High-Pressure Processing of Reduced Salt Pangasius Catfish (Pangasianodon hypophthalmus) Minced Muscle: The Effects on Selected Quality Properties of Its Gels
Abstract
Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Fish Gel Preparation
2.2. High-Pressure and Thermal Treatment of Barramundi Paste
2.3. Proximate Analysis
2.4. Total Plate Count (TPC)
2.5. Color Analysis
2.6. Mechanical Properties
2.7. Water-Holding Capacity
2.8. Protein Solubility
2.9. SDS-Polyacrylamide Gel Eminlectrophoresis
2.10. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
2.11. Scanning Electron Microscope
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Proximate Analysis
3.2. Total Plate Count (TPC)
3.3. Color Analysis
3.4. Mechanical Properties
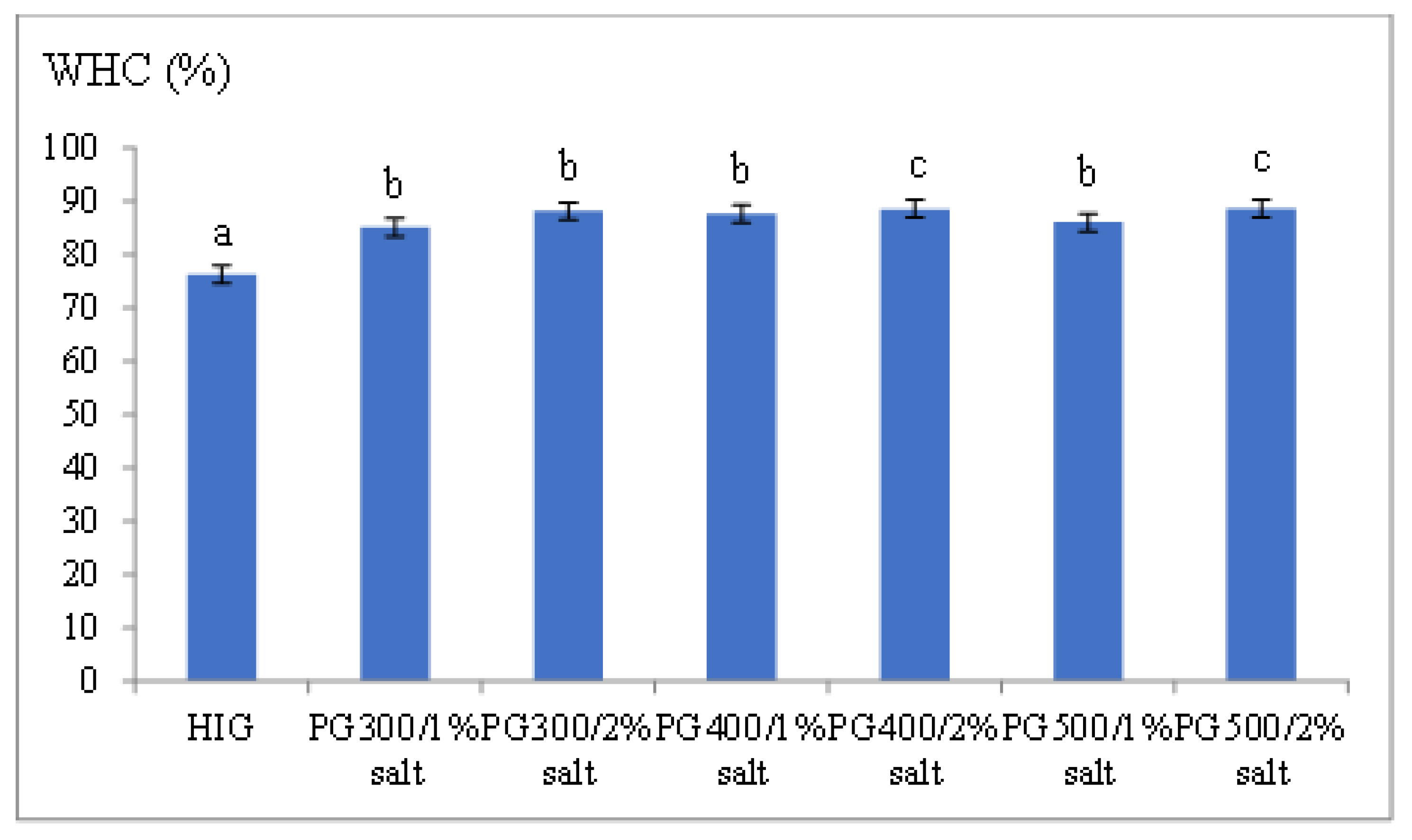
3.5. Water-Holding Capacity
3.6. Protein Solubility
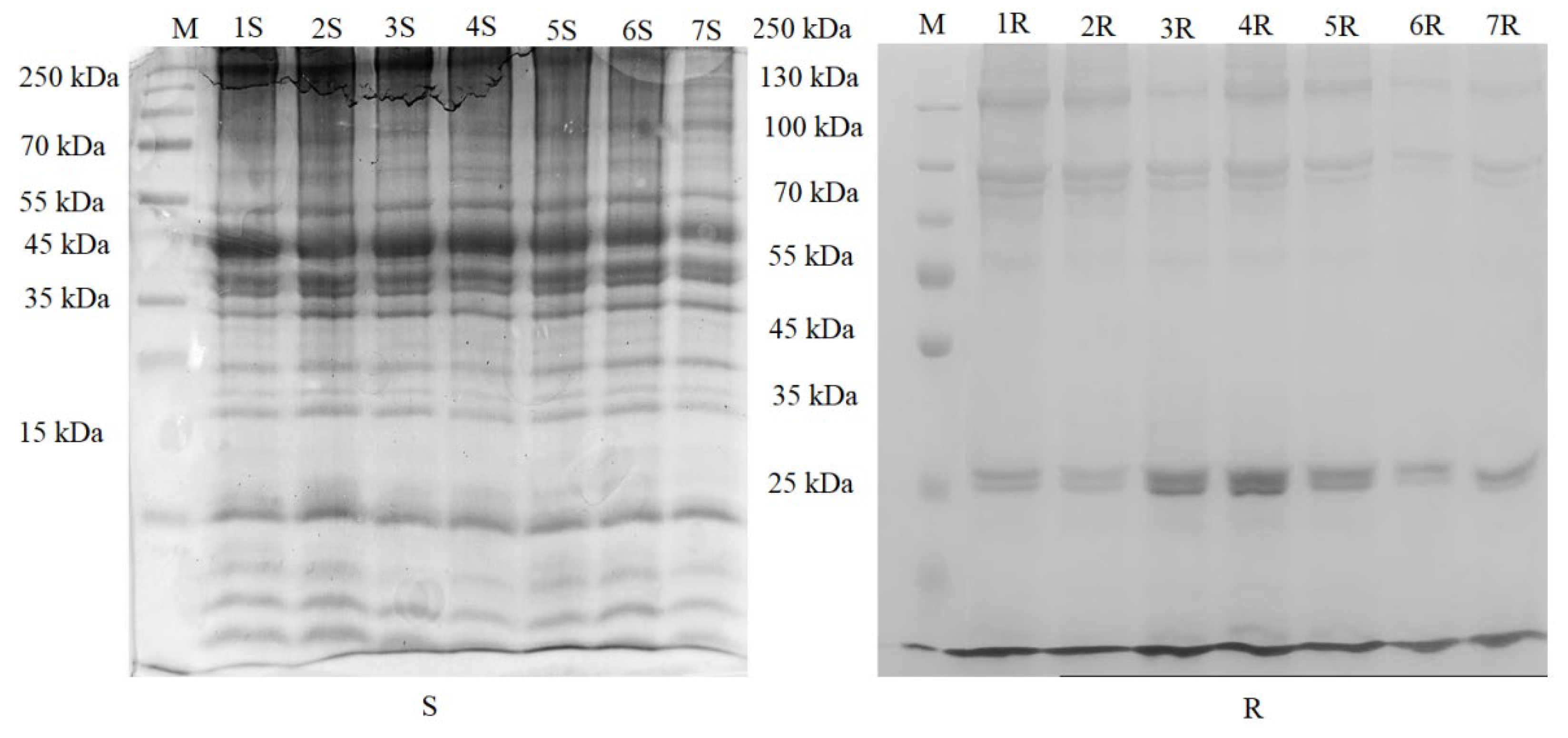
3.7. SDS-Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis
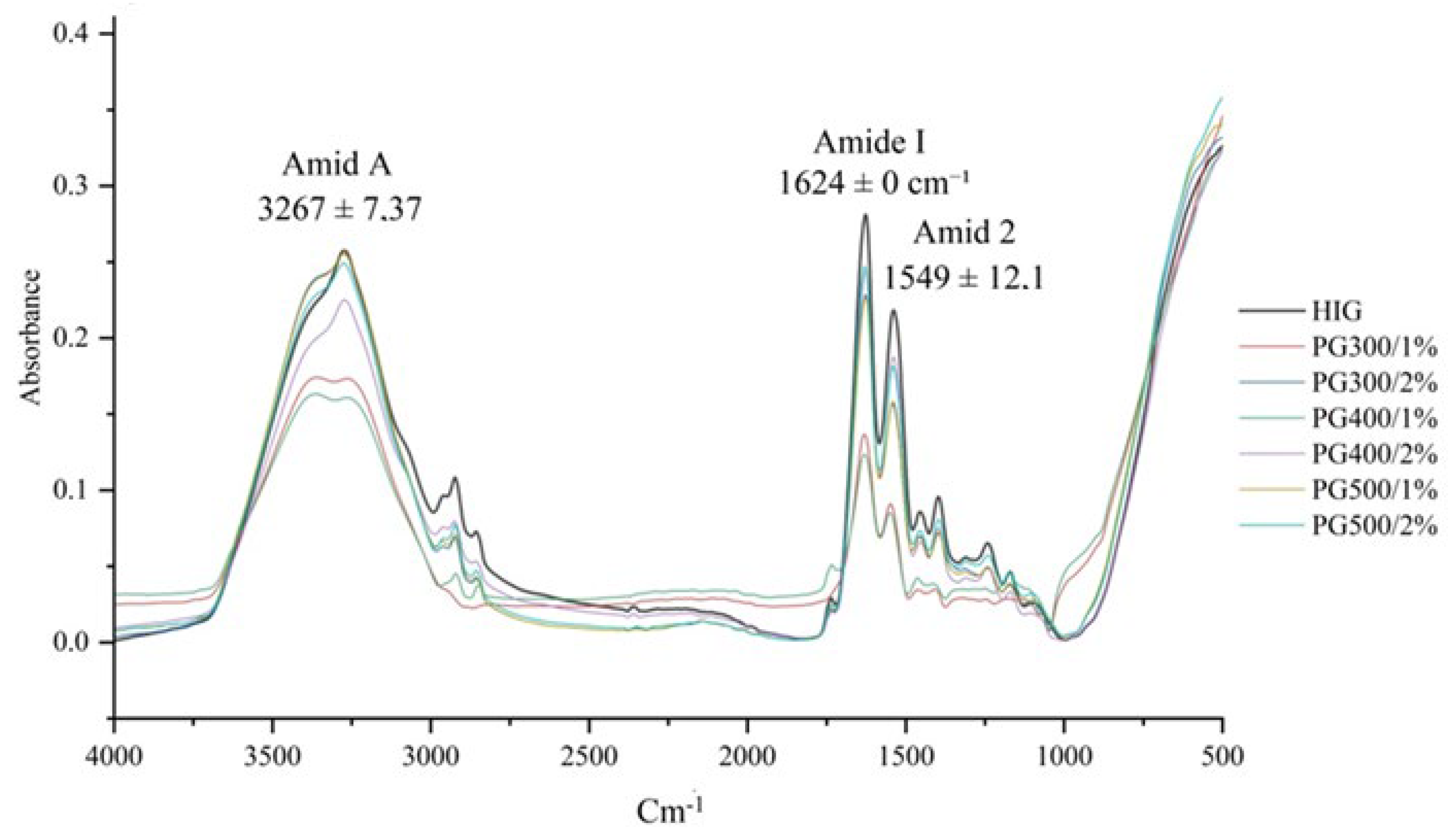
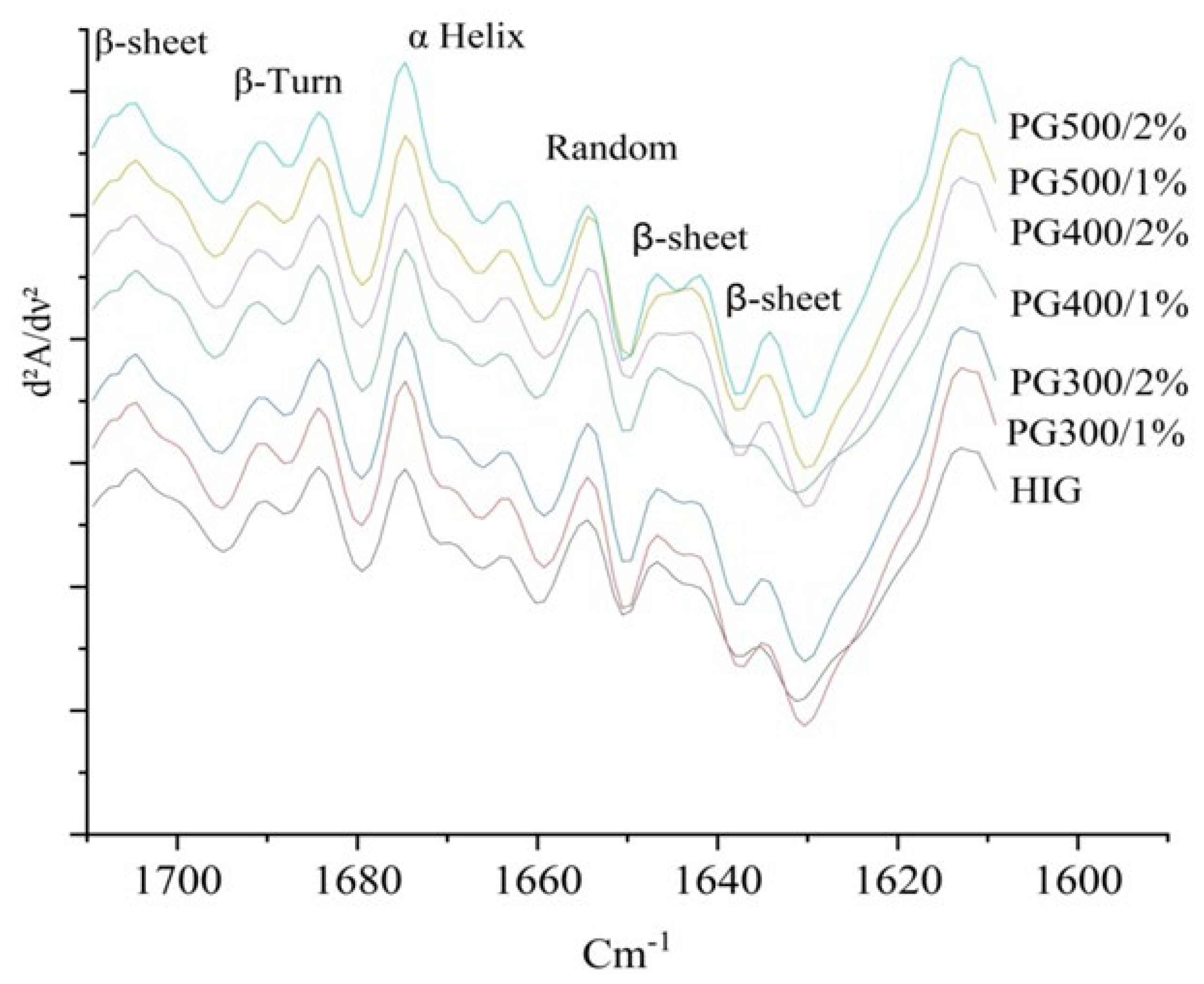
3.8. FTIR Analysis
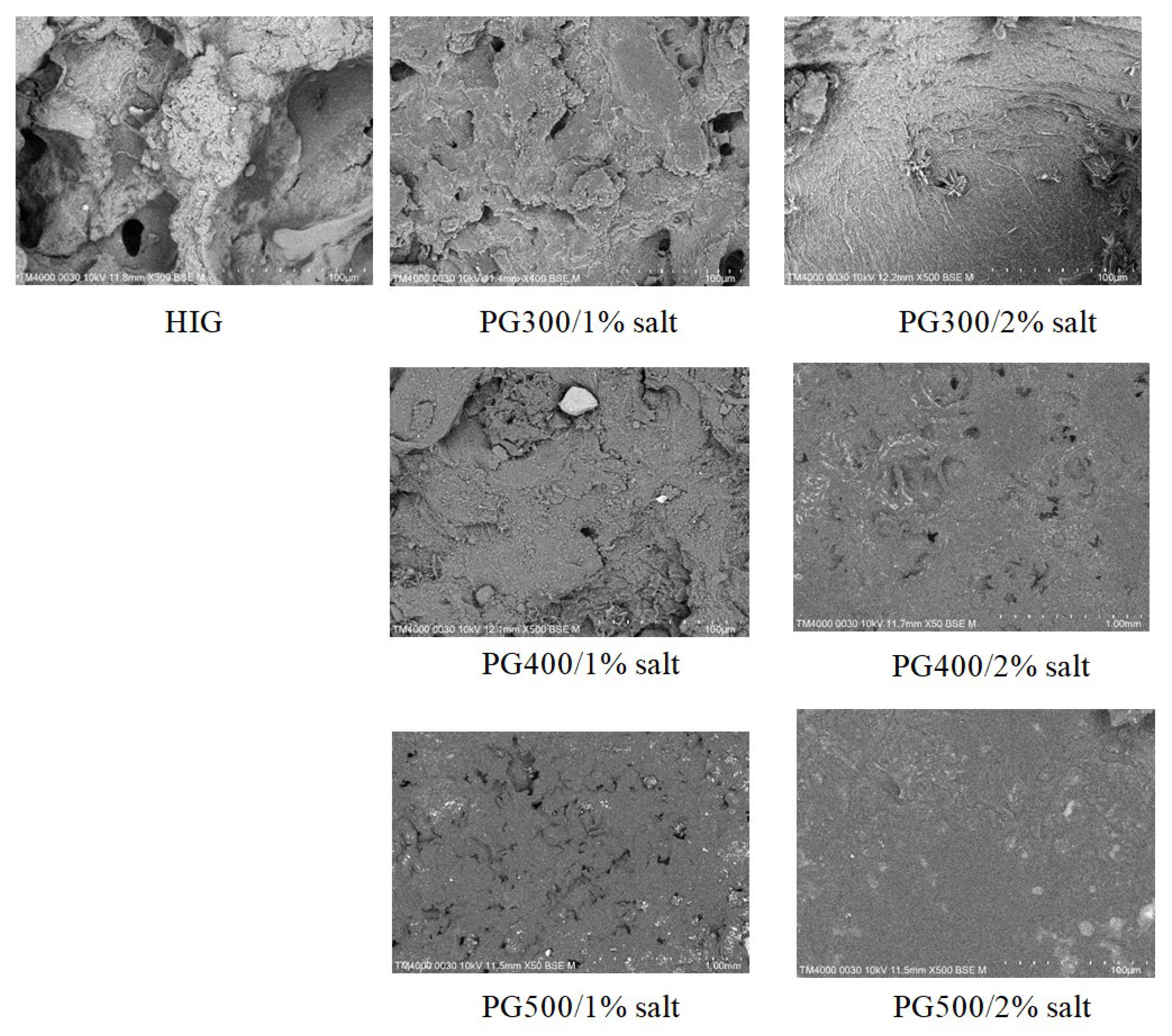
3.9. Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HPP | High-pressure processing |
| HIGs | Heat-induced gels |
| FTIR | Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscope |
| TPC | Total plate count |
| WHC | Water-holding capacity |
| MHC | Myosin heavy chain |
References
- Ma, X.-S.; Yi, S.-M.; Yu, Y.-M.; Li, J.-R.; Chen, J.-R. Changes in gel properties and water properties of Nemipterus virgatus surimi gel induced by high-pressure processing. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 61, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, B.Q.; Buckow, R.; Nguyen, M. Mechanical and Functional Properties of Unwashed Barramundi (Lates calcarifer) Gels as Affected by High-Pressure Processing at three Different Temperatures and Salt Concentrations. J. Aquat. Food Prod. Technol. 2020, 29, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, B.Q.; Buckow, R.; Stathopoulos, C.; Nguyen, M. Advances in High-Pressure Processing of Fish Muscles. Food Eng. Rev. 2015, 7, 109–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, B.Q.; Buckow, R.; Nguyen, M.H.; Furst, J. Effect of high-pressure treatments prior to cooking on gelling properties of unwashed protein from barramundi (Lates calcarifer) minced muscle. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 52, 1383–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cando, D.; Herranz, B.; Borderías, A.J.; Moreno, H.M. Effect of high pressure on reduced sodium chloride surimi gels. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 51, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikes, A.L.; Tobin, A.B.; Tume, R.K. Use of high pressure to reduce cook loss and improve texture of low-salt beef sausage batters. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2009, 10, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, A.; Barbut, S. Effect of chloride salts on protein extraction and interfacial protein film formation in meat batters. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1992, 58, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilar, M.; Gomez-Guillen, M.C. High-Pressure Applications on Myosystems. In Novel Food Processing Technologies; Food Science and Technology; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004; pp. 311–342. [Google Scholar]
- Macfarlane, J.J.; McKenzie, I.J.; Turner, R.H.; Jones, P.N. Binding of comminuted meat: Effect of high pressure. Meat Sci. 1984, 10, 307–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Ni, X.; Liu, Q.; Chen, C.; Deng, X.; Wang, X.; Yu, R. Ultra-high pressure improved gelation and digestive properties of Tai Lake whitebait myofibrillar protein. Food Chem. X 2024, 21, 101061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasaki, T.; Noshiroya, K.; Saitoh, N.; Okano, K.; Yamamoto, K. Studies of the effect of hydrostatic pressure pretreatment on thermal gelation of chicken myofibrils and pork meat patty. Food Chem. 2006, 95, 474–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huppertz, T.; Fox, P.F.; Kelly, A.L. High pressure-induced denaturation of α-lactalbumin and β-lactoglobulin in bovine milk and whey: A possible mechanism. J. Dairy Res. 2004, 71, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Mateos, M.; Lourenço, H.; Montero, P.; Borderías, A.J. Rheological and Biochemical Characteristics of High-Pressure- and Heat-Induced Gels from Blue Whiting (Micromesistius poutassou) Muscle Proteins. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1997, 45, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.T.; Bao, H.N.D.; Dang, H.T.T.; Tómasson, T.; Arason, S.; Gudjónsdóttir, M. Protein Characteristics and Bioactivity of Fish Protein Hydrolysates from Tra Catfish (Pangasius hypophthalmus) Side Stream Isolates. Foods 2022, 11, 4102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, H.T.T.; Gudjónsdóttir, M.; Tómasson, T.; Nguyen, M.V.; Karlsdóttir, M.G.; Arason, S. Influence of processing additives, packaging and storage conditions on the physicochemical stability of frozen Tra catfish (Pangasius hypophthalmus) fillets. J. Food Eng. 2018, 238, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathod, N.B.; Pagarkar, A.U.; Pujari, K.H.; Shingare, P.; Satam, S.; Phadke, G.G.; Gaikwad, B. Status of valuable components from pangasius: A review. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2018, 7, 2106–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Chen, S.; You, J.; Hu, Y.; Yin, T.; Liu, R. A comprehensive unraveling of the mystery of reduced-salt surimi gels: From molecular mechanism to future prospects. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 154, 104783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Xiong, J.; Li, P.; Zhang, Y.; Li, F.; Yin, T.; Huang, Q. Dual enhancement effects of different yeast extract on gel properties and saltiness perception of low-salt surimi gel from silver carp. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 152, 109925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Chen, L.; Lu, M.; Ai, C.; Cao, H.; Xiao, J.; Teng, H. Effect of cellulose on gel properties of heat-induced low-salt surimi gels: Physicochemical characteristics, water distribution and microstructure. Food Chem. X 2023, 19, 100820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Guo, Q.; Shi, W. Ultrasound-assisted processing: Changes in gel properties, water-holding capacity, and protein aggregation of low-salt Hypophthalmichthys molitrix surimi by soy protein isolate. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2023, 92, 106258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelce Mailoa, M.; Marthina Tapotubun, A.; Matrutty, T.E.A.A. Analysis Total Plate Counte (TPC) On Fresh Steak Tuna Applications Edible Coating Caulerpa sp During Stored at Chilling Temperature. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2017, 89, 012014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez-Suarez, J.C.; Morrissey, M.T. Effect of high pressure processing (HPP) on shelf life of albacore tuna (Thunnus alalunga) minced muscle. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2006, 7, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Romero, M.; Kelly, A.L.; Kerry, J.P. Effects of high-pressure and heat treatments on physical and biochemical characteristics of oysters (Crassostrea gigas). Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2007, 8, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Mateos, M.; Montero, P. High-pressure-induced gel of sardine (Sardina pilchardus) washed mince as affected by pressure-time-temperature. J. Food Sci. 1997, 62, 1183–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uresti, R.M.; Velazquez, G.; Vázquez, M.; Ramírez, J.A.; Torres, J.A. Effect of sugars and polyols on the functional and mechanical properties of pressure-treated arrowtooth flounder (Atheresthes stomias) proteins. Food Hydrocoll. 2005, 19, 964–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowry, O.H.; Rosebrough, N.J.; Farr, A.L.; Randall, R.J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 193, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pazos, M.; Méndez, L.; Vázquez, M.; Aubourg, S.P. Proteomics analysis in frozen horse mackerel previously high-pressure processed. Food Chem. 2015, 185, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasaki, T.; Washio, M.; Yamamoto, K.; Nakamura, K. Rheological and Morphological Comparison of Thermal and Hydrostatic Pressure-Induced Filamentous Myosin Gels. J. Food Sci. 2005, 70, e432–e436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muntean, M.; Ovidiu, M.; Barbieru, V.; Catunescu, G.; Ranta, O.; Drocas, I.; Terhes, S. High Pressure Processing in Food Industry–Characteristics and Applications. Agric. Agric. Sci. Procedia 2016, 10, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, C.A.; Moreira, S.A.; Fidalgo, L.G.; Inácio, R.S.; Barba, F.J.; Saraiva, J.A. Effects of high-pressure processing on fungi spores: Factors affecting spore germination and inactivation and impact on ultrastructure. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 553–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Muralidharan, S.; Lee, N.A.; Lo, R.; Stokes, J.R.; Fitzgerald, M.A.; Turner, M.S. The impact of variable high pressure treatments and/or cooking of rice on bacterial populations after storage using culture-independent analysis. Food Control 2018, 92, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunnath, S.; Jaganath, B.; Panda, S.K.; Ravishankar, C.N.; Gudipati, V. Modifying textural and functional characteristics of fish (Nemipterus japonicus) mince using high pressure technology. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 59, 4122–4133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Oliveira, F.A.; Neto, O.C.; dos Santos, L.M.R.; Ferreira, E.H.R.; Rosenthal, A. Effect of high pressure on fish meat quality—A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 66, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uresti, R.M.; Velazquez, G.; Ramírez, J.A.; Vázquez, M.; Torres, J.A. Effect of high-pressure treatments on mechanical and functional properties of restructured products from arrowtooth flounder (Atheresthes stomias). J. Sci. Food Agric. 2004, 84, 1741–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckow, R.; Bull, M. Advanced food preservation technologies. Microbiol. Aust. 2013, 34, 108–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Zhu, L.; Shang, H.; Xuan, X.; Lin, X. Effects of Combined ε-Polylysine and High Hydrostatic Pressure Treatment on Microbial Qualities, Physicochemical Properties, Taste, and Volatile Flavor Profile of Large Yellow Croaker (Larimichthys crocea). Food Bioprocess Technol. 2024, 18, 3610–3627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Watkins, P.; Oiseth, S.; Cochet-Broch, M.; Sikes, A.L.; Chen, C.; Buckow, R. High pressure processing improves the sensory quality of sodium-reduced chicken sausage formulated with three anion types of potassium salt. Food Control 2021, 126, 108008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabilo-Munizaga, G.; Barbosa-Cánovas, G.V. Ultra high pressure technology and its use in surimi manufacture: An overview. Food Sci. Technol. Int. 2004, 10, 207–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez, J.A.; Martín-Polo, M.O.; Bandman, E. Fish myosin aggregation as affected by freezing and initial physical state. J. Food Sci. 2000, 65, 556–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagné, C.; Isambert, M.-F.; Gasnier, B. SDS-resistant aggregation of membrane proteins: Application to the purification of the vesicular monoamine transporter. Biochem. J. 1996, 316 Pt 3, 825–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herranz, B.; Tovar, C.A.; Borderias, A.J.; Moreno, H.M. Effect of high-pressure and/or microbial transglutaminase on physicochemical, rheological and microstructural properties of flying fish surimi. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2013, 20, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojagh, S.M.; Núñez-Flores, R.; López-Caballero, M.E.; Montero, M.P.; Gómez-Guillén, M.C. Lessening of high-pressure-induced changes in Atlantic salmon muscle by the combined use of a fish gelatin–lignin film. Food Chem. 2011, 125, 595–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, J.; Yu, S. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopic Analysis of Protein Secondary Structures. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2007, 39, 549–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández, B.; Pflüger, F.; Adenier, A.; Kruglik, S.G.; Ghomi, M. Vibrational Analysis of Amino Acids and Short Peptides in Hydrated Media. VIII. Amino Acids with Aromatic Side Chains: L-Phenylalanine, l-Tyrosine, and l-Tryptophan. J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 15319–15330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadat, A.; Joye, I.J. Peak Fitting Applied to Fourier Transform Infrared and Raman Spectroscopic Analysis of Proteins. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 5918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venyaminov, S.Y.; Kalnin, N.N. Quantitative IR spectrophotometry of peptide compounds in water (H2O) solutions. II. Amide absorption bands of polypeptides and fibrous proteins in α-, β-, and random coil conformations. Biopolymers 1990, 30, 1259–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.-S.; Mu, T.-H.; Guo, X.; Zhu, S.; Azuma, N.; Kanno, C. Comparison of the gel-forming ability and gel properties of α-lactalbumin, lysozyme and myoglobin in the presence of β-lactoglobulin under high pressure. Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 33, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolumar, T.; Middendorf, D.; Toepfl, S.; Heinz, V. Structural Changes in Foods Caused by High-Pressure Processing; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 509–537. [Google Scholar]
- Knorr, D.; Heinz, V.; Buckow, R. High pressure application for food biopolymers. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Proteins Proteom. 2006, 1764, 619–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, H.M.; Bargiela, V.; Tovar, C.A.; Cando, D.; Borderias, A.J.; Herranz, B. High pressure applied to frozen flying fish (Parexocoetus brachyterus) surimi: Effect on physicochemical and rheological properties of gels. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 48, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhou, A.; Benjakul, S.; Zou, Y.; Liu, X.; Xiao, S. The mechanism of low-level pressure coupled with heat treatment on water migration and gel properties of Nemipterus virgatus surimi. LWT 2021, 150, 112086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Treatment | Whiteness | ∆E |
|---|---|---|
| HIGs | 61.21 ± 0.55a | |
| PG300/1% salt | 64.56 ± 2.04b | 6.53 ± 0.88 |
| PG300/2% salt | 63.17 ± 0.26b | 6.15 ± 0.99 |
| PG400/1% salt | 63.45 ± 0.91b | 6.59 ± 0.47 |
| PG400/2% salt | 64.06 ± 0.50b | 6.18 ± 0.71 |
| PG500/1% salt | 63.81 ± 1.43b | 6.42 ± 0.59 |
| PG500/2% salt | 63.26 ± 0.67b | 6.54 ± 0.49 |
| Treatment | Hardness (N) | Springiness (mm) | Gel Strength (N.mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| HIGs | 7.93 ± 0.64a | 0.88 ± 0.02a | 346.21 ± 16.96a |
| PG300/1% salt | 8.34 ± 0.52a | 0.87 ± 0.01a | 417.65 ± 50.95b |
| PG300/2% salt | 10.39 ± 1.68bc | 0.89 ± 0.02a | 424.85 ± 25.29b |
| PG400/1% salt | 8.29 ± 0.42a | 0.87 ± 0.01a | 408.38 ± 12.43b |
| PG400/2% salt | 10.32 ± 0.87bc | 0.88 ± 0.02a | 436.92 ± 42.25b |
| PG500/1% salt | 8.96 ± 0.59ac | 0.89 ± 0.01a | 425.30 ± 23.09b |
| PG500/2% salt | 11.56 ± 1.76b | 0.89 ± 0.02a | 464.92 ± 13.56b |
| Treatment | α-Helix (%) | β-Sheet (%) | β-Turn (%) | Random Structure (%) | Aromatic Side Chain |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HIGs | 19.41 ± 2.27a | 31.18 ± 0.73a | 19.64 ± 1.33a | 10.57 ± 0.51a | 19.17 ± 0.37a |
| PG300/1% salt | 24.74 ± 1.99b | 29.55 ± 0.96a | 20.14 ± 0.81a | 8.49 ± 0.66b | 17.05 ± 3.76a |
| PG300/2% salt | 24.14 ± 1.07b | 29.54 ± 1.32a | 19.84 ± 0.84a | 8.95 ± 1.36ab | 17.52 ± 3.89a |
| PG400/1% salt | 24.66 ± 1.87b | 29.22 ± 2.86a | 19.85 ± 1.08a | 8.02 ± 1.26b | 18.21 ± 1.34a |
| PG400/2% salt | 23.53 ± 1.11b | 30.72 ± 1.72a | 19.89 ± 1.33a | 9.06 ± 0.45ab | 16.77 ± 3.73a |
| PG500/1% salt | 23.65 ± 0.98b | 30.18 ± 1.73a | 20.11 ± 1.03a | 7.69 ± 1.38b | 18.32 ± 3.16a |
| PG500/2% salt | 23.82 ± 1.76b | 29.43 ± 0.89a | 20.16 ± 1.96a | 9.19 ± 1.12ab | 17.37 ± 3.81a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Truong, B.Q.; Buckow, R.; Nguyen, K.N.H.; Nguyen, L.T.; Huynh, T.N.A.; Hoang, V.C. High-Pressure Processing of Reduced Salt Pangasius Catfish (Pangasianodon hypophthalmus) Minced Muscle: The Effects on Selected Quality Properties of Its Gels. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 4727. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15094727
Truong BQ, Buckow R, Nguyen KNH, Nguyen LT, Huynh TNA, Hoang VC. High-Pressure Processing of Reduced Salt Pangasius Catfish (Pangasianodon hypophthalmus) Minced Muscle: The Effects on Selected Quality Properties of Its Gels. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(9):4727. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15094727
Chicago/Turabian StyleTruong, Binh Q., Roman Buckow, Kha N. H. Nguyen, Linh T. Nguyen, Tuan N. A. Huynh, and Van Chuyen Hoang. 2025. "High-Pressure Processing of Reduced Salt Pangasius Catfish (Pangasianodon hypophthalmus) Minced Muscle: The Effects on Selected Quality Properties of Its Gels" Applied Sciences 15, no. 9: 4727. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15094727
APA StyleTruong, B. Q., Buckow, R., Nguyen, K. N. H., Nguyen, L. T., Huynh, T. N. A., & Hoang, V. C. (2025). High-Pressure Processing of Reduced Salt Pangasius Catfish (Pangasianodon hypophthalmus) Minced Muscle: The Effects on Selected Quality Properties of Its Gels. Applied Sciences, 15(9), 4727. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15094727










