Abstract
Titanium and its alloys have been extensively used as implant materials in clinic settings. However, implant-associated bacterial infection or inflammation remains a primary cause of implantation failure, which threatens human health, and has already become a global issue. Recently, a superhydrophobic surface endowed with a water contact angle higher than 150° has attracted widespread attention in antibacterial applications for their self-cleaning and low-adhesion properties, which has emerged as an important path in preventing biofilm formation. This review first describes the basic theories of wettability. In the second section, we explain biofilm formation, which is a primary pathogenic occurrence in the development of infection in implants. In the last and most important section, we summarize the progress of superhydrophobic titanium-based implants and recent antibacterial applications. This review will attract great interest from both research scientists and clinicians, which will help to rapidly expand superhydrophobic titanium-based implants for antibacterial applications.
1. Introduction
Currently, bone and joint pathology is linked to approximately 50% of chronic illnesses in patients in Europe who are over 65 years old [1]. This situation gives rise to an increasing need for a series of implants. Although autografts are considered as the gold standard [2], in numerous cases, it is still impossible for all patients to have their own tissues transplanted [3]. In such cases, artificial prosthetic materials are generally considered to be an alternative solution. Besides the demand for artificial bone and joint implants, in the past several decades, dental implants have also developed into a crucial component in the prosthetic rehabilitation of the tooth root [1]. It is estimated that the number of implants is still increasing and will exceed one million per year [4].
It is well known that titanium-based alloys, as the gold standard, are utilized in applying repair to a bone or a specific part replacement, such as dental implants, bone plates, and screws, due to their high strength, good anticorrosion performance, and sufficient biocompatibility [5]. Typically, ASTM grade V titanium (Ti6Al4V) is one of the applied materials, which is most frequently used in orthopedic applications. The mechanical characteristics and chemical reactivity of titanium alloys of grades II, III, and IV are significantly different to those of grade V, making them more appropriate to be utilized in dental implant applications [6]. As a kind of biophilic metal, titanium is highly biocompatible with bone, which is reliant on surface characteristics, such as surface roughness [7], chemistry [8], and wettability. In comparison to smoother surfaces, surface topographical changes at the micrometer level, such as those caused by acid etching and sandblasting, have a remarkable impact on cell differentiation, local factor creation, bone formation, and (ultimately) osseointegration [9,10]. The surface roughness, chemistry, and wettability can be controlled to support osseointegration properties [11]. For example, the titanium substrates of nanoscale structures can enhance osteoblast differentiation and local factor creation when combined with micro-/submicro-scale roughness, suggesting the possibility of better implant osseointegration abilities [12]. However, infection may occur after medical device implantation due to bacterial adhesion in a certain period [13,14]. According to a previous report, there are signs that 90% of implants are related to inflammation and 50% of implants are related to irreversible tissue destruction [15]. Taking dental implants as an example, the most common failure cause is a peri-implant inflammatory disease, such as peri-implantitis. This can result in bone loss and even cause damage to the service life of the implant [16].
Therefore, more and more researchers are interested in strategies used to prevent bacterial growth and biofilm formation, relying on either the chemical approaches of bactericidal activity to kill the bacteria attached to the surface or the physical approaches of antibiofouling activity to inhibit the initial bacterial attachment to the surface [17]. A wide range of antimicrobial agents, including antibiotics, bacteriostatic and bactericidal chemicals (such as chlorhexidine, triclosan, silver preparations, and antimicrobial peptides) [18], fluoride, and plant extracts, inhibiting metabolic enzymes and their small molecular substances [19,20,21], have been used to prevent biofilm maturation by bactericidal inhibition, the inhibition of bacterial adhesion, and the destruction of the extracellular matrix of plaque. However, such methods do not have the value of long-term use and may carry certain risks, such as toxicity and drug resistance. For the bactericidal method, the layer of bacteria killed on the surface may have an inhibitory effect on the further bacterial killing in a deeper surface, and the remaining bacterial film could be conducive to the attachment of live bacteria [22]. It is highly desirable to prevent biofilm formation using antimicrobials, rather than biocidal agents. Consequently, it is generally considered that approaches to prevent the initial bacterial attachment are much better than those aiming to kill the attached bacteria. Thus, more research should focus on the inhibition of the initial bacterial adhesion on the surface of the implants.
Over the past several years, superhydrophobic surfaces endowed with a water contact angle more than 150° have attracted great attention because of their unique properties, such as water repellency [23,24], self-cleaning [25,26,27], anticorrosion [28,29,30,31], anti-icing [32,33], and oil–water separation [34,35]. It was not until 1997 that Barthlott and Neinhuis concluded that the self-cleaning effect of the lotus leaf (called the lotus effect) is attributed to the presence of the papilla on the microstructure and epicuticular wax [36]. Based on this principle, Jiang et al. revealed that the primary cause generating the superhydrophobicity of lotus leaves was due to the synergistic effect of hierarchical micro/nanoscale structures and low-surface energy material modification [37], which can form an air layer on the surface and physically inhibit bacterial adhesion. From that point, research on wettability of solid surfaces was renewed as a dynamic research topic [38]. It was reported that superhydrophobic surfaces have minimal bacterial attachment after 24 h without any observation of biofilm formation [39]. The antibiofouling performance for a superhydrophobic surface is ascribed to the entrapped air layer, which can effectively reduce the contact area between bacteria and material surfaces, leading to reduced bacterial adhesion [40]. Therefore, superhydrophobicity has received increasing attention in the bacteriostatic field of titanium-based implants.
In this review, we first briefly describe the basic theories of wettability [13,38]. In addition, the second section explains biofilm formation, which is considered to be the most essential pathogenic factor in the production process of infection in implants [13]. In the last and most important section, we summarize the recent progress of bioinspired superhydrophobic titanium-based implants and their antibacterial applications. Superhydrophobic titanium-based implants could minimize microbial adhesion by altering the surface-free energy of the titanium dioxide–polytetrafluorethylene (TiO2-PTFE) nanocomposite coatings, which was significantly influenced by both PTFE and TiO2 concentrations [41]. We hope this review will enhance the prosperous development of superhydrophobic titanium-based implants in antibacterial applications.
2. Theories of Wettability
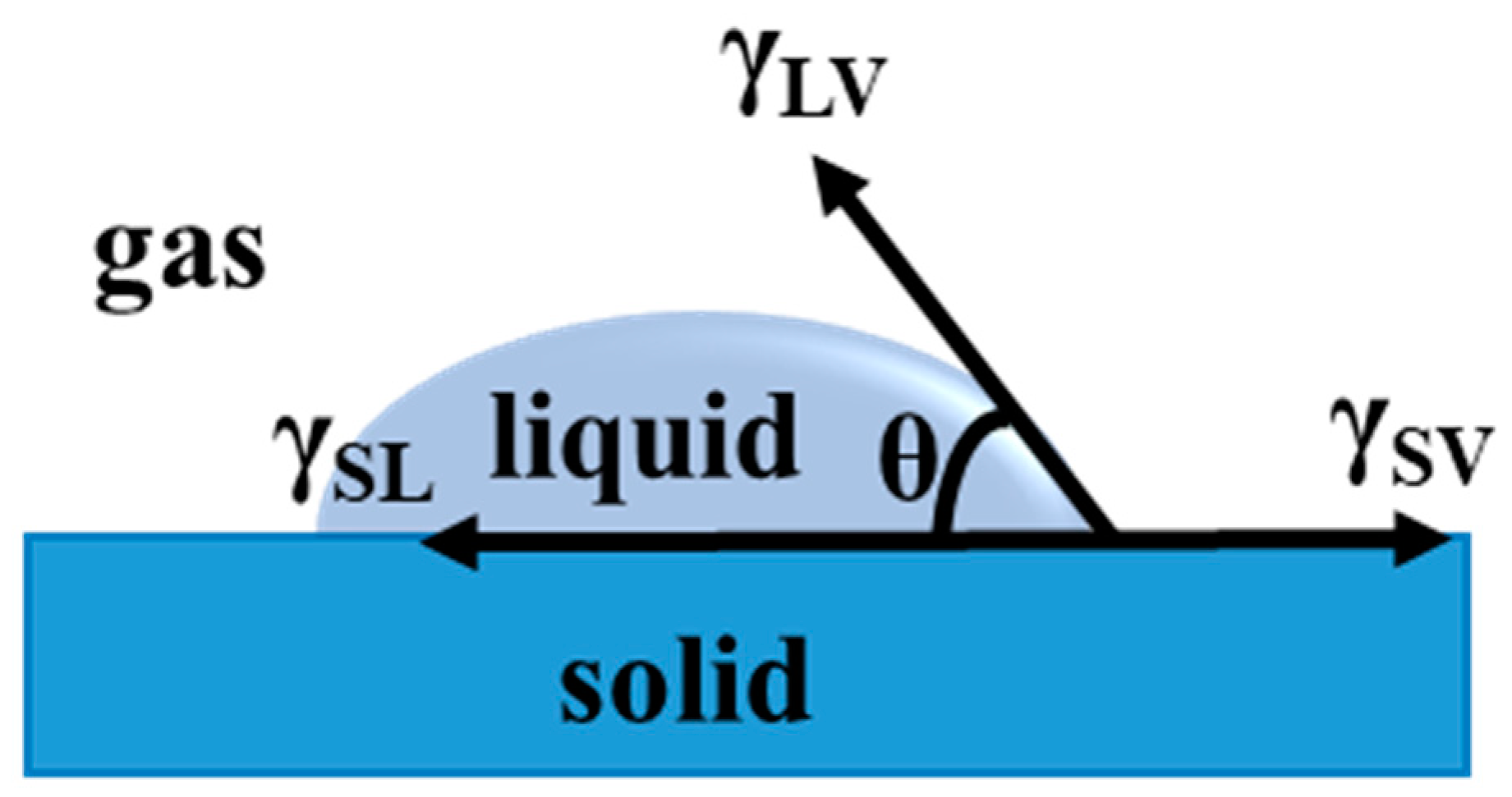
Wettability, as one of the most important properties on solid surfaces, can affect a variety of processes, such as adsorption, adhesion, wetting, friction, and lubrication [42]. According to wettability, the liquid can spread on the solid surface when they make contact with each other [43]. The wettability on a solid surface is synergistically determined by the microscopic structure and surface chemical composition. When a liquid is dropped onto the solid surface to contact the substrate, a solid-liquid-gas three-phase contact line is formed. The droplet can form a certain angle once it reaches a stable state on the solid surface. In such a case, the contact angle of the droplet on a solid surface is defined as the angle between the tangent plane of the liquid-gas boundary and the solid-liquid boundary at the intersection of three-phase (solid-liquid-gas) contact. The contact angle value is an essential indicator to qualitatively assess wettability on solid surfaces [44].
2.1. Young’s Equation
In 1805, a classical equation for wettability was given by Thomas Young, representing a force equilibrium at the three-interface (solid-liquid-vapor) contact line [45]. The balance of interfacial tensions is γSV, γSL, and γLVcosθ at the contact line. A droplet is spread onto a flat surface to form a contact angle on the solid surface. At equilibrium, there interfacial tensions should be counteracted, so the state can be expressed by Young’s equation (1), according to Figure 1:
which can be evolved as following form:
where γSV, γSL, and γLV represent the interfacial tensions of solid-vapor, solid-liquid, and liquid-vapor, respectively; θ means the intrinsic contact angle on an ideal smooth solid surface.
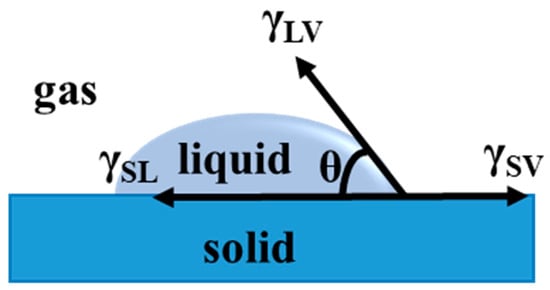
Figure 1.
Definition of the contact angle.
2.2. Wenzel’s Model
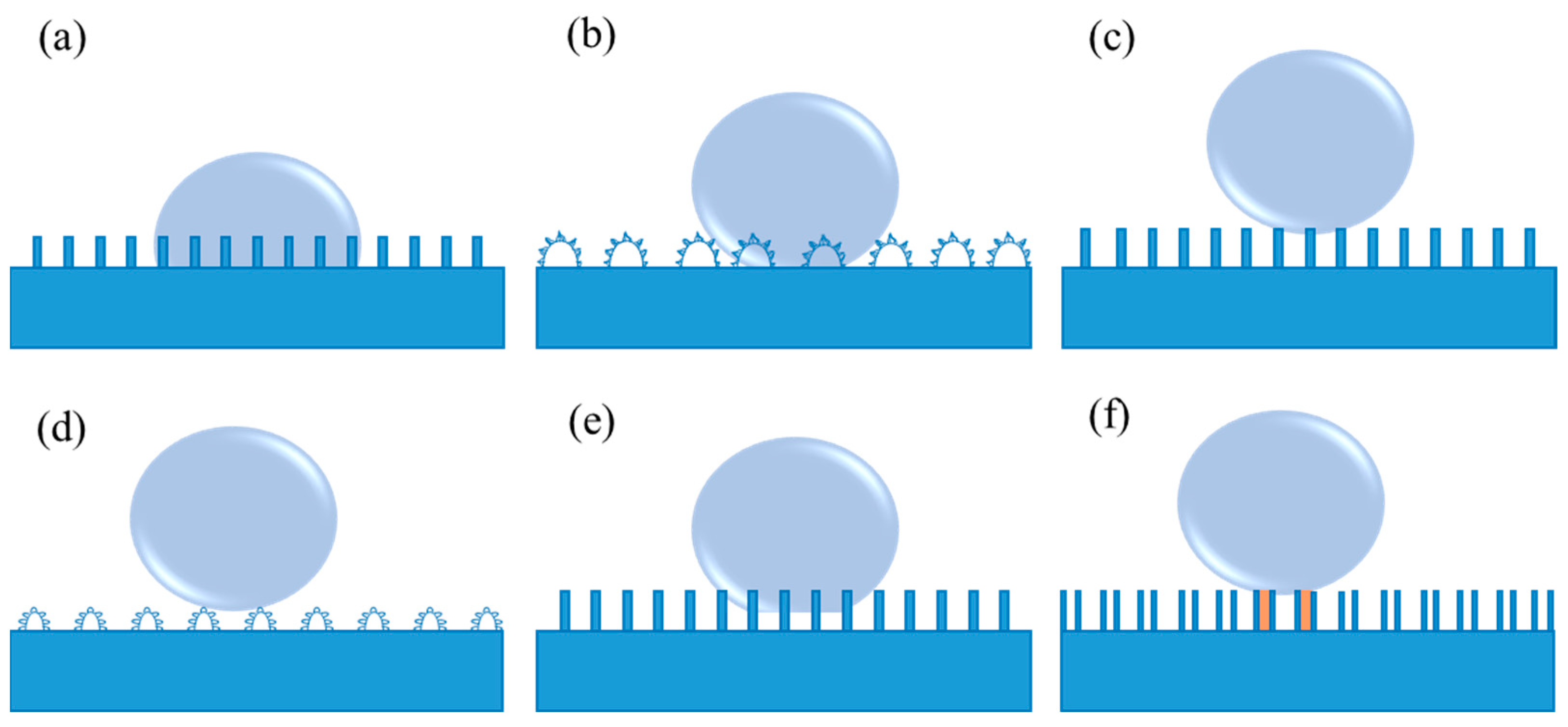
As is well known, Young’s equation is applicable to an ideal smooth solid surface, neglecting the influence factors containing roughness, swelling, dissolution, as well as chemical heterogeneity. In this case, it is difficult to measure the genuine contact angle for the rough surfaces using Young’s equation. As a consequence, Wenzel’s model was introduced by considering the surface roughness [46,47]. In Wenzel’s model, grooves on solid surfaces can be entirely filled with the liquid when the liquid droplet contacts the rough solid surface, as shown in Figure 2a. Thus, it is difficult for the droplet to move or roll off from the solid surface due to the large contact area and the strong adhesion between them. In this situation, Wenzel’s equation is proposed (3):
where ( ≥ 1) is the roughness factor (defined as the ratio of the actual contact area of the solid-liquid interface to the geometric projected contract area [46,47]), and θ∗ represents the apparent contact angle. Wenzel’s equation indicates that both hydrophilicity and hydrophobicity are increased with the increase in roughness. In other words, a rough hydrophilic surface becomes more hydrophilic when θ < 90°, and a rough hydrophobic surface turns more hydrophobic when θ > 90°, as compared to a smooth surface under the same surface chemical modification condition. Hence, it has been pointed out that it is an effective way to realize the non-wettability of a surface endowed with a high contact angle more than 150° by constructing a rough surface structure according to Wenzel’s equation [38]. Rose petal is a particular example of Wenzel’s model (as shown in Figure 2b), called the “Petal” state. When a water droplet is dripped onto the rose petal, the droplet can hang even if the rose petal turns upside down [48]. In such a case, a sticky superhydrophobic surface with high adhesion to water is formed on the rose petal.
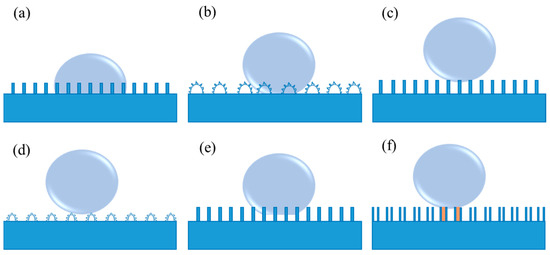
Figure 2.
(a) Wenzel’s model, (b) the “Petal” state (a particular example of Wenzel’s model), (c) Cassie’s model, (d) the “Lotus” state (a particular example of Cassie’s model), (e) coexistence of Wenzel’s and Cassie’s model, and (f) the “Gecko” model of the PS nanotube surface. The orange region shows the sealed air, while the remaining air pockets connected to the atmosphere represent the open air.
2.3. Cassie–Baxter Model
Wenzel’s equation discloses the relationship between the apparent contact angle and the intrinsic contact angle on a homogeneous rough surface. For another alternative contact between the liquid surface and the solid surface, the liquid no longer fully contacts the solid surface at every point below the droplets [49]. In this condition, Wenzel’s equation is not applicable because it cannot explain the reason why the water droplets on the lotus leaves exhibit an extremely low sliding angle, as well as contact angle hysteresis. Due to the low adhesive force of the water droplets in Cassie’s model, they behave in a non-wet-contact mode on the solid surfaces, which can readily roll off, as exhibited in Figure 2c [43]. The apparent contact angle on this rough surface in the form of Cassie’s model can be characterized in the following Cassie–Baxter Equation (4):
In the Cassie–Baxter equation, f1 and f2 are the surface area fractions of substances 1 and 2 (f1 + f2 = 1). θ1 and θ2 are the intrinsic contact angles of the liquid on two different substances. θ∗ is the apparent contact angle on material surfaces. If the surface is composed of a porous structure or other kind of rough structure which can preserve air, substances 1 and 2 can represent solid and air, respectively. In such a case, f2 is the area fraction of trapped air. Due to f1 + f2 = 1, and θ2 = 180°, Equation (4) can be simplified as:
Based on Equation (5), the apparent contact angle increases when the area fraction of trapped air, denoted as (1−f1), increases. The trapped air on the microgrooves of the rough solid surface can effectively prevent wetting and greatly contribute to improving the surface hydrophobicity. In general, a smaller f1 indicates the lower interfacial fraction of solid at the contact line. In Cassie’s model, the liquid no longer passes through the gaps that separate them [49], which can result in a high apparent contact angle on a rough hydrophobic surface. The “Lotus” state should be regarded as a particular example of Cassie’s model (shown in Figure 2d) due to the self-cleaning properties of the lotus leaf that are vitally dependent on its micro- and nanoscale hierarchical structure [50]. Currently, since the self-cleaning effect of such surfaces is extremely beneficial to a variety of applications, investigations of superhydrophobic surfaces are mostly concentrated on the fabrication of surfaces in the "Lotus" state. In fact, when a droplet makes contact with the majority of realistic samples, the coexistence of Wenzel’s and Cassie’s model frequently exists (as shown in Figure 2e). Additionally, a high-adhesive example of the "Gecko" model is also present (Figure 2f), which derives from a novel superhydrophobic condition of the polystyrene (PS) nanotube surface [51]. In such model, there are two different types of entrapped air, i.e., open air that is connected to the atmosphere and sealed air inside the PS nanotubes.
A stronger understanding of the different types of wetting states is necessary to improve the theoretical development and effectively design new superhydrophobic surfaces. Furthermore, studies on superhydrophobic surfaces with various states have a significant effect on both basic research and actual applications.
3. Interaction between Bacteria and Material Surfaces
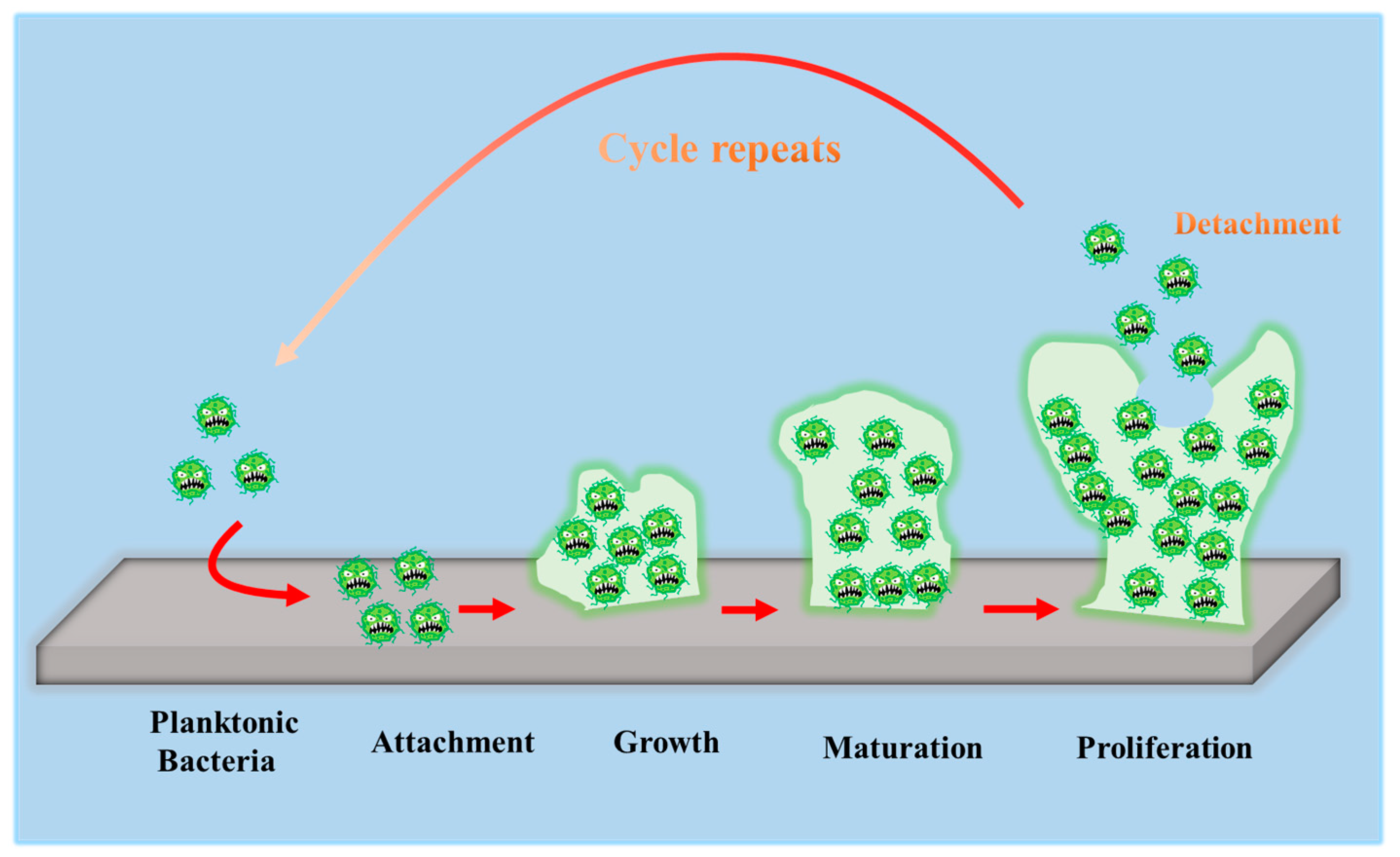
To develop antibacterial superhydrophobic titanium-based implants, it is necessary to understand the interaction between bacteria and material surfaces. Bacteria are essentially single-celled organisms. However, they can attach to both inactive and active surfaces to create well-organized three-dimensional (3D) colonies that are known as biofilms in nature [52]. Biofilm formation is a multi-step (often periodic) process with several distinct stages, and the interaction between bacteria and material surfaces can be approximately separated into four steps [16], which are graphically summarized in Figure 3.
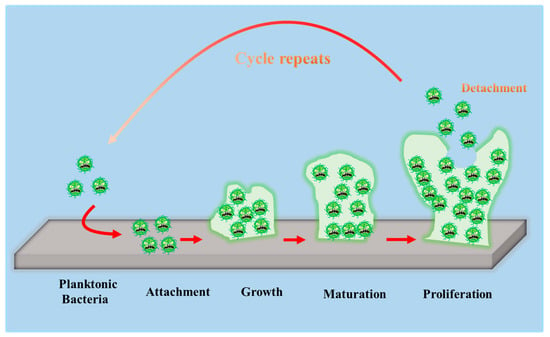
Figure 3.
Schematic representation of biofilm formation.
- The first step involves the bacterial attachment to material surfaces via cell-surface-associated adhesion [53,54,55]. The bacterial attachment to materials is primarily governed by steric interactions, electrostatic interplays, van der Waals forces, and protein adhesion, all of which are beneficial to making bacteria attach to the surface [56,57]. The process of bacterial attachment is invertible.
- The subsequent step is the bacterial colonization on material surfaces, which is mediated through particular cellular and molecular interactions, such as adhesion proteins, protein appendages, and extracellular polymeric substance (EPS) generation [58]. The process of the bacterial colonization is nonreversible.
- The third step is the formation and maturation of the biofilm. Bacteria that colonize surfaces will develop bacterial microcolonies and produce EPS (primarily polysaccharides and other macro-molecules), which can be helpful to biofilm formation. The maturation process includes EPS formation, cell agglomeration, chemical reactions, quorum sensing, and microcolony production. A biofilm will shield bacteria in a self-generated polysaccharidic matrix from the fluid shear force and protect the effects of systematic pharmaceutical treatments once it has grown on the surfaces [58].
- The last step is bacterial proliferation. Bacteria start to proliferate under the protection of the biofilm on material surfaces. Consequently, bacteria will cover the surfaces entirely.
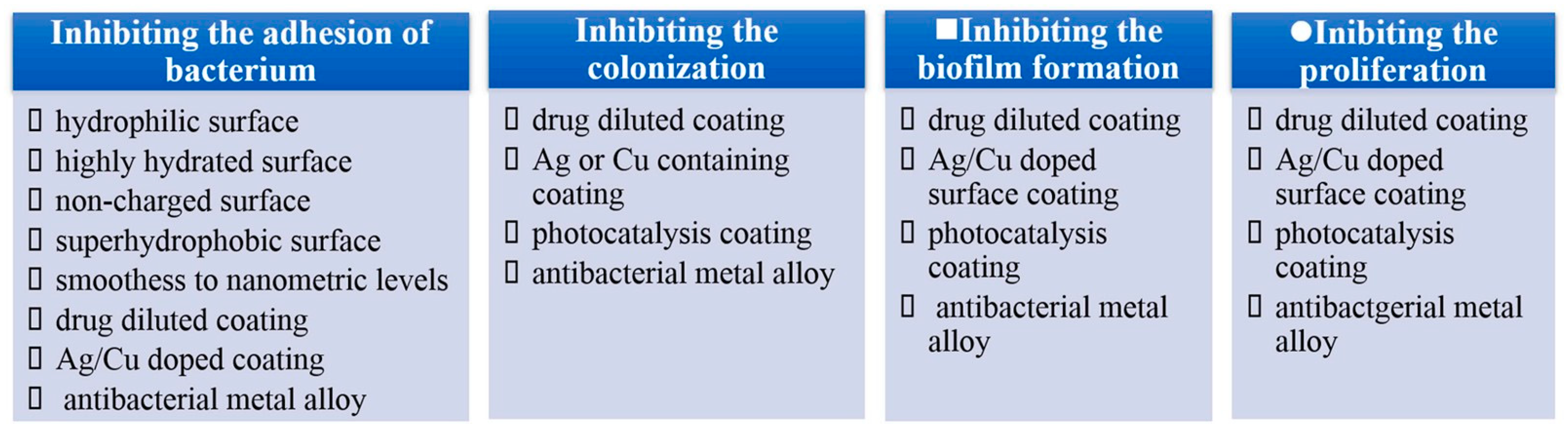
From the point of interaction between bacteria and material surfaces, it is easy to deduce that the bacterial reduction strategies can be split into four steps according to the four-step interplay mentioned above, as illustrated in Figure 4. Currently, the strategies primarily concentrate on inhibiting bacterial proliferation. It is confirmed that although surface coatings containing Ag or Cu can prevent bacterial attachment, colonization and biofilm growth, they are proven to be excessively toxic due to the release of metal ions [58,59,60,61,62,63,64,65,66,67]. Superhydrophobic surfaces can inhibit bacterial adhesion on the surfaces from etiology, which has become an important path to prevent biofilm formation [68]. These kinds of surfaces can weaken bacterial adhesion to a solid surface, enabling bacteria to be easily removed before a dense biofilm is formed on material surfaces [69].
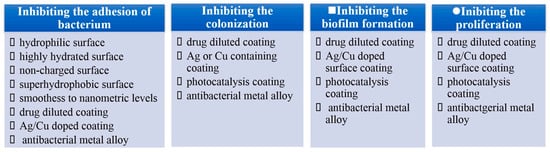
Figure 4.
Antibacterial strategies of four steps. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [16]. Copyright 2021, Elsevier.
4. Antibacterial Applications
The most common causes of healthcare-associated infections (HCAIs) are Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) and Staphylococcus epidermidis (S. epidermidis), which are responsible for 31–52% of infections in orthopedic prostheses, 40–50% of infections in prosthetic heart valves, 50–70% of infections in prosthetic catheter biofilm, and 87% of infections in the bloodstream [70]. Pseudomonas aeruginosa (P. aeruginosa), a bacterium frequently present in soil and water, can also cause surgical site infections after hip replacement operations as well as chronic infections. Furthermore, P. aeruginosa has the ability to quickly form strong biofilms that can support other pathogenic types. Recent studies have pointed out that the appearance of bacterial biofilms is still a significant factor in triggering the implant looseness and hastening the failure of implant surgical procedures [71,72,73]. Once biofilm-associated infection occurs in clinics, secondary revision surgery will be unavoidable, resulting in additional pain, economic costs, and even significant psychological trauma for patients [74]. As a result, it is critical to conduct related research to confer the implants with antibacterial properties.
The most frequent cause of implant-related infections is attributed to Escherichia coli (E. coli) and S. aureus in the development of antibacterial titanium-based alloys [16]. The accumulation of bacterial biofilms on the implant surface is vulnerable to bacterial attachment, leading to peri-implant infection. When bacteria fully attach to the surface, the implant will most probably lose its effectiveness because biomaterial-associated infections (BAIs) are highly resistive to the innate immune system, antimicrobial agents, and chemotherapy drugs. The concept of antibacterial implants was introduced to titanium-based implants which are widely applied in orthopedic, dental, craniofacial surgeries and so on [75,76,77,78]. Recently, superhydrophobic titanium-based implants with bacterial inhibition properties have attracted significant attention, especially in medical fields. Therefore, we will now summarize superhydrophobic titanium-based implants known for their antibacterial applications in orthopedic, dental, and cardiovascular implants.
4.1. Orthopedic Implants
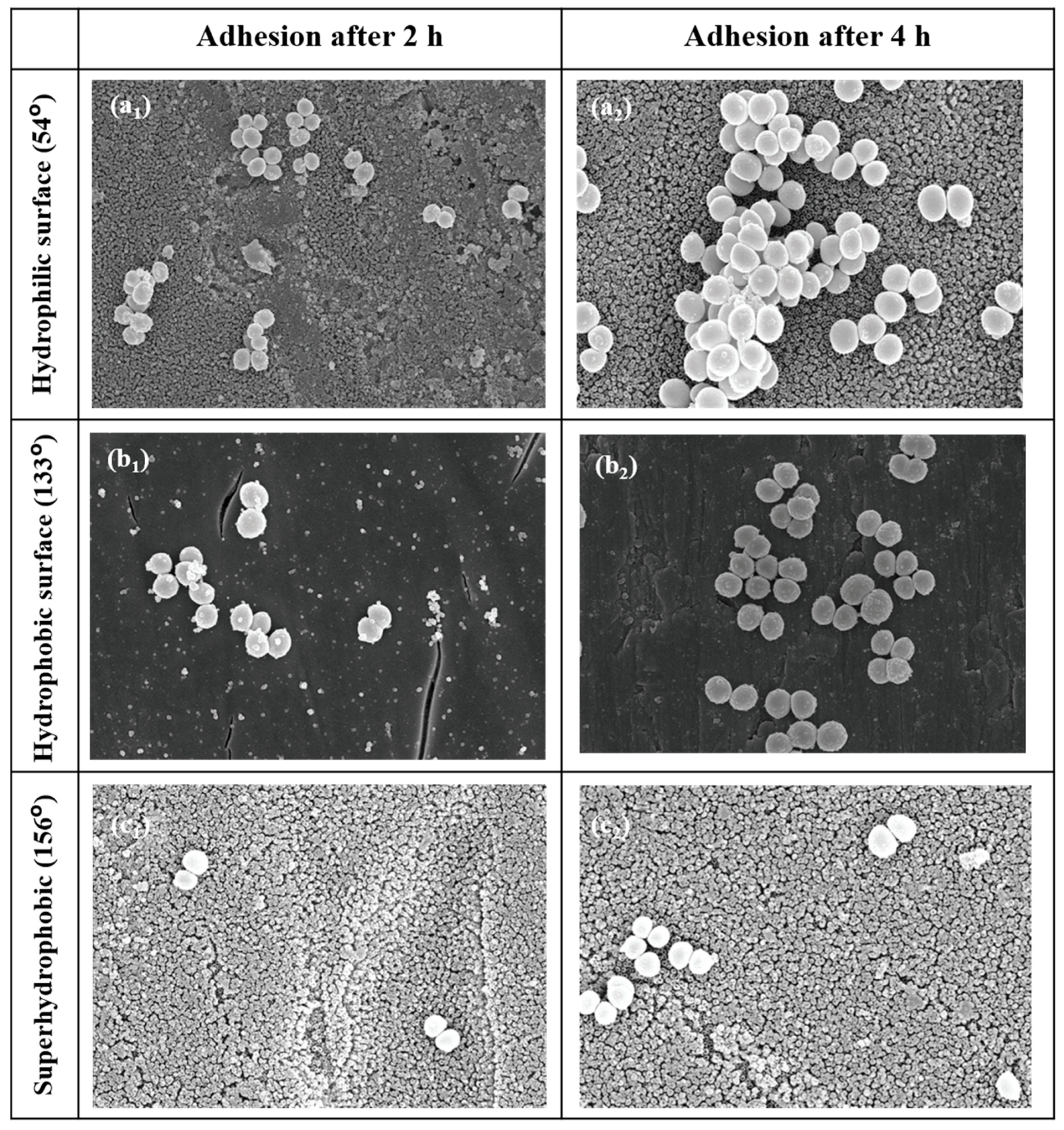
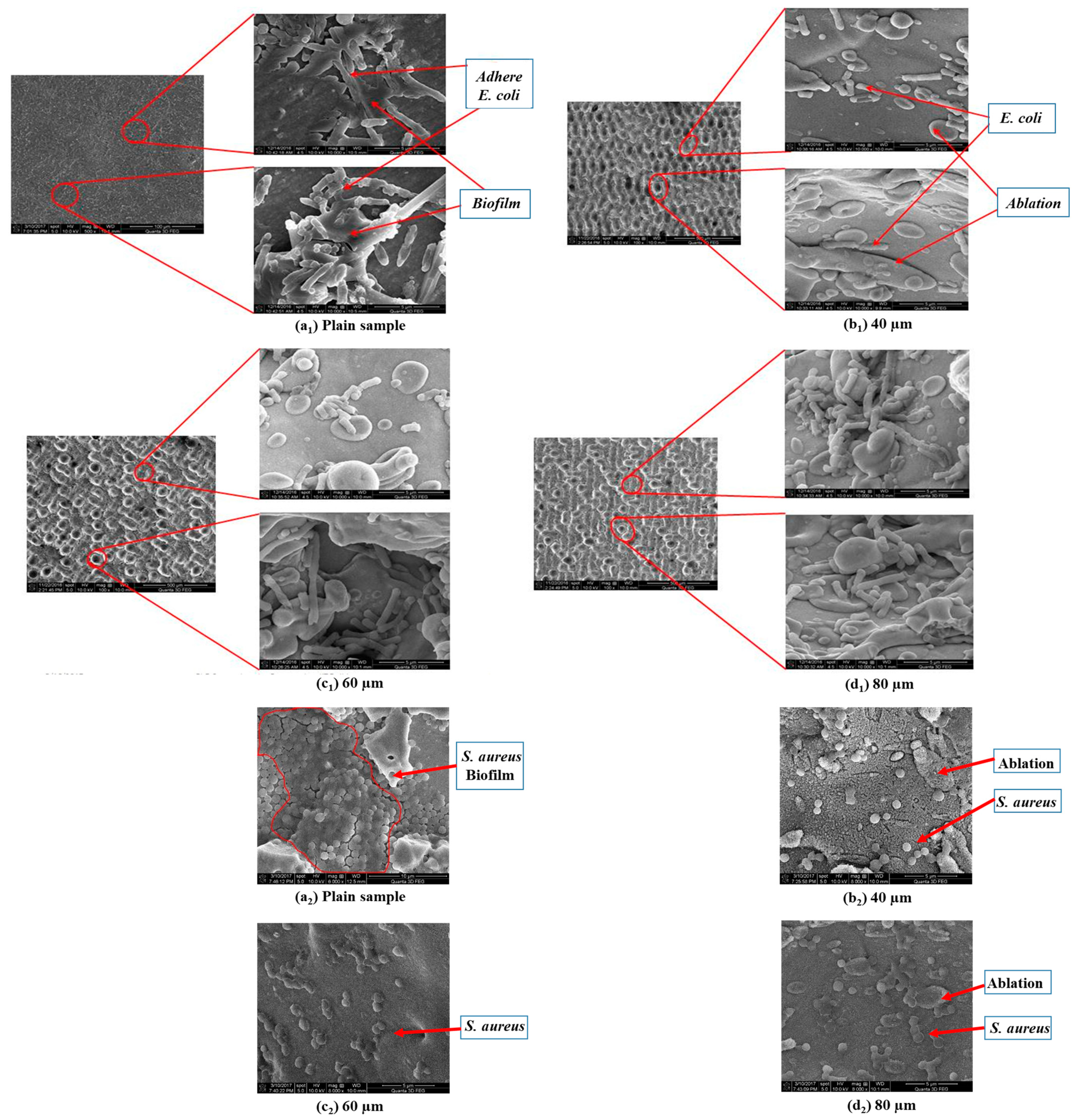
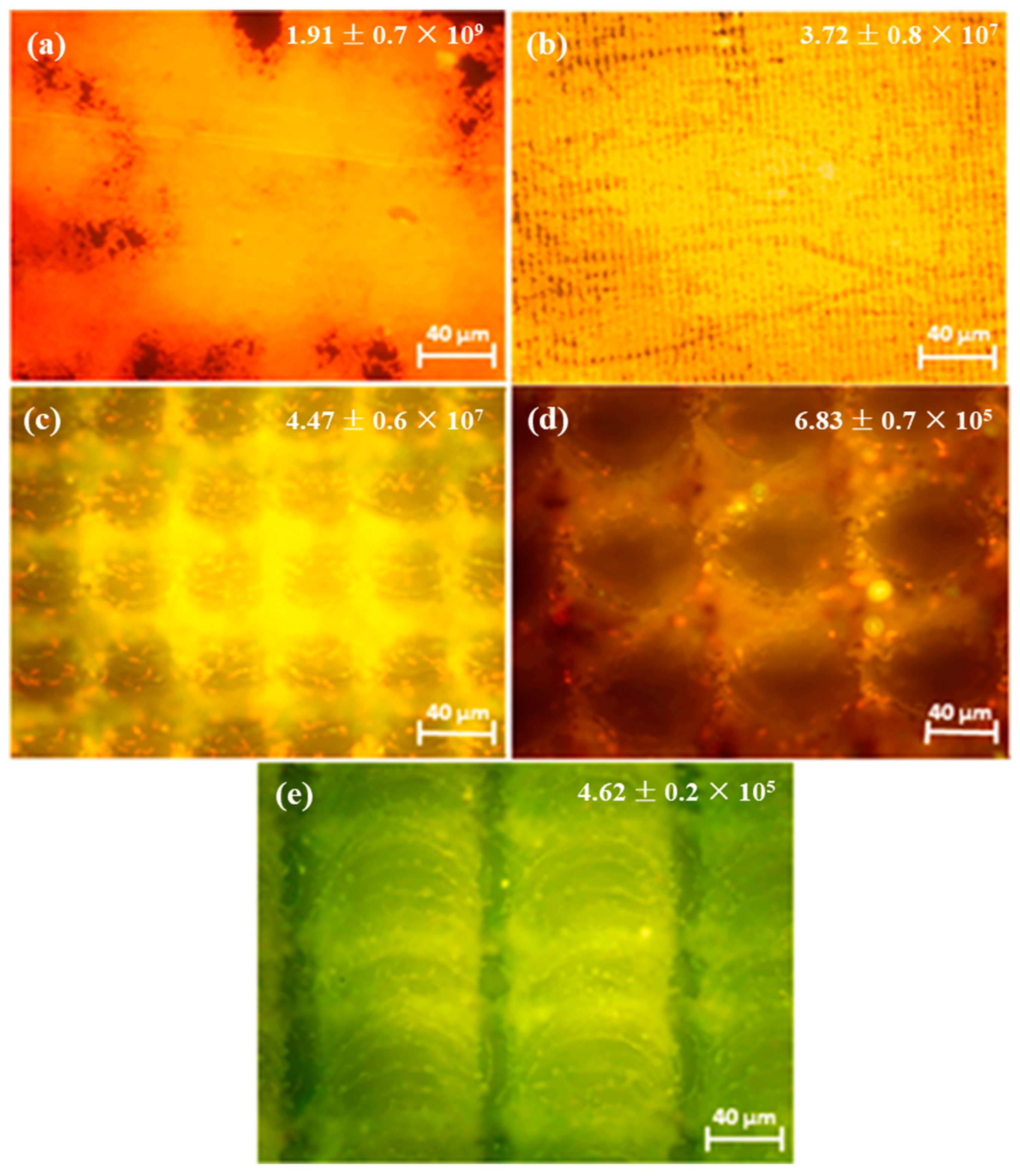
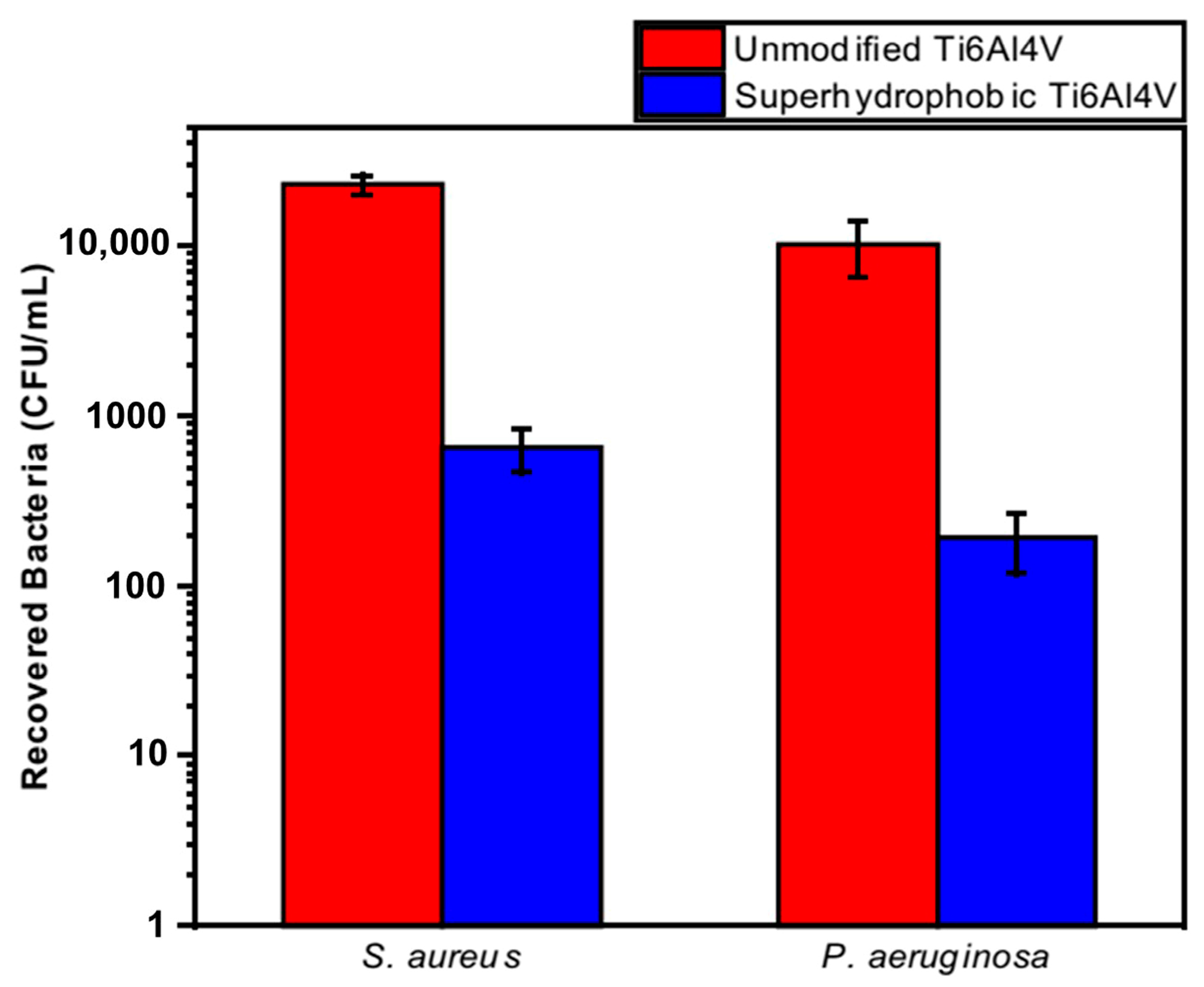
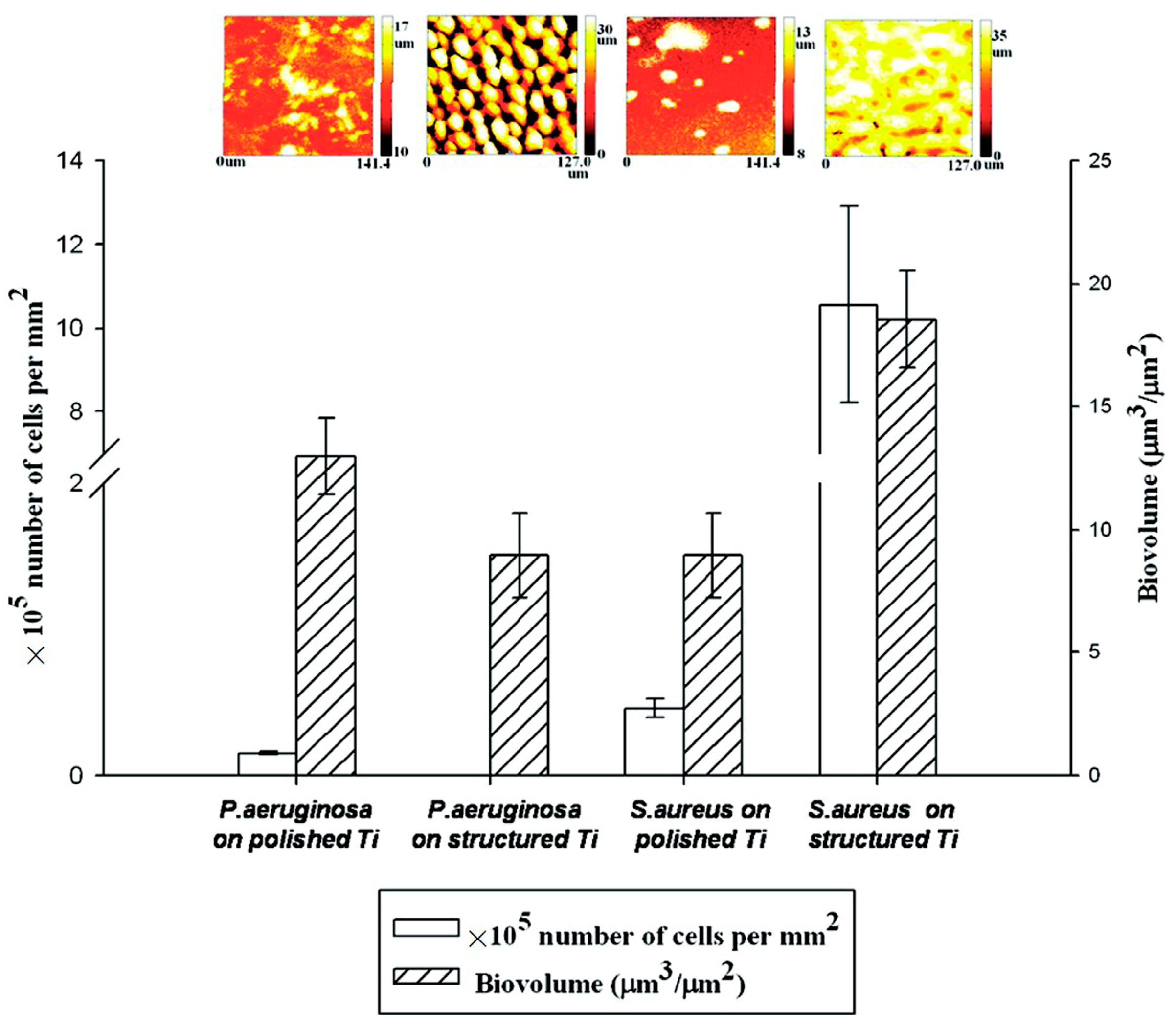
Orthopedic implants, including hip or knee prostheses, spine screws, and spine fusion cages, are often quickly infected in a very few number of days or weeks after surgery due to the surgical wound infection [79]. Similar pathobiology involves titanium reconstruction plates, temporomandibular joint prostheses, trauma mini-plates, and other maxillofacial operation devices. As a result, BAIs that emerge up to a few days or weeks after the surgery are regarded as a surgical site infection (SSI) [80]. Generally, a material infection that emerges up to three months after the surgery is considered a peri-operative infection (early infection) caused by SSI or wound contamination. In this situation, antibacterial activity is required during the peri-operative and initial post-operative stages. Tang et al. [81] prepared superhydrophobic nanotube-structured TiO2 films through the following processes: electrochemical oxidation with 0.5 wt.% HF electrolyte; calcination; and self-assembly in a methanol solution of hydrolyzed 1wt.% 1H, 1H, 2H, 2H-perfluorooctyltriethoxysilane (PTES). S. aureus adhesion on surfaces with different wettability levels for 2 h and 4 h, respectively, is demonstrated in Figure 5. The TiO2 nanotube-structured superhydrophobic surface showed a water contact angle as high as 156°, while the hydrophilic surface (titanium treated with anodic oxidation and calcination) and the hydrophobic surface (titanium treated by PTES) had water contact angles of 54° and 133°, respectively. The amounts of bacteria adhered on the surfaces was quite different according to the surface wettability. After cocultivation for 2 h, S. aureus attached to the hydrophobic and superhydrophobic surfaces was much less and more scattered (as shown in Figure 5b1,c1), whereas S. aureus attached to the hydrophilic surfaces was more and tended to aggregate (as shown in Figure 5a1). Similar trends were also found after cocultivation for 4 h. The researchers came to the conclusion that although bacteria were not entirely absent on superhydrophobic surfaces and the number of attached bacteria slightly increased with increases in the cocultivation time, they were far less and more scattered as compared to those on the hydrophilic and hydrophobic surfaces. To be more specific, superhydrophobic surfaces can resist S. aureus adhesion most effectively among the three types of titanium-based surfaces. Lotus-inspired superhydrophobic TiO2 nanotube arrays were capable of preventing S. aureus adhesion because of the self-cleaning effect, revealing that superhydrophobic surfaces might help to decrease the device-related infection risks and might be applied in orthopedic implants. Patil et al. [82] prepared a biologically active superhydrophobic Ti-6Al-4V alloy surface by combining annealing with a laser ablation process within the minimum processing time. On Ti-6Al-4V surfaces, a sequence of pits with spacings of 40 µm, 60 µm, and 80 µm were created using a nanosecond Nd:YAG laser. After annealing for 120 min, a 40 µm superhydrophobic Ti-6Al-4V alloy surface, a 60 µm superhydrophobic Ti-6Al-4V alloy surface, and an 80 µm hydrophobic Ti-6Al-4V alloy surface had water contact angles of 162°, 150°, and 136°, respectively. The antibacterial experiment of the superhydrophobic surface was tested against E. coli and S. aureus, as shown in Figure 6. It is investigated that E. coli and S. aureus developed biofilms on plain Ti-6Al-4V alloy surfaces (as shown in Figure 6a1,a2). As illustrated in Figure 6b–d, no such kind of biofilm forms on superhydrophobic and hydrophobic surfaces because of their hydrophobic nature, the presence of nano titania, and their corresponding antibacterial properties. Therefore, it can be extensively applied in orthopedic and dental implants applications. Vanithakumari et al. [83] created a superhydrophobic titanium surface with anti-biofouling and self-cleaning characteristics through direct laser patterning. As shown in Figure 7a, the bare titanium, used as the control group, was completely covered by bright red fluorescence, suggesting the existence of the highest amount of actively metabolizing bacterial cells. Figure 7b–d indicate a certain amount of reduction in actively metabolizing bacterial cells. However, as compared to the valley region, far more active cells were present in the spiky area. It is amazing that there was no red fluorescence in Figure 7e, suggesting that the actively metabolizing cells were absent on it. In comparison to the control titanium samples, the total viable count (TVC) values for 20 μm and 50 μm superhydrophobic titanium surfaces revealed a decrease of two orders of magnitude in bacterial adhesion, while 80 μm and 100 μm superhydrophobic titanium surfaces revealed a decrease of four orders of magnitude. With the increase in the line spacing for the superhydrophobic titanium surface, it was observed that bacteria adhesion was significantly reduced. DeFlorio et al. [84] fabricated a long-lasting fluorine-free superhydrophobic Ti6Al4V surface with a water contact angle reaching up to 169.9 ± 0.3° through an alkaline hydrothermal process and alkyl silane modification. As shown in Figure 8, the adhesion for both kinds of bacteria, including S. aureus and P. aeruginosa, to superhydrophobic surfaces was decreased by more than one order of magnitude. A 1.72 ± 0.23 order reduction (98.1 ± 50.7% reduction) for P. aeruginosa and a 1.55 ± 0.13 order reduction (97.2 ± 18.1% reduction) for S. aureus, as compared to the unmodified Ti6Al4V, were calculated. These superhydrophobic titanium alloy surfaces may considerably improve arthroplasty patient outcomes and reduce the risk of nosocomial infections when employed in applications of hard-tissue fracture fixation apparatus or total joint arthroplasty.
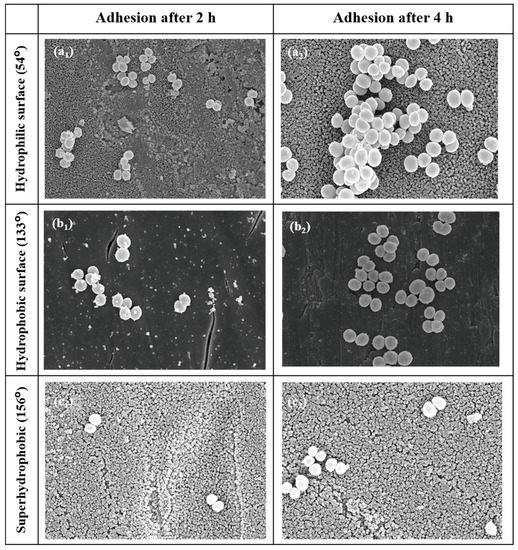
Figure 5.
SEM photographs of S. aureus on the hydrophilic surface for 2 h (a1) and 4 h (a2), the hydrophobic surface for 2 h (b1) and 4 h (b2), and the superhydrophobic surface for 2 h (c1) and 4 h (c2) with contact angle values shown on the left (×10 K). Reprinted with permission from Ref. [81]. Copyright 2011, Hindawi.
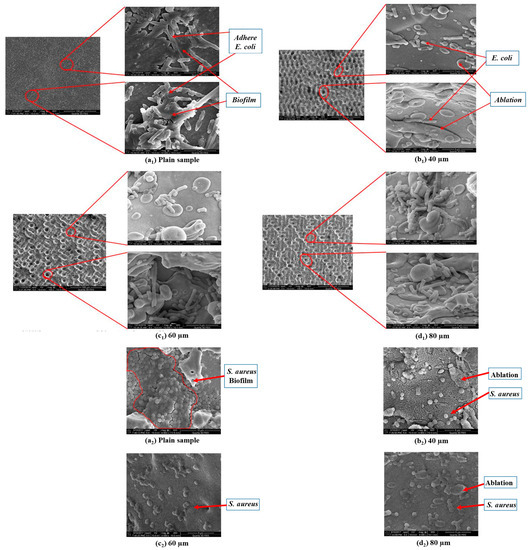
Figure 6.
Representative SEM micrographs for E. coli (a1–d1) and S. aureus (a2–d2) evaluated on (a1,a2) the plain Ti-6Al-4V alloy surface, (b1,b2) the 40 µm superhydrophobic Ti-6Al-4V alloy surface, (c1,c2) the 60 µm superhydrophobic Ti-6Al-4V alloy surface, and (d1,d2) the 80 µm hydrophobic Ti-6Al-4V alloy surface samples. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [82]. Copyright 2018, American Society of Mechanical Engineers.
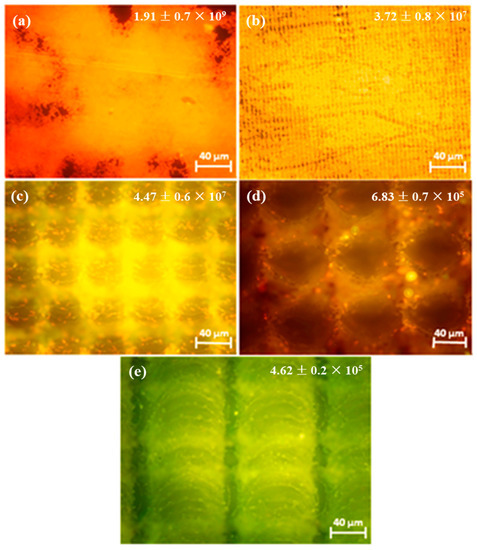
Figure 7.
Epifluorescence pictures for (a) bare titanium laser-patterned superhydrophobic titanium with different line spacings, (b) 20 μm spacings, (c) 50 μm spacings, (d) 80 μm spacings, and (e) 100 μm spacings. The samples were dyed with acridine orange after being exposed to Pseudomonas sp. culture for 6 h. The insets provide the total viable count (TVC) values (CFU/cm2) for various samples exposed to Pseudomonas sp. culture. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [83]. Copyright 2021, Elsevier.
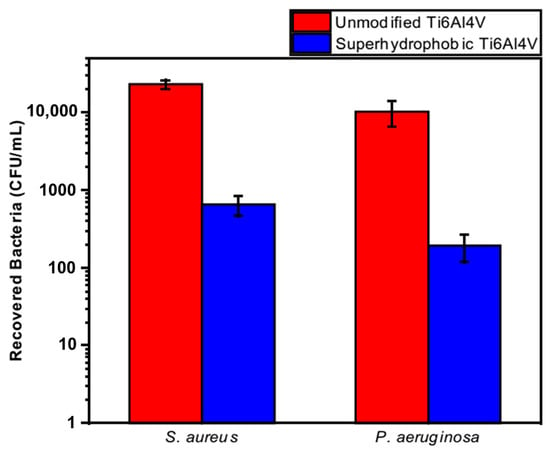
Figure 8.
The adhesion for S. aureus and P. aeruginosa to the unmodified Ti6Al4V and superhydrophobic Ti6Al4V surfaces. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [84]. Copyright 2022, Elsevier.
4.2. Dental Implants
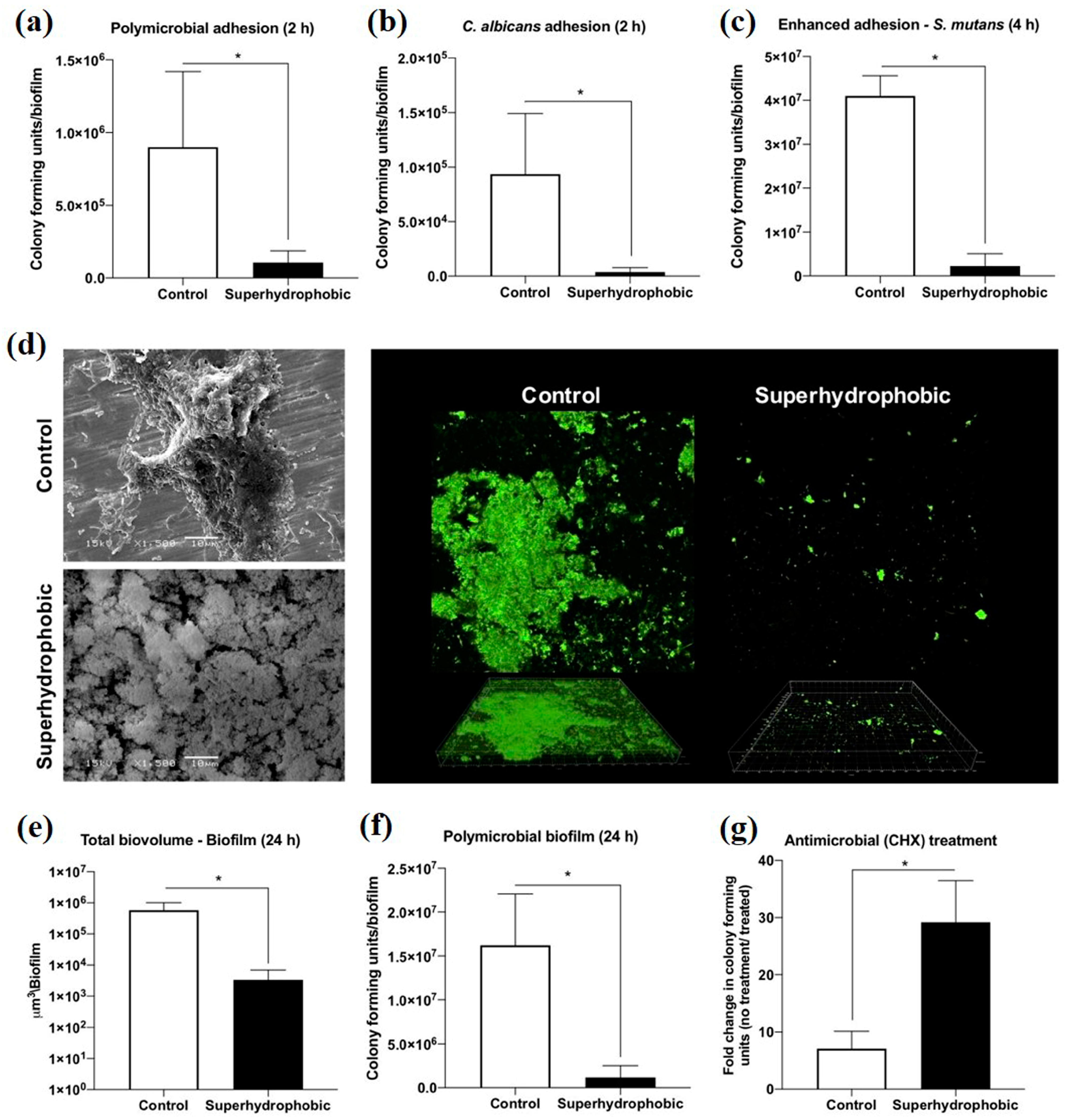
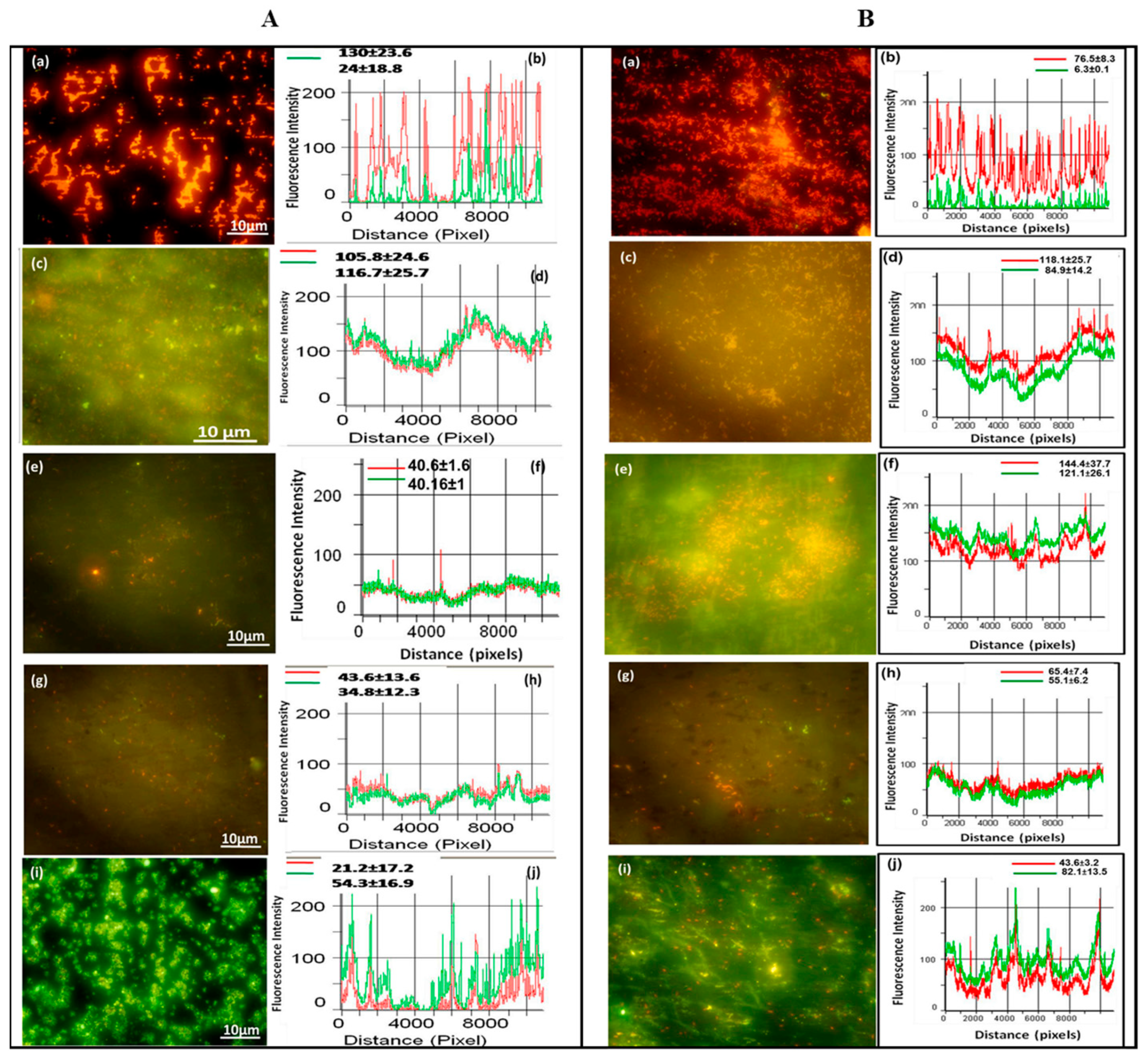
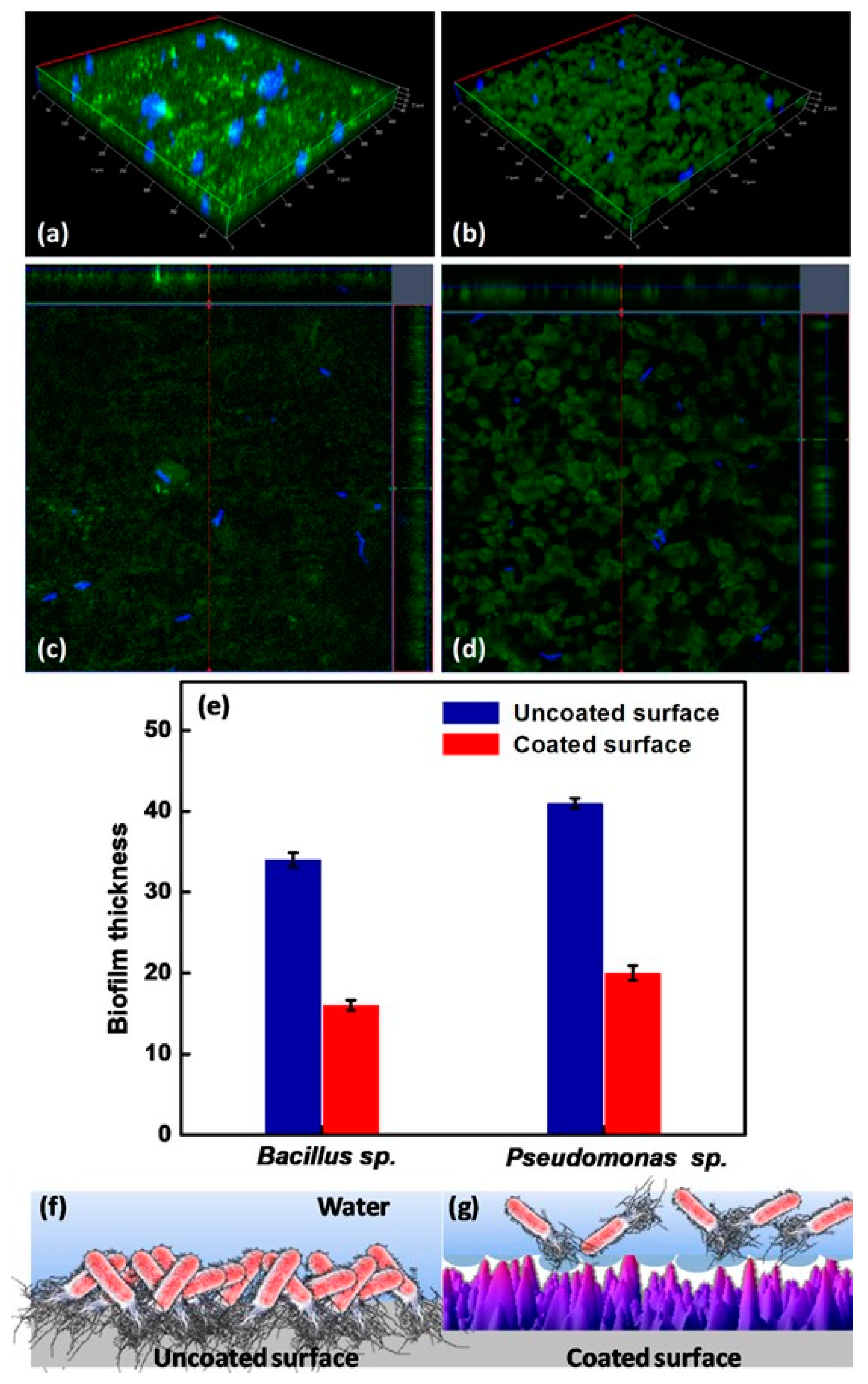
Peri-implantitis, a kind of late infection, is a mechanism that causes dental implants to be frequently infected a couple of months or even years later after being implanted [85,86]. This is because of the unique features of the peri-implant mucosa [87] and the diversity of oral biofilm formation. Usually, infections related to dental implants are extremely complex, multifactorial, and difficult to treat. The most frequent bacterial infections associated with dental implants are Gram-positive bacteria (such as S. epidermidis, S. aureus, and Enterococcus spp.) and Gram-negative bacteria (such as P. aeruginosa) [88,89,90]. Gherlone et al. [91] investigated bacterial microleakage from inside to outside the implant-abutment component with a novel design of comparing internal conical connections to eight different internal connections in vitro. The internal portion of each implant was cultivated with E. coli suspension to assess the bacterial microleakage. The results indicate that no contamination can be found for the test connection (an internal connection featured by a double-taper principle) group in the first 6 h, with 7 out of 10 implants exhibiting no contamination even after 96 h. It was concluded that the best combination to obtain a lower rate of infection will be the association between surface treatment and innovative conical connection without bacterial microleakage. Since infection prevention is a requirement for a successful implant, superhydrophobic titanium-based surfaces are desired. Souza et al. [92] fabricated a novel superhydrophobic coating via the one-step glow discharge plasma technique, which is a potential biocompatible method used to significantly decrease microbial adhesion and biofilm formation on titanium-based medical implants, as shown in Figure 9. It drastically decreased (approximately eight-fold) the change for polymicrobial adhesion (bacterial and fungal) and biofilm formation in vitro (as shown in Figure 9a). Surprisingly, it can be seen that the superhydrophobic coating can alter the microbiological profile of biofilms developed in the mouth cavity, decreasing pathogens associated with peri-implant disease by up to ≈seven-fold (as shown in Figure 9f). As compared to control titanium discs, biofilms produced on superhydrophobic surfaces are more sensitive to chlorhexidine (CHX) (0.5%) antibacterial agents (as shown in Figure 9g). It is noted that the silanization of titanium implant materials is one of the most common applications. Siliconizing the titanium surface with a silane primer can drastically lower the surface energy and increase the hydrophobicity. Matinlinna et al. [93] demonstrated that the fabrication of silane primer using 3-acryloxypropyltrimethoysilane + bis-1,2- (triethoxysilyl) ethane can increase the hydrophobicity and lower the surface energy without influencing the surface roughness. It was subsequently proven that the property changes reduced the formation of Candida albicans (C. albicans) colonies in a previous study [94]. Fadeeva et al. [95] constructed the lotus leaf mimics on titanium substrates using the femtosecond laser ablation method with large grain-like convex characteristics of 10-20 μm and dual roughness characteristics of about 200 nm. In contrast to the non-laser ablated surface with an apparent contact angle of 73°, the prepared biomimetic superhydrophobic titanium surface showed a contact angle value as high as 166°. As illustrated in Figure 10, the biomimetic superhydrophobic surface can resist the rod-like P. aeruginosa adhesion effectively while the spherical S. aureus colonized, which could be due to the biophysical impacts of tough nano-scale pillars (independent of trapped air) on Gram-negative bacteria [96]. Vanithakumari et al. [97] described a novel method that can be used to fabricate stable superhydrophobic titanium surfaces with excellent antibacterial characteristics via anodization and annealing, in combination with coating graphene oxide (GO) and silane treatment. The GO coated the anodized and annealed titanium samples via the electrophoretic deposition (EPD) technique in an aqueous GO suspension, followed by immersion in the perfluorooctyltriethoxy silane solution with the addition of silica nanoparticles (Si nps). In comparison to the control samples, the silane–graphene oxide (SGA) samples coated with a water contact angle value around 173° showed a reduction of 3–5 orders in the bacterial density of Gram-negative Pseudomonas sp. and Gram-positive Bacillussp. As shown in Figure 11, there was no orange fluorescence over the whole superhydrophobic SGA sample surface with the minimum magnitude of bacterial adhesion, indicating the best resistance to bacterial attachment among all the samples. The excellent anti-biofouling property of the SGA surface can be attributed to the synergistic effect of silanized silica nanoparticles with a low surface energy and the antibacterial property of GO sheets for the corresponding sharp edges, which can make the surface less favorable to bacterial adhesion. Manoj et al. [98] fabricated a superhydrophobic titanium surface utilizing an ethanol solution of myristic acid and HCl via concurrent anodic oxidation and adsorption. Similar to epifluorescence micrographs, CLSM imaging reveals green fluorescence on the sample surfaces, as shown in Figure 12a–d. After a long incubation period for 48 h, Bacillus sp. covered the uncoated titanium surface to develop a dense biofilm with a thickness of 34 ± 0.9 µm, while the coated superhydrophobic surface showed a thickness of 16 ± 0.7 µm, as shown in Figure 12e. Pseudomonas sp. showed similar trends in biofilm formation reduction (the thickness values of uncoated and coated superhydrophobic surfaces were 41 ± 0.6 µm and 20 ± 1 µm, respectively). As compared to the uncoated titanium surface, the superhydrophobic surface showed a 0.5% reduction in biofilm formation in both of the bacterial cultures.
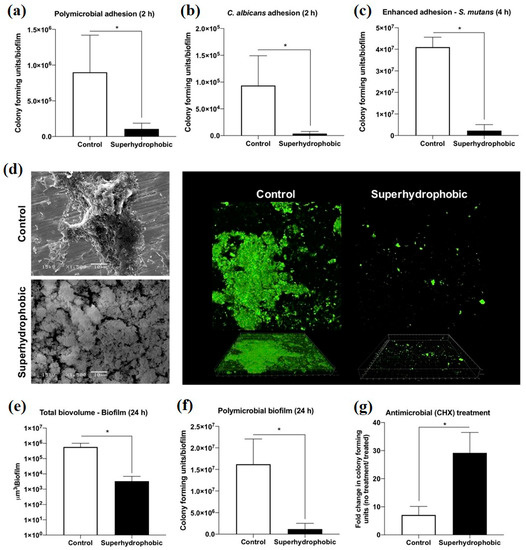
Figure 9.
The antimicrobial activity of the control and superhydrophobic titanium samples in vitro: (a) polymicrobial adhesion after 2 h, (b) Candida albicans (C. albicans) adhesion after 2 h, (c) Streptococcus mutans (S. mutans) adhesion after 4 h, (d) SEM and the CLSM pictures for the biofilm, (e) average total biovolume biofilm after 24 h, (f) average colony-forming units of polymicrobial biofilm after 24 h, and (g) average colony-forming units of biofilm after 24 h with exposure to chlorhexidine (CHX) (0.5%) for 3 h. * means p < 0.05, using the Bonferroni t-test. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [92]. Copyright 2020, American Chemical Society.
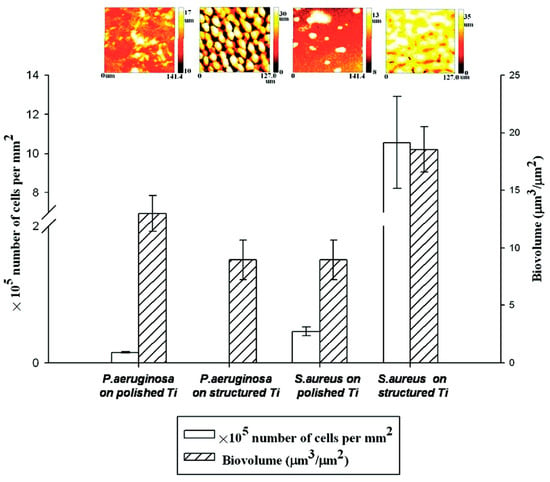
Figure 10.
S. aureus and P. aeruginosa biovolume with the corresponding biofilm thickness on different surfaces quantified using COMSTAT (n = 6, if p < 0.05): polished titanium (hydrophilic) and structured titanium (superhydrophobic). Reprinted with permission from Ref. [95]. Copyright 2011, American Chemical Society.
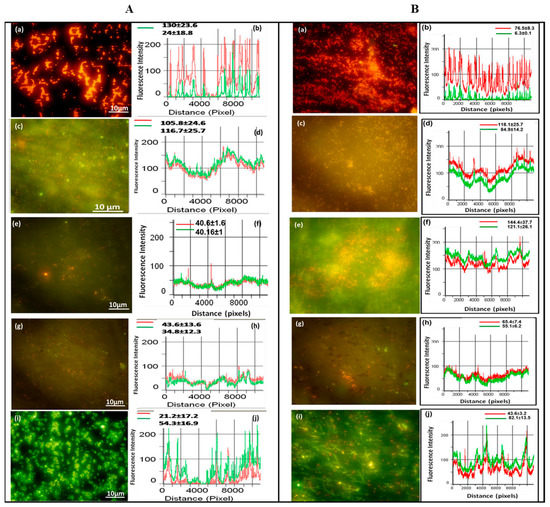
Figure 11.
Epifluorescence photomicrographs and line intensity profiles for different samples incubated in (A) Gram-negative bacteria (Pseudomonas sp.) and (B) Gram-positive bacteria (Bacillus sp.) for 6 h. (a,b) polished titanium, (c,d) anodized titanium, (e,f) anodized and annealed titanium, (g,h) GO coated on anodized and annealed titanium, and (i,j) silane and GO coated on anodized and annealed titanium. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [97], Copyright 2020, Elsevier.
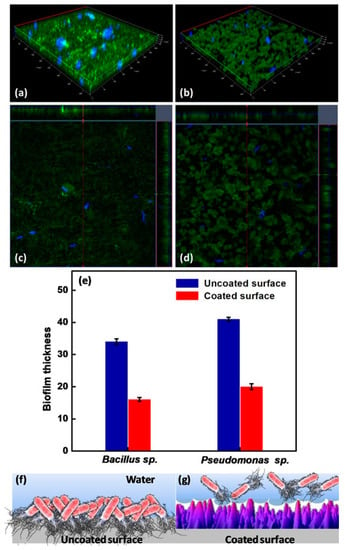
Figure 12.
CLSM images of the uncoated surface (a,c) and the coated superhydrophobic surface (b,d) incubated in Bacillus sp. for 48 h. (e) biofilm thickness for the uncoated and coated superhydrophobic surfaces after exposure to Bacillus sp. and Pseudomonas sp. for 48 h, and a diagrammatic illustration of bacterial adhesion for (f) the uncoated surface and (g) the coated superhydrophobic surface. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [98]. Copyright 2020, Elsevier.
4.3. Cardiovascular Implants
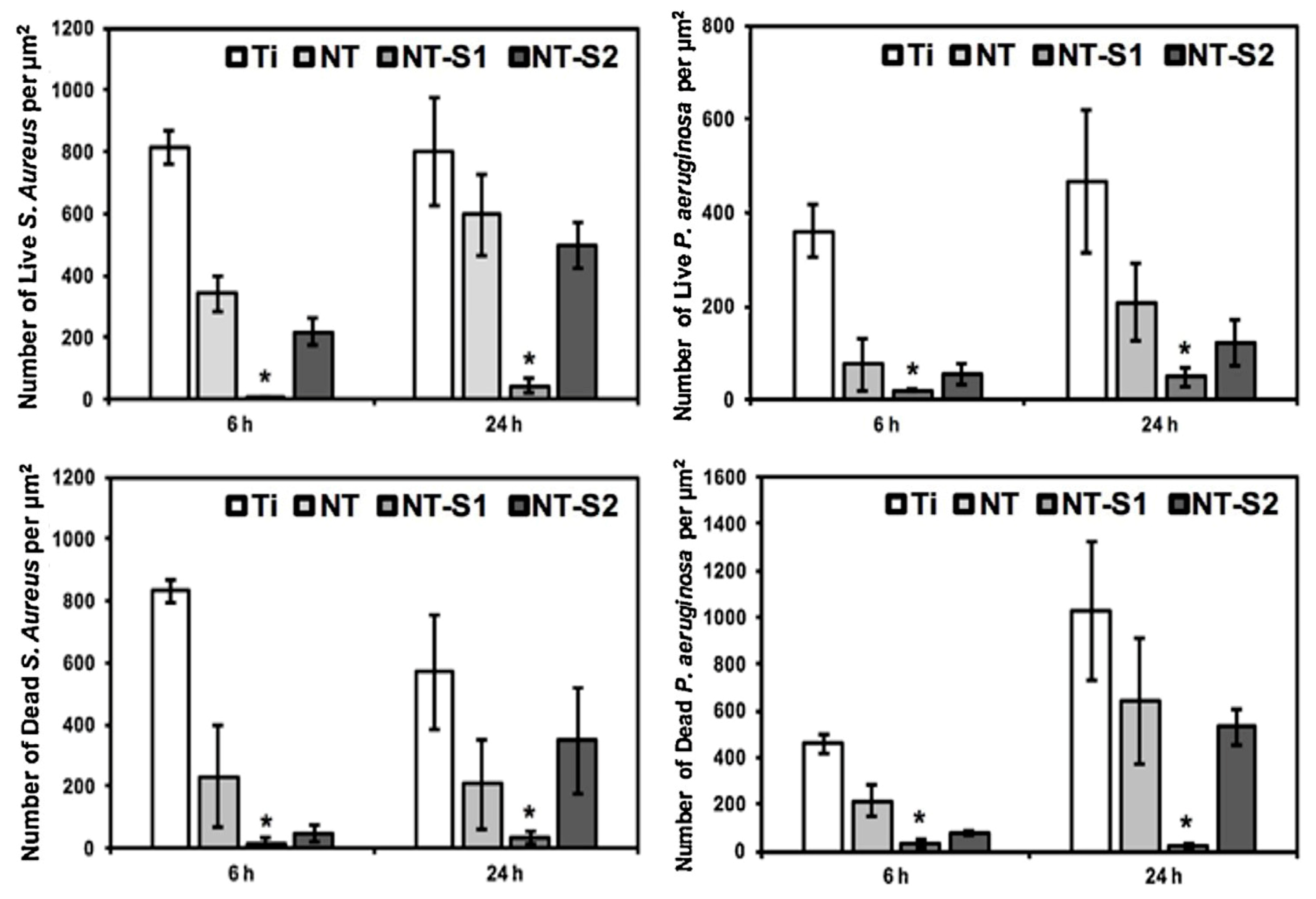
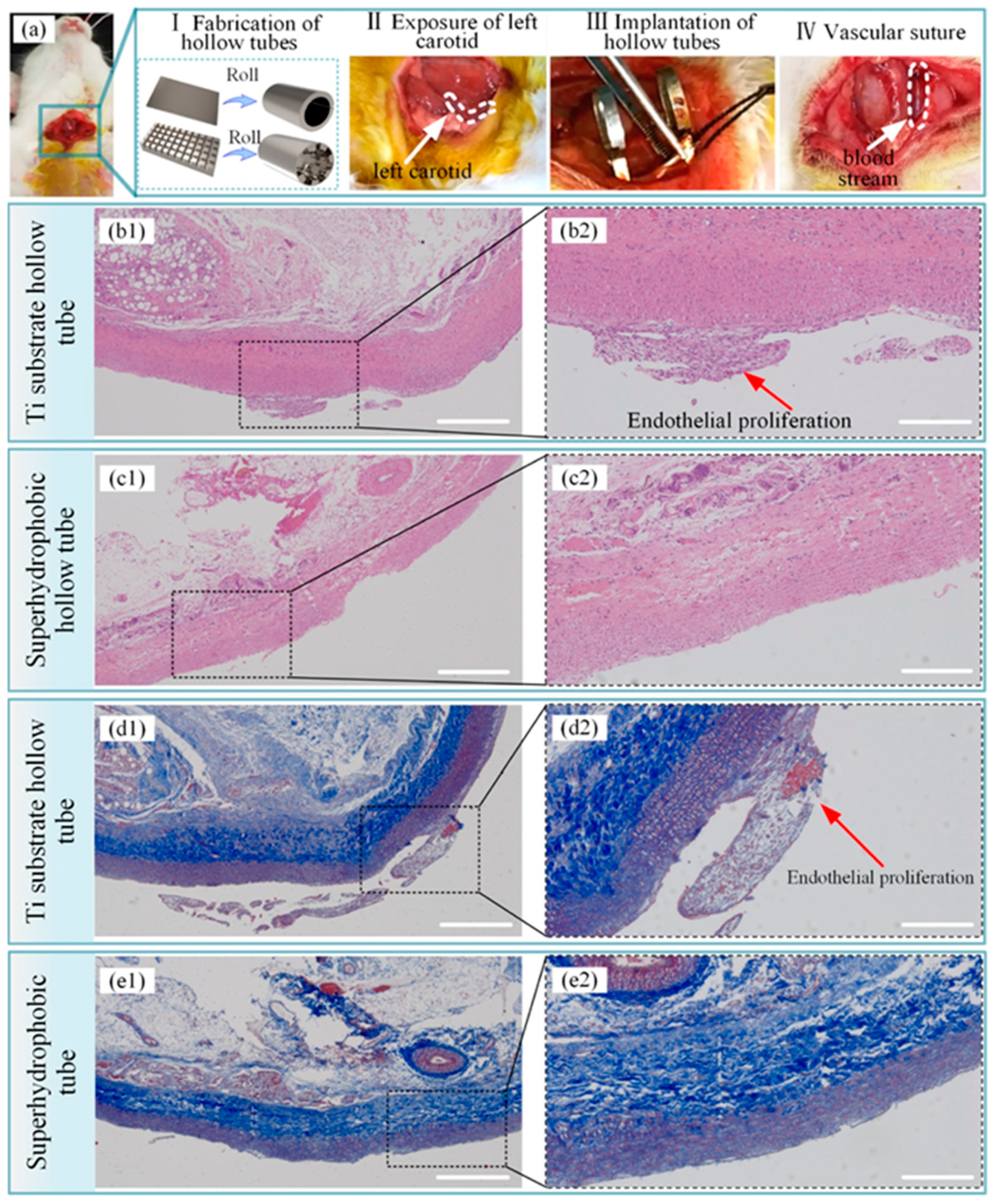
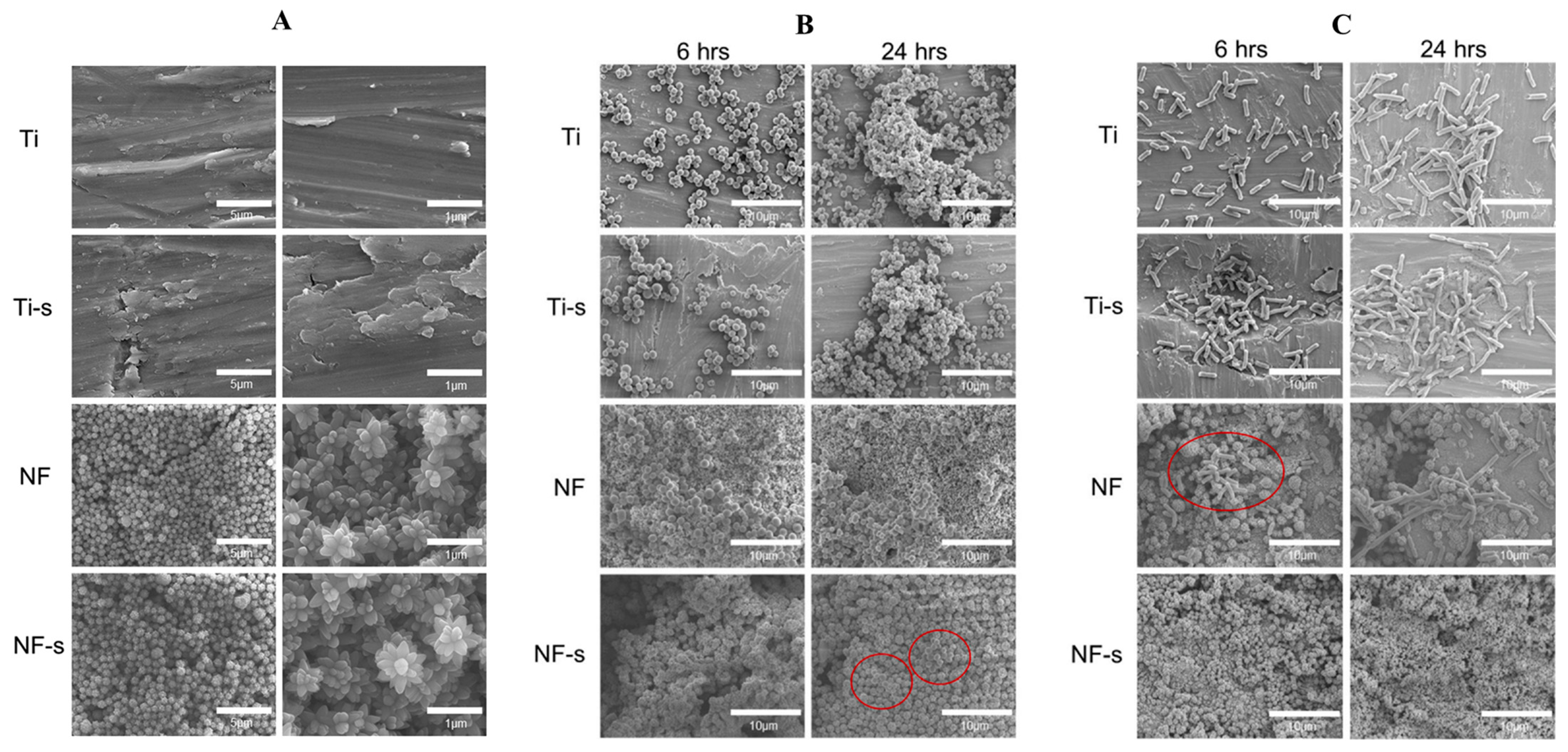
Titanium implants for long-term intravascular usage (such as heart valves, blood pumps, and pacemaker leads) and short-term intravascular usage (such as catheters and guide wires) are biomaterials made from titanium, which can be brought into contact with blood. The preservation of uninterrupted blood flow is fundamentally dependent on the high hemocompatibility of implanted or interventional medical apparatus, such as stents or lead wires. Moreover, the inflammation and hyperplasia of tissue are also the main problems of stent implantation, and can significantly impact the risk of in-stent restenosis and biosecurity [99]. The superhydrophobic surfaces can be employed as antibacterial surfaces endowed with the self-cleaning effect in cardiovascular implants. Bartlet et al. [40] created an array of titanium dioxide nanotubes via anodic oxidation, chemical etching, and surface silanization in sequence, exhibiting superhydrophobicity. ImageJ was utilized to calculate the amounts of both live and dead bacteria on different sample surfaces. It can be concluded that the superhydrophobic titanium nanotube can inhibit S. aureus and P. aeruginosa effectively (as shown in Figure 13), preventing bacteria from forming biofilms on the surfaces of the implanted medical apparatus for a long time, such as mechanical heart valves, pacemakers, and heart assist devices. Zhang et al. [99] constructed a controllable superhydrophobic surface on a medically pure titanium with following steps of an ultraviolet laser treatment, ultrasonic acid process, and surface modification in sequence. Figure 14 shows that there is no distinct inflammation and excessive proliferation through the histological evaluation, showing that the superhydrophobic surface is effective in eliminating the adhesion of blood cells and thrombosis. Montgomerie et al. [100] created a superhydrophobic surface by constructing titania nanoflowers using the hydrothermal synthesis method and vapor-phase silanization with 1H, 1H, 2H, 2H-perfluorooctyltriethoxysilane. As shown in Figure 15, almost no bacteria can be observed on the nanoflower surface followed by silanization treatment (NF-s), i.e., superhydrophobic titanium surface after incubation for 6 h and 24 h. The findings mentioned above indicate that the prepared superhydrophobic NF-s surface is of great help to inhibit adhesion and biofilm formation for both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, which has a promising application prospect in blood-contacting medical apparatus, such as stents and heart valves.
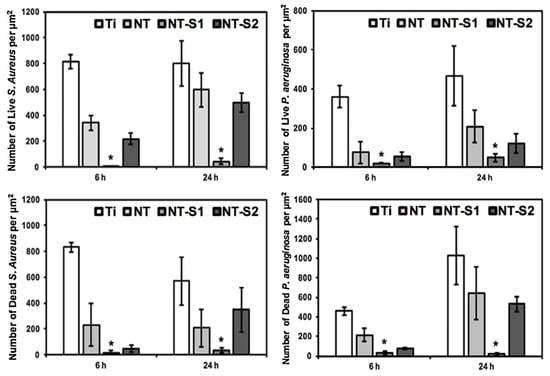
Figure 13.
S. aureus and P. aeruginosa adhesion on various sample surfaces after cultivation for 6 h and 24 h. Ti, NT, NT-S1, and NT-S2 represent unmodified titanium, unmodified TiO2 nanotube arrays, superhydrophobic TiO2 nanotube arrays, and superhydrophilic titania nanotube arrays, respectively (* means p < 0.05). Reprinted with permission from Ref. [40]. Copyright 2018, Elsevier.
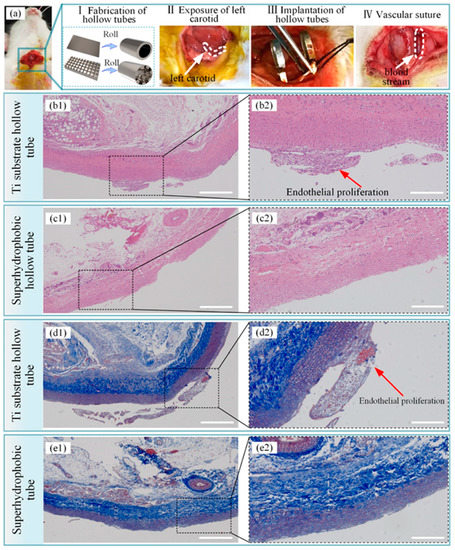
Figure 14.
Histopathological evaluation of a blood vessel at the stent implantation site. (a) process of implanting a hollow tube in a rabbit, (b1) results of hematoxylin–eosin staining of the blood vessel after implanting the hollow titanium substrate tube, (b2) amplified photographs of (b1), (c1) results of hematoxylin–eosin staining of the blood vessel after implantation of the hollow superhydrophobic tube, (c2) amplified photographs of (c1), (d1) results of the Masson staining of the blood vessel after implanting the hollow titanium substrate tube, (d2) amplified photographs of (d1), (e1) results of the Masson staining of the blood vessel after implantation of the hollow superhydrophobic tube, (e2) amplified photographs of (e1). The scale bars for (b1, c1, d1, and e1) and (b2, c2, d2, and e2) are 500 nm and 200 nm, respectively. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [99]. Copyright 2021, American Chemical Society.
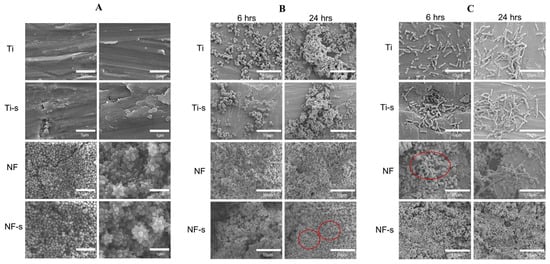
Figure 15.
SEM images: (A) different surfaces, (B) S. aureus adhesion on different surfaces and (C) E. coli. adhesion on different surfaces. (Ti, Ti-s, NF, and NF-s represent the Ti-6Al-4V titanium alloy, the titanium alloy after silanization, the nanoflower surface, and the nanoflower surface after silanization). Reprinted with permission from Ref. [100]. Copyright 2021, Elsevier.
5. Conclusions and Perspectives
In this review, the basic theories of wettability were described at first. The second section interpreted biofilm formation, which is a primary pathogenic occurrence in the development of infection in implants. In the last section, recent progresses in designing superhydrophobic titanium-based implants and their antibacterial applications were summarized and discussed in detail. The mechanism used to prevent bacterial adhesion for superhydrophobic titanium-based implant surfaces was attributed to the trapped air layer on material surfaces. Nevertheless, there are still some problems to overcome in future research.
- (1)
- The antibacterial mechanism of superhydrophobic titanium-based implants. To date, there is no efficient way of promoting biofilm elimination or totally preventing infection recurrence, especially in clinical practice. It is generally assumed that the mechanism to prevent bacterial adhesion for superhydrophobic titanium-based implant surfaces is ascribed to the trapped air layer on material surfaces to reduce the contact area between bacteria and material surfaces, resulting in reduced bacterial adhesion from etiology. Nevertheless, bacterial adhesion on surfaces made of superhydrophobic titanium has not yet been studied thoroughly and systematically. Therefore, it is essential to investigate the antibacterial mechanism on superhydrophobic surfaces that can inhibit bacterial adhesion from etiology.
- (2)
- The bacteria types tested on superhydrophobic surfaces. At present, bacteria tested on superhydrophobic surfaces are limited to a certain extent, mainly focusing on S. aureus, E. coli, and P. aeruginosa in most previous studies. As a variety of bacteria may play different functions in the bacteria–implants interplay, more bacteria species should be investigated to identify whether superhydrophobic surfaces have broad-spectrum antibacterial activity.
- (3)
- The durability of superhydrophobic surfaces. Studies have focused on the long-lasting antimicrobial activity of superhydrophobic surfaces. Once the entrapped air-bubble layer is lost, superhydrophobic titanium-based implants will most probably fail, and the biofilm will subsequently be formed. Although some initial advancements have been reported, further research is necessary to enhance the durability of superhydrophobic surfaces.
Currently, more and more scientists are focused on dealing with various challenges and enhancing the characteristics of titanium-based implant coatings in different ways. Further investigation on the potential applications of superhydrophobic coatings in titanium-based implants is required. Research in the future should be extra focused on bridging the gap between existing research and practical applications. We believe that more superhydrophobic titanium-based implants with improved antibacterial properties and biocompatibility can become more available for scientific and clinical applications in the foreseeable future and benefit to an enormous number of patients.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.Z.; methodology, Q.R.; validation, S.Z.; formal analysis, Q.R., L.W. and J.Z.; investigation, Q.R., D.L., W.Z., S.C. and Y.C.; resources, S.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, S.Z. and Q.R.; writing—review and editing, S.Z., J.C., X.L., Q.R., H.Q. and Q.L.; supervision, S.Z.; project administration, S.Z.; funding acquisition, S.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 82101070); the Key Research and Development Program of Anhui Province (grant no. 2022e07020051); the Anhui Province Translational Medical College Research Fund Project (grant no. 2021zhyxC51); the Anhui Medical University Basic and Clinical Collaborative Research Enhancement Program (2019xkjT019); the Research Improvement Program in Stomatologic Hospital & College of Anhui Medical University (grant no. 2020kqkyT02); Grants for Scientific Research of BSKY (grant no. XJ201918) from Anhui Medical University; 2022 Disciplinary Construction Project in the School of Dentistry, Anhui Medical University (grant no. 2022xkfyts09); and 2021 Disciplinary Construction Project in the School of Dentistry, Anhui Medical University (grant no. 2021kqxkFY17).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Pałka, K.; Pokrowiecki, R. Porous titanium implants: A review. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2018, 20, 1700648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreifke, M.B.; Jayasuriya, A.A.; Jayasuriya, A.C. Current wound healing procedures and potential care. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2015, 48, 651–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suarez, L.S.; Richmond, J.C. Overview of procurement, processing, and sterilization of soft tissue allografts for sports medicine. Sports Med. Arthrosc. Rev. 2007, 15, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Guehennec, L.; Soueidan, A.; Layrolle, P.; Amouriq, Y. Surface treatments of titanium dental implants for rapid osseointegration. Dent. Mater. 2007, 23, 844–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.L.; Liu, X.M.; Yeung, K.W.K.; Guo, H.; Li, P.H.; Hu, T.; Chung, C.Y.; Chu, P.K. Surface nano-architectures and their effects on the mechanical properties and corrosion behavior of Ti-based orthopedic implants. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2013, 233, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anene, F.A.; Aiza Jaafar, C.N.; Zainol, I.; Azmah Hanim, M.A.; Suraya, M.T. Biomedical materials: A review of titanium based alloys. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C 2020, 235, 3792–3805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyan, B.D.; Bonewald, L.F.; Paschalis, E.P.; Lohmann, C.H.; Rosser, J.; Cochran, D.L.; Dean, D.D.; Schwartz, Z.; Boskey, A.L. Osteoblast-mediated mineral deposition in culture is dependent on surface microtopography. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2002, 71, 519–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Lim, J.Y.; Donahue, H.J.; Dhurjati, R.; Mastro, A.M.; Vogler, E.A. Influence of substratum surface chemistry/energy and topography on the human fetal osteoblastic cell line hFOB 1.19: Phenotypic and genotypic responses observed in vitro. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 4535–4550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, Z.; Raz, P.; Zhao, G.; Barak, Y.; Tauber, M.; Yao, H.; Boyan, B.D. Effect of micrometer-scale roughness of the surface of Ti6Al4V pedicle screws in vitro and in vivo. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2008, 90, 2485–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wall, I.; Donos, N.; Carlqvist, K.; Jones, F.; Brett, P. Modified titanium surfaces promote accelerated osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stromal cells in vitro. Bone 2009, 45, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gittens, R.A.; Olivares-Navarrete, R.; Cheng, A.; Anderson, D.M.; McLachlan, T.; Stephan, I.; Geis-Gerstorfer, J.; Sandhage, K.H.; Fedorov, A.G.; Rupp, F.; et al. The roles of titanium surface micro/nanotopography and wettability on the differential response of human osteoblast lineage cells. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 6268–6277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gittens, R.A.; McLachlan, T.; Olivares-Navarrete, R.; Cai, Y.; Berner, S.; Tannenbaum, R.; Schwartz, Z.; Sandhage, K.H.; Boyan, B.D. The effects of combined micron-/submicron-scale surface roughness and nanoscale features on cell proliferation and differentiation. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 3395–3403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; He, Y.; Lin, C.C.; Liu, P.; Cai, K.Y. Antibacterial surface design of biomedical titanium materials for orthopedic applications. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 78, 51–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Orto, B.; Polizzi, E.; Nagni, M.; Tete, G.; Cappare, P. Full arch implant-prosthetic rehabilitation in patients with type I diabetes mellitus: Retrospective clinical study with 10 year follow-up. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 11735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grischke, J.; Eberhard, J.; Stiesch, M. Antimicrobial dental implant functionalization strategies—A systematic review. Dent. Mater. J. 2016, 35, 545–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, E.; Zhao, X.; Hu, J.; Wang, R.; Fu, S.; Qin, G. Antibacterial metals and alloys for potential biomedical implants. Bioact. Mater. 2021, 6, 2569–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, E.P.; Hasan, J.; Webb, H.K.; Truong, V.K.; Watson, G.S.; Watson, J.A.; Baulin, V.A.; Pogodin, S.; Wang, J.Y.; Tobin, M.J.; et al. Natural bactericidal surfaces: Mechanical rupture of Pseudomonas aeruginosa cells by cicada wings. Small 2012, 8, 2489–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lansdown, A.B. Silver in health care: Antimicrobial effects and safety in use. Curr. Probl. Dermatol. 2006, 33, 17–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahiropoulos, V.; Helvatjoglu-Antoniades, M.; Papadogiannis, Y. In vitro fluoride uptake by bovine enamel from aesthetic restorative materials. Int. J. Paediatr. Dent. 2008, 18, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evaristo, F.F.V.; de Vasconcelos, M.A.; Arruda, F.V.S.; Pereira, A.L.; Andrade, A.L.; de Alencar, D.B.; do Nascimento, M.F.; Sampaio, A.H.; Saker-Sampaio, S.; Bandeira, P.N.; et al. Antibacterial effect on mature biofilms of oral streptococci and antioxidant activity of 3β,6β,16β-trihydroxylup-20(29)-ene from Combretum leprosum. Med. Chem. Res. 2017, 26, 3296–3306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Sun, L.; Liu, W.; Guo, L.; Liu, Z.; Wei, X.; Ling, J. A nuclease from streptococcus mutans facilitates biofilm dispersal and escape from killing by neutrophil extracellular traps. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozturk, O.; Sudagidan, M.; Turkan, U. Biofilm formation by staphylococcus epidermidis on nitrogen ion implanted CoCrMo alloy material. J. Biomed. Mater. Res., Part A 2007, 81, 663–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schutzius, T.M.; Jung, S.; Maitra, T.; Graeber, G.; Kohme, M.; Poulikakos, D. Spontaneous droplet trampolining on rigid superhydrophobic surfaces. Nature 2015, 527, 82–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Chen, Z.; Tiwari, M.K. All-organic superhydrophobic coatings with mechanochemical robustness and liquid impalement resistance. Nat. Mater. 2018, 17, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, S.; Li, C.; Zhang, Y.; Xiang, T.; Cao, Y.; Li, Q.; Chen, Z. A general strategy towards superhydrophobic self-cleaning and anti-corrosion metallic surfaces: An example with aluminum alloy. Coatings 2021, 11, 788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurbanova, A.; Myrzakhmetova, N.; Akimbayeva, N.; Kishibayev, K.; Nurbekova, M.; Kanagat, Y.; Tursynova, A.; Zhunussova, T.; Seralin, A.; Kudaibergenova, R.; et al. Superhydrophobic SiO2/trimethylchlorosilane coating for self-cleaning application of construction materials. Coatings 2022, 12, 1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Li, C.; Fu, Q.; Hu, W.; Xiang, T.; Wang, Q.; Du, M.; Liu, X.; Chen, Z. Development of stable superhydrophobic coatings on aluminum surface for corrosion-resistant, self-cleaning, and anti-icing applications. Mater. Des. 2016, 93, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Li, C.; Fu, Q.; Xiang, T.; Hu, W.; Wang, J.; Ding, S.; Liu, P.; Chen, Z. Fabrication of a micro-nanostructured superhydrophobic aluminum surface with excellent corrosion resistance and anti-icing performance. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 79389–79400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Bellido-Aguilar, D.A.; Huang, Y.; Zeng, X.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, Z. Mechanically robust hydrophobic bio-based epoxy coatings for anti-corrosion application. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2019, 363, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, B.; Hongliang, L.; Guochen, Z.; Minrui, R.; Lili, C.; Hanjie, G.; Yanpeng, X. Robust super-hydrophobic coating prepared by electrochemical surface engineering for corrosion protection. Coatings 2019, 9, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, W.; Kan, Q.; Bai, X.; Wang, C. Robust superhydrophobic coatings for enhanced corrosion resistance and dielectric properties. Coatings 2022, 12, 1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Gong, Q.; Zhan, S.; Jiang, L.; Zheng, Y. Robust anti-icingg performance of a flexible superhydrophobic surface. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 7729–7735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Wang, G.; Tao, J.; Zhu, C.; Liu, S.; Jin, M.; Xie, Y.; Chen, Z. Anti-icing performance of superhydrophobic texture surfaces depending on reference environments. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 4, 1700836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Dong, X.; Huang, J.; Li, S.; Li, Y.; Chen, Z.; Lai, Y. Rational construction of highly transparent superhydrophobic coatings based on a non-particle, fluorine-free and water-rich system for versatile oil-water separation. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 333, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Yang, Y.; Luo, S.; Cheng, C.; Wang, S.; Liu, B. Fabrication of superhydrophobic composite membranes with honeycomb porous structure for oil/water separation. Coatings 2022, 12, 1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barthlott, W.; Neinhuis, C. Purity of the sacred lotus, or escape from contamination in biological surfaces. Planta 1997, 202, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Wang, R.; Yang, B.; Li, T.J.; Tryk, D.A.; Fujishima, A.; Hashimoto, K.; Zhu, D.B. Binary cooperative complementary nanoscale interfacial materials. Pure Appl. Chem. 2000, 72, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, T.F.; Lv, Z.; Wei, F.F.; Liu, J.; Dong, W.; Li, C.; Zhao, Y.X.; Chen, D.P. Superhydrophobic civil engineering materials: A review from recent developments. Coatings 2019, 9, 753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, G.B.; Page, K.; Patir, A.; Nair, S.P.; Allan, E.; Parkin, I.P. The anti-biofouling properties of superhydrophobic surfaces are short-lived. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 6050–6058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartlet, K.; Movafaghi, S.; Dasi, L.P.; Kota, A.K.; Popat, K.C. Antibacterial activity on superhydrophobic titania nanotube arrays. Colloids Surf. B 2018, 166, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Liang, X.J.; Gadd, G.M.; Zhao, Q. Advanced titanium dioxide-polytetrafluorethylene (TiO2-PTFE) nanocomposite coatings on stainless steel surfaces with antibacterial and anti-corrosion properties. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 490, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanmohammadi Chenab, K.; Sohrabi, B.; Rahmanzadeh, A. Superhydrophobicity: Advanced biological and biomedical applications. Biomater. Sci. 2019, 7, 3110–3137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassie, A.B.D.; Baxter, S. Wettability of porous surfaces. Trans. Faraday Soc. 1944, 40, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wan, Y.; Ren, B.; Wang, H.; Yu, M.; Liu, A.; Liu, Z. Preparation of superhydrophobic surface on titanium alloy via micro-milling, anodic oxidation and fluorination. Micromachines 2020, 11, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, T. An essay on the cohesion of fluids. Phil. Trans. 1997, 1, 171–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenzel, R.N. Resistance of solid surfaces to wetting by water. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2002, 28, 988–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenzel, R.N. Surface roughness and contact angle. J. Phys. Chem. C 2002, 53, 1466–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Zhang, Y.; Xi, J.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, N.; Xia, F.; Jiang, L. Petal effect: A superhydrophobic state with high adhesive force. Langmuir 2008, 24, 4114–4119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirtcliffe, N.J.; McHale, G.; Atherton, S.; Newton, M.I. An introduction to superhydrophobicity. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 161, 124–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; McCarthy, T.J. The "lotus effect" explained: Two reasons why two length scales of topography are important. Langmuir 2006, 22, 2966–2967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.H.; Feng, X.J.; Feng, L.; Sun, T.L.; Zhai, J.; Li, T.J.; Jiang, L. Superhydrophobic aligned polystyrene nanotube films with high adhesive force. Adv. Mater. 2005, 17, 1977–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, D.; Shivapriya, P.M.; Gautam, P.K.; Misra, K.; Sahoo, A.K.; Samanta, S.K. A review on basic biology of bacterial biofilm infections and their treatments by nanotechnology-based approaches. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. India Sect. B Biol. Sci. 2019, 90, 243–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, H.; Allan, R.N.; Howlin, R.P.; Stoodley, P.; Hall-Stoodley, L. Targeting microbial biofilms: Current and prospective therapeutic strategies. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2017, 15, 740–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirrone, M.; Pinciroli, R.; Berra, L. Microbiome, biofilms, and pneumonia in the ICU. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2016, 29, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harriott, M.M. Biofilms and antibiotics. In Reference Module in Biomedical Sciences; Caplan, M., Mitchell, R., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Stoica, P.; Chifiriuc, M.C.; Rapa, M.; Lazăr, V. Overview of biofilm-related problems in medical devices. In Biofilms and Implantable Medical Devices; Deng, Y., Lv, W., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2017; pp. 3–23. [Google Scholar]
- Rimondini, L.; Cochis, A.; Varoni, E.; Azzimonti, B.; Carrassi, A. Biofilm formation on implants and prosthetic dental materials. In Handbook of Bioceramics and Biocomposites, 1st ed.; Antoniac, I.V., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 991–1027. [Google Scholar]
- Ferraris, S.; Spriano, S. Antibacterial titanium surfaces for medical implants. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2016, 61, 965–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.J.; Zhang, G.N.; Wang, X.; Hang, R.Q.; Huang, X.B.; Qin, L.; Tang, B.; Zhang, X.Y. Biocompatibility, corrosion resistance and antibacterial activity of TiO2/CuO coating on titanium. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 16185–16195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, S.; Li, G.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, R.; Dong, A.; Zhang, R. Preparation and in vitro antibacterial properties of anodic coatings co-doped with Cu, Zn, and P on a Ti–6Al–4V alloy. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 241, 122360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadidi, M.; Bigham, A.; Saebnoori, E.; Hassanzadeh-Tabrizi, S.A.; Rahmati, S.; Alizadeh, Z.M.; Nasirian, V.; Rafienia, M. Electrophoretic-deposited hydroxyapatite-copper nanocomposite as an antibacterial coating for biomedical applications. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2017, 321, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Liu, X.; Meng, F.; Chu, P.K. Biological actions of silver nanoparticles embedded in titanium controlled by micro-galvanic effects. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 693–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.B.; Qiao, Y.Q.; Ding, Z.H.; Liu, X.Y. Microstructure and properties of Ag/N dual ions implanted titanium. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2011, 205, 5430–5436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Qiao, Y.; Liu, X.; Lu, T.; Cui, T.; Meng, F.; Chu, P.K. Electron storage mediated dark antibacterial action of bound silver nanoparticles: Smaller is not always better. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 5100–5110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojcieszak, D.; Mazur, M.; Kalisz, M.; Grobelny, M. Influence of Cu, Au and Ag on structural and surface properties of bioactive coatings based on titanium. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2017, 71, 1115–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Xu, D.; Yang, C.; Chen, J.; Shahzad, M.B.; Sun, Z.; Zhao, J.; Gu, T.; Yang, K.; Wang, G. Inhibition of staphylococcus aureus biofilm by a copper-bearing 317L-Cu stainless steel and its corrosion resistance. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2016, 69, 744–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.F.; Zhang, B.B.; Wang, B.L.; Wang, Y.B.; Li, L.; Yang, Q.B.; Cui, L.S. Introduction of antibacterial function into biomedical TiNi shape memory alloy by the addition of element Ag. Acta Biomater. 2011, 7, 2758–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.; Shi, J.; Wang, L.; Chen, Y.; Liang, C.; Yang, L.; Wang, L.-N. Bacterial anti-adhesion surface design: Surface patterning, roughness and wettability: A review. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 99, 82–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crick, C.R.; Ismail, S.; Pratten, J.; Parkin, I.P. An investigation into bacterial attachment to an elastomeric superhydrophobic surface prepared via aerosol assisted deposition. Thin Solid Film. 2011, 519, 3722–3727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatoon, Z.; McTiernan, C.D.; Suuronen, E.J.; Mah, T.F.; Alarcon, E.I. Bacterial biofilm formation on implantable devices and approaches to its treatment and prevention. Heliyon 2018, 4, e01067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, L.; Li, J.; Liu, X.; Cui, Z.; Yang, X.; Zhu, S.; Li, Z.; Yuan, X.; Zheng, Y.; Yeung, K.W.K.; et al. Rapid biofilm eradication on bone implants using red phosphorus and near-infrared light. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1801808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Li, L.; Su, K.; Liu, X.; Zhang, T.; Liang, Y.; Jing, D.; Yang, X.; Zheng, D.; Cui, Z.; et al. Highly effective and noninvasive near-infrared eradication of a staphylococcus aureus biofilm on implants by a photoresponsive coating within 20 min. Adv. Sci. 2019, 6, 1900599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurtz, S.M.; Lau, E.; Watson, H.; Schmier, J.K.; Parvizi, J. Economic burden of periprosthetic joint infection in the United States. J. Arthroplast. 2012, 27, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Chu, P.K.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Z. Antibacterial coatings on titanium implants. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2009, 91, 470–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, X.; Yan, C.; Tian, Q.; Lin, J.; Yang, S. BSA-assisted synthesis of ultrasmall gallic acid-Fe(III) coordination polymer nanoparticles for cancer theranostics. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 7207–7223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.M.; Hong, G.; Hayashida, K.; Maeda, T.; Murata, H.; Sasaki, K. Influence of composition on the adhesive strength and initial viscosity of denture adhesives. Dent. Mater. J. 2014, 33, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosheger, G.; Hardes, J.; Ahrens, H.; Streitburger, A.; Buerger, H.; Erren, M.; Gunsel, A.; Kemper, F.H.; Winkelmann, W.; Von Eiff, C. Silver-coated megaendoprostheses in a rabbit model--an analysis of the infection rate and toxicological side effects. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 5547–5556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arciola, C.R.; Campoccia, D.; Ehrlich, G.D.; Montanaro, L. Biofilm-based implant infections in orthopaedics. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2015, 830, 29–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trampuz, A.; Zimmerli, W. Diagnosis and treatment of infections associated with fracture-fixation devices. Injury 2006, 37 (Suppl. 2), S59–S66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangram, A.J.; Horan, T.C.; Pearson, M.L.; Silver, L.C.; Jarvis, W.R. Guideline for prevention of surgical site infection, 1999. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 1999, 20, 246–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, P.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Wang, H.; Lin, C.; Zhang, L. Effect of superhydrophobic surface of titanium on staphylococcus aureus adhesion. J. Nanomater. 2011, 2011, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, D.; Aravindan, S.; Kaushal Wasson, M.; Rao, P.V. Fast fabrication of superhydrophobic titanium alloy as antibacterial surface using nanosecond laser texturing. J. Micro. Nanomanuf. 2018, 6, 011002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanithakumari, S.C.; Choubey, A.K.; Thinaharan, C.; Gupta, R.K.; George, R.P.; Kaul, R.; Bindra, K.S.; Philip, J. Laser patterned titanium surfaces with superior antibiofouling, superhydrophobicity, self-cleaning and durability: Role of line spacing. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2021, 418, 127257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeFlorio, W.; Crawford, K.; Liu, S.H.; Hua, Y.Y.; Cisneros-Zevallos, L.; Akbulut, M. Facile, fluorine-free fabrication of bacterial antifouling titanium alloy Ti6Al4V surfaces for surgically implanted devices. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2022, 443, 128580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignoletti, F.; Matesanz, P.; Rodrigo, D.; Figuero, E.; Martin, C.; Sanz, M. Surgical protocols for ridge preservation after tooth extraction. A systematic review. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2012, 23 (Suppl. 5), 22–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, G.R.; Renvert, S. Cluster of bacteria associated with peri-implantitis. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2014, 16, 783–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomasi, C.; Tessarolo, F.; Caola, I.; Wennstrom, J.; Nollo, G.; Berglundh, T. Morphogenesis of peri-implant mucosa revisited: An experimental study in humans. Clin. Oral. Implants Res. 2014, 25, 997–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.W.; Yun, Y.P.; Park, K.; Kim, S.E. Gentamicin and bone morphogenic protein-2 (BMP-2)-delivering heparinized-titanium implant with enhanced antibacterial activity and osteointegration. Bone 2012, 50, 974–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yarramaneni, V.; Balakrishnan, D.; Aparna, I.N.; Sachdeva, A.; Prabhu, N. Emerging antibacterial coated dental implants: A preventive measure for peri-implantitis. J. Dent. 2016, 7, 195–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inzana, J.A.; Schwarz, E.M.; Kates, S.L.; Awad, H.A. Biomaterials approaches to treating implant-associated osteomyelitis. Biomaterials 2016, 81, 58–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gherlone, E.F.; Cappare, P.; Pasciuta, R.; Grusovin, M.G.; Mancini, N.; Burioni, R. Evaluation of resistance against bacterial microleakage of a new conical implant-abutment connection versus conventional connections: An in vitro study. New Microbiol. 2016, 39, 49–56. [Google Scholar]
- Souza, J.G.S.; Bertolini, M.; Costa, R.C.; Cordeiro, J.M.; Nagay, B.E.; de Almeida, A.B.; Retamal-Valdes, B.; Nociti, F.H.; Feres, M.; Rangel, E.C.; et al. Targeting pathogenic biofilms: Newly developed superhydrophobic coating favors a host-compatible microbial profile on the titanium surface. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 10118–10129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matinlinna, J.P.; Tsoi, J.K.; de Vries, J.; Busscher, H.J. Characterization of novel silane coatings on titanium implant surfaces. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2013, 24, 688–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villard, N.; Seneviratne, C.; Tsoi, J.K.; Heinonen, M.; Matinlinna, J. Candida albicans aspects of novel silane system-coated titanium and zirconia implant surfaces. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2015, 26, 332–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fadeeva, E.; Truong, V.K.; Stiesch, M.; Chichkov, B.N.; Crawford, R.J.; Wang, J.; Ivanova, E.P. Bacterial retention on superhydrophobic titanium surfaces fabricated by femtosecond laser ablation. Langmuir 2011, 27, 3012–3019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pogodin, S.; Hasan, J.; Baulin, V.A.; Webb, H.K.; Truong, V.K.; Phong Nguyen, T.H.; Boshkovikj, V.; Fluke, C.J.; Watson, G.S.; Watson, J.A.; et al. Biophysical model of bacterial cell interactions with nanopatterned cicada wing surfaces. Biophys. J. 2013, 104, 835–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanithakumari, S.C.; Jena, G.; Sofia, S.; Thinaharan, C.; George, R.P.; Philip, J. Fabrication of superhydrophobic titanium surfaces with superior antibacterial properties using graphene oxide and silanized silica nanoparticles. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2020, 400, 126074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoj, T.P.; Rasitha, T.P.; Vanithakumari, S.C.; Anandkumar, B.; George, R.P.; Philip, J. A simple, rapid and single step method for fabricating superhydrophobic titanium surfaces with improved water bouncing and self cleaning properties. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 512, 145636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, G.; Li, D.; Zhang, X.; Li, Q.; Liu, Z.; Fang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Man, J. In vivo blood-repellent performance of a controllable facile-generated superhydrophobic surface. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 29021–29033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomerie, Z.; Popat, K.C. Improved hemocompatibility and reduced bacterial adhesion on superhydrophobic titania nanoflower surfaces. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2021, 119, 111503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).