Abstract
This study investigates the influence of limestone powder and metakaolin as sustainable eco-friendly additives on the properties and behavior of cementitious composite boards, with a focus on mechanical strength, physical properties, and microstructural characteristics. The experimental investigation begins with the characterization of the raw materials, including limestone powder, and metakaolin, to assess their particle sizes, elemental composition, and microstructural features. Cement composite boards were fabricated using an innovatively developed lab-simulated vacuum dewatering process, by varying the proportions of limestone powder and metakaolin as partial replacements for cement, along with waste kraft fibres as reinforcement. Mechanical testing was conducted to evaluate the flexural strength and behaviour of the composite boards according to standardized procedures. A microstructural analysis was performed using scanning electron microscopy (SEM) to examine the effect of additives on the cementitious matrix, fibrematrix interaction, and hydration products. The findings from the experimental study reveal insights into the influence of limestone powder and metakaolin on the mechanical properties and microstructure of waste kraft fibre-reinforced cement composite boards. Our analysis of the results shows that adding 9% limestone powder as partial cement replacement produces a 24% and 50% enhancement in flexural strength at 7 and 28 days of hydration, while that of metakaolin as partial cement replacement was optimum at 6% with an enhancement of 4% and 36%, respectively, at 7 and 28 days of hydration. The implications of these findings for the development of sustainable cementitious composite are discussed, including the potential benefits of using limestone powder and metakaolin as supplementary cementitious materials in waste kraft fibre-reinforced cement composite boards. Finally, recommendations for optimizing additive proportions are also provided to enhance the understanding and application of these materials in the construction and building industries.
1. Introduction
The impact of the industrial production of cement on the environment, particularly concerning CO2 emissions and material costs, is a critical topic in contemporary trends surrounding sustainable development [1,2,3,4,5,6]. Cement, a fundamental component in construction, plays a pivotal role in infrastructure development worldwide [7,8,9]. However, its production process is inherently resource-intensive, contributing significantly to greenhouse gas emissions, notably carbon dioxide (CO2) [6,9,10]. Moreover, the rising costs of materials further exacerbate the economic challenges associated with cement production [1,11]. Therefore, understanding and addressing these issues is imperative for adopting environmentally responsible practices and mitigating the adverse effects of cement production on the environment.
Indeed, exploring alternative supplementary cementitious materials offers a promising avenue for mitigating the environmental impact of cement production while addressing cost concerns [4,11,12,13]. Incorporating materials like limestone powder and metakaolin as partial replacements for cement in producing fibre cement boards for building applications presents a promising solution. These materials not only help to reduce the carbon footprint associated with cement production but also offer potential economic benefits by offsetting the escalating costs of traditional cement [14,15,16]. By utilizing limestone powder and metakaolin, which can function as pozzolanic materials [17,18], the cement content in fibre cement boards can be lowered without compromising performance or structural integrity [13,19,20]. This innovative approach not only aligns with sustainability goals but also underscores the importance of adopting environmentally conscious practices in the construction industry [3,21,22,23]. Embracing such alternatives signifies a proactive step towards achieving a more sustainable and cost-effective future for building materials and construction practices.
Cement composite boards reinforced with natural fibres have become widely known in recent times due to their advantages as environmentally friendly building materials and sustainable alternatives to conventional construction materials [24,25,26,27]. Among the various additives used to enhance the performance of these boards, limestone powder and metakaolin emerge as promising candidates, offering unique properties that can positively influence both mechanical strength and morphological characteristics [28,29,30].
The integration of limestone powder and metakaolin into cementitious matrices represents an important aspect of modern construction materials research. Limestone powder, a byproduct of limestone quarrying and processing [31], possesses pozzolanic properties, contributing to the improvement of cement hydration, densification, and the mechanical strength of composite materials [32,33,34]. Metakaolin, derived from the calcination of kaolin clay [35,36], exhibits high reactivity and pozzolanic activity, thereby enhancing the microstructure and durability of cementitious composites [36,37,38].
This comparative investigation aims to elucidate and contrast the effects of limestone powder and metakaolin on the mechanical properties and morphological characteristics of cement composite boards reinforced with waste kraft fibre. Kraft pulp fibre, renowned for its crack-bridging ability [39,40], serves as an environmentally friendly reinforcement in cementitious materials, offering a sustainable solution for the construction industry. An understanding of the intricate interplay between these additives and fibre reinforcement is paramount for optimizing the performance and sustainability of cement composite boards. Through a comprehensive analysis encompassing mechanical testing, microstructural examination, and morphological characterization, several studies [16,41,42,43,44,45] have attempted to unravel the underlying mechanisms governing the synergistic interactions between cement matrix particles and various supplementary cementitious materials.
An extensive, yet most recent literature survey, covering the key aspects of materials sustainability, including the various synergistic interactions between these materials, and the ensuing mechanical, morphological, and durability properties, is presented as follows.
Cao et al. [46], conducted an elaborate study reviewing the contributions of many researchers [47,48,49,50,51,52] who have worked on the effects of calcium carbonate on the properties of cementitious composites. The authors concluded in their review that to contribute to the strength of hardened cementitious composites, macro-calcium carbonate (>1 mm) is primarily used as an inert filler and can be used to construct the framework of the materials. Furthermore, the authors explained that, through dilution, nucleation, and even chemical reactions, micro-calcium carbonate (1 µm–1 mm) not only fills the spaces between cement grains but also speeds up the hydration process and influences workability, mechanical characteristics, and durability. In addition, they also highlighted the fact that nano-calcium carbonate (<1 µm) exhibits significantly more potent physical and chemical effects on the characteristics of cementitious composites than macro- and micro-calcium carbonate.
Antonija et al. [53] reported the effects of the synergistic integration of waste fibres, limestone powder, and metakaolin on the compressive strength and capillary water-absorption properties of ultra-high-performance concrete. The authors concluded that the addition of limestone powder and metakaolin as supplementary cementitious materials resulted in a 25% increase in the modulus of elasticity and a 35% reduction in capillary water absorption over time. Additionally, they reported that reduction in compressive strength at early ages was quite minimal, suggesting that this combination of supplementary cementitious materials can refine the microstructure.
Natalija and Gregor [54] studied the combined effects of metakaolin and hybridized fibres on self-compacting concrete’s mechanical characteristics, durability, and microstructural performance. The authors reported that concrete composite containing 5–15% metakaolin as partial cement replacement showed higher fracture energy and better pore refinement, as well as improved compressive strength up to 31% higher than the reference concrete sample without a metakaolin and fibre addition. Furthermore, the strong bond at the fibrematrix interface was confirmed in the microstructural analysis of the hybridized fibre-reinforced concrete. They concluded that the concrete microstructure becomes denser as a result of the metakaolin particles filling the pores of the concrete composite.
Konduru et al. [55] studied the performance of metakaolin as a partial cement replacement on the flexural, compressive, and durability properties of grade M80 high-strength concrete. The authors studied the 0–15% replacement of cement with metakaolin and reported that, after 28, 56, and 90 days of hydration, the flexural and compressive strength of the concrete was optimum at 10% metakaolin replacement, with values of 15.94, 18.40, and 18.44 MPa, respectively, for flexural strength and 102.16, 114.41, and 116.32 MPa, respectively, for compressive strength. They concluded that the replacement of cement with 10% metakaolin resulted in a 10%, 13%, and 15% enhancement in flexural strength, while the compressive strength was increased by 8%, 12%, and 14%, respectively, compared to the control sample without metakaolin addition.
Consequently, the following benefits (among others) of adding limestone powder and metakaolin to cement-based composite materials were identified in the literature: improvement in mechanical properties, including compressive strength, flexural strength [56], and modulus of elasticity [53]; reduced permeability, including improving resistance against water penetration and chemical ingress [57]; enhanced durability, including improving resistance to various degradation mechanisms, such as freeze–thaw cycling [58] and chloride penetration [59]; reduced workability [60]; and reduced carbon footprint [61].
Despite these potential benefits, the incorporation of these materials presents several challenges, such as the need to understand the interaction between these additives and cement matrices, how the additives influence the mechanical and durability properties, and how these sustainable eco-friendly additives can be optimized to enhance composite performance. Furthermore, the lack of comprehensive studies on the microstructural behaviour of these composites limits the ability to predict long-term performance and their applicability in real-world scenarios. Therefore, the current research aims to fill this gap by assessing the mechanical, physical, and microstructural performance of waste kraft fibre-reinforced cement composite boards containing sustainable eco-friendly additives, providing insights that could lead to the development of sustainable building materials for construction applications.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
The following materials were utilized in the course of this research.
Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC) HS 52 BSEN 197-1 BSEN I 52.5 N, was supplied by Hanson Heidelberg Cement Group, Maidenhead, England. Kraft pulp fibres were obtained mainly from waste brown cardboard papers collected from stationaries and mail stores around Cranfield University, Cranfield United Kingdom. Fisher Scientific Ltd., UK supplied pure grade, beige Kaolin powder, and Calcium carbonate, 98% pure, light powder.
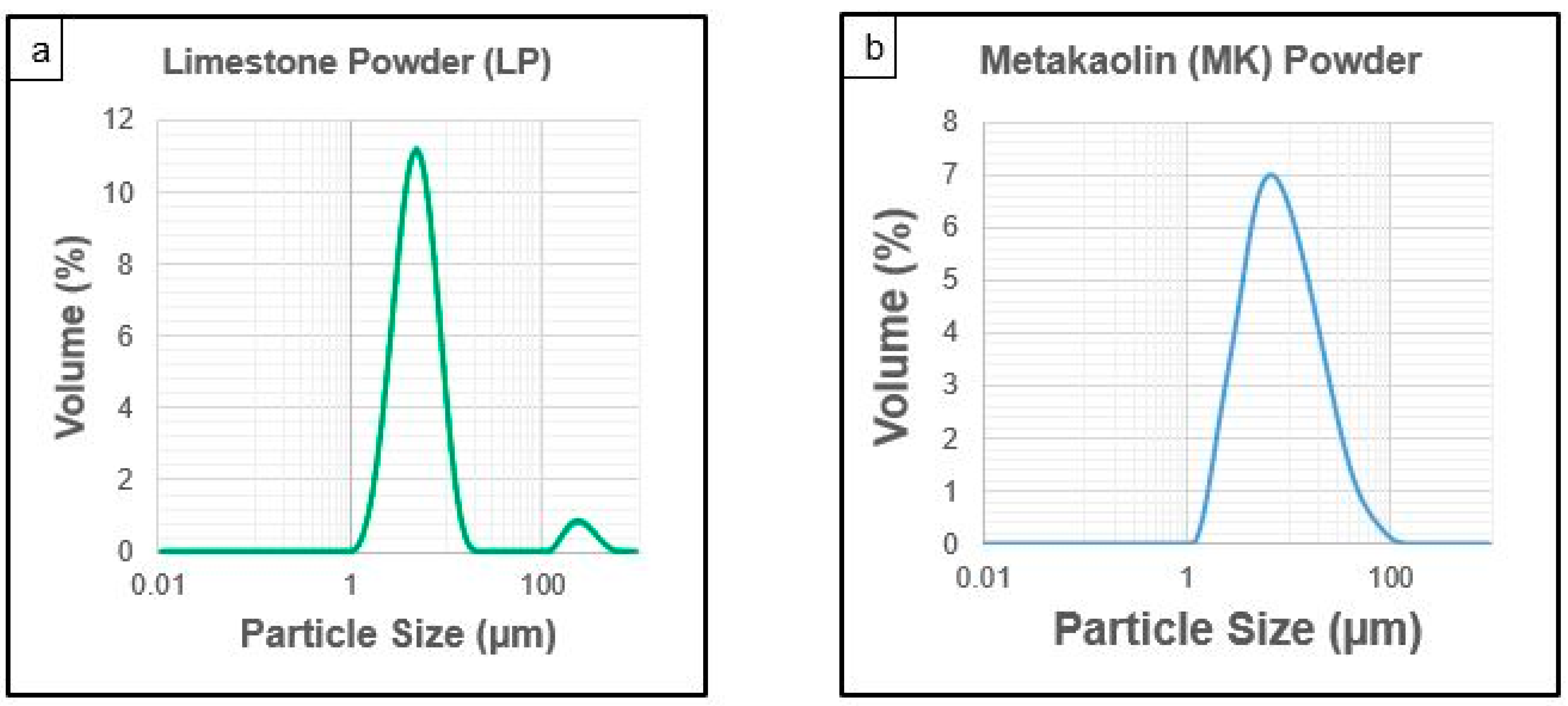
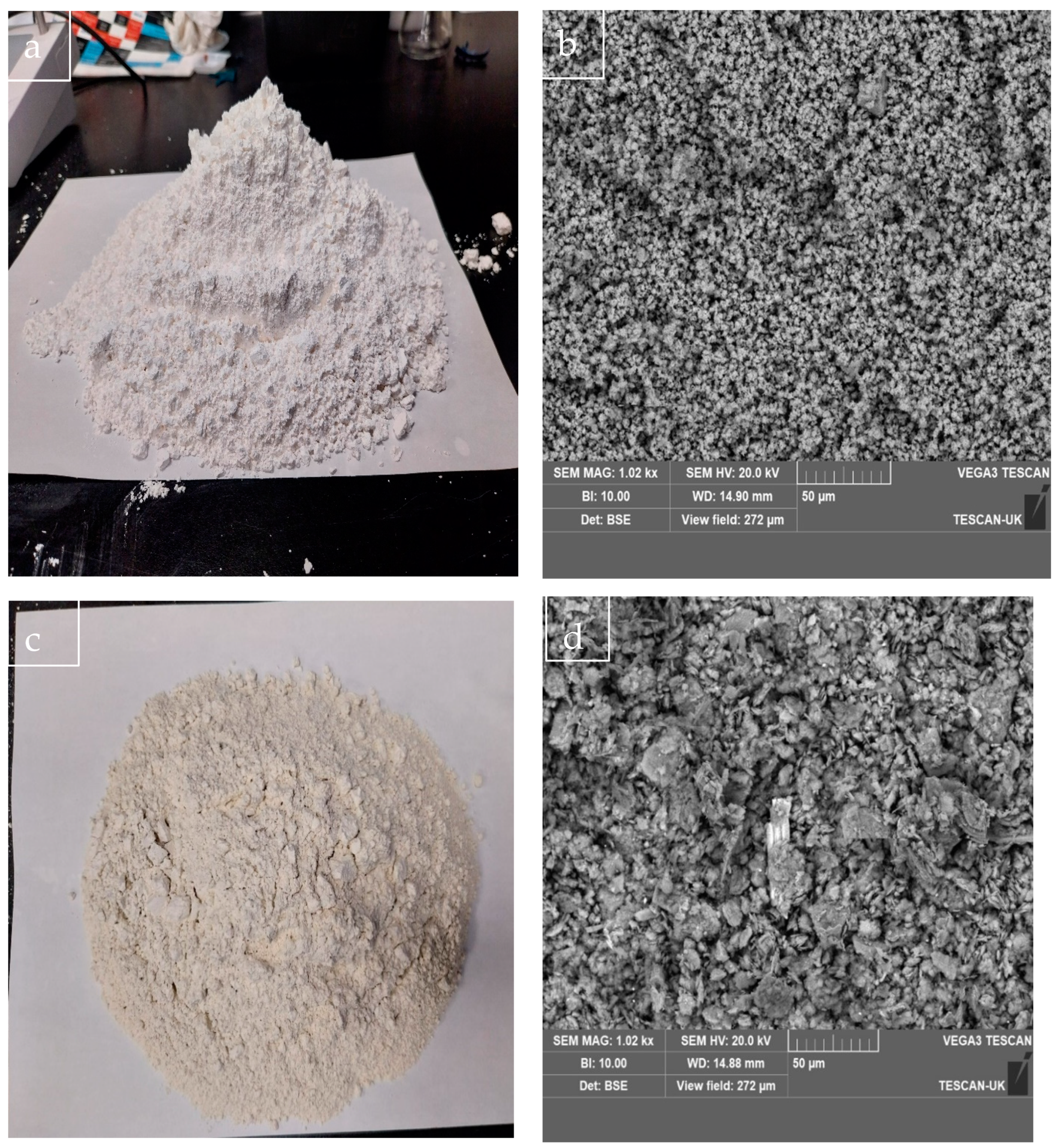
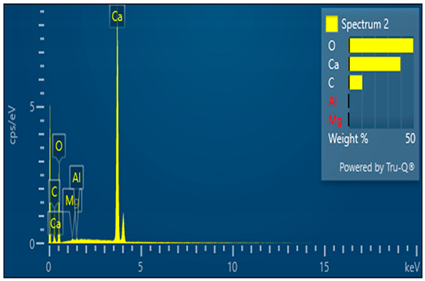
The elemental composition (SEM-EDS) and master sizer particle size analysis of the limestone powder (LP) and metakaolin (MK) powder are presented in Table 1 and Figure 1a,b, respectively, while the photographic and scanning electron microscope (SEM) images of the limestone powder and metakaolin powders employed in this study are shown Figure 2a–d. The rectangular steel mold was supplied by the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Coventry University, while the conical flask, vacuum pump, rubber bung, hose, and other items required to successfully mimic the Hatschek method in the laboratory were supplied internally by the Composite and Advanced Materials Centre, Cranfield University, United Kingdom.

Table 1.
Elemental composition (SEM-EDS) analysis of metakaolin and limestone powder.
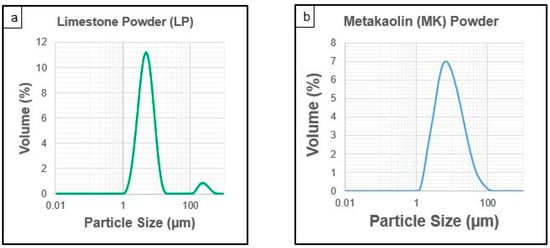
Figure 1.
Master sizer particle size analysis of (a) limestone powder and (b) metakaolin powder.
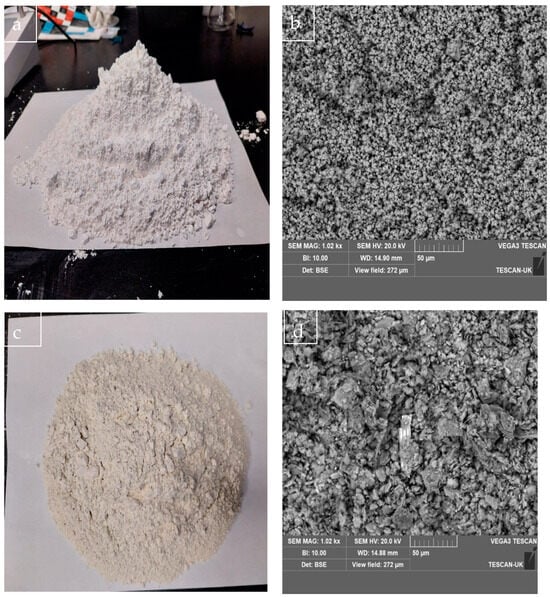

Figure 2.
(a,b) Photographic and SEM image of limestone powder. (c,d) Photographic and SEM image of metakaolin powder.
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Waste Kraft Fibre Production
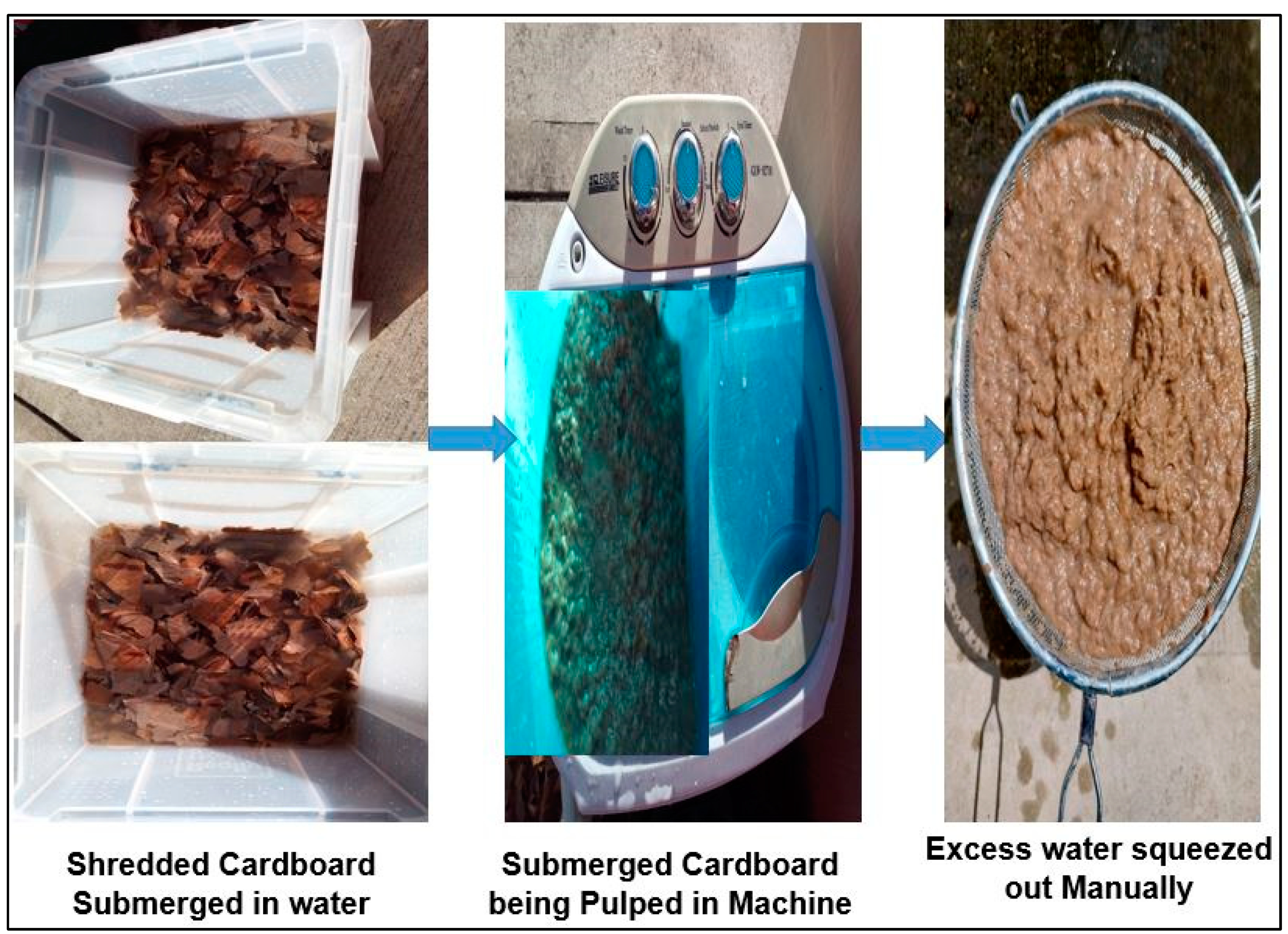
Stationaries and mail stores on the Cranfield University campus provided waste cardboard papers, which served as the main source of waste kraft fibre utilized in this research. To begin with, the waste cardboard papers were shredded manually into smaller pieces with the aid of scissors, while removing all the foreign materials, such as glue and pins, from the shredded pieces. After that, the carton papers were soaked in clean water for 48 h in the laboratory, applying a 5:1 water-to-cardboard weight ratio. Thereafter, the soaked carton papers were continuously pulped for 2 h by gently agitating in water. The pulped carton paper was further pulverized in a blender at a low speed for a further 8–10 min. The product obtained from the blender was manually drained of the water used for the pulping process. The final product was stored in zip bags and refrigerated at 3 ± 1 °C. The weight of the wet kraft pulp fibre divided by the weight of the oven-dried kraft pulp fibre produces a kraft pulp fibre with 70% average moisture content. Figure 3 demonstrates a pictorial representation of the production technique employed for producing the kraft pulp fibre.

Figure 3.
Camera photo explaining the steps involved in producing the waste kraft Fibre.
2.2.2. Production of Waste Kraft FibreReinforced Cement Composite Boards Incorporating LP and MK as Partial Cement Replacement
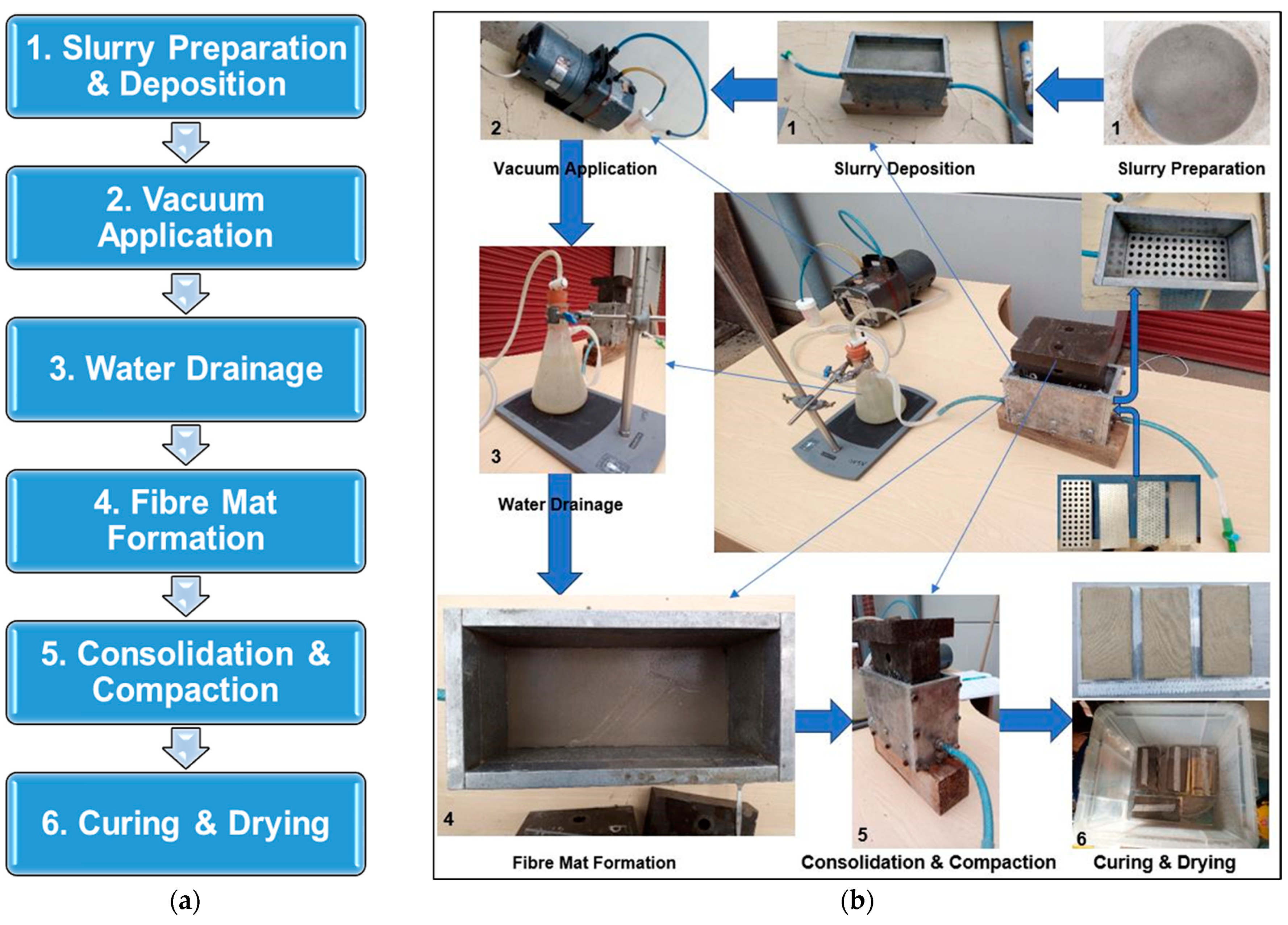
The process of composite manufacture was conducted using the guidelines provided in Taiwo et al.’s study [24]. Using a compact handheld mixer set to spin at 600–1900 rpm, 750 mL of water and 8 g of kraft pulp fibre were first mixed thoroughly for about 5 min. This guarantees that fibres from the kraft pulp are dispersed evenly throughout the water. Next, 192 g of cement matrix was added, and either limestone powder or metakaolin was introduced in the appropriate amount, as detailed in Table 2. After that, the kraft pulp mixture was vigorously mixed for a further 5 min to achieve homogeneity. Following mixing, the resultant slurry was gradually poured into the 180 mm by 80 mm rectangular steel mould which was pre-assembled as shown in Figure 4a.

Table 2.
Mix design for the production of waste kraft Fibre-reinforced cement board.
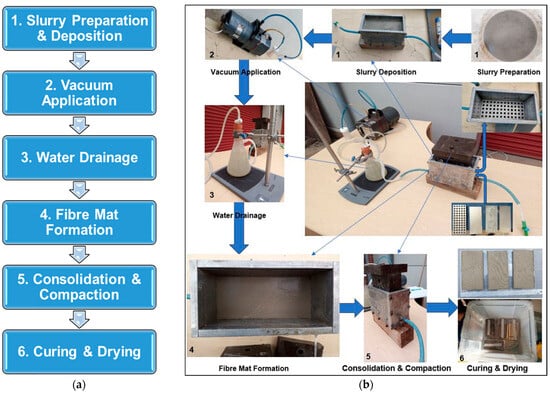
Figure 4.
(a) Flowchart for vacuum dewatering process. (b) Laboratory setup for composite production.
The vacuum pump that was fastened to the mould was turned on to extract the excess water from the mixed slurry. One end of the mold had a conical flask attached to it which was meant to hold the excess water. Any leftover water that might have become trapped in the now-thickened slurry was pushed out of the specimen by compressing it uniformly with a weight of 12 kg, while keeping the vacuum pump operating. After running the vacuum pump for a further 2–3 min, the sample was carefully demoulded onto a levelled rectangular surface. Following a 15–20 min exposure to the air in the laboratory, the specimen was thereafter placed in a high-humidity chamber to complete the cement hydration and/or curing process for a specified number of days. The fibre cement board samples made with this technique were placed in a high-humidity chamber with a constant temperature of 25 ± 2 °C and 95% relative humidity to allow for cement hydration and/or curing. The specimens were cured for the required number of days, and then their flexural performance was assessed following BS EN 12467 [62]. Ten samples were made for each mix design; five were evaluated after 7 days, and the other five after 28 days of hydration. Each specimen is between 8 and 10 mm thick. Figure 4a shows the flowchart for the vacuum dewatering process, while Figure 4b displays the laboratory setup for composite sample production.
2.2.3. Characterization of the Produced Waste Kraft FibreReinforced Cement Composite Boards
- (1)
- Mechanical Properties Test
The manufactured cement composite boards were subjected to mechanical properties test (flexural strength and flexural behaviour) through bending, using an Instron 4467 electromechanical testing machine following BS EN 12467 [62] standards. The 7-day and 28-day cured specimens were simply supported on the testing machine using two supports with a radius rounded to more than 3 mm but less than 25 mm each. The distance between the two supports was fixed and maintained at 125 mm throughout the test. By following the standard, the individual specimen was tested to fracture within a time frame of 10 to 30 s by applying a constant crosshead speed of 5 mm/min. This is to ensure that the specimen satisfies the requirements specified in the BS EN 12467 [57] standards. The flexural strength of the cement composite board is known as the modulus of rupture (MOR), and it is calculated by Equation (1).
where F = the breaking load (N), Ls = the span between the axes of the supports (mm), b = the width of the specimen (mm), and e = the thickness of the specimen (mm).
- (2)
- Determination of Moisture Movement of Waste Kraft FibreReinforced Composite Boards
Following ASTM C1185-08 [63], the specimens were examined for moisture movement using a Gallenkamp TH340L environmental conditioning chamber, which can condition specimens at temperatures ranging from −40 °C to 180 °C and relative humidity levels from 10 to 98%. This was performed to gain an understanding of the distinctive behaviour of the fibrecement boards when they are exposed to various climate conditions. For testing, three (3) samples were prepared. The samples have dimensions of 80 mm in width and 100 mm in length. The samples underwent practical equilibrium conditioning at 23 ± 2 °C and 30 ± 2% relative humidity for 24 h. Following conditioning, the length of each sample was measured to the nearest 0.02 mm. The samples underwent additional conditioning to reach practical equilibrium at 23 ± 2 °C and 90 ± 5% relative humidity for another 24 h. The length of each sample was measured and recorded one more time. Equation (2) was applied to determine the moisture movement (% change in length) based on these measurements.
where Lm = the change in length or linear moisture movement (%); L90RH = the length of the specimen at a relative humidity of 90%, (mm); and L30RH = the length of the specimen at a relative humidity of 30%, (mm).
- (3)
- Water-Absorption Characteristics of Waste Kraft FibreReinforced Composite Boards
Water absorption was carried out per ASTM C1185-08 [63]. A temperature of 90 ± 2 °C was used to dry three (3) 180 mm by 80 mm specimens of each board composition to a constant weight. Following the process of drying, the samples were allowed to cool inside the desiccator before being weighed to the closest 0.01 g. After that, the samples were soaked for 48 ± 8 h in clean water at 23 ± 2 °C. After the allotted time, every sample was meticulously dried with a blotting paper and weighed once more. Equation (3) was employed to obtain the percentage of water absorption.
where WA = the water absorption, (%); WD = the dry weight of the specimen, (g); WS = the saturated weight of the specimen, (g).
- (4)
- Determination of the Density of Manufactured Specimens
The density of the produced fibrecement composite boards was determined in accordance with ASTM C1185-08 [41] by applying the water displacement method and adhering to Archimedes’ principles. Initially, three (3) 180 mm by 80 mm specimens of each board composition were dried to constant weight in an oven set to 90 ± 2 °C. Following the process of drying, the samples were allowed to cool inside the desiccator before being weighed to the closest 0.01 g. Following that, the samples were soaked in clean water at a temperature of 23 ± 2 °C for 48 ± 8 h. After this time, each specimen was weighed underwater using the Archimedes principles to determine the suspended weight. Following a meticulous process of blotting the specimens dry, the saturated weight was determined and documented. The density of the samples was computed using Equation (4), as defined below.
where D = density, in. (g/cm3); WD = dry weight of specimen, (g); WS = saturated weight of specimen, (g); Ww = weight underwater (suspended weight), (g); and ρw = density of water, (g/cm3).
- (5)
- Morphological Examination of the Fractured Specimen Using SEM
The fracture mechanism and the additive interaction within the composites were investigated on the broken surfaces of the waste kraft fibre cement board specimens by utilizing a scanning electron microscope (SEM) Tescan VEGA 3 equipped with an Oxford instrument detector. All fractured samples were inspected using the low vacuum mode in order to reduce specimen charging and improve conductivity for better imaging.
- (6)
- Results and Discussion
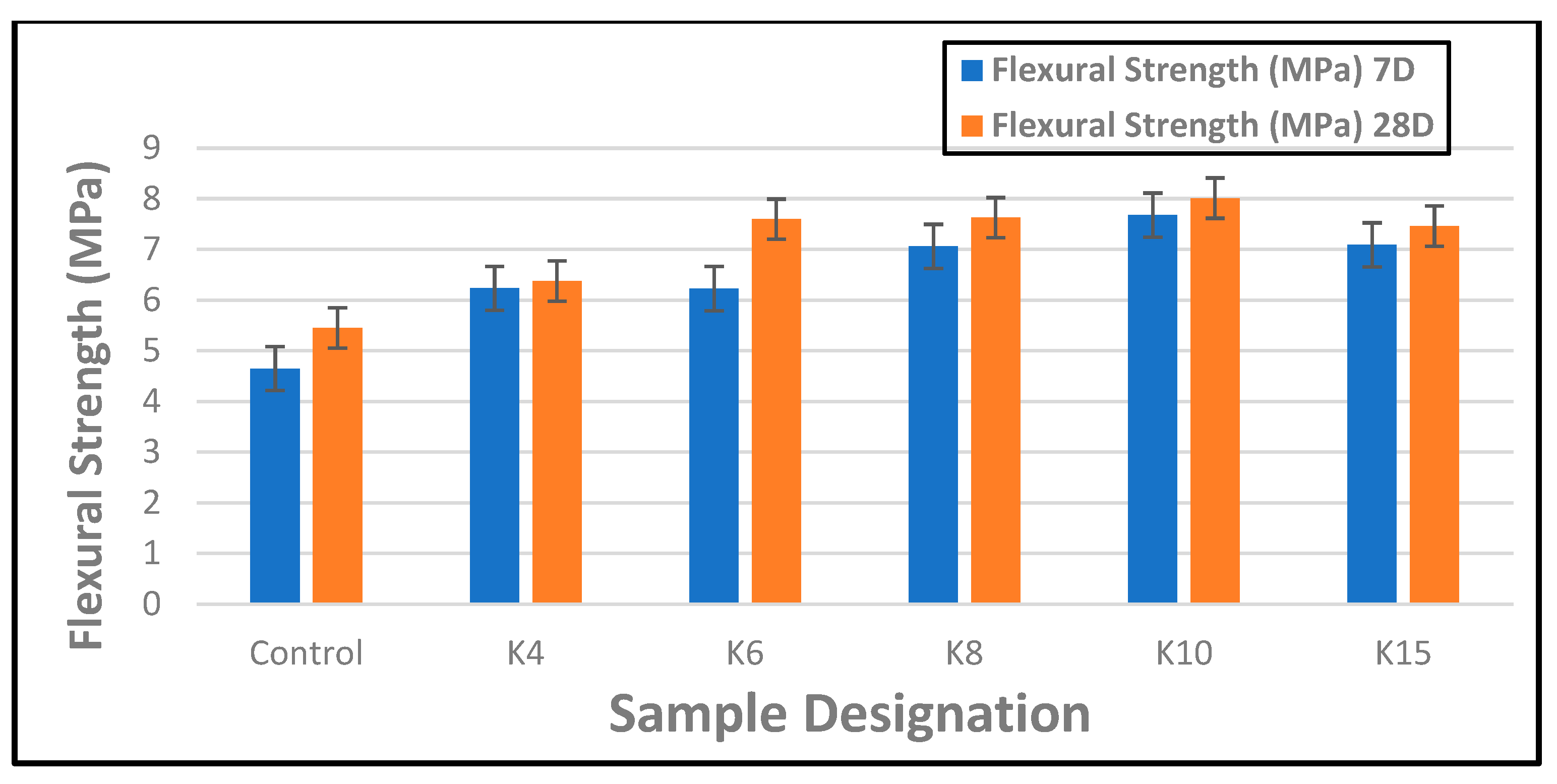
The performance of waste kraft fibre-reinforced cement composite boards in terms of their response to bending load is presented in Figure 5. It was observed that the presence of the waste kraft fibre as reinforcement improved the strength characteristics of the cement board. Hence, all the composite samples containing waste kraft fibre reinforcement had better flexural strength than the control sample both at 7 and 28 days of hydration. The observed characteristic improvement in strength by the addition of the waste kraft fibre as reinforcement can be traced to the fibrous structure of the waste kraft fibre which enables the formation of a mechanical interlock between the fibres and cement matrix. This enhances the bonding at the fibrematrix interface, leading to a more efficient load transfer mechanism within the composite board. Additionally, because cement-based materials are typically weak in tension but strong in compression, the high tensile strength of the waste kraft fibre also improves the tensile strength of the cement composite boards; hence, its resistance to bending or flexural stresses is improved significantly. From the graph, it was observed that an increase in the reinforcement contents led to a steady and consistent increase in the flexural strength of the composite boards up to a maximum of 10 wt.% before a gradual decrease was noticed at 15 wt.% reinforcement contents. A similar observation was reported in the work of Khorami and Ganjian [64] when they examined the effect of fibre content on the flexural behavior of cement composite boards. The initial presence of the waste kraft fibre as reinforcement in the 4 wt.% fibre-reinforced cement composite board (K4 sample) produced a 34% and 17% improvement in flexural strength at 7 and 28 days, respectively, compared to the control sample. Overall, the 10 wt.% fibre-reinforced cement composite board (K10 sample) showed the highest flexural strength, with a 65% and 47% improvement in strength compared to the control sample without any fibre addition. A similar result was reported in another research study conducted by the authors [24].
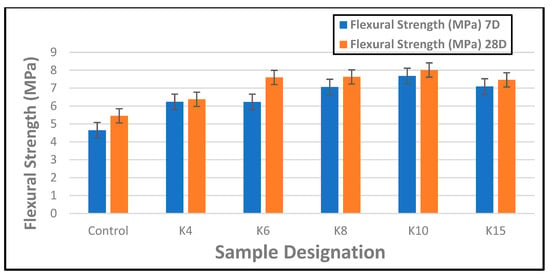
Figure 5.
Flexural strength of composite boards reinforced with waste kraft fibre (7 and 28 days).
- (7)
- Comparing the Effect of Varying Limestone Powder and Metakaolin Content on the Flexural Strength of Waste Kraft Fibre-Reinforced Cement Composite Board
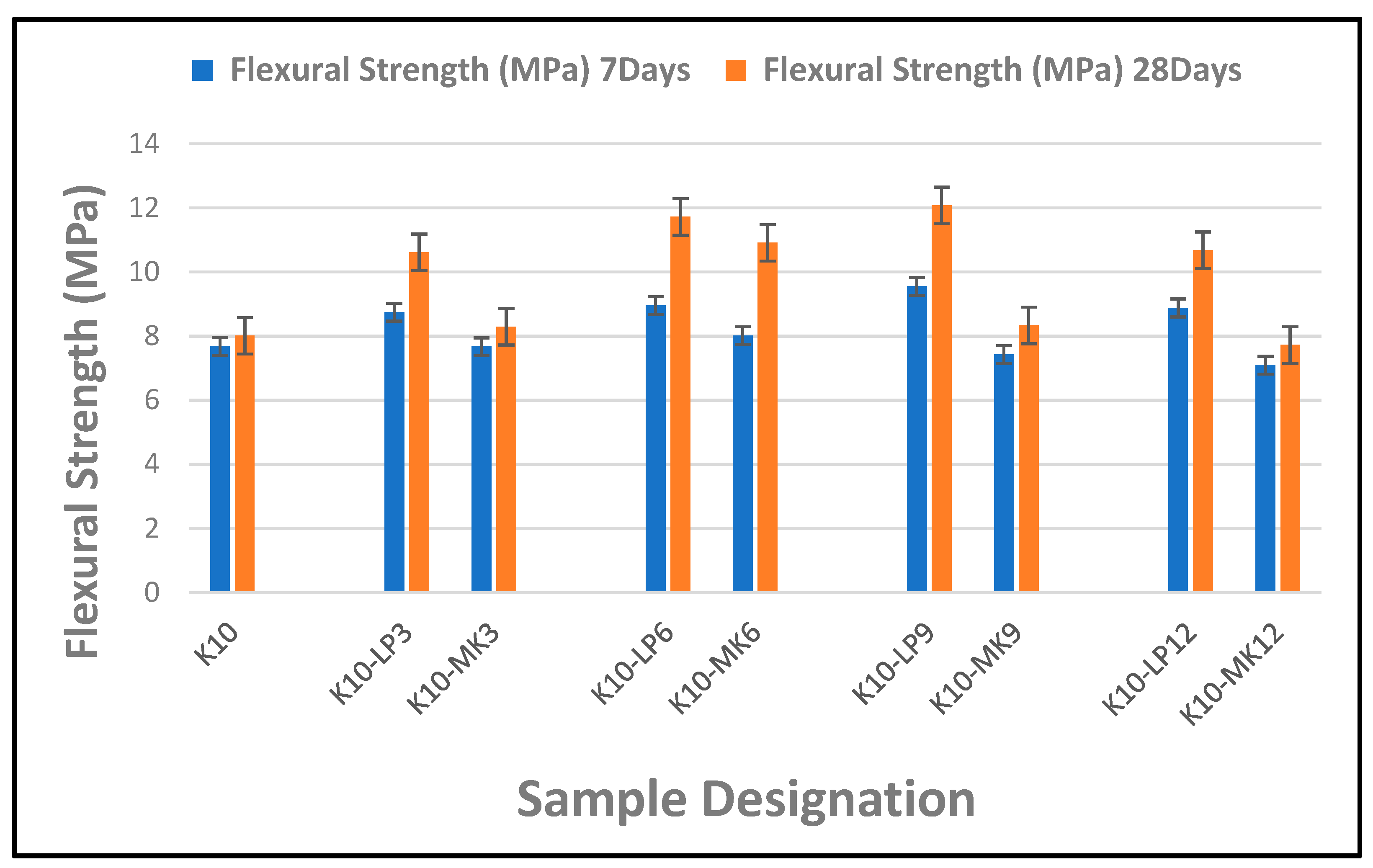
Figure 6 presents the results of composite boards containing 3–12% limestone or metakaolin powder as partial cement replacement in composite samples reinforced by 10 wt.% of waste kraft fibre. It was observed that the inclusion of the limestone powder as a partial cement replacement had a pronounced effect on the flexural strength of the waste kraft fibre-reinforced cement composite board. This could be attributed to the filler effect and the densification of the cementitious matrix as a result of the formation of additional calcium carbonate by the interaction between the particles of the limestone powder and that of the cementitious matrix. Yu et al. [65] reported a similar observation in their study on the use of limestone calcined clay for the improvement of tensile performance of high-strength cementitious composites. Furthermore, it was observed that different dosages of the limestone powder addition produce varied effects on the flexural performance of the composite board. Hence, the K10-LP9 composite sample containing 9% limestone powder as a partial cement replacement displayed the best flexural strength, with values of 9.55 and 12.07 MPa, compared to the reference sample, K10, with values of 7.68 and 8.01 MPa, at 7 and 28 days of hydration, respectively (an increase of 24% and 50% for 7 and 28 days of hydration, respectively).
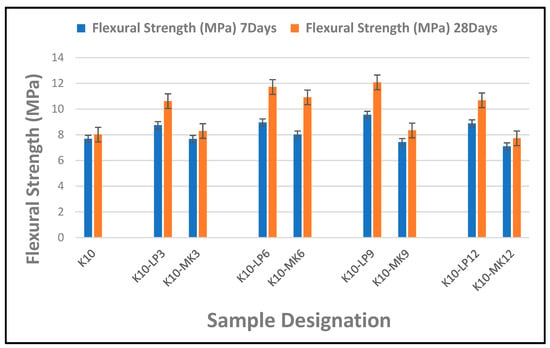
Figure 6.
Flexural strength of composite boards reinforced by 10 wt.% of waste kraft fibre and 3–12% of limestone/metakaolin powder as partial cement replacement (7 and 28 days).
In a similar vein, the addition of metakaolin as partial cement replacement produces a noticeable effect on the flexural strength of the cement composite board. However, its presence at lower dosages (≤3%) seems to produce very little to no effect on the flexural strength of the composite board. However, at an intermediate dosage of 6%, the effect of the metakaolin on the flexural performance of the cement composite board was notably evident. According to a study conducted by Qin et al. [66], the fine particle size and the amorphous structure of the metakaolin contributed to the formation of extra calcium silicate hydrate gel, thus enhancing the effectiveness of the binding matrix. Hence, the K10-MK6 composite sample containing 6% metakaolin powder as a partial cement replacement showed an optimum result, with a value of 8.01 and 10.91 MPa at 7 and 28 days of hydration, respectively, when compared to the reference sample K10. This resulted in a 4% and 36% improvement in the flexural strength at 7 and 28 days, respectively, for the K10-MK6 composite sample.
From Figure 6, we can see that comparing the individual effects of limestone and metakaolin powders on the flexural strength of the cement composite boards showed that the presence of the limestone powder had a much greater effect on the flexural strength of the composite board than that of the metakaolin addition at lower, intermediate, and higher dosage levels. This could be a result of the much finer particle size of the limestone powder as compared to that of the metakaolin. Therefore, according to the current study, the recommended maximum percentage of limestone powder permitted for partial cement replacement in waste kraft fibre-reinforced cement composite board is 9%; a similar dosage was reported in the study conducted by Khorami and Ganjian [33], while metakaolin is 6% by mass of the cement matrix. Dosages above this threshold result in a decrease in the flexural strength of the composite boards for both instances of metakaolin and limestone powder addition.
- (8)
- Comparing the Effect of Varying Limestone Powder and Metakaolin on Flexural Behaviour of Waste Kraft FibreReinforced Cement Composite Board
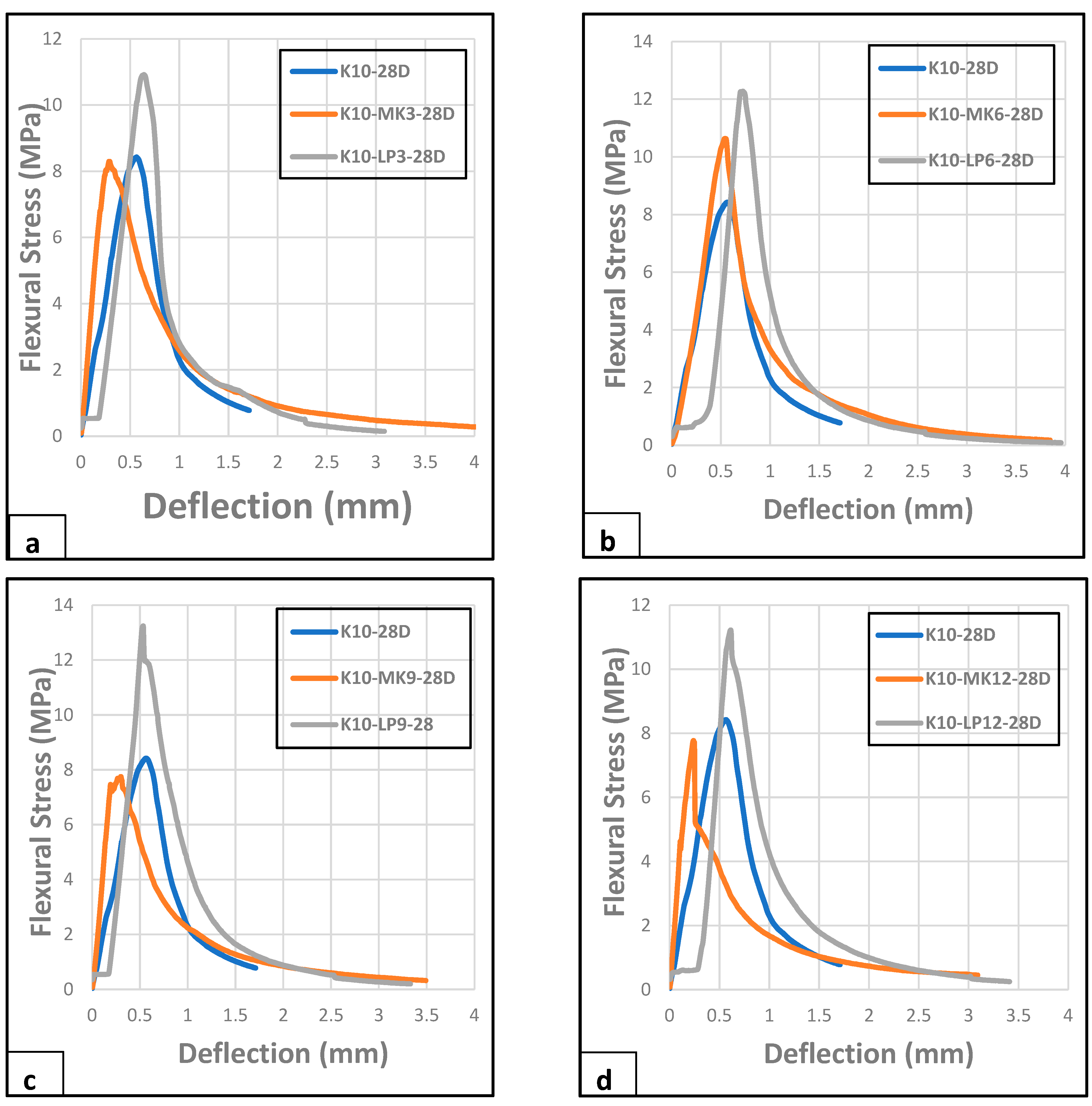
The flexural behaviour of waste kraft fibre-reinforced cement composite board incorporating varying percentages of limestone and metakaolin powders as a partial cement replacement is presented in Figure 7a–d. From Figure 7a, which depicts the 3% replacement of cement by metakaolin and limestone powder, it is observed that the addition of the limestone powder increased the flexural strength of the composite board. This is potentially due to the pozzolanic reaction between the particles of the limestone powder and cement hydration product (calcium hydroxide), resulting in the formation of additional calcium carbonate. Khorami and Ganjian [64] gave a similar report in their research on the effect of limestone powder, silica fume, and fibre content on the flexural behaviour of cement composite reinforced by waste fibre. The presence of this extra calcium carbonate enhances the cohesion and interlocking of particles within the cementitious matrix, leading to improved resistance to bending or flexural stresses. A similar assertion was reported in the work of Eshmaiel [33] and Li et al. [57]. However, the presence of the metakaolin did not show any improvement in the flexural stress of the composite board at this replacement percentage. However, when the percentage of metakaolin and limestone powder was increased to 6%, the effect of the metakaolin was noticed, as there was an improvement in the flexural strength of the composite board. However, the limestone powder replacement still performs better than the metakaolin replacement. A justification for this could be the much finer particle size of the limestone powder as compared to that of the metakaolin, as shown in Figure 1. The additional increase in the metakaolin and limestone powder as a cement replacement showed that the limestone powder further improved the flexural stress of the composite board up to a maximum of 9% replacement, as shown in Figure 7c, while such an increase in the case of metakaolin resulted in a gradual decrease in the flexural stress of the composite board. This could be due to the coarse particle size of the metakaolin powder, which already filled the voids in the composite boards at a lower percentage of replacement; thus, increasing the percentage of metakaolin as a cement replacement causes the formation of a weaker matrix, which resulted in the observed decrease in flexural strength, as seen in Figure 7c,d. Overall, the composite board with 9% limestone powder as a cement replacement displayed the optimum results, with a flexural stress value of 13.20 MPa, as compared to its metakaolin counterpart, with a value of 7.46 MPa. This shows a significant improvement in flexural strength over the reference sample, K10, producing a 59% overall enhancement in flexural strength. Finally, it was observed that all the composite samples containing limestone powder as a partial cement replacement exhibited a similar displacement at failure, as they all peak between 0.5 mm and 0.75 mm, while all the composite samples containing metakaolin as a partial cement replacement failed at a deflection less than 0.5 mm.
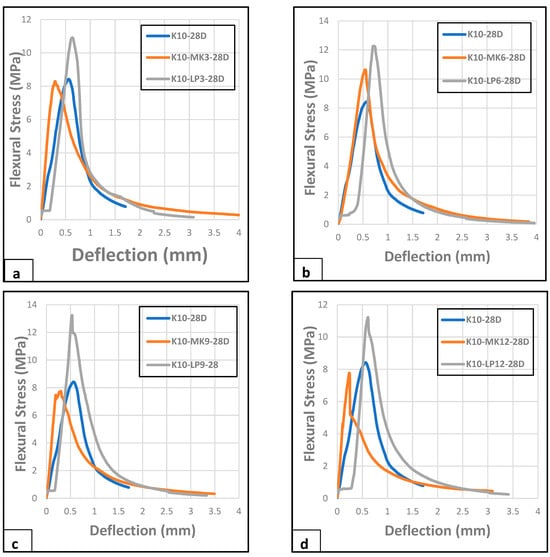
Figure 7.
Flexural behaviour of composite boards reinforced by 10 wt.% of waste kraft fibre and (a) 3%, (b) 6%, (c) 9%, and (d) 12% of limestone powder/metakaolin as partial cement replacement (28 days).
- (9)
- Comparing the Effect of Limestone Powder and Metakaolin on Moisture Movement Characteristics of Waste Kraft FibreReinforced Cement Composite Board
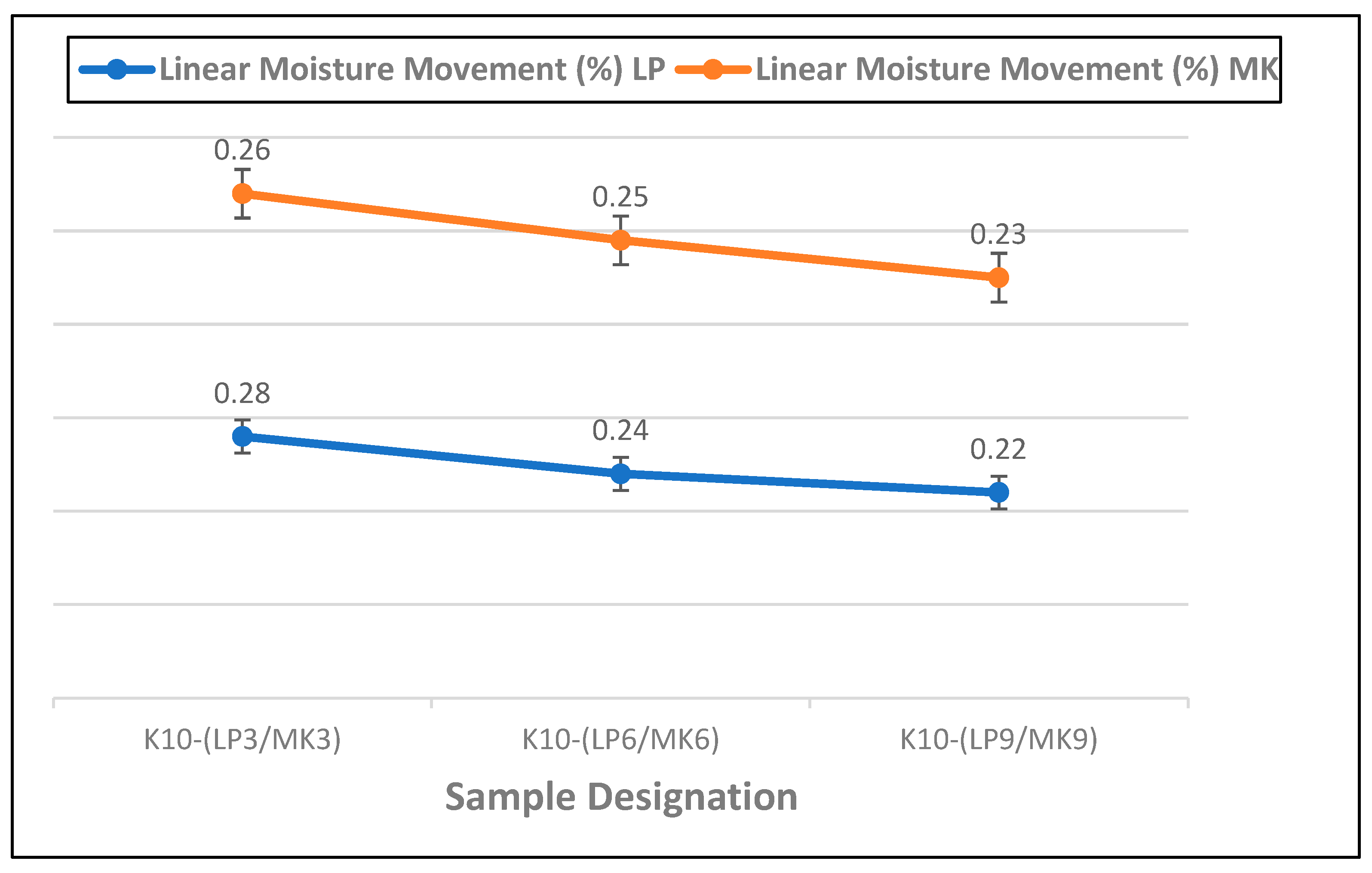
Figure 8 shows the effect of increasing the percentage of metakaolin and limestone powder on the moisture movement characteristics of waste kraft fibre-reinforced cement composite boards. It was observed that increasing the percentage of either metakaolin or limestone powder reduces the ingress of water into the composite board. This is because the incorporation of the metakaolin and limestone powder contributes to a denser and more compact cementitious matrix. This densification leads to a reduction in the size and connectivity of pores and voids within the composite board, thus decreasing its overall permeability to moisture. This could be attributed to the filler effect and the fine particle size of the additives, as well as their pozzolanic reaction, which contributed to the formation of additional hydration products which fill the voids and capillary pores within the cementitious matrix. A similar assertion was reported in the work of Yang et al. [67] when they incorporated quarry-stone powders into ultra-high-performance concrete. Hence, the ingress of water into the composite board is minimized, and this helps to prevent and/or reduce the occurrence of issues such as dimensional changes and moisture-related deterioration. Therefore, the composite board containing 9% limestone and metakaolin powder shows the highest resistance to moisture movement, with respective values of 0.22% and 0.23%.
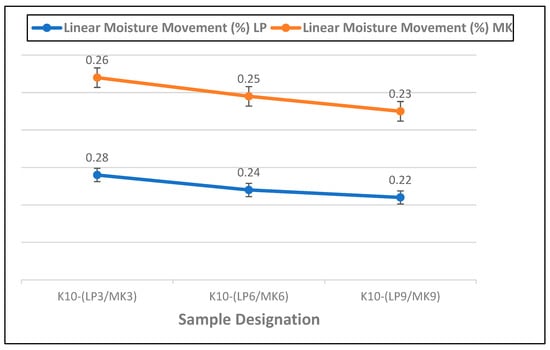
Figure 8.
Linear moisture movement of composite boards containing 3–9% metakaolin and limestone powder as partial cement replacement.
- (10)
- Comparing the Effect of Metakaolin and Limestone Powder on Water-Absorption Characteristics of Waste Kraft FibreReinforced Cement Composite Board
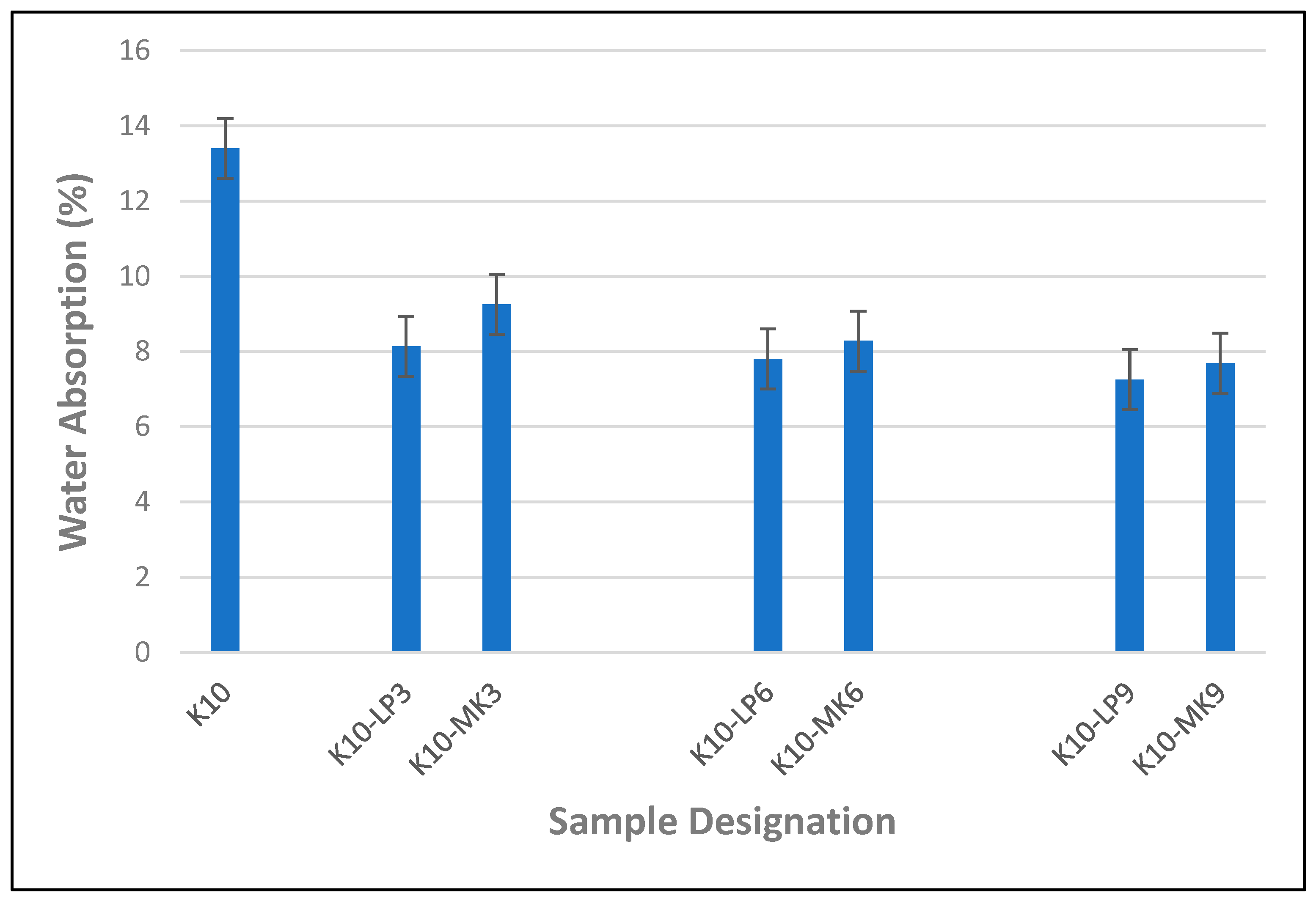
The effect of metakaolin and limestone powder on the water-absorption property of composite boards reinforced with waste kraft fibre is presented in Figure 9. It was observed that the addition of both the metakaolin and limestone powder had a positive influence on the water-absorption property of the cement composite board. This is because the metakaolin and limestone powder particles fill the voids and pores within the composite board, reducing the pathways for water to penetrate the composite boards; hence, the overall water-absorption capacity of the composite board is reduced. From Figure 9, it can be seen that the addition of metakaolin and limestone powder at 3% cement replacement produced a sudden decrease in the water-absorption capacity of the composite board, resulting in a respective 31% and 39% reduction in the volume of water absorbed by the composite board. It was also observed that a further increase in the percentage of metakaolin and limestone powder as partial cement replacement also led to a further decrease in the percentage of water absorbed by the composite board. Hence, the composite board containing 9% metakaolin and limestone powder as partial cement replacement displayed the optimum results by absorbing the least volume of water with a value of 7.69% and 7.25%, respectively, resulting in a 43% and 46% enhancement in the water-resistance capacity of the composite boards, respectively, when compared to the reference sample, K10. From the foregoing, by comparing the impact of metakaolin and limestone powder on the water-absorption property of the cement composite board, it was noted that the presence of limestone powder as a partial cement replacement offered a higher resistance to water absorption than its counterpart containing metakaolin powder. This result agreed with the previous result discussed in Figure 8.
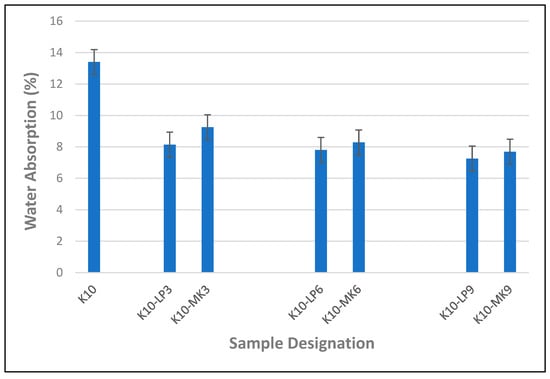
Figure 9.
Water-absorption characteristics of waste kraft fibre-reinforced cement composite boards containing 3–9% metakaolin and limestone powder as partial cement replacement.
- (11)
- Comparing the Effect of Limestone Powder and Metakaolin on the Density of Waste Kraft FibreReinforced Cement Composite Board
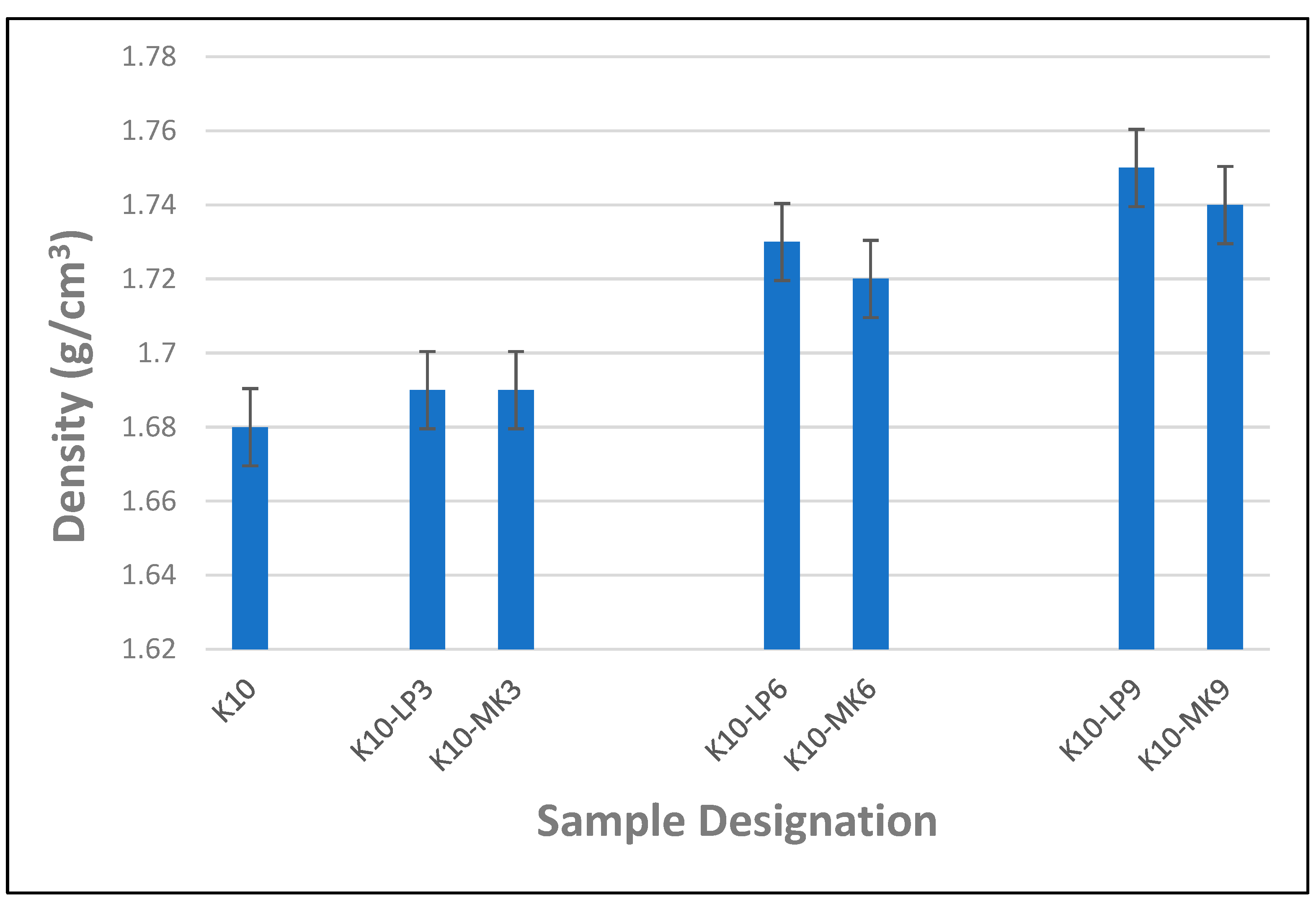
Figure 10 shows the impact of the addition of metakaolin and limestone powder as partial cement replacement on the density of cement composite boards reinforced with waste kraft fibre. It was observed that adding metakaolin and limestone powder increased the density of the composite boards. This is primarily due to the improved particle packing caused by the metakaolin and limestone powder particles interacting with the cement particles in the composite mixture. This improved particle parking contributes to a denser microstructure, hence increasing the overall density of the composite board. From Figure 10, it is observed that incorporating 3% metakaolin and limestone powder as a partial cement replacement in the waste kraft fibre-reinforced cement composite board produced a slight but equal increase in the density of the composite board. Increasing the percentage of metakaolin and limestone powder to 6% produced a subsequent increase in the density of the composite board, resulting in a 2.4% and 3% increase, respectively. The composite board containing 9% metakaolin and limestone powder as a partial cement replacement displayed the maximum density, with a value of 1.74 and 1.75 g/cm3, respectively. This culminated in an overall increase of 3.6% and 4.2%, respectively, compared to the reference sample, K10. Consequently, by comparing the impact of adding metakaolin and limestone powder as a partial cement replacement on the density of waste kraft fibre-reinforced cement composite board, it was noted that limestone powder had a slightly higher influence on the density of the composite board than its counterpart containing metakaolin powder. This could be due to the finer particle size of the limestone powder as compared to that of the metakaolin.
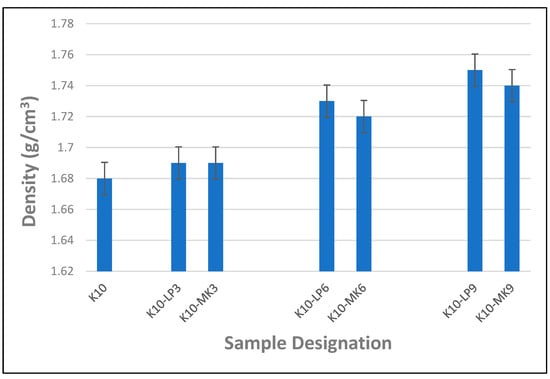
Figure 10.
Density of waste kraft fibre-reinforced cement composite boards containing 3–9% metakaolin and limestone powder as partial cement replacement.
- (12)
- SEM Micrographs of Cement Composite Boards with LP and MK Powders as Partial Cement Replacement
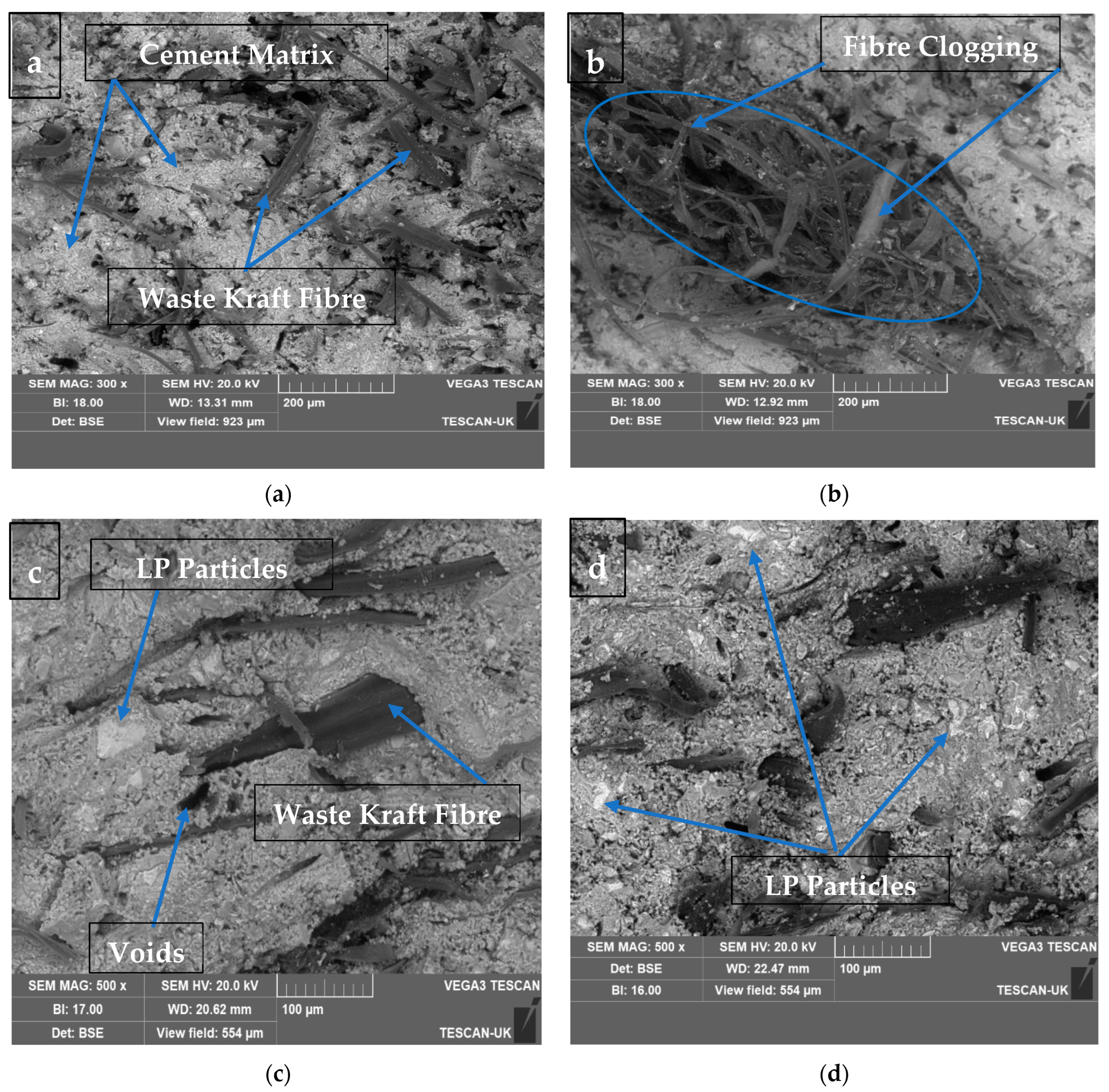
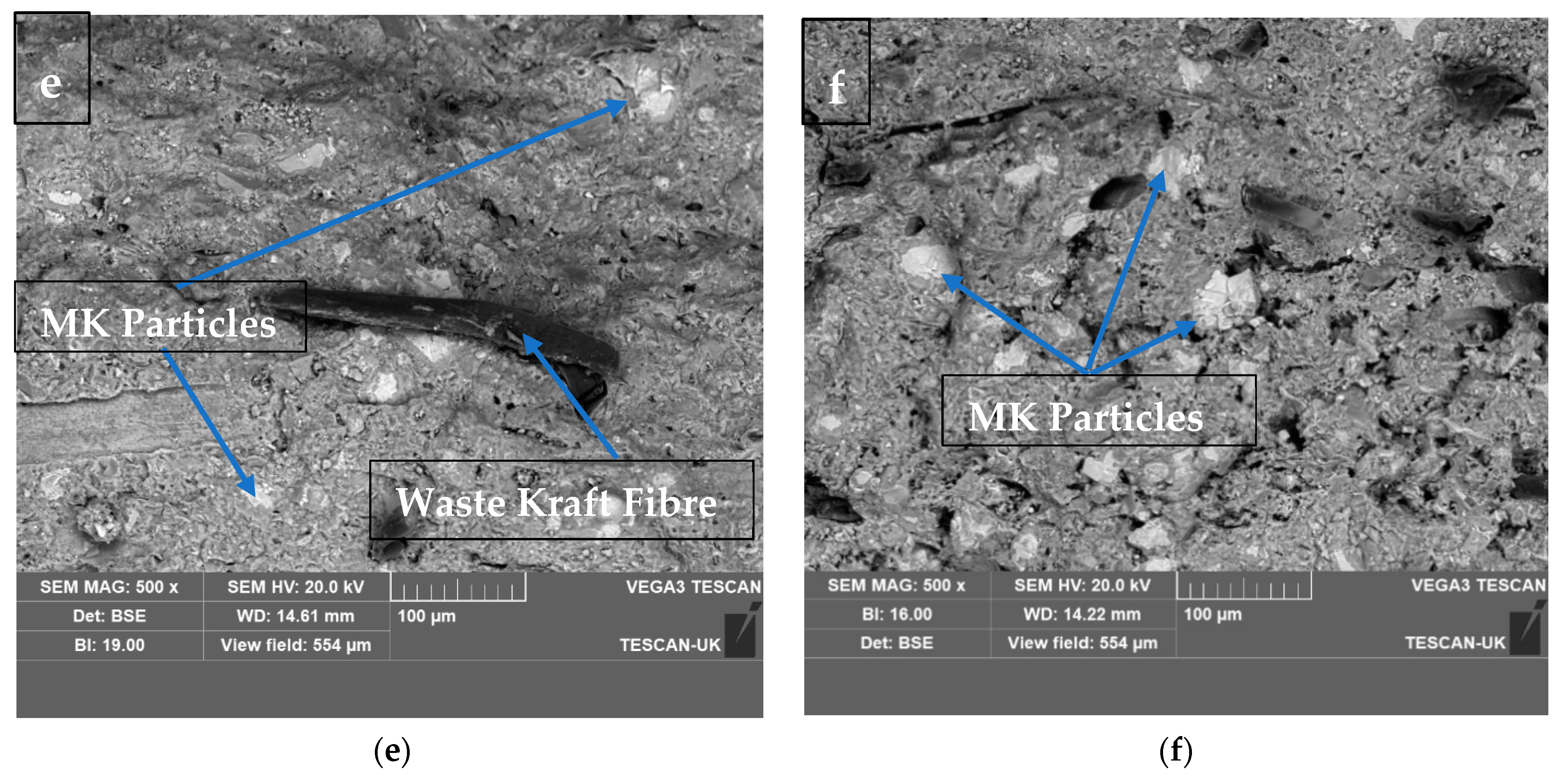
Figure 11a,b show the SEM morphology of the fractured surfaces of 10 wt.% and 15 wt.% waste kraft fibre-reinforced cement composite boards. It was observed that the composite board reinforced with 10 wt.% waste kraft fibre displayed homogeneity and uniform fibre distribution; this culminated in the high strength observed in the composite sample. On the other hand, in the composite board reinforced with 15 wt.% waste kraft fibre, there was a significant occurrence of fibre clogging and/or clumping which was primarily due to the presence of the excess fibre in the composite board. Hence, the flexural strength of the composite sample decreased gradually as a result of the formation of a weak point within the composite (shown and explained earlier in Figure 5). From Figure 11c,d, it was observed that the addition of the limestone powder as a partial cement replacement fulfills its role as an inert additive by filling the voids and capillary pores within the composite boards, thereby contributing to and increasing the densification and the particle parking within the composite. Hence, the flexural strength of the composite boards improved, as noted previously, in Figure 6. In the same vein, in Figure 11e,f, the addition of the metakaolin as a partial cement replacement also fulfilled its role as a pozzolanic material and a filler. It was observed that the composite board containing 6% metakaolin as a partial cement replacement showed a refined microstructure when compared to that of Figure 11a. This is due to the presence of the metakaolin, which forms additional calcium silicate hydrate gel through the pozzolanic reaction with the calcium hydroxide produced during the cement hydration process. This additional calcium silicate hydrate gel and the refined microstructure contribute to the densification and, hence, the overall strength of the composite board. This evidence agreed with the submissions of other researchers [68,69].
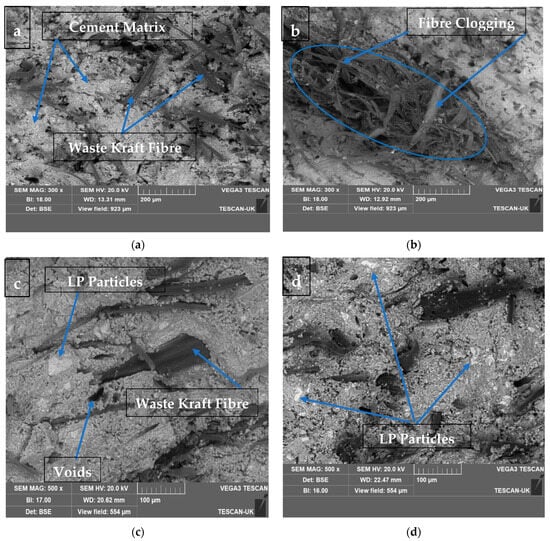
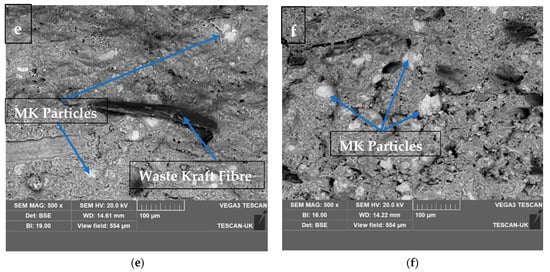
Figure 11.
SEM micrographs of fractured surfaces of (a) K10, (b) K15, (c) K10-LP6, (d) K10-LP9, (e) K10-MK6, and (f) K10-MK9.
3. Conclusions
After a detailed investigation of the mechanical properties and morphological characteristics of cement composite boards reinforced with waste kraft fibre, elucidating the distinct impacts of limestone powder and metakaolin as sustainable eco-friendly individual additives, the following conclusions can be drawn from this study:
- Waste kraft fibres can be employed as a traditional or local reinforcement in cement composite boards by utilizing an appropriate dosage not exceeding 10 wt.% of the composite composition. This would contribute to the sustainability and recycling of waste products and hence, contribute to a circular economy.
- The addition of limestone powder at lower, intermediate, and higher dosages not exceeding 9% by mass of the cement matrix had a better influence on the flexural performance of the waste kraft fibre-reinforced cement composite boards when compared to its counterparts containing metakaolin powders at similar dosage levels.
- The addition of the metakaolin and limestone powder as partial cement replacement enhances the water-resistance capability of the composite board; however, the limestone powder replacement had a much higher influence than that of the metakaolin replacement.
- The individual addition of both additives increased the density of the cement composite board; however, a slightly higher density was recorded in the composite boards containing the limestone powder addition.
- The replacement of a significant fraction of cement with limestone powder or metakaolin will result in lowering the CO2 emissions associated with the cement board production process and, hence, may lead to a reduction in the overall cost of composite production.
- The morphological study of the composite boards incorporating metakaolin and limestone powders as partial cement replacement showed improved particle packing, densification, and microstructural refinement.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.S.T., D.S.A. and S.S.R.; methodology, A.S.T., D.S.A. and M.K.; investigation, A.S.T. and D.S.A.; data curation, A.S.T.; formal analysis, A.S.T., D.S.A. and M.K.; writing—original draft preparation, A.S.T.; writing—review and editing, D.S.A., M.K. and S.S.R.; supervision, D.S.A., M.K. and S.S.R.; project administration, D.S.A. and M.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available in the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Ige, O.E.; Olanrewaju, O.A.; Duffy, K.J.; Obiora, C. A Review of the Effectiveness of Life Cycle Assessment for Gauging Environmental Impacts from Cement Production. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 324, 129213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etim, M.-A.; Babaremu, K.; Lazarus, J.; Omole, D. Health Risk and Environmental Assessment of Cement Production in Nigeria. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ighalo, J.O.; Adeniyi, A.G. A Perspective on Environmental Sustainability in the Cement Industry. Waste Dispos. Sustain. Energy 2020, 2, 161–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamad, N.; Muthusamy, K.; Embong, R.; Kusbiantoro, A.; Hashim, M.H. Environmental Impact of Cement Production and Solutions: A Review. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 48, 741–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, U.C.; Sarsaiya, S.; Gupta, A. A Systematic Review on the Impact of Cement Industries on the Natural Environment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 18440–18451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cormos, C.C. Decarbonization Options for Cement Production Process: A Techno-economic and Environmental Evaluation. Fuel 2022, 320, 123907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrew, R.M. Global CO2 Emissions from Cement Production. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2018, 10, 195–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, C.; Jung, E.; Lee, S.; Jang, C.; Shin, K.N. Global Trend of Cement Production and Utilization of Circular Resources. J. Energy Eng. 2020, 29, 57–63. [Google Scholar]
- Poudyal, L.; Adhikari, K. Environmental Sustainability in Cement Industry: An Integrated Approach for Green and Economical Cement Production. Resources. Environ. Sustain. 2021, 4, 100024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, M.; Romer, M.; Tschudin, M.; Bolio, H. Sustainable Cement Production—Present and Future. Cem. Concr. Res. 2011, 41, 642–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardarsdottir, S.O.; De Lena, E.; Romano, M.; Roussanaly, S.; Voldsund, M.; Pérez-Calvo, J.-F.; Berstad, D.; Fu, C.; Anantharaman, R.; Sutter, D.; et al. Comparison of Technologies for CO2 Capture from Cement Production—Part 2: Cost Analysis. Energies 2019, 12, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohr, B.J.; Biernacki, J.J.; Kurtis, K.E. Supplementary Cementitious Materials for Mitigating Degradation of Kraft pulp Fiber-cement Composites. Cem. Concr. Res. 2007, 37, 1531–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.J.; Chun, B.; Choi, H.-J.; Shin, W.; Yoo, D.Y. Effects of Supplementary Cementitious Materials and Curing Condition on Mechanical Properties of Ultra-High-Performance, Strain-Hardening Cementitious Composites. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.P.; Brouwers, H.J.H.; Chen, W.; Yu, Q. Optimization and Characterization of High-volume Limestone Powder in Sustainable Ultra-high Performance Concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 242, 118112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thankam, G.L.; Thurvas Renganathan, N. Ideal Supplementary Cementing Material—Metakaolin: A Review. Int. Rev. Appl. Sci. Eng. 2020, 11, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Wei, S.; Li, W.; Ma, S.; Ji, P.; Shen, X. Synergistic Effect of Metakaolin and Limestone on the Hydration Properties of Portland Cement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 223, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, S.S.; Hagrass, A.A.; Boulos, T.R.; Youssef, S.I.; El-Hossiny, F.I.; Moharam, M.R. Metakaolin as an Active Pozzolan for Cement That Improves Its Properties and Reduces Its Pollution Hazard. J. Miner. Mater. Charact. Eng. 2018, 6, 86–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Diadamony, H.; Amer, A.A.; Sokkary, T.M.; El-Hoseny, S. Hydration and Characteristics of Metakaolin Pozzolanic Cement Pastes. HBRC J. 2018, 14, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankar, B.; Ramadoss, P. Assessment of Mechanical and Durability Performance of Silica Fume and Metakaolin as Cementitious Materials in High-performance Concrete. Int. Rev. Appl. Sci. Eng. 2024, 15, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majstorović, F.; Sebera, V.; Mrak, M.; Dolenec, S.; Wolf, M.; Marrot, L. Impact of Metakaolin on Mechanical Performance of Flax Textile-reinforced Cement-based Composites. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2022, 126, 104367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afolalu, S.A.; Salawu, E.; Ogedengbe, T.; Joseph, O.O.; Okwilagwe, O.; Emetere, M.E.; O Yusuf, O.; Noiki, A.; Akinlabi, S. Bio-Agro Waste Valorization and its Sustainability in the Industry: A Review. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2021; p. 1170. [Google Scholar]
- Petrella, A.; Spasiano, D.; Liuzzi, S.; Ayr, U.; Cosma, P.; Rizzi, V.; Petrella, M.; Di Mundo, R. Use of Cellulose Fibers from Wheat Straws for Sustainable Cement Mortars. J. Sustain. Cem. Mater. 2018, 8, 161–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, F.d.A.; Mobasher, B.; Filho, R.D.T. Advances in Natural Fiber Cement Composites: A Material for the Sustainable Construction Industry. In Proceedings of the 4th Colloquium on Textile Reinforced Structures (CTRS4), Dresden, Germany, 3–5 June 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Taiwo, A.S.; Ayre, D.S.; Khorami, M.; Rahatekar, S.S. Optimizing the Mechanical Properties of Cement Composite Boards Reinforced with Cellulose Pulp and Bamboo Fibers for Building Applications in Low-Cost Housing Estates. Materials 2024, 17, 646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taiwo, A.S.; Egbodion, E.O.; Adediran, A.A.; Shittu, S.A.; Balogun, S.O.; Adesina, O.S. Mechanical Properties and Water-Absorption Characteristics of Selected Natural Fibers as a Replacement for Asbestos. Mater. Technol. 2021, 55, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassar, R.-U.; Soroushian, P.; Balachandra, A.; Nassar, S.; Weerasiri, R.; Darsanasiri, N.; Abdol, N. Effect of Fiber Type and Content on the Performance of Extruded Wood Fiber Cement Products. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2022, 16, e00968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, K.M.F.; Horváth, P.G.; Alpár, T. Development of Lignocellulosic Fiber Reinforced Cement Composite Panels Using Semi-dry Technology. Cellulose 2021, 28, 3631–3645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, P.; Shui, Z.; Chen, W.; Shen, C. Effects of Metakaolin, Silica fume and Slag On Pore Structure, Interfacial Transition Zone and Compressive Strength of Concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 44, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouli, K.C.; Pannirselvam, N.; Anitha, V.; Kumar, D.V.; Rao, S.V. Strength Studies On Banana Fibre Concrete with Metakaolin. Int. J. Civ. Eng. Technol. 2019, 10, 684–689. [Google Scholar]
- Kaffayatullah, K.; Megat, A.M.J.; Muhammad, N.A.; Mudassir, I. Evaluation of the mechanical properties, microstructure, and environmental impact of mortar incorporating metakaolin, micro, and nano-silica. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2024, 20, e02699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oates, J.A.H. Part 1—Production of Limestone. In Lime and Limestone: Chemistry and Technology, Production and Uses; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008; pp. 9–59. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.; Wu, H.-L.; Leung, C.K.Y. Feasibility of Using Ultrahigh-volume Limestone-calcined Clay Blend to Develop Sustainable Medium-strength Engineered Cementitious Composites (ECC). J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 262, 121343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganjiane, E.; Khorami, M. Effect of Limestone Powder on Mechanical Properties of Cement Composite Board. In Proceedings of the International Inorganic Bonded Fibre Composites Conference, Aalborg, Denmark, 21–24 September 2010; pp. 48–57. [Google Scholar]
- Turk, K.; Kina, C.; Nehdi, M. Durability of Engineered Cementitious Composites Incorporating High-Volume Fly Ash and Limestone Powder. Sustainability 2022, 14, 10388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Kovler, K.; Provis, J.L.; Buchwald, A.; Cyr, M.; Patapy, C.; Kamali-Bernard, S.; Courard, L.; Sideris, K. Metakaolin. In Properties of Fresh and Hardened Concrete Containing Supplementary Cementitious Materials; De Belie, N., Soutsos, M., Gruyaert, E., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 153–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasiopoulou, T.; Katsourinis, D.; Giannopoulos, D.; Founti, M. Production-Process Simulation and Life-Cycle Assessment of Metakaolin as Supplementary Cementitious Material. Eng 2023, 4, 761–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakera, A.T.; Alexander, M.G. Use of Metakaolin as Supplementary Cementitious Material in Concrete, with Focus on Durability Properties. RILEM Tech. Lett. 2019, 4, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macquarie Supit, S.W.; Rumbayan, R.; Ticoalu, A. Influence of Ultrafine Metakaolin in Improving the Compressive Strength and Durability Properties of Concrete. Adv. Civ. Eng. Mater. 2021, 10, 210–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohr, B.J.; Nanko, H.; Kurtis, K.E. Durability of Kraft pulp Fiber–cement Composites to Wet/Dry Cycling. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2004, 27, 435–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haigh, R.; Bouras, Y.; Sandanayake, M.; Vrcelj, Z. The Mechanical Performance of Recycled Cardboard Kraft Fibres Within Cement and Concrete Composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 317, 125920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booya, E.; Gorospe, K.; Ghaednia, H.; Das, S. Durability Properties of Engineered Pulp Fibre Reinforced Concretes Made With and Without Supplementary Cementitious Materials. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 172, 376–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seungjun, R.; Mina, S.; Hyunsik, K.; Rakhyun, K. The Use of Metakaolin as a Supplementary Cementitious Material to Reduce the Environmental Impacts of Ready-mixed Concrete. Int. J. Sustain. Build. Technol. Urban Dev. 2023, 14, 418–425. [Google Scholar]
- Khorami, M.; Ganjian, E.; Mortazavi, A.; Saidani, M.; Olubanwo, A.; Gand, A. Utilisation of Waste Cardboard and Nano Silica Fume in the Production of Fibre Cement Board Reinforced by Glass Fibres. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 152, 746–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mármol, G.; Savastano, H.; Monzó, J.; Borrachero, M.V.; Soriano, L.; Payá, J. Portland Cement, Gypsum and Fly Ash Binder Systems Characterization for Lignocellulosic Fiber-cement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 124, 208–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maghfouri, M.; Alimohammadi, V.; Azarsa, P.; Asadi, I.; Doroudi, Y.; Balakrishnan, B. Impact of Fly Ash on Time-Dependent Properties of Agro-Waste Lightweight Aggregate Concrete. J. Compos. Sci. 2021, 5, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.; Ming, X.; He, K.; Li, L.; Shen, S. Effect of Macro-, Micro- and Nano-Calcium Carbonate on Properties of Cementitious Composites—A Review. Materials 2019, 12, 781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turk, K.; Nehdi, M.L. Coupled Effects of Limestone Powder and High-volume Fly Ash on Mechanical Properties of ECC. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 164, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Shi, C.; Khayat, K.H. Multi-scale Investigation of Microstructure, Fiber Pullout Behavior, and Mechanical Properties of Ultra-high Performance Concrete with Nano-CaCO3 Particles. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2018, 86, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medjigbodo, G.; Rozière, E.; Charrier, K.; Izoret, L.; Loukili, A. Hydration, Shrinkage, and Durability of Ternary Binders Containing Portland Cement, Limestone Filler, and Metakaolin. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 183, 114–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-Y. Analysis of Hydration and Strength Optimization of Cement-fly-ash-limestone Ternary Blended Concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 166, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.; Zhang, C.; Lv, H.; Xu, L. Characterization of Mechanical Behavior and Mechanism of Calcium Carbonate Whisker-reinforced Cement Mortar. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 66, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Cai, J.; Ma, H.; Leung, C.K.Y. Development of Multiscale Fiber-Reinforced Engineered Cementitious Composites with PVA Fiber and CaCO3 Whisker. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2018, 30, 04018106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocelić, A.; Baričević, A.; Smrkić, M.F. Synergistic Integration of Waste Fibres and Supplementary Cementitious Materials to Enhance the Sustainability of Ultra-high-performance Concrete (UHPC). Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2024, 20, e02772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natalija, B.O.; Gregor, K. Combined Effects of Metakaolin and Hybrid Fibers on Self-Compacting Concrete. Materials 2022, 15, 5588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasikala, K.; Vamsi, S.; Prasad, H.; Venkateswarlu, D. An Experimental Study on Metakaolin on the Performance of High Strength Concrete as a Partial Replacement to Cement. Int. J. Mod. Trends Sci. Technol. 2022, 8, 62–73. [Google Scholar]
- Segura, J.; Aponte, D.; Pelà, L.; Roca, P. Influence of Recycled Limestone Filler Additions on the Mechanical Behaviour of Commercial Premixed Hydraulic Lime-based Mortars. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 238, 117722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.-T.; Cheng, A.; Černý, R. Effect of Limestone Powder on Strength and Permeability of Cementitious Mortars. MATEC Web Conf. 2020, 322, 01009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gołaszewski, J.; Gołaszewska, M.; Cygan, G. Performance of Ordinary and Self-Compacting Concrete with Limestone after Freeze–Thaw Cycles. Buildings 2022, 12, 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palm, S.; Proske, T.; Rezvani, M.; Hainer, S.; Müller, C.; Graubner, C.-A. Cement with a High Limestone Content—Mechanical Properties, Durability, and Ecological Characteristics of the Concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 119, 308–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Oh, S.; Wang, X.-Y.; Lin, R.-S. Hydration–Strength–Workability–Durability of Binary, Ternary, and Quaternary Composite Pastes. Materials 2021, 15, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- BS EN 12467; Fibre Cement Flat Sheets—Product Specification and Test Methods. British Standards Institution: London, UK, 2012.
- ASTM C1185-08; Standard Test Methods for Sampling and Testing Non-asbestos Fibre Cement Flat Sheet, Roofing and Siding Shingles, and Clapboards. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2016.
- Khorami, M.; Ganjian, E. The Effect of Limestone Powder, Silica Fume, and Fibre Content on Flexural Behaviour of Cement Composite Reinforced by Waste Kraft Pulp. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 46, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Leung, C.K.Y. Using Limestone Calcined Clay to Improve Tensile Performance and Greenness of High-Tensile Strength Strain-Hardening Cementitious Composites (SHCC). In Calcined Clays for Sustainable Concrete; Springer: Singapore, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, C.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Y.; Zou, Y.; Al Sairafia, F.A.; Jiang, C.A. Comparative Study of Metakaolin and Silica Fume on the Properties and Microstructure of Ultrafine Dredged Sand Mortars. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2023, 2023, 6176098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Yu, R.; Shui, Z.; Gao, X.; Han, J.; Lin, G.; Qian, D.; Liu, Z.; He, Y. Environmental and Economical Friendly Ultra-high Performance Concrete Incorporating Appropriate Quarry-stone Powders. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 260, 121112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, W.; Peng, Y.; Tang, S.; Wang, L.; Shi, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Geng, Z.; Wu, K. Hydration and Fractal Analysis on Low-heat Portland Cement Pastes Using Thermodynamics-based Methods. Fractal Fract. 2023, 7, 606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Y.; Fang, H.; Yuan, J.; Tang, S. The Early-age Cracking Sensitivity, Shrinkage, Hydration Process, Pore Structure and Micromechanics of Cement-based Materials Containing Alkalis with Different Metal Ions. Dev. Built Environ. 2024, 18, 100454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Tian, L.; Zhao, W.; Lazaro, S.A.; Li, X.; Tang, S. Dielectric and Mechanical Properties of Cement Pastes Incorporated with Magnetically Aligned Reduced Graphene Oxide. Dev. Built Environ. 2024, 18, 100471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).