Adaptive Quick Sliding Mode Reaching Law and Disturbance Observer for Robust PMSM Control Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
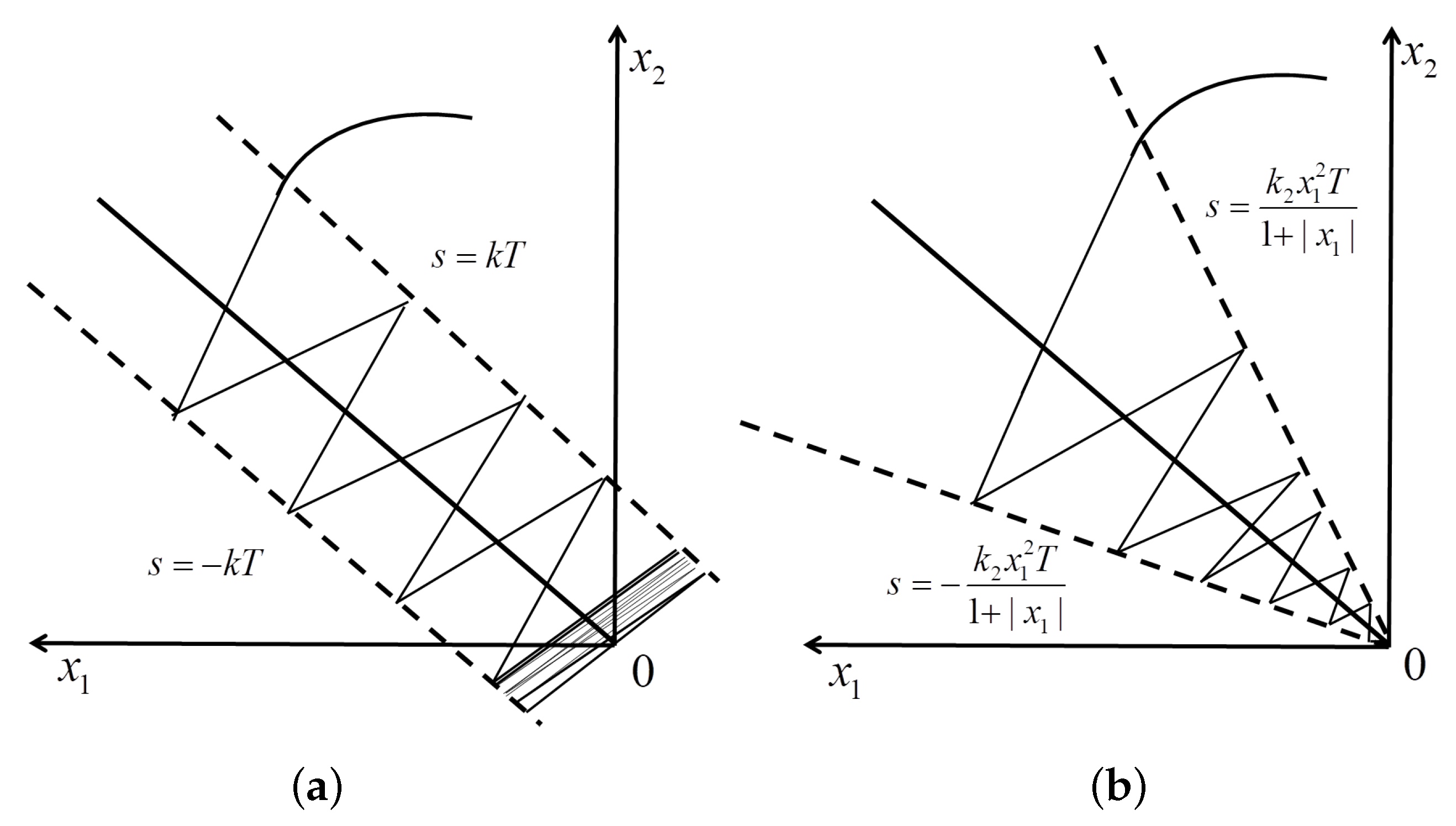
- To reduce the strength of the trade-off between large constant switching gains and improve the reaching time, in this paper, a novel reaching law termed the adaptive quick reaching law (AQRL) is proposed. The AQRL is based on second-order sliding mode characteristics and switching function. In addition, the switching function is based on an exponential term and system state.
- By utilizing a sliding mode disturbance observer (SMDO), we obtain robustness against a sudden disturbance and parameter uncertainty. SMDO methods have been studied to estimate disturbance and mismatched parameter uncertainty [24,25]. Moreover, to respond to disturbance more accurately and avoid the immoderate switching gain for SMDO, a high-order terminal sliding mode observer (HOTSMO) is also used in this paper.
- The proposed AQRL is verified by the Lyapunov second method, and it is also mathematically demonstrated that this reaching time is faster than that of the conventional reaching law.
2. Adaptive Quick Reaching Law Design and Analysis
2.1. Adaptive Quick Reaching Law-Based Sliding Mode Control Design
2.2. Numerical Simulation
3. Mathematical Model of PMSM and Control Schemes
3.1. PMSM Electrical Model
3.2. Design of the PMSM Sliding Mode Controller Using the Adaptive Quick Reaching Law
3.3. Design of a Second-Order Fast Terminal Sliding Mode Observer for PMSM
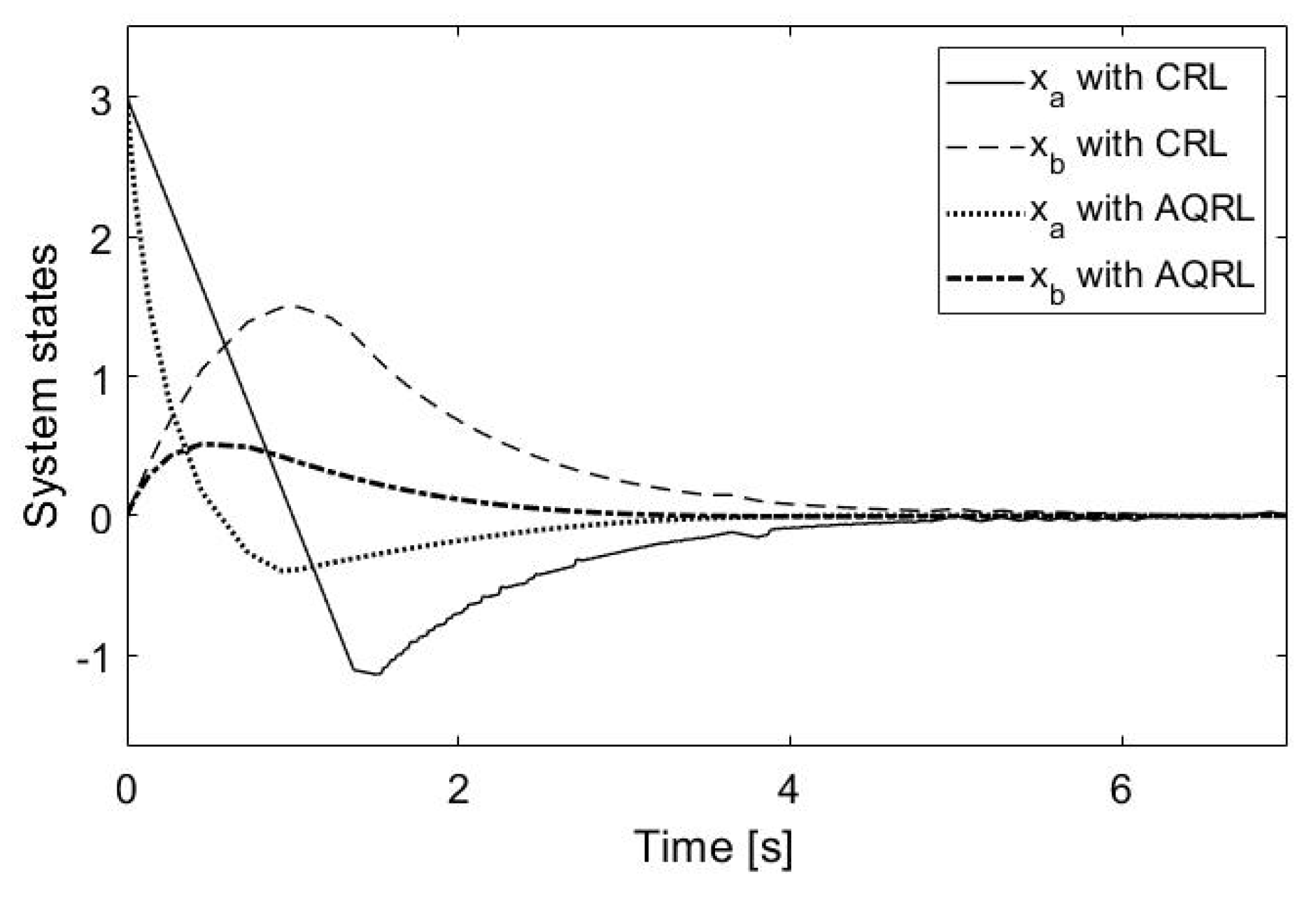
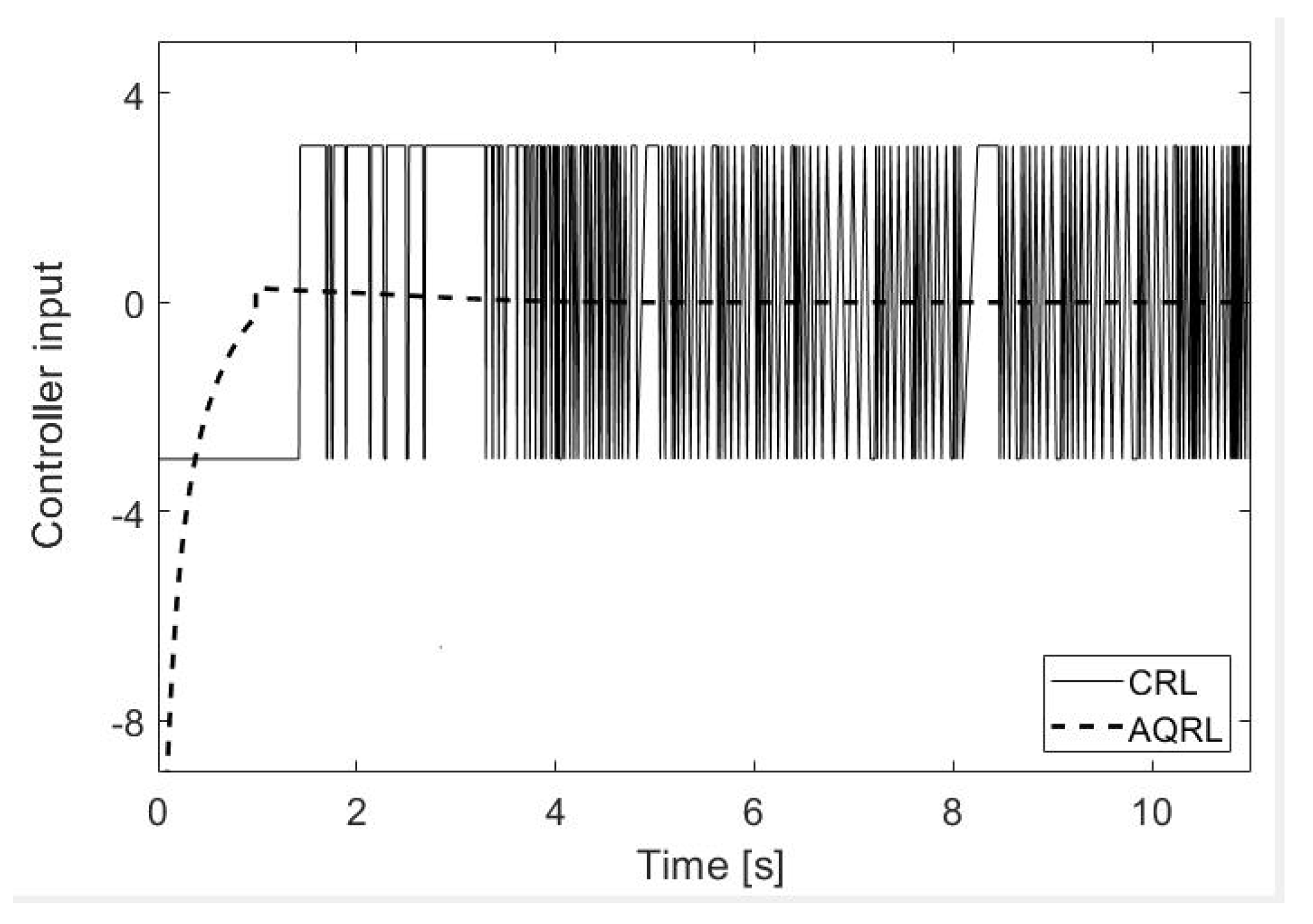
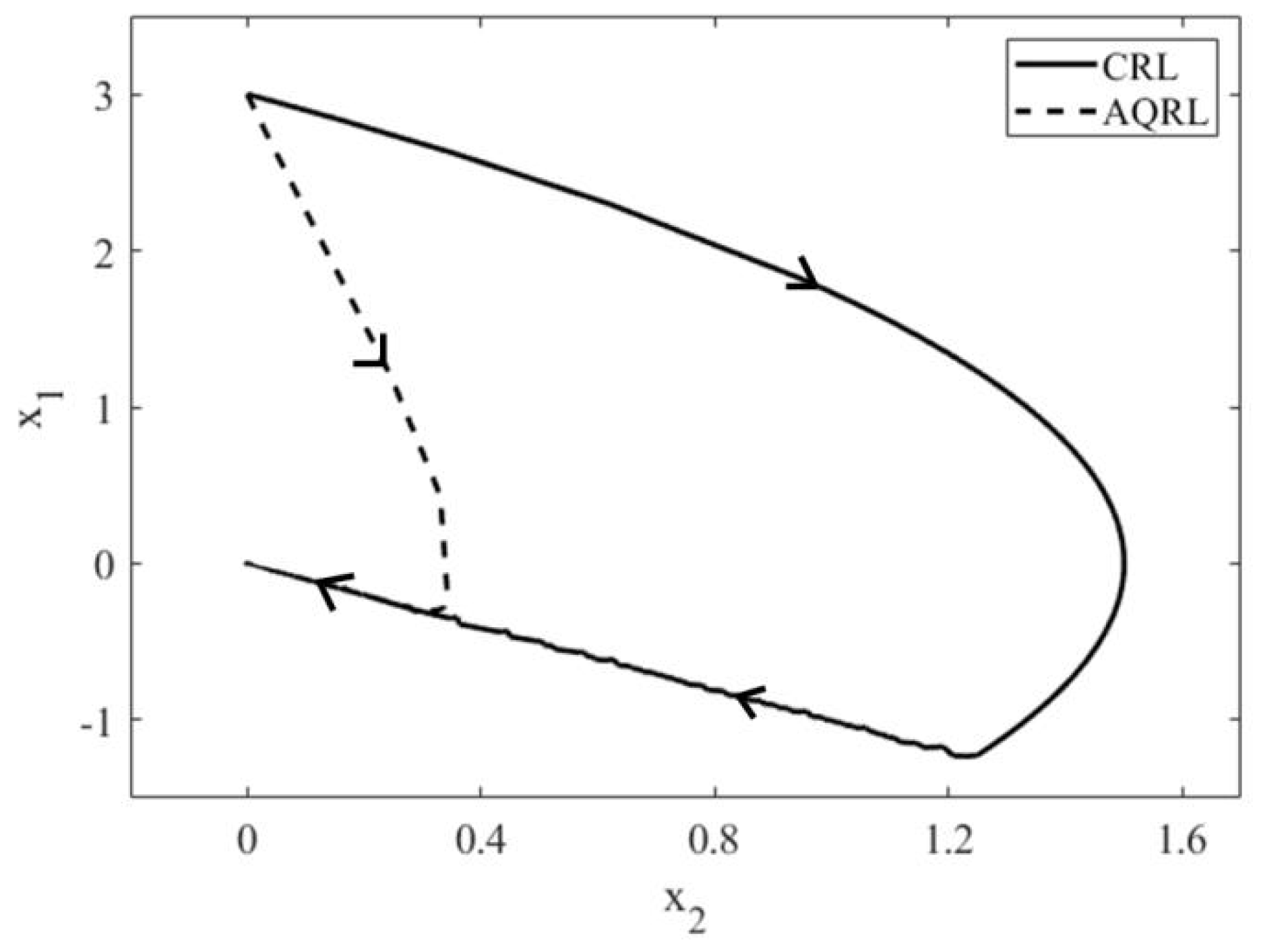
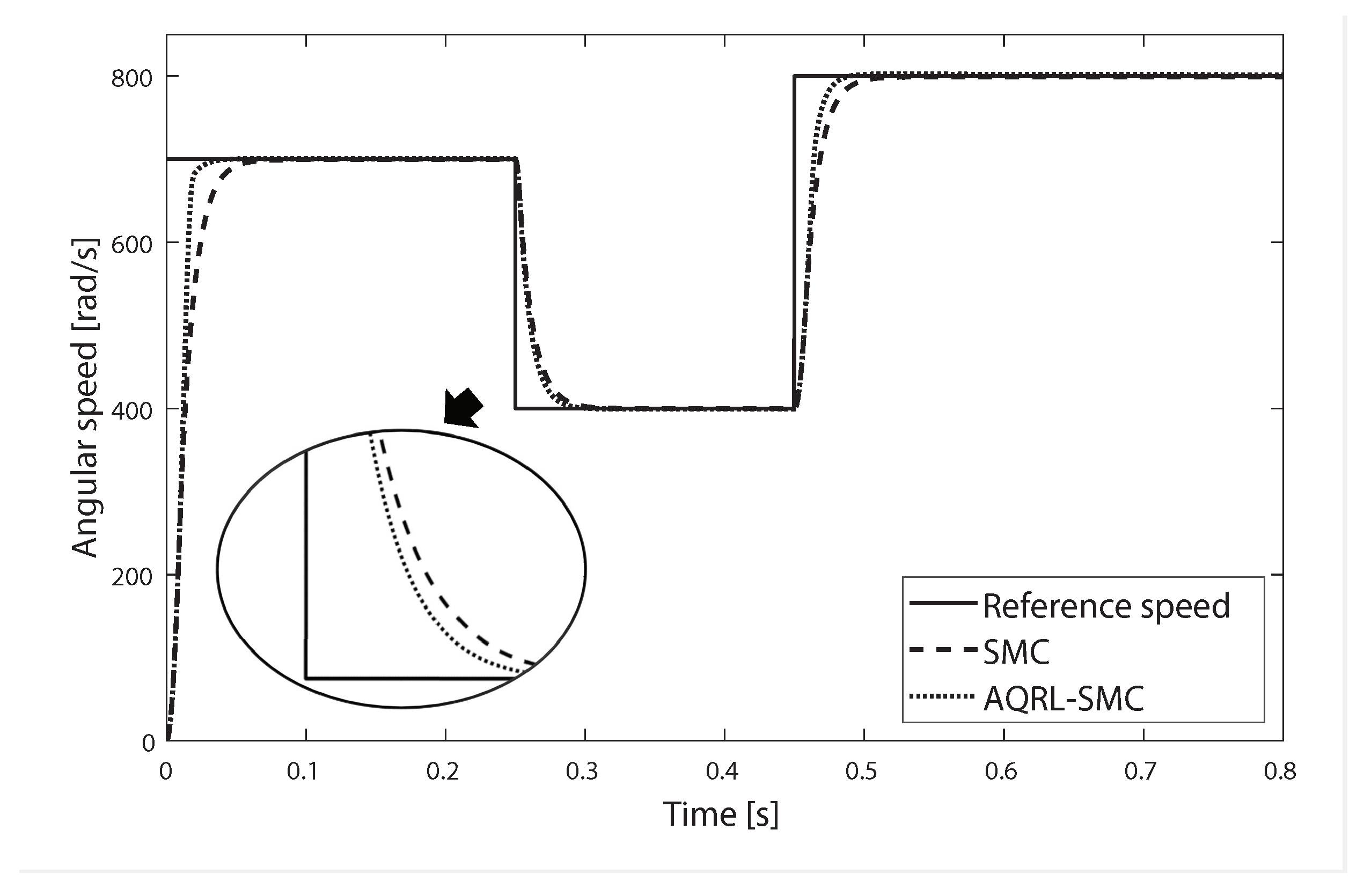
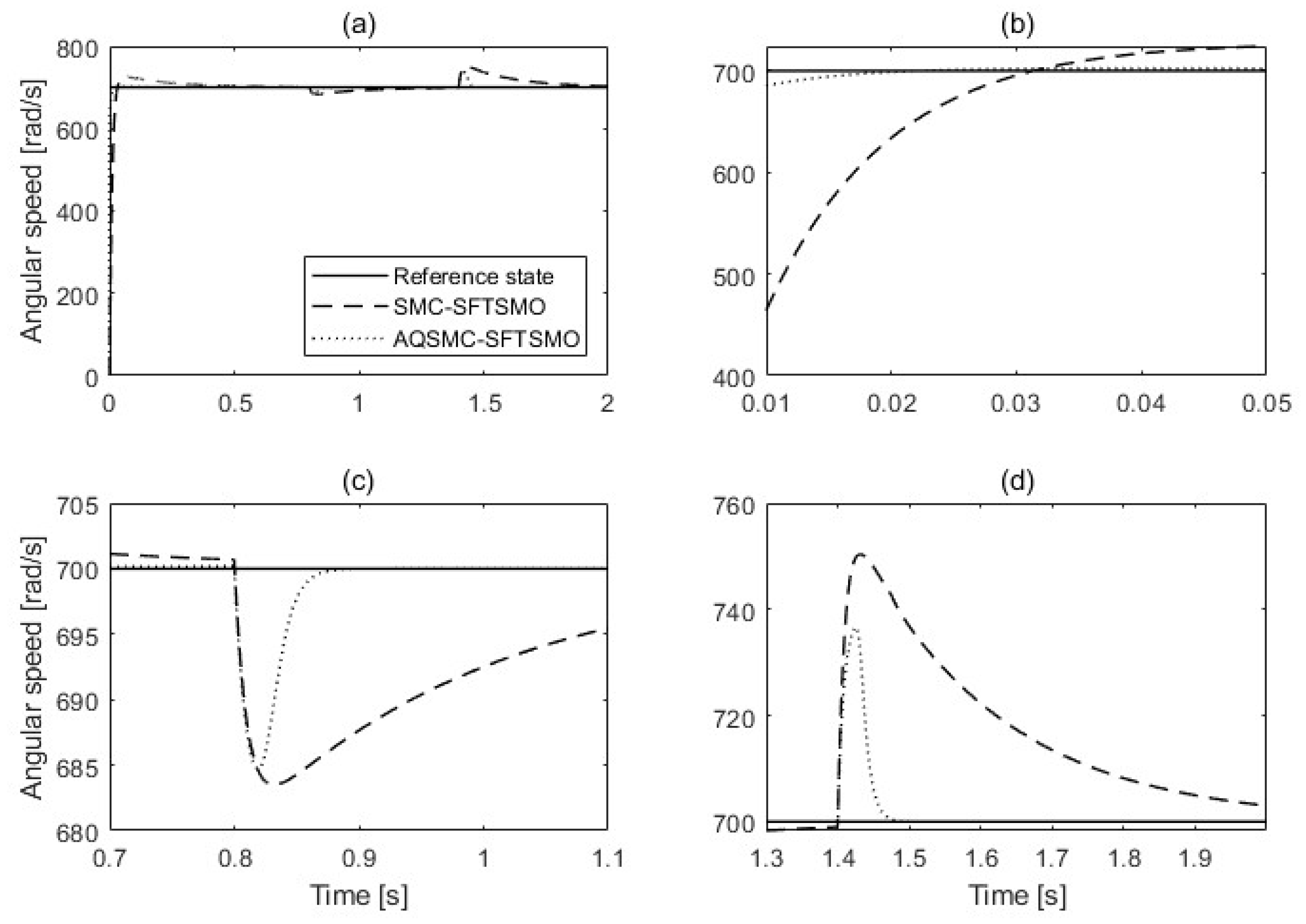
4. Simulation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PMSM | permanent magnet synchronous motor |
| PI | proportional-integral |
| SMC | sliding mode control |
| AQRL | adaptive quick reaching law |
| SMDO | sliding mode disturbance observer |
| HOTSMO | high-order terminal sliding mode observer |
| SFTSMO | second-order fast terminal sliding mode observer |
| SISO | single-input single-output |
| CRL | conventional reaching law |
| FOC | field-oriented control |
| SPMSM | surface-mounted PMSM |
| AQSMC | AQRL- based SMC |
References
- Fodorean, D.; Sarrazin, M.; Marţiş, C.; Anthonis, J.; Auweraer, H. Electromagnetic and structural analysis for a surface-mounted PMSM used for light-EV. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2016, 52, 2892–2899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kefalas, T.; Kladas, A. Thermal investigation of permanent-magnet synchronous motor for aerospace applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 4404–4411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, R.; Kung, Y.; Wu, G. Dynamic analysis and system identification of an LCD glass-handling robot driven by a PMSM. Appl. Math. Model. 2010, 34, 1360–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Liu, Z. Adaptive speed control for permanent-magnet synchronous motor system with variations of load inertia. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2009, 56, 3050–3059. [Google Scholar]
- Pisano, A.; Davila, A.; Fridman, L.; Usai, E. Cascade control of PM DC drives via second-order sliding-mode technique. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2008, 55, 3846–3854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Li, S. Speed control for PMSM servo system using predictive functional control and extended state observer. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2012, 59, 1171–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes, E.; Silva, C.; Kennel, R. MPC implementation of a quasi-time-optimal speed control for a PMSM drive, with inner modulated-FS-MPC torque control. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 3897–3905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pajchrowski, T.; Zawirski, K. Application of artificial neural network to robust speed control of servodrive. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2007, 54, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pajchrowski, T.; Zawirski, K.; Nowopolski, K. Neural speed controller trained online by means of modified RPROP algorithm. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2015, 11, 560–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Chen, C.; Zhu, Z.; Huang, Y. Speed control of the surface-mounted permanent-magnet synchronous motor based on Takagi–Sugeno fuzzy models. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2016, 31, 6504–6510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Shi, P.; Zhao, L. Finite-time command filtered backstepping control for a class of nonlinear systems. Automatica 2018, 92, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd Zaihidee, F.; Mekhilef, S.; Mubin, M. Robust speed control of PMSM using sliding mode control (SMC)—A review. Energies 2019, 12, 1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Pi, Y.; Luo, Y. Fractional order sliding-mode control based on parameters auto-tuning for velocity control of permanent magnet synchronous motor. ISA Trans. 2012, 51, 649–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, X. Speed global integral sliding mode control with a load sliding mode observer for PMSM. IEICE Electron. Express 2018, 15, 20171270. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Yu, H.; Yu, J.; Zhao, L. Combined speed and current terminal sliding mode control with nonlinear disturbance observer for PMSM drive. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 29594–29601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leu, V.; Choi, H.; Jung, J. Fuzzy sliding mode speed controller for PM synchronous motors with a load torque observer. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2012, 27, 1530–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, R.; Luo, M.; Sun, P. Improved nonlinear sliding mode control based on load disturbance observer for permanent magnet synchronous motor servo system. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2016, 8, 1687814016642670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merabet, A. Cascade second order sliding mode control for permanent magnet synchronous motor drive. Electronics 2019, 8, 1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Baldi, S.; Fridman, L. On adaptive sliding mode control without a priori bounded uncertainty. Automatica 2020, 111, 108650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Ho, D.; Lam, J. Robust sliding mode control for uncertain stochastic systems with time-varying delay. Automatica 2005, 41, 873–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utkin, V. Discussion aspects of high-order sliding mode control. IEEE Trans. Automat. Control 2016, 61, 829–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, B.; Yan, F.; Chen, B. Practical adaptive fractional-order nonsingular terminal sliding mode control for a cable-driven manipulator. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control 2018, 29, 1396–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faieghi, M.; Delavari, H.; Baleanu, D. Control of an uncertain fractional-order Liu system via fuzzy fractional-order sliding mode control. J. Vib. Control 2012, 18, 1366–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, C.; Shtessel, Y. Sliding mode disturbance observer-based control for a reusable launch vehicle. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 2006, 29, 1315–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woldegiorgis, A.; Ge, X.; Li, S.; Hassan, M. Extended sliding mode disturbance observer-based sensorless control of IPMSM for medium and high-speed range considering railway application. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 175302–175312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Kim, S.; Kwak, S.; You, K. Quadrotor stabilization and tracking using nonlinear surface sliding mode control and observer. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobayen, S. An adaptive chattering-free PID sliding mode control based on dynamic sliding manifolds for a class of uncertain nonlinear systems. Nonlinear Dyn. 2015, 82, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liang, J.; Cheng, X. New reaching law control for permanent magnet synchronous motor with extended disturbance observer. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 186296–186307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiu, C.; Guo, P. Global terminal sliding mode control with the quick reaching law and its application. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 49793–49800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, H.; Honda, Y.; Kiriyama, H.; Morimoto, S.; Takeda, Y. The performance comparison of SPMSM, IPMSM and SynRM in use as air-conditioning compressor. In Proceedings of the Conference Record of the 1999 IEEE Industry Applications Conference, 34th IAS Annual Meeting, Phoenix, AZ, USA, 3–7 October 1999; Volume 2, pp. 840–845. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.; Junejo, A.; Liu, Y.; Islam, M. Improved continuous fast terminal sliding mode control with extended state observer for speed regulation of PMSM drive system. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2019, 68, 10465–10476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhou, M.; Yu, X. Design and implementation of terminal sliding mode control method for PMSM speed regulation system. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2013, 9, 1879–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Sun, L.; Zhao, K.; Sun, L. Nonlinear speed control for PMSM system using sliding-mode control and disturbance compensation techniques. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2013, 28, 1358–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abolvafaei, M.; Ganjefar, S. Maximum power extraction from a wind turbine using second-order fast terminal sliding mode control. Renew. Energy 2019, 139, 1437–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Han, F.; Yu, X. Chattering free full-order sliding-mode control. Automatica 2014, 50, 1310–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Zhihong, M. Fast terminal sliding-mode control design for nonlinear dynamical systems. IEEE Tran. Circuits Syst. I Fundam. Theory Appl. 2002, 49, 261–264. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.; Ahn, H.; Hu, M.; You, K. Improved non-singular fast terminal sliding mode control for SPMSM speed regulation. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 65924–65933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameter | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| 2.4 | ||
| 0.65 | [mH] | |
| 0.003 | [Wb] | |
| J | 0.004 × | [kg· m2] |
| B | 0.004 × | [N· m· s/rad] |
| 4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahn, H.; Kim, S.; Park, J.; Chung, Y.; Hu, M.; You, K. Adaptive Quick Sliding Mode Reaching Law and Disturbance Observer for Robust PMSM Control Systems. Actuators 2024, 13, 136. https://doi.org/10.3390/act13040136
Ahn H, Kim S, Park J, Chung Y, Hu M, You K. Adaptive Quick Sliding Mode Reaching Law and Disturbance Observer for Robust PMSM Control Systems. Actuators. 2024; 13(4):136. https://doi.org/10.3390/act13040136
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhn, Hyeongki, Sangkyeum Kim, Jihoon Park, Yoonuh Chung, Mingyuan Hu, and Kwanho You. 2024. "Adaptive Quick Sliding Mode Reaching Law and Disturbance Observer for Robust PMSM Control Systems" Actuators 13, no. 4: 136. https://doi.org/10.3390/act13040136
APA StyleAhn, H., Kim, S., Park, J., Chung, Y., Hu, M., & You, K. (2024). Adaptive Quick Sliding Mode Reaching Law and Disturbance Observer for Robust PMSM Control Systems. Actuators, 13(4), 136. https://doi.org/10.3390/act13040136








