Investigation of Deficits in Auditory Emotional Content Recognition by Adult Cochlear Implant Users through the Study of Electroencephalographic Gamma and Alpha Asymmetry and Alexithymia Assessment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample
2.2. Protocol
2.3. Stimuli
2.4. EEG
2.5. Alexithymia
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
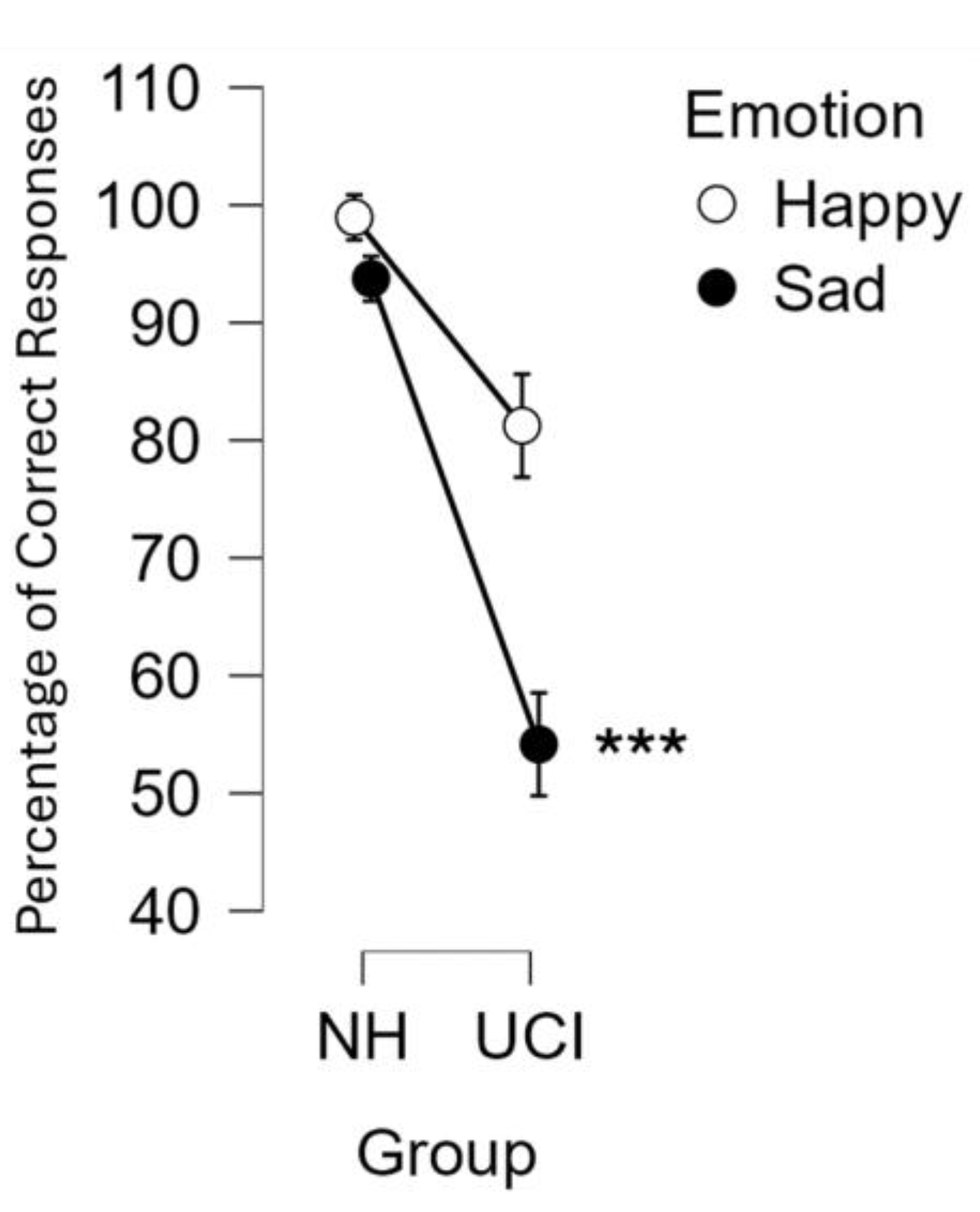
3.1. Behavioural
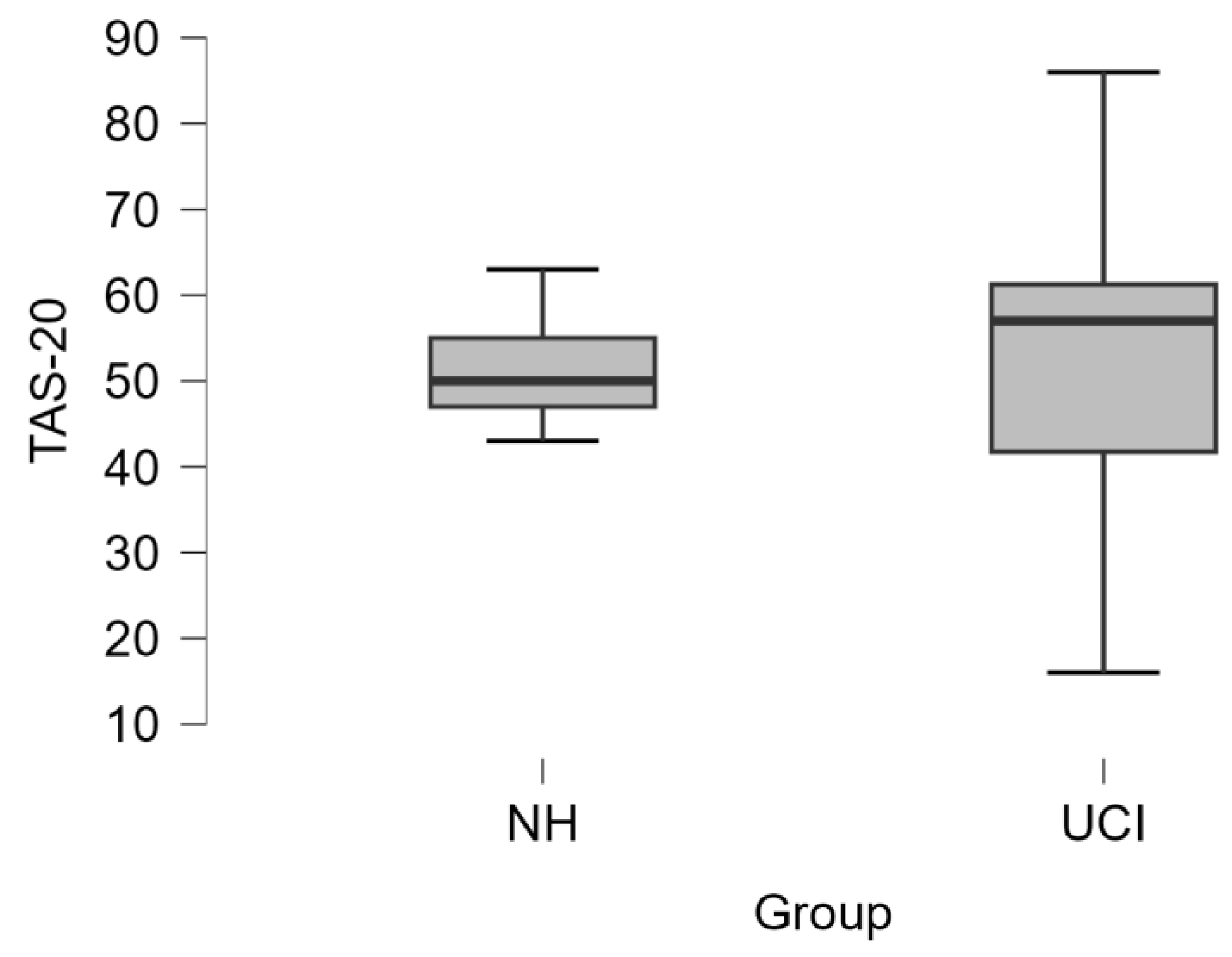
3.2. TAS-20
3.3. EEG
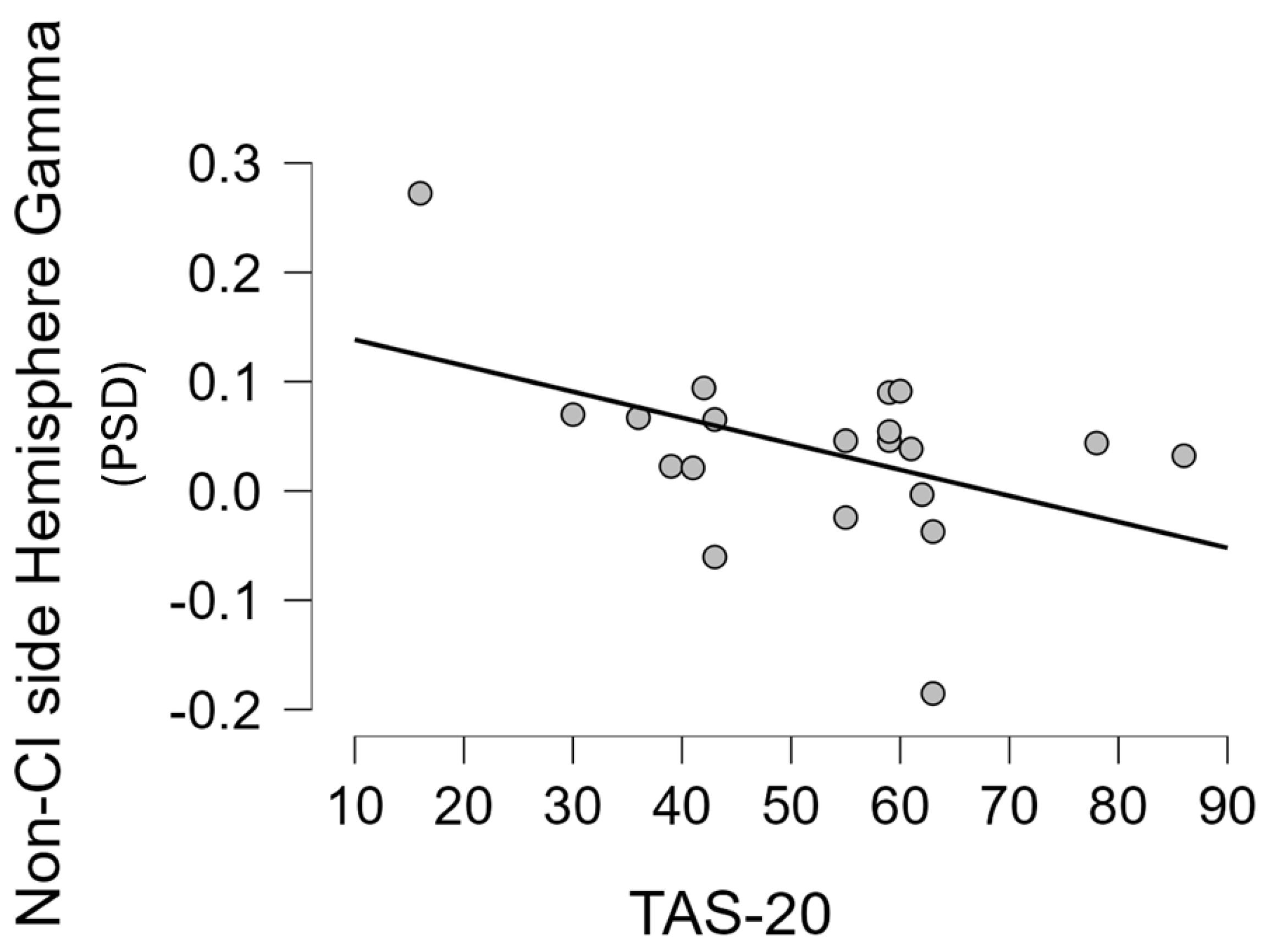
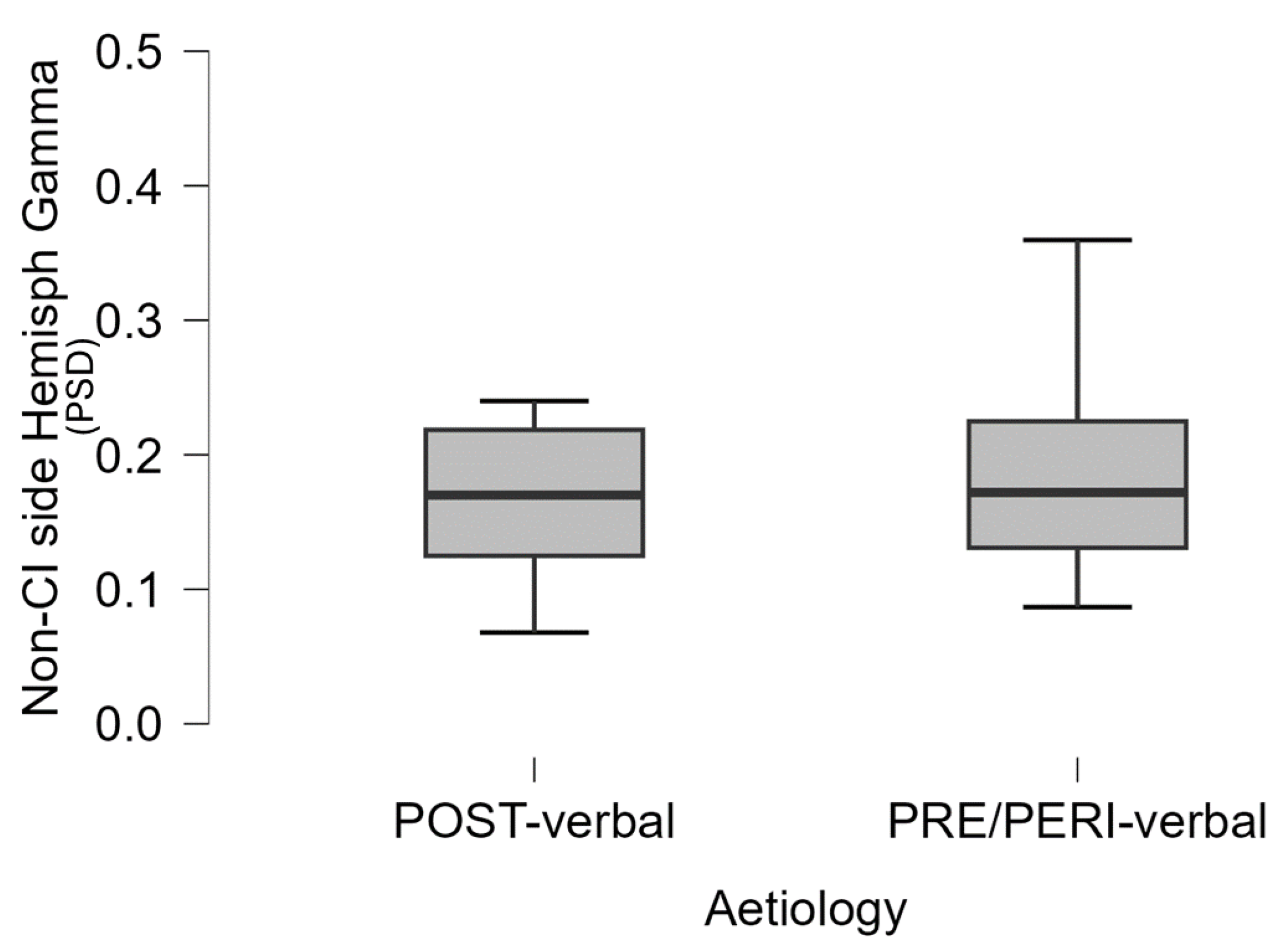
3.3.1. Gamma Asymmetry
3.3.2. Frontal Gamma Asymmetry
3.3.3. Frontal Alpha Asymmetry
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baldwin, D.A.; Moses, L.J. The Ontogeny of Social Information Gathering. Child Dev. 1996, 67, 1915–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, N.; Gernsbacher, M.A. On Privileging the Role of Gaze in Infant Social Cognition. Child Dev. Perspect. 2008, 2, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paparella, M.M.; Fox, R.Y.; Schachern, P.A. Diagnosis and Treatment of Sensorineural Hearing Loss in Children. Otolaryngol. Clin. N. Am. 1989, 22, 51–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manrique, M.; Ramos, Á.; Vernetta, C.d.P.; Gil-Carcedo, E.; Lassaletta, L.; Sanchez-Cuadrado, I.; Espinosa, J.M.; Batuecas, Á.; Cenjor, C.; Lavilla, M.J.; et al. Guideline on Cochlear Implants. Acta Otorrinolaringol. (Engl. Ed.) 2019, 70, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonard, L.; Brotto, D.; Moreno-Pelayo, M.A.; del Castillo, I.; Kremer, H.; Pennings, R.; Caria, H.; Fialho, G.; Boudewyns, A.; Van Camp, G.; et al. Genetic Evaluation of Prelingual Hearing Impairment: Recommendations of an European Network for Genetic Hearing Impairment. Audiol. Res. 2023, 13, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dettman, S.J.; Pinder, D.; Briggs, R.J.S.; Dowell, R.C.; Leigh, J.R. Communication Development in Children Who Receive the Cochlear Implant Younger than 12 Months: Risks versus Benefits. Ear Hear. 2007, 28, 11S–18S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Dorman, M.F.; Spahr, A.J. A Sensitive Period for the Development of the Central Auditory System in Children with Cochlear Implants: Implications for Age of Implantation. Ear Hear. 2002, 23, 532–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Dorman, M.F. Central Auditory Development in Children with Cochlear Implants: Clinical Implications. Cochlear Brainstem Implant. 2006, 64, 66–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Nash, A.A.; Dorman, M. Cortical development, plasticity and re-organization in children with cochlear implants. J. Commun. Disord. 2009, 42, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiam, N.T.; Limb, C. Music perception and training for pediatric cochlear implant users. Expert Rev. Med. Devices 2020, 17, 1193–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, M.; Kulkarni, A.M.; Siddiqui, R.M.; Christensen, J.A.; Hozan, M.; Sis, J.L.; Damm, S.A. Acoustics of Emotional Prosody Produced by Prelingually Deaf Children with Cochlear Implants. Front. Psychol. 2019, 10, 2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, M.; Zion, D.J.; Deroche, M.L.; Burianek, B.A.; Limb, C.J.; Goren, A.P.; Kulkarni, A.M.; Christensen, J.A. Voice emotion recognition by cochlear-implanted children and their normally-hearing peers. Hear. Res. 2015, 322, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damm, S.A.; Sis, J.L.; Kulkarni, A.M.; Chatterjee, M. How Vocal Emotions Produced by Children with Cochlear Implants Are Perceived by Their Hearing Peers. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2019, 62, 3728–3740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiam, N.; Caldwell, M.; Deroche, M.; Chatterjee, M.; Limb, C. Voice emotion perception and production in cochlear implant users. Hear. Res. 2017, 352, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannon, S.A.; Chatterjee, M. Age-Related Changes in Voice Emotion Recognition by Postlingually Deafened Listeners with Cochlear Implants. Ear Hear. 2022, 43, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, M.E.; Chatterjee, M. Weighting of Prosodic and Lexical-Semantic Cues for Emotion Identification in Spectrally Degraded Speech and with Cochlear Implants. Ear Hear. 2021, 42, 1727–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cullington, H.E.; Zeng, F.-G. Comparison of bimodal and bilateral cochlear implant users on speech recognition with competing talker, music perception, affective prosody discrimination, and talker identification. Ear. Hear. 2011, 32, 16–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias-Vergara, T.; Batliner, A.; Rader, T.; Polterauer, D.; Högerle, C.; Müller, J.; Orozco-Arroyave, J.-R.; Nöth, E.; Schuster, M. Adult Cochlear Implant Users Versus Typical Hearing Persons: An Automatic Analysis of Acoustic–Prosodic Parameters. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2022, 65, 4623–4636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambert-Dahan, E.; Giraud, A.-L.; Sterkers, O.; Samson, S. Judgment of musical emotions after cochlear implantation in adults with progressive deafness. Front. Psychol. 2015, 6, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gfeller, K.; Turner, C.; Oleson, J.; Zhang, X.; Gantz, B.; Froman, R.; Olszewski, C. Accuracy of cochlear implant recipients on pitch perception, melody recognition, and speech reception in noise. Ear Hear. 2007, 28, 412–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gfeller, K.E.; Olszewski, C.; Turner, C.; Gantz, B.; Oleson, J. Music Perception with Cochlear Implants and Residual Hearing. Audiol. Neurotol. 2006, 11, 12–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Y.-Y.; Cruz, R.; Jones, J.A.; Zeng, F.-G. Music perception with temporal cues in acoustic and electric hearing. Ear Hear. 2004, 25, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorrentino, F.; Gheller, F.; Favaretto, N.; Franz, L.; Stocco, E.; Brotto, D.; Bovo, R. Music perception in adult patients with cochlear implant. Hear. Balance Commun. 2020, 18, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paquette, S.; Deroche, M.L.D.; Goffi-Gomez, M.V.; Hoshino, A.C.H.; Lehmann, A. Predicting emotion perception abilities for cochlear implant users. Int. J. Audiol. 2022, 62, 946–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peretz, I.; Gagnon, L.; Bouchard, B. Music and emotion: Perceptual determinants, immediacy, and isolation after brain damage. Cognition 1998, 68, 111–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopyan, T.; Peretz, I.; Chan, L.P.; Papsin, B.C.; Gordon, K.A. Children Using Cochlear Implants Capitalize on Acoustical Hearing for Music Perception. Front. Psychol. 2012, 3, 32749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stabej, K.K.; Smid, L.; Gros, A.; Zargi, M.; Kosir, A.; Vatovec, J. The music perception abilities of prelingually deaf children with cochlear implants. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2012, 76, 1392–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volkova, A.; Trehub, S.E.; Schellenberg, E.G.; Papsin, B.C.; Gordon, K.A. Children with bilateral cochlear implants identify emotion in speech and music. Cochlea Implant. Int. 2013, 14, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emotion Regulation in Adulthood: Timing Is Everything—James J. Gross, 2001. Available online: https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/abs/10.1111/1467-8721.00152?casa_token=Uk0L_U1ZuOcAAAAA:5h-3vXQHsmT1AKhFIU5tA2yPUfM9fH0N7tNI_wFJNenzpMq-pblK36H2JZk7Ii-cUngX6syA4pC2eDs&casa_token=3b-F1uVEX3kAAAAA:Go3PvryT5MHEZiJU67JLjd8WPk8TDIYSkjwqfapVdIASG27n1wW0l1myluWqsqS1E5_SaI1JZhKq7Ek (accessed on 30 July 2024).
- Sifneos, P. The Prevalence of ‘Alexithymic’ Characteristics in Psychosomatic Patients. Psychother. Psychosom. 1973, 22, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, G.J. Alexithymia: Concept, measurement, and implications for treatment. Am. J. Psychiatry 1984, 141, 725–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicastri, M.; D’Alessandro, H.D.; Giallini, I.; D’Amico, A.; Geraci, A.; Inguscio, B.M.S.; Guerzoni, L.; Cuda, D.; Vestri, A.; Fegatelli, D.A.; et al. Emotional abilities in preadolescents and adolescents with long-term cochlear implant use. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2024, 177, 111866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peñacoba, C.; Garvi, D.; Gómez, L.; Álvarez, A. Psychological Well-Being, Emotional Intelligence, and Emotional Symptoms in Deaf Adults. Am. Ann. Deaf 2020, 165, 436–452. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Taylor, G.J.; Bagby, R.M. New Trends in Alexithymia Research. Psychother. Psychosom. 2004, 73, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryff, C.D. Beyond Ponce de Leon and Life Satisfaction: New Directions in Quest of Successful Ageing. Int. J. Behav. Dev. 1989, 12, 35–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salovey, P.; Mayer, J.D.; Goldman, S.L.; Turvey, C.; Palfai, T.P. Emotional attention, clarity, and repair: Exploring emotional intelligence using the Trait Meta-Mood Scale. In Emotion, Disclosure, and Health; Pennebaker, J.W., Ed.; American Psychological Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1995; pp. 125–154. [Google Scholar]
- Peñacoba, C.; Garvi, D.; Gómez, L.; Álvarez, A. Emotional Functioning, Positive Relationships, and Language Use in Deaf Adults. J. Deaf. Stud. Deaf. Educ. 2020, 25, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Lu, B. Emotion classification based on gamma-band EEG. In Proceedings of the 2009 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2–6 September 2009; pp. 1223–1226. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, K.; Tong, L.; Shu, J.; Zhuang, N.; Yan, B.; Zeng, Y. High Gamma Band EEG Closely Related to Emotion: Evidence From Functional Network. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balconi, M.; Lucchiari, C. Consciousness and arousal effects on emotional face processing as revealed by brain oscillations. A gamma band analysis. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2008, 67, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, D.; Thorne, J.; Viola, F.; Timm, L.; Debener, S.; Büchner, A.; Dengler, R.; Wittfoth, M. Electrophysiological responses to emotional prosody perception in cochlear implant users. NeuroImage Clin. 2013, 2, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cartocci, G.; Giorgi, A.; Inguscio, B.M.S.; Scorpecci, A.; Giannantonio, S.; De Lucia, A.; Garofalo, S.; Grassia, R.; Leone, C.A.; Longo, P.; et al. Higher Right Hemisphere Gamma Band Lateralization and Suggestion of a Sensitive Period for Vocal Auditory Emotional Stimuli Recognition in Unilateral Cochlear Implant Children: An EEG Study. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 608156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mockevičius, A.; Šveistytė, K.; Griškova-Bulanova, I. Individual/Peak Gamma Frequency: What Do We Know? Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, K.S.; Luvizutto, G.J.; Bruno, A.C.M.; de Oliveira, S.F.; Costa, S.C.; da Silva, G.M.; Andrade, M.J.C.; Pereira, J.M.; Andrade, A.O.; de Souza, L.A.P.S. Gamma-Band Frequency Analysis and Motor Development in Music-Trained Children: A Cross-Sectional Study. J. Mot. Behav. 2021, 54, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cartocci, G.; Maglione, A.G.; Vecchiato, G.; Modica, E.; Rossi, D.; Malerba, P.; Marsella, P.; Scorpecci, A.; Giannantonio, S.; Mosca, F.; et al. Frontal brain asymmetries as effective parameters to assess the quality of audiovisual stimuli perception in adult and young cochlear implant users. Acta Otorhinolaryngol. Ital. 2018, 38, 346–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagné, J.-P.; Besser, J.; Lemke, U. Behavioral Assessment of Listening Effort Using a Dual-Task Paradigm. Trends Hear. 2017, 21, 2331216516687287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhanbali, S.; Dawes, P.; Millman, R.E.; Munro, K.J. Measures of Listening Effort Are Multidimensional. Ear Hear. 2019, 40, 1084–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, J.D.; Taylor, G.J.; Bagby, R. The 20-Item Toronto Alexithymia Scale: III. Reliability and factorial validity in a community population. J. Psychosom. Res. 2003, 55, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, G.J.; Bagby, R.; Parker, J.D. The 20-Item Toronto Alexithymia Scale: IV. Reliability and factorial validity in different languages and cultures. J. Psychosom. Res. 2003, 55, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagby, R.M.; Parker, J.D.A.; Taylor, G.J. The twenty-item Toronto Alexithymia scale—I. Item selection and cross-validation of the factor structure. J. Psychosom. Res. 1994, 38, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagby, R.; Taylor, G.J.; Parker, J.D. The twenty-item Toronto Alexithymia scale—II. Convergent, discriminant, and concurrent validity. J. Psychosom. Res. 1994, 38, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruns, L.; Mürbe, D.; Hahne, A. Understanding music with cochlear implants. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levitt, H. Adaptive testing in audiology. Scand. Audiol. Suppl. 1978, 1, 241–291. [Google Scholar]
- Bubbico, L.; Ferlito, S.; Antonelli, G.; Martini, A.; Pescosolido, N. Hearing and Vision Screening Program for newborns in Italy. Ann. Ig. 2021, 33, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blamey, P.; Artieres, F.; Başkent, D.; Bergeron, F.; Beynon, A.; Burke, E.; Dillier, N.; Dowell, R.; Fraysse, B.; Gallégo, S.; et al. Factors Affecting Auditory Performance of Postlinguistically Deaf Adults Using Cochlear Implants: An Update with 2251 Patients. Audiol. Neurotol. 2012, 18, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopyan, T.; Gordon, K.A.; Papsin, B.C. Identifying emotions in music through electrical hearing in deaf children using cochlear implants. Cochlea- Implant. Int. 2011, 12, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannantonio, S.; Polonenko, M.J.; Papsin, B.C.; Paludetti, G.; Gordon, K.A. Experience Changes How Emotion in Music Is Judged: Evidence from Children Listening with Bilateral Cochlear Implants, Bimodal Devices, and Normal Hearing. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0136685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inguscio, B.M.S.; Mancini, P.; Greco, A.; Nicastri, M.; Giallini, I.; Leone, C.A.; Grassia, R.; Di Nardo, W.; Di Cesare, T.; Rossi, F.; et al. ‘Musical effort’ and ‘musical pleasantness’: A pilot study on the neurophysiological correlates of classical music listening in adults normal hearing and unilateral cochlear implant users. Hear. Balance Commun. 2022, 20, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turrini, M.; Cutugno, F.; Maturi, P.; Prosser, S.; Leoni, F.A.; Arslan, E. Bisyllabic words for speech audiometry: A new italian material. Acta Otorhinolaryngol. Ital. 1993, 13, 63–77. [Google Scholar]
- Cartocci, G.; Maglione, A.G.; Rossi, D.; Modica, E.; Borghini, G.; Malerba, P.; Piccioni, L.O.; Babiloni, F. Alpha and Theta EEG Variations as Indices of Listening Effort to Be Implemented in Neurofeedback Among Cochlear Implant Users. In Symbiotic Interaction; Ham, J., Spagnolli, A., Blankertz, B., Gamberini, L., Jacucci, G., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gfeller, K.; Christ, A.; Knutson, J.F.; Witt, S.; Murray, K.T.; Tyler, R.S. Musical backgrounds, listening habits, and aesthetic enjoyment of adult cochlear implant recipients. J. Am. Acad Audiol. 2020, 11, 390–406. [Google Scholar]
- Di Flumeri, G.; Arico, P.; Borghini, G.; Colosimo, A.; Babiloni, F. A new regression-based method for the eye blinks artifacts correction in the EEG signal, without using any EOG channel. In Proceedings of the 38th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Orlando, FL, USA, 16–20 August 2016; Volume 2016, pp. 3187–3190. [Google Scholar]
- Delorme, A.; Makeig, S. EEGLAB: An open source toolbox for analysis of single-trial EEG dynamics including independent component analysis. J. Neurosci. Methods 2004, 134, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borghini, G.; Aricò, P.; Di Flumeri, G.; Cartocci, G.; Colosimo, A.; Bonelli, S.; Golfetti, A.; Imbert, J.P.; Granger, G.; Benhacene, R.; et al. EEG-Based Cognitive Control Behaviour Assessment: An Ecological study with Professional Air Traffic Controllers. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aricò, P.; Borghini, G.; Di Flumeri, G.; Colosimo, A.; Pozzi, S.; Babiloni, F. A passive brain-computer interface application for the mental workload assessment on professional air traffic controllers during realistic air traffic control tasks. Prog. Brain Res. 2016, 228, 295–328. [Google Scholar]
- Klimesch, W. EEG alpha and theta oscillations reflect cognitive and memory performance: A review and analysis. Brain Res. Rev. 1999, 29, 169–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidson, R.J.; Ekman, P.; Saron, C.D.; Senulis, J.A.; Friesen, W.V. Approach-withdrawal and cerebral asymmetry: Emotional expression and brain physiology. I. J. Pers Soc. Psychol. 1990, 58, 330. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sutton, S.K.; Davidson, R.J. Prefrontal Brain Asymmetry: A Biological Substrate of the Behavioral Approach and Inhibition Systems. Psychol. Sci. 1997, 8, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanvooren, S.; Hofmann, M.; Poelmans, H.; Ghesquière, P.; Wouters, J. Theta, beta and gamma rate modulations in the developing auditory system. Hear. Res. 2015, 327, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bressi, C.; Taylor, G.; Parker, J.; Bressi, S.; Brambilla, V.; Aguglia, E.; Allegranti, I.; Bongiorno, A.; Giberti, F.; Bucca, M.; et al. Cross validation of the factor structure of the 20-item Toronto Alexithymia Scale: An Italian multicenter study. J. Psychosom. Res. 1996, 41, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inguscio, B.M.S.; Cartocci, G.; Palmieri, S.; Menicocci, S.; Vozzi, A.; Giorgi, A.; Ferrara, S.; Canettieri, P.; Babiloni, F. Poetry in Pandemic: A Multimodal Neuroaesthetic Study on the Emotional Reaction to the Divina Commedia Poem. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 3720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inguscio, B.M.S.; Rossi, D.; Giliberto, G.; Vozzi, A.; Borghini, G.; Babiloni, F.; Greco, A.; Attanasio, G.; Cartocci, G. Bridging the Gap between Psychophysiological and Audiological Factors in the Assessment of Tinnitus: An EEG Investigation in the Beta Band. Brain Sci. 2024, 14, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glass, G.V.; Peckham, P.D.; Sanders, J.R. Consequences of Failure to Meet Assumptions Underlying the Fixed Effects Analyses of Variance and Covariance. Rev. Educ. Res. 1972, 42, 237–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harwell, M.R.; Rubinstein, E.N.; Hayes, W.S.; Olds, C.C. Summarizing Monte Carlo Results in Methodological Research: The One- and Two-Factor Fixed Effects ANOVA Cases. J. Educ. Stat. 1992, 17, 315–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lix, L.M.; Keselman, J.C.; Keselman, H.J. Consequences of Assumption Violations Revisited: A Quantitative Review of Alternatives to the One-Way Analysis of Variance F Test. Rev. Educ. Res. 1996, 66, 579–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrushina, O.R.; Dobrynina, L.A.; Arina, G.A.; Pechenkova, E.V.; Kremneva, E.I.; Gubanova, M.V.; Novikova, E.S.; Kazantseva, D.A.; Suslina, A.D.; Krotenkova, M.V. Age-related changes of interoceptive brain networks: Implications for interoception and alexithymia. Emotion 2024, 24, 1536–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattila, A.K.; Salminen, J.K.; Nummi, T.; Joukamaa, M. Age is strongly associated with alexithymia in the general population. J. Psychosom. Res. 2006, 61, 629–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inguscio, B.M.S.; Cartocci, G.; Sciaraffa, N.; Nicastri, M.; Giallini, I.; Greco, A.; Babiloni, F.; Mancini, P. Gamma-Band Modulation in Parietal Area as the Electroencephalographic Signature for Performance in Auditory–Verbal Working Memory: An Exploratory Pilot Study in Hearing and Unilateral Cochlear Implant Children. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paquette, S.; Ahmed, G.; Goffi-Gomez, M.; Hoshino, A.; Peretz, I.; Lehmann, A. Musical and vocal emotion perception for cochlear implants users. Hear. Res. 2018, 370, 272–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, C.; Xin, T.; He, Q.; Hou, X.; Liu, Y. The Neural Processing of Vocal Emotion After Hearing Reconstruction in Prelingual Deaf Children: A Functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy Brain Imaging Study. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 705741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whipple, C.M.; Gfeller, K.; Driscoll, V.; Oleson, J.; McGregor, K. Do Communication Disorders Extend to Musical Messages? An Answer from Children with Hearing Loss or Autism Spectrum Disorders. J. Music. Ther. 2015, 52, 78–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartocci, G.; Inguscio, B.M.S.; Giorgi, A.; Vozzi, A.; Leone, C.A.; Grassia, R.; Di Nardo, W.; Di Cesare, T.; Fetoni, A.R.; Freni, F.; et al. Music in noise recognition: An EEG study of listening effort in cochlear implant users and normal hearing controls. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0288461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gainotti, G. Emotions and the Right Hemisphere: Can New Data Clarify Old Models? Neuroscientist 2019, 25, 258–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, J.; Sharma, A. Cross-Modal Re-Organization in Adults with Early Stage Hearing Loss. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e90594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandmann, P.; Plotz, K.; Hauthal, N.; de Vos, M.; Schönfeld, R.; Debener, S. Rapid bilateral improvement in auditory cortex activity in postlingually deafened adults following cochlear implantation. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2015, 126, 594–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irvine, D.R. Plasticity in the auditory system. Hear. Res. 2017, 362, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKay, C.M. Brain Plasticity and Rehabilitation with a Cochlear Implant. Adv. Otorhinolaryngol. 2018, 81, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, A.S.; Purdy, S.C. Change in Speech Perception and Auditory Evoked Potentials over Time after Unilateral Cochlear Implantation in Postlingually Deaf Adults. Semin. Hear. 2016, 37, 062–073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzouni, L.; Lepore, F. Compensatory plasticity: Time matters. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherer, K.R. Vocal communication of emotion: A review of research paradigms. Speech Commun. 2003, 40, 227–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koelsch, S. Towards a neural basis of processing musical semantics. Phys. Life Rev. 2011, 8, 89–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koelsch, S.; Kasper, E.; Sammler, D.; Schulze, K.; Gunter, T.; Friederici, A.D. Music, language and meaning: Brain signatures of semantic processing. Nat. Neurosci. 2004, 7, 302–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koelsch, S.; Gunter, T.C.; Wittfoth, M.; Sammler, D. Interaction between Syntax Processing in Language and in Music: An ERP Study. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2005, 17, 1565–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannemann, R.; Obleser, J.; Eulitz, C. Top-down knowledge supports the retrieval of lexical information from degraded speech. Brain Res. 2007, 1153, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silani, G.; Lamm, C.; Ruff, C.C.; Singer, T. Right supramarginal gyrus is crucial to overcome emotional egocentricity bias in social judgments. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 15466–15476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riva, F.; Lenger, M.; Kronbichler, M.; Lamm, C.; Silani, G. The role of right supra-marginal gyrus and secondary somatosensory cortex in age-related differences in human emotional egocentricity. Neurobiol. Aging 2022, 112, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glick, H.; Sharma, A. Cross-modal plasticity in developmental and age-related hearing loss: Clinical implications. Hear. Res. 2017, 343, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, S.D.; Garrard, S.; Hoskins, T. Emotion and Word Recognition for Unprocessed and Vocoded Speech Stimuli. Ear Hear. 2021, 43, 398–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vozzi, A.; Levy, A.M.; Ronca, V.; Giorgi, A.; Ferrara, S.; Mancini, M.; Capotorto, R.; Cherubino, P.; Trettel, A.; Babiloni, F.; et al. Time-Dependent Analysis of Human Neurophysiological Activities during an Ecological Olfactory Experience. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancini, M.; Cherubino, P.; Cartocci, G.; Martinez, A.; Borghini, G.; Guastamacchia, E.; di Flumeri, G.; Rossi, D.; Modica, E.; Menicocci, S.; et al. Forefront Users’ Experience Evaluation by Employing Together Virtual Reality and Electroencephalography: A Case Study on Cognitive Effects of Scents. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherubino, P.; Cartocci, G.; Modica, E.; Rossi, D.; Mancini, M.; Trettel, A.; Babiloni, F. Wine Tasting: How Much Is the Contribution of the Olfaction? In Problems, Methods and Tools in Experimental and Behavioral Economics; Nermend, K., Łatuszyńska, M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Levy, A.C.; Moneta, E.; Rossi, D.; Trettel, A.; Peparaio, M.; Civitelli, E.S.; Di Flumeri, G.; Cherubino, P.; Babiloni, F.; Sinesio, F. Taste Responses to Chocolate Pudding with Different Sucrose Concentrations through Physiological and Explicit Self-Reported Measures. Foods 2021, 10, 1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inguscio, B.M.S.; Cartocci, G.; Sciaraffa, N.; Nicastri, M.; Giallini, I.; Aricò, P.; Greco, A.; Babiloni, F.; Mancini, P. Two are better than one: Differences in cortical EEG patterns during auditory and visual verbal working memory processing between Unilateral and Bilateral Cochlear Implanted children. Hear. Res. 2024, 446, 109007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentin, O.; Lehmann, A.; Nguyen, D.; Paquette, S. Integrating Emotion Perception in Rehabilitation Programs for Cochlear Implant Users: A Call for a More Comprehensive Approach. J. Speech, Lang. Hear. Res. 2024, 67, 1635–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| UCI GROUP | ALEXITHYMIC | NON-ALEXITHYMIC/ALEXITHYMIC TRAITS |
|---|---|---|
| PRE-/PERI-LINGUAL | 2 (22.22%) | 7 (77.78%) |
| POST-LINGUAL | 4 (36.36%) | 7 (63.64%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cartocci, G.; Inguscio, B.M.S.; Giorgi, A.; Rossi, D.; Di Nardo, W.; Di Cesare, T.; Leone, C.A.; Grassia, R.; Galletti, F.; Ciodaro, F.; et al. Investigation of Deficits in Auditory Emotional Content Recognition by Adult Cochlear Implant Users through the Study of Electroencephalographic Gamma and Alpha Asymmetry and Alexithymia Assessment. Brain Sci. 2024, 14, 927. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14090927
Cartocci G, Inguscio BMS, Giorgi A, Rossi D, Di Nardo W, Di Cesare T, Leone CA, Grassia R, Galletti F, Ciodaro F, et al. Investigation of Deficits in Auditory Emotional Content Recognition by Adult Cochlear Implant Users through the Study of Electroencephalographic Gamma and Alpha Asymmetry and Alexithymia Assessment. Brain Sciences. 2024; 14(9):927. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14090927
Chicago/Turabian StyleCartocci, Giulia, Bianca Maria Serena Inguscio, Andrea Giorgi, Dario Rossi, Walter Di Nardo, Tiziana Di Cesare, Carlo Antonio Leone, Rosa Grassia, Francesco Galletti, Francesco Ciodaro, and et al. 2024. "Investigation of Deficits in Auditory Emotional Content Recognition by Adult Cochlear Implant Users through the Study of Electroencephalographic Gamma and Alpha Asymmetry and Alexithymia Assessment" Brain Sciences 14, no. 9: 927. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14090927
APA StyleCartocci, G., Inguscio, B. M. S., Giorgi, A., Rossi, D., Di Nardo, W., Di Cesare, T., Leone, C. A., Grassia, R., Galletti, F., Ciodaro, F., Galletti, C., Albera, R., Canale, A., & Babiloni, F. (2024). Investigation of Deficits in Auditory Emotional Content Recognition by Adult Cochlear Implant Users through the Study of Electroencephalographic Gamma and Alpha Asymmetry and Alexithymia Assessment. Brain Sciences, 14(9), 927. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14090927