A Review for Artificial Intelligence Based Protein Subcellular Localization
Abstract
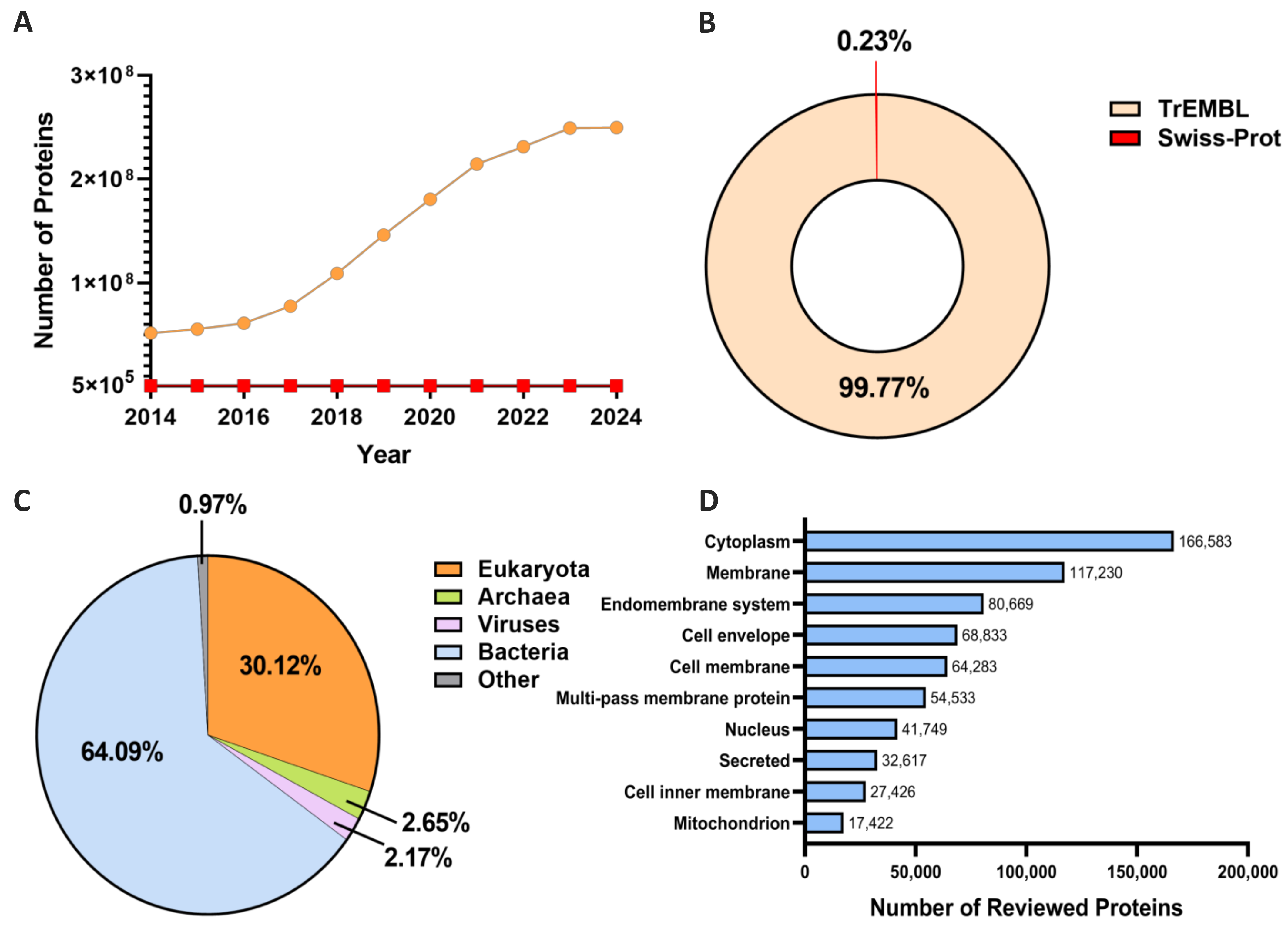
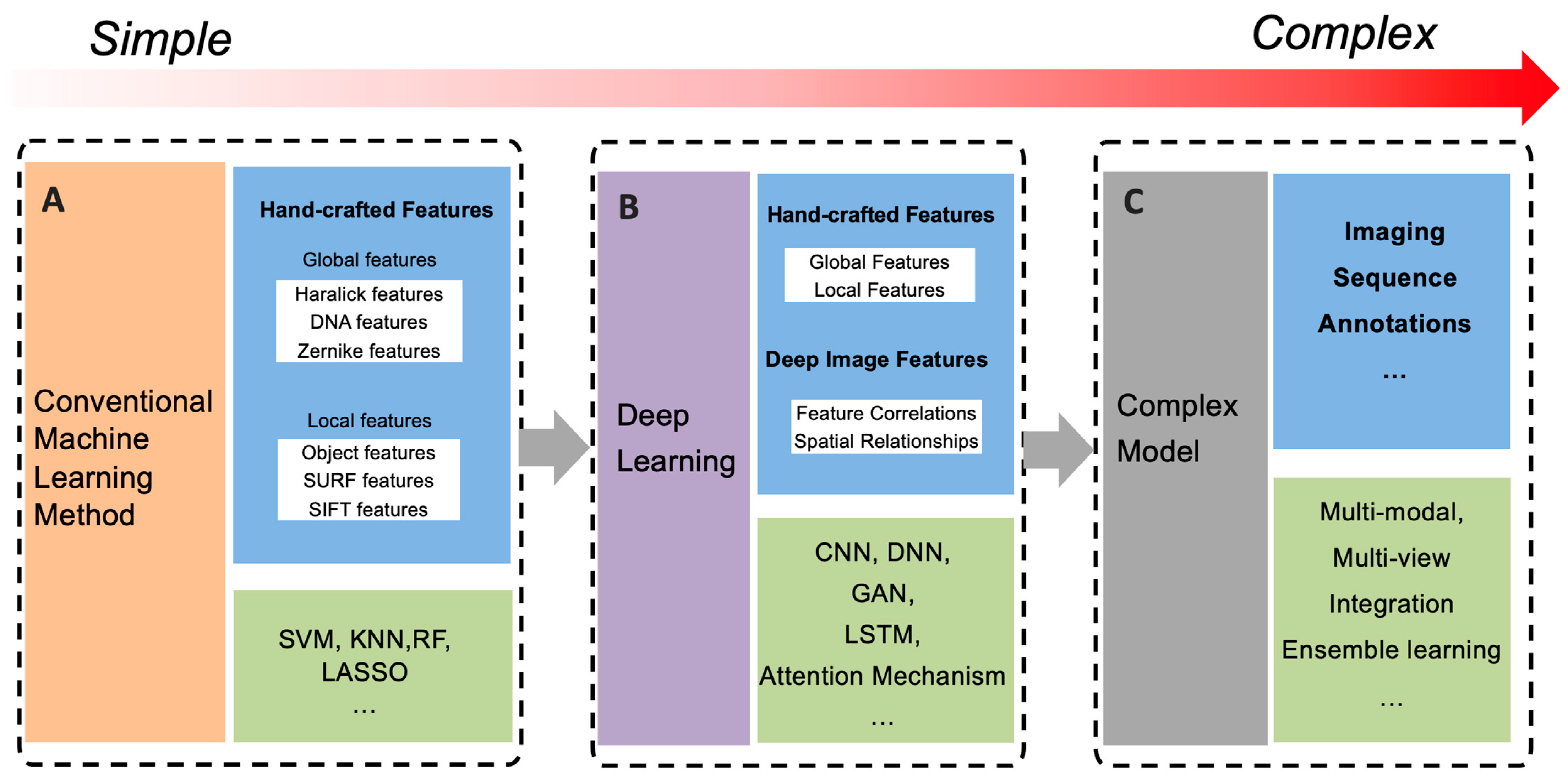
1. Introduction
2. Sequence-Based Methods
2.1. Sequence-Based Features
2.2. Sequences-Based AI Approaches
3. Knowledge-Based Methods
3.1. Legitimacy of Using Gene Ontology (GO) Features
3.2. Knowledge-Based AI Approaches
| Method | Features | Algorithm | S/M-Location | Species | Performance Metrics 1 | Pub | Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ML-FGAT | GO, PsePSSM, PC, CT, | DE, wMLDAe, F-GAN, GAT, KNN, CNN | M | Human, Virus, Gram-negative Bacteria, Plants, SARS-CoV-2 | Acc: 0.91~0.96 Prec: 0.92~0.99 F1: 0.94~0.98 HL: 0.01~0.04 RL: 0.02~0.06 OE: 0.04~0.07 | [76] | 2024 |
| PMPSL-GRAKEL | GO | RF, Random k-label sets algorithm | M | Human, Bacteria, Animal | Acc: 0.89~0.97 CV: 0.92~0.98 AT: 0.82~0.95 AF: 0.01~0.02 | [89] | 2024 |
| Wang et al. | GO, CDD, PseAAC, PSSM | NN | M | Human | Acc: 0.84 F1: 0.76 | [75] | 2023 |
| Zhang et al. | PPI, KEGG, GO | mRMR, MCFS, LightGBM, IFS, RF, SVM, SMOTE | M | Human | Acc: 0.75~1.00 MCC: 0.80~0.85 | [105] | 2022 |
| ML-locMLFE | GO, PseAAC, EBGW, RPT, EDT, MCD | MLSI, IRWLS, MLFE | M | Bacteria, Plants, Virus | Acc: 0.94~0.99 Prec: 0.99~1.00 AUC: 0.98~0.99 OLA: 0.99~1.00 HL: 0.00~0.01 CV: 0.07~0.08 RL: 0.00 | [77] | 2021 |
| Chen et al. | GO, KEGG, PPI, PC | RF, mRMR, IFS, SVM, KNN, DT, SMOTE | S | Human | Acc: 0.56~0.80 MCC: 0.49~0.76 | [96] | 2021 |
| Gpos-ECC-mPLoc | GO, DC | BR, CC, ECC, SVM | M | Gram-positive Bacteria | Acc: 0.90~0.93 | [110] | 2015 |
| mGOASVM | GO | SVM | M | Virus, Plants | Acc: 0.87~0.89 | [92] | 2012 |
| iLoc-Euk | GO, PseAAC, PSSM, SCF | ML-KNN | M | Eukaryotes | Acc: 0.79 | [111] | 2011 |
| Gneg-mPLoc 2 | GO, FunD, PSSM | OET-KNN | M | Gram-negative Bacteria | Acc: 0.85~0.98 | [85] | 2010 |
| PSORTb 3.0 | SwissSCL | SVM | S | Eukaryotes, Prokaryotes | Acc: 0.97~0.98 Prec: 0.97~0.98 Rec: 0.93~0.94 MCC: 0.79~0.85 | [112] | 2010 |
4. Bioimage-Based Methods
4.1. Bioimage-Based Features
4.2. Bioimage-Based AI Methods
5. Protein Subcellular Localization in Different Species
6. Current Challenges and Future Directions
6.1. Challenges
6.2. Future Directions
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, Q.; Hu, D.H.; Xue, H.; Yu, W.; Yang, Q. Semi-Supervised Protein Subcellular Localization. BMC Bioinform. 2009, 10, S47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, S.; Mak, M.-W.; Kung, S.-Y. HybridGO-Loc: Mining Hybrid Features on Gene Ontology for Predicting Subcellular Localization of Multi-Location Proteins. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e89545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, M. Molecular Mechanism of the Nuclear Protein Import Cycle. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 8, 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayor, S.; Pagano, R.E. Pathways of Clathrin-Independent Endocytosis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 8, 603–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.; Byun, K.; Hong, W.; Chuang, H.-Y.; Pack, C.-G.; Bayarsaikhan, E.; Paek, S.H.; Kim, H.; Shin, H.Y.; Ideker, T.; et al. Proteome-Wide Discovery of Mislocated Proteins in Cancer. Genome Res. 2013, 23, 1283–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Li, S. Protein Mislocalization: Mechanisms, Functions and Clinical Applications in Cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta—Rev. Cancer 2014, 1846, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barmada, S.J.; Skibinski, G.; Korb, E.; Rao, E.J.; Wu, J.Y.; Finkbeiner, S. Cytoplasmic Mislocalization of TDP-43 Is Toxic to Neurons and Enhanced by a Mutation Associated with Familial Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 639–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziff, O.J.; Harley, J.; Wang, Y.; Neeves, J.; Tyzack, G.; Ibrahim, F.; Skehel, M.; Chakrabarti, A.M.; Kelly, G.; Patani, R. Nucleocytoplasmic mRNA Redistribution Accompanies RNA Binding Protein Mislocalization in ALS Motor Neurons and Is Restored by VCP ATPase Inhibition. Neuron 2023, 111, 3011–3027.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundberg, E.; Borner, G.H.H. Spatial Proteomics: A Powerful Discovery Tool for Cell Biology. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 20, 285–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, L.; Yang, Q.-L.; Xie, B.-T.; Zeng, H.-Y.; Ding, L.-J.; Rao, F.-Q.; Yan, T.; Lu, F.; Chen, Q.; Huang, X.-F. Dysregulated Arginine Metabolism Is Linked to Retinal Degeneration in Cep250 Knockout Mice. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2023, 64, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohnhorst, C.L.; Schmitt, D.L.; Sundaram, A.; An, S. Subcellular Functions of Proteins under Fluorescence Single-Cell Microscopy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)—Proteins Proteom. 2016, 1864, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Sekine, S.; Pessino, V.; Li, H.; Leonetti, M.D.; Huang, B. Improved Split Fluorescent Proteins for Endogenous Protein Labeling. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brzozowski, R.S.; White, M.L.; Eswara, P.J. Live-Cell Fluorescence Microscopy to Investigate Subcellular Protein Localization and Cell Morphology Changes in Bacteria. J. Vis. Exp. 2020, 153, e59905. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, F.-X.; Sall, J.; Petzold, C.; Van Opbergen, C.J.M.; Liang, X.; Delmar, M. Nanogold Based Protein Localization Enables Subcellular Visualization of Cell Junction Protein by SBF-SEM. In Methods in Cell Biology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; Volume 177, pp. 55–81. ISBN 978-0-323-91607-3. [Google Scholar]
- Schornack, S.; Fuchs, R.; Huitema, E.; Rothbauer, U.; Lipka, V.; Kamoun, S. Protein Mislocalization in Plant Cells Using a GFP-binding Chromobody. Plant J. 2009, 60, 744–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orbán, T.I.; Seres, L.; Özvegy-Laczka, C.; Elkind, N.B.; Sarkadi, B.; Homolya, L. Combined Localization and Real-Time Functional Studies Using a GFP-Tagged ABCG2 Multidrug Transporter. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 367, 667–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The UniProt Consortium; Bateman, A.; Martin, M.-J.; Orchard, S.; Magrane, M.; Ahmad, S.; Alpi, E.; Bowler-Barnett, E.H.; Britto, R.; Bye-A.-Jee, H.; et al. UniProt: The Universal Protein Knowledgebase in 2023. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D523–D531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Digre, A.; Lindskog, C. The Human Protein Atlas—Spatial Localization of the Human Proteome in Health and Disease. Protein Sci. 2021, 30, 218–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thul, P.J.; Lindskog, C. The Human Protein Atlas: A Spatial Map of the Human Proteome. Protein Sci. 2018, 27, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, K.-J.; Kanehisa, M. Prediction of Protein Subcellular Locations by Support Vector Machines Using Compositions of Amino Acids and Amino Acid Pairs. Bioinformatics 2003, 19, 1656–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, K.-C. Using Pair-Coupled Amino Acid Composition to Predict Protein Secondary Structure Content. J. Protein Chem. 1999, 18, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, K. Prediction of Protein Cellular Attributes Using Pseudo-amino Acid Composition. Proteins 2001, 43, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Heijne, G.; Steppuhn, J.; Herrmann, R.G. Domain Structure of Mitochondrial and Chloroplast Targeting Peptides. Eur. J. Biochem. 1989, 180, 535–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, S.; Mak, M.-W. Machine Learning for Protein Subcellular Localization Prediction; De Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 2015; ISBN 978-1-5015-1048-9. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, S.; Liu, X.; Pan, Y.; Xiao, C.; Feng, Y.; Zheng, L.; Zhao, M.; Huang, M. Comprehensive Analysis of Signal Peptides in Saccharomyces Cerevisiae Reveals Features for Efficient Secretion. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, 2203433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martoglio, B.; Dobberstein, B. Signal Sequences: More than Just Greasy Peptides. Trends Cell Biol. 1998, 8, 410–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almagro Armenteros, J.J.; Salvatore, M.; Emanuelsson, O.; Winther, O.; von Heijne, G.; Elofsson, A.; Nielsen, H. Detecting Sequence Signals in Targeting Peptides Using Deep Learning. Life Sci. Alliance 2019, 2, e201900429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teufel, F.; Almagro Armenteros, J.J.; Johansen, A.R.; Gíslason, M.H.; Pihl, S.I.; Tsirigos, K.D.; Winther, O.; Brunak, S.; Von Heijne, G.; Nielsen, H. SignalP 6.0 Predicts All Five Types of Signal Peptides Using Protein Language Models. Nat. Biotechnol. 2022, 40, 1023–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, Y.; Ohno, Y.; Kubota, Y.; Fukagawa, T.; Kihara, A.; Haraguchi, T.; Hiraoka, Y. Ceramide Synthase Homolog Tlc4 Maintains Nuclear Envelope Integrity via Its Golgi Translocation. J. Cell Sci. 2023, 136, jcs260923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Tang, J.; Guo, F. Identification of Protein Subcellular Localization via Integrating Evolutionary and Physicochemical Information into Chou’s General PseAAC. J. Theor. Biol. 2019, 462, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mak, M.-W.; Guo, J.; Kung, S.-Y. PairProSVM: Protein Subcellular Localization Based on Local Pairwise Profile Alignment and SVM. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinf. 2008, 5, 416–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahir, M.; Khan, F.; Hayat, M.; Alshehri, M.D. An Effective Machine Learning-Based Model for the Prediction of Protein–Protein Interaction Sites in Health Systems. Neural Comput. Appl. 2024, 36, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Nabil, M.; Zhang, J. Deep Forest-Based Prediction of Protein Subcellular Localization. Curr. Gene Ther. 2018, 18, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, J.; Chen, Y.; Cao, Y.; Zhao, Y. Accurate Identification of Submitochondrial Protein Location Based on Deep Representation Learning Feature Fusion. In Proceedings of the ICIC 2023: Advanced Intelligent Computing Technology and Applications, Zhengzhou, China, 10–13 August 2023; Huang, D.-S., Premaratne, P., Jin, B., Qu, B., Jo, K.-H., Hussain, A., Eds.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2023; pp. 587–596. [Google Scholar]
- Javed, F.; Hayat, M. Predicting Subcellular Localization of Multi-Label Proteins by Incorporating the Sequence Features into Chou’s PseAAC. Genomics 2019, 111, 1325–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, L.; Meng, Q.; Chen, Y.; Wu, P. Subcellular Location Prediction of Apoptosis Proteins Using Two Novel Feature Extraction Methods Based on Evolutionary Information and LDA. BMC Bioinform. 2020, 21, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, T.; Liu, C. Prediction of Apoptosis Protein Subcellular Localization via Heterogeneous Features and Hierarchical Extreme Learning Machine. SAR QSAR Environ. Res. 2019, 30, 209–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alaa, A.; Eldeib, A.M.; Metwally, A.A. Protein Subcellular Localization Prediction Based on Internal Micro-Similarities of Markov Chains. In Proceedings of the 2019 41st Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Berlin, Germany, 23–27 July 2019; pp. 1355–1358. [Google Scholar]
- Murphy, R.F. Communicating Subcellular Distributions. Cytom. Pt. A 2010, 77A, 686–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, S.E.; Erb, M.L.; Selimkhanov, J.; Dong, G.; Hasty, J.; Pogliano, J.; Golden, S.S. Dynamic Localization of the Cyanobacterial Circadian Clock Proteins. Curr. Biol. 2014, 24, 1836–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.; Jeon, T.J. Dynamic Subcellular Localization of DydA in Dictyostelium Cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2023, 663, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, E.; Cao, D.; Qu, C.; Zhao, P.; Wu, Z.; Yin, D.; Zhao, Q.; Gong, F. Multilocation Proteins in Organelle Communication: Based on Protein–Protein Interactions. Plant Direct 2022, 6, e386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Wang, D.; Wu, P.; Chen, Y.; Shang, H.; Wang, L.; Xie, H. Predicting Subcellular Localization of Multisite Proteins Using Differently Weighted Multi-Label k-Nearest Neighbors Sets. THC 2019, 27, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.-C.; Lin, C.-J. LIBSVM: A Library for Support Vector Machines. ACM Trans. Intell. Syst. Technol. 2011, 2, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Tang, J.; Guo, F. Human Protein Subcellular Localization Identification via Fuzzy Model on Kernelized Neighborhood Representation. Appl. Soft Comput. 2020, 96, 106596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.A.M.; Ahmad, S.; Molla, M.K.I. Protein Subcellular Localization Prediction Using Multiple Kernel Learning Based Support Vector Machine. Mol. BioSyst. 2017, 13, 785–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boutell, M.R.; Luo, J.; Shen, X.; Brown, C.M. Learning Multi-Label Scene Classification. Pattern Recognit. 2004, 37, 1757–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liu, S. Protein Sub-Nuclear Localization Based on Effective Fusion Representations and Dimension Reduction Algorithm LDA. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 30343–30361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, D.; Wu, X.; Shen, H.; Yang, J.; Tang, Z.; Qi, Y.; Yang, J. Enhancing Membrane Protein Subcellular Localization Prediction by Parallel Fusion of Multi-View Features. IEEE Trans. Nanobiosci. 2012, 11, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, R.; Li, Y.; Xue, L.; Liu, F.; Li, M.; Luo, J. autoBioSeqpy: A Deep Learning Tool for the Classification of Biological Sequences. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2020, 60, 3755–3764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semwal, R.; Varadwaj, P.K. HumDLoc: Human Protein Subcellular Localization Prediction Using Deep Neural Network. Curr. Genom. 2020, 21, 546–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, L.; Wang, J.; Zhao, L.; Wang, C.; Zhan, H. A Novel Protein Subcellular Localization Method With CNN-XGBoost Model for Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Genet. 2019, 9, 751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaleel, M.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, J.; Feng, X.; Simpson, J.C.; Pollastri, G.; Mooney, C. SCLpred-EMS: Subcellular Localization Prediction of Endomembrane System and Secretory Pathway Proteins by Deep N-to-1 Convolutional Neural Networks. Bioinformatics 2020, 36, 3343–3349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, H.; Liu, H.; Chen, Y.; Cao, Y. Self-Evoluting Framework of Deep Convolutional Neural Network for Multilocus Protein Subcellular Localization. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2020, 58, 3017–3038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, H.; Liu, H.; Cao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liang, C. Multiple Protein Subcellular Locations Prediction Based on Deep Convolutional Neural Networks with Self-Attention Mechanism. Interdiscip. Sci. Comput. Life Sci. 2022, 14, 421–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Z.; Pan, G.; Sun, C.; Tang, J. Predicting Subcellular Location of Protein with Evolution Information and Sequence-Based Deep Learning. BMC Bioinform. 2021, 22, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Wang, D.; Yao, Y.; Eubel, H.; Künzler, P.; Møller, I.M.; Xu, D. MULocDeep: A Deep-Learning Framework for Protein Subcellular and Suborganellar Localization Prediction with Residue-Level Interpretation. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2021, 19, 4825–4839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Gao, S.; Yao, S.; Wu, F.; Li, J.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, Y. Gm-PLoc: A Subcellular Localization Model of Multi-Label Protein Based on GAN and DeepFM. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 912614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chawla, N.V.; Bowyer, K.W.; Hall, L.O.; Kegelmeyer, W.P. SMOTE: Synthetic Minority over-Sampling Technique. J. Artif. Int. Res. 2002, 16, 321–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elnaggar, A.; Heinzinger, M.; Dallago, C.; Rehawi, G.; Wang, Y.; Jones, L.; Gibbs, T.; Feher, T.; Angerer, C.; Steinegger, M.; et al. ProtTrans: Toward Understanding the Language of Life Through Self-Supervised Learning. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2022, 44, 7112–7127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Han, L.; Wang, R.; Chen, H. DaDL-SChlo: Protein Subchloroplast Localization Prediction Based on Generative Adversarial Networks and Pre-Trained Protein Language Model. Brief. Bioinform. 2023, 24, bbad083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosna, A.; Merry, E.; Gyalmo, J.; Alom, Z.; Aung, Z.; Azim, M.A. Transfer Learning: A Friendly Introduction. J. Big Data 2022, 9, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinzinger, M.; Elnaggar, A.; Wang, Y.; Dallago, C.; Nechaev, D.; Matthes, F.; Rost, B. Modeling Aspects of the Language of Life through Transfer-Learning Protein Sequences. BMC Bioinform. 2019, 20, 723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofer, D. The Language of Proteins: NLP, Machine Learning & Protein Sequences. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2021, 19, 1750–1758. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, J.; Ruder, S. Universal Language Model Fine-Tuning for Text Classification. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1801.06146. [Google Scholar]
- Jumper, J. Highly Accurate Protein Structure Prediction with AlphaFold. Nature 2021, 596, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandes, N.; Ofer, D.; Peleg, Y.; Rappoport, N.; Linial, M. ProteinBERT: A Universal Deep-Learning Model of Protein Sequence and Function. Bioinformatics 2022, 38, 2102–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devlin, J.; Chang, M.-W.; Lee, K.; Toutanova, K. BERT: Pre-Training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understanding. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1810.04805. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Z.; Wang, R.; Sun, Y.; Liu, J.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Y.-J. Interpretable Feature Extraction and Dimensionality Reduction in ESM2 for Protein Localization Prediction. Brief. Bioinform. 2024, 25, bbad534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thumuluri, V.; Almagro Armenteros, J.J.; Johansen, A.R.; Nielsen, H.; Winther, O. DeepLoc 2.0: Multi-Label Subcellular Localization Prediction Using Protein Language Models. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, W228–W234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Jiang, L.; Akhil, C.S.; Wang, D.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Xu, D. MULocDeep Web Service for Protein Localization Prediction and Visualization at Subcellular and Suborganellar Levels. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, W343–W349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Rao, R.S.P.; Salvato, F.; Havelund, J.F.; Møller, I.M.; Thelen, J.J.; Xu, D. MU-LOC: A Machine-Learning Method for Predicting Mitochondrially Localized Proteins in Plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Q.; Li, G.-Z. MultiP-SChlo: Multi-Label Protein Subchloroplast Localization Prediction with Chou’s Pseudo Amino Acid Composition and a Novel Multi-Label Classifier. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 2639–2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryngajllo, M.; Childs, L.; Lohse, M.; Giorgi, F.M.; Lude, A.; Selbig, J.; Usadel, B. SLocX: Predicting Subcellular Localization of Arabidopsis Proteins Leveraging Gene Expression Data. Front. Plant Sci. 2011, 2, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zou, K.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, S.; Yang, F. A Novel Multi-Label Human Protein Subcellular Localization Model Based on Gene Ontology and Functional Domain. In Proceedings of the 2023 3rd International Conference on Bioinformatics and Intelligent Computing, Sanya, China, 10–12 February 2023; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2023; pp. 376–380. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Ding, P.; Li, S.; Yu, X.; Yu, B. ML-FGAT: Identification of Multi-Label Protein Subcellular Localization by Interpretable Graph Attention Networks and Feature-Generative Adversarial Networks. Comput. Biol. Med. 2024, 170, 107944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Jin, S.; Gao, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, C.; Zhou, W.; Yu, B. Predicting the Multi-Label Protein Subcellular Localization through Multi-Information Fusion and MLSI Dimensionality Reduction Based on MLFE Classifier. Bioinformatics 2022, 38, 1223–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Z.; Szafron, D.; Greiner, R.; Lu, P.; Wishart, D.S.; Poulin, B.; Anvik, J.; Macdonell, C.; Eisner, R. Predicting Subcellular Localization of Proteins Using Machine-Learned Classifiers. Bioinformatics 2004, 20, 547–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, R.; Rost, B. Sequence Conserved for Subcellular Localization. Protein Sci. 2002, 11, 2836–2847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fyshe, A.; Liu, Y.; Szafron, D.; Greiner, R.; Lu, P. Improving Subcellular Localization Prediction Using Text Classification and the Gene Ontology. Bioinformatics 2008, 24, 2512–2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brady, S.; Shatkay, H. EpiLoc: A (working) text-based system for predicting protein subcellular location. In Biocomputing 2008; WORLD SCIENTIFIC: Kohala Coast, HI, USA, 2007; pp. 604–615. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, W.-L.; Tung, C.-W.; Ho, S.-W.; Hwang, S.-F.; Ho, S.-Y. ProLoc-GO: Utilizing Informative Gene Ontology Terms for Sequence-Based Prediction of Protein Subcellular Localization. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, L.; Liu, X. The Development and Progress in Machine Learning for Protein Subcellular Localization Prediction. Open Bioinform. J. 2022, 15, e187503622208110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, S.; Mak, M.-W.; Kung, S.-Y. GOASVM: A Subcellular Location Predictor by Incorporating Term-Frequency Gene Ontology into the General Form of Chou’s Pseudo-Amino Acid Composition. J. Theor. Biol. 2013, 323, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.-B.; Chou, K.-C. Gneg-mPLoc: A Top-down Strategy to Enhance the Quality of Predicting Subcellular Localization of Gram-Negative Bacterial Proteins. J. Theor. Biol. 2010, 264, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, H.-B.; Yang, J.; Chou, K.-C. Euk-PLoc: An Ensemble Classifier for Large-Scale Eukaryotic Protein Subcellular Location Prediction. Amino Acids 2007, 33, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, K.-C.; Shen, H.-B. Hum-PLoc: A Novel Ensemble Classifier for Predicting Human Protein Subcellular Localization. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 347, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, S.; Fei, W.; Zhou, S. Gene Ontology Based Transfer Learning for Protein Subcellular Localization. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Qu, R.; Liu, X. Improved Multi-Label Classifiers for Predicting Protein Subcellular Localization. Math. Biosci. Eng. 2024, 21, 214–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, S.; Yu, B.; Zhang, Q.; Han, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, Q. DMLDA-LocLIFT: Identification of Multi-Label Protein Subcellular Localization Using DMLDA Dimensionality Reduction and LIFT Classifier. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2020, 206, 104148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Chen, L.-X.; Zou, X.-Y.; Cai, P.-X. Predicting Protein Structural Class Based on Multi-Features Fusion. J. Theor. Biol. 2008, 253, 388–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, S.; Mak, M.-W.; Kung, S.-Y. mGOASVM: Multi-Label Protein Subcellular Localization Based on Gene Ontology and Support Vector Machines. BMC Bioinform. 2012, 13, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, S.; Mak, M.-W. Predicting Subcellular Localization of Multi-Location Proteins by Improving Support Vector Machines with an Adaptive-Decision Scheme. Int. J. Mach. Learn. Cyber. 2018, 9, 399–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, K.-C.; Shen, H.-B. A New Method for Predicting the Subcellular Localization of Eukaryotic Proteins with Both Single and Multiple Sites: Euk-mPLoc 2.0. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, S. Multi-Label Multi-Kernel Transfer Learning for Human Protein Subcellular Localization. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Li, Z.; Zeng, T.; Zhang, Y.-H.; Zhang, S.; Huang, T.; Cai, Y.-D. Predicting Human Protein Subcellular Locations by Using a Combination of Network and Function Features. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 783128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garapati, H.S.; Male, G.; Mishra, K. Predicting Subcellular Localization of Proteins Using Protein-Protein Interaction Data. Genomics 2020, 112, 2361–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.Q.; Wu, M. Predicting Multiplex Subcellular Localization of Proteins Using Protein-Protein Interaction Network: A Comparative Study. BMC Bioinform. 2012, 13, S20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Li, W.; Wu, F.-X.; Pan, Y.; Wang, J. Identifying Essential Proteins Based on Sub-Network Partition and Prioritization by Integrating Subcellular Localization Information. J. Theor. Biol. 2018, 447, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.-H.; Luo, T.; Zhang, H.-L.; Du, P.-F. PLA-GNN: Computational Inference of Protein Subcellular Location Alterations under Drug Treatments with Deep Graph Neural Networks. Comput. Biol. Med. 2023, 157, 106775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huttlin, E.L. Architecture of the Human Interactome Defines Protein Communities and Disease Networks. Nature 2017, 545, 505–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huttlin, E.L. The BioPlex Network: A Systematic Exploration of the Human Interactome. Cell 2015, 162, 425–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Y. A Multi-Scale Map of Cell Structure Fusing Protein Images and Interactions. Nature 2021, 600, 536–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Cai, L.; Liao, B.; Fu, X.; Bing, P.; Yang, J. Prediction of Protein Subcellular Localization Based on Fusion of Multi-View Features. Molecules 2019, 24, 919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.-H.; Ding, S.; Chen, L.; Huang, T.; Cai, Y.-D. Subcellular Localization Prediction of Human Proteins Using Multifeature Selection Methods. BioMed Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 3288527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zhai, Y.-J.; Xue, Z.-Z.; Xu, Y.-Y. Improving Protein Subcellular Location Classification by Incorporating Three-Dimensional Structure Information. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Li, S.; Han, Y.; Jin, S.; Gu, H.; Yu, B. Accurate Prediction of Multi-Label Protein Subcellular Localization through Multi-View Feature Learning with RBRL Classifier. Brief. Bioinform. 2021, 22, bbab012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picard, M.; Scott-Boyer, M.-P.; Bodein, A.; Périn, O.; Droit, A. Integration Strategies of Multi-Omics Data for Machine Learning Analysis. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2021, 19, 3735–3746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Liu, F.; Ju, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, C. Human Protein Subcellular Localization with Integrated Source and Multi-Label Ensemble Classifier. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Li, G.-Z. Multi-Location Gram-Positive and Gram-Negative Bacterial Protein Subcellular Localization Using Gene Ontology and Multi-Label Classifier Ensemble. BMC Bioinform. 2015, 16, S1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, K.-C.; Wu, Z.-C.; Xiao, X. iLoc-Euk: A Multi-Label Classifier for Predicting the Subcellular Localization of Singleplex and Multiplex Eukaryotic Proteins. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, N.Y.; Wagner, J.R.; Laird, M.R.; Melli, G.; Rey, S.; Lo, R.; Dao, P.; Sahinalp, S.C.; Ester, M.; Foster, L.J.; et al. PSORTb 3.0: Improved Protein Subcellular Localization Prediction with Refined Localization Subcategories and Predictive Capabilities for All Prokaryotes. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 1608–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uhlén, M.; Fagerberg, L.; Hallström, B.M.; Lindskog, C.; Oksvold, P.; Mardinoglu, A.; Sivertsson, Å.; Kampf, C.; Sjöstedt, E.; Asplund, A.; et al. Tissue-Based Map of the Human Proteome. Science 2015, 347, 1260419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, W.; Winsnes, C.F.; Hjelmare, M.; Cesnik, A.J.; Åkesson, L.; Xu, H.; Sullivan, D.P.; Dai, S.; Lan, J.; Jinmo, P.; et al. Analysis of the Human Protein Atlas Image Classification Competition. Nat. Methods 2019, 16, 1254–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.-Y.; Yao, L.-X.; Shen, H.-B. Bioimage-Based Protein Subcellular Location Prediction: A Comprehensive Review. Front. Comput. Sci. 2018, 12, 26–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanni, L.; Lumini, A.; Brahnam, S. Survey on LBP Based Texture Descriptors for Image Classification. Expert. Syst. Appl. 2012, 39, 3634–3641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahir, M.; Khan, A.; Majid, A. Protein Subcellular Localization of Fluorescence Imagery Using Spatial and Transform Domain Features. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Haralick, R.M.; Shanmugam, K.; Dinstein, I. Textural Features for Image Classification. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1973, SMC-3, 610–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godil, A.; Lian, Z.; Wagan, A. Exploring Local Features and the Bag-of-Visual-Words Approach for Bioimage Classification. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Bioinformatics, Computational Biology and Biomedical Informatics, Washington, DC, USA, 22 September 2013; pp. 694–695. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.-H.; Zhang, B.-W.; Qian, G.; Wang, B.; Mao, B.; Bichindaritz, I. Bioimage-Based Prediction of Protein Subcellular Location in Human Tissue with Ensemble Features and Deep Networks. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinf. 2020, 17, 1966–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newberg, J.; Murphy, R.F. A Framework for the Automated Analysis of Subcellular Patterns in Human Protein Atlas Images. J. Proteome Res. 2008, 7, 2300–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, K.; Wang, S.; Wang, Z.; Zou, H.; Yang, F. Dual-Signal Feature Spaces Map Protein Subcellular Locations Based on Immunohistochemistry Image and Protein Sequence. Sensors 2023, 23, 9014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Xiong, L.; Schneider, J.; Murphy, R.F. Protein Subcellular Location Pattern Classification in Cellular Images Using Latent Discriminative Models. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, i32–i39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ullah, M.; Han, K.; Hadi, F.; Xu, J.; Song, J.; Yu, D.-J. PScL-HDeep: Image-Based Prediction of Protein Subcellular Location in Human Tissue Using Ensemble Learning of Handcrafted and Deep Learned Features with Two-Layer Feature Selection. Brief. Bioinform. 2021, 22, bbab278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pärnamaa, T.; Parts, L. Accurate Classification of Protein Subcellular Localization from High-Throughput Microscopy Images Using Deep Learning. G3 Genes Genomes Genet. 2017, 7, 1385–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Wei, L. Multi-Scale Deep Learning for the Imbalanced Multi-Label Protein Subcellular Localization Prediction Based on Immunohistochemistry Images. Bioinformatics 2022, 38, 2602–2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, R.; He, L.; Liu, T.; Liu, X.; Wei, L. Protein Subcellular Localization Based on Deep Image Features and Criterion Learning Strategy. Brief. Bioinform. 2021, 22, bbaa313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar]
- Long, W.; Yang, Y.; Shen, H.-B. ImPLoc: A Multi-Instance Deep Learning Model for the Prediction of Protein Subcellular Localization Based on Immunohistochemistry Images. Bioinformatics 2020, 36, 2244–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Xu, Z.; Wang, X.; Tao, S.; MacDonald, W.A.; He, K.; Poholek, A.C.; Chen, K.; Huang, H.; Chen, W. Innovative Super-Resolution in Spatial Transcriptomics: A Transformer Model Exploiting Histology Images and Spatial Gene Expression. Brief. Bioinform. 2024, 25, bbae052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, L.; Ding, Y.; Su, R.; Tang, J.; Zou, Q. Prediction of Human Protein Subcellular Localization Using Deep Learning. J. Parallel Distrib. Comput. 2018, 117, 212–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Z.-Z.; Wu, Y.; Gao, Q.-Z.; Zhao, L.; Xu, Y.-Y. Automated Classification of Protein Subcellular Localization in Immunohistochemistry Images to Reveal Biomarkers in Colon Cancer. BMC Bioinform. 2020, 21, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, J.; Xu, J.; Wei, J.; Tang, J.; Guo, F. A Multi-Scale Multi-Model Deep Neural Network via Ensemble Strategy on High-Throughput Microscopy Image for Protein Subcellular Localization. Expert. Syst. Appl. 2023, 212, 118744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Liu, W.; Yu, W.; Liu, X.; Yan, R.; Liu, Q.; Guo, Q. Multiple Parallel Fusion Network for Predicting Protein Subcellular Localization from Stimulated Raman Scattering (SRS) Microscopy Images in Living Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Zhang, M.; Liu, H.; Yang, Y. Prediction of Protein Subcellular Localization Based on Microscopic Images via Multi-Task Multi-Instance Learning. Chin. J. Electron. 2022, 31, 888–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Yang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Shen, H. Incorporating Label Correlations into Deep Neural Networks to Classify Protein Subcellular Location Patterns in Immunohistochemistry Images. Proteins 2022, 90, 493–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Y.; Lei, H.; Shen, H.-B.; Yang, Y. SIFLoc: A Self-Supervised Pre-Training Method for Enhancing the Recognition of Protein Subcellular Localization in Immunofluorescence Microscopic Images. Brief. Bioinform. 2022, 23, bbab605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.-Y.; Yang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, H.-B. Bioimaging-Based Detection of Mislocalized Proteins in Human Cancers by Semi-Supervised Learning. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 1111–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Huang, M.; Liu, X.; Han, K.; Wang, Z.; Sun, G.; Guo, Q. Swin Transformer Based Neural Network for Organelles Prediction from Quantitative Label-Free Imaging with Phase and Polarization (Qlipp) in Unlabeled Live Cells and Tissue Slices; SSRN. 2023. Available online: https://ssrn.com/abstract=4604469 (accessed on 28 February 2024). [CrossRef]
- Husain, S.S.; Ong, E.-J.; Minskiy, D.; Bober-Irizar, M.; Irizar, A.; Bober, M. Single-Cell Subcellular Protein Localisation Using Novel Ensembles of Diverse Deep Architectures. Commun. Biol. 2023, 6, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullah, M.; Hadi, F.; Song, J.; Yu, D.-J. PScL-DDCFPred: An Ensemble Deep Learning-Based Approach for Characterizing Multiclass Subcellular Localization of Human Proteins from Bioimage Data. Bioinformatics 2022, 38, 4019–4026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahir, M.; Anwar, S.; Mian, A.; Muzaffar, A.W. Deep Localization of Subcellular Protein Structures from Fluorescence Microscopy Images. Neural Comput. Appl. 2022, 34, 5701–5714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerfeld, C.A.; Aussignargues, C.; Zarzycki, J.; Cai, F.; Sutter, M. Bacterial Microcompartments. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 277–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeates, T.O.; Crowley, C.S.; Tanaka, S. Bacterial Microcompartment Organelles: Protein Shell Structure and Evolution. Annu. Rev. Biophys. 2010, 39, 185–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forster, B.M.; Marquis, H. Protein Transport across the Cell Wall of Monoderm Gram-positive Bacteria. Mol. Microbiol. 2012, 84, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, A.K.; Singla, D. VacPred: Sequence-Based Prediction of Plant Vacuole Proteins Using Machine-Learning Techniques. J. Biosci. 2020, 45, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Peña, R.; Mounadi, K.E.; Garcia-Ruiz, H. Changes in Subcellular Localization of Host Proteins Induced by Plant Viruses. Viruses 2021, 13, 677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Wu, Z.-C.; Chou, K.-C. iLoc-Virus: A Multi-Label Learning Classifier for Identifying the Subcellular Localization of Virus Proteins with Both Single and Multiple Sites. J. Theor. Biol. 2011, 284, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.C.; Xiao, X.; Chou, K.C. iLoc-Plant: A Multi-Label Classifier for Predicting the Subcellular Localization of Plant Proteins with Both Single and Multiple Sites. Mol. BioSystems 2011, 7, 3287–3297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, S.; Mak, M.-W.; Kung, S.-Y. mPLR-Loc: An Adaptive Decision Multi-Label Classifier Based on Penalized Logistic Regression for Protein Subcellular Localization Prediction. Anal. Biochem. 2015, 473, 14–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, S.; Mak, M.-W.; Kung, S.-Y. Gram-LocEN: Interpretable Prediction of Subcellular Multi-Localization of Gram-Positive and Gram-Negative Bacterial Proteins. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2017, 162, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camon, E. The Gene Ontology Annotation (GOA) Database: Sharing Knowledge in Uniprot with Gene Ontology. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 262D–266D. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dehzangi, A. Gram-Positive and Gram-Negative Protein Subcellular Localization by Incorporating Evolutionary-Based Descriptors into Chou׳s General PseAAC. J. Theor. Biol. 2015, 364, 284–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, H.-B.; Chou, K.-C. Virus-mPLoc: A Fusion Classifier for Viral Protein Subcellular Location Prediction by Incorporating Multiple Sites. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2010, 28, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, K.-C.; Shen, H.-B. Plant-mPLoc: A Top-Down Strategy to Augment the Power for Predicting Plant Protein Subcellular Localization. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Cruz-Cosme, R.; Zhuang, M.-W.; Liu, D.; Liu, Y.; Teng, S.; Wang, P.-H.; Tang, Q. A Systemic and Molecular Study of Subcellular Localization of SARS-CoV-2 Proteins. Sig. Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boland, M.V.; Murphy, R.F. A Neural Network Classifier Capable of Recognizing the Patterns of All Major Subcellular Structures in FLuorescence Microscope Images of HeLa Cells. Bioinformatics 2001, 17, 1213–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binder, J.X.; Pletscher-Frankild, S.; Tsafou, K.; Stolte, C.; O’Donoghue, S.I.; Schneider, R.; Jensen, L.J. COMPARTMENTS: Unification and Visualization of Protein Subcellular Localization Evidence. Database 2014, 2014, bau012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinken, J.; Asch, D.K.; Neizer-Ashun, K.A.; Chang, G.-H.; Cooper, C.R., Jr.; Min, X.J. FunSecKB2: A Fungal Protein Subcellular Location Knowledgebase. Comput. Mol. Biol. 2014, 4, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lum, G.; Meinken, J.; Orr, J.; Frazier, S.; Min, X. PlantSecKB: The Plant Secretome and Subcellular Proteome KnowledgeBase. Comput. Mol. Biol. 2014, 4, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinken, J.; Walker, G.; Cooper, C.R.; Min, X.J. MetazSecKB: The Human and Animal Secretome and Subcellular Proteome Knowledgebase. Database 2015, 2015, bav077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, S.; Mak, M.-W.; Kung, S.-Y. Mem-mEN: Predicting Multi-Functional Types of Membrane Proteins by Interpretable Elastic Nets. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinf. 2016, 13, 706–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, S.; Mak, M.-W.; Kung, S.-Y. FUEL-mLoc: Feature-Unified Prediction and Explanation of Multi-Localization of Cellular Proteins in Multiple Organisms. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 749–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, S.; Mak, M.-W.; Kung, S.-Y. Sparse Regressions for Predicting and Interpreting Subcellular Localization of Multi-Label Proteins. BMC Bioinform. 2016, 17, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, S.; Mak, M.-W.; Kung, S.-Y. mLASSO-Hum: A LASSO-Based Interpretable Human-Protein Subcellular Localization Predictor. J. Theor. Biol. 2015, 382, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundberg, S.M.; Lee, S.-I. A Unified Approach to Interpreting Model Predictions. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ancona, M.; Ceolini, E.; Öztireli, C.; Gross, M. Towards Better Understanding of Gradient-Based Attribution Methods for Deep Neural Networks. arXiv 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrikumar, A.; Greenside, P.; Kundaje, A. Learning Important Features through Propagating Activation Differences. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, 2017; Available online: http://proceedings.mlr.press/v70/shrikumar17a (accessed on 28 February 2024).
- Zecha, J.; Gabriel, W.; Spallek, R.; Chang, Y.-C.; Mergner, J.; Wilhelm, M.; Bassermann, F.; Kuster, B. Linking Post-Translational Modifications and Protein Turnover by Site-Resolved Protein Turnover Profiling. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramazi, S.; Zahiri, J. Post-Translational Modifications in Proteins: Resources, Tools and Prediction Methods. Database 2021, 2021, baab012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickchi, P.; Jafari, M.; Kalantari, S. PEIMAN 1.0: Post-Translational Modification Enrichment, Integration and Matching ANalysis. Database 2015, 2015, bav037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacharawongsakda, E.; Theeramunkong, T. Predict Subcellular Locations of Singleplex and Multiplex Proteins by Semi-Supervised Learning and Dimension-Reducing General Mode of Chou’s PseAAC. IEEE Trans. Nanobiosci. 2013, 12, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, S.; Mak, M.-W.; Kung, S.-Y. Transductive Learning for Multi-Label Protein Subchloroplast Localization Prediction. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinf. 2017, 14, 212–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, S.; Mak, M.-W.; Kung, S.-Y. Ensemble Linear Neighborhood Propagation for Predicting Subchloroplast Localization of Multi-Location Proteins. J. Proteome Res. 2016, 15, 4755–4762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.-L.; Bao, L.-X.; Xue, M.-Q.; Xu, Y.-Y. Automatic Recognition of Protein Subcellular Location Patterns in Single Cells from Immunofluorescence Images Based on Deep Learning. Brief. Bioinform. 2023, 24, bbac609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zhang, X.; Xu, C.; Han, X.; Wang, Y.; Situ, C.; Li, Y.; Guo, X. DeepSP: A Deep Learning Framework for Spatial Proteomics. J. Proteome Res. 2023, 22, 2186–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, Y.; Li, F.; Guo, X.; Wang, Z.; Pan, T.; Guo, Y.; Webb, G.I.; Yao, J.; Jia, C.; Song, J. Clarion Is a Multi-Label Problem Transformation Method for Identifying mRNA Subcellular Localizations. Brief. Bioinform. 2022, 23, bbac467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zou, Q.; Yuan, L. A Review from Biological Mapping to Computation-Based Subcellular Localization. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2023, 32, 507–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villanueva, E.; Smith, T.; Pizzinga, M.; Elzek, M.; Queiroz, R.M.L.; Harvey, R.F.; Breckels, L.M.; Crook, O.M.; Monti, M.; Dezi, V.; et al. System-Wide Analysis of RNA and Protein Subcellular Localization Dynamics. Nat. Methods 2024, 21, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Wang, T.; Deng, X.; Tang, L.; Liu, L. GM-lncLoc: LncRNAs Subcellular Localization Prediction Based on Graph Neural Network with Meta-Learning. BMC Genom. 2023, 24, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; He, L.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Bao, W.; Cheng, H. Mit Protein Transformer: Identification Mitochondrial Proteins with Transformer Model. In Proceedings of the ICIC 2023: Advanced Intelligent Computing Technology and Applications, Zhengzhou, China, 10–13 August 2023; Huang, D.-S., Premaratne, P., Jin, B., Qu, B., Jo, K.-H., Hussain, A., Eds.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2023; pp. 607–616. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.-L.; Su, W.; Guan, Z.-X.; Zhang, D.; Chen, W.; Liu, L.; Ding, H. An Overview on Predicting Protein Subchloroplast Localization by Using Machine Learning Methods. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2020, 21, 1229–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, B.R.; Vural, S.; Pandey, S.; Barteau, A.; Guda, C. ngLOC: Software and Web Server for Predicting Protein Subcellular Localization in Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes. BMC Res. Notes 2012, 5, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, S.; Kim, J.; Won, K.J. SHARP: Hyperfast and Accurate Processing of Single-Cell RNA-Seq Data via Ensemble Random Projection. Genome Res. 2020, 30, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Method | Features | Algorithm | S/M-Location | Species | Performance Metrics 1 | Pub | Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DaDL-SChlo | Deep- and Hand-crafted features | ProtBERT, XGBoost, GAN, CNN | M | Plants | Acc: 0.86~0.94 Prec: 0.88~0.95 Rec: 0.86~0.94 F1: 0.86~0.95 GM: 0.84~0.94 | [61] | 2023 |
| DeepLoc—2.0 | Masked-LM Objective | MLP, Protein LM | M | Eukaryotes | Acc: 0.39~0.73 MicroF1: 0.60~0.73 MacroF1: 0.46~0.66 MCC: 0.17~0.90 Jaccard: 0.53~0.69 | [70] | 2022 |
| SignalP—6.0 | SP | Transformer Protein LM | M | Archaea, Gram-positive Bacteria, Gram-negative Bacteria and Eukaryotes | MCC: 0.65~0.89 Prec: 0.53~0.94 Rec: 0.50~0.88 | [28] | 2022 |
| MULocDeep 2 | PC, PSSM | LSTM | M | Viridiplantae, Metazoa, Fungi | AUC: 0.74~0.95 | [71] | 2021 |
| SCLpred-EMS 3 | Sequence Motifs | Deep N-to-1 CNN | S | Eukaryotes | MCC: 0.75~0.86 Spec: 0.89~0.97 Sen: 0.75~0.89 FPR: 0.02~0.05 | [53] | 2020 |
| CTM-AECA-PSSM-LDA | CTM, AECA-PSSM | LDA, SVM | S | Apoptosis Proteins on CL317 and ZW225 datasets | Acc: 0.95~0.99 MCC: 0.90~1.00 Spec: 0.94~1.00 Sen: 0.91~0.95 | [36] | 2020 |
| TargetP—2.0 | SP | LSTM, MAM | S | Plants and Non-plants | Prec: 0.75~0.98 Rec: 0.75~0.98 F1: 0.75~0.98 MCC: 0.75~0.97 | [27] | 2019 |
| Javed and Hayat | PseAAC, SAAC | ML-KNN, Rank-SVM | M | Bacteria, Virus | Acc: 0.80~0.85 Prec: 0.88~0.90 HL: 0.07~0.09 RL: 0.07~0.08 OE: 0.17~0.20 CV: 0.26~0.51 | [35] | 2019 |
| MU-LOC 4 | AAF, PSSM, GCF | DNN, SVM | S | Plants (Mitochondrian) | Acc: 0.74~0.94 Prec: 0.74~0.82 MCC: 0.50~0.67 Spec: 0.88~0.97 Sen: 0.60~0.70 | [72] | 2018 |
| MultiP-SChlo | PseAAC | SVM | M | Plants (Subchloroplast) | Acc: 0.55~0.60 Prec: 0.64~0.65 Rec: 0.66~0.71 F1: 0.65~0.67 | [73] | 2015 |
| SlocX | AAC, Gene Expression Profile | SVM | S | Plants | Prec: 0.83 MCC: 0.48 Sen: 0.33 | [74] | 2011 |
| Method | Features | Algorithm | S/M-Location | Species | Performance Metrics 1 | Pub | Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zou et al. | Haralick, LBP, PSSM, PseAAC, PC | LASSO, BR, SDA, CNN | S | Human | Acc: 0.75~0.86 Prec: 0.80~0.85 Rec: 0.74~0.85 | [122] | 2023 |
| ST-Net | Low- and High-Level features | MSA, Swin, CAFE, CNN, | S | Human | MAE: 0.15~0.23 NRMSE: 0.30~0.31 SSIM: 0.78~0.89 PCC: 0.94~0.95 R2: 0.87~0.88 | [139] | 2023 |
| HCPL | Cell- and Image-Level Information | DNN, CLH, CLA, VID | M | Human | Prec: 0.55~0.57 | [140] | 2023 |
| Ding et al. | Features Generated from ResNet | ResNet-34, SE, GAP-net, DNN | M | Yeast | Acc: 0.91 Prec: 0.89 Rec: 0.90 F1: 0.89 | [133] | 2023 |
| Muti-task Learning Strategy | Features Generated from ResNet and DenseNet | ResNet, DenseNet, MIL, CNN | M | Human | MicroF1: 0.78 MacroF1: 0.71 | [135] | 2022 |
| MPFnetwork | SRS and Fluorescence Signal | MPFNet, CNN, MSA, MLP | M | Human | NRMSE: 0.19~0.20 SSIM: 0.89~0.92 PCC: 0.90~0.91 Dice: 0.93~0.94 mIOU: 0.87~0.88 | [134] | 2022 |
| PScL-DDCFPred | SLFs, LBP, CLBP, LETRIST, RICLBP | SDA-GDA, DNN-DCF | M | Human | Acc: 0.88 Rec: 0.88 Prec: 0.89 F1: 0.88 MCC: 0.86 | [141] | 2022 |
| PLCNN | Image block structure | CNN | M | Human, Yeast | Acc: 0.91~1.00 | [142] | 2022 |
| SIFLoc | IF images | GNT-Xent, RandAugment, ResNet18 | M | Human | Acc: 0.67~0.73 Prec: 0.77~0.81 Rec: 0.69~0.74 F1: 0.73~0.77 | [137] | 2022 |
| DeepYeast | Haralick, Gabor, Zernike Features | CNN, DNN | M | Yeast | Acc: 0.97~0.99 Prec: 0.70~0.95 Rec: 0.65~0.92 | [125] | 2017 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiao, H.; Zou, Y.; Wang, J.; Wan, S. A Review for Artificial Intelligence Based Protein Subcellular Localization. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 409. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14040409
Xiao H, Zou Y, Wang J, Wan S. A Review for Artificial Intelligence Based Protein Subcellular Localization. Biomolecules. 2024; 14(4):409. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14040409
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiao, Hanyu, Yijin Zou, Jieqiong Wang, and Shibiao Wan. 2024. "A Review for Artificial Intelligence Based Protein Subcellular Localization" Biomolecules 14, no. 4: 409. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14040409
APA StyleXiao, H., Zou, Y., Wang, J., & Wan, S. (2024). A Review for Artificial Intelligence Based Protein Subcellular Localization. Biomolecules, 14(4), 409. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14040409






