Mapping of the Upper Limb Work-Space: Benchmarking Four Wrist Smoothness Metrics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
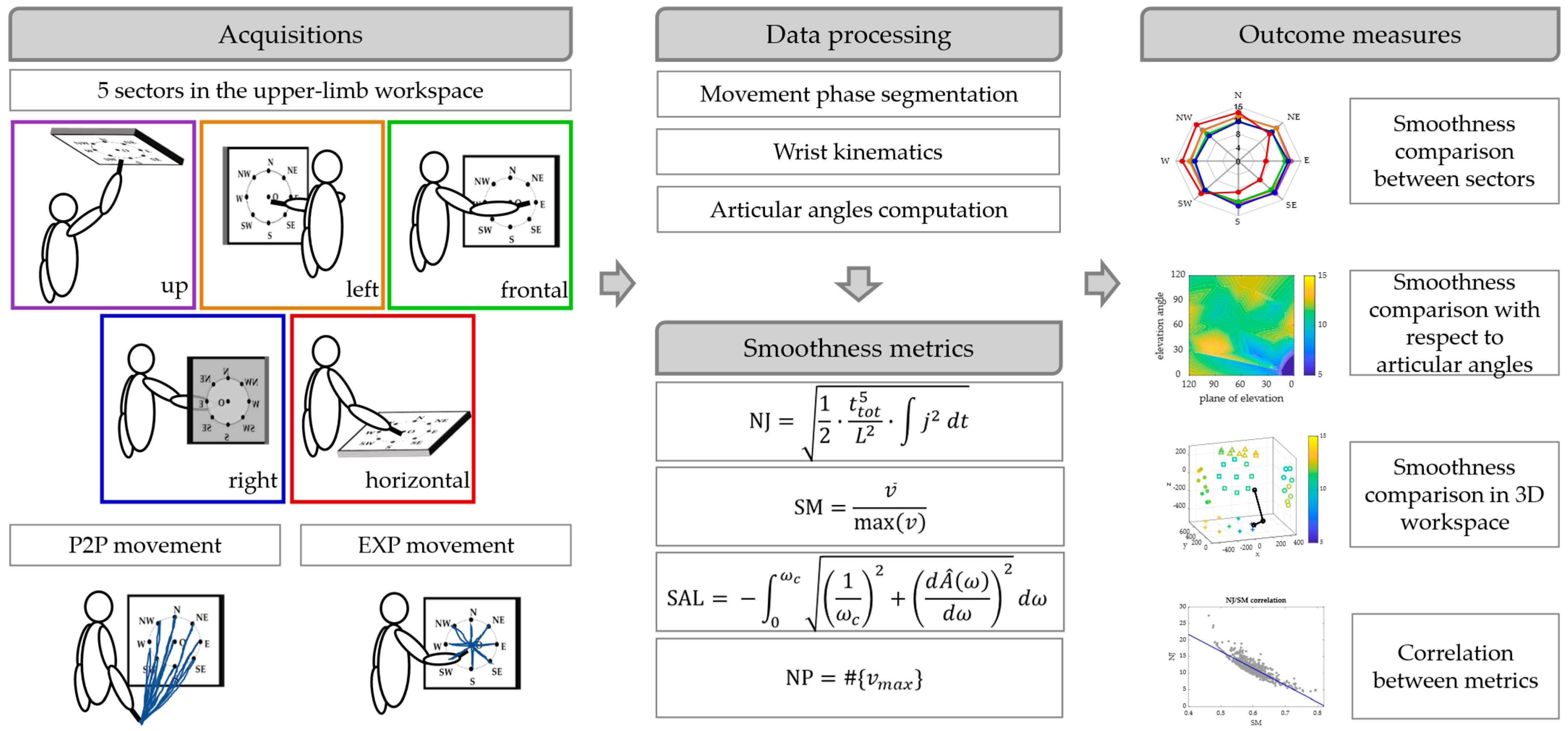
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Laboratory Acquisition Set Up
2.3. Data Analysis
2.3.1. Movement Segmentation
2.3.2. Articular Kinematics
2.3.3. Smoothness Metrics
2.4. Outcome Measures and Statistical Analysis
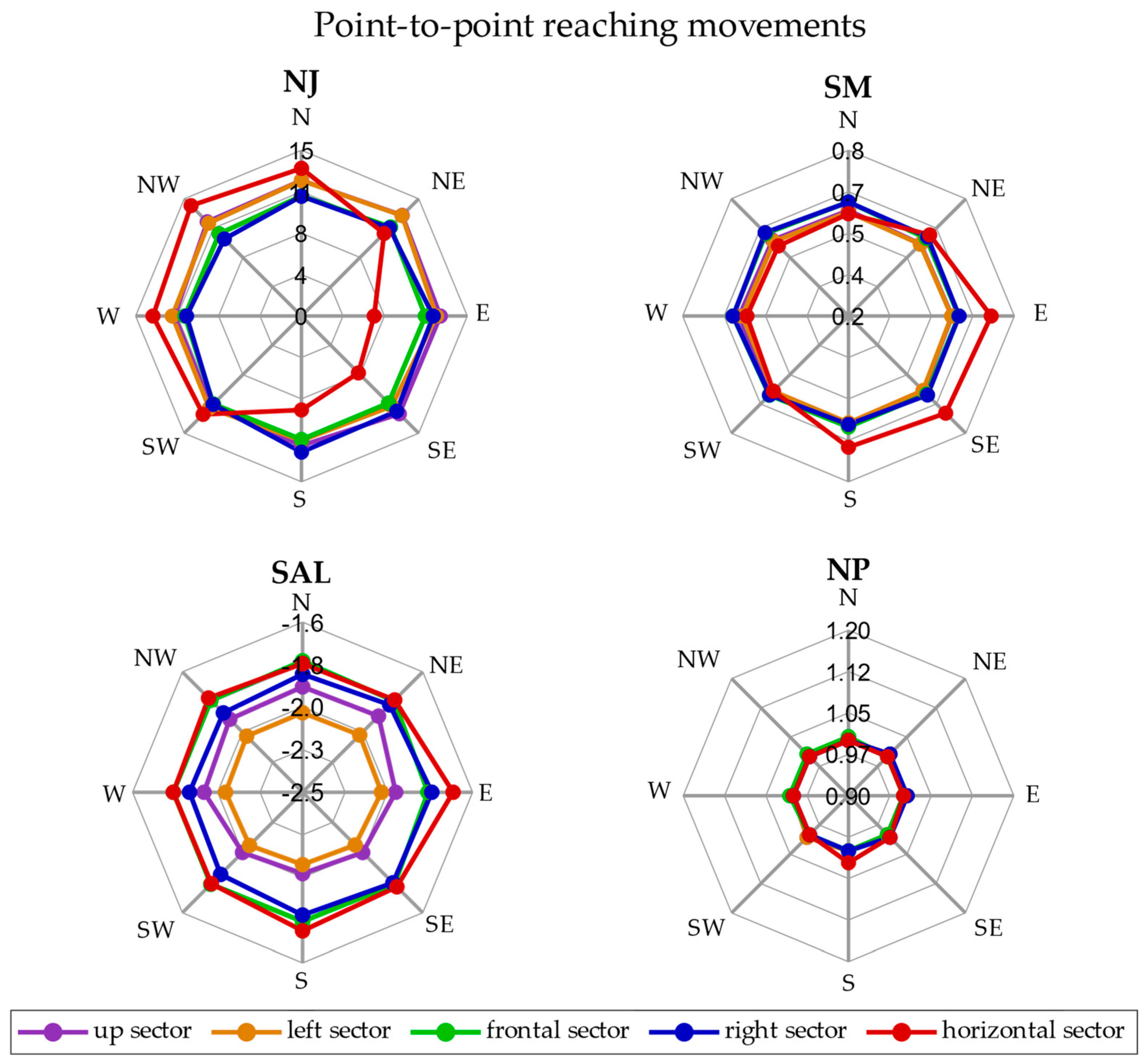
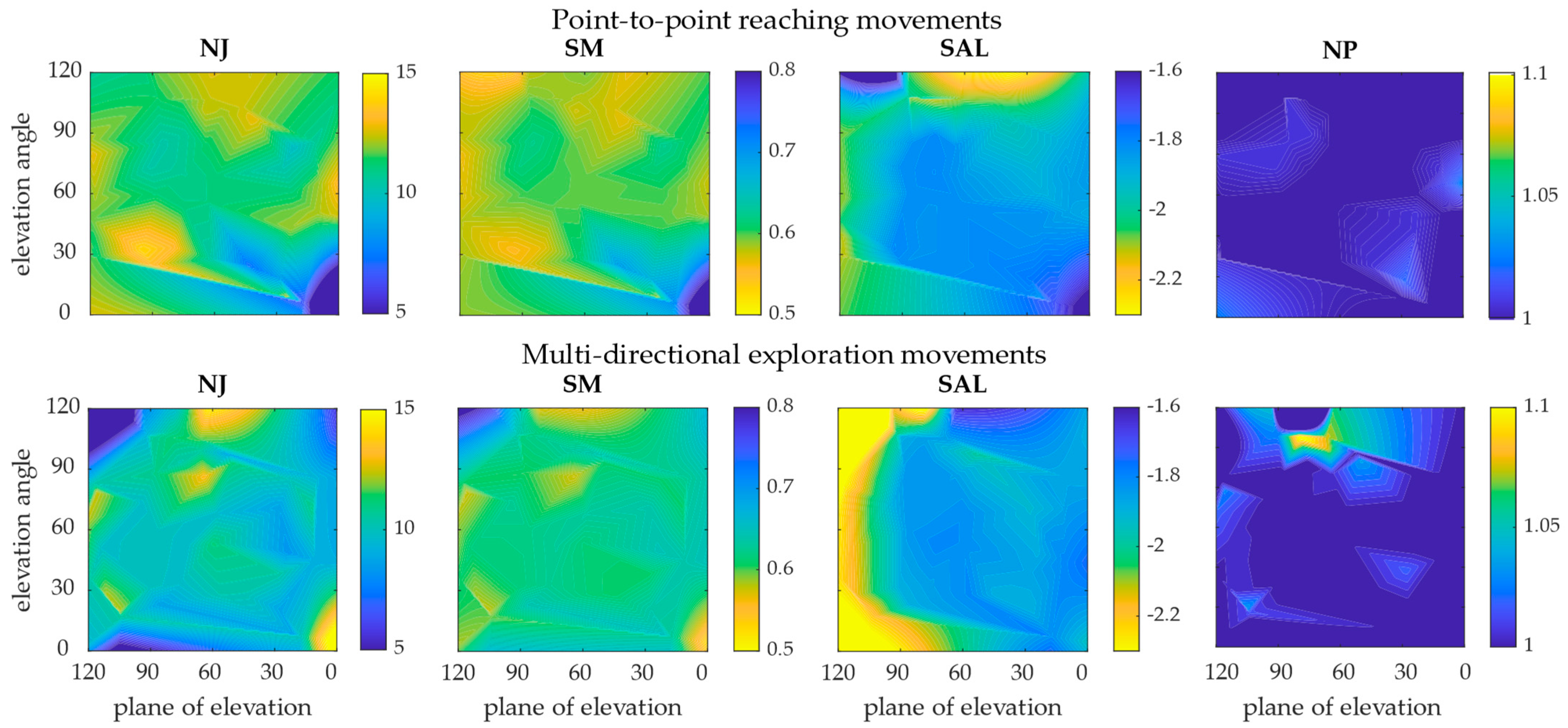
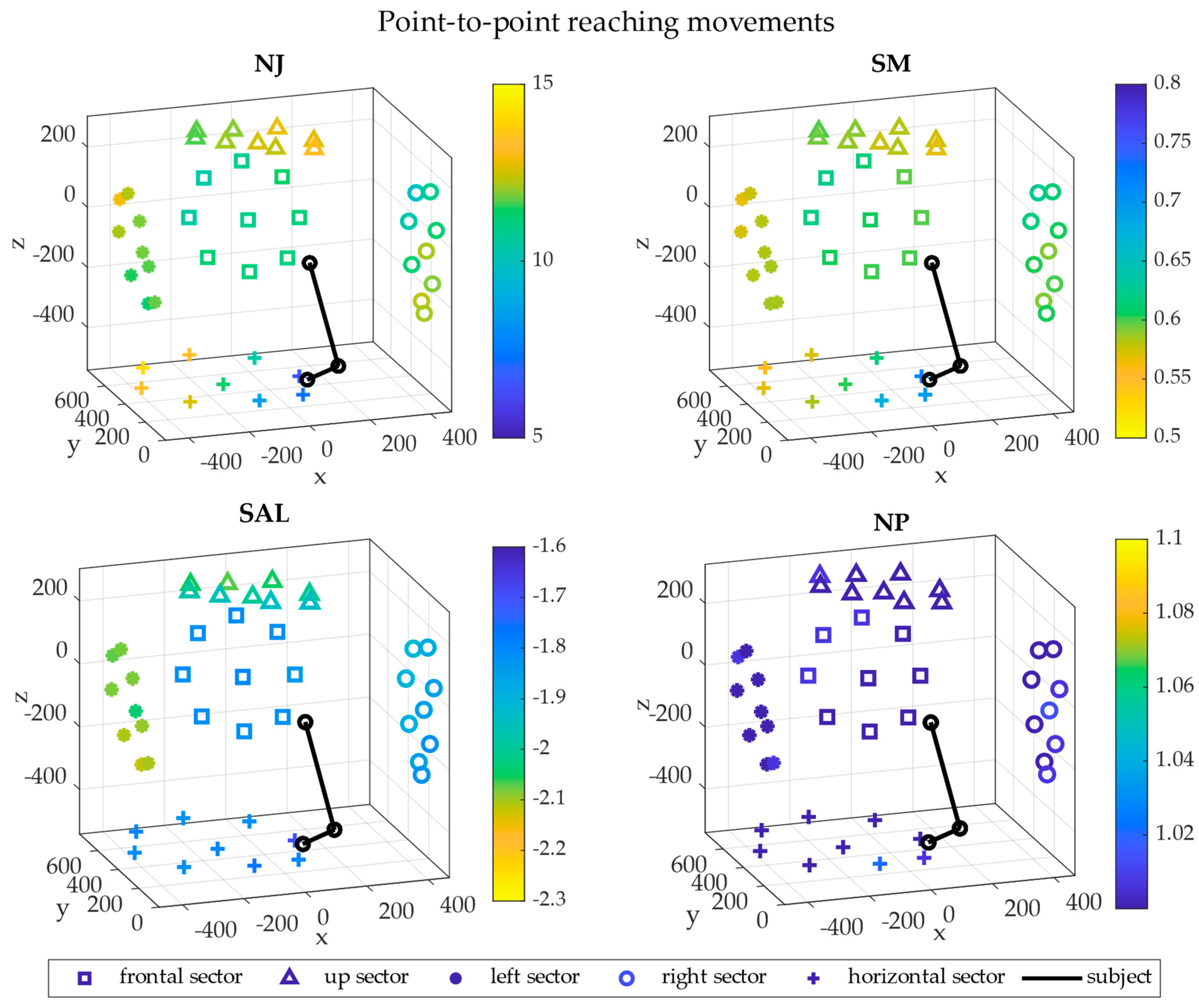
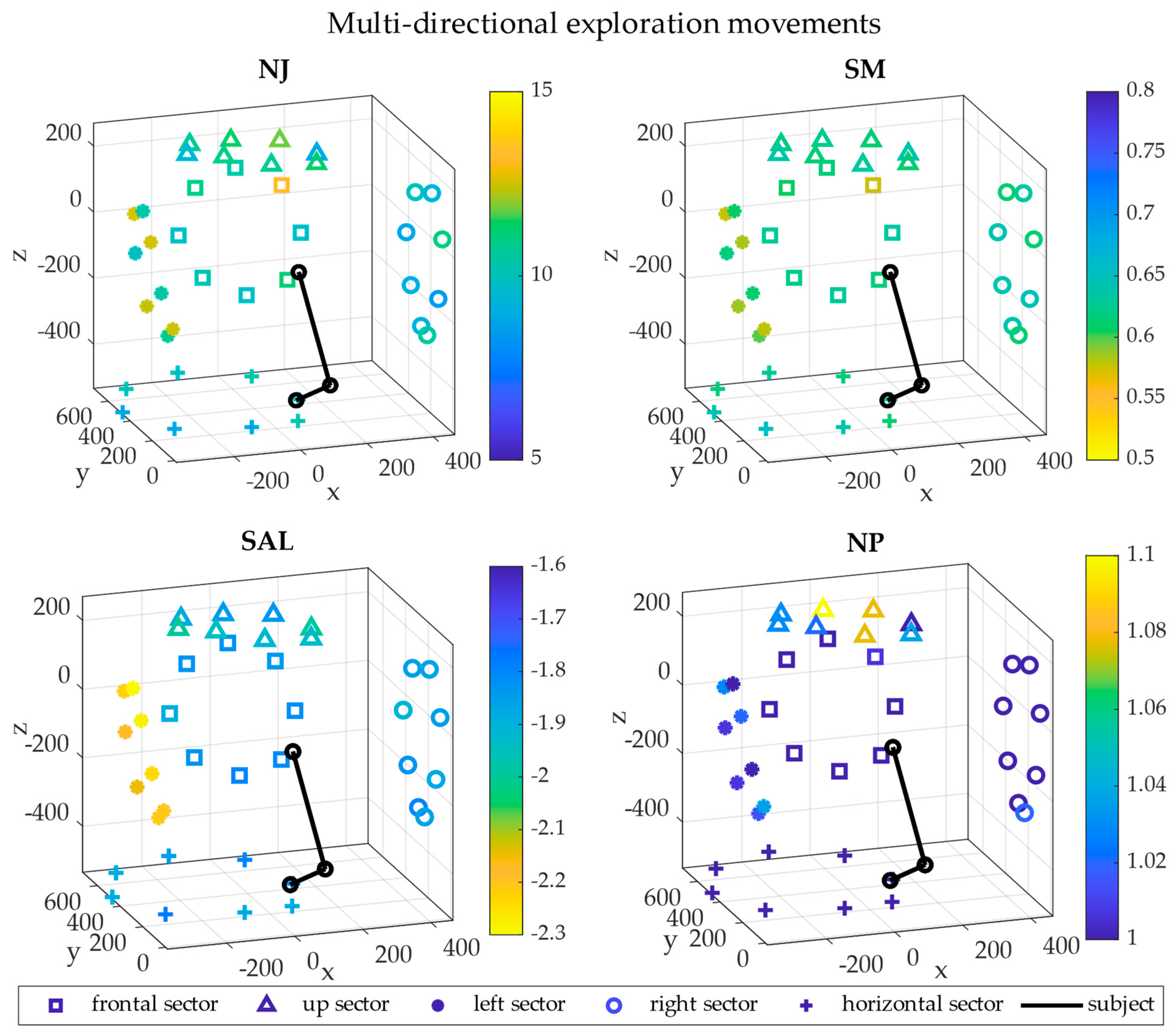
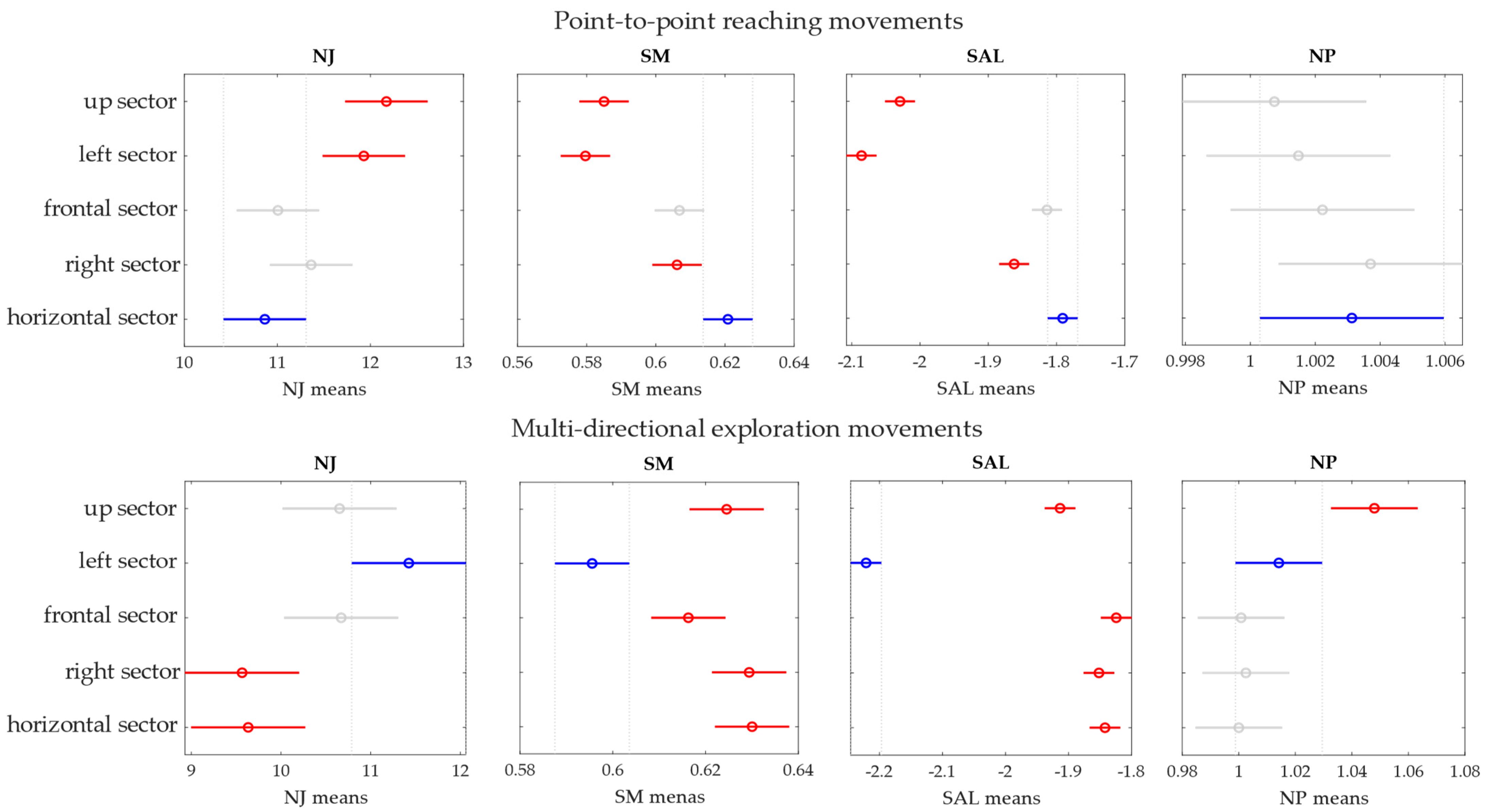
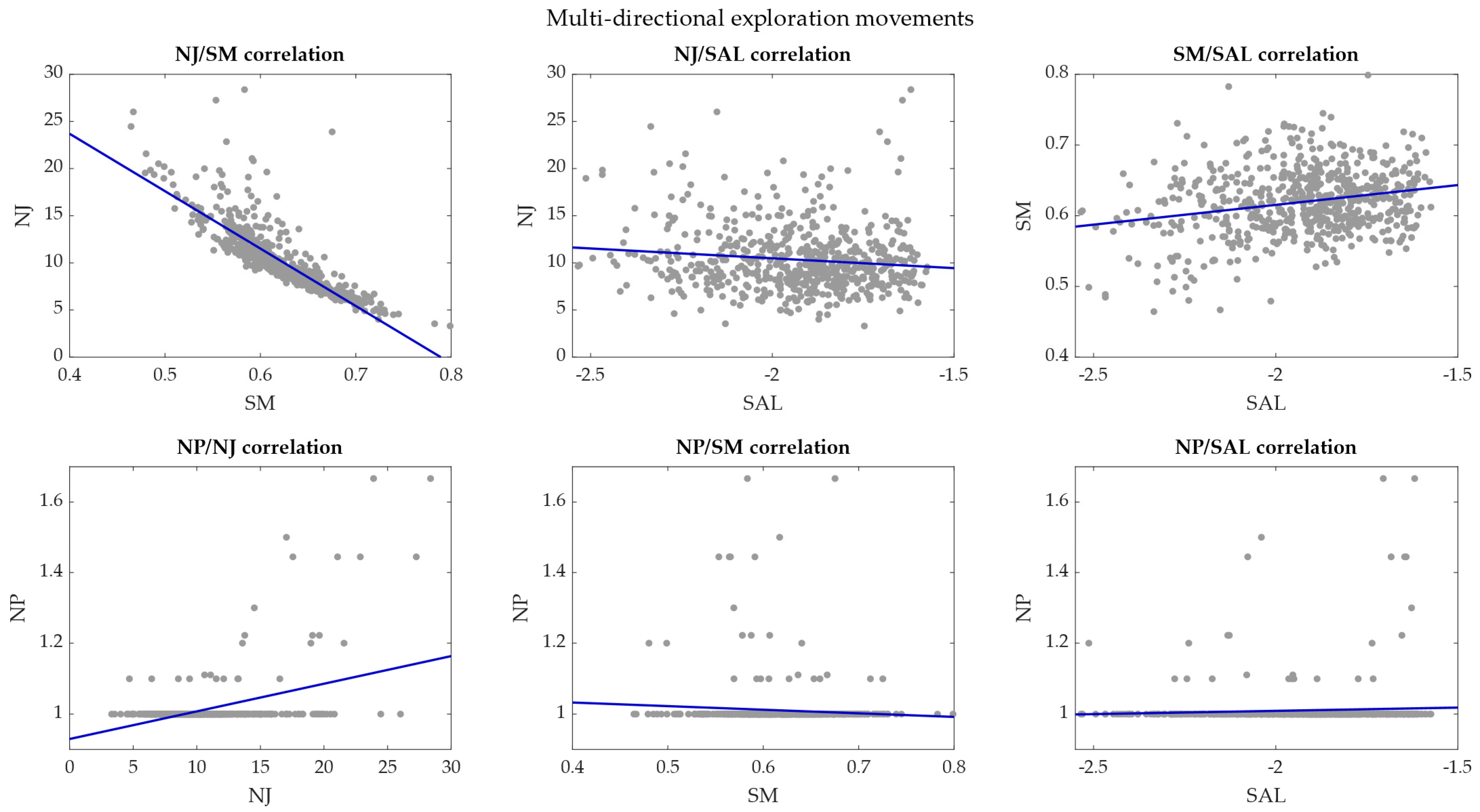
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kiely, J.; Pickering, C.; Collins, D.J. Smoothness: An Unexplored Window into Coordinated Running Proficiency. Sport. Med.-Open 2019, 5, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulde, P.; Hermsdörfer, J. Smoothness metrics in complex movement tasks. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Scano, A.; Chiavenna, A.; Malosio, M.; Tosatti, L.M. Kinect V2 Performance Assessment in Daily-Life Gestures: Cohort Study on Healthy Subjects for a Reference Database for Automated Instrumental Evaluations on Neurological Patients. Appl. Bionics Biomech. 2017, 2017, 8567084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caimmi, M.; Carda, S.; Giovanzana, C.; Maini, E.S.; Sabatini, A.M.; Smania, N.; Molteni, F. Using kinematic analysis to evaluate constraint-induced movement therapy in chronic stroke patients. Neurorehabil. Neural Repair 2008, 22, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, M.A.; Willén, C.; Sunnerhagen, K.S. Kinematic variables quantifying upper-extremity performance after stroke during reaching and drinking from a glass. Neurorehabil. Neural Repair 2011, 25, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Flash, T.; Hogan, N. The coordination of arm movements: An experimentally confirmed mathematical model. J. Neurosci. 1985, 5, 1688–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruse, H.; Wischmeyer, E.; Brüwer, M.; Brockfeld, P.; Dress, A. On the cost functions for the control of the human arm movement. Biol. Cybern. 1990, 62, 519–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Kordelaar, J.; Van Wegen, E.; Kwakkel, G. Impact of time on quality of motor control of the paretic upper limb after stroke. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2014, 95, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed Refai, M.I.; Saes, M.; Scheltinga, B.L.; van Kordelaar, J.; Bussmann, J.B.J.; Veltink, P.H.; Buurke, J.H.; Meskers, C.G.M.; van Wegen, E.E.H.; Kwakkel, G.; et al. Smoothness metrics for reaching performance after stroke. Part 1: Which one to choose? J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2021, 18, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montes, V.R.; Quijano, Y.; Chong Quero, J.E.; Ayala, D.V.; Perez Moreno, J.C. Comparison of 4 different smoothness metrics for the quantitative assessment of movement’s quality in the upper limb of subjects with cerebral palsy. In Proceedings of the Pan American Health Care Exchanges, PAHCE, Brasilia, Brazil, 7–12 April 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Teulings, H.L.; Contreras-Vidal, J.L.; Stelmach, G.E.; Adler, C.H. Parkinsonism reduces coordination of fingers, wrist, and arm in fine motor control. Exp. Neurol. 1997, 146, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sire, A.; Bigoni, M.; Priano, L.; Baudo, S.; Solaro, C.; Mauro, A. Constraint-Induced Movement Therapy in multiple sclerosis: Safety and three-dimensional kinematic analysis of upper limb activity. A randomized single-blind pilot study. NeuroRehabilitation 2019, 45, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jebsen, R.H.; Taylor, N.; Trieschmann, R.B.; Trotter, M.J.; Howard, L.A. An objective and standardized test of hand function. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 1969, 50, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lyle, R.C. A performance test for assessment of upper limb function in physical rehabilitation treatment and research. Int. J. Rehabil. Res. 1981, 4, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathiowetz, V.; Weber, K.; Kashman, N.; Volland, G. Adult norms for the nine hole peg test of finger dexterity. Occup. Ther. J. Res. 1985, 5, 24–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Los Reyes-Guzmán, A.; Dimbwadyo-Terrer, I.; Trincado-Alonso, F.; Monasterio-Huelin, F.; Torricelli, D.; Gil-Agudo, A. Quantitative assessment based on kinematic measures of functional impairments during upper extremity movements: A review. Clin. Biomech. 2014, 29, 719–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Merlo, A.; Longhi, M.; Giannotti, E.; Prati, P.; Giacobbi, M.; Ruscelli, E.; Mancini, A.; Ottaviani, M.; Montanari, L.; Mazzoli, D. Upper limb evaluation with robotic exoskeleton. Normative values for indices of accuracy, speed and smoothness. NeuroRehabilitation 2013, 33, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, V.B.; Cooke, J.D.; Thomas, J.S. The Continuity of Movements; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1973; pp. 257–272. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, R.J.; Lichter, M.D.; Krepkovich, E.T.; Ellington, A.; White, M.; Diamond, P.T. Assessing Upper Extremity Motor Function in Practice of Virtual Activities of Daily Living. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2015, 23, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohrer, B.; Fasoli, S.; Krebs, H.I.; Hughes, R.; Volpe, B.; Frontera, W.R.; Stein, J.; Hogan, N. Movement smoothness changes during stroke recovery. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 8297–8304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramanian, S.; Melendez-Calderon, A.; Burdet, E. A robust and sensitive metric for quantifying movement smoothness. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2012, 59, 2126–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogan, N.; Sternad, D. Sensitivity of smoothness measures to movement duration, amplitude, and arrests. J. Mot. Behav. 2009, 41, 529–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, Y.; Herman, T.; Brozgol, M.; Giladi, N.; Mirelman, A.; Hausdorff, J.M. SPARC: A new approach to quantifying gait smoothness in patients with Parkinson’s disease. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2018, 15, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Temporiti, F.; Mandaresu, S.; Calcagno, A.; Coelli, S.; Bianchi, A.M.; Gatti, R.; Galli, M. Kinematic evaluation and reliability assessment of the Nine Hole Peg Test for manual dexterity. J. Hand Ther. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson, G.M.; Häger, C.K. A modified standardized nine hole peg test for valid and reliable kinematic assessment of dexterity post-stroke. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2019, 16, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Dokkum, L.; Hauret, I.; Mottet, D.; Froger, J.; Métrot, J.; Laffont, I. The contribution of kinematics in the assessment of upper limb motor recovery early after stroke. Neurorehabil. Neural Repair 2014, 28, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rickham, P.P. Human Experimentation Code of Ethics of the World Medical Association. Br. Med. J. 1964, 2, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- D’Avella, A.; Portone, A.; Fernandez, L.; Lacquaniti, F. Control of fast-reaching movements by muscle synergy combinations. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 7791–7810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scano, A.; Dardari, L.; Molteni, F.; Giberti, H.; Tosatti, L.M.; D’Avella, A. A comprehensive spatial mapping of muscle synergies in highly variable upper-limb movements of healthy subjects. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scano, A.; Molteni, F.; Tosatti, L.M. Low-Cost Tracking Systems Allow Fine Biomechanical Evaluation of Upper-Limb Daily-Life Gestures in Healthy People and Post-Stroke Patients. Sensors 2019, 19, 1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schiefelbein, M.L.; Salazar, A.P.; Marchese, R.R.; Rech, K.D.; Schifino, G.P.; Figueiredo, C.S.; Cimolin, V.; Pagnussat, A.S. Upper-limb movement smoothness after stroke and its relationship with measures of body function/structure and activity–A cross-sectional study. J. Neurol. Sci. 2019, 401, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rech, K.D.; Salazar, A.P.; Marchese, R.R.; Schifino, G.; Cimolin, V.; Pagnussat, A.S. Fugl-Meyer Assessment Scores Are Related With Kinematic Measures in People with Chronic Hemiparesis after Stroke. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2020, 29, 104463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik, O.; O’Malley, M.K.; Boake, C.; Levin, H.S.; Yozbatiran, N.; Reistetter, T.A. Normalized movement quality measures for therapeutic robots strongly correlate with clinical motor impairment measures. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2010, 18, 433–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Scano, A.; Caimmi, M.; Chiavenna, A.; Malosio, M.; Tosatti, L.M. Kinect One-based biomechanical assessment of upper-limb performance compared to clinical scales in post-stroke patients. In Proceedings of the Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, EMBS, Milan, Italy, 25–29 August 2015; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2015; Volume 2015, pp. 5720–5723. [Google Scholar]
- Schuch, C.P.; Balbinot, G.; Bonilla, M.N.; Guedes Machado, A.; Oliveira, A.A. de Feasibility of a Short-Term Virtual Reality Balance Intervention to Improve Mobility Smoothness in Parkinson’s Disease. Front. Virtual Real. 2020, 1, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, Á.; Sepúlveda-Muñoz, D.; Gil-Agudo, Á.; de los Reyes Guzmán, A. Serious game platform with haptic feedback and EMG monitoring for upper limb rehabilitation and smoothness quantification on spinal cord injury patients. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scano, A.; Guanziroli, E.; Mira, R.M.; Brambilla, C.; Molinari Tosatti, L.; Molteni, F. Biomechanical assessment of the ipsilesional upper limb in post-stroke patients during multi-joint reaching tasks: A quantitative study. Front. Rehabil. Sci. 2022, 3, 943397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, M.A.; Brandt, J.; Shadmehr, R. Motor disorder in Huntington’s disease begins as a dysfunction in error feedback control. Nature 2000, 403, 544–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Plamondon, R.; Alimi, A.M.; Yergeau, P.; Leclerc, F. Modelling velocity profiles of rapid movements: A comparative study. Biol. Cybern. 1993, 69, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, L.E.; Zygman, M.L.; Rymer, W.Z.; Reinkensmeyer, D.J. Effect of robot-assisted and unassisted exercise on functional reaching in chronic hemiparesis. In Proceedings of the Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology-Proceedings, Istanbul, Turkey, 25–28 October 2001; Volume 2, pp. 1344–1347. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, N.; Zhang, M.; Huang, C.; Jin, D. Motion quality evaluation of upper limb target-reaching movements. Med. Eng. Phys. 2002, 24, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ao, D.; Song, R.; Tong, K.Y. Sensorimotor control of tracking movements at various speeds for stroke patients as well as age-matched and young healthy subjects. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0128328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramanian, S.; Melendez-Calderon, A.; Roby-Brami, A.; Burdet, E. On the analysis of movement smoothness. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2015, 12, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Scano, A.; Brambilla, C.; Müller, H.; Atzori, M. Mapping of the Upper Limb Work-Space: Benchmarking Four Wrist Smoothness Metrics. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 12643. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122412643
Scano A, Brambilla C, Müller H, Atzori M. Mapping of the Upper Limb Work-Space: Benchmarking Four Wrist Smoothness Metrics. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(24):12643. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122412643
Chicago/Turabian StyleScano, Alessandro, Cristina Brambilla, Henning Müller, and Manfredo Atzori. 2022. "Mapping of the Upper Limb Work-Space: Benchmarking Four Wrist Smoothness Metrics" Applied Sciences 12, no. 24: 12643. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122412643







