Origin of Compositional Diversity of Marine Tephra during the Late Middle Pleistocene B-KY1 Baekdusan Volcanic Eruption
Abstract
:Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
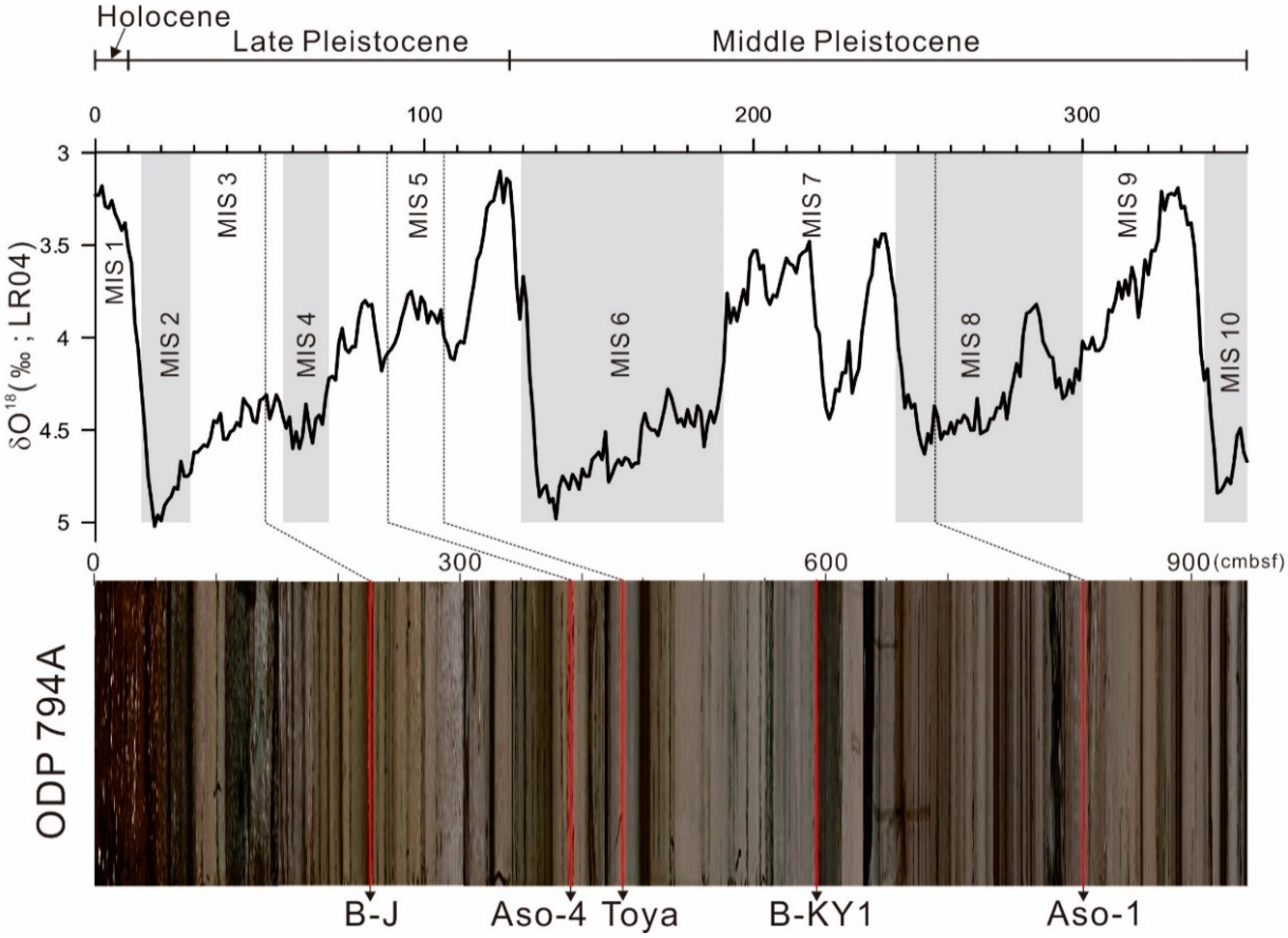
2. Geological and Physiographical Settings
3. Materials and Methods
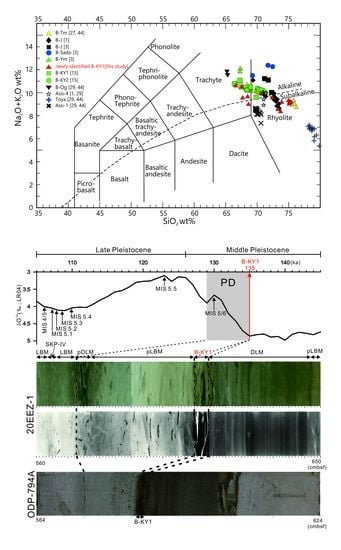
4. Results
4.1. Late Pleistocene Toya Tephra
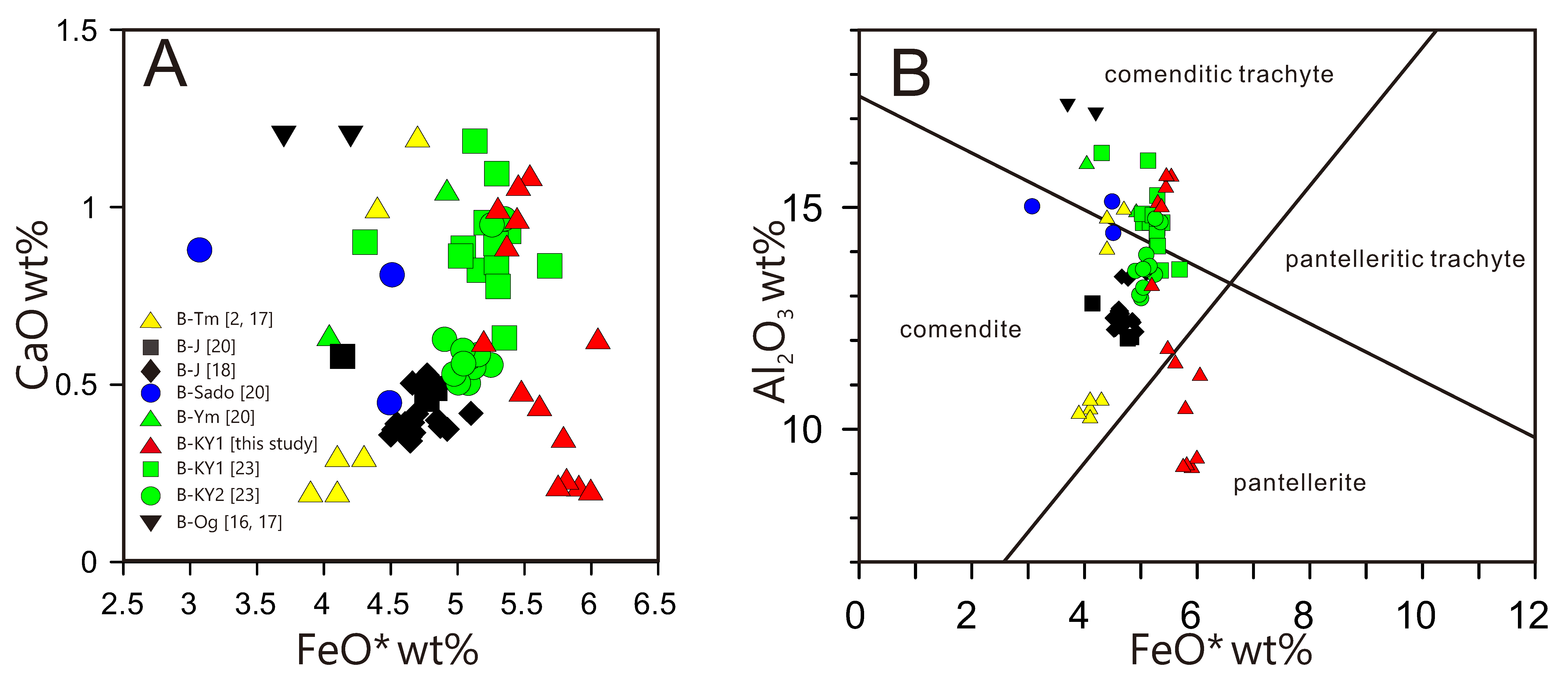
4.2. Late Middle Pleistocene B-KY1 Tephra between Toya and Aso-1 Tephras
4.3. Middle Pleistocene Aso-1 Tephra
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Machida, H.; Aria, F. Extensive ash falls in and around the Sea of Japan from large late Quaternary eruptions. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 1983, 18, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuta, T.; Fujioka, K.; Arai, F. Widespread submarine tephras around Japan-Petrographic and chemical properties. Mar. Geol. 1986, 72, 125–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Liu, G.; Gill, J. Review of eruptive activity at Tianchi volcano, Changbaishan, northeaste China: Implications for possible future eruptions. Bull. Volcanol. 2013, 75, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, S.; Schmincke, H.-U. Volatile emission during the eruption of Baitoushan volcano (China/North Korea) ca. 969 ADD. Bull. Volcanol. 2000, 61, 537–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Wang, Y.; Jin, J.; Gao, L.; Yun, S.-H.; Jin, B. Timescale and evolution of the intracontinental Tianchi volcanic shield and ignimbrite-forming eruption, Changbaishan, Northeast China. Lithos 2007, 96, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Liu, J.; You, H.; Nemeth, K. Tephrostratigraphy of Changbaishan volcano, northeast China, since mid-Holocene. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2017, 177, 104–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.Y.; Blockley, S.P.E.; Tarasov, P.E.; Xu, Y.G.; McLean, D.; Tomlinson, E.; Albert, P.G.; Liu, J.; Muller, S.; Wagner, M.; et al. Clarifying the distal to proximal tephrochrology of the Millennium (B-Tm) Eruption, Changbaishan, northeast China. Quat. Geochronol. 2016, 33, 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McLean, D.; Albert, P.G.; Nakagawa, T.; Staff, R.A.; Suzuki, T.; Smith, V.C. Identification of the Changbaishan ‘Millennium’ (B-Tm) eruption deposit in the Lake Suigetsu (SC06) sedimentary archive, Japan: Synchronization of hemispheric-wide palaeoclimte archive. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2016, 150, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oppenheimer, C.; Wacker, L.; Xu, J.; Galvan, J.D.; Stoffel, M.; Guilet, S.; Corona, C.; Sigl, M.; Cosmo, N.D.; Hajdas, I.; et al. Multi-proxy dating the ‘Millennium Eruption’ of Changbaishan to late 946 CE. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2017, 158, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hughes, P.D.M.; Mallon, G.; Brown, A.; Essex, H.J.; Stanford, J.D.; Hotes, S. The impact of high tephra loading on late-Holocene carbon accumulation and vegetation succession in peatland communities. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2013, 67, 160–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, B.; Silva, S.L.; Xu, J.; Chen, Z.; Miggins, D.P.; Wei, H. The VEI-7 millennium eruption, Changbaishan-Tianchi volcano, China/DPRK: New field, petrological, and chemical constrains on stratigraphy, volcanology, and magma dynamics. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2017, 343, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Plunkett, G.; Liu, J.; Zhao, H.; Sigl, M.; McConnell, J.R.; Pilcher, J.R.; Vinther, B.; Steffensen, J.P.; Hall, V. Ash from Changbaishan Millennium eruption recorded in Greenland ice: Implications for determining the eruption’s timing and impact. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 694–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramos, F.C.; Wolff, J.A.; Buettner, J.E.; Wie, H.Q.; Xu, J. Ra/Th ages of sanidine in young trachytes erupted at Changbaishan Volcano, China. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2019, 374, 226–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, J.; Wang, P.-J.; Shan, X.-L.; Wang, H.-F.; Sun, S.; Chen, H. Lahar deposits generated after the Millennium eruption of the Changbaishan Tianchi volcano in the Erdaobaihe river system, China. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2019, 380, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuno, M.; Torii, M.; Yamada, K.; Shinozuka, Y.; Danhara, T.; Gotanda, K.; Yonenbu, H.; Yasuda, Y. Widespread tephras in sediments from lake Ichi-no-Megata in northern Japan: Their description, correlation and significance. Quat. Int. 2011, 246, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirai, M.; Tada, R.; Fujioka, K. Identification and chronostratigraphy of middle to upper Quaternary marker tephras occurring in the Anden coast based on comparison with ODP cores in the Sea of Japan. Quat. Res. 1997, 36, 183–196, (In Japanese with English abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machida, H.; Arai, F. Atals of Tephra in and Around Japan, revised ed.; University Tokyo: Tokyo, Japan, 2003; p. 336. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Chun, J.-H.; Cheong, D.; Lee, Y.-J.; Kwon, Y.-I.; Kim, B.-C. Stratigraphic implications as a time marker of the B-J tephra erupted from Baegdusan volcano discovered in the marine cores of the East sea/Japan Sea during the late Pleistocene. J. Geol. Soc. Korea 2006, 42, 31–42, (In Korean with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Ikehara, K. Late Quaternary seasonal sea-ice history of the north-eastern Japan Sea. J. Oceanogr. 2003, 59, 585–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, C.; Toyoda, K.; Ikehara, K.; Peate, D.W. Late Quaternary tephrostratigraphy of Beagdusan and Ulleung volcanoes using marine sediments in the Japan Sea/East Sea. Quat. Res. 2013, 80, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagashima, K.; Tada, R.; Tani, A.; Sun, Y.; Isozaki, Y.; Toyoda, S.; Hasegawa, H. Millennial-scale oscillations of the westerly jet path during the last glacial period. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2011, 40, 1214–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikehara, K. Marine tephra in the Japan Sea sediments as a tool for paleoceanography and paleoclimatology. Prog. Earth Planet. Sci. 2015, 2, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chun, J.-H.; Cheong, D.; Han, S.-J.; Huh, S.; Yoo, H.-S. Tephrostratigraphy and paleoenvironments of marine core in the Kita-Yamato Trough, East Sea/Japan Sea. Econ. Environ. Geol. 2006, 39, 83–93, (In Korean with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Chun, J.-H.; Han, S.-J.; Cheong, D. Tephrostratigraphy in the Ulleung Basin, East Sea: Late Pleistocene to Holocene. Geosci. J. 1997, 1, 154–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, J.-H.; Cheong, D.; Ikehara, K.; Han, S.-J. Age of the SKP-I and SKP-II tephras from the southern East Sea/Japan Sea: Implications for interstadial events recorded in sediment from marine isotope stages 3 and 4. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2007, 247, 100–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, J.-H.; Ikehara, K.; Han, S.-J. Evidence in Ulleung Basin sediment cores for a Termination II (penultimate deglaciation) eruption of the Aso-3 tephra. Quat. Res. 2004, 43, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheong, A.C.-S.; Jeong, Y.-J.; Jo, H.J.; Sohn, Y.K. Recurrent Quaternary magma generation at Baekdusan (Changbaishan) volcano: New zircon U-Th ages and Hf isotopic constraints from the Millennium Eruption. Gondwana Res. 2019, 68, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Fan, Q.; Zhang, H.; Schmitt, A.K. U-series zircon age constraints on the plumbing system and magma residence times of the Changbai volcano, China/North Korea border. Lithos 2014, 200–201, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsu’ura, T.; Kimur, J.; Chang, Q.; Komatsubara, J. Using tephrostratigraphy and cryptotephrostratigraphy to re-evaluate and improve the Middle Pleistocene age model for marine sequences in northeast Japan (Chikyu C9001C). Quat. Geochronol. 2017, 40, 129–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Han, J.; Fyfe, W.S. Cenozoic episodic volcanism and continental rifting in northeast China and possible link to Japan Sea development as revealed from K-Ar geochronology. Tectonophysics 2001, 339, 385–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuritani, T.; Kimura, J.; Miyamoto, T.; Wei, H.; Shimano, T.; Maeno, F.; Jin, X.; Taniguchi, H. Intraplate magmatism related to deceleration of upwelling asthenospheric mantle: Implications from the Changbaishan shield basalts, northeast China. Lithos 2009, 112, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Tian, Y.; Lei, J.; Liu, L.; Zheng, S. Seismic image and origin of the Changbai intraplate volcano in East Asia: Role of big mantle wedge above the stagnant Pacific slab. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 2009, 173, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, G.C.; Iwamori, H. Stagnant slab, wet plumes and Cenozoic volcanism in East Asia. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 2010, 183, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.-Q.; Chen, S.-S.; Guo, Z.-F.; Guo, W.-F.; He, H.-Y.; You, H.-T.; Kim, H.-M.; Sung, G.-H.; Kim, H. Geological background and geodynamic mechanism of Mt. Changbai volcanoes on the China-Korea border. Lithos 2015, 236–237, 46–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, F.; Xu, J.; Shangguan, Z.; Pan, B.; Yu, H.; Wie, W.; Bai, X.; Chen, Z. Helium and carbon isotopes in the hot springs of Changbaishan Volcano, northeastern China: A material connection between Changbaishan Volcano and the west Pacific plate? J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2016, 327, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, J.; Zhao, D. P-wave tomography and origin of the Changbai intraplate volcano in Northeast Asia. Tectonophysics 2005, 397, 281–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.-O.; Choi, S.H.; Schiano, P.; Cho, M.; Cluzel, N.; Devidal, J.-L.; Ha, K. Geochemistry of olivine-hosted melt inclusions in the Baekdusan (Changbaishan) basalts: Implications for recycling of oceanic crustal materials into the mantle source. Lithos 2017, 284–285, 194–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Sparks, R.S.J.; Liu, R.; Fan, Q.; Wang, Y.; Hong, H.; Zhang, H.; Chen, H.; Jiang, C.; Dong, J.; et al. Three active volcanoes in China and their hazards. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2003, 21, 515–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, R.V. Settling velocity of glass shards. Deep-Sea Res. 1965, 12, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, C.S.; Froggatt, P.C.; Gosson, G.J. Nature, chemistry, and origin of late Cenozoic megascopic tephras in Leg 90 cores from the southwest Pacific. In Initial reports DSDP, Leg 90, Noumea, New Caledonia to Wellington, New Zealand. Part 2; Blakeslee, J.H., Ed.; U.S. Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1986; Volume 26, pp. 1161–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamaki, K.; Pisciotto, K.; Allan, J.; Alexandrovich, J.M.; Barenes, D.A.; Boggs, S.; Brumsack, H.-J.; Brunner, C.A.; Cramp, A.; Jolivet, L.; et al. 4. SITE 794. In Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program, Initial Reports; Stewart, N.J., Winkler, W.R., Eds.; Ocean Drilling Program Texas A&M University: College Station, TX, USA, 1990; Volume 127, pp. 71–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Bas, B.J.; Le Maitre, R.W.; Streckeisen, A.; Zanettin, B. A chemical classification of volcanic rocks based on the total alkali-silica diagram. J. Petrol. 1986, 27, 745–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gioncada, A.; Landi, P. The pre-eruptive volatile contents of recent basaltic and pantelleritic magmas at Pantelleria (Italy). J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2010, 189, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratzmann, D.J.; Carey, S.; Scasso, R.; Naranjo, J.-A. Compositional variations and magma mixing in the 1991 eruptions of Hudson volcano, Chile. Bull. Volcanol. 2009, 71, 419–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacon, C.R.; Druitt, T.H. Compositional evolution of the zoned calcalkaline magma chamber of Mount Mazama, Crater Lake, Oregon. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 1988, 98, 224–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, R.D.; Donato, P.; Ventura, G. Fractal analysis mingled/mixed magmas: An example for the Upper Pollara eruption (Salina Island, southern Tyrhenian Sea, Italy). Lithos 2002, 65, 299–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donoghue, S.L.; Gamble, J.A.; Palmer, A.S.; Stewart, R.B. Magma mingling in an andesite pyroclastic flow of the Pourahu Member, Puapehu volcano, New Zealand. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 1995, 68, 177–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Tephra | Textural Composition | Degree of Vesicularity | Degree of Stretching | Maximum Grain Size (μm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Toya in the ODP 794A core | Ps >> Bs > Ph | low to moderate | low to moderate | Bs: 120, Ps: 100, Ph: 90 |
| B-KY1 in the ODP 794A core | Bs ≅ Ps > Ph | moderate to high | moderate to high | Bs: 180, Ps: 130, Ph: 130 |
| B-KY1 in the 20EEZ-1 core [23] | Ps > Bs >Ph | moderate to high | moderate to high | Bs: 210, Ps:170, Ph: 150 |
| Aso-1 in the ODP 794A core | Bs >> Ph > Ps | low to moderate | moderate to high | Bs: 250, Ps: 140, Ph: 140 |
| Depth (cmbsf) | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | FeO* | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | Tephra |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 428.2–429.3 | 78.82 | 0.09 | 12.99 | 0.79 | 0.07 | 0.04 | 0.34 | 4.10 | 2.75 | Toya |
| 78.67 | 0.16 | 13.18 | 0.81 | 0.14 | - | 0.36 | 3.80 | 2.88 | ||
| 78.51 | - | 13.31 | 0.80 | 0.08 | 0.02 | 0.33 | 4.17 | 2.79 | ||
| 79.06 | 0.11 | 13.44 | 0.88 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.29 | 3.22 | 2.94 | ||
| 78.55 | 0.08 | 13.38 | 0.81 | 0.06 | 0.01 | 0.32 | 4.11 | 2.69 | ||
| 79.83 | 0.07 | 13.45 | 0.85 | 0.09 | 0.03 | 0.33 | 2.65 | 2.70 | ||
| 78.09 | 0.02 | 13.46 | 0.89 | 0.09 | 0.07 | 0.34 | 4.39 | 2.65 | ||
| 79.02 | 0.09 | 13.76 | 0.86 | 0.07 | 0.04 | 0.36 | 3.01 | 2.81 | ||
| 78.78 | 0.07 | 12.90 | 0.81 | 0.12 | 0.05 | 0.34 | 3.73 | 3.19 | ||
| 79.37 | 0.08 | 12.95 | 0.85 | 0.09 | 0.04 | 0.30 | 3.84 | 2.47 | ||
| 78.25 | 0.09 | 13.53 | 0.84 | 0.12 | - | 0.34 | 3.44 | 3.39 | ||
| 78.31 | 0.20 | 13.32 | 0.79 | 0.08 | - | 0.28 | 4.17 | 2.86 | ||
| 78.25 | 0.05 | 13.38 | 0.72 | 0.09 | - | 0.34 | 3.94 | 3.23 | ||
| 79.10 | - | 12.74 | 0.95 | 0.08 | - | 0.28 | 3.88 | 2.97 | ||
| 585.6–587.2 | 75.14 | 0.23 | 9.17 | 5.91 | 0.12 | - | 0.22 | 5.02 | 4.18 | B-KY1 |
| 75.08 | 0.15 | 9.39 | 6.00 | 0.11 | - | 0.21 | 4.83 | 4.24 | ||
| 73.88 | 0.10 | 10.51 | 5.79 | 0.15 | - | 0.35 | 4.71 | 4.50 | ||
| 72.41 | 0.03 | 11.86 | 5.48 | 0.13 | - | 0.48 | 5.21 | 4.40 | ||
| 73.69 | 0.16 | 11.53 | 5.61 | 0.15 | - | 0.44 | 3.90 | 4.50 | ||
| 70.60 | 0.15 | 13.28 | 5.20 | 0.15 | 0.02 | 0.62 | 5.38 | 4.60 | ||
| 73.26 | 0.07 | 11.26 | 6.05 | 0.14 | - | 0.63 | 4.23 | 4.36 | ||
| 74.96 | 0.22 | 9.24 | 5.81 | 0.13 | 0.04 | 0.24 | 5.06 | 4.29 | ||
| 75.36 | 0.12 | 9.20 | 5.75 | 0.13 | - | 0.22 | 4.90 | 4.32 | ||
| 67.53 | 0.22 | 15.15 | 5.30 | 0.16 | 0.09 | 1.00 | 5.34 | 5.21 | ||
| 68.63 | 0.20 | 15.50 | 5.44 | 0.14 | 0.09 | 0.97 | 3.67 | 5.35 | ||
| 68.47 | 0.27 | 15.06 | 5.37 | 0.19 | 0.05 | 0.89 | 4.37 | 5.32 | ||
| 66.59 | 0.16 | 15.74 | 5.54 | 0.15 | 0.08 | 1.09 | 5.47 | 5.17 | ||
| 67.68 | 0.22 | 15.76 | 5.45 | 0.13 | 0.12 | 1.06 | 4.30 | 5.29 | ||
| 802.9–803.7 | 69.91 | 0.23 | 16.32 | 2.73 | 0.08 | 0.54 | 1.75 | 3.63 | 4.82 | Aso-1 |
| 70.16 | 0.34 | 16.26 | 2.64 | 0.10 | 0.53 | 1.85 | 3.45 | 4.68 | ||
| 69.87 | 0.28 | 16.13 | 2.59 | 0.13 | 0.52 | 1.92 | 3.54 | 5.03 | ||
| 69.91 | 0.22 | 16.48 | 2.73 | 0.11 | 0.57 | 1.86 | 2.98 | 5.14 | ||
| 69.77 | 0.32 | 16.25 | 2.85 | 0.07 | 0.52 | 1.79 | 3.57 | 4.86 | ||
| 69.71 | 0.23 | 16.23 | 2.73 | 0.08 | 0.55 | 1.85 | 3.70 | 4.93 | ||
| 69.89 | 0.17 | 16.25 | 2.64 | 0.05 | 0.55 | 1.82 | 3.77 | 4.86 | ||
| 70.60 | 0.23 | 16.47 | 2.83 | 0.06 | 0.53 | 1.93 | 2.49 | 4.85 | ||
| 70.49 | 0.17 | 16.03 | 2.59 | 0.14 | 0.59 | 1.77 | 3.36 | 4.86 | ||
| 70.62 | 0.33 | 15.93 | 2.68 | 0.04 | 0.58 | 1.73 | 3.26 | 4.83 | ||
| 70.37 | 0.30 | 16.04 | 2.71 | 0.03 | 0.52 | 1.77 | 3.39 | 4.87 | ||
| 70.36 | 0.41 | 16.09 | 2.47 | 0.06 | 0.47 | 1.89 | 3.31 | 4.93 | ||
| 69.68 | 0.29 | 16.23 | 2.62 | 0.07 | 0.53 | 1.94 | 3.59 | 5.06 | ||
| 69.94 | 0.21 | 15.98 | 2.83 | 0.06 | 0.57 | 1.90 | 3.52 | 5.01 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chun, J.-H.; Cheong, D. Origin of Compositional Diversity of Marine Tephra during the Late Middle Pleistocene B-KY1 Baekdusan Volcanic Eruption. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 4469. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10134469
Chun J-H, Cheong D. Origin of Compositional Diversity of Marine Tephra during the Late Middle Pleistocene B-KY1 Baekdusan Volcanic Eruption. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(13):4469. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10134469
Chicago/Turabian StyleChun, Jong-Hwa, and Daekyo Cheong. 2020. "Origin of Compositional Diversity of Marine Tephra during the Late Middle Pleistocene B-KY1 Baekdusan Volcanic Eruption" Applied Sciences 10, no. 13: 4469. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10134469
APA StyleChun, J.-H., & Cheong, D. (2020). Origin of Compositional Diversity of Marine Tephra during the Late Middle Pleistocene B-KY1 Baekdusan Volcanic Eruption. Applied Sciences, 10(13), 4469. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10134469