Abstract
Ionic gelation is among the simplest processes for the development of chitosan nanoparticles reported so far in the literature. Its one-shot synthesis process in conjunction with the mild reaction conditions required are among the main causes for its success. In this work, we sought to optimize a set of physical parameters associated with the ionic gelation process at two different pH values. Following that, the NPs’ freeze-drying and long-term storage stability were assayed, and their biocompatibility with HaCat cells was evaluated. The results show that NPs were more homogenously produced at pH 5, and that at this pH value, it was possible to obtain a set of optimum production conditions. Furthermore, of the assayed parameters, TPP addition time and overall reaction time were the parameters which had a significant impact on the produced NPs. Nanoparticle freeze-drying led to particle aggregation, and, of the cryoprotectants, assayed mannitol at 10% (w/v) presented the best performance, as the NPs were stable to freeze-drying and maintained their size and charge in the long-term stability assay. Lastly, the chitosan NPs presented no toxicity towards the HaCat cell line.
1. Introduction
Among all biopolymers, chitosan (CS) is among the most interesting ones, as being a polycationic biopolymer obtained from chitin grants it elevated biodegradability, biocompatibility and an almost complete lack of toxicity. This led the FDA to approve it for various biomedical topical applications, particularly in those related to wound healing [1]. Furthermore, the plethora of biological properties presently ascribed to chitosan, namely antimicrobial, make this molecule a highly sought one for the advancement of biomaterial solutions for tissue engineering, wound healing and drug delivery [2,3,4,5,6]. When considering this particular set of characteristics, chitosan was selected as a material of interest for the development of nanoparticles (NPs) [7,8].
Chitosan NP’s production was first described by Ohya, Shiratani [9]. Since then, various NP production methods have appeared, with electrostatic complexation being the most used one, as it permits the production of small-sized NPs with narrow population distributions in a highly reproducible manner in an aqueous solution and without requiring the use of organic solvents or cross-linking agents with known toxicity [10,11]. The formation process per se is based on the protonated amino groups present in chitosan (only in acid medium) interacting through electronic complexation, with anionic compounds such as citrate or (poly)phosphate resulting in the production of the NPs. This method is dubbed ionic gelation and is the preferred one to produce chitosan NPs, especially through the use of the ionic agent sodium tripolyphosphate (TPP) [10,12]. Widely used as a nanometric delivery system for bioactive molecules, chitosan–TPP NPs’ inherent biological properties (non-toxic [13,14,15], antimicrobial activity [16,17,18], mucoadhesivity [19,20] and haemocompatibility [21]) make them an interesting option for various industries, including the cosmetic and textile industries. Additionally, the ionic gelation method is highly controllable and customizable. Authors showed that alterations to chitosan and TPP concentration, environmental pH value and even the biopolymer-to-TPP ratio may alter the size and charge of the produced NPs [22,23]. With this in mind, this work sought to understand how a fixed-point optimization of three physical parameters (TPP addition time, overall reaction time and rotation speed) associated with chitosan NP production at two different pH values would modulate particle charge and size. Additionally, freeze-drying with and without cryoprotectants and long-term storage stability for the optimized NPs produced were also assessed. Finally, considering potential skin related applications, the biocompatibility of the NPs with human keratinocytes was also assessed.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Solutions Preparation and Chemical Origins
Low molecular weight chitosan (LMW, molecular weight (MW) of 107 kDa, deacetylation degree (DD) between 75% and 85%) and Sodium Tripolyphosphate (TPP) were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). Phenazine Methosulfate (PMS) and 2,3-bis (2-methoxy-4-nitro-5-sulfophenyl)-2H-tetrazolium-5-carboxanilide sodium salt (XTT) solution was obtained from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Medium (DMEM) with 4.5 g/L glucose, L-glutamine without pyruvate containing 10% foetal bovine serum (FBS), 1% (v/v) Non-Essential Amino Acids (NEAA) and 1% (v/v) Penicillin-Streptomycin-Fungizone were obtained from Thermofisher (ThermoScientific, Waltham, MA, USA).
2.2. Chitosan–TPP Nanoparticles Production and Optimization
Nanoparticle production occurred via ionic gelation as previously described by Costa and Silva [16] following the blueprint described by their basic procedure and the solutions’ working volumes (4 mL of chitosan, 1 mL of ultra-pure water and 2 mL of TPP). The test parameters of addition time, reaction time, rotation speed and pH value were varied according to Table 1. All assays were performed at room temperature in quadruplicate.

Table 1.
Assayed production parameters.
2.3. NP Characterization
2.3.1. Size and Zeta Potential Determination
Nanoparticles’ average sizes and average zeta potential were determined using a dynamic light scattering (DLS) instrument (Malvern Instruments NanoZSP, Worcestershire, UK) with a disposable folded capillary cell at room temperature (25 °C). All values were determined based on the intensity of distribution. All samples were evaluated in sextuplicate.
2.3.2. FTIR-ATR Analysis
The IR spectra of the chitosan NPs and their individual constituents were recorded using a Fourier transform infrared spectrometer with a horizontal attenuated total reflectance (FTIR-ATR) (PerkinElmer Spectrum-100), an (ATR) accessory and a diamond/ZnSe crystal. All samples’ spectra were acquired with 128 scans and 32 cm−1 resolution in the region of 4500 to 450 cm−1. Each sample was analysed in triplicate.
2.4. Nanoparticles Freeze-Drying and Long-Term Storage Stability
The effect of freeze-drying was assessed over the produced chitosan nanoparticles in the presence and absence of cryoprotectants. The cryoprotectants tested were mannitol, glucose and sorbitol (10, 5 and 2.5 (w/v)). After the addition of cryoprotectants, they were aliquoted and frozen overnight. Following this, samples were freeze-dried using a Christ Alpha 1–4 (B. Braun Biotech International, Berlin, Germany).
Long-term storage stability tests were performed over a three-month study. After freeze-drying, the samples were kept at room temperature and protected from light. After 30, 60 and 90 days, aliquots from samples were obtained, and freeze-dried nanoparticles were reconstituted by slowly adding distilled water and gently stirring with a roll and tilt mixer (Movil-Rod, J.P. Selecta, Barcelona, Spain) until complete dissolution was obtained.
Sample stability was assessed through physical properties analysis using DLS scattering, as referred to in Section 2.3.1.
2.5. Cellular Assays
2.5.1. Cell Lines and Culture Conditions
Human keratinocyte cell lines (HaCat; used between passages 45 and 55) were obtained from Cell Line Services (Appenheim, Denmark) and grown as monolayers at 37 °C in 95% air and 5% CO2 as well as in DMEM with 10% (v/v) FBS and 1% (v/v) Penicillin-Streptomycin-Fungizone.
2.5.2. XTT Assay
The nanoparticles’ biocompatibility against HaCat cells was evaluated through analysis of their impact on cellular metabolism using the XTT viable dye, as previously described [24,25]. Briefly, cells were seeded at 1 × 105 cells/mL in a 96-well microplate and, after 24 h, the media was replaced with media with NPs (7 mg/mL to 0.5 mg/mL). After 24 h, XTT solution was added, and cells were incubated for 2 h. The optical density (OD) at 485 nm was measured using a microplate reader (FLUOstar, OPTIMA, BMG Labtech, Ortenberg, Germany). All assays were performed in quintuplicate.
2.5.3. LDH Assay
The nanoparticles’ impact on cellular integrity was evaluated using the LDH leakage assay, as previously described [26]. Following exposure of cells to nanoparticles (7 mg/mL to 0.5 mg/mL), the volume of LDH in the medium was determined using a commercial kit from ThermoScientific (Rockford, IL, USA). Data were processed according to the manufacturer’s instructions, and the results were given according to the following equation:
% Cytotoxicity = [(Compound treated LDH activity − Spontaneous LDH
activity)/(Maximum LDH activity − Spontaneous LDH activity)] × 100
activity)/(Maximum LDH activity − Spontaneous LDH activity)] × 100
2.6. Statistical Analysis
The statistical analysis of the data obtained was performed using IBM SPSS Statistics v21.0.0 (New York, NY, USA). Considering that the data followed a normal distribution, results were analysed using a one-way ANOVA coupled with Turkey’s post hoc test, with differences being considered significant for p-values below 0.05.
3. Results
3.1. Nanoparticles Production Optimization
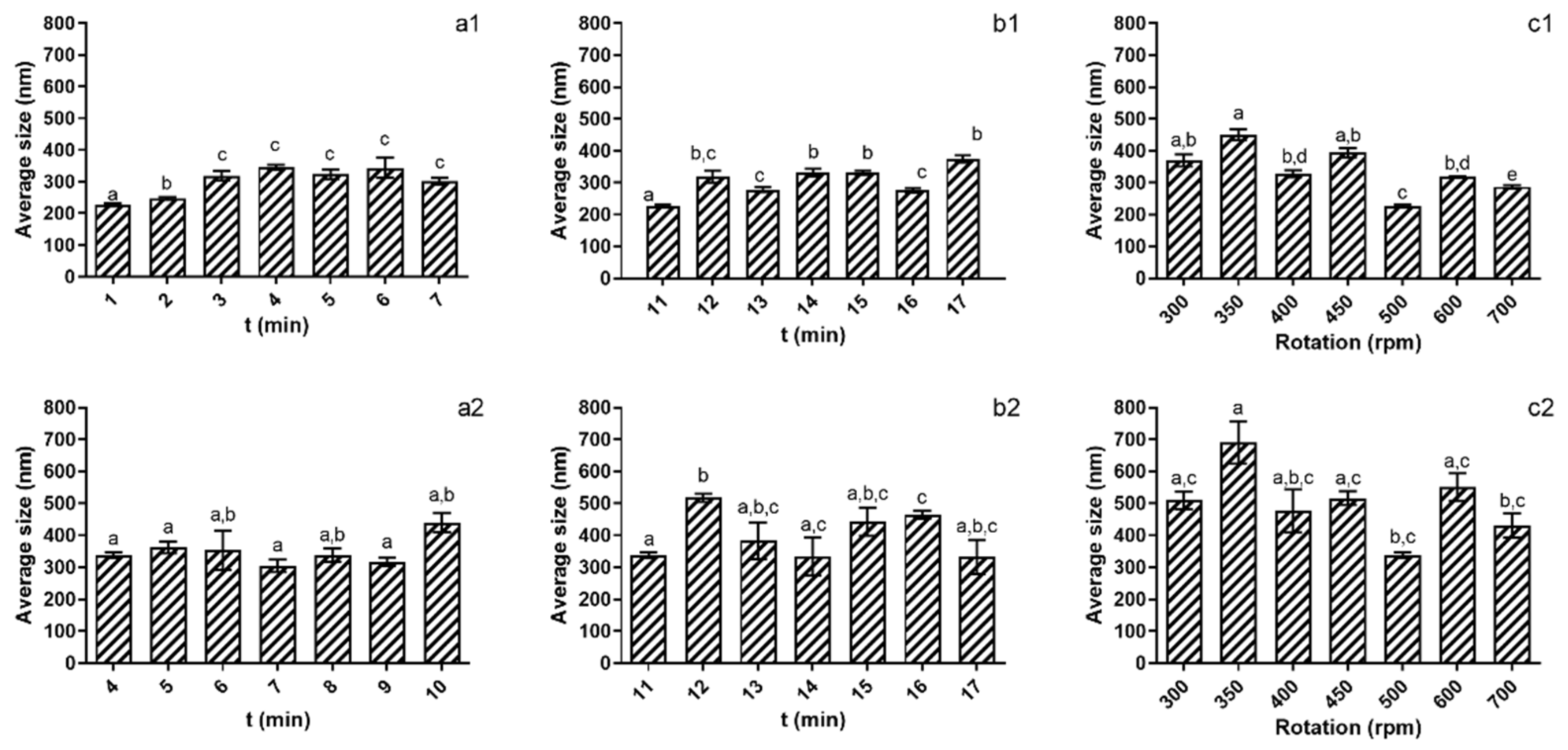
The impact of the studied variables on the nanoparticles was evaluated through size and ZP analysis using DLS scattering. The results regarding the optimization parameters effect on particle size can be seen in Figure 1.
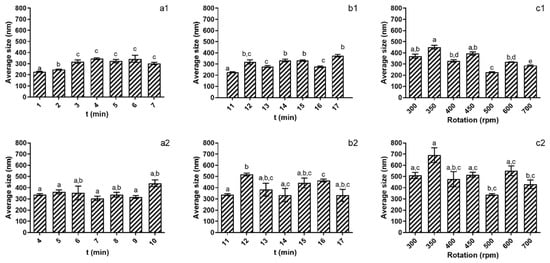
Figure 1.
Evaluation of the studied parameters on nanoparticles’ size at pH 5 (1) and pH 4 (2). (a)—TPP addition time; (b)—Reaction time; (c)—rotation speed. Different letters represent the statistical differences found between conditions assayed.
Comparing the results obtained at both pH values tested, it is possible to see that at pH 4 (Figure 1(a2,b2,c2)), it was not possible to ascertain optimal conditions for the assayed parameters. As for addition time, reaction time and rotation speed, no significant differences (p > 0.05) were registered. On the other hand, for pH 5 (Figure 1(a1,b1,c1)) it is possible to see that among the parameters assayed, the 4 min of addition time, 11 min of reaction time and 500 rpm of rotation speed presented NPs with significantly (p < 0.05) smaller sizes. On a condition-by-condition analysis, one can see that when regarding the TPP addition time (Figure 1(a1)) from 4 min of addition time onwards, particle size increased, with the NPs’ size increase reaching a maximum value of 345.1 nm (±7845 nm) at 7 min of addition time. From 7 to 10 min of addition time, the nanoparticles’ average size fluctuated slightly, but this was not significant (p > 0.05). When considering the reaction times assayed, the standout condition was 11 min, as it produced NPs that were significantly (p < 0.05) smaller than NPs obtained in the remaining conditions assayed. Lastly, regarding rotation speed, a similar behaviour was observed, as at 500 rpm, the NPs produced were statistically significantly smaller (p < 0.05), with size differences reaching almost 100 nm compared to the next smallest particles produced.
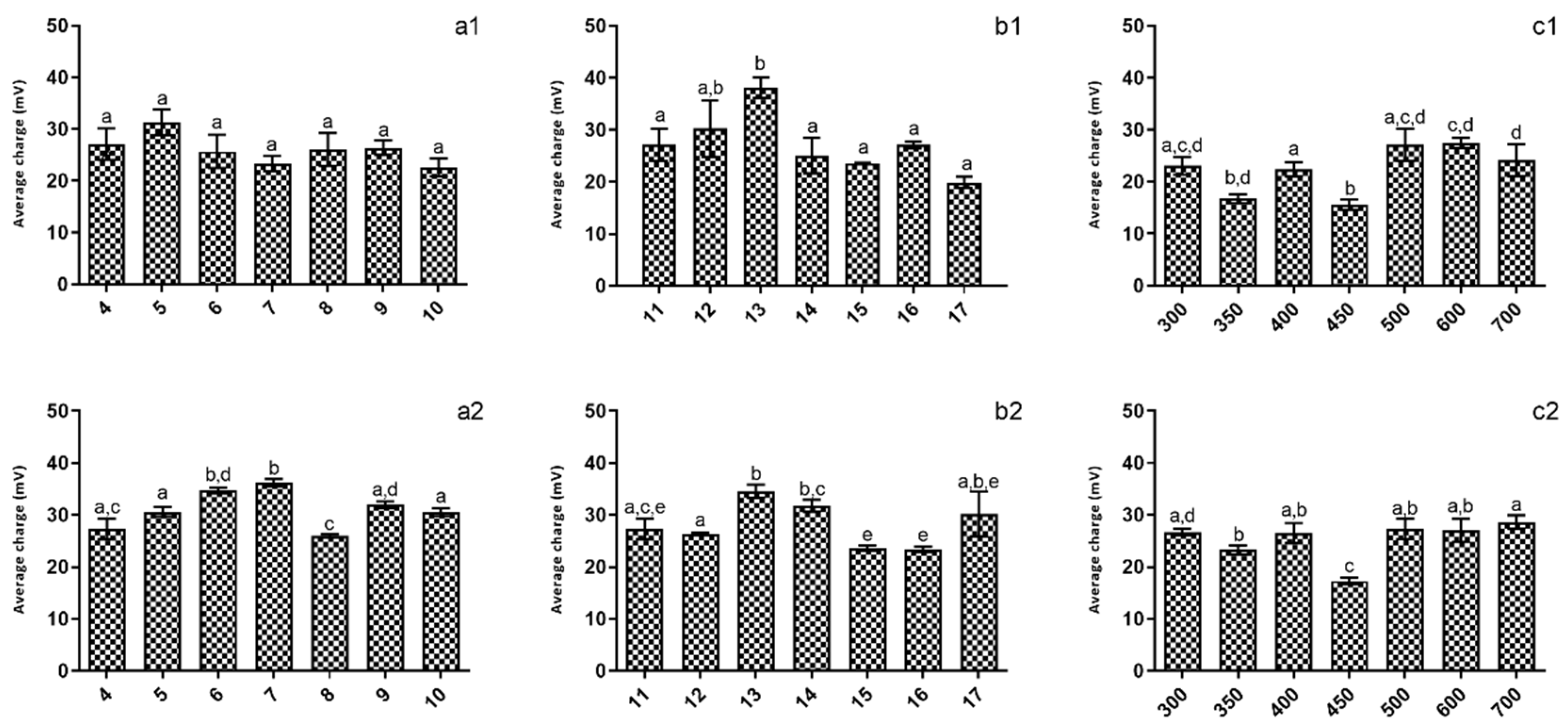
When considering the impact of production conditions on the chitosan NPs’ charge (Figure 2), it is possible to see that for both tested pH values, it was not possible to ascertain any optimum production conditions, as no significant (p > 0.05) differences were registered.
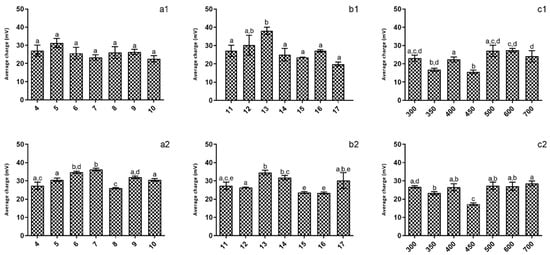
Figure 2.
Evaluation of the studied parameters on nanoparticles’ charges at pH 5 (1) and pH 4 (2). (a)—TPP addition time; (b)—Reaction time; (c)—rotation speed. Different letters represent the statistical differences found between conditions assayed.
Based on the results obtained both for NP size and charge, the optimum conditions for their production were defined as being pH 5, 4 min of addition time, 11 min of reaction time and 500 rpm of rotation speed, as they individually produced the smallest particles in each of their individual assays. The conjunction of these parameters produced NPs with an average size of 226.6 ± 5.2 nm, a PDI of 0.339 and a ZP of +27.1 ± 3.1. Nanoparticles produced under these conditions were used for all of the remaining assays.
3.2. FTIR-ATR Analysis
The NPs produced under optimized conditions were validated through FTIR analysis. As can be seen in Table 2, six characteristic chitosan peaks can be observed (3320, 1655, 1581, 1413, 1374 and 1061 cm−1), which correspond to O-H stretching, stretching C=O from amide I, N-H bending and C-N stretching from amide II, -CH2 bending, -CH3 symmetrical deformation and skeletal vibration of C-O stretching, respectively. For TPP, four characteristic peaks were identified (1210, 1130, 1090 and 888 cm−1) that correspond to the stretching vibration of P=O, the symmetric and anti-symmetric vibration of O-P=O, PO3 symmetric and anti-symmetric vibration and the P-O-P bridge stretching vibration, respectively [27,28].

Table 2.
Peaks identified for the tested samples in the FTIR assay.
Regarding the chitosan NPs formed, it is possible to observe the peaks representing the NPs characteristic increased hydrogen bonding (3292–3356 cm−1), the pyranose ring’s asymmetric and symmetric CH2 vibration (2910 cm−1), the C=O (1657 cm−1) and the C=O symmetric (1397 cm−1) stretching in the NPs and the amide I peak (1373 cm−1). The characteristic chitosan–TPP interactions peaks start with the P=O stretching (at 1100 cm−1), followed by the C-C-C skeletal linkage (1066 cm−1), the P–O for PO4 and COH stretching (1056 cm−1), the C–N vibrations (1028 cm−1) and the N-H deformations’ vibrations (890 cm−1), with the latter representing the interaction between CS and TPP. Lastly, at 1586 cm−1, the peak representing the chitosan-TPP crosslinking was observed, and that indicated the interaction of TPP with the chitosan amino groups [29,30,31].
3.3. Freeze-Drying and Storage Evaluation
The results regarding the freeze-drying impact on the particle stability can be observed in Table 3. Comparing the NP size and charge before and after freeze-drying, it is possible to see that the process led to the increase in particle size by ca. 23% of the PDI, indicating that particle aggregation occurred and, therefore, a reduction of the particles’ ZP was observed.

Table 3.
Chitosan nanoparticles’ physical characteristics before and after freeze-drying.
Considering the particle aggregation observed, several cryoprotectants were assayed. As can be seen from Table 4, of the three cryoprotectants tested, only mannitol was a viable alternative. As for sorbitol and glucose, the freeze-drying process originated an aggregated, viscous product that was not suitable for later assays.

Table 4.
Effect of the selected cryoprotectants on the NP freeze-drying process.
Analysing the results obtained for the various mannitol concentrations assayed, it is possible to see that the best performance was obtained with 10% mannitol, with the freeze-dried NPs obtained under these conditions being similar (p > 0.05) to the ones obtained before freeze-drying. For the other mannitol concentrations tested, the results obtained showed that NPs lost some ZP, and some particle aggregation was observed.
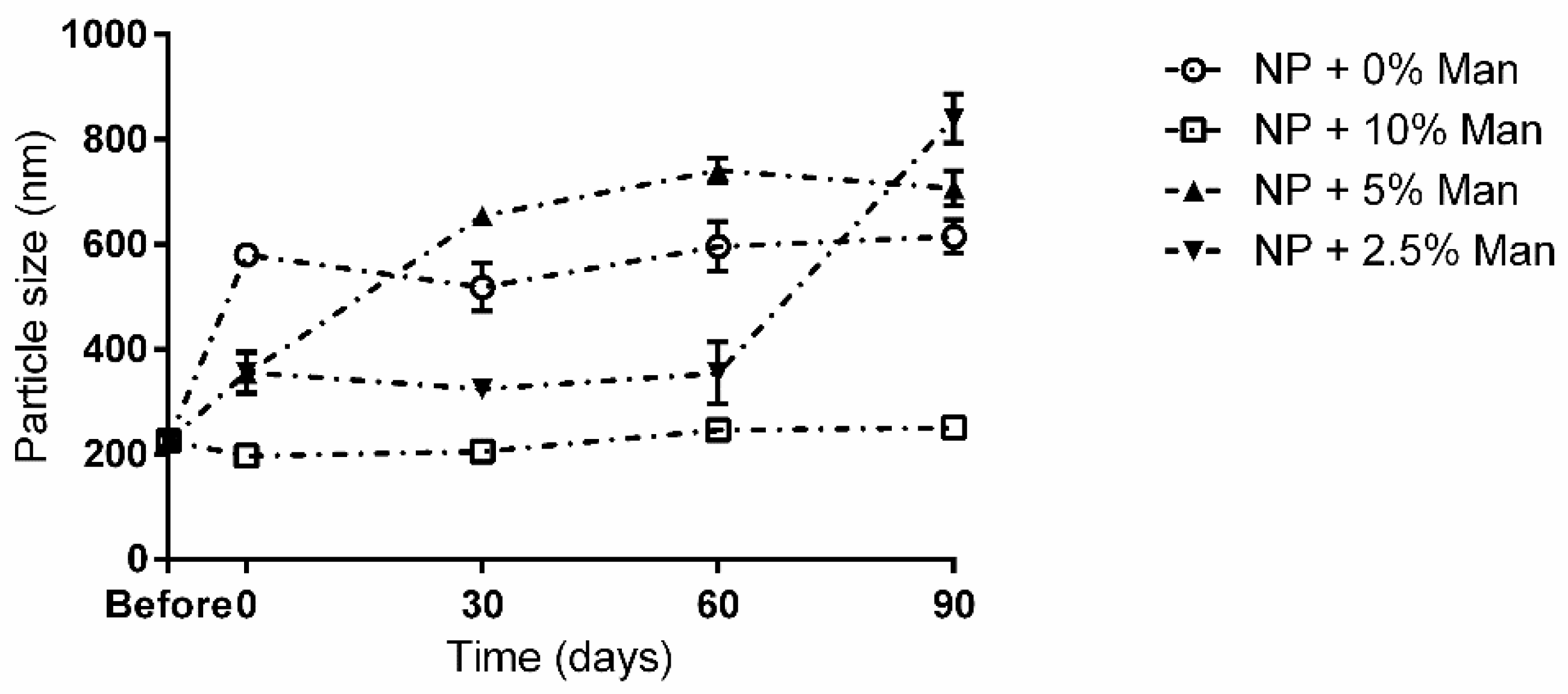
When analysing the stability of the viable formulations over 90 days, it is possible to see that in terms of particle size (Figure 3), when freeze-dried in the presence of 10% mannitol, the NPs remained stable up to the 90-day mark with no significant differences (p < 0.05) being observed.
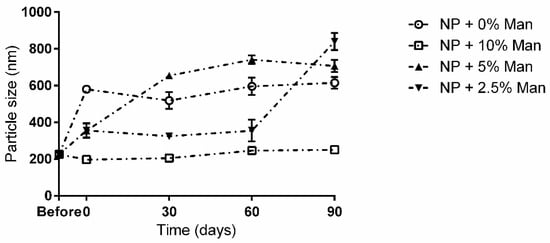
Figure 3.
Long term storage impact on NP size in the presence and absence of mannitol. ○—NPs without cryoprotectant; ☐—NPs with 10% (w/v) mannitol; ▲—NPs with 5% (w/v) mannitol; ▼—NPs with 2.5% (w/v) mannitol.
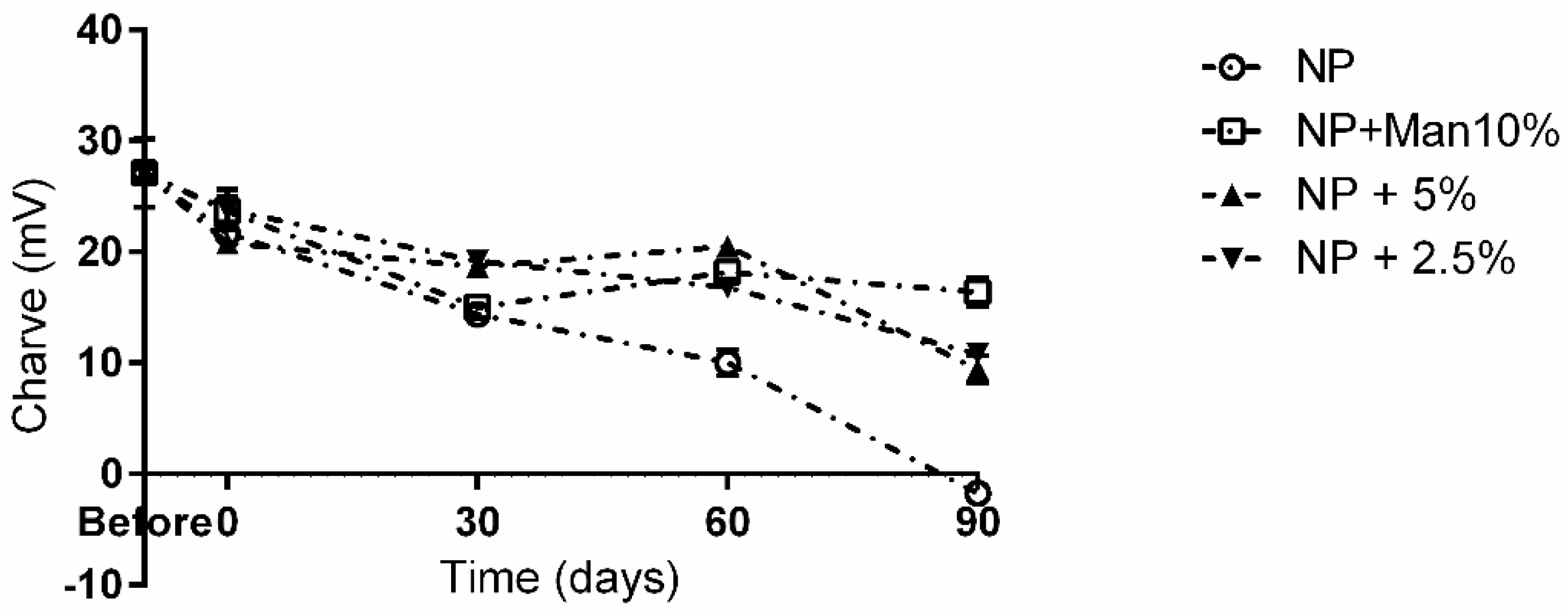
For the remaining conditions, at 90 days, NPs appeared to be completely aggregated, with particle sizes varying between 600 and 850 nm. Interestingly, up to the 60-day mark, NPs freeze-dried with 2.5% (m/v) appeared to be stable despite a small increase in size (p < 0.05) being observed immediately after freeze-drying. Regarding the evolution of the particles’ charges over the storage time (Figure 4), it is possible to see that for all tested conditions, there was a significant (p < 0.05) drop in ZP.
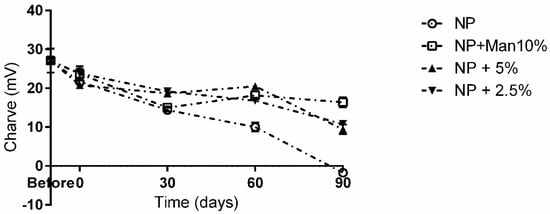
Figure 4.
Long term storage impact on NP charge in the presence and absence of mannitol. ○—NPs without cryoprotectant; ☐—NPs with 10% (w/v) mannitol; ▲—NPs with 5% (w/v) mannitol; ▼—NPs with 2.5% (w/v) mannitol.
Once again, at the 90-day mark, the best performance was obtained in the presence of 10% (m/v) mannitol, with a drop of ca. 9 mV being registered, whereas the worst result was observed for the unprotected particles, where a drop of ca. 28 mV was observed, and the ZP at the 90-day mark was −1.71 mV.
3.4. Biocompatibility Assays
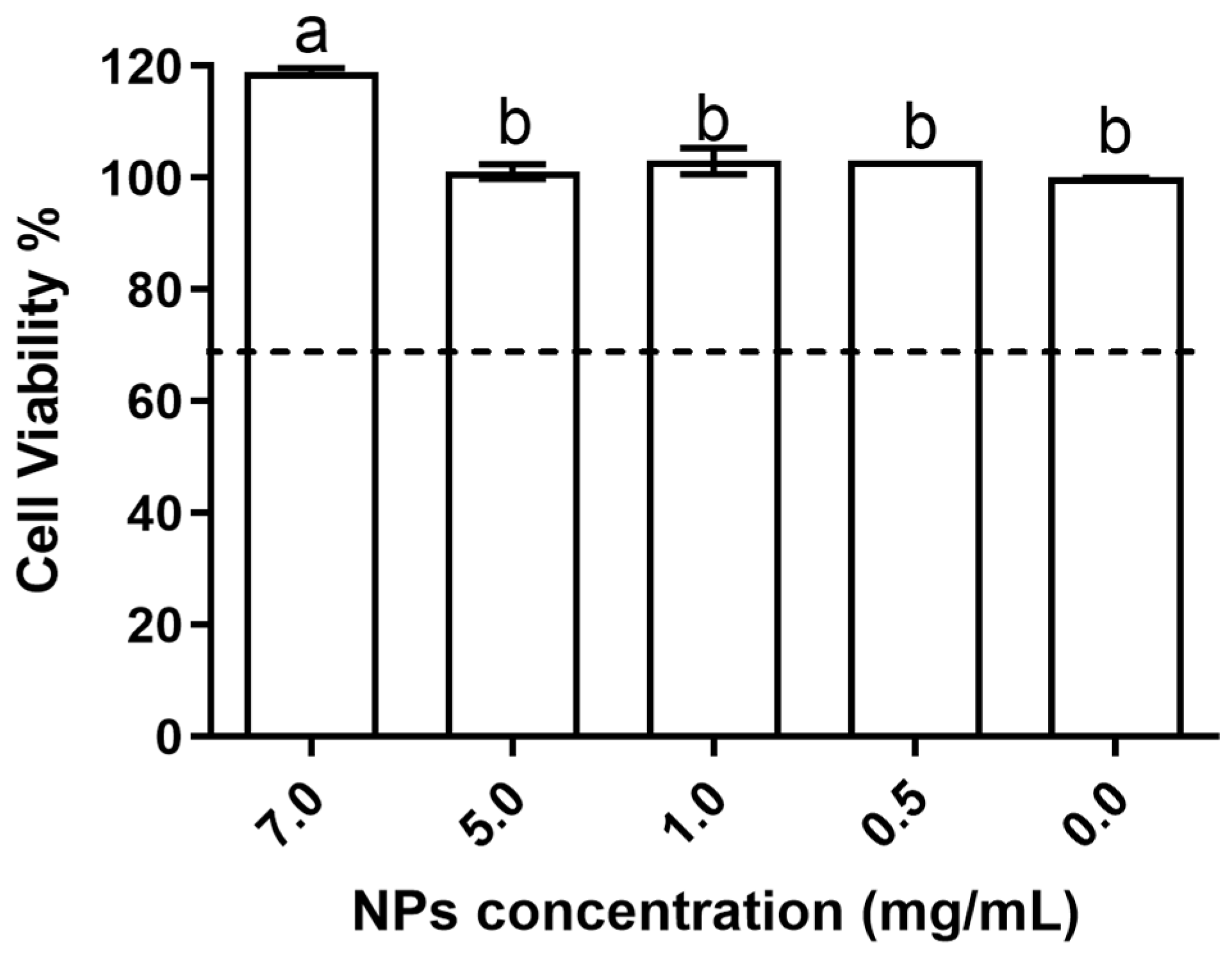
The biocompatibility results obtained show that the evaluated nanoparticles had no deleterious effects on the studied cell line. The data obtained for the impact on cellular metabolism (Figure 5) showed that when comparing the conditions for chitosan NPs with the control (no chitosan—0 mg/mL in the figure), it is possible to see that all tested concentrations were biocompatible with the HaCat cells.
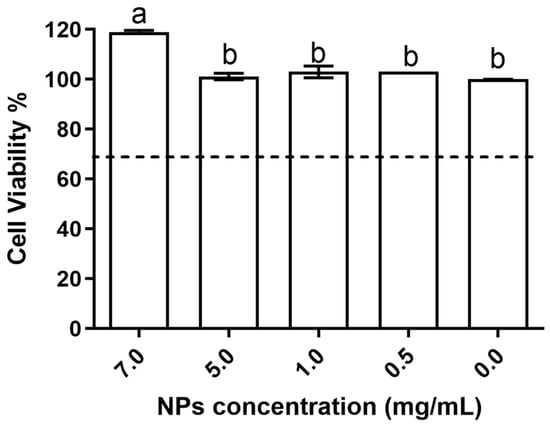
Figure 5.
Produced NPs’ biocompatibility with the HaCat cell line at the tested concentrations. Results given in terms of cell viability %. Different letters represent the statistical differences found between conditions assayed. The dotted line represents the 30% cytotoxicity limit as defined by the ISO 10993-5:2009 standard [32].
In fact, in up to 5 mg/mL of NPs, no statistically significant differences (p > 0.05) were observed relative to the control, whereas at 7 mg/mL, the results obtained were significantly (p < 0.05) higher than the those obtained in all of the other assayed conditions; thus, this indicated a rise in cellular metabolism and possibility a promotion of cellular viability.
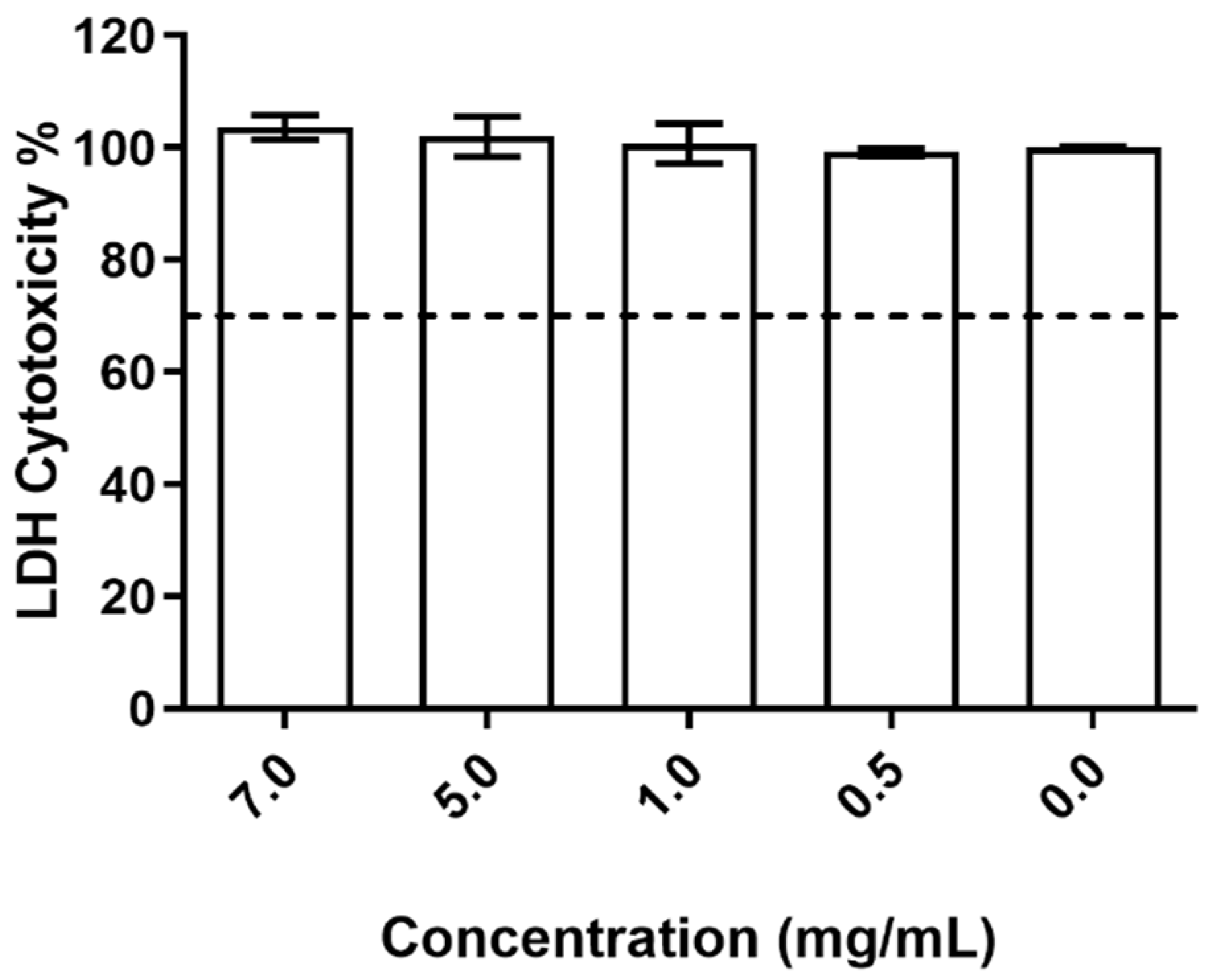
In relation to the impact on cell membrane integrity, the data obtained (Figure 6) shows that the studied nanoparticles had no deleterious effect on the HaCat cell wall, with no relevant releases of LDH being detected and no statistical differences being registered between all tested conditions.
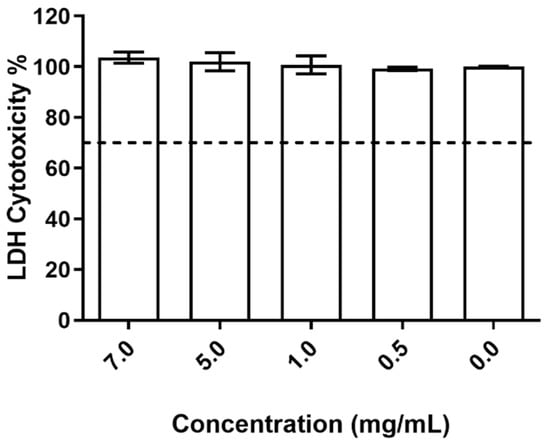
Figure 6.
Evaluation of the produced NPs on HaCat cell wall integrity at the different concentrations tested. The dotted line represents the 30% cytotoxicity limit as defined by the ISO 10993-5:2009 standard [32].
4. Discussion
Chitosan’s quick gelling ability on contact with polyanions relies on the creation of inter- and intramolecular cross-linkages mediated by polyanions. This process was shown to be easy to modulate through variation of intrinsic or extrinsic variables, leading to the production of particles with different sizes and charges. Although most previous works focused on the modulation of reaction intrinsic factors (such as chitosan and TPP concentration, chitosan MW or chitosan-to-TPP ratio) [22,23,33,34], this work focused on four reaction extrinsic factors. Of the studied factors, the best described in the literature is environmental pH value, as it was described as being fundamental to ionic gelation, with high pH values leading to chitosan deprotonation. This, in turn, will not be able to interact ionically with TPP’s tripolyphosphoric ions. In fact, Fan and Yan [34] showed that at pH values below 4.5, it was difficult to obtain a unimodal NP population, whereas at pH values above 5.2, microparticle formation occurred. Similarly, Gan and Wang [22] stated that at higher pH values, NPs with large size are produced, as deprotonation leads to lower electrostatic repulsion and thereby increases the probability of particle aggregation. Nasti, Zaki [33] showed that when the pH value is three, there is a scarcity of NPs produced due to the TPP’s decreasing charge density. This behaviour is in line with the results reported in this work, as NPs were only stably produced at pH 5. Interestingly, the influence of the pH value on the NPs’ ZP is quite contentious, as some authors have stated that the environmental pH has no effect on NP ZP as long as it stays within the range where stable NPs are produced [33], whereas others have described NP ZP as being highly sensitive to environmental pH value variation [22]. When considering the other assayed factors, the existing body of work is almost non-existent. Fàbregas, Miñarro [35] reported rotation speed as being a significant factor in NP formation, and Fan, Yan [34] reported that an increase in rotation speed from 200 to 800 rpm led to a narrowing in particle size distribution, which is probably due an acceleration in TPP dispersion and a shear force increase which, in turn, improves monodispersity. Similarly, Thandapani, P [36] reported that an increase from 200 to 600 rpm led to a reduction of particle size, whereas further increases in rotation speed had no effects. This falls in line with the results obtained at pH 5, as the increase of rotation speed created smaller NPs. Furthermore, the existence of a spot of activity at 500 rpm is similar to the pattern observed by Thandapani, P [36], as in their work, they also reported an optimum rotation speed for their test conditions. On the other hand, for addition and reaction time, our results contradict previous research, as these were found to be non-influential in NP formation [35,36].
The FTIR data obtained showed that chitosan and TPP interacted at a molecular level, an observation which is in line with previous works, and the spectra acquired showed the previously reported chitosan and TPP electrostatic interaction and subsequent complex formation [27,30,37].
Freeze-drying is one of the most common techniques used to ensure long term stability of polymeric NPs, as storage in aqueous suspension leads to solubilisation and/or degradation of the polymers, and dried NPs are more easily redispersed. However, freeze-drying has some drawbacks, as aggregation or fusion of NPs may occur, and the formation of ice crystals may lead to their destabilization [23]. These drawbacks were evident in this work, as NPs’ size and PDI levels rose after freeze-drying, which is a possible consequence of aggregation due to strong inter- and intramolecular hydrogen bonding. This was also reported by Diop, Auberval [38] and Abdelwahed Abdelwahed, Degobert [39], but was contrary to the findings of Thandapani, P [36], who reported that freeze-drying led to a decrease in particle size. These differences may be attributed to various factors, such as chitosan purity, deacetylation degree, reaction ratios or even to the centrifugation as executed by Thandapani, P [36] in the end of the NP formation process and prior to freeze-drying. This may have removed any remaining non-reacted chitosan that, with the protonated amino groups, may have contributed to the NPs’ aggregation during freeze-drying. In an effort to protect NPs during this process, cryoprotectants were employed. The usage of sugars as cryoprotectants is widely described in the literature, as their addition prior to freeze-drying allows them to interact with the solute via hydrogen bonding, which will maintain the solute in a “pseudo hydrated” state during the dehydrating process, thus protecting the NPs from damage [23]. Of the tested cryoprotectants, only mannitol was able to prevent NP aggregation. This could be related to peculiar characteristics between sugars [23]. Furthermore, these results are in line with the work of Diop, Auberval [38], where mannitol was successfully used as a cryoprotectant for chitosan NPs. It formed an envelope around the particles and, thus, inhibited aggregation. In addition, as it is neutral in terms of charge, it did not modify the NPs’ ZP. However, and as seen in this work, cryoprotectant concentration also plays a key role in NPs stabilization. Rampino, Borgogna [23] showed that at least a 5% (w/v) concentration of cryoprotectant was required, whereas Abdelwahed, Degobert [39] stated that high cryoprotectant concentrations may destabilize NPs and lead to their aggregation.
Chitosan NPs’ biocompatibility is also a contentious topic in the literature. Thandapani, P [36] found them non-toxic for MCF-12F cells, and MubarakAli, LewisOscar [40] found similar results for the HeLa cell line. Janes, Fresneau [41] reported no toxicity on C26 murine colorectal carcinoma and A375 human melanoma cell lines, Grenha, Grainger [14] showed that there was no NP-based toxicity towards lung epithelial cells and De Campos, Diebold [15] reported no toxicity towards conjunctival epithelial cells, all results in line with those here observed for the HaCat cell line. On the other hand, Nasti, Zaki [33] reported chitosan NPs as being responsible for decreases in viability for two murine cell lines (J774 macrophages and L929 fibroblasts), and Vllasaliu, Exposito-Harris [13], despite reporting NPs as being less toxic than chitosan, still found some toxicity towards the Calu-3 cell line. The authors attributed this cytotoxicity to NPs entering the cells, thereby leading to a toxic effect directly affecting cell metabolism. Considering that the methodology employed in this work to measure cell viability was a metabolism-based one, as the assay was based on mitochondrial dehydrogenase capacity to reduce XTT and produce a spectrophotometrically measurable orange formazan product [42], it is possible that this internalisation and consequent toxicity on the cells’ metabolism did not occur for the HaCat cells in contact with chitosan NPs.
5. Conclusions
Overall, the present work demonstrates that the chitosan TPP ionic gelation method was passive to modulation by the physical parameters at play in the reaction, and that it was possible to obtain an optimized procedure. Furthermore, it was also possible to see that, of the assayed parameters, the ones that had significant influence on NP production were the addition time and reaction time, and that the environmental pH value was also critical in obtaining a homogeneous NP population. Additionally, the NPs’ stability through freeze-drying and storage required the addition of a cryoprotectant, with the best solution being mannitol at 10 (w/v). Lastly, as the produced NPs presented no toxicity against the HaCat cell line, the possibility is open for the application of this optimization process in an industrial setting.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.S. and E.M.C.; methodology, S.S. and E.M.C.; validation, M.P.; writing—original draft preparation, E.M.C.; writing—review and editing, E.M.C. and S.S.; supervision, M.P.; funding acquisition, E.M.C. and M.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by FUNDAÇÃO PARA A CIENCIA E A TECNOLOGIA through grant number UIDB/50016/2020 and E.M. Costa’s PhD fellowship (SFRH/BDE/103957/2014) and through QREN-ANI via project 17819.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to confidentiality agreements.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Kumar, A.; Vimal, A. Why Chitosan? From properties to perspective of mucosal drug delivery. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 91, 615–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabea, E.I.; Badawy, M.E.; Stevens, C.V.; Smagghe, G.; Steurbaut, W. Chitosan as antimicrobial agent: Applications and mode of action. Biomacromolecules 2003, 4, 1457–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, M.N.V.R. A review of chitin and chitosan applications. React. Funct. Polym. 2000, 46, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raafat, D.; Sahl, H.G. Chitosan and its antimicrobial potential--a critical literature survey. Microb. Biotechnol. 2009, 2, 186–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anitha, A.; Divya Rani, V.V.; Krishna, R.; Sreeja, V.; Selvamurugan, N.; Nair, S.V.; Tamura, H.; Jayakumar, R. Synthesis, characterization, cytotoxicity and antibacterial studies of chitosan, O-carboxymethyl and N,O-carboxymethyl chitosan nanoparticles. Carbohydr. Polym. 2009, 78, 672–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soleimani, N.; Mobarez, A.M.; Olia, M.S.J.; Atyabi, F. Synthesis, characterization and effect of the antibacterial activity of chitosan nanoparticles on vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus and other gram negative or gram positive bacteria. Int. J. Pure Appl. Sci. Technol. 2015, 26, 14. [Google Scholar]
- Ing, L.Y.; Zin, N.M.; Sarwar, A.; Katas, H. Antifungal Activity of Chitosan Nanoparticles and Correlation with Their Physical Properties. Int. J. Biomater. 2012, 2012, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madureira, A.R.; Pereira, A.; Castro, P.M.; Pintado, M. Production of antimicrobial chitosan nanoparticles against food pathogens. J. Food Eng. 2015, 167, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohya, Y.; Shiratani, M.; Kobayashi, H.; Ouchi, T. Release behavior of 5-fluorouracil from chitosan-gel nanospheres immobilizing 5-fluorouracil coated with polysaccharides and their cell specific cytotoxicity. J. Macromol. Sci. Part A 1994, 31, 629–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bugnicourt, L.; Ladavière, C. Interests of chitosan nanoparticles ionically cross-linked with tripolyphosphate for biomedical applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2016, 60, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, T.; Mitra, S.; Kumar Singh, A.; Kumar Sharma, R.; Maitra, A. Preparation, characterization and biodistribution of ultrafine chitosan nanoparticles. Int. J. Pharm. 2002, 243, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grenha, A. Chitosan nanoparticles: A survey of preparation methods. J. Drug Target. 2012, 20, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vllasaliu, D.; Exposito-Harris, R.; Heras, A.; Casettari, L.; Garnett, M.; Illum, L.; Stolnik, S. Tight junction modulation by chitosan nanoparticles: Comparison with chitosan solution. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 400, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grenha, A.; Grainger, C.I.; Dailey, L.A.; Seijo, B.; Martin, G.P.; Remuñán-López, C.; Forbes, B. Chitosan nanoparticles are compatible with respiratory epithelial cells in vitro. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2007, 31, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Campos, A.M.; Diebold, Y.; Carvalho, E.L.S.; Sánchez, A.; Alonso, M.J. Chitosan nanoparticles as new ocular drug delivery systems: In vitro stability, in vivo fate, and cellular toxicity. Pharm. Res. 2004, 21, 803–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, E.M.; Silva, S.; Vicente, S.; Neto, C.; Castro, P.M.; Veiga, M.; Madureira, R.; Tavaria, F.; Pintado, M.M. Chitosan nanoparticles as alternative anti-staphylococci agents: Bactericidal, antibiofilm and antiadhesive effects. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 79, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, S.W.; Joshi, M.; Rajendran, S. Modulation of Size, Shape and Surface Charge of Chitosan Nanoparticles with Reference to Antimicrobial Activity. Adv. Sci. Lett. 2010, 3, 452–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.-L.; Niu, S.-S.; Xu, Y.-L.; Xu, Z.-R.; Fan, C.-L. Antibacterial activity of chitosan tripolyphosphate nanoparticles loaded with various metal ions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2009, 75, 385–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudhani, A.R.; Kosaraju, S.L. Bioadhesive chitosan nanoparticles: Preparation and characterization. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 81, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Li, J.; Kong, M.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, X.J.; Li, Y.; Park, H.J.; Chen, X.G. Surface charge effect on mucoadhesion of chitosan based nanogels for local anti-colorectal cancer drug delivery. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 128, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadesh, R.; Narayanan, D.; Pr, S.; Vadakumpully, S.; Mony, U.; Koyakkutty, M.; Nair, S.V.; Menon, D. Hematotoxicological analysis of surface-modified and -unmodified chitosan nanoparticles. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2013, 101, 2957–2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, Q.; Wang, T.; Cochrane, C.; McCarron, P. Modulation of surface charge, particle size and morphological properties of chitosan–TPP nanoparticles intended for gene delivery. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2005, 44, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rampino, A.; Borgogna, M.; Blasi, P.; Bellich, B.; Cesàro, A. Chitosan nanoparticles: Preparation, size evolution and stability. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 455, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, E.M.; Pereira, C.F.; Ribeiro, A.A.; Casanova, F.; Freixo, R.; Pintado, M.; Ramos, O.L. Characterization and Evaluation of Commercial Carboxymethyl Cellulose Potential as an Active Ingredient for Cosmetics. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 6560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, E.M.; Silva, S.; Veiga, M.; Baptista, P.; Tavaria, F.K.; Pintado, M.E. Textile dyes loaded chitosan nanoparticles: Characterization, biocompatibility and staining capacity. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 251, 117120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, E.M.; Silva, S.; Tavaria, F.K.; Pintado, M. Insights into the Biocompatibility and Biological Potential of a Chitosan Nanoencapsulated Textile Dye. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashad, R.A.; Ishak, R.A.H.; Fahmy, S.; Mansour, S.; Geneidi, A.S. Chitosan-tripolyphosphate nanoparticles: Optimization of formulation parameters for improving process yield at a novel pH using artificial neural networks. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 86, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loutfy, S.A.; Alam El-Din, H.M.; Elberry, M.H.; Allam, N.G.; Hasanin, M.T.M.; Abdellah, A.M. Synthesis, characterization and cytotoxic evaluation of chitosan nanoparticles: In vitro liver cancer model. Adv. Nat. Sci. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2016, 7, 035008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, J.J.; Sangeetha, D.; Gomathi, T. Sunitinib loaded chitosan nanoparticles formulation and its evaluation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 82, 952–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, J.; Majeed, H.; Williams, P.A.; Safdar, W.; Zhong, F. Formation of chitosan nanoparticles to encapsulate krill oil (Euphausia superba) for application as a dietary supplement. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 63, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, K.; Hu, Q. Biomimetic multi-layered hollow chitosan-tripolyphosphate rod with excellent mechanical performance. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 37346–37352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO. Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices in Tests for In Vitro Cytotoxicity; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009; p. 34. [Google Scholar]
- Nasti, A.; Zaki, N.M.; de Leonardis, P.; Ungphaiboon, S.; Sansongsak, P.; Rimoli, M.G.; Tirelli, N. Chitosan/TPP and Chitosan/TPP-hyaluronic Acid Nanoparticles: Systematic Optimisation of the Preparative Process and Preliminary Biological Evaluation. Pharm. Res. 2009, 26, 1918–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, W.; Yan, W.; Xu, Z.; Ni, H. Formation mechanism of monodisperse, low molecular weight chitosan nanoparticles by ionic gelation technique. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2012, 90, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fàbregas, A.; Miñarro, M.; García-Montoya, E.; Pérez-Lozano, P.; Carrillo, C.; Sarrate, R.; Sánchez, N.; Ticó, J.R.; Suñé-Negre, J.M. Impact of physical parameters on particle size and reaction yield when using the ionic gelation method to obtain cationic polymeric chitosan–tripolyphosphate nanoparticles. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 446, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thandapani, G.; Prasad, S.; Sudha, P.N.; Sukumaran, A. Size optimization and in vitro biocompatibility studies of chitosan nanoparticles. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 104, 1794–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galante, R.; Rediguieri, C.F.; Kikuchi, I.S.; Vasquez, P.A.S.; Colaço, R.; Serro, A.P.; Pinto, T.J.A. About the Sterilization of Chitosan Hydrogel Nanoparticles. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0168862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diop, M.; Auberval, N.; Viciglio, A.; Langlois, A.; Bietiger, W.; Mura, C.; Peronet, C.; Bekel, A.; Julien David, D.; Zhao, M.; et al. Design, characterisation, and bioefficiency of insulin–chitosan nanoparticles after stabilisation by freeze-drying or cross-linking. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 491, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelwahed, W.; Degobert, G.; Stainmesse, S.; Fessi, H. Freeze-drying of nanoparticles: Formulation, process and storage considerations. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2006, 58, 1688–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MubarakAli, D.; LewisOscar, F.; Gopinath, V.; Alharbi, N.S.; Alharbi, S.A.; Thajuddin, N. An inhibitory action of chitosan nanoparticles against pathogenic bacteria and fungi and their potential applications as biocompatible antioxidants. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 114, 323–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janes, K.A.; Fresneau, M.P.; Marazuela, A.; Fabra, A.; Alonso, M.J. Chitosan nanoparticles as delivery systems for doxorubicin. J. Control. Release 2001, 73, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martens, J.S.; Lougheed, M.; Gómez-Muñoz, A.; Steinbrecher, U.P. A Modification of Apolipoprotein B Accounts for Most of the Induction of Macrophage Growth by Oxidized Low Density Lipoprotein. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 10903–10910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).