Machine Learning-Based Pain Severity Classification of Lumbosacral Radiculopathy Using Infrared Thermal Imaging
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Dataset of Patients with Lumbosacral Radiculopathy and Ethical Approval
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Clinical Data Collection, Labeling, Preprocessing, ML-Based Classification Modeling, and Calibration Algorithm
- (1)
- N = the number of items for which a Brier score is being calculated;
- (2)
- ft is the forecast probability (i.e., 25% chance);
- (3)
- ot is the outcome (1 if it happened, 0 if it did not);
- (4)
- ∑ is the summation symbol, indicating that all of the values must be added together.
3. Results
3.1. Demographic Characteristics
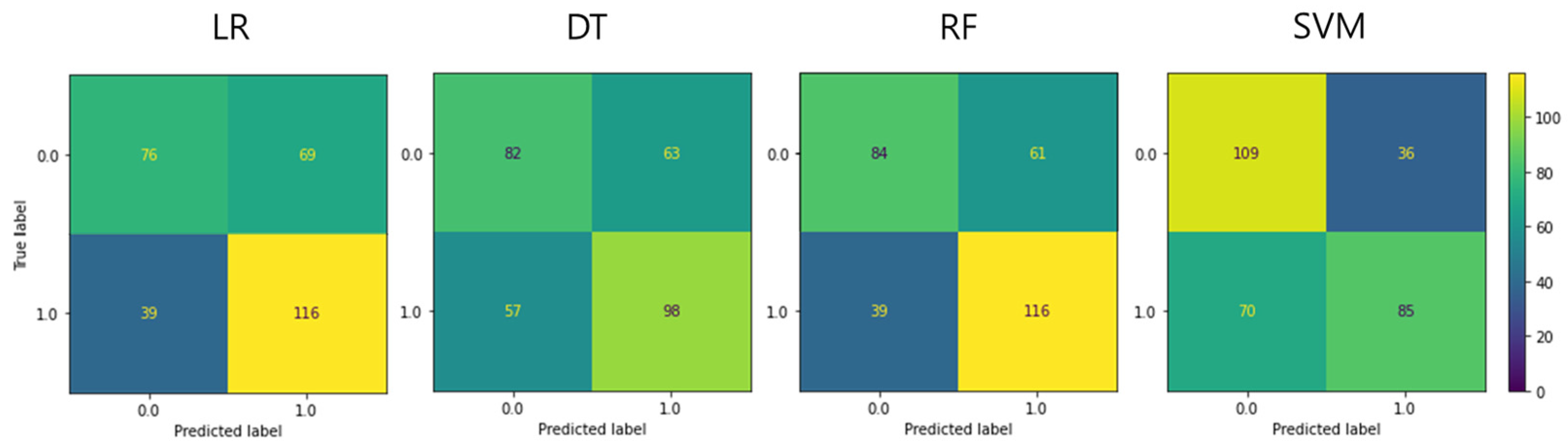
3.2. ML Model Comparison
3.3. Calibration of the RF Model
3.4. Case Discussion
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lauder, T.D. Physical examination signs, clinical symptoms, and their relationship to electrodiagnostic findings and the presence of radiculopathy. Phys. Med. Rehabil. Clin. N. Am. 2002, 13, 451–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Der Windt, D.A.; Simons, E.; Riphagen, I.I.; Ammendolia, C.; Verhagen, A.P.; Laslett, M.; Devillé, W.; Deyo, R.A.; Bouter, L.M.; de Vet, H.C.; et al. Physical examination for lumbar radiculopathy due to disc herniation in patients with low-back pain. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2010, 2, CD007431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modic, M.T.; Obuchowski, N.A.; Ross, J.S.; Brant-Zawadzki, M.N.; Grooff, P.N.; Mazanec, D.J.; Benzel, E.C. Acute low back pain and radiculopathy: MR imaging findings and their prognostic role and effect on outcome. Radiology 2005, 237, 597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fisher, M.A. Electrophysiology of radiculopathies. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2002, 113, 317–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pochaczevsky, R.; Wexler, C.E.; Meyers, P.H.; Epstein, J.A.; Marc, J.A. Liquid crystal thermography of the spine and extremities: Its value in the diagnosis of spinal root syndromes. J. Neurosurg. 1982, 56, 386–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brelsford, K.L.; Uematsu, S. Thermographic presentation of cutaneous sensory and vasomotor activity in the injured peripheral nerve. J. Neurosurg. 1985, 62, 711–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuzgen, S.; Dursun, S.; Abuzayed, B. Electrical skin resistance and thermal findings in patients with lumbar disc herniation. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2010, 27, 303–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosny, A.; Parmar, C.; Quackenbush, J.; Schwartz, L.H.; Aerts, H.J.W.L. Artificial intelligence in radiology. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 18, 500–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Zhang, F.; Li, X. Machine learning in ultrasound computer-aided diagnostic systems: A survey. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 5137904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, S.T.C. Is pathology prepared for the adoption of artificial intelligence? Cancer Cytopathol. 2018, 126, 373–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.Y.; Chin, D.K.; Cho, Y.E.; Kim, Y.S. Correlation between pain scale and infrared thermogram in lumbar disc herniations. J. Korean Neurosurg. Soc. 1999, 28, 253–258. [Google Scholar]
- Park, T.Y.; Son, S.; Lim, T.G.; Jeong, T. Hyperthermia associated with spinal radiculopathy as determined by digital infrared thermographic imaging. Medicine 2020, 99, e19483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kukreja, V.; Kumar, D. Automatic Classification of Wheat Rust Diseases Using Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2021 9th International Conference on Reliability, Infocom Technologies and Optimization (Trends and Future Directions) (ICRITO), Noida, India, 3–4 September 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, D.; Kukreja, V. Quantifying the Severity of Loose Smut in Wheat Using MRCNN. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Decision Aid Sciences and Applications (DASA), Chiangrai, Thailand, 23–25 March 2022; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Bennett, K.P.; Campbell, C. Support vector machines: Hype or hallelujah? ACM SIGKDD Explor. Newsl. 2000, 2, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, G.N.; Zhang, H.Y.; Cho, Y.E.; Ryu, S.J. Differential screening of herniated lumbar discs based on bag of visual words image classification using digital infrared thermographic images. Healthcare 2022, 10, 1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.S.; Cho, Y.E. Pre- and post-operative thermographic imagings in lumbar disc herniations. J. Korean Neurosurg. Soc. 1991, 22, 71–82. [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi, Y.; Takahashi, K.; Moriya, H. Thermal deficit in lumbar radiculopathy. Correlations with pain and neurologic signs and its value for assessing symptomatic severity. Spine 1994, 19, 2443–2449; discussion 2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sokolova, M.; Japkowicz, N.; Szpakowicz, S. Beyond accuracy, F-score and ROC: A family of discriminant measures for performance evaluation. In Proceedings of the Australasian Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Hobart, Australia, 4–8 December 2006; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, J.; Tian, W.; Tang, Y.; Zou, Y.; Zheng, S.; Wu, L.; Zeng, Y.; Wu, S.; Xie, X. Establishment of a Cell Necroptosis Index to Predict Prognosis and Drug Sensitivity for Patients With Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 9, 834593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, J.; Zheng, S.; Zou, Y.; Tang, Y.; Tian, W.; Wong, C.W.; Wu, S.; Ou, X.; Zhao, W.; Cai, M.; et al. Turning up a new pattern: Identification of cancer-associated fibroblasts-related clusters in TNBC. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1022147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Actual Values | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Positive | Negative | |||
| Predicted Values | Positive | a (True Positive) | b (False Positive) | PPV = a/(a + b) |
| Negative | c (False Negative) | d (True Negative | NPV = d/(c + d) | |
| Sensitivity = a/(a + c) | Specificity = d/(b + d) | |||
| Mild-to-Moderate Pain | Severe-to-Intractable Pain | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age Group | <6 Months | >6 Months | <6 Months | >6 Months |
| 0–19 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| 20–29 | 10 | 17 | 20 | 13 |
| 30–39 | 26 | 43 | 30 | 46 |
| 40–49 | 20 | 36 | 43 | 65 |
| 50–59 | 45 | 74 | 40 | 61 |
| 60–69 | 30 | 76 | 60 | 70 |
| 70 | 40 | 49 | 35 | 46 |
| Parameter | LR | DT | RF | SVM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BA | 0.636 | 0.599 | 0.664 | 0.650 |
| F1 score | 0.682 | 0.620 | 0.699 | 0.616 |
| Sensitivity | 0.748 | 0.632 | 0.748 | 0.548 |
| Specificity | 0.524 | 0.566 | 0.579 | 0.752 |
| PPV | 0.627 | 0.609 | 0.655 | 0.702 |
| NPV | 0.661 | 0.590 | 0.683 | 0.609 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rim, J.; Ryu, S.; Jang, H.; Zhang, H.; Cho, Y. Machine Learning-Based Pain Severity Classification of Lumbosacral Radiculopathy Using Infrared Thermal Imaging. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 3541. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13063541
Rim J, Ryu S, Jang H, Zhang H, Cho Y. Machine Learning-Based Pain Severity Classification of Lumbosacral Radiculopathy Using Infrared Thermal Imaging. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(6):3541. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13063541
Chicago/Turabian StyleRim, Jinu, Seungjun Ryu, Hyunjun Jang, Hoyeol Zhang, and Yongeun Cho. 2023. "Machine Learning-Based Pain Severity Classification of Lumbosacral Radiculopathy Using Infrared Thermal Imaging" Applied Sciences 13, no. 6: 3541. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13063541
APA StyleRim, J., Ryu, S., Jang, H., Zhang, H., & Cho, Y. (2023). Machine Learning-Based Pain Severity Classification of Lumbosacral Radiculopathy Using Infrared Thermal Imaging. Applied Sciences, 13(6), 3541. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13063541





