Microwave-Assisted Chemical Ablation (MA-CA): A Novel Microwave-Assisted Tissue Ablation Procedure—Preliminary Assessment of Efficiency
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Microwaves in the Medical Field
2.2. Microwave-Assisted Chemical Ablation (MA-CA)
2.3. Innovative Aspects of This MW-Assisted Ablation Technology Approach
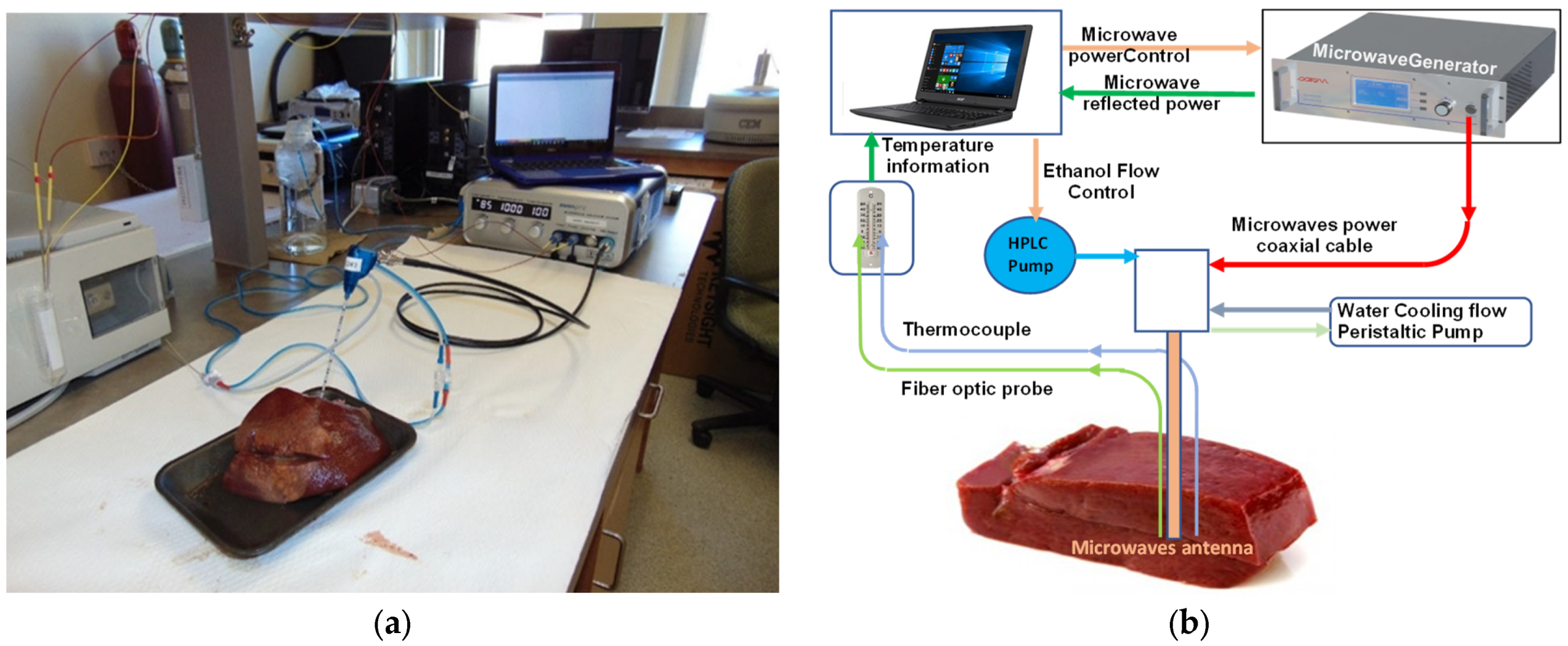
2.4. Experimental Ex Vivo Ablation Conditions
3. Results
Ex Vivo Ablation Work
4. Discussion
- Typical experiments were performed for a single value of applied power (100 W) and applied energy (12,000 Joules)—only the sequence of the applied power differed.
- The volume of the ablated tissue was calculated as an ellipsoid (not a sphere), although MA-CA was closer to a sphere than MWA alone.
- The ablated volumes of MA-CA were larger than MWA alone by 20–50%.
- The volumes of ethanol used were small, at less than 10 mL. This was important as it led to no significant loss of ethanol outside the target zone. This is also an important factor when in vivo ablation procedures are performed.
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Uzel, R.A. Microwave-Assisted Green Extraction Technology for Sustainable Food Processing. In Emerging Microwave Technologies in Industrial, Agricultural, Medical and Food Processing; You, K.Y., Ed.; Chapter 9; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moret, S.; Conchione, C.; Srbinovska, A.; Lucci, P. Microwave-Based Technique for Fast and Reliable Extraction of Organic Contaminants from Food, with a Special Focus on Hydrocarbon Contaminants. Foods 2019, 8, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khalkhali, R.; Peyravi, A.; Hashisho, Z.; Choi, P. Microwave-Assisted Removal of Cyclohexane from Oil Sands Gangue. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2022, 61, 6611–6617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagade, S.B.; Patil, M. Recent Advances in Microwave Assisted Extraction of Bioactive Compounds from Complex Herbal Samples: A Review. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2021, 51, 138–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadeghi, A.; Hakimzadeh, V.; Karimifar, B. Microwave Assisted Extraction of Bioactive Compounds from Food: A Review. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. Eng. 2017, 7, 19–27. [Google Scholar]
- Valizadehderakhshan, M.; Shahbazi, A.; Kazem-Rostami, M.; Todd, M.S.; Bhowmil, A.; Wang, L. Extraction of Cannabinoids from Cannabis sativa L. (Hemp)—Review. Agriculture 2021, 11, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernàndez, J.I.; Cepeda, M.F.J.; Valdés, F.; Guerrero, G.D. Microwave Ablation: State-of the-Art Review. Onco Targets Ther. 2015, 8, 1627–1632. [Google Scholar]
- Meloni, M.F.; Chiang, J.; Laeseke, P.F.; Dietrich, C.F.; Sannino, A.; Solbiati, M.; Nocerino, E.; Brace, C.; Lee, F.T. Microwave ablation in primary and secondary liver tumours: Technical and clinical approaches. Int. J. Hyperth. 2017, 33, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pusceddu, C.; Sotgia, B.; Fele, R.M.; Ballicu, N.; Melis, L. Combined Microwave Ablation and Cementoplasty in Patients with Painful Bone Metastases at High Risk of Fracture. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2016, 39, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korkusuz, Y.; Mader, O.M.; Kromen, W.; Happel, C.; Ahmad, S.; Gröner, D.; Koca, M.; Mader, A.; Grünwald, F.; Korkusuz, H. Cooled microwave ablation of thyroid nodules: Initial experience. Eur. J. Radiol. 2016, 85, 2127–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, J.; Cristescu, M.; Lee, M.H.; Moreland, A.; Hinshaw, J.L.; Lee, F.T.; Brace, C. Effects of Microwave Ablation on Arterial and Venous Vasculature after Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Radiology 2016, 281, 617–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiong, L.; Dupuy, D.E. Lung Ablation Whats New? J. Thorac. Imaging 2016, 31, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolock, A.R.; Cristescu, M.M.; Potretzke, T.A.; Ziemlewicz, T.J.; Lubner, M.G.; Hinshaw, J.L.; Brace, C.L.; Lee, F.T., Jr. Microwave Ablation for the Treatment of Hepatic Adenomas. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2016, 27, 244–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Liang, P.; Yu, X.; Yu, J.; Cheng, Z.; Han, Z.; Duan, S.; Huang, H. Microwave Treatment of Renal Cell Carcinoma Adjacent to Renal Sinus. Eur. J. Radiol. 2016, 85, 2083–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.W.; Gao, F.; Ma, Y.; Feng, S.F.; Liu, X.L.; Zhou, H.K. Percutaneous Microwave Ablation in the Spleen for Treatment of Hypersplenism in Cirrhosis Patients. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2016, 61, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Egashira, Y.; Singh, S.; Bandula, S.; Illing, R. Percutaneous High-Energy Microwave Ablation for the Treatment of Pulmonary Tumors: A Retrospective Single-Center Experience. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2016, 27, 474–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristescu, M.; Abel, E.J.; Wells, S.; Ziemlewicz, T.J.; Hedican, S.P.; Lubner, M.G.; Hinshaw, J.L.; Brace, C.L.; Lee, F.T., Jr. Percutaneous Microwave Ablation of Renal Angiomyolipomas. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol 2016, 39, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolock, A.R.; Lubner, M.G.; Ziemlewicz, T.J.; Hinshaw, J.L.; Kitchin, D.R.; Brace, C.L.; Lee, F.T., Jr. Microwave Ablation of Hepatic Tumors Abutting the Diaphragm Is Safe and Effective. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2015, 204, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belfiore, M.P.; Sciandra, M.; Romano, F.; Tartaglione, T.; De Lucia, G.; Volpe, T.D.; Buonomo, C.; Cappabianca, S.; Rotondo, A.; Belfiore, G. Preliminary Results in Unresectable Head and Neck Cancer Treated by Radiofrequency and Microwave Ablation: Feasibility, Efficacy, and Safety. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2015, 26, 1189–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knavel, E.M.; Brace, C.L. Tumor Ablation: Common Modalities and General Practices. Tech. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2013, 16, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Baere, T.; Deschamps, F. New tumor ablation techniques for cancer treatment (microwave, electroporation). Diagn. Interv. Imaging 2014, 95, 677–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hinshaw, J.L.; Lubner, M.G.; Ziemlewicz, T.J.; Lee, F.T.; Brace, C.L. Percutaneous Tumor Ablation Tools: Microwave, Radiofrequency, or Cryoablation—What Should You Use and Why? Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2014, 34, 1344–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, M.J.; Willatt, J.; Majdalany, B.S.; Kielar, A.Z.; Chong, S.; Ruma, J.A.; Pandya, A. Ablation Techniques for Primary and Metastatic Liver Tumors. World J. Hepatol. 2016, 8, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreozzi, A.; Brunese, L.; Iasiello, M.; Tucci, C. Numerical Analysis of the Pulsating Heat Source Effects in a Tumor Tissue. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2021, 200, 105887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, D.; Namgung, B.; Woo, D.G.; Choi, J.S.; Kim, H.S.; Tack, G.R. Effect of Input Waveform Pattern and Large Blood Vessel Existence on Destruction of Liver Tumor Using Radiofrequency Ablation: Finite Element Analysis. J. Biomech. Eng. 2010, 132, 061003-1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreozzi, A.; Brunese, L.; Iasiello, M.; Tucci, C.; Vanoli, G.P. A Novel Local Thermal Non-Equilibrium Model for Biological Tissue Applied to Multiple-Antennas Configurations for Thermal Ablation. Numer. Heat Transf. Part A Appl. 2021, 79, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trujillo-Romero, C.J.; Merida, J.D.; Ramirez-Guzman, T.J.; Martinez-Valdez, R.; Leija-Salas, L.; Vera-Hernandez, A.; Rico-Martinez, G.; Flores-Cuautle, J.J.A.; Gutierrez-Martinez, J.; Sacristan-Rock, E. Thermal Evaluation of Multi-Antenna Systems Proposed to Treat Bone Tumors: Finite Element Analysis. Sensors 2022, 22, 7604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paré, J.R.J.; Sigouin, M.; Lapointe, J.; Her Majesty the Queen in right of Canada, as represented by the Minister of the Environment, Ottawa, Canada. Microwave Assisted Natural Products Extraction. U.S. Patent 5,002,784, 26 March 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Paré, J.R.J.; Her Majesty the Queen in right of Canada, as represented by the Minister of the Environment, Ottawa, Canada. Microwave-Assisted Generation of Volatiles, of Supercritical Fluid, and Apparatus Therefor. U.S. Patent 5,377,426, 3 January 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Paré, J.R.J.; Her Majesty the Queen in right of Canada, as represented by the Minister of the Environment, Ottawa, Canada. Microwave-Assisted Generation of Volatiles, of Supercritical Fluid, and Apparatus Therefor. U.S. Patent 5,519,947, 28 May 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Paré, J.R.J.; Her Majesty the Queen in right of Canada, as represented by the Minister of the Environment, Ottawa, Canada. Microwave-Assisted Separations Using Volatiles. U.S. Patent 5,675,909, 14 October 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Paré, J.R.J.; Her Majesty the Queen in right of Canada, as represented by the Minister of the Environment, Ottawa, Canada. Microwave-Assisted Separation using Volatiles, and Apparatus Therefor. U.S. Patent 5,732,476, 31 March 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Paré, J.R.J.; Bélanger, J.M.R.; Atlantic Cancer Research Institute. Microwave-Assisted Medical Technologies and Apparatus Therefore. Canadian Patent No. 3,017,029, 3 November 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Paré, J.R.J.; Bélanger, J.M.R.; Atlantic Cancer Research Institute. Microwave-Assisted Medical Technologies and Apparatus Therefore. Japanese Patent No. 6,854,827, 18 March 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, T.; Sabharwal, T.; Lee, M.J.; Watkinson, A.F. (Eds.) Interventional Radiology Techniques in Ablation; Springer: London, UK, 2013; pp. 1–188. [Google Scholar]
- Persson, M.; Fhager, A.; Dobsicek Trefna, H.; Yu, Y.; McKelvey, T.; Pegenius, G.; Karlsson, J.-E.; Elam, M. Microwave-Based Stroke Diagnosis Making Global Prehospital Thrombolytic Treatment Possible. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2014, 61, 2806–2817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paré, J.R.J.; Bélanger, J.M.R.; Punt, M.M.; Her Majesty the Queen in right of Canada as represented by the Minister of the Environment, Ottawa, Canada. Controlled Energy Density Microwave-Assisted Processes. U.S. Patent 6,061,926, 16 May 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Cavagnaro, M.; Amabile, C.; Cassarino, S.; Tosoratti, N.; Pinto, R.; Lopresto, V. Influence of the Target Tissue Size on the Shape of ex vivo Microwave Ablation Zones. Int. J. Hyperth. 2015, 31, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Ablation Conditions | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | Step 2 | Step 3 | Step 4 | Step 5 | ||||||||||||||
| EXP | P | Flow Rate | t | P | Flow Rate | t | P | Flow Rate | t | P | Flow Rate | t | P | Flow Rate | t | Total time | Total Energy | Ethanol Required |
| Conditions | (W) | (mL/min) | (s) | (W) | (mL/min) | (s) | (W) | (mL/min) | (s) | (W) | (mL/min) | (s) | (W) | (mL/min) | (s) | (s) | (J) | (mL) |
| 1 | 100 | 0 | 120 | 120 | 12,000 | 0 | ||||||||||||
| 2 | 100 | 0 | 30 | 0 | 0 | 60 | 100 | 0 | 90 | 180 | 12,000 | 0 | ||||||
| 3 | 100 | 0 | 30 | 0 | 0 | 60 | 100 | 0 | 30 | 100 | 5 | 60 | 180 | 12,000 | 5 | |||
| 4 | 100 | 0 | 30 | 0 | 0 | 60 | 100 | 0 | 30 | 0 | 2.5 | 30 | 100 | 5 | 60 | 210 | 12,000 | 7.5 |
| Ablation Measurements | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EXP | Max. Width | Min. Width | Avg. Width | Max. Height | Min. Height | Avg. Height | Max. Length | Min. Length | Avg. Length | Avg. Rad. | Vol. |
| Conditions | (mm) | (mm) | (mm) | (mm) | (mm) | (mm) | (mm) | (mm) | (mm) | (cm) | (mL) |
| 1 | 22 | 14 | 18 | 41 | 38 | 39 | 17 | 14 | 16 | 1.22 | 5.82 |
| 13 | 10 | 11 | 46 | 41 | 44 | 22 | 10 | 16 | 1.19 | 4.18 | |
| Ave. | 17.3 | 12.0 | 14.7 | 43.7 | 39.4 | 41.6 | 19.6 | 12.2 | 15.9 | 1.2 | 5.0 |
| Std. Dev. | 26.0% | 15.2% | 21.6% | 5.8% | 4.6% | 5.2% | 11.3% | 17.8% | 0.2% | 1.3% | 16.4% |
| Conditions | |||||||||||
| 2 | 20 | 15 | 17 | 36 | 24 | 30 | 19 | 13 | 16 | 1.06 | 4.37 |
| 22 | 13 | 17 | 40 | 23 | 32 | 20 | 10 | 15 | 1.07 | 4.28 | |
| Ave. | 20.8 | 13.8 | 17.3 | 38.4 | 23.5 | 31.0 | 19.3 | 11.6 | 15.5 | 1.1 | 4.3 |
| Std. Dev. | 3.8% | 6.7% | 0.4% | 5.4% | 1.5% | 2.8% | 2.6% | 13.2% | 3.3% | 0.4% | 0.9% |
| Conditions | |||||||||||
| 3 | 28 | 24 | 26 | 37 | 35 | 36 | 25 | 19 | 22 | 1.40 | 10.75 |
| 20 | 14 | 17 | 39 | 24 | 31 | 22 | 19 | 20 | 1.15 | 5.78 | |
| 21 | 12 | 17 | 31 | 19 | 25 | 18 | 10 | 14 | 0.93 | 3.06 | |
| Ave. | 23.2 | 16.7 | 19.9 | 35.5 | 26.1 | 30.8 | 21.6 | 16.1 | 18.8 | 1.2 | 6.5 |
| Std. Dev. | 15.2% | 29.8% | 21.0% | 8.7% | 26.0% | 14.5% | 13.8% | 27.3% | 19.0% | 16.5% | 48.8% |
| Conditions | |||||||||||
| 4 | 28 | 15 | 21 | 41 | 21 | 31 | 28 | 23 | 25 | 1.28 | 8.56 |
| 18 | 14 | 16 | 46 | 23 | 35 | 26 | 14 | 20 | 1.18 | 5.81 | |
| 24 | 6 | 15 | 47 | 24 | 36 | 18 | 10 | 14 | 1.08 | 3.94 | |
| Ave. | 23.2 | 11.7 | 17.4 | 44.7 | 22.7 | 33.7 | 23.8 | 15.7 | 19.7 | 1.2 | 6.1 |
| Std. Dev. | 17.8% | 35.2% | 15.5% | 6.7% | 7.1% | 6.8% | 17.6% | 34.5% | 23.3% | 4.3% | 31.1% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Paré, J.R.J.; Bélanger, J.M.R.; Cormier, G.; Foucher, D.; Thériault, A.; Savoie, J.-C.; Rochas, J.-F. Microwave-Assisted Chemical Ablation (MA-CA): A Novel Microwave-Assisted Tissue Ablation Procedure—Preliminary Assessment of Efficiency. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 7177. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13127177
Paré JRJ, Bélanger JMR, Cormier G, Foucher D, Thériault A, Savoie J-C, Rochas J-F. Microwave-Assisted Chemical Ablation (MA-CA): A Novel Microwave-Assisted Tissue Ablation Procedure—Preliminary Assessment of Efficiency. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(12):7177. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13127177
Chicago/Turabian StyleParé, J. R. Jocelyn, Jacqueline M. R. Bélanger, Gabriel Cormier, Delphine Foucher, Antony Thériault, Jean-Christophe Savoie, and Jean-François Rochas. 2023. "Microwave-Assisted Chemical Ablation (MA-CA): A Novel Microwave-Assisted Tissue Ablation Procedure—Preliminary Assessment of Efficiency" Applied Sciences 13, no. 12: 7177. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13127177
APA StyleParé, J. R. J., Bélanger, J. M. R., Cormier, G., Foucher, D., Thériault, A., Savoie, J.-C., & Rochas, J.-F. (2023). Microwave-Assisted Chemical Ablation (MA-CA): A Novel Microwave-Assisted Tissue Ablation Procedure—Preliminary Assessment of Efficiency. Applied Sciences, 13(12), 7177. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13127177










