Comparative Gene Expression Analysis of Salmonella Typhimurium DT104 in Ground Chicken Extract and Brain Heart Infusion Broth
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains and Culture Conditions
2.2. RNA Isolation, Library Construction, and Sequencing
2.3. RNA-Seq Data Analysis
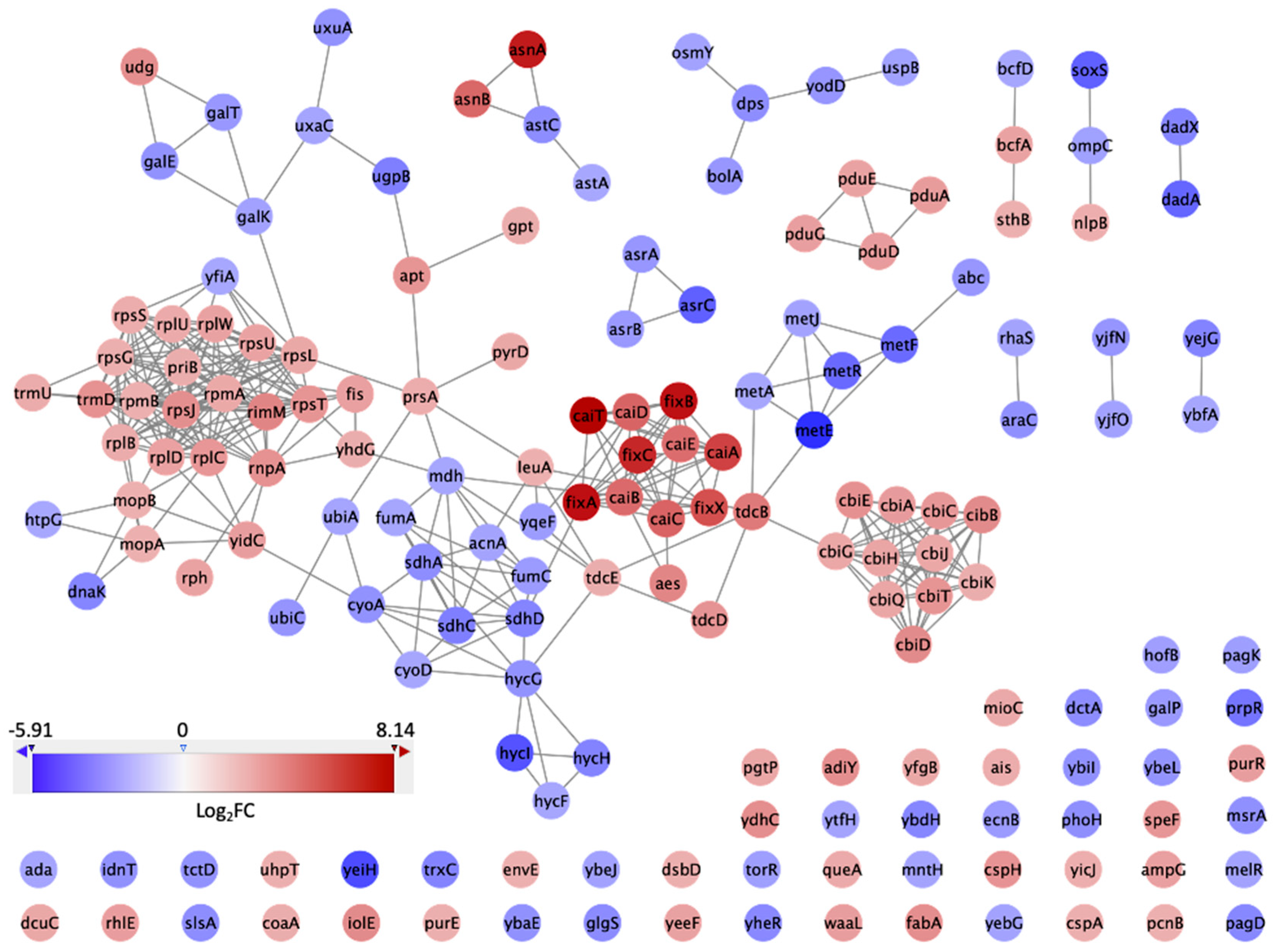
2.4. Network Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
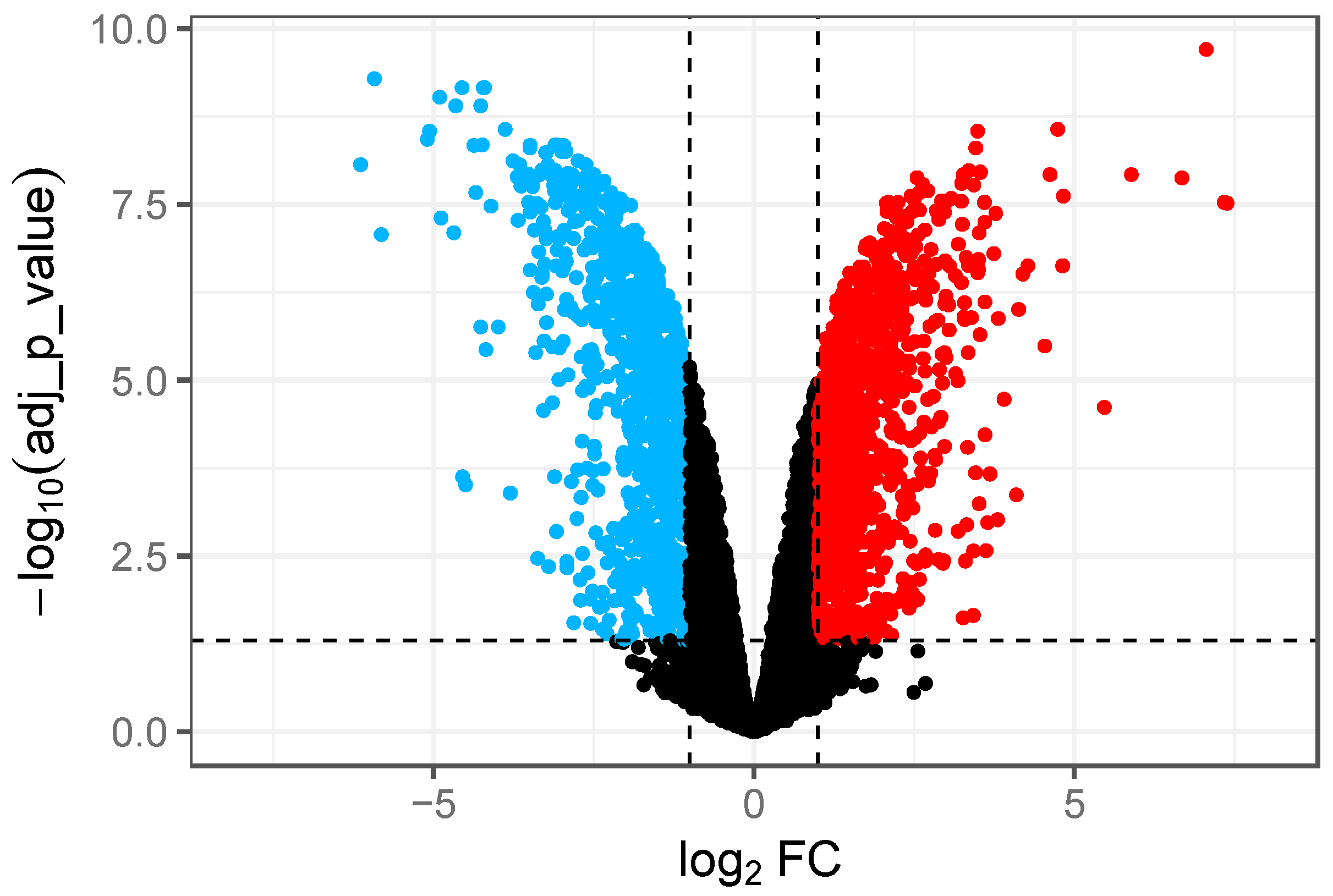
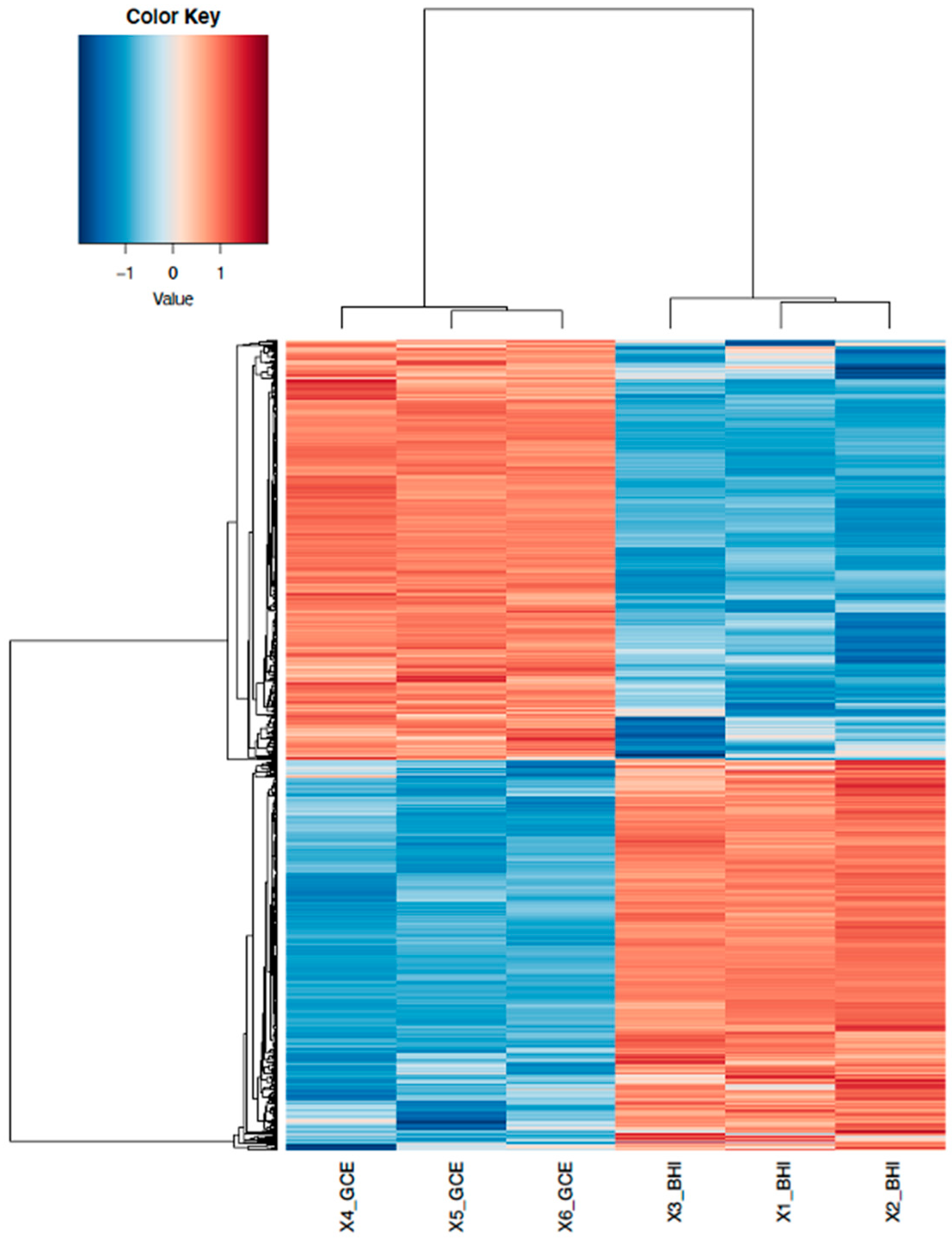
3.1. RNA-Seq Data Analysis and Identification of DEGs in GCE
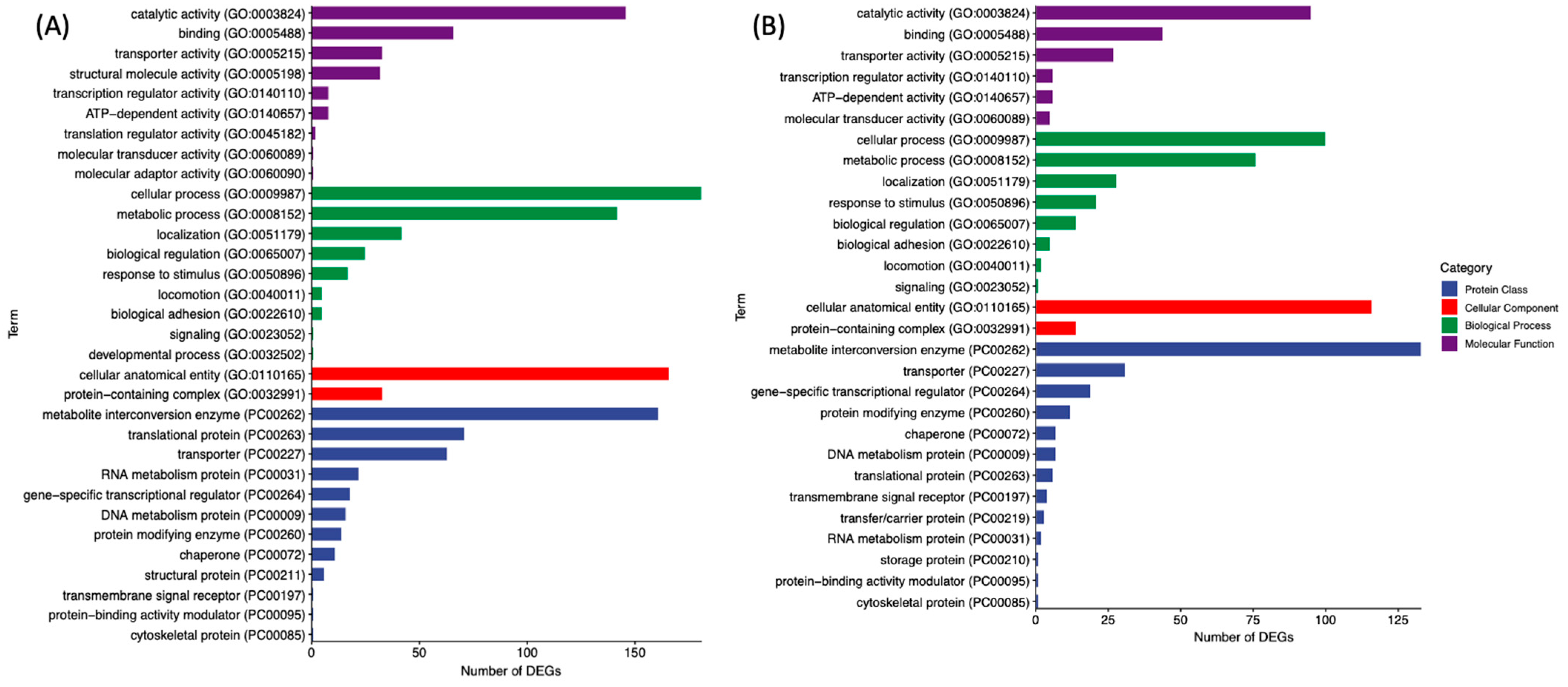
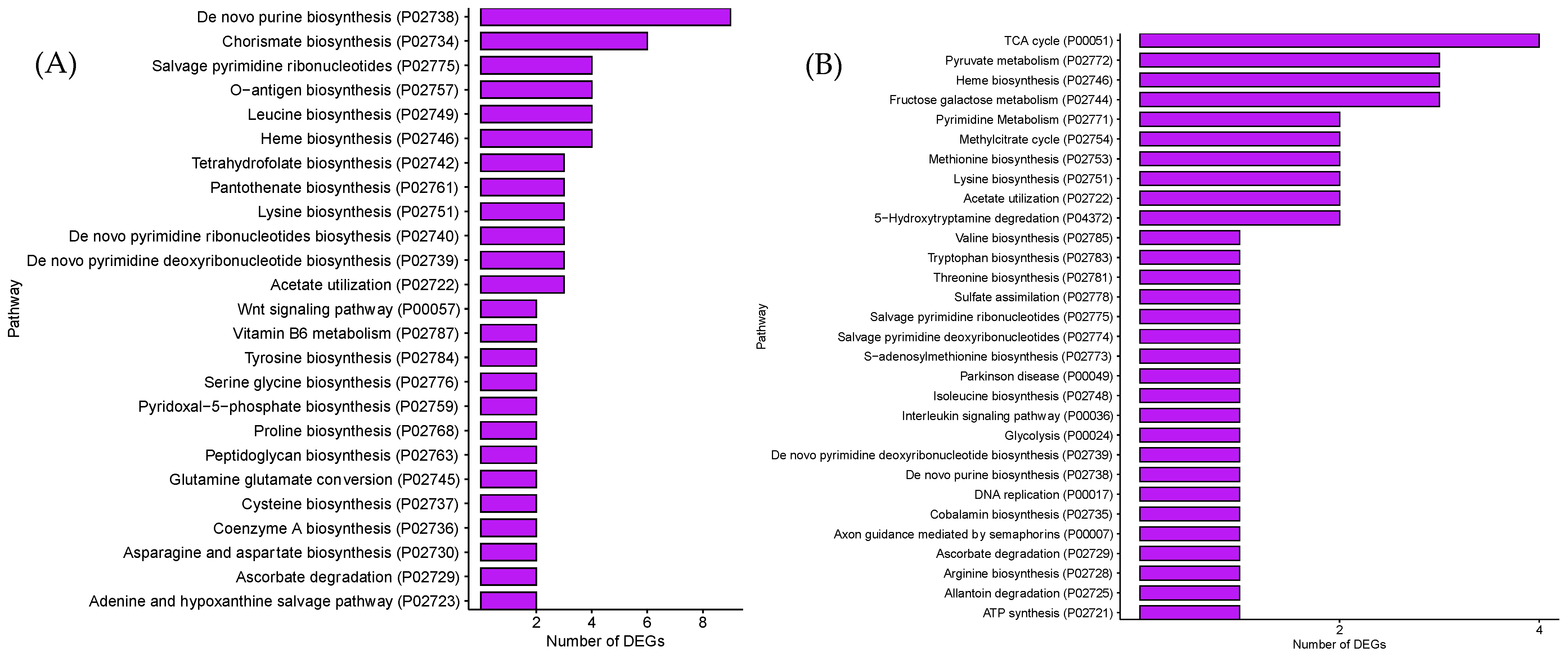
3.2. GO and PANTHER Pathway Analysis of DEGs in GCE
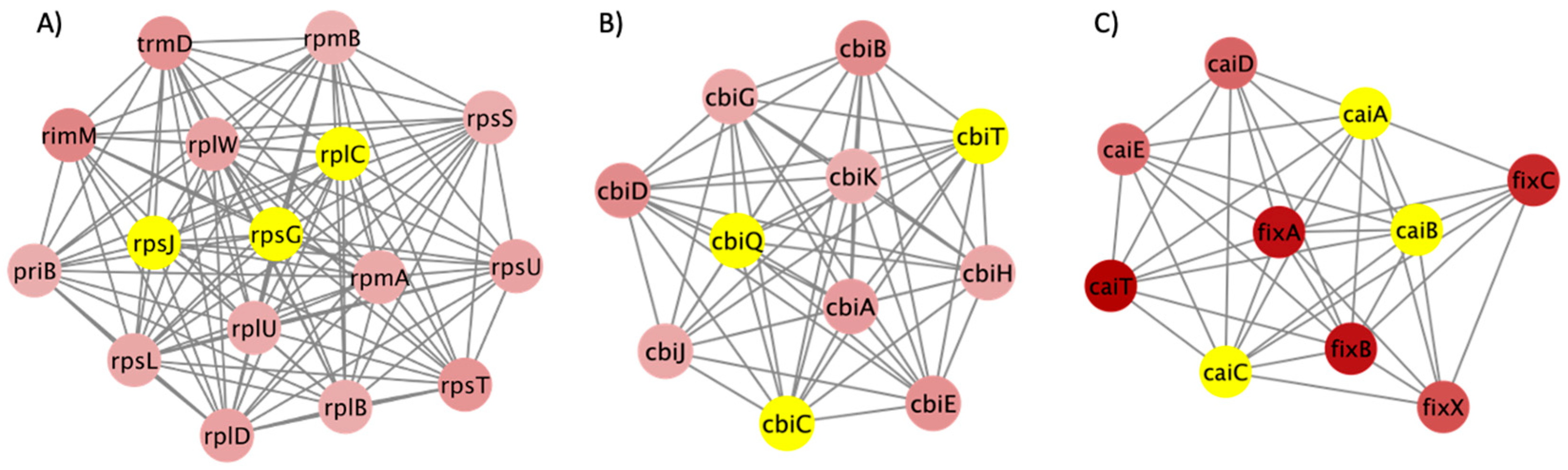
3.3. PPI Network and Clusters of DEGs
3.4. Comparative Analysis of DEGs That Were Expressed in Response to GCE
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Scallan, E.; Hoekstra, R.M.; Angulo, F.J.; Tauxe, R.V.; Widdowson, M.A.; Roy, S.L.; Jones, J.L.; Griffin, P.M. Foodborne illness acquired in the United States--major pathogens. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Emerging and Zoonotic Infectious Diseases (NCEZID), Division of Foodborne, Waterborne, and Environmental Diseases (DFWED). Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/salmonella/backyardpoultry-05-23/index.html (accessed on 9 January 2023).
- GBD 2017 Non-Typhoidal Salmonella Invasive Disease Collaborators. The global burden of non-typhoidal salmonella invasive disease: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet Infect Dis. 2019, 19, 1312–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaji, S.; Selvaraj, R.K.; Shanmugasundaram, R. Salmonella Infection in Poultry: A Review on the Pathogen and Control Strategies. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Galanis, E.; Lo Fo Wong, D.M.; Patrick, M.E.; Binsztein, N.; Cieslik, A.; Chalermchikit, T.; Aidara-Kane, A.; Ellis, A.; Angulo, F.J.; Wegener, H.C.; et al. Web-based surveillance and global Salmonella distribution, 2000–2002. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2006, 12, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, S. The Big Five: Most Common Salmonella Strains in Foodborne Illness Outbreaks. Available online: https://www.foodsafetynews.com/2013/08/the-five-most-common-salmonella-strains/ (accessed on 9 January 2024).
- Leekitcharoenphon, P.; Hendriksen, R.S.; Le Hello, S.; Weill, F.X.; Baggesen, D.L.; Jun, S.R.; Ussery, D.W.; Lund, O.; Crook, D.W.; Wilson, D.J.; et al. Global genomic epidemiology of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium DT104. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 2516–2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller-Doblies, D.; Speed KC, R.; Kidd, S.; Davies, R.H. Salmonella Typhimurium in livestock in Great Britain—Trends observed over a 32-year period. Epidemiol. Infect. 2018, 146, 409–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajashekara, G.; Haverly, E.; Halvorson, D.A.; Ferris, K.E.; Lauer, D.C.; Nagaraja, K.V. Multidrug-resistant Salmonella Typhimurium DT104 in poultry. J. Food Prot. 2000, 63, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andino, A.; Hanning, I. Salmonella enterica: Survival, colonization, and virulence differences among serovars. Sci. World J. 2015, 2015, 520179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goudeau, D.M.; Parker, C.T.; Zhou, Y.; Sela, S.; Kroupitski, Y.; Brandl, M.T. The Salmonella transcriptome in lettuce and cilantro soft rot reveals a niche overlap with the animal host intestine. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 250–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhawi, A.A.; Elazomi, A.; Jones, M.A.; Lovell, M.A.; Li, H.; Emes, R.D.; Barrow, P.A. Adaptation to the chicken intestine in Salmonella Enteritidis PT4 studied by transcriptional analysis. Vet. Microbiol. 2011, 153, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiennimitr, P.; Winter, S.E.; Winter, M.G.; Xavier, M.N.; Tolstikov, V.; Huseby, D.L.; Sterzenbach, T.; Tsolis, R.M.; Roth, J.R.; Baumler, A.J. Intestinal inflammation allows Salmonella to use ethanolamine to compete with the microbiota. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 17480–17485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, X.; Li, Z.; Zhang, W. Transcriptome sequencing of Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis under desiccation and starvation stress in peanut oil. Food Microbiol. 2012, 30, 311–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kjeldgaard, J.; Henriksen, S.; Cohn, M.T.; Aabo, S.; Ingmer, H. Method enabling gene expression studies of pathogens in a complex food matrix. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 8456–8458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Bae, D.; Crowley, M.R.; Wang, C. Transcriptome analysis of Listeria monocytogenes grown on a ready-to-eat meat matrix. J. Food Prot. 2011, 74, 1104–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Ream, A. Gene expression profiling of Listeria monocytogenes strain F2365 during growth in ultrahigh-temperature-processed skim milk. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 6859–6866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suo, Y.; Gao, S.; Baranzoni, G.M.; Xie, Y.; Liu, Y. Comparative transcriptome RNA-Seq analysis of Listeria monocytogenes with sodium lactate adaptation. Food Control 2018, 91, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fratamico, P.; Wang, S.; Yan, X.; Zhang, W.; Li, Y. Differential gene expression of E. coli O157:H7 in ground beef extract compared to tryptic soy broth. J. Food Sci. 2011, 76, M79–M87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, J.L.; Uknalis, J.; Oscar, T.P.; Schwarz, J.G.; Vimini, B.; Parveen, S. The effect of previous life cycle phase on the growth kinetics, morphology, and antibiotic resistance of Salmonella Typhimurium DT104 in brain heart infusion and ground chicken extract. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parveen, S.; Taabodi, M.; Schwarz, J.G.; Oscar, T.P.; Harter-Dennis, J.; White, D.G. Prevalence and antimicrobial resistance of Salmonella recovered from processed poultry. J. Food Prot. 2007, 70, 2466–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Leary, D.; McCabe, E.M.; McCusker, M.P.; Martins, M.; Fanning, S.; Duffy, G. Acid environments affect biofilm formation and gene expression in isolates of Salmonella enterica Typhimurium DT104. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2015, 206, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mather, A.E.; Reid, S.W.J.; Maskell, D.J.; Parkhill, J.; Fookes, M.C.; Harris, S.R.; Brown, D.J.; Coia, J.E.; Mulvey, M.R.; Gilmour, M.W.; et al. Distinguishable epidemics of multidrug-resistant Salmonella Typhimurium DT104 in different hosts. Science 2013, 341, 1514–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.; Smyth, G.K.; Shi, W. FeatureCounts: An efficient general purpose program for assigning sequence reads to genomic features. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritchie, M.E.; Phipson, B.; Wu, D.; Hu, Y.; Law, C.W.; Shi, W.; Smyth, G.K. Limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, H.; Thomas, P. PANTHER Pathway: An ontology-based pathway database coupled with data tools. Methods Mol. Biol. 2009, 563, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Gable, A.L.; Nastou, K.C.; Lyon, D.; Kirsch, R.; Pyysalo, S.; Doncheva, N.T.; Legeay, M.; Fang, T.; Bork, P.; et al. The STRING database in 2021: Customizable protein-protein networks, and functional characterization of user-uploaded gene/measurement sets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D605–D612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozhilova, L.V.; Whitmore, A.V.; Wray, J.; Reinert, G.; Deane, C.M. Measuring rank robustness in scored protein interaction networks. BMC Bioinform. 2019, 20, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chin, C.H.; Chen, S.H.; Wu, H.H.; Ho, C.W.; Ko, M.T.; Lin, C.Y. CytoHubba: Identifying hub objects and sub-networks from complex interactome. BMC Syst. Biol. 2014, 8, S11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanes, R.; Zhang, F.; Huang, Z. Protein Interaction Network Analysis to Investigate Stress Response, Virulence, and Antibiotic Resistance Mechanisms in Listeria monocytogenes. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, U.; Abdullah, S.; Chau, D.M.; Chia, S.L.; Yusoff, K.; Chan, S.C.; Ong, T.A.; Razack, A.H.; Veerakumarasivam, A. Analysis of PPI networks of transcriptomic expression identifies hub genes associated with New castle disease virus persistent infection in bladder cancer. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 7323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruzdev, N.; McClelland, M.; Porwollik, S.; Ofaim, S.; Pinto, R.; Saldinger-Sela, S. Global transcriptional analysis of dehydrated Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 7866–7875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva, J.B.; Penha Filho, R.A.; Junior, A.B.; Lemos, M.V. Requirement for cobalamin by Salmonella enterica serovars Typhimurium, Pullorum, Gallinarum and Enteritidis during infection in chickens. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2011, 42, 1409–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- U.S. Department of Agriculture—Agricultural Research Service, National Nutrient Database for Standard Reference Release 28: Full Report (All Nutrients): 05011, Chicken, Broilers or Fryers, Meat Only Raw. 2016. Available online: https://ods.od.nih.gov/pubs/usdandb/EPA-Content.pdf (accessed on 9 January 2024).
- Walt, A.; Kahn, M.L. The fixA and fixB genes are necessary for anaerobic carnitine reduction in Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 2002, 184, 4044–4047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Golzar Adabi, S.H.; Cooper, R.G.; Ceylan, N.; Corduk, M. L-carnitine and its functional effects in poultry nutrition. World’s Poult. Sci. J. 2011, 67, 277–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, A.; Nijhof, A.M.; Sauter-Louis, C.; Schauer, B.; Staubach, C.; Conraths, F.J. Distribution of ticks infesting ruminants and risk factors associated with high tick prevalence in livestock farms in the semi-arid and arid agro-ecological zones of Pakistan. Parasit. Vectors 2017, 10, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rebouche, C.J. Carnitine. In Modern Nutrition in Health and Disease, 9th ed.; Shils, M., Olson, J.A., Shike, M., Ross, A.C., Eds.; Lippincott Williams and Wilkins: New York, NY, USA, 1999; pp. 505–512. [Google Scholar]
- Kleber, H.P. Bacterial carnitine metabolism. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1997, 47, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meadows, J.A.; Wargo, M.J. Carnitine in bacterial physiology and metabolism. Microbiology 2015, 161, 1161–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seim, H.; Löster, H.; Claus, R.; Kleber, H.P.; Strack, E. Stimulation of the anaerobic growth of Salmonella typhimurium by reduction of L-carnitine, carnitine derivatives and structure-related trimethylammonium compounds. Arch. Microbiol. 1982, 132, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viala, J.P.; Méresse, S.; Pocachard, B.; Guilhon, A.A.; Aussel, L.; Barras, F. Sensing and adaptation to low pH mediated by inducible amino acid decarboxylases in Salmonella. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faber, F.; Thiennimitr, P.; Spiga, L.; Byndloss, M.X.; Litvak, Y.; Lawhon, S.; Andrews-Polymenis, H.L.; Winter, S.E.; Bäumler, A.J. Respiration of microbiota-derived 1,2-propanediol drives Salmonella expansion during colitis. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeter, R.M. Cobalamin-dependent 1,2-propanediol utilization by Salmonella typhimurium. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1990, 136, 887–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Zadeh, M.; Mohamadzadeh, M. Vitamin B12 coordinates ileal epithelial cell and microbiota functions to resist Salmonella infection in mice. J. Exp. Med. 2022, 219, e20220057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, S.; Orsi, R.H.; den Bakker, H.C.; Wiedmann, M.; Boor, K.J.; Bergholz, T.M. Transcriptomic analysis of the adaptation of Listeria monocytogenes to growth on vacuum-packed cold smoked salmon. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 6812–6824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Nam, E.W.; Kim, Y.; Lee, S.; Kim, S.I.; Yoon, H. Transcriptomic approach for understanding the adaptation of Salmonella enterica to contaminated produce. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 30, 1729–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Sample Name | Total Reads | Percentage Mapped | Percentage Assigned |
|---|---|---|---|
| X1-BHI | 2,519,286 | 99.7 | 92.6 |
| X2-BHI | 2,631,410 | 99.7 | 93.8 |
| X3-BHI | 2,336,974 | 98.1 | 93.3 |
| X4-GCE | 2,565,122 | 98.8 | 93 |
| X5-GCE | 3,093,996 | 99.6 | 90.1 |
| X6-GCE | 3,298,803 | 99.7 | 92.4 |
| Gene Locus | Gene Function | Log2FC | Fold Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| caiT | Probable carnitine transporter | 8.14 | 282.80 |
| fixA | FixA protein | 7.38 | 167.15 |
| fixB | FixB protein | 7.34 | 162.02 |
| asnA | Asparagine synthetase A | 7.06 | 133.51 |
| fixC | FixC protein | 6.68 | 102.42 |
| caiA | Probable carnitine operon oxidoreductase CaiA | 5.89 | 59.29 |
| fixX | Ferredoxin like protein FixX | 5.47 | 44.26 |
| caiC | Probable crotonobetaine/carnitine-CoA ligase | 4.83 | 28.42 |
| caiD | Carnitine racemase | 4.82 | 28.21 |
| asnB | Asparagine synthetase B | 4.74 | 26.77 |
| caiB | L-carnitine dehydratase | 4.62 | 24.65 |
| caiE | Carnitine operon protein CaiE | 4.54 | 23.25 |
| tdcB | Catabolic threonine dehydratase | 4.28 | 19.41 |
| pefB | Plasmid-encoded fimbriae regulation | 4.20 | 18.35 |
| rim | 16S rRNA processing protein RimM | 4.13 | 17.56 |
| aes | Acetyl esterase | 4.10 | 17.09 |
| gtrB | Glycosyltransferase | 3.90 | 14.97 |
| iolE | Inosose dehydratase ec= altname: full = 2-keto-myo-inositol dehydratase | 3.82 | 14.08 |
| cbiB | Cobalamin biosynthesis protein | 3.80 | 13.97 |
| cbiD | Putative cobalt-precorrin-6A synthase | 3.77 | 13.67 |
| Gene Locus | Gene Function | Log2FC | Fold Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| hslT | Heat shock protein A | −6.13 | −70.0 |
| metE | 5-methyltetrahydropteroyltriglutamate-homocysteine methyltransferase | −5.92 | −60.6 |
| hslS | Heat shock protein B | −5.81 | −56.1 |
| yeiH | Putative membrane protein | −5.09 | −34.1 |
| ybiY | Putative pyruvate formate-lyase 3 activating enzyme | −5.06 | −33.4 |
| hycI | Hydrogenase 3 maturation protease | −4.90 | −29.9 |
| ybiW | Putative formate acetyltransferase 3 | −4.65 | −25.1 |
| asrC | Anaerobic sulfite reductase subunit C | −4.55 | −23.4 |
| soxS | Regulatory protein SoxS | −4.54 | −23.3 |
| dadA | D-amino acid dehydrogenase small subunit | −4.37 | −20.7 |
| metR | Trans-activator of MetE and MetH | −4.24 | −18.9 |
| metF | 5,10 methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase | −4.22 | −18.6 |
| prpR | Propionate catabolism operon regulatory protein | −3.99 | −15.9 |
| exuT | Hexuronate transporter | −3.88 | −14.7 |
| sdhC | Succinate dehydrogenase cytochrome b-556 subunit | −3.65 | −12.6 |
| ugpB | Glycerol-3-phosphate-binding periplasmic protein | −3.63 | −12.4 |
| hycH | Formate hydrogenlyase maturation protein | −3.52 | −11.5 |
| dadX | Alanine racemase | −3.50 | −11.3 |
| trxC | Thioredoxin 2 | −3.49 | −11.2 |
| sdhD | Succinate dehydrogenase hydrophobic membrane anchor protein | −3.45 | −10.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Zhang, F.; Hawkins, J.L.; Elder, J.R.; Baranzoni, G.M.; Huang, Z.; Fratamico, P.M.; Parveen, S. Comparative Gene Expression Analysis of Salmonella Typhimurium DT104 in Ground Chicken Extract and Brain Heart Infusion Broth. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1461. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12071461
Liu Y, Zhang F, Hawkins JL, Elder JR, Baranzoni GM, Huang Z, Fratamico PM, Parveen S. Comparative Gene Expression Analysis of Salmonella Typhimurium DT104 in Ground Chicken Extract and Brain Heart Infusion Broth. Microorganisms. 2024; 12(7):1461. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12071461
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yanhong, Fangyuan Zhang, Jabari L. Hawkins, Jake R. Elder, Gian Marco Baranzoni, Zuyi Huang, Pina M. Fratamico, and Salina Parveen. 2024. "Comparative Gene Expression Analysis of Salmonella Typhimurium DT104 in Ground Chicken Extract and Brain Heart Infusion Broth" Microorganisms 12, no. 7: 1461. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12071461
APA StyleLiu, Y., Zhang, F., Hawkins, J. L., Elder, J. R., Baranzoni, G. M., Huang, Z., Fratamico, P. M., & Parveen, S. (2024). Comparative Gene Expression Analysis of Salmonella Typhimurium DT104 in Ground Chicken Extract and Brain Heart Infusion Broth. Microorganisms, 12(7), 1461. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12071461








