A Novel Noninvasive Screening Tool for Dry Eye Disease
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study and Patients
2.2. Statistical Analysis
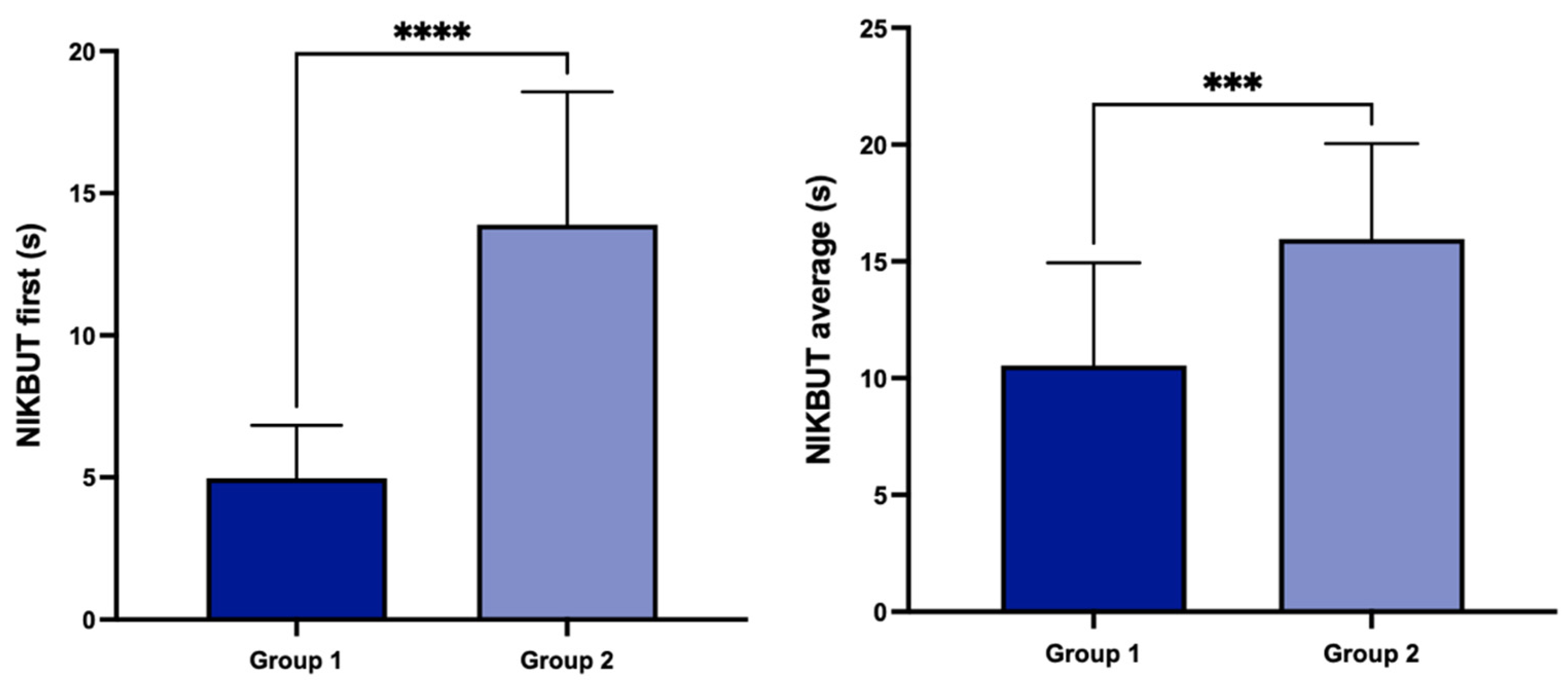
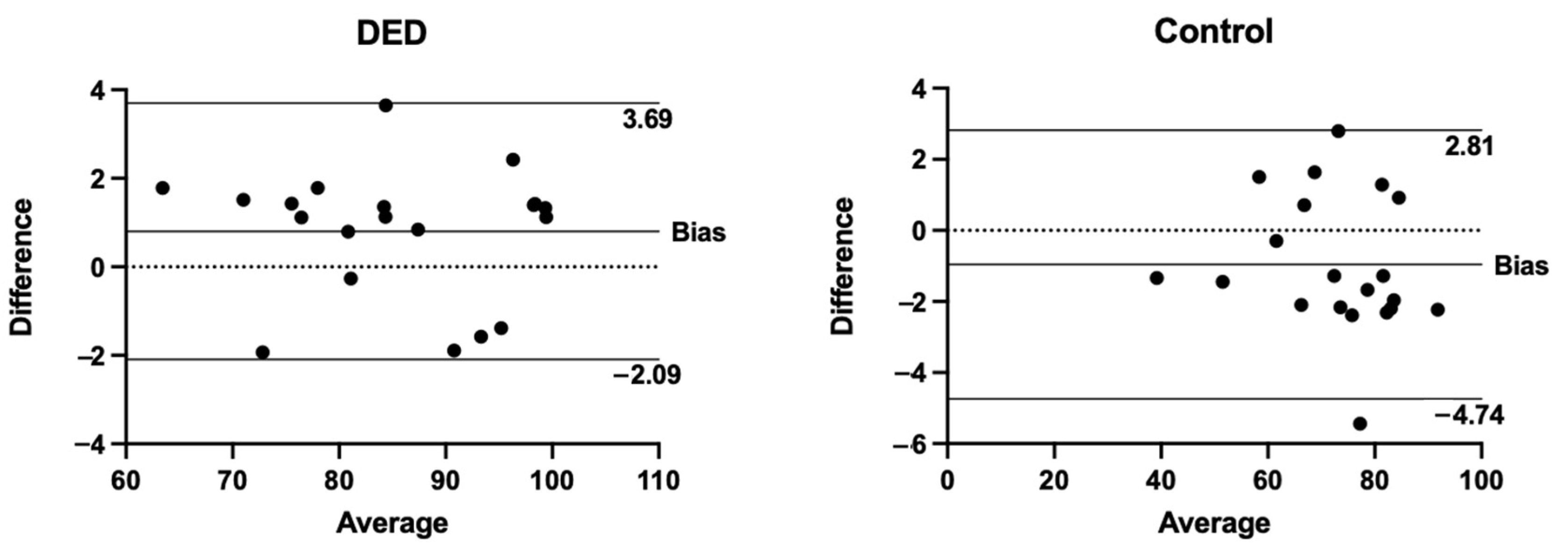
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Craig, J.P.; Nichols, K.K.; Akpek, E.K.; Caffery, B.; Dua, H.S.; Joo, C.-K.; Liu, Z.; Nelson, J.D.; Nichols, J.J.; Tsubota, K.; et al. TFOS DEWS II Definition and Classification Report. Ocul. Surf. 2017, 15, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moss, S.E.; Klein, R.; Klein, B.E. Prevalence of and risk factors for dry eye syndrome. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2000, 118, 1264–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pflugfelder, S.C. Prevalence, burden, and pharmacoeconomics of dry eye disease. Am. J. Manag. Care 2008, 14, S102–S106. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stapleton, F.; Alves, M.; Bunya, V.Y.; Jalbert, I.; Lekhanont, K.; Malet, F.; Na, K.-S.; Schaumberg, D.; Uchino, M.; Vehof, J.; et al. TFOS DEWS II Epidemiology Report. Ocul. Surf. 2017, 15, 334–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willcox, M.D.; Argüeso, P.; Georgiev, G.A.; Holopainen, J.M.; Laurie, G.W.; Millar, T.J.; Papas, E.B.; Rolland, J.P.; Schmidt, T.A.; Stahl, U.; et al. TFOS DEWS II Tear Film Report. Ocul. Surf. 2017, 15, 366–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dartt, D.; Willcox, M. Complexity of the tear film: Importance in homeostasis and dysfunction during disease. Exp. Eye Res. 2013, 117, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhee, M.K.; Mah, F.S. Inflammation in Dry Eye Disease: How Do We Break the Cycle? Ophthalmology 2017, 124, S14–S19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Li, D.-Q.; Corrales, R.M.; Pflugfelder, S.C. Hyperosmolar saline is a proinflammatory stress on the mouse ocular surface. Eye Contact Lens Sci. Clin. Pract. 2005, 31, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, L.; Li, D.-Q.; Doshi, A.; Farley, W.; Corrales, R.M.; Pflugfelder, S.C. Experimental dry eye stimulates production of inflammatory cytokines and MMP-9 and activates MAPK signaling pathways on the ocular surface. Investig. Opthalmology Vis. Sci. 2004, 45, 4293–4301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bron, A.J.; Willshire, C. Tear osmolarity in the diagnosis of systemic dehydration and dry eye disease. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobi, C.; Jacobi, A.; E Kruse, F.; Cursiefen, C. Tear film osmolarity measurements in dry eye disease using electrical impedance technology. Cornea 2011, 30, 1289–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiffman, R.M.; Christianson, M.D.; Jacobsen, G.; Hirsch, J.D.; Reis, B.L. Reliability and Validity of the Ocular Surface Disease Index. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2000, 118, 615–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashmani, N.; Munaf, U.; Saleem, A.; Javed, S.O.; Hashmani, S. Comparing SPEED and OSDI Questionnaires in a Non-Clinical Sample. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2021, 15, 4169–4173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, J.; Sun, X.; Wei, A.; Cui, X.; Li, Y.; Qian, T.; Wang, W.M.; Xu, J. Assessment of tear film stability in dry eye with a newly developed keratograph. Cornea 2013, 32, 716–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillon, M.; Maïssa, C. Tear film evaporation—Effect of age and gender. Contact Lens Anterior Eye 2010, 33, 171–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craig, J.P.; Tomlinson, A. Age and gender effects on the normal tear film. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1998, 438, 411–415. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rohit, A.; Ehrmann, K.; Naduvilath, T.; Willcox, M.; Stapleton, F. Validating a new device for measuring tear evaporation rates. Ophthalmic Physiol. Opt. 2014, 34, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Cello, L.; Pellegrini, M.; Vagge, A.; Borselli, M.; Ferro Desideri, L.; Scorcia, V.; Traverso, C.E.; Giannaccare, G. Advances in the noninvasive diagnosis of dry eye disease. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 10384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luca, A.; Ferraro, A.; De Gregorio, C.; Laborante, M.; Coassin, M.; Sgrulletta, R.; Di Zazzo, A. Promising High-Tech Devices in Dry Eye Disease Diagnosis. Life 2023, 13, 1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaudenzi, D.; Mori, T.; Crugliano, S.; Grasso, A.; Frontini, C.; Carducci, A.; Yadav, S.; Sgrulletta, R.; Schena, E.; Coassin, M.; et al. AS-OCT and Ocular Hygrometer as Innovative Tools in Dry Eye Disease Diagnosis. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Qu, J.-H.; Zhang, X.-Y.; Sun, X.-G. Repeatability and Reproducibility of Noninvasive Keratograph 5M Measurements in Patients with Dry Eye Disease. J. Ophthalmol. 2016, 2016, 8013621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Montero, M.; Rico-Del-Viejo, L.; Lorente-Velázquez, A.; Martínez-Alberquilla, I.; Hernández-Verdejo, J.L.; Madrid-Costa, D. Repeatability of Noninvasive Keratograph 5M Measurements Associated With Contact Lens Wear. Eye Contact Lens Sci. Clin. Pract. 2019, 45, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rico-Del-Viejo, L.; Benítez-Del-Castillo, J.M.; Gómez-Sanz, F.J.; García-Montero, M.; Llorens-Quintana, C.; Madrid-Costa, D. The influence of meibomian gland loss on ocular surface clinical parameters. Contact Lens Anterior Eye 2019, 42, 562–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jerchel, N.N.; Sickenberger, W.; Schulze, M.M. Objective classification and documentation of bulbar redness using a corneal to-pographer. Contact Lens Anterior Eye 2012, 35, e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Versura, P.; Giannaccare, G.; Fresina, M.; Campos, E.C. Subjective Discomfort Symptoms Are Related to Low Corneal Temperature in Patients With Evaporative Dry Eye. Cornea 2015, 34, 1079–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, X.; Zhao, L.; Xu, L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, K.; Wang, Y.; Chen, G.Y.; Liu, T.; Wang, Y. Review of Optical Humidity Sensors. Sensors 2021, 21, 8049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, H.; Brown, S.; Danby, S.; Flohr, C. Research Techniques Made Simple: Transepidermal Water Loss Measurement as a Research Tool. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2018, 138, 2295–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abusharha, A.A.; Al Yami, A.; Alsreea, K.; Fagehi, R.; Alsaqr, A.; Alanazi, S.; Masmali, A. Repeatability and re-producibility of tear film evaporation rate measurement using a new closed-chamber evaporimeter. Open Ophthalmol. J. 2021, 15, TOOPHTJ-15-117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, E.; Endo, K.; Suzuki, A.; Fujikura, Y.; Matsumoto, Y.; Tsubota, K. tear evaporation dynamics in normal subjects and subjects with obstructive meibomian gland dysfunction. Investig. Opthalmology Vis. Sci. 2003, 44, 533–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tesón, M.; González-García, M.J.; López-Miguel, A.; Enríquez-de-Salamanca, A.; Martín-Montañez, V.; Benito, M.J.; Mateo, M.E.; Stern, M.E.; Calonge, M. Influence of a controlled environment simulating an in-flight airplane cabin on dry eye disease. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2013, 54, 2093–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novaes, P.; Saldiva, P.H.D.N.; Matsuda, M.; Macchione, M.; Rangel, M.P.; Kara-José, N.; Berra, A. The effects of chronic exposure to traffic derived air pollution on the ocular surface. Environ. Res. 2010, 110, 372–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-García, M.J.; González-Sáiz, A.; de la Fuente, B.; Morilla-Grasa, A.; Mayo-Iscar, A.; San-José, J.; Feijó, J.; Stern, M.E.; Calonge, M. Exposure to a controlled adverse environment impairs the ocular surface of subjects with minimally symptomatic dry eye. Investig. Opthalmology Vis. Sci. 2007, 48, 4026–4032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petznick, A.; Tan, J.H.; Boo, S.K.; Lee, S.Y.; Acharya, U.R.; Tong, L. Repeatability of a new method for measuring tear evaporation rates. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2013, 90, 366–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milner, M.S.; Beckman, K.A.; Luchs, J.I.; Allen, Q.B.; Awdeh, R.M.; Berdahl, J.; Boland, T.S.; Buznego, C.; Gira, J.P.; Goldberg, D.F.; et al. Dysfunctional tear syndrome: Dry eye disease and associated tear film disorders—New strategies for diagnosis and treatment. Curr. Opin. Ophthalmol. 2017, 27 (Suppl. S1), 3–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimball, S.H.; King-Smith, P.E.; Nichols, J.J. Evidence for the major contribution of evaporation to tear film thinning between blinks. Investig. Opthalmology Vis. Sci. 2010, 51, 6294–6297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King-Smith, P.E.; Hinel, E.A.; Nichols, J.J. Application of a novel interferometric method to investigate the relation between lipid layer thickness and tear film thinning. Investig. Opthalmology Vis. Sci. 2010, 51, 2418–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, C.-C.; Cerretani, C.; Li, Y.; Bowers, S.; Shahsavarani, S.; Lin, M.C.; Radke, C.J. Flow Evaporimeter To Assess Evaporative Resistance of Human Tear-Film Lipid Layer. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 18130–18139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannaccare, G.; Borselli, M.; Rossi, C.; Scalzo, G.C.; Pellegrini, M.; Vaccaro, S.; Scalia, G.; Lionetti, G.; Mancini, A.; Bianchi, P.; et al. Noninvasive screening of ocular surface disease in otherwise healthy patients scheduled for cataract surgery. Eur. J. Ophthalmol. 2024, 34, 11206721241228621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolffsohn, J.S.; Arita, R.; Chalmers, R.; Djalilian, A.; Dogru, M.; Dumbleton, K.; Gupta, P.K.; Karpecki, P.; Lazreg, S.; Pult, H.; et al. TFOS DEWS II Diagnostic Methodology report. Ocul. Surf. 2017, 15, 539–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sweeney, D.F.; Millar, T.J.; Raju, S.R. Tear film stability: A review. Exp. Eye Res. 2013, 117, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borselli, M.; Toro, M.D.; Rossi, C.; Taloni, A.; Khemlani, R.; Nakayama, S.; Nishimura, H.; Shimizu, E.; Scorcia, V.; Giannaccare, G. Feasibility of tear meniscus height measurements obtained with a smartphone-attachable portable device and agreement of the results with standard slit lamp examination. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| RH | TMH | NIKBUT-First | NIKBUT-Average | OSDI | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RH | Pearson’s r | - | ||||
| df | - | |||||
| p-value | - | |||||
| TMH | Pearson’s r | −0.091 | - | |||
| df | 38 | - | ||||
| p-value | 0.577 | - | ||||
| NIKBUT-first | Pearson’s r | −0.295 | −0.358 | - | ||
| df | 38 | 38 | - | |||
| p-value | 0.065 | 0.023 | - | |||
| NIKBUT-average | Pearson’s r | −0.101 | −0.262 | 0.810 | - | |
| df | 38 | 38 | 38 | - | ||
| p-value | 0.534 | 0.102 | <0.001 | - | ||
| OSDI | Pearson’s r | 0.406 | 0.241 | −0.585 | −0.425 | - |
| df | 38 | 38 | 38 | 38 | - | |
| p-value | 0.009 | 0.134 | <0.001 | 0.006 | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vaccaro, S.; Borselli, M.; Scalia, G.; Rossi, C.; Toro, M.D.; Rejdak, R.; Pellegrini, M.; Scorcia, V.; Giannaccare, G. A Novel Noninvasive Screening Tool for Dry Eye Disease. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 1209. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14121209
Vaccaro S, Borselli M, Scalia G, Rossi C, Toro MD, Rejdak R, Pellegrini M, Scorcia V, Giannaccare G. A Novel Noninvasive Screening Tool for Dry Eye Disease. Diagnostics. 2024; 14(12):1209. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14121209
Chicago/Turabian StyleVaccaro, Sabrina, Massimiliano Borselli, Giovanni Scalia, Costanza Rossi, Mario Damiano Toro, Robert Rejdak, Marco Pellegrini, Vincenzo Scorcia, and Giuseppe Giannaccare. 2024. "A Novel Noninvasive Screening Tool for Dry Eye Disease" Diagnostics 14, no. 12: 1209. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14121209
APA StyleVaccaro, S., Borselli, M., Scalia, G., Rossi, C., Toro, M. D., Rejdak, R., Pellegrini, M., Scorcia, V., & Giannaccare, G. (2024). A Novel Noninvasive Screening Tool for Dry Eye Disease. Diagnostics, 14(12), 1209. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14121209












