenerability and stable structures for removing sulfur compounds.
One of the important problems in oil refining is the increased sulfur content in the incoming hydrocarbon raw materials. For example, according to the Energy Agency of the Republic of Kazakhstan, the sulfur content is in the range of 0.35–1.69%. According to international standards, a significant restriction of the content of sulfur, benzene, aromatic and olefin hydrocarbons in motor fuels is required. Sulfur-containing compounds poison catalysts and, in complexes with metals, they not only block the surface but also precipitate on reactor installations, causing corrosion and deteriorating their performance.
Therefore, refineries need to radically change the technology of catalytic processing in order to reduce the sulfur content in the resulting fuel and synthesized petroleum products to meet European standards. The hydro desulfurization required to reduce the sulfur content in oil fractions requires high costs, especially to achieve ultra-deep desulfurization <10 ppm. For the deep hydrotreating of various oil fractions, it is necessary to use new effective catalysts and technologies [15,16,17,18].
The removal of sulfur from motor fuels using zeolites as sorbents is an attractive desulfurization method due to its low energy and financial costs. However, diffusion limitations in the microporous structure of zeolites can reduce their adsorption capacity, especially when porphyrin and thiophene sulfur compounds are present in the fuel. Moreover, the selective adsorption of sulfur compounds from a mixture of hydrocarbons can be a very difficult task. The solution to the above-mentioned problem of the adsorption desulfurization of fuel was the use of metal exchange mesoporous Y-zeolites. Mesoporous catalysts were obtained by introducing surfactants into zeolites Y and by desilicatization. The metals Ce and Cu were introduced by ion exchange. The results showed that mesoporous Y reduces diffusion limitations and is a very effective sorbent for removing sulfur compounds with a high kinetic diameter, such as dibenzothiophene. The introduced metals significantly increase the selectivity of zeolite with respect to heteroaromatic sulfur compounds [10].
In [12], a review of the catalytic cracking of triglycerides on zeolite catalysts was conducted with an emphasis on the main achievements in the field of zeolite crystallization for their adaptation to triglyceride-based oils. The technology of obtaining zeolite crystals by reducing the length of the diffusion path and including heteroatoms for the catalytic cracking of triglycerides based on examples from the scientific literature has been studied. Several areas of future research on the development of zeolite catalysts for the efficient conversion of triglycerides into renewable hydrocarbon fuels and chemicals have been identified.
Thus, currently, the world is actively searching for and developing new catalysts for the deep hydrotreating of petroleum fractions for the production of low-sulfur motor fuels with a high octane number. At the same time, much attention is paid to the development of hydroprocessing technology and efficient and stable catalytic systems for a certain type of petroleum product, for example, gasoline fractions of oil [19,20,21,22,23].
The creation of a scientific basis for new environmentally friendly technologies for processing hydrocarbon raw materials requires studying the mechanism of reactions of the hydrotreating process occurring on zeolite catalysts, taking into account the assumed structure and state of the catalytically active component, as well as the formation of the necessary texture of the carrier matrix.
The purpose of this work is to develop a new composition of catalysts based on aluminum oxide modified with additives of rare earth metals, phosphorus and zeolite, and to determine their effectiveness in the process of the catalytic hydrotreating of straight-run gasoline to obtain a high-octane product with a low sulfur content.
2. Results and Discussion
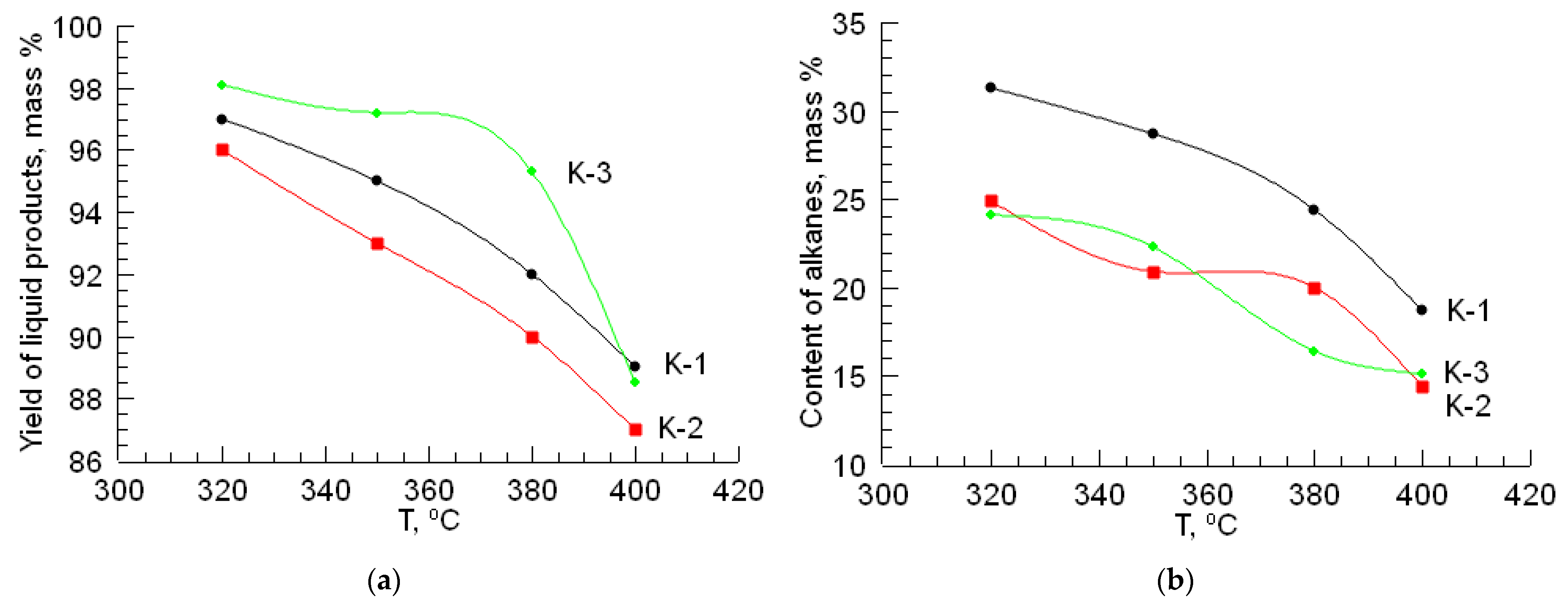
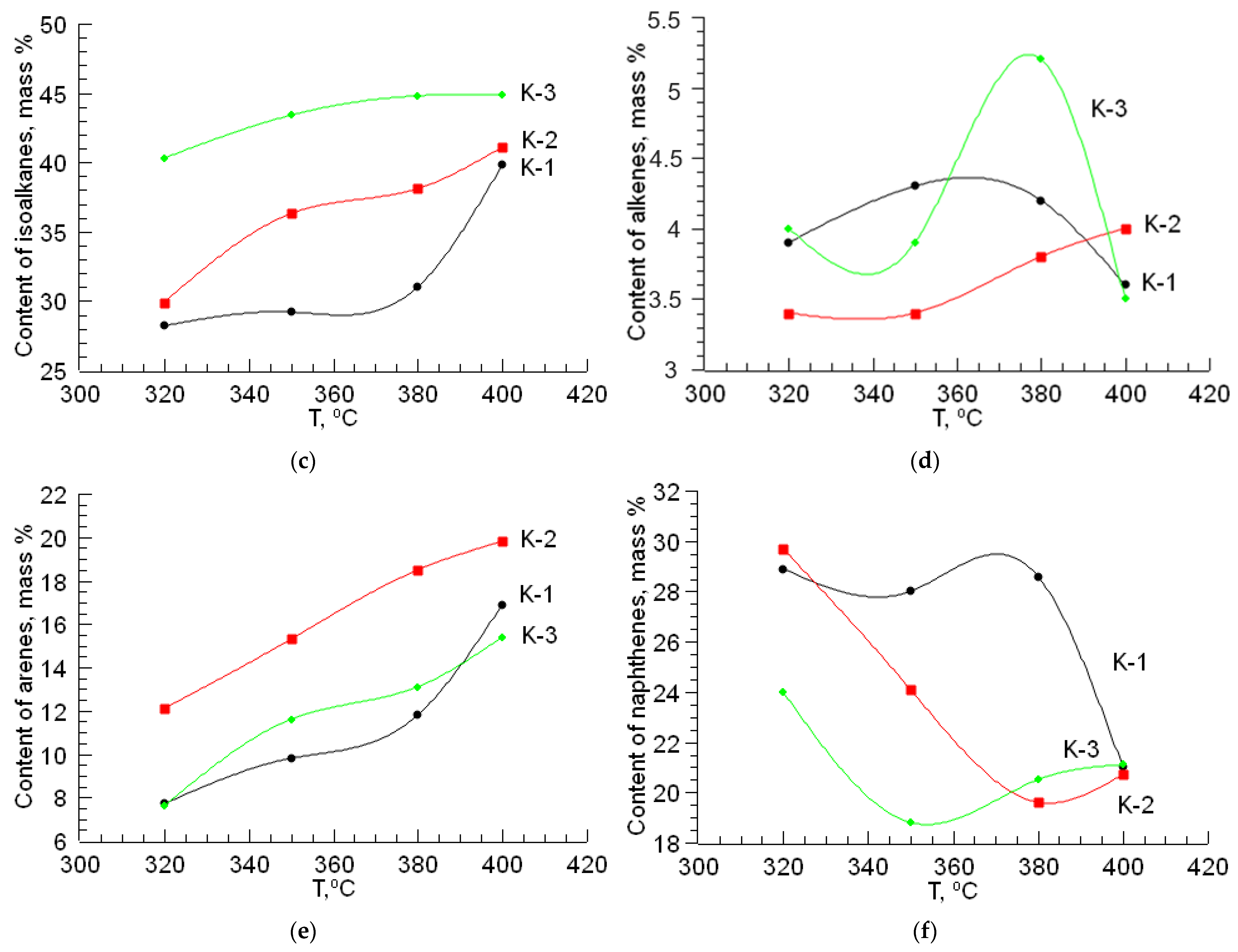
In the process of hydrotreating raw materials, the effect of temperature on the change in the composition of straight-run gasoline was studied. The results are presented in the form of graphs in Figure 1.
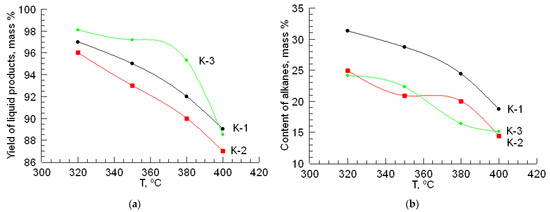
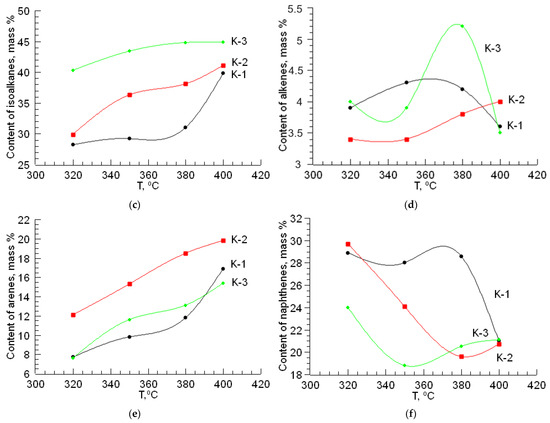
Figure 1.
The effect of temperature on the yield and content of hydrocarbon classes of liquid products in hydrotreating gasoline: (a) yield of liquid products; (b) content of alkanes; (c) content of isoalkanes; (d) content of alkenes; (e) content of arenes; (f) content of naphthenes.
During the hydroprocessing of straight-run gasoline using a CoO-MoO3-La-P-HZSM-HY-Al2O3 catalyst (K-1), the yield of the liquid products decreases from 97 to 89 mass% when the temperature increases from 320 to 400 °C. With an increase in temperature to 400 °C, the amounts of isoalkanes and aromatic hydrocarbons compared to the original increase from 26.3 to 39.8 mass% and from 5.6 to 16.9 mass%, respectively. The yield of naphthenic hydrocarbons in the catalyzate under these conditions decreases from 28.9 to 21.0 mass%. In this case, a decrease in the content of alkanes is observed from 31.3 to 18.7 mass%. The amount of alkenes in the resulting catalysate ranges from 3.6 to 4.3 mass%.
During the hydroprocessing of the gasoline fraction on the CoO-WO3-La-P-HZSM-HY-Al2O3 catalyst (K-2), the yield of the liquid products decreases from 96 to 87 mass% when the temperature increases from 320 to 400 °C. The amount of isoalkanes increases to 41.1 mass%. The yield of aromatic hydrocarbons increases from 12.1 to 19.8 mass% when increasing the process temperature to 400 °C. The amount of naphthenes decreases from 29.7 to 20.7 mass%. The content of alkenes in the catalyzate varies within 3.4–4.0 mass%.
The maximum content of isoalkanes in the resulting catalyst is observed on the NiO-MoO3-La-P-HZSM-HY-Al2O3 catalyst (K-3) at 400 °C and is equal to 44.9 mass%. The NiO-MoO3-La-P-HZSM-HY-Al2O3 catalyst (K-3) has high hydroisomerizing activity. With an increase in temperature from 320 to 400 °C, the yield of the liquid products decreases from 98.1 to 88.5 mass%. The content of aromatic hydrocarbons in the liquid phase increases from 7.6 to 15.4 mass%, while the amount of naphthenic hydrocarbons decreases to 21.1 mass%. In the temperature range 320–400 °C, the yield of alkenes is 3.5–4.0 mass%.
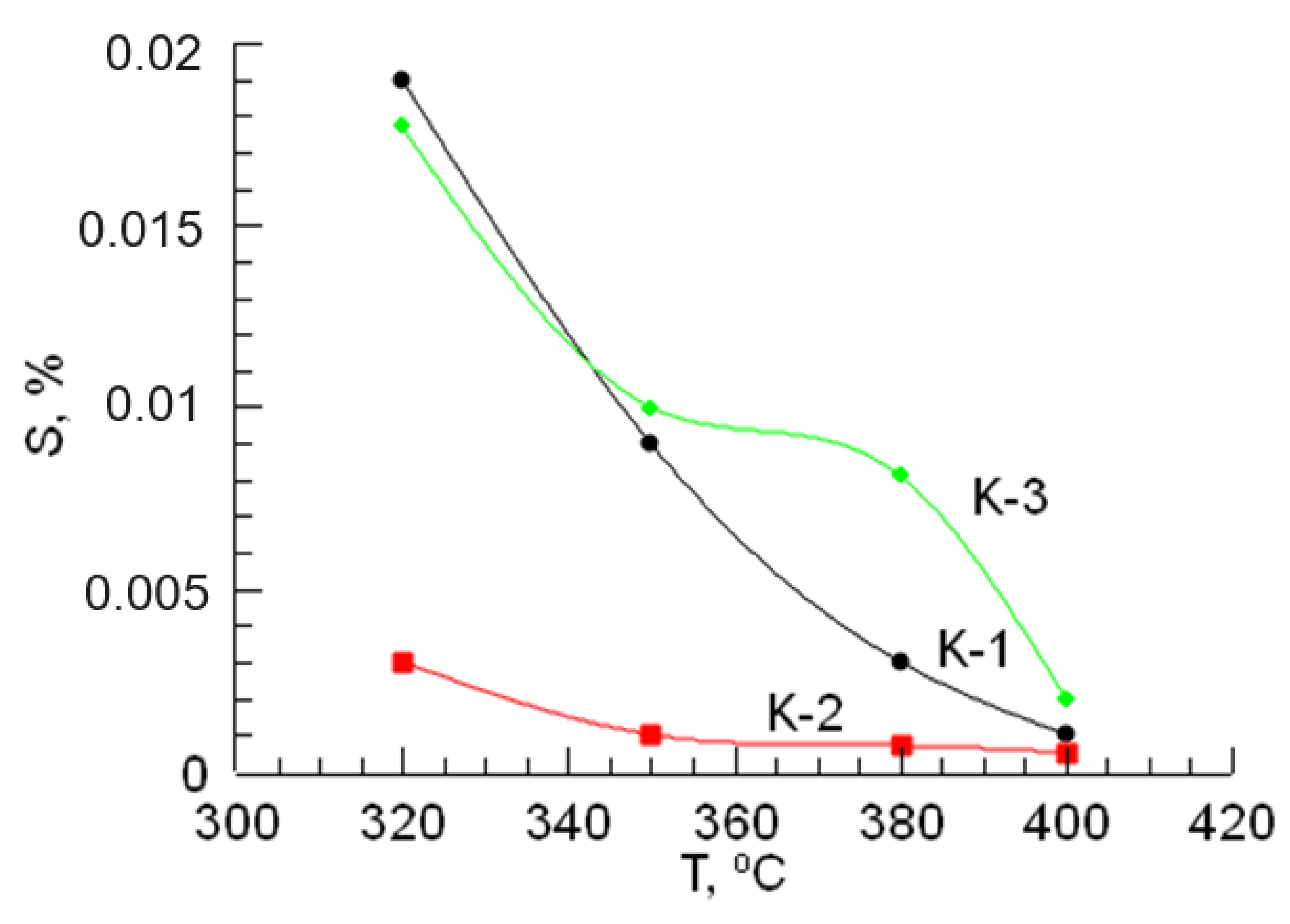
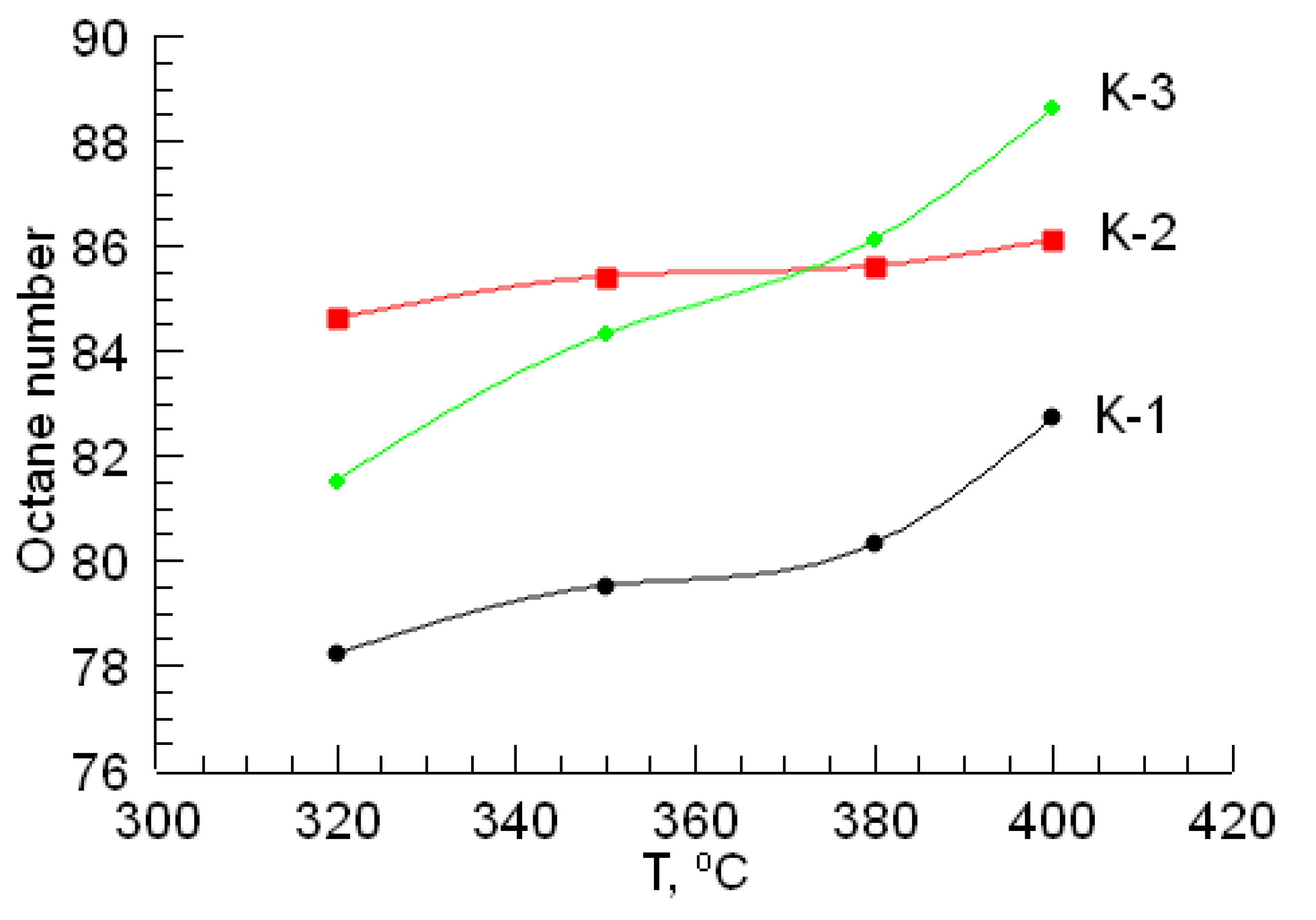
According to the dependencies shown in Figure 2 and Figure 3, changes in the sulfur content in gasoline, caused by an increase in temperature in the hydrotreating reaction, and the octane number increase. In the hydrotreating of gasoline, the CoO-WO3-La-P-HZSM-HY-Al2O3 catalyst (K-2) sample exhibits the activity of the catalyst in terms of sulfur content. If we consider the growth of the octane number, then the most active catalyst sample for gasoline is the NiO-MoO3-La-P-HZSM-HY-Al2O3 catalyst (K-3).
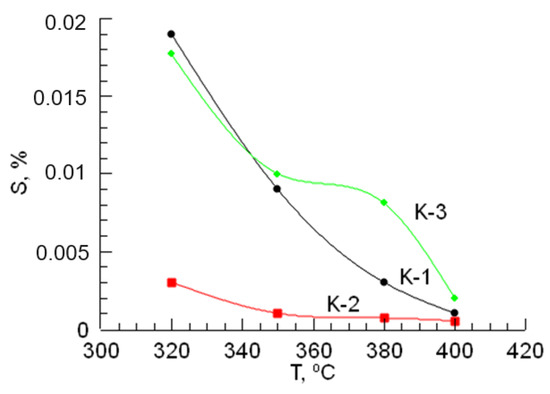
Figure 2.
The effect of temperature on the sulfur content in the final sample after the hydrotreating of gasoline.
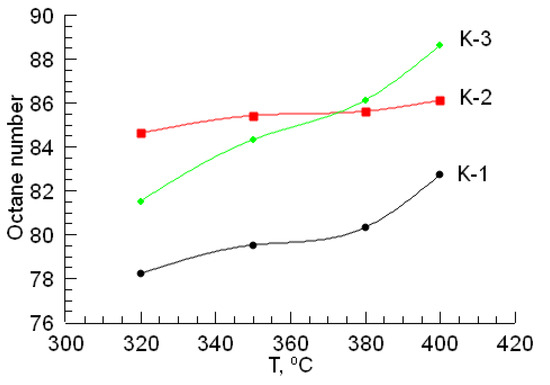
Figure 3.
The effect of temperature on the octane number in the final sample after the hydrotreating of gasoline.
The testing of the NiO-MoO3-La-P-HZSM-HY-Al2O3 catalyst (K-3) in the process of gasoline hydrotreating led to an increase in its octane number to 88.6, which is significantly higher compared to the test results of other catalysts. The catalyst CoO-WO3-La-P-HZSM-HY-Al2O3 (K-2) showed the best result in gasoline desulfurization; during its testing, the sulfur content decreased to 0.0005 mass%. This value of the amount of sulfur turned out to be even lower than the value required by the Euro-5 standard. According to the efficiency of reducing sulfur content, catalysts can be arranged in the following series: K-3 < K-1 < K-2. It is noted that the amount of sulfur found in the final sample decreases with increasing temperature. In general, this tendency was observed for all catalyst samples. With an increase in temperature, the sulfur content decreased and the octane number increased; that is, the quality of the gasoline fraction increased. In this case, the most impressive results from the considered temperature range were found at 400 °C.
Environmentally friendly lanthanum is a low-cost rare earth element that has been added to catalysts and supports improved thermal stability and surface basicity. For example, reducing the acidity of aluminum oxides by 60% contributed to increasing the stability of ethanol conversion by reducing coke formation. The higher stability of the La-modified HZSM-5 catalysts during the decomposition of methyl mercaptan compared to the undoped material was due to the lower Brønsted acidity [24,25].
It was shown in [26] that modifying a Ni-Mo hydrotreating catalyst with the rare earth elements, Ce and La, allows for increasing the stability of operation. Lanthanum is a better activity stabilizer than cerium, and also increases the hydrodesulfurization activity of the Ni-Mo catalyst by 5–10%.
To establish the acid–base characteristics of the catalysts, the method of temperature-programmed ammonia desorption was used (Table 1). Ammonia adsorption on the surface of catalysts occurs in two forms. The composition of acid centers may include metals in various degrees of oxidation, fixed both inside the zeolite cavities and on their outer side. The functioning of various types of centers in catalytic processes is often considered as independent, without taking into account the possibility of their joint action on the reactant molecule. However, it can be assumed that it is their simultaneous presence that ensures the polyfunctionality of the catalytic system.

Table 1.
Results of temperature-programmed desorption of ammonia on test catalysts.
Acid sites predominate on the surface of the CoO-WO3-La-P-HZSM-HY-Al2O3 catalyst (K-2) Tdesorbtion = 250 °C; their content in the catalyst is 8.57 × 10−4 mol/g. The temperature of desorption of ammonia from the surface of the CoO-MoO3-La-P-HZSM-HY-Al2O3 catalyst (K-1) is 220 °C; the content of substances in the catalyst is 9.48 × 10−4 mol/g. In addition, the amounts of desorbed ammonia in various forms are close to the CoO-MoO3-La-P-HZSM-HY-Al2O3 catalyst (K-1), at 10.2 × 10−4 and 9.48 × 10−4 mol NH3des/g, respectively. The maximum amount of desorbed ammonia in the NiO-MoO3-La-P-HZSM-HY-Al2O3 catalyst (K-3) is 31.3 × 10−4 mol/g. In the CoO-WO3-La-P-HZSM-HY-Al2O3 catalyst (K-2), the number of weakly bound acid sites falling to 150 °C is small and amounts to 1.88 × 10−4 mol/g. The total amount of ammonia obtained from the surface of the CoO-WO3-La-P-HZSM-HY-Al2O3 catalyst (K-2) is 10.45 × 10−4 mol/g of catalyst.
According to the Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) surface area analysis method, the surface area of the synthesized catalysts ranges from 211 to 274 m2/g with a pore size diameter 4–10 nm and a total pore volume that does not exceed 0.28–0.41 cm3/g.
The mechanical strength of the catalyst granules was also determined. Depending on the composition, the different mechanical strengths of the CoO-MoO3-La-P-HZSM-HY-Al2O3 (K-1), CoO-WO3-La-P-HZSM-HY-Al2O3 (K-2) and NiO-MoO3-La-P-HZSM-HY-Al2O3 (K-3) catalysts are in the range of 26.1–65.4 kg/mm2.
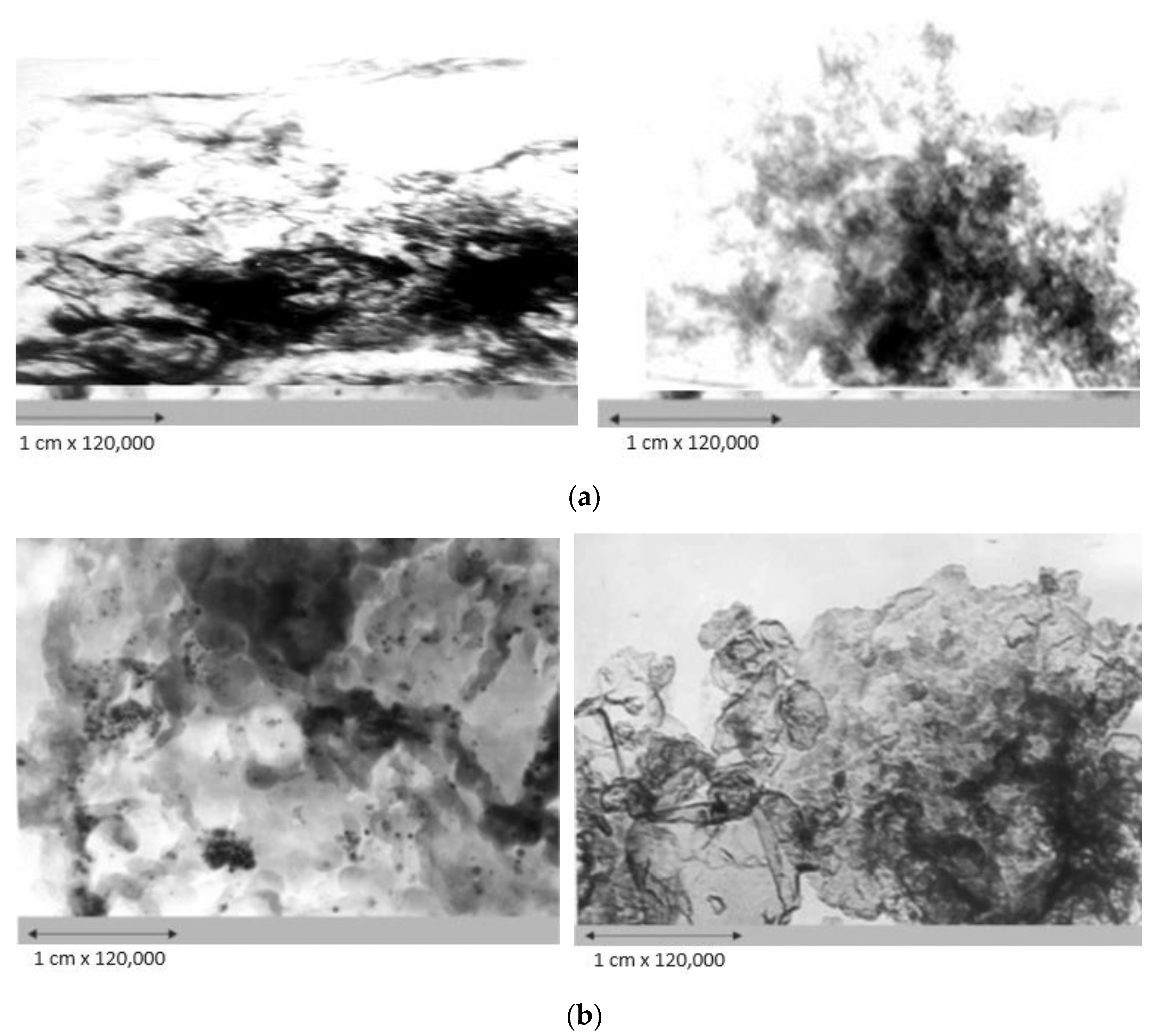
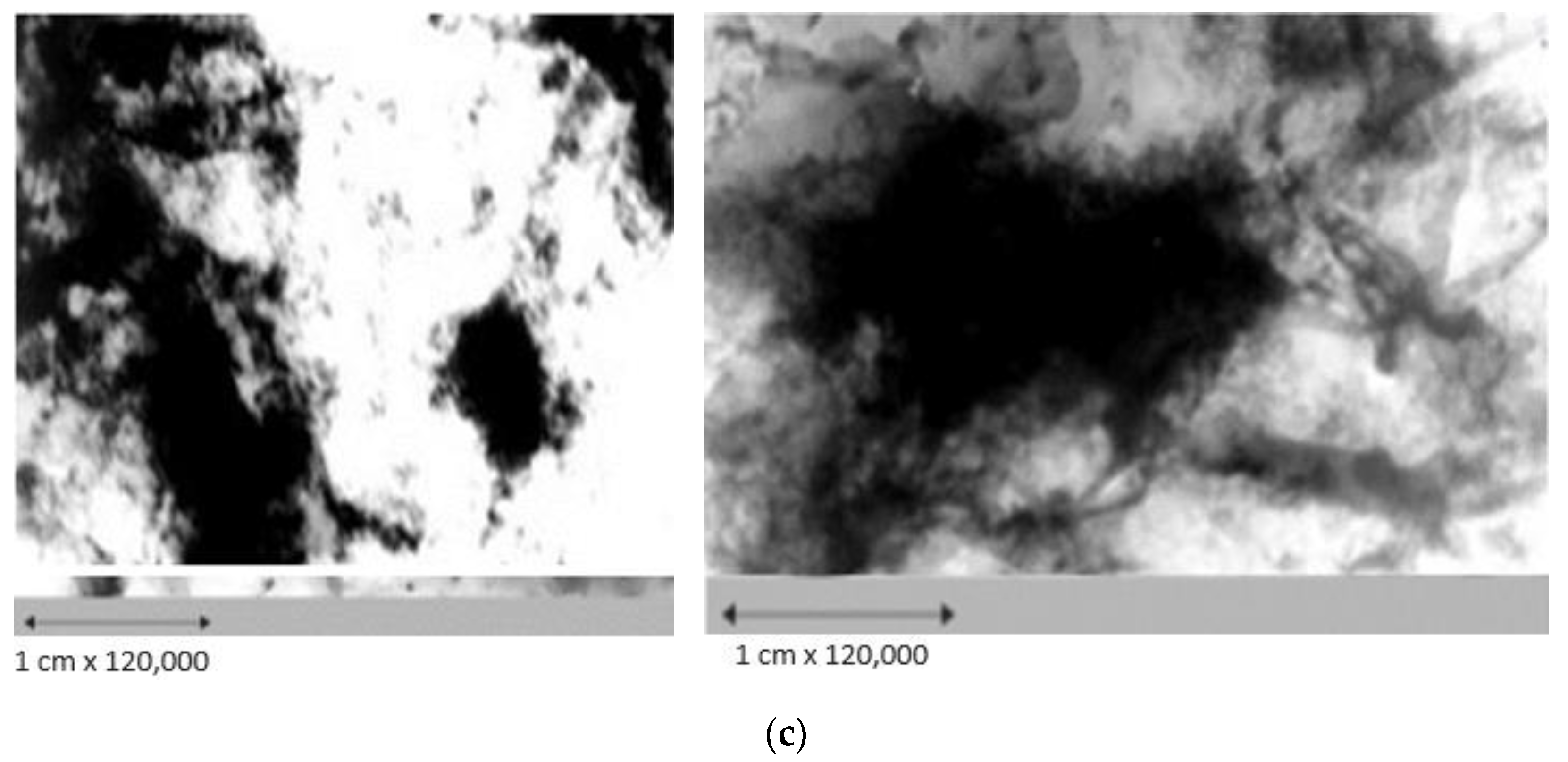
The results of analyses using transmission electron microscopy and X-ray diffraction analysis showed that the synthesized catalysts are highly dispersed, and the active phase metals are predominantly in the oxidized state. There are associated clusters on the surface of catalysts and their characteristics, such as dispersity and structure, are determined by the nature of the catalyst components. Electron microscopic studies of the CoO-MoO3-La-P-HZSM-HY-Al2O3 catalyst (K-1) (Figure 4a) showed that, on the surface, there are small aggregates with particle sizes of 3.0–4.0 nm, identified as Mo3Si and La-P, and structures with a particle diameter of about 5.0–10.0 nm, formed by La2O3, MoSi2 and MoP. The structure of the catalyst is also dominated by formations with a particle diameter of 4.0–6.0 nm, consisting of Al-La3, Co2O3, Co2, SiO3 and La6O11.
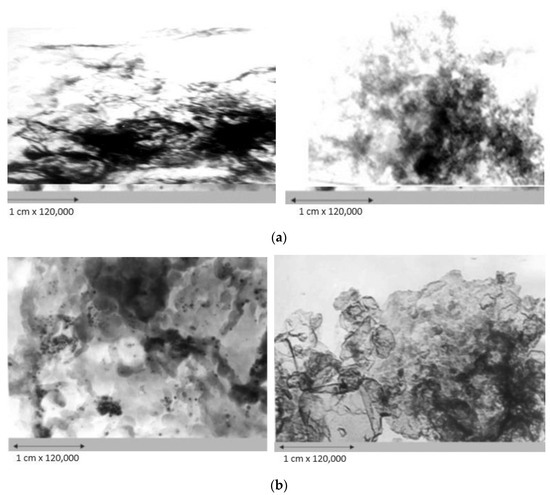
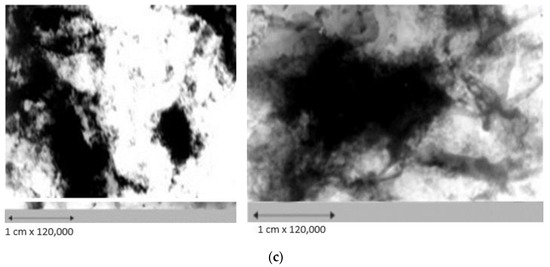
Figure 4.
Electron microscopic images of the catalysts: (a) K-1—CoO-MoO3-La-P-HZSM-HY-Al2O3; (b) K-2—CoO-WO3-La-P-HZSM-HY-Al2O3; (c) K-3—NiO-MoO3-La-P-HZSM-HY-Al2O3.
On the surface of the catalyst CoO-WO3-La-P-HZSM-HY-Al2O3 (K-2) (Figure 4b), structures were found, the size of which ranged from 2.5 to 3.0 nm, consisting of La2O3. Clusters with diameters of 5.0 and 20.0 nm were observed from highly dispersed particles with sizes of 0.20–0.25 nm, which consisted of La4W9O33 and WO3. Also, areas formed with small accumulations of dense particles with a diameter of 5.0–7.0 nm, the microdiffraction of which can be attributed to LaO2, CoSi, AlP and Co2Si, as well as aggregates with a diameter of 20.0–40.0 nm, identified as a mixture Al5Co2 and Al3La. Extensive accumulations of small and large dense particles with diameters of 4.0 and 70.0 nm, respectively, were also discovered, which included La2W2O9 and AlLa3.
The surface of the NiO-MoO3-La-P-HZSM-HY-Al2O3 catalyst (K-3) (Figure 4c) is represented by small, evenly spaced NiO and MoNiSi particles with sizes of 4.0–5.0 nm and a cluster of Ni2O3 particles with sizes of 7.0–10.0 nm. There are film-type structures with a diameter of 15.0 nm, the microdiffraction of which is shown by symmetric reflections and can be attributed to a mixture of modifications of Mo9O26, MoSi and LaMo3O13. The formation of translucent aggregates with a diameter of 20.0 nm from loose and smaller particles was also observed, which were identified as a mixture of states including lanthanum: LaO2, La2O3, La(MoO4), MoP, SiP and NiOOH. It should be noted that electron microscopy and electron diffraction methods have revealed clusters in the composition of catalysts, for example, MoSi, SiP and MoNiSi, which indicate the direct interaction of matrix atoms with modifying metals and other additives. These structures can work as Lewis acid centers, which is consistent with the data of the thermal desorption of ammonia.
A comparison of the data obtained by electron microscopic studies shows that the particle dispersion on the surface of the CoO-WO3-La-P-HZSM-HY-Al2O3 catalyst (K-2) is higher than that of other catalytic systems studied in this work. This is probably due to the high hydrodesulfurizing activity of the CoO-WO3-La-P-HZSM-HY-Al2O3 catalyst (K-2).
It should be noted that the catalysts are characterized by the formation of structures, AlLa3 Al5Co2, Al3La, CoSi, AlP, Co2Si, SiP2O7, Ni3Si, Ni3Si2, AlNi2Si, NiSi2, Mo3Si, MoAl1,3 Si0,4, AlNi3, AlMo3, MoSi2, Al3La, LaAlO3, MoSi2 and MoP, indicating the introduction of metal components of the active phase into the zeolite structure, with the formation of new centers that can work as Lewis acid centers.
An analysis of the results of the temperature-programmed desorption of ammonia, transmission electron microscopy and X-ray diffraction shows that these catalysts are characterized by the simultaneous presence of acidic (Brønsted and Lewis), M0 or Mn+—metal and mixed centers. The composition of acid centers may include metals in various degrees of oxidation, fixed both inside the zeolite cavities and on their outer side. The functioning of various types of centers in catalytic processes is often considered as independent, without taking into account the possibility of their joint action on the reactant molecule. However, it can be assumed that it is their simultaneous presence that ensures the polyfunctionality of the catalytic system.
The ability to carry out several reactions simultaneously on the developed catalysts is apparently due to the combined actions of modifying additives that contribute to the formation of active centers of multifunctional directional action that favor the course of hydrodesulfurization and hydroisomerization reactions.
The modification of zeolite with rare earth elements leads to a redistribution of its acid sites in strength and the formation of new active centers, which include modifier elements. Changing the ratio of acid sites of modified zeolites affects their catalytic properties in the process of natural gas conversion. To obtain an effective catalyst for the conversion of gasoline into aromatic hydrocarbons, a certain combination of weak and strong acid sites is required in the catalyst, which is achieved by regulating the amount of modifiers in the catalytic system.
In this work, cheaper platinum-free catalysts have been developed in the process of converting low-octane gasoline into high-octane fuel. The process takes place under less severe conditions than the industrial reforming process where platinum-containing systems are used as catalysts. During the hydrotreating of industrial catalysts, the octane number does not increase; only the sulfur content decreases. On the catalysts we have developed, the process of hydrotreating and hydroisomerization occurs simultaneously; as a result of these reactions, low-sulfur and high-octane gasolines are obtained.
Thus, the data obtained during the study of the process of hydrotreating the gasoline fraction show that multifunctional, modified zeolite-containing catalysts for the hydrotreating of the gasoline fraction have been developed and synthesized, which, in one stage, carry out hydrotreating, hydroisomerization, hydrocracking and allow the obtaining of high-octane gasoline with a low sulfur content corresponding to European Standards.
The developed modified zeolite-containing catalysts are highly stable. During long-term operation in the hydroprocessing of gasoline fractions, the activity of the catalysts practically does not decrease. During hydroprocessing, the spent catalyst retains its original hydrodesulfurization activity.
3. Materials and Methods
In this study, catalytic systems with a new composition based on zeolites with the addition of lanthanum and phosphorus were prepared: CoO-MoO3-La-P-HZSM-HY-Al2O3 (K-1), CoO-WO3-La-P-HZSM-HY-Al2O3 (K-2) and NiO-MoO3-La-P-HZSM-HY-Al2O3 (K-3).
A mixture of aluminum hydroxide with zeolites HZSM-5 and HY, water-soluble salts of nickel, cobalt, molybdenum, tungsten, lanthanum and phosphoric acid were used for catalyst preparation. The synthesis of catalysts was carried out as follows. The catalysts were prepared by the simultaneous impregnation of a mixture of peptized aluminum hydroxide with zeolites HZSM-5 and HY and water-soluble salts of nickel, cobalt, molybdenum, tungsten and lanthanum: Ni(NO3)2·6H2O, Co(NO3)3·6H2O, (NH4)6Mo7O24·4H2O, (NH4)10W12O41·5H2O, La (NO3)3·6H2O, as well as phosphoric acid and the introduction of modifying additives. The type of aluminum hydroxide used was pseudoboehmite.
The catalyst contained 20% HZSM and 5% HY; the HZSM:HY ratio was 4:1. The residual sodium content in the HZSM zeolite was 0.018 wt.%, and in the HY zeolite it was 0.001 wt.%.
Procedure of preparation includes stages of impregnation. When heated, the liquid catalyst solidifies. Using a special device, the catalyst was pulled out, lengthened and poured onto filter paper. The catalyst was left to cure. Then, the modified catalysts were separated into small pieces. Next, the catalyst samples were heated in a laboratory oven at 150 °C for 5 h. After that, the catalyst samples were heated in a muffle furnace at 550 °C for 5 h. The preparation process of the described catalyst is typical for the same type of catalyst, which allows for the preparation of sufficiently large batches of modified zeolite-containing catalysts for industrial applications.
The effectiveness of the developed catalysts was studied in the process of the catalytic hydrotreating of straight-line gasoline. For this study, a gasoline fraction containing 0.037 mass% sulfur, alkanes 33.4 mass%, alkenes 3.7 mass%, aromatic hydrocarbons 5.6 mass%, isoalkanes 26.3 mass% and naphthenic hydrocarbons 31.0 mass% was used. The starting gasoline had an octane number of 77.7 according to the research method.
The reaction process was carried out at the common flow installation with a fixed bed at temperatures of 320–400 °C, volume rate of 2.0 h−1 and pressure 4.0 MPa by the method developed earlier in the laboratory and described in [3]. The reactor was made of a metal tube and the lower part was equipped with glass nozzles, which were filled with a layer of stationary catalyst at the required height and placed on top of another porcelain nozzle. The upper layer of the nozzle provided the evaporation of the feedstock supplied to the reactor. A thermocouple for temperature control was installed in the middle of the reactor.
The final products of the process were cooled in the receiver by means of a capacitor placed in a special immersion refrigerator.
The hydrocarbon reaction products were analyzed by gas chromatography using a “Chromatec-Crystal 5000” (ZAO SKB “Khromatek”, Yoshkar-Ola, Russia) chromatograph with a katharometer and a flame ionization detector. The chromatograph calculated the fractional composition automatically. For the analysis of hydrocarbons, a glass column 3 m long, 4 mm in diameter and filled with γ-Al2O3 was used. For the analysis of oxygen-containing compounds, a similar column with 15% PEG-300/PS-1 (LLC “Tsvet”, Dzerzhinsk, Russia) was used. Carrier gas (argon) rate was 30 mL/min, hydrogen rate was 40 mL/min and air speed was 400 mL/min. The detector temperature was 443 K, the evaporator temperature was 443 K and the column temperature was 403 K.
The sulfur content in the starting material and products was defined using a Spectroscan Instrument. The physico-chemical characteristics of the catalysts were studied using Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) surface area analysis, electron microscopy and the temperature-programmed desorption of ammonia methods [27].
To confirm the presence of the phases on the catalysts, the method of electron microscopy was used on a transmission electron microscope “EM-125K” (NPO “Electron”, Kyiv, Ukraine), U = 75 kV, using electron microdiffraction. Samples were prepared using the carbon replica method. The shape and size of zeolite particles were determined using a SEMLEO-420 (Carl Zeiss, Jena, Germany) electron microscope with a resolution of 15 A at a magnification of 1000 to 5000. In a number of cases, the synthesized products were characterized using crystalloptic analysis (MIN-8 (LLC “Asma-pribor”, Svetlovodsk, Ukraine) optical microscope). Microdiffraction images were interpreted using standard ASTM tables.
The combination of electron crystallography (EMV-100AK electron microscope (JSC “SELMI”, Sumy, Ukraine) and X-ray diffraction (DRON-0.5 diffractometer (NPP Burevestnik, St. Petersburg, Russia) was used to determine the structure of the obtained catalysts. Identification of obtained images was provided via ICDD (International Center for Diffraction Data).
The ammonia temperature-programmed desorption method was used to determine the numbers and strengths of centers of catalysts capable of interacting with specific molecules. Desorption was carried out on a USGA-101 (LLC “UNISIT”, Moscow, Russia) device. To calculate the activation energy values, ammonia was desorbed from the samples at different linear heating rates—5, 10, 15 and 20 deg/min. To carry out the analysis, the sample was preliminarily saturated with the analyte, loosely bound molecules were stripped off and then linear heating was started in a flow of inert gas.
4. Conclusions
Studies of catalysts prepared on the basis of aluminum oxide, modified with additives of lanthanum, phosphorus and zeolites, testify to the prospects of their use in the processes of the catalytic hydrotreating and hydroisomerization of straight-run gasoline. The amount of sulfur found in the final sample decreased with increasing temperature. In fact, this tendency was observed for all catalyst samples. With an increase in temperature, the sulfur content decreased and the octane number increased; that is, the quality of the gasoline fraction increased and the best results were found at 400 °C. Catalysts are characterized by the simultaneous presence of acidic, metallic and mixed centers. Using the catalysts developed in this study, it is possible to obtain high-octane low-sulfur gasoline conforming to the Euro-5 standard.
Thus, in order to create flexible high-tech schemes and all kinds of catalytic processes for processing hydrocarbon fractions into valuable chemical products and motor fuels, it is of great importance to develop effective catalysts and technologies, which are a high-priority scientific direction for oil refining and petrochemistry.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.T.; methodology, G.S.; investigation, B.T. and G.S.; writing—original draft preparation, B.T. and G.S.; writing—review and editing, S.N. and Y.O.; supervision, B.T.; project administration, B.T.; funding acquisition, B.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by grant funding under the project: IRN ARO8857065 “Creation of scientific foundations for the development of new efficient catalysts and technology for deep hydroprocessing of vacuum gas oil to produce high-quality motor fuels”.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are included within the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Qureshi, Z.S.; Arudra, P.; Bari Siddiqui, M.A.; Aitani, A.M.; Tanimu, G.; Alasiri, H. Enhanced light olefins production via n-pentane cracking using modified MFI catalysts. Heliyon 2022, 8, e09181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garba, M.D.; Galadima, A. Catalytic Hydrogenation of Hydrocarbons for Gasoline Production. J. Phys. Sci. 2018, 29, 153–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuktin, B.; Omarova, A.A.; Sassykova, L.R.; Saidilda, G.T.; Khamlenko, A.A.; Sendilvelan, S.; Tulepov, M.I. Modified zeolite catalysts for efficient processing of n-hexane and gasoline fraction. Rasayan J. Chem. 2022, 15, 2442–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Ke, M.; Song, Z.; Li, J.; Sun, J. Benzene Reduction Process Simulation and Optimization in Catalytic Cracking Gasoline Distillation. Processes 2023, 11, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alabdullah, M.A.; Gomez, A.R.; Vittenet, J.; Bendjeriou-Sedjerari, A.; Xu, W.; Abba, I.A.; Gascon, J. A Viewpoint on the Refinery of the Future: Catalyst and Process Challenges. ACS Catal. 2020, 10, 8131–8140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanimu, A.; Tanimu, G.; Ganiyu, S.A.; Gambo, Y.; Alasiri, H.; Alhooshani, K. Metal-Free Catalytic Oxidative Desulfurization of Fuels. A Review. Energy Fuels 2022, 36, 3394–3419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostyniuk, A.; Key, D.; Mdleleni, M. Effect of Fe-Mo promoters on HZSM-5 zeolite catalyst for 1-hexene aromatization. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2019, 23, 612–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velichkina, L.M.; Barbashin, Y.E.; Vosmerikov, A.V. Physicochemical and Catalytic Properties of Rhenium-Containing Zeolites in the Course of Straight-Run Gasoline Upgrading. J. Sib. Fed. Univ. 2021, 14, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimova, A.R.; Davletshin, A.R.; Khamzin, Y.A.; Imasheva, M.U. Investigation of the influence of zeolite catalysts on the structure of ZSM+5 and FAU on the qualitative yield of the target products in the processing of straight-run gasolines. Bashkir Chem. J. 2018, 25, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asaftei, I.V.; Sandu, I.; Lungu, N.C.; Spac, A.F.; Ignat, M. Transformation of Gaseous Technical Mixture of the Alkanes and Alkenes into Liquid Fraction over Ni-HZSM-5 Obtained by Ionic Exchange. Rev. Chim. 2018, 69, 938–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erofeev, V.I.; Khomyakov, I.S.; Egorova, L.A. Production of High-Octane Gasolines from Straight-Run Gasolines on Modified Zeolites. Theoret. Found. Chem. Technol. 2014, 48, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Ortuno, J.C.; Klimova, T.E. Development of new hydrodesulfurization NiMo catalysts supported on Al2O3-TiSBA-15 hybrid materials. Fuel 2017, 198, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdellatief Tamer, M.M.; Ershov, M.A.; Kapustin, V. New recipes for producing a high-octane gasoline based on naphtha from natural gas condensate. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2023, 56, 103103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghan, R.; Anbia, M. Zeolites for adsorptive desulfurization from fuels: A review. Fuel Process. Technol. 2017, 167, 99–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, A.; Siddiqui, M.A.B.; Hussain, A.; Aitani, A.; Al-Khattaf, S. Catalytic cracking of crude oil to light olefins and naphtha: Experimental and kinetic modeling. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2017, 120, 121–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, K.X.; Valla, J.A. Investigation of metal-exchanged mesoporous Y zeolites for the adsorptive desulfurization of liquid fuels. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2017, 201, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taj, R.; Pervaiz, E.; Hussain, A. Synthesis and catalytic activity of IM-5 zeolite as naphtha cracking catalyst for light olefins: A review. J. Chem. Soc. Pak. 2020, 42, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, X.H.; Armbruster, U. Engineering of zeolite crystals for catalytic cracking of triglycerides to renewable hydrocarbon fuels and chemicals: A review. Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 2021, 13, 3521–3541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klerk, A. Zeolites as Catalysts for Fuels Refining after Indirect Liquefaction. Molecules 2018, 23, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltanali, S.; Mohaddecy, S.R.S.; Mashayekhi, M.; Rashidzadeh, M. Catalytic upgrading of heavy naphtha to gasoline: Simultaneous operation of reforming and desulfurization in the absence of hydrogen. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 104548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J. Study on preparation of fuel oil from three kinds of molecular sieve catalytic cracking waste lubricating oil. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2022, 2168, 012010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velázquez, H.D.; Cerón-Camacho, R.; Mosqueira-Mondragón, M.L.; Hernández-Cortez, J.G.; Montoya de la Fuente, J.A.; Hernández-Pichardo, M.L.; Beltrán-Oviedo, T.A.; Martínez-Palou, R. Recent progress on catalyst technologies for high quality gasoline production. Catal. Rev. 2022, 65, 1079–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, Z.; Rong, D.; Hou, X.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, P.; Liu, Y.; Sun, D. Catalytic cracking of endothermic fuels over meso-HZSM-5/MCM-41 coatings. Energy Fuels 2019, 33, 12696–12703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobar, J.; Barrera, M.C.; Valente, J.S.; Solís-Casados, D.A.; Santes, V.; Terrazas, J.E.; Fouconnier, B.A.R. Dibenzothiophene Hydrodesulfurization over P-CoMo on Sol-Gel Alumina Modified by La Addition. Effect of Rare-Earth Content. Catalysts 2019, 9, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobar, J.; Ramírez, J.; Cuevas, R.; Ángeles, C.; Barrera, M.C.; Gutiérrez, A. Thiophene HDS on La-Modified CoMo/Al2O3 Sulfided Catalysts. Effect of Rare-Earth Content. Top. Catal. 2020, 63, 529–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morozova, Y.V.; Kashkina, E.I.; Loginova, A.N.; Bakanev, I.A.; Fadeev, I.I. Catalysts for hydrorefining of vacuum gas oil: Modifiers, type and method of their introduction. Oil Refin. Petrochem. 2017, 11, 3–7. [Google Scholar]
- Tuktin, B.; Zhandarov, E.; Nurgaliyev, N.; Tenizbayeva, A.; Shapovalov, A. Hydrotreating of gasoline and diesel oil fractions over modified alumina/zeolite catalysts. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2019, 37, 1770–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).