Abstract
During roof renovations, large quantities of waste BBRM (bitumen-based roofing materials) are generated, and the possibilities for recycling these materials have so far been very limited. In general, they can be crushed and mixed with asphalt to pave roads or can be burned for energy. While waste plastic materials are often recycled, the remelting process significantly degrades their durability and mechanical properties. Unlike conventional methods, our recycling process results in a material with properties that are in many ways superior to the original materials. It is durable, weather resistant, and has exceptionally high mechanical strength. This material can be used to produce various construction components, including replacing quickly degradable wooden parts in structures. The composite material demonstrates increased flexibility, enhanced tensile strength, and improved resistance to ultraviolet (UV) radiation and environmental degradation compared to standard bitumen. The process is simple and can be carried out directly at the renovation site using a portable device.
1. Introduction
Bitumen has been widely used in construction for waterproofing and as a binder in road surfaces due to its adhesive properties and resistance to water. However, bitumen on its own can be brittle at low temperatures and soften excessively at high temperatures [1], limiting its application range [2]. Bitumen-based roofing materials (BBRM) are widely used in the construction industry due to their durability, weather resistance, and flexibility [3]. They are available in two forms: modified bitumen membranes (MBR) and built-up roofing (BUR) systems. BUR systems consist of multiple layers of bitumen and reinforcing fabrics such as felt or fiberglass. The layers are alternated and then topped with gravel or other surfacing materials to create a waterproof and durable roof. MBR consist of a bitumen base mixed with synthetic rubbers or plastics like SBS (styrene–butadiene–styrene) or APP (atactic polypropylene). Recycling bitumen-based roofing materials is gaining importance as the construction industry moves toward sustainability. Unfortunately, the existing methods for recycling are quite limited: old roofing materials can be crushed and mixed with asphalt to pave roads or can be burned for energy [4].
Polyethylene and polypropylene are polymers known for their flexibility, strength and resistance to various chemicals. Polyethylene, in particular, is noted for its toughness and ductility, while polystyrene offers rigidity and impact resistance. Used plastics can be shredded and reformed into new products [5]. Unfortunately, the recycling degrades the material’s quality due to heat exposure. Polyethylene and polypropylene waste is generated in large amounts also during construction, renovation and demolition works.
1.1. Use on Bitumen Products in Construction Works
Bitumen for waterproofing is a byproduct of oil distillation, specifically from vacuum distillation, where lighter fractions are separated [6]. In its raw form, this material is not suitable for roofing because it loses elasticity due to decomposition, evaporation, and the washing out of oils. This results in shrinking and brittle cracking. Nevertheless, it has been widely used due to its ready availability.
Bitumen can also be derived from vegetable sources like tall oil [7]. It has a crystalline structure similar to salts.
Air blowing modifies bitumen by increasing asphaltene content relative to aromatic oils and resins, creating a gel-like structure and appropriate viscosity. Bitumen can also be modified with polymer additives, causing a phase inversion where bitumen becomes the dispersed phase in a polymer matrix. This transformation imparts viscoelastic properties and enhances stability. Polymer-modified bitumen, commonly using SBS or APP, provides the flexibility and mechanical properties needed for waterproofing [8,9,10,11].
In manufacturing waterproof membranes, reinforcing materials such as polyester fabric, glass cloth, or metal foils are coated with bitumen. The surface may be covered with sand, crushed stone, or foil. Historically, jute and asbestos fibers were used, but asbestos has been discontinued due to health risks. Bitumen membranes vary by source material, polymer matrix, and production method [12,13]. While widely used in roofing, particularly in Estonia, recycling these materials is challenging. Reinforcing fibers degrade the melted bitumen’s quality, limiting its reuse in new insulation materials.
For improvement of the properties, bitumen modification of various polymer blends that improve specific properties of bitumen is widely used. Notable among these are the following:
APP-Modified Bitumen: This blend uses atactic polypropylene (APP), a plastic that melts at approximately 160 °C, transforming into a liquid wax-like substance. This ease of melting makes APP-modified bitumen popular for residential and small commercial roofing applications, offering a user-friendly experience due to its high-temperature tolerance [12].
SBS-Modified Bitumen: SBS-modified bitumen incorporates styrene–butadiene–styrene (SBS), which provides a “sticky” melt rather than a free-flowing liquid. This type of bitumen requires less heat during installation, leading to faster application times. The synthetic rubber in SBS enhances the flexibility and stress recovery of the material, making it more resistant to environmental stressors like wind and temperature fluctuations [13].
Recycled rubber and PET can be used for modifying the properties of bitumen mixes. Theses combinations provide a material that maintains a balance between flexibility and durability, making it suitable for a variety of applications [13,14].
Bitumen with Polyethylene: At elevated temperatures (around 50 °C), blends of bitumen with high-density polyethylene (HDPE) and linear low-density polyethylene (LLDPE) have demonstrated improved flow characteristics and mechanical stability. Increasing the proportion of HDPE has been shown to elevate the temperature of onset of flow from 80 °C to 120 °C. This demonstrates the ability of polyethylene to enhance the performance of bitumen under thermal stress [15,16,17,18].
Bitumen modified with polymers is also used in road construction for the improvement of thermal and rheological parameters of asphalt mixtures.
The rheological properties of polymer-modified bitumen (PMB) can be tailored using polyethylene (PE) of varying molecular weights, allowing for the development of binders suited to different climates [19,20].
Recycled polyethylene (r-PE) shows considerable variability in thermal behavior, including melting temperature, crystallinity, and polydispersity. As a blend of HDPE, LLDPE, and LDPE, r-PE contains both linear and branched macromolecules, with type assessed by melting temperature.
The proportions of HDPE, LLDPE, and LDPE in r-PE significantly influence compatibility with bitumen and PMB performance. r-PE with a melting temperature above 130 °C primarily consists of HDPE, which has low compatibility with bitumen. Incorporating this PE increases viscosity and heat resistance, but can cause phase instability and asphaltene precipitation at high concentrations. Conversely, r-PE with a melting temperature around 115 °C is mostly LDPE and shows high compatibility with bitumen, enhancing elasticity. r-PE with a melting temperature of about 125 °C is mainly LLDPE. When added in high concentrations, it forms a polymer network that stabilizes the bitumen across a temperature range of 20–110 °C, due to the high sorption capacity of r-LLDPE for bitumen components. Lower melting temperatures and crystallinity improve compatibility with bitumen, as more branched LDPE macromolecules increase solubility.
At low r-PE concentrations (approximately 3% by mass), the internal structure and rheological properties of PMBs remain similar regardless of r-PE type, resembling the base bitumen’s rheological behavior. Bitumens modified with r-HDPE have enhanced heat resistance.
At higher r-PE concentrations (around 7% by mass), the type of r-PE significantly affects the PMB’s internal structure and rheological properties. Only r-LLDPE forms a polymer network within bitumen, making it especially suitable for roofing PMB applications [19,20,21,22].
Despite these advancements, there remains a need for a composite material that combines the best properties of these existing technologies while offering improved performance characteristics, particularly in terms of flexibility, tensile strength, and environmental resistance.
1.2. Recycling of BBRM
The reuse of remelted residues from comminuted bitumen-based roofing materials (BBRM) in the production of new products or materials is notably underrepresented in scientific literature. While some studies and industrial initiatives have explored recycling BBRM for applications such as road construction, there is limited research on utilizing remelted residues to create entirely new products.
BBRM recycling is particularly challenging due to the complexity of its composition, which often includes reinforcing materials like polyester or glass fibers. These components can degrade the quality of remelted bitumen, restricting its reuse in high-value applications. According to a report by the Asphalt Roofing Manufacturers Association, the recycling potential of asphaltic roof membranes remains underexplored, particularly in North America [21].
The report identifies several potential applications for recycled BBRM, including:
Cold Patch Material. Utilizing recycled BBRM for pothole repairs.
New Roofing Products. Incorporating recycled materials into the production of new bitumen-based roofing products.
Road Base Filler. Employing recycled BBRM as a filler in road base layers.
Dust Suppression. Using BBRM-derived substances to suppress dust on gravel or unpaved roads.
These applications underscore the versatility of recycled BBRM and its potential to enhance sustainability in construction and maintenance sectors.
Globally, the large-scale recycling of roofing materials remains limited, with small amounts of recycled material often incorporated into asphalt mixtures. However, innovative processes are paving the way for more efficient recycling practices, as follows:
BiELSo (“Bitumen Endless Life Solutions”). Developed by Icopal, this process crushes bitumen-containing materials like roofing felt, melts the bitumen, and removes non-bituminous components. The recycled bitumen is mixed with virgin bitumen to produce new roofing materials of comparable quality to those made with primary bitumen. Each square meter produced reduces CO₂ emissions by approximately 100 g, equivalent to the emissions from driving one kilometer [22].
BitumenMix Granules. Created by Tarpaper Recycling ApS, these granules consist of 45% stone material and 55% recycled bituminous material. This waste-free process is directly integrated into asphalt production, replacing up to 50% of virgin bitumen and reducing CO₂ emissions by approximately 60 kg per ton of asphalt [23],
Derbigum’s Patented Process. This method involves recycling bituminous waste, such as production scraps and demolition materials, into modified bitumen-based waterproofing membranes. The waste is ground, melted, and mixed with fresh bitumen, resulting in products containing 2–12% fibers [24].
Our innovative solution aims to develop a novel material that performs multiple functions within the construction sector, leveraging recycled BBRM for enhanced sustainability and functionality.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
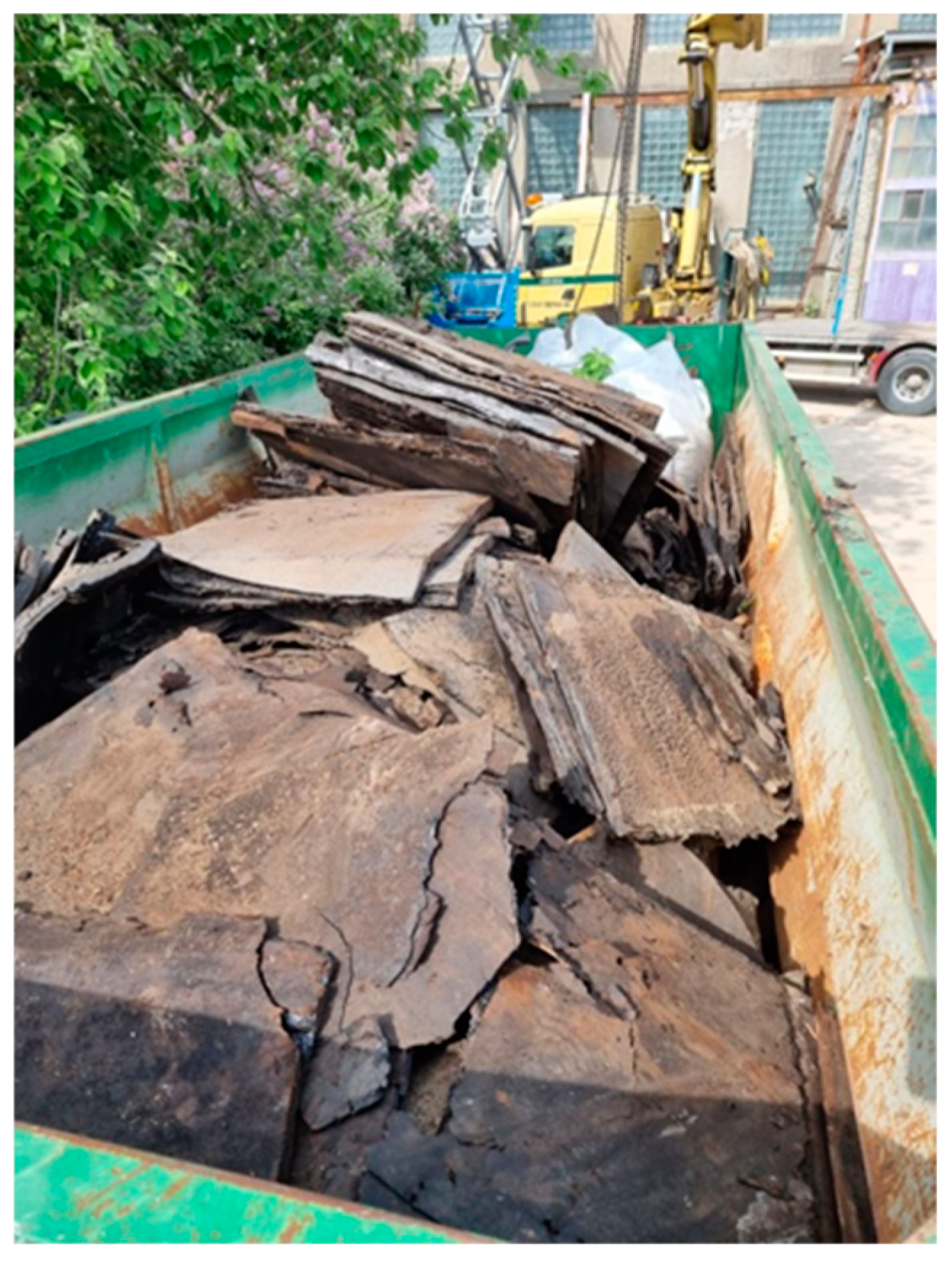
The roofing materials used in this study—including BBRM residues from renovation and demolition works, as well as SBS-containing BBRM strips cut from the edges of intact new panels during installation—were sourced from the construction company Katevara OÜ, located in Jõhvi, Ida-Virumaa, Estonia. The BBRM residues from renovation and demolition works originated largely from Soviet time (pre-1991) and consisted mainly of thick layers of bitumen and cardboard up to 40 cm (Figure 1) being in use and exposed to weather conditions for decades. For the sake of brevity, we will use the terms “old” BBRM and “new” BBRM. Both the BBRM waste from renovation and demolition works and SBS-containing BBRM strip waste from installation works were crushed into fragments approximately a few centimeters in size using a modified universal crusher OW-400.
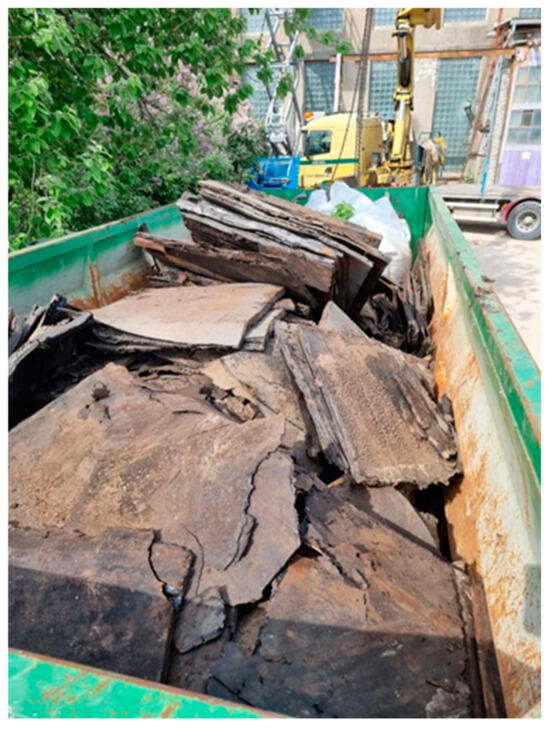

Figure 1.
BBRM waste from a demolition site.
Plastic waste was also obtained from construction and demolition sites and consisted of about a half of packaging film (LDPE) and other half of liquid containers (HDPE). The plastic waste was crushed similarly with BBRM.
2.2. Composition of Test Specimen
The test specimen series were composed as follows, on the basis of weight: 1 consisted entirely of 100% remelted “new” BBRM. 2 was a mixture of 45% remelted “new” BBRM, 45% “old” BBRM, and 10% plastic (PE) waste. 3 contained 90% “old” BBRM and 10% PE waste, while 4 comprised 90% “new” BBRM and 10% PE waste. Percentages indicate the proportion of a particular component in the total mass.
2.3. Preparation of Bitumen–Plastic Composites
The preliminary experiments were performed using a thermostatic laboratory asphalt mixer BH-10 (Cangzhou Oubeiruike Instrument and Equipment Co., Cangzhou, Hebei, China). The material was weighed with an accuracy of ±5 g, and 1.0–1.5 kg of mixed BBRM and plastic fragments were transferred to a preheated 10-liter asphalt mixer.
The mixture was heated with constant stirring at 200–250 °C until it melted or became a soft viscous mass. In the mixtures containing newer SBS containing BBRM, complete melting was not achieved. The molten or softened material was then transferred into metal molds that had been lined with baking paper or covered with a thin layer of silicone to prevent sticking. The surface of the composite was leveled, and the molds were allowed to cool to room temperature.
Once cooled, the composite blocks were removed from the molds, and any baking paper residues were cleaned off the surface. FTIR-ATR analyses and compressive and flexural strength tests were conducted on the finished composites.
2.4. Pilot Equipment
In order to obtain results similar to real industrial conditions, a pilot-scale production apparatus was constructed.
Building on the insights gained from producing composite test specimens using a 10-liter laboratory-scale device, a pilot-scale system was developed for larger-scale testing. The main challenges encountered during laboratory experiments included slow heating, primarily due to the low thermal conductivity of the raw materials, and the high viscosity of certain mixtures, particularly those containing SBS roofing materials. These issues not only hindered efficient mixing, but also limited the volume of material that could be processed and further slowed the heating process.
To address these challenges, the pilot plant was designed with gas heating, enabling faster thermal response. Additionally, a high-torque agitator was incorporated to enhance mixing efficiency and minimize the risk of agitator jams, ensuring smoother operation even with highly viscous materials (Figure 2).
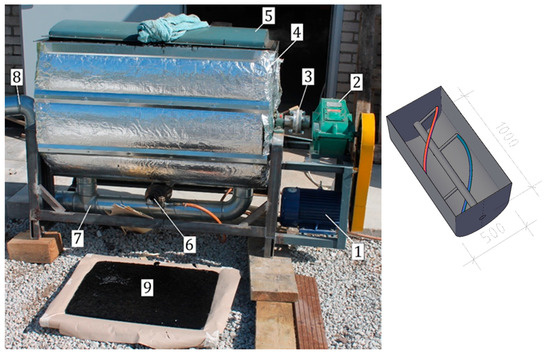
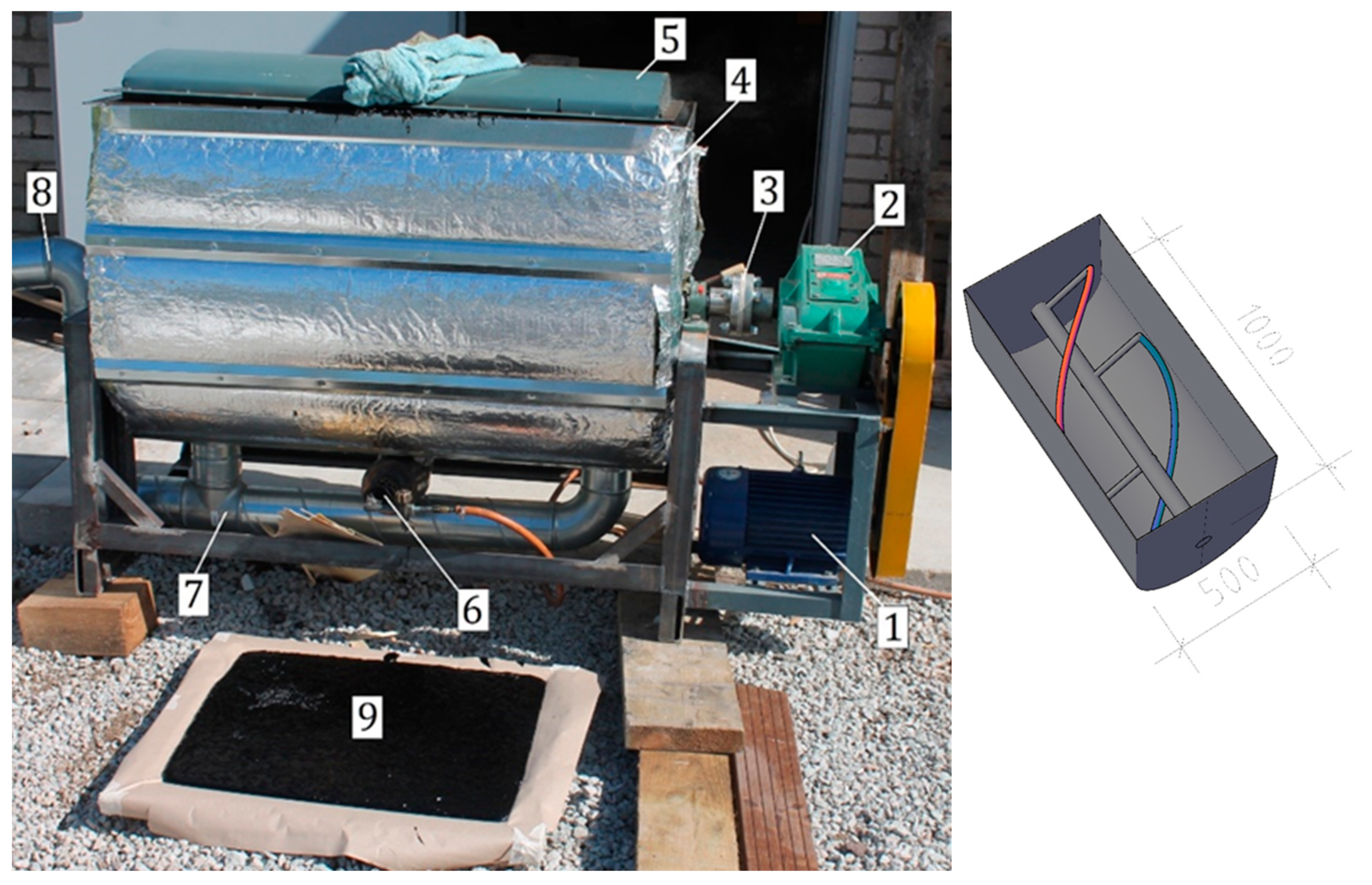
Figure 2.
(Left): Photograph of experimental mixer. Position number markings are as follows: 1—three-phase asynchronous motor, 2—reduction gear 1:50, 3—thermal insulator, 4—insulated gas jacket hopper, free to rotate around the axle for emptying, 5—hatch, 6—gas burner with excess oxygen above stoichiometry, 7— exhaust piping, 8—chimney connection, coaxial with the mixer shaft to allow rotation of the hopper, 9—filled mold. (Right): High-torque agitator with a spiral beater made from round steel.
The mixer was an experiment in itself, as it was a gas-heated bitumen mixer built without an oil jacket. The purpose of the oil jacket would have been to prevent localized overheating beyond the self-ignition point, which could potentially lead to an explosion. The decision to use gas was driven by uncertainty regarding the availability of industrial electric power in various locations and, on the other hand, the ready availability and cost efficiency of gas energy. With electricity, there would have been no risk of explosion and no construction complexity. Nevertheless, the new machine operated satisfactorily.
A novel feature is a spiral beater made from round steel, designed to test the mixing of textiles with bitumen without the material wrapping around the blades (Figure 2). However, this did not help; even the fiber contained in SBS (styrene–butadiene–styrene) was sufficient to entangle both the blades and the shaft.
The press molds were initially designed to withstand a pressure of 50 tons, which later proved excessive. Warm bitumen is easily molded with pressures ranging from 10 to 20 tons. The mold surfaces were successfully made of bitumen–repellent using a coating of silicone dissolved in octane.
2.5. Chemical Testing
The goal of the thermal treatment was to create a homogeneous composite material by thoroughly mixing different components for practical application. The materials produced were analyzed using Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) with Attenuated Total Reflectance (ATR), a technique suited for examining gaseous, liquid, and solid materials in their natural state. This method requires no processing or dissolving of the samples. Since FTIR identifies chemical bonds, it helps determine whether new bonds were formed or existing bonds were broken during composite production. In some cases, FTIR can also reveal interactions between the starting materials, such as hydrogen bonding. These factors are crucial in understanding the structure and properties of new materials, as they influence their physical behavior under various conditions.
For this project, a Spectrum BXII FTIR spectrometer (PerkinElmer, Waltham, MA, USA) was utilized, applying the attenuated total reflection (ATR) technique with a Zn–Se crystal. FTIR spectra were recorded at room temperature over a range of 4000 to 600 cm−1, with a resolution of 4 cm−1 and 16 scans. The samples, taken both from the surface and at a depth of approximately 1 cm, were pressed directly against the ATR crystal without any special preparation. Additionally, spectra of key substances such as polyethylene, polypropylene, and polystyrene, as well as the initial materials (plastics and BBRM), were analyzed for comparison.
FTIR can also assess the homogeneity of the material by comparing spectra from different sections (e.g., surface and interior) to check for consistency. This method is valuable for optimizing manufacturing processes and evaluating process reproducibility, using statistical tools like Principal Component Analysis (PCA). Consequently, FTIR studies play a vital role in advancing material production technologies.
2.6. Mechanical Testing
The procedures for determining the compressive and flexural strength of the test specimens were carried out in accordance with the Estonian standards EVS-EN 772-1:2011+A1:2015 [25] (for compressive strength testing) and EVS-EN 772-6:2005 [26] (for flexural strength testing, see Figure 3).

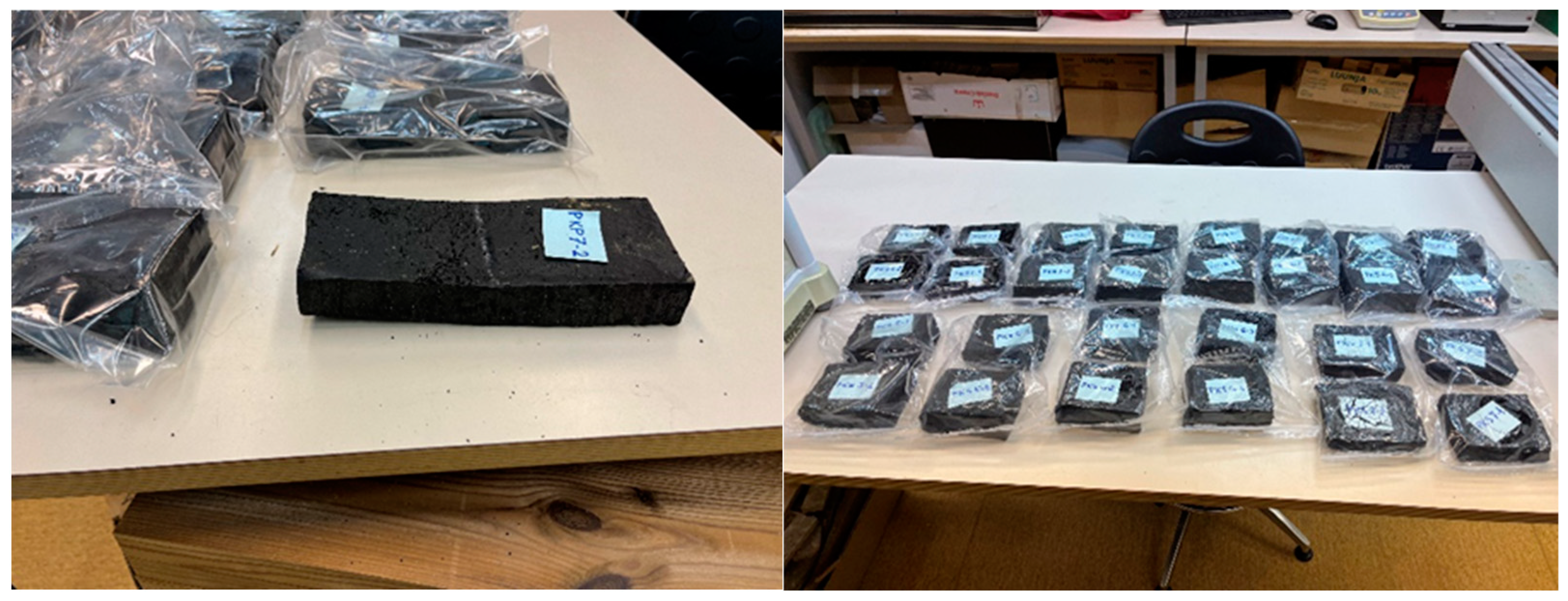
Figure 3.
Test specimens for the measurements of flexural strength (on the left) and compressive strength (on the right).
For flexural tests, 2 test specimens of every composition were cut to a length of approx. 25 cm, and the more precise measurements are given with the designation 1-1-4-2 (8 test specimens).
Cutting posed challenges as the bitumen heated up during the process, and the scattered plastic bitumen grains and droplets smeared the area around the cutter. To minimize the thermal effects on the test specimens, they were cooled to −20 °C in a freezer. Attempts to use a jigsaw with intermittent cooling of the blade in cold water proved ineffective, as the blade quickly dulled due to the sand and grit in the material. Therefore, the frozen specimens were ultimately cut using a circular saw.
The digital press Instron 3396 was used as the device for performing the tests of compressive strength and flexural strength. The device allows monitoring of the compressive displacement.
The specimens had an uneven surface flatness and their unification was unfeasible. Since at room temperature during the tests, which was in the range of 24.0–24.7 °C, bitumen is plastic, the maximum compressive displacement was chosen to be 10 mm for both bending and compression tests in order to even out the curvatures.
2.7. Thermogravimetric Analyses
Samples were analyzed using a NETZSCH STA 449 F3 Jupiter® TG-DSC instrument (NETZSCH-Gerätebau GmbH, Selb, Germany). Samples were weighed into open Al2O3 crucibles and heated in a pure nitrogen (99.999 vol%) atmosphere at a nitrogen flow rate of 40 mL/min from room temperature to 700 °C, at a constant heating rate of 5 K/min. The sample mass used ranged from 3.5 to 7 mg. A total inert gas flow rate of 60 mL/min of nitrogen was used. To eliminate buoyancy effects, background mass data were recorded using an empty crucible experiment and subtracted from each of the sample measurement data sets. The results obtained are averages of the repeated measurements.
3. Results
3.1. Mechanical Properties of the Composites

Table 1.
Experimental data of compressive strength of the test specimen.
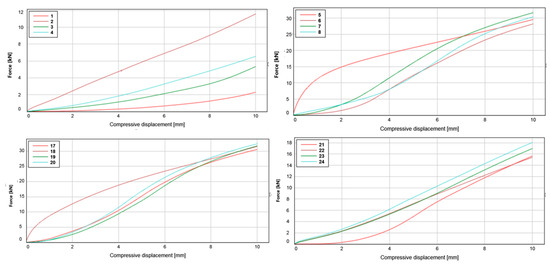
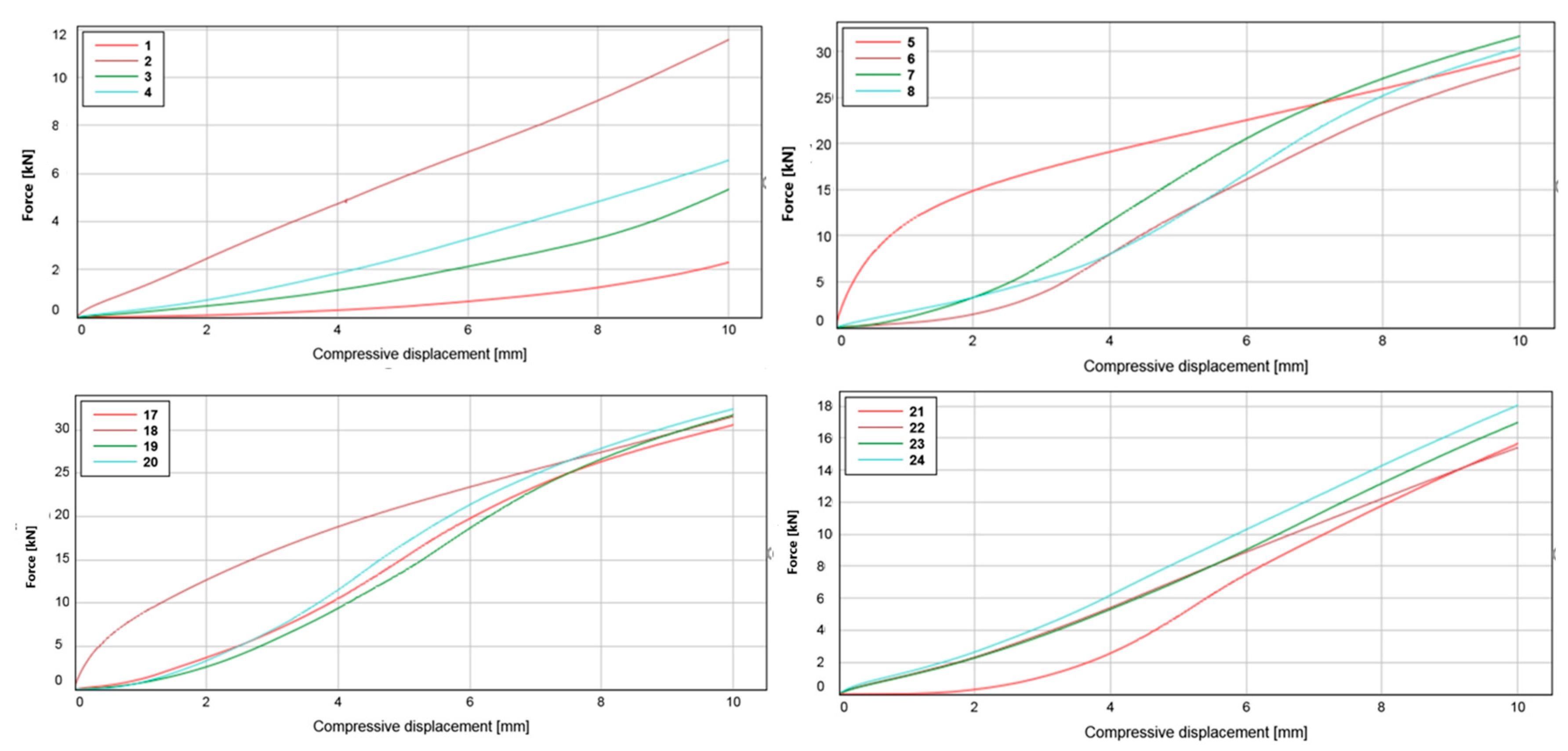
Figure 4.
Compressive displacement of test series 1 (top left), 2 (top right), 3 (bottom left) and 4 (bottom right). The numbers shown in the legends are the identification numbers of the individual test specimens.

Table 2.
Experimental data of flexural strength of the test specimen. The gap between the supports of the press was 100 mm in all tests.
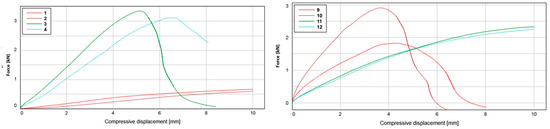
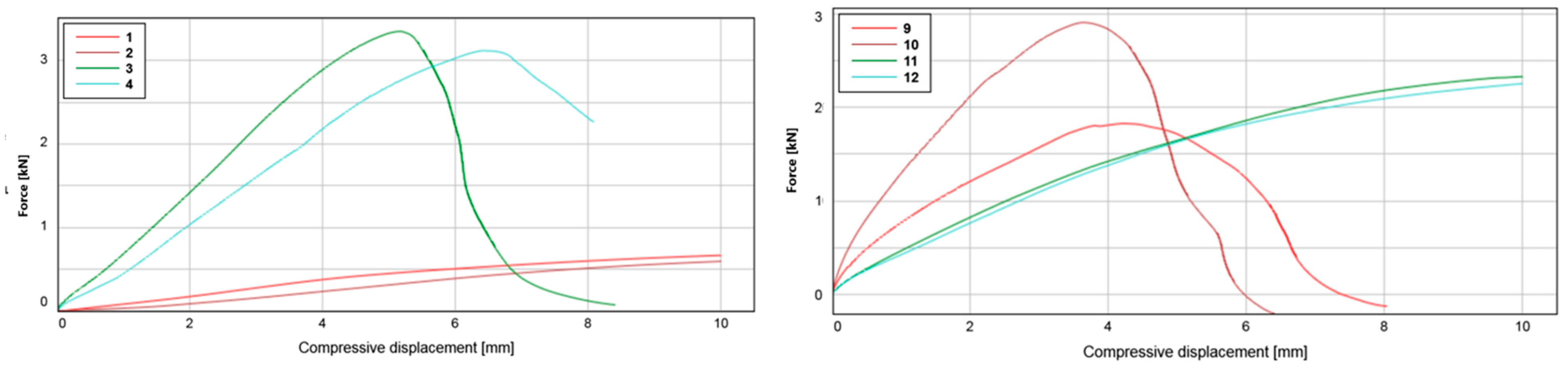
Figure 5.
(Left): Compressive displacement of test series 1 (identification numbers 1 and 2 as shown in the legend) and 2 (identification numbers 3 and 4); (Right): Compressive displacement of test series 3 (identification numbers 9 and 10) and 4 (identification numbers 11 and 12).
3.2. FTIR-ATR Analyses
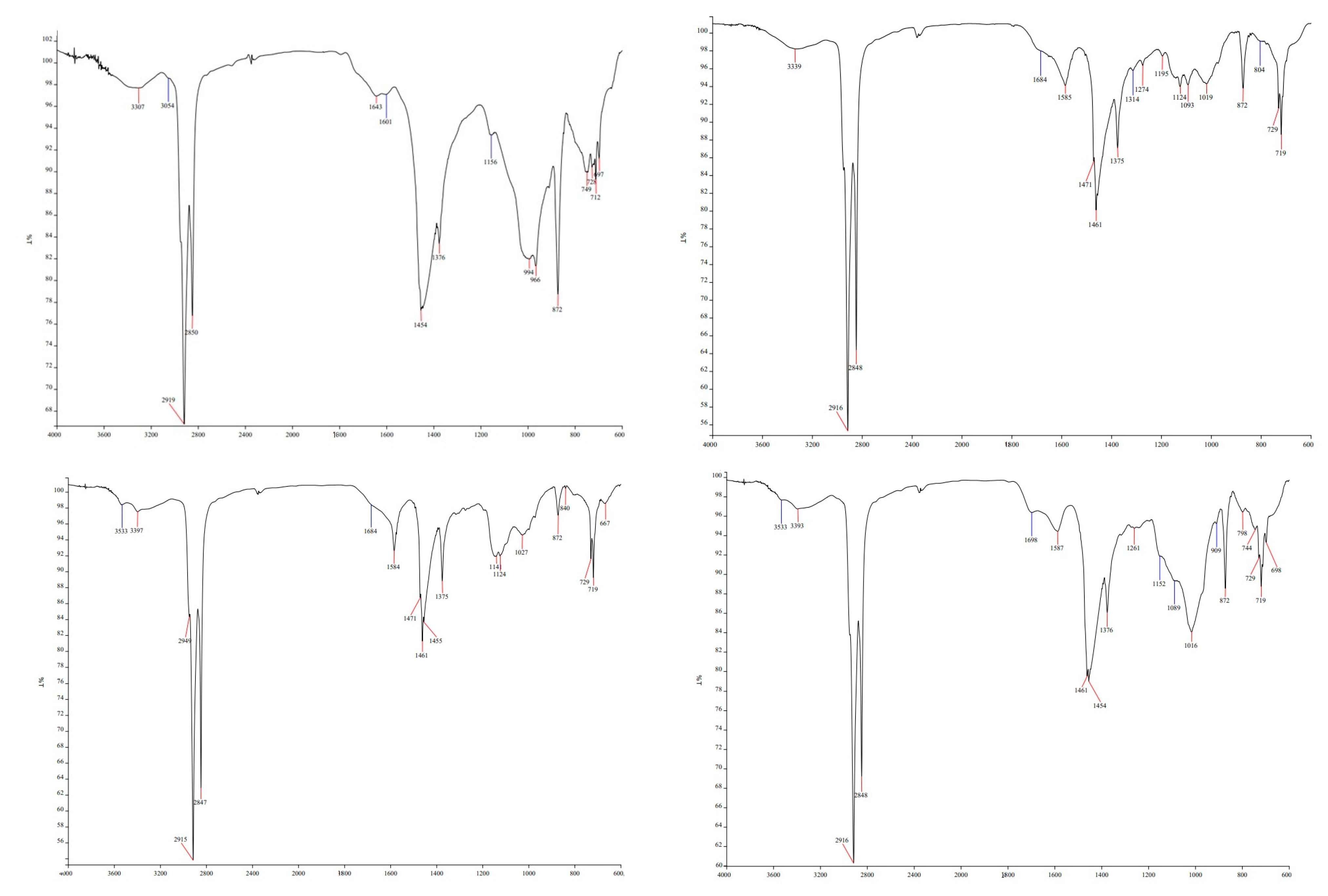
In the FTIR spectrum of sample 1 (Figure 6 top left), the characteristic maxima of unmelted “new” BBRM (1417 and 872 cm−1) are still detectable, although their intensity has been significantly reduced. The maximum at 1417 cm−1 partially overlaps with the -CH₂ -scissoring deformation vibration peak at 1460–1470 cm−1. Additionally, a shift is observed in the 1018 cm−1 signal to 998 cm−1, indicating alterations in the C-O bond system [24]. These changes are attributed to heating the material to approximately 200 °C.
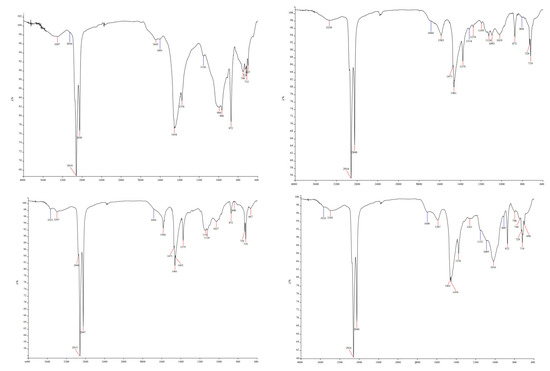
Figure 6.
FTIR spectra of samples 1 (100% remelted “new” BBRM; (top left)), 2 (45% remelted “new” BBRM, 45% “old” BBRM, and 10% PE waste; (top right)), 3 (90% “old” BBRM and 10% PE waste, (bottom left)), and 4 (90% “new” BBRM and 10% PE waste, (bottom right)).
The FTIR spectrum of sample 2 is presented on Figure 6, top right. Interestingly, although the spectrum of BBRM normally includes a signal at 697 cm−1, this signal is absent in 2. The absence of this signal in sample 2 may result from the thermal treatment. This hypothesis could be tested by heating pure BBRM, which originally shows the signal, at the same temperature. Furthermore, signals specific to the C-H bond stretching vibrations in polypropylene, typically found in the 2800–3000 cm−1 range, are not detectable thus proving that polypropylene is absent in the waste plastic. However, signals characteristic of polyethylene are present.
The FTIR spectrum of sample 3 is presented on Figure 6, bottom left. The FTIR spectrum of this sample closely resembles that of sample 2, with a few notable differences. Thermal treatment appears to have caused the release of several compounds from the BBRM, particularly water, as indicated by a significant decrease in the intensity of O-H stretching vibrations at 3300 cm−1 and a reduction in bending vibrations at 1626 cm−1. Additionally, two weak signals have emerged at 3397 cm−1 and 3533 cm−1, corresponding to vibrations of either OH or NH groups [27]. To determine their origin, separate thermal treatments of the starting materials should be conducted to assess their effect on the FTIR spectrum. These maxima may have been present in the original material but masked by the high water content. Upon water removal at elevated temperatures, absorption maxima of free OH groups from cellulose may become apparent.
The composition of the tar used in the “old” BBRM is unknown. It is also important to note that the raw materials used (BBRM and plastics) are technical-grade materials, not pure chemicals, and may contain additives designed to enhance their performance.
Regarding the plastic content, the presence of polypropylene is minimal, on the trace level, with polyethylene being the predominant component.
The FTIR spectrum of sample 4 is presented on Figure 6, bottom right. The spectra of sample 3 and 4 are nearly identical, with some differences observed in the region of symmetrical and asymmetrical stretching vibrations of -C-O- bonds between 1000 and 1160 cm−1. These differences may be attributed to the varying behavior of the cellulose underlying the BBRM in the presence of different components. The spectrum of this sample reveals the primary maxima associated with new BBRM (except for the peak at 1417 cm−1), with the previously discussed signal at 872 cm−1 being particularly notable.
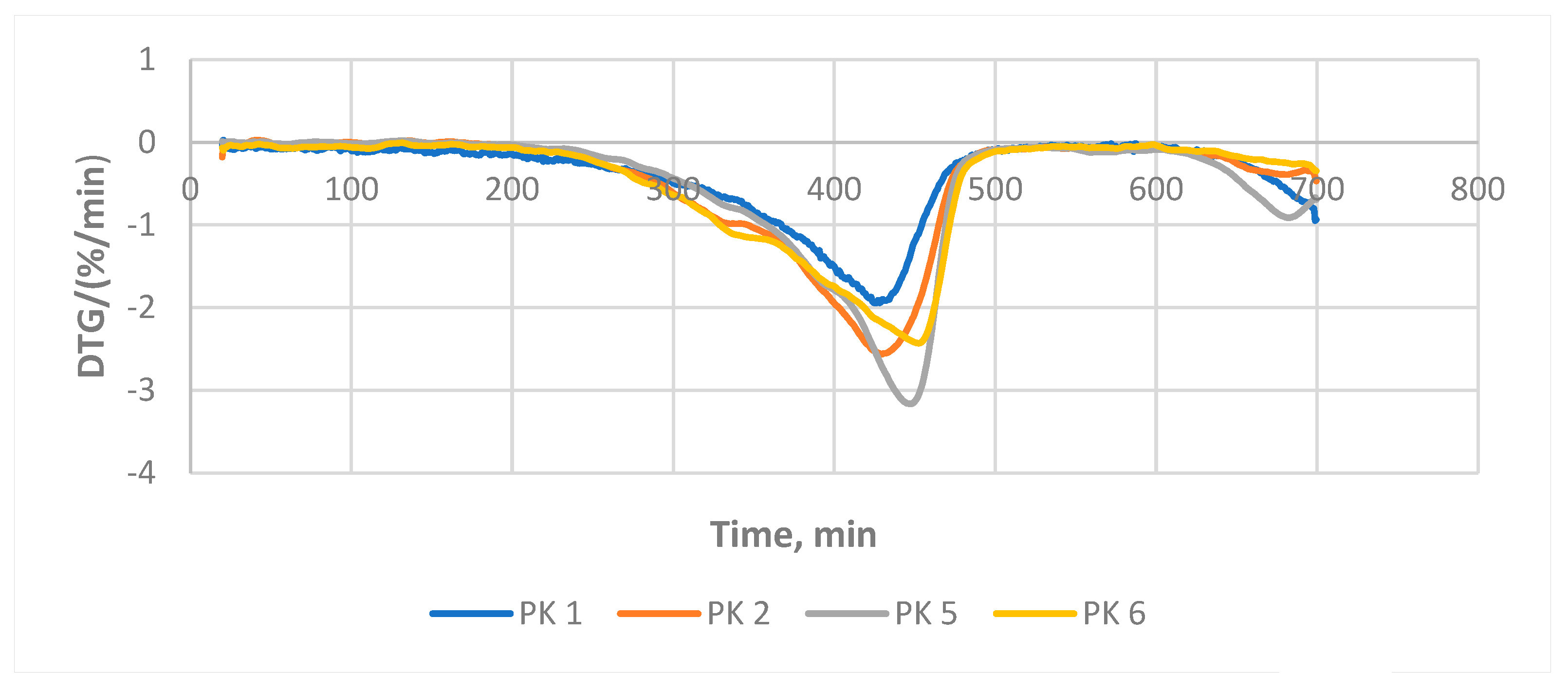
3.3. Thermogravimetric Analysis
As Figure 7 and Table 3 show, PE evaporates massively at the range of 350–470 °C, while pure bitumen samples evaporate only to a limited quantity of the light fraction. A sample consisting of 50% PE and 50% bituminous material the evaporation of polyethylene follows the same trend. However, the thermogravimetric graph of the samples containing 10% PE and bituminous material 90% does not differ from the graphs of pure bituminous material. This indicates that 10% addition of PE is likely chemically bonded to bitumen, which agrees with the data published in the literature. The eminent increase in mechanical properties of the composite material can be explained with the formation of chemical bond.
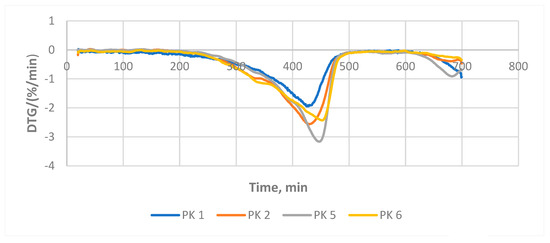
Figure 7.
Thermogravimetric analyses.

Table 3.
Key thermogravimetric data of the samples.
4. Discussion
The study demonstrates a novel approach to recycling bitumen-based roofing materials (BBRM) by integrating them with plastic waste to create composite materials with superior mechanical properties. Unlike conventional recycling methods that primarily involve crushing BBRM for road paving or energy recovery, this process yields a material with improved tensile strength, flexibility, and resistance to environmental degradation. These advancements highlight significant progress toward sustainable construction practices.
The results reveal that composites prepared with specific ratios of polyethylene (PE) and BBRM exhibit distinct improvements in mechanical properties, particularly compressive and flexural strength. These improvements can be attributed to the chemical bonding between bitumen and PE, as evidenced by thermogravimetric analysis. The presence of a matrix structure within the composite contributes to its enhanced performance, with bitumen particles occupying voids within the matrix and bonding weakly to the plastic.
Flexural strength results suggest a steep decrease under certain conditions, which is hypothesized to stem from the tearing of the matrix structure beyond its tensile limit. This phenomenon emphasizes the composite’s potential to achieve significant material performance gains with proper formulation and processing conditions.
Challenges during material preparation, such as achieving uniform heating and mixing of high-viscosity SBS-containing materials, underscore the need for further refinement of processing techniques. The pilot-scale apparatus addressed some of these limitations, offering insights into practical scalability and operational efficiency.
The results also highlight the limitations of current analytical methods in fully characterizing the composite’s structure and bonding mechanisms. Advanced techniques like atomic force microscopy (AFM) and environmental scanning electron microscopy (SEM) could provide deeper insights into the material’s microstructure, enabling further optimization.
The process described aligns with the principles of the circular economy by repurposing construction waste into high-value materials, reducing dependency on virgin resources, and minimizing greenhouse gas emissions. The successful fabrication and testing of roofing components for real-world applications further validate the composite’s potential for widespread industrial use. However, long-term monitoring of these components is essential to establish durability under varying environmental conditions.
To enhance the utility and applicability of the developed composite material, future research should focus on the following:
- Refining the pilot-scale apparatus for industrial production.
- Exploring alternative polymer blends to further enhance material properties.
- Conducting long-term field studies to evaluate performance under real-world conditions.
- Expanding the range of applications for the composite beyond roofing, such as structural reinforcements or thermal insulation.
This study lays a robust foundation for advancing sustainable materials in construction, addressing the pressing need to mitigate waste and reduce environmental impacts in the industry.
5. Conclusions
The most interesting result is the steep decrease in the graphs of flexural strength, which indicates that the properties of the obtained composites differ significantly from the raw materials. We hypothesize that the process results in a spatial matrix structure, significantly increasing the material’s strength and elasticity. Bitumen particles are located in the voids of the resulting matrix, weakly bonded to the plastic through individual links. Formation of chemical bonds between PE and bituminous material has been proven by the thermogravimetric analyses. The steep decrease is likely caused by the tearing in the matrix structure when tensile force exceeds the limit value corresponding to the structure of current composite.
We succeeded in the development of the process per se, but the available analysis methods were insufficient to finally confirm our scientific hypotheses. Different analysis methods such as AFM, environmental SEM etc. are needed to characterize the structure of the material.
We can report that we achieved a material with superior mechanical properties. The composite material is expected to demonstrate increased flexibility, enhanced tensile strength, and improved resistance to ultraviolet (UV) radiation and environmental degradation compared to standard bitumen. In proving these properties, hundreds of roofing details were fabricated using the described apparatus and places in the real construction objects. Their properties will be closely monitored in the coming five years.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization and methodology was conducted by J.L.; experimental and investigation by E.R.; FTIR-ATR analyses and data curation by U.M.; procurement, design, assembly, fine-tuning and maintenance of equipment by N.V.; mechanical testing (compression and flexural tests) and data curation by V.P.; thermogravimetric analyses and data curation by O.J.; writing—original draft preparation by E.R. and J.L.; writing—review and editing by N.V., supervision J.L.; project administration by E.R.; funding acquisition by J.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Estonian Business and Innovation Agency, project RE.5.04.23-0336.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable as the study involved neither human participants nor animal subjects.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable as the study involved no human participants.
Data Availability Statement
Data are available from the corresponding author, E.R., upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
We would like to express our gratitude to Teet Enok, Jan Erik Enok, Thiago Dantas, Tiit Lepik, Dmitri Gerasimov, Valdeko Reisenbuk, OÜ Katevara, OÜ Plekipood, the Estonian Roof and Facade Masters Association, and the Estonian Circular Economy Enterprises Association for enabling and supporting the completion of this article.
Conflicts of Interest
Authors Jüri Liiv and Neeme Vaino are now both employed full-time at Cellula Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Fazaeli, H.; Behbahani, H.; Amini, A.A.; Rahmani, J.; Yadollahi, G. High and low temperature properties of FT-paraffin-modified bitumen. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2012, 1, 406791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pipintakos, G.; Sreeram, A.; Mirwald, J.; Bhasin, A. Engineering bitumen for future asphalt pavements: A review of chemistry, structure and rheology. Mater. Des. 2024, 244, 113157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neşer, G.; Aytekin, V. Modification of bitumen-based roof covering material by glass reinforced polyester recyclate. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2015, 17, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerbeek, T. Bitumen Roofing Can Be Recycled … But Isn’t. Phys.org. 2013. Available online: https://phys.org/news/2013-09-bitumen-roofing-recycled-isnt.html (accessed on 23 April 2024).
- Fawcett, A.H.; McNally, T.; McNally, G. An attempt at engineering the bulk properties of blends of a bitumen with polymers. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2002, 21, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pannekens, M.; Voskuhl, L.; Mohammadian, S.; Köster, D.; Meier, A.; Köhne, J.M.; Kulbatzki, M.; Akbari, A.; Haque, S.; Meckenstock, R.U. Microbial Degradation Rates of Natural Bitumen. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 8700–8708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ball, G.F.A.; Herrington, P.A.; Patrick, J.E. Tall oil pitch as bitumen extender. N. Z. J. For. Sci. 1993, 23, 236–242. Available online: https://www.scionresearch.com/__data/assets/pdf_file/0016/17701/NZJFS2321993BALL236-242.pdf (accessed on 27 December 2024).
- Kleinschmidt, R.; Snoke, H.R. Changes in the Properties of an Asphalt During the Blowing Operation. J. Res. Natl. Bur. Stand. 1958, 60, 2835. Available online: https://nvlpubs.nist.gov/nistpubs/jres/60/jresv60n3p169_A1b.pdf (accessed on 27 December 2024). [CrossRef]
- Greenfeld, S.H. Air Oxidation of Asphalt; National Bureau of Standards Report 7420; National Institute of Standards and Technology: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Tan, G.; Liang, C.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, Y. Study on Viscoelastic Properties of Asphalt Mixtures Incorporating SBS Polymer and Basalt Fiber under Freeze–Thaw Cycles. Polymers 2020, 12, 1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, D.; Xing, C.; Jiang, W.; Xiao, J.; Wu, W.; Li, P.; Li, Y. Viscoelastic Behavior and Phase Structure of High-Content SBS-Modified Asphalt. Polymers 2022, 14, 2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- APP vs. SBS Roof Membranes—Polyglass U.S.A., Inc. Available online: https://polyglass.us/blog/app-vs-sbs-roof-membranes/ (accessed on 28 December 2024).
- Imanbayev, Y.; Bussurmanova, A.; Ongarbayev, Y.; Serikbayeva, A.; Sydykov, S.; Tabylganov, M.; Akkenzheyeva, A.; Izteleu, N.; Mussabekova, Z.; Amangeldin, D.; et al. Modification of Bitumen with Recycled PET Plastics from Waste Materials. Polymers 2022, 14, 4719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzotta, F.; Lantieri, C.; Vignali, V.; Simone, A.; Dondi, G.; Sangiorgi, C. Performance evaluation of recycled rubber waterproofing bituminous membranes for concrete bridge decks and other surfaces. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 136, 524–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jew, P.; Shimizu, J.A.; Svazic, M.; Woodhams, R.T. Polyethlene-modified bitumen for paving applications. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1986, 31, 2685–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tembe, E.; Tamele, L., Jr.; Buonocore, G.; Madivate, C.; Muiambo, H. Rheological and Thermo-Oxidative Aging Properties of Asphalt Modified with a Combination of Sasobit and Linear Low-Density Polyethylene. Sustainability 2023, 15, 4460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, A.A. Polyethylene dispersions in bitumen: The effects of the polymer structural parameters. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2003, 90, 3183–3190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes-Audén, C.; Sandoval, J.A.; Jerez, A.; Navarro, F.J.; Martínez-Boza, F.J.; Partal, P.; Gallegos, C. Evaluation of thermal and mechanical properties of recycled polyethylene modified bitumen. Polym. Test. 2008, 27, 1005–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, M.; Xin, X.; Fan, W.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, H.; Yao, Z. Comparison of rheological properties and compatibility of asphalt modified with various polyethylene. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2019, 22, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eraky, A.; Ayoub, H.S.; Osman, O.; Ouf, M.E.; Mostafa, A.Z.E.A. Improving the Performance Grade and Traffic Loading of Egyptian Asphalt Binders by Recycled Polyethylene Modification. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, Cairo, Egypt, 29 March 2021–31 March 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asphalt Roofing Manufacturers Association, Low-Slope Asphalt Roofing Recycling. 2024. Available online: www.asphaltroofing.org (accessed on 28 December 2024).
- Icopal, Citumen. Available online: https://citumen.com/ (accessed on 27 November 2024).
- Tarpaper: No more Roofing-Felt Waste!|European Circular Economy Stakeholder Platform. Available online: https://circulareconomy.europa.eu/platform/en/good-practices/tarpaper-no-more-roofing-felt-waste (accessed on 23 April 2024).
- Guillaume, M.; Julien, D.; Caroline, M.; Koen, S.; Patrick, C. Process for Recycling a Bituminous Waste Product such as a Bituminous Waste Membrane. Product. Patent WO2021105451A1, 3 June 2021. Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/WO2021105451A1/en (accessed on 28 December 2024).
- EVS-EN 772-1:2011+A1:2015 Müürikivide katsemeetodid. Osa 1, Survetugevuse Määramine. Methods of Test for Masonry Units. Part 1, Determination of Compressive Strength|Digar Viewer. Available online: https://www.digar.ee/viewer/et/nlib-digar:252645/222323/page/1 (accessed on 27 November 2024).
- EVS-EN 772-6:2005 Müürikivide katsemeetodid. Osa 6, Betoonmüürikivide Paindetõmbetugevuse Määramine. Methods of Test for Masonry Units. Part 6, Determination of Bending Tensile Strength of Aggregate Concrete Masonry Units|Digar. Available online: https://www.digar.ee/arhiiv/et/raamatud/49042 (accessed on 27 November 2024).
- Silverstein, R.M.; Bassler, G.C.; Morrill, T. Chapter Three: Infrared Spectrometry: In Spectrometric Identification of Organic Compounds, 5th ed.; Sawicki, D., Stiefel, J., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1991; pp. 91–164. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).