[18F]Mefway: Imaging Serotonin 5HT1A Receptors in Human Postmortem Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Disease Anterior Cingulate. Potential Applications to Human Positron Emission Tomography Studies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. General Methods
2.2. Postmortem Human Brain
2.3. [3H]WAY 100635 for Serotonin 5HT-1AR Imaging
2.4. [18F]Mefway for Serotonin 5HT-1AR Imaging
2.5. [18F]Fallypride for Dopamine D2/D3 Receptor Imaging
2.6. Immunohistochemistry
2.7. Image Analysis
2.7.1. [3H]WAY 100635
2.7.2. [18F]Mefway
2.7.3. [18F]Fallypride
2.7.4. [18F]FAZIN3
2.7.5. [125I]IBETA and [125I]IPPI
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Postmortem Human CN, PD and AD Brains
3.2. Frontal Cortex Serotonin 5HT1A Receptors
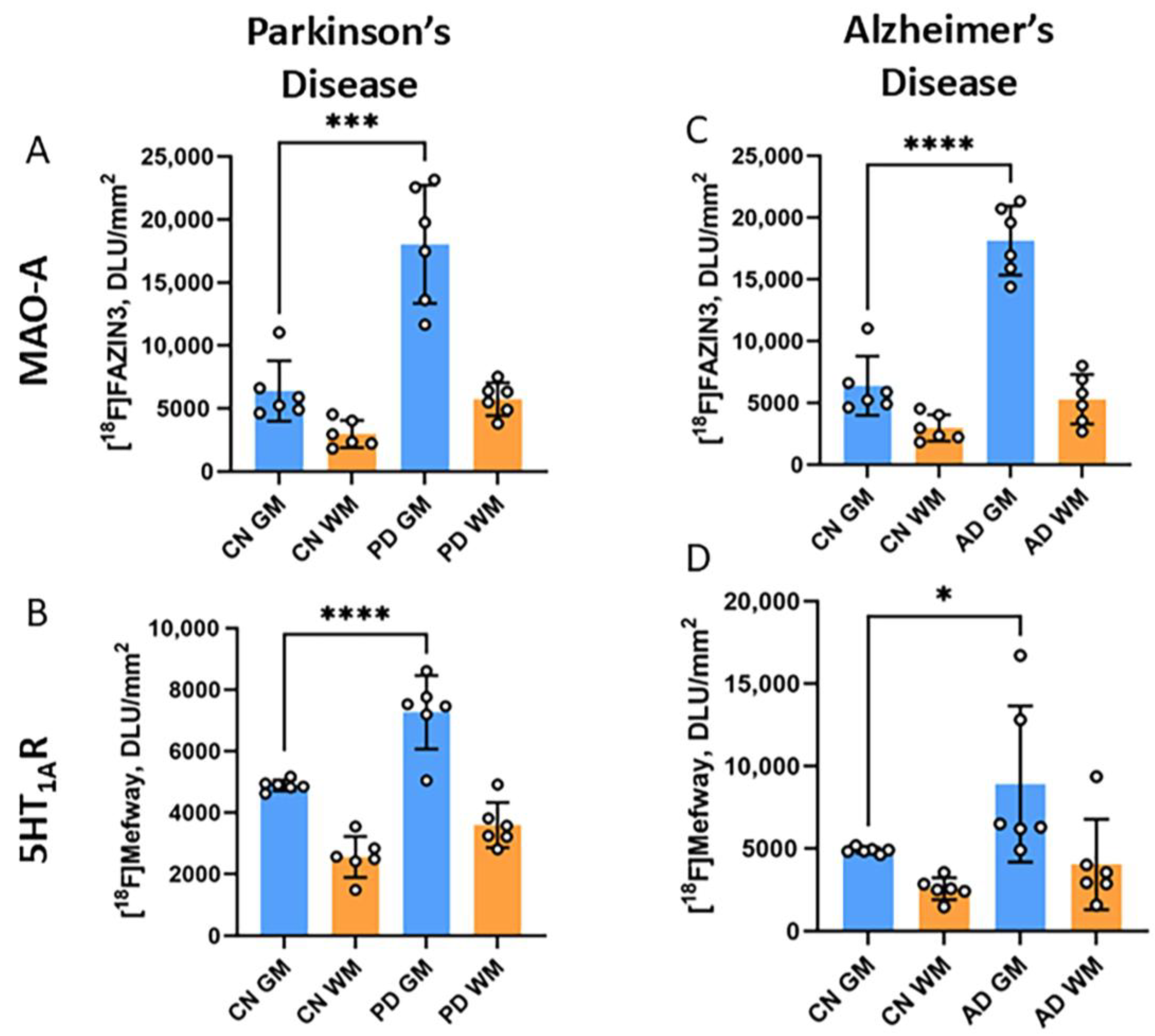
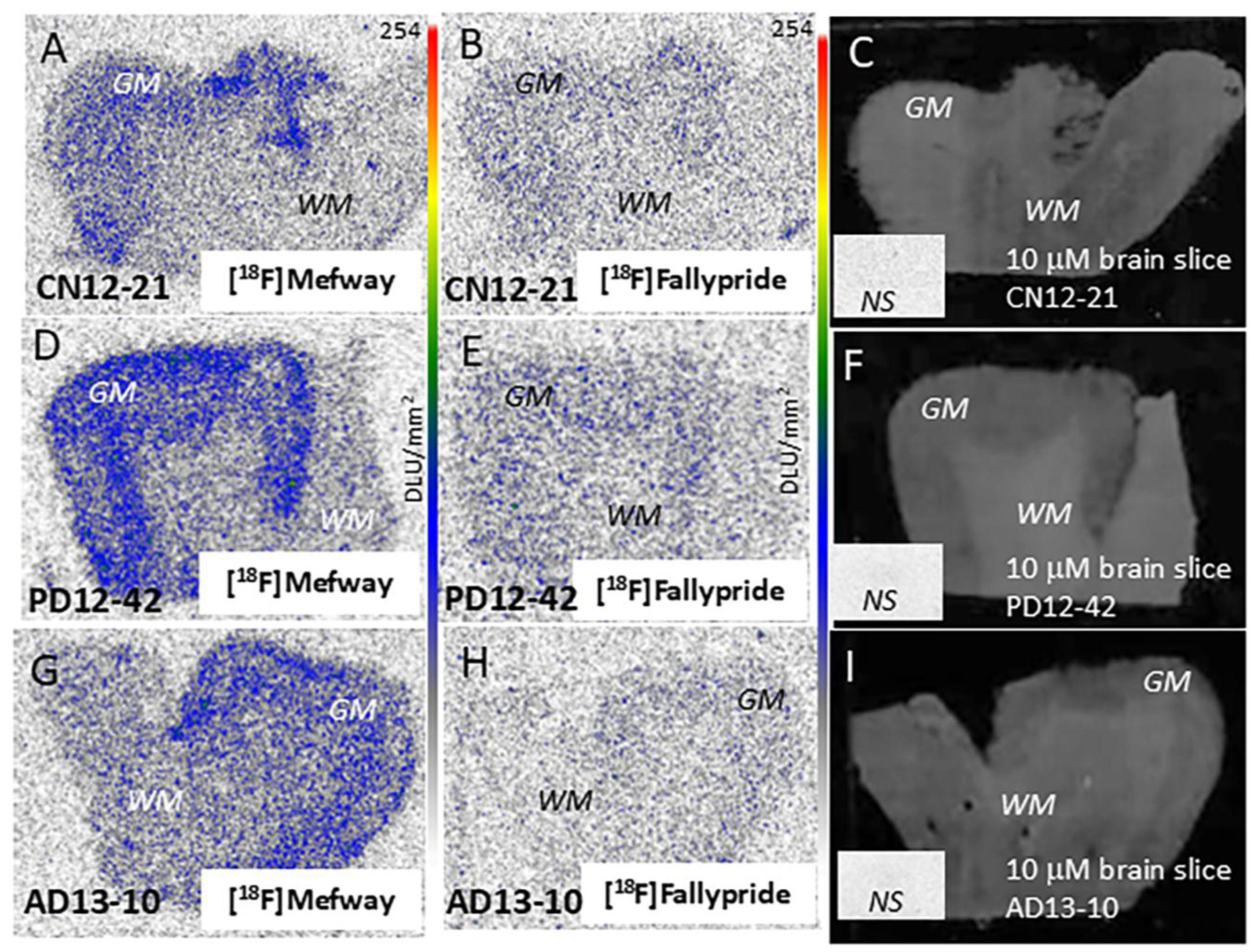
3.3. [18F]Mefway Imaging in AD Anterior Cingulate
3.4. [18F]Mefway Imaging in PD Anterior Cingulate
3.5. [18F]Mefway and [18F]FAZIN3 Comparison in PD and AD Anterior Cingulate
3.6. [18F]Fallypride Imaging in PD and AD Anterior Cingulate
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Caligiore, D.; Giocondo, F.; Silvetti, M. The neurodegenerative elderly syndrome (NES) hypothesis: Alzheimer and Parkinson are two faces of the same disease. IBRO Neurosci. Rep. 2022, 13, 330–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, T.-S.; Li, G.; Gao, W.; Chen, G.; Gan, S.; Zhang, M.; Li, H.; Wu, S.; Du, Y. G protein-coupled receptors in neurodegenerative disease and psychiatric disorders. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azargoonjahromi, A. Serotonin enhances neurogenesis biomarkers, hippocampal volumes, and cognitivie functions in Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Brain 2024, 17, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aaldijk, E.; Vermeiren, Y. The role of serotonin within the microbiota-gut-brain axis in the development of Alzheimer’s disease: A narrative review. Ageing Res. Rev. 2022, 75, 101556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akyuz, E.; Arulsamy, A.; Aslan, F.S.; Sarisozen, B.; Guney, B.; Hekimoglu, A.; Yilmaz, B.N.; Retinasamy, T.; Shaikh, M.F. An expanded narrative review of neurotransmitter on Alzheimer’s disease: The role of therapeutic interventions on neurotransmission. Mol. Neurobiol. 2025, 62, 1631–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, S.H.; Chuang, R.; Brotchie, J.M. Serotonin and Parkinson’s disease: On movement, mood, and Madness. Mov. Disord. 2009, 24, 1255–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaacson, S.H.; Goldstein, M.; Pahwa, R.; Singer, C.; Klos, K.; Pucci, M.; Zhang, Y.; Crandall, D.; Koblan, K.S.; Navia, B.; et al. Ulotaront, a trace amine-associated receptor 1/serotonin 5HT1A agonist, in patients with Parkinsons disease psychosis. Neurol. Clin. Pract. 2023, 13, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinna, A.; Parekh, P.; Morelli, M. Serotonin 5HT1A receptors and their inteactions with adenosine A2A receptors in Parkinson’s disease and dyskinesia. Neuropharmacology 2023, 226, 109411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, R.; Hikima, A.; Morris, R.; Jackson, M.J.; Rose, S.; Varney, M.A.; Depoortere, R.; Newman-Tancredi, A. The selective HT1A receptor agonist, NLX-112, exerts anti-dyskinetic and anti-parkinsonian-like effects in MPTP-treated marmosets. Neuropharmacology 2020, 167, 107997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, G.; Streichenberger, N.; Billard, T.; Newman-Tancredi, A.; Zimmer, L. A postmortem study to compare agonist and antagonist 5HT1A receptor-binding sites in Alzheimer’s disease. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2014, 20, 930–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdurand, M.; Zimmer, L. Hippocampal 5HT1A receptor expression changes in prodromal stages of Alzheimers disease: Beneficial or deleterious. Neuropharmacology 2017, 123, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Billard, T.; Le Bars, D.; Zimmer, L. PET radiotracers for molecular imaging of serotonin 5HT1A receptors. Curr. Med. Chem. 2014, 21, 70–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keep, V.; Barrio, J.R.; Huang, S.C.; Huang, S.C.; Ercoli, L.; Siddarth, P.; Shoghi-Jadid, K.; Cole, G.M.; Satyamurthy, N.; Cummings, J.L.; et al. Serotonin 1A receptors in the living brain of Alzheimer’s disease patients. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 702–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truchot, L.; Costes, S.N.; Zimmer, L.; Laurent, B.; Le Bars, D.; Thomas-Anterion, C.; Croisile, B.; Mercier, B.; Hermier, M.; Vighetto, A.; et al. Up-regulation of hippocampal serotonin metabolism in mild cognitive impairment. Neurology 2007, 69, 1012–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truchot, L.; Costes, S.N.; Zimmer, L.; Laurent, B.; Le Bars, D.; Thomas-Anterion, C.; Mercier, B.; Hermier, M.; Vighetto, A.; Krolak-Salmon, P. A distinct [18F]MPPF PET profile in amnestic mild cognitive impairment compared to mild Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroimage 2008, 40, 1251–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doder, M.; Rabiner, E.A.; Turjanski, N.; Lees, A.J.; Brooks, D.J. Tremor in Parkinson’s disease and serotonergic dysfunction: An 11C-WAY 100635 PET study. Neurology 2003, 60, 601–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, M.V.; Marsden, C.A.; Fone, K.C. A role for the 5HT1A, 5HT4 and 5HT6 receptors in learning and memory. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2008, 29, 482–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michelsen, K.A.; Prickaerts, J.; Steinbusch, H.W.M. The dorsal raphe nucleus and serotonin: Implications for neuroplasticity linked to major depression and Alzheimer’s disease. Prog. Brain Res. 2008, 172, 233–264. [Google Scholar]
- Borg, J. Molecular imaging of the 5HT1A receptor in relation to human cognition. Behav. Brain Res. 2008, 195, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsey, R.V. Serotonin receptor imaging: Clinically useful? J. Nucl. Med. 2010, 51, 1495–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendez, P.C.; Surace, E.; Bérgamo, Y.; Calandri, I.; Vázquez, S.; Sevlever, G.; Allegri, R.F. Biomarkers for Alzheimers disease. Where we stand and where we are headed. Medicina 2019, 79, 546–551. [Google Scholar]
- Sandhu, Y.K.; Bath, H.S.; Shergill, J.; Liang, C.; Syed, A.U.; Ngo, A.; Karim, F.; Serrano, G.E.; Beach, T.G.; Mukherjee, J. [18F]Flotaza for Ab plaque diagnostic imaging: Evaluation in postmortem human Alzheimer’s disease brain hippocampus and PET/CT imaging in 5xFAD transgenic mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cummings, J.; Aisen, P.; Lemere, C.; Atri, A.; Sabbagh, M.; Salloway, S. Aducanumab produced a clinically meaningful benefit in association with amyloid lowering. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2021, 13, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, C.; Paclibar, C.G.; Gonzaga, N.L.; Sison, S.A.; Bath, H.S.; Biju, A.P.; Mukherjee, J. [125I]IPC-Lecanemab: Synthesis and Evaluation of Ab plaque binding antibody and comparison with small molecule [18F]Flotaza and [125I]IBETA in postmortem human Alzheimer’s disease. Neurol. Int. 2024, 16, 419–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, A.U.; Liang, C.; Patel, K.K.; Mondal, R.; Kamalia, V.M.; Moran, T.R.; Ahmed, S.T.; Mukherjee, J. Comparison of Monoamine oxidase-A, Ab plaques, Tau and Translocator protein in postmortem human Alzheimer’s disease brain. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, J.; Ladwa, R.M.; Liang, C.; Syed, A.U. Elevated monoamine oxidase-A in anterior cingulate of postmortem human Parkinson’s disease: A potential surrogate biomarker for Lewy bodies? Cells 2022, 11, 4000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, J.; Bajwa, A.K.; Wooten, D.W.; Hillmer, A.T.; Pan, M.-L.; Pandey, S.K.; Saigal, N.; Christian, B.T. Comparative assessment of 18F-Mefway as a serotonin 5-HT1A receptor PET imaging agent across species-rodents, nonhuman primates and humans. J. Comp. Neurol. 2016, 524, 1457–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barth, M.; Dunzinger, A.; Wimmer, J.; Rittmannsberger, H.; Nader, M.; Pichler, R. Serotonin 1A receptor density measured by F-18 mefway PT/CT in mesolimbic cortex and raphe does not discriminate therapeutic response in patients with major depressive episode. Ed. Minerva Medica 2020, 64, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.J.; Lyoo, C.H.; Ryu, Y.H.; Choi, J.U. Assessing the applicability of PMOD residence times model for PET image-based radiation dosimetry. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 19387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, H.; Lundkvist, C.; Halldin, C.; Farde, L.; Pike, V.W.; McCarron, J.A.; Fletcher, A.; Cliffe, I.A.; Barf, T.; wikstrom, H.; et al. Autoradiographic localization of 5HT1A receptors in the post-mortem human brain using [3H]WAY-100635 and [11C]WAY-100635. Brain Res. 1997, 745, 96–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, J.; Christian, B.T.; Dunigan, K.; Shi, B.; Narayanan, T.K.; Satter, M.; Mantil, J. Brain Imaging of 18F-fallypride in normal volunteers: Blood analysis, distribution, test-retest studies and preliminary assessment of sensitivity to aging effects on dopamine D-2/D-3 receptors. Synapse 2002, 46, 170–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, J.; Liang, C.; Patel, K.K.; Lam, P.Q.; Mondal, R. Development and evaluation [125I]IPPI for tau imaging in post-mortem human Alzheimer’s disease brain. Synapse 2021, 74, e22183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pezzoli, S.; Giorgio, J.; Martersteck, A.; Dobyns, L.; Harrison, T.M.; Jagust, W.J. Successful cognitive aging is associated with thicker anterior cingulate cortex and lower tau deposition compared to typical aging. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2023, 20, 341–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmqvist, S.; Scholl, M.; Strandberg, O.; Mattson, N.; Stomrud, E.; Zetterburg, H.; Blennow, K.; Landau, S.; Jagust, W.; Hansson, O. Earliest accumulation of b-amyloid occurs within the default-mode network and concurrently affects brain connectivity. Nat. Commun. 2018, 8, 1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnadas, N.; Huang, K.; Schultz, S.A.; Dore, V.; Bourgeat, P.; Goh, A.M.Y.; Lamb, F.; Bozinovski, S.; Burnham, S.C.; Robertson, J.S.; et al. Visually identified Tau 18F-MK6240 PET patterns in symptomatic Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2022, 88, 1627–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cakmak, J.D.; Liu, L.; Poirier, S.E.; Schaefer, B.; Poolacheria, R.; Burham, A.M.; Sabesan, P.; Lawrence, K.S.; Thebarge, J.; Hicks, J.W.; et al. The functional and structural associations of aberrant microglial activity in major depressive disorder. J. Psychiatry Neurosci. 2022, 47, E197–E208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, F.L.; Hurley, R.A.; Taber, K.H. Anterior cingulate cortex: Unique role in cognition and emotion. J. Neuropsychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2011, 23, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saigal, N.; Pichika, R.; Easwaramoorthy, B.; Collins, D.; Christian, B.T.; Shi, B.; Narayanan, T.K.; Potkin, S.G.; Mukherjee, J. Synthesis and biological evaluation of a novel serotonin 5-HT1a receptor radioligand, N-{2-[4-(2-methoxyphenyl)piperazinyl]ethyl}-N-(2-pyridyl)-N-(4-18F-fluoromethylcyclohexane)carboxamide in rodents and imaging by PET in non-human primate. J. Nucl. Med. 2006, 47, 1697–1706. [Google Scholar]
- Mukherjee, J.; Yang, Z.Y.; Das, M.K.; Brown, T. Fluorinated benzamide neuroleptics 3. Development of (S)-N-[(1-allyl-2-pyrrolidinyl)methyl]-5-(3[F-18]-fluoropropyl)-2,3-dimethoxy-benzamide as an improved dopamine D-2 receptor tracer. Nucl. Med. Biol. 1995, 22, 283–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beach, T.G.; Adler, C.H.; Sue, L.I.; Serrano, G.; Shill, H.A.; Walker, D.G.; Lue, L.; Roher, A.E.; Dugger, B.N.; Maarouf, C.; et al. Arizona study of aging and neurodegenerative disorders and brain and body donation program. Neuropathology 2015, 35, 354–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braak, H.; Thal, D.R.; Ghebremedhin, E.; Tredici, K.D. Stages of the pathologic process in Alzheimer’s disease age categories from 1 to 100 years. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2011, 70, 960–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondal, R.; Sandhu, Y.K.; Kamalia, V.M.; Delaney, B.A.; Syed, A.U.; Nguyen, G.A.H.; Moran, T.R.; Limpengco, R.R.; Liang, C.; Mukherjee, J. Measurement of Ab amyloid and Tau in postmortem human Alzheimer’s disease brain by immunohistochemistry analysis using QuPath and autoradiography using [18F]flotaza, [125I]IBETA and [124/125I]IPPI. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villemagne, V.L.; Harada, R.; Doré, V.; Furumoto, S.; Mulligan, R.; Kudo, Y.; Burnham, S.; Krishnadas, N.; Bozinovski, S.; Huang, K.; et al. First-in-humans evaluation of 18F-SMBT-1, a novel 18F-labeled monoamine oxidase-B PET tracer for imaging reactive astrogliosis. J. Nucl. Med. 2022, 63, 1551–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, D.N.; Raghanti, M.A. The role of monoamine oxidase enzymes in the pathophysiology of neurological disorders. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2021, 114, 101957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanderigo, F.; D’Agostino, A.E.; Josh, N.; Schain, M.; Kumar, D.; Parsey, R.V.; DeLorenzo, C.; Mann, J.J. [11C]Harmine binding to brain monoamine oxidase A: Test-retest properties and noninvasive quantification. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2018, 20, 667–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, G.S.; Protas, H.; Kuwabara, H.; Savonenko, A.; Nassery, N.; Gould, N.F.; Kraut, M.; Avramopoulous, D.; Holt, D.; Dannals, R.F.; et al. Moelcular imaging of the association between serotonin degeneration and beta-amyloid deposition in mild cognitive impairment. Neuroimage Clin. 2023, 37, 103322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaasinen, V.; Vahlberg, T.; Stoessl, A.J.; Strafella, A.P.; Antonini, A. Dopamine receptors in Parkinson’s disease: A meta-analysis of imaging studies. Mov. Disord. 2021, 36, 1781–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, A.J.; Smith, C.T.; Peterson, K.J.; Trujillo, P.; van Wouwe, N.C.; Donahue, M.J.; Kessler, R.M.; Deutch, A.Y.; Zald, D.H.; Claassen, D.O. [18F]Fallypride characterization of striatal and extrastriatal D2/3 receptors in Parkinson’s disease. Neuroimage Clin. 2018, 18, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, J.T.; Clark-Papasavas, C.; Marsden, P.; Baker, S.; Cleij, M.; Kapur, S.; Kessler, R.; Howard, R.; Reeves, S.J. Establishing test-retest reliability of an adapted [18F]fallypride imaging protocol. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2013, 33, 1098–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Duin, E.D.A.; Ceccarini, J.; Booij, J.; Kasanova, Z.; Vingerhoets, C.; Huijstee, J.V.; Heinzel, A.; Mohammadkhani-Shali, S.; Winz, O.; Mottaghy, F.; et al. Lower [18F]fallypride binding to dopamine D2/D3 receptors in frontal brain areas in adults with 22q11.2 deletion syndrome: A positron emission tomography study. Psychol. Med. 2019, 50, 799–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lumme, V.; Aalto, S.; Ilonen, T.; Nagren, K.; Hietala, J. Dopamine D2/D3 receptor binding in the anterior cingulate cortex and executive functioning. Psychiatry Res. 2007, 156, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Hu, S.H.; Shi, Y.; Li, B.-M. The roles of the anterior cingulate cortex and its dopamine receptors in self-paced cost-benefit decision making in rats. Learn. Behav. 2017, 45, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suhara, T.; Okubo, Y.; Yasuno, F.; Sudo, Y.; Inoue, M.; Ichimiya, T.; Nakashima, Y.; Nakayama, K.; Tanada, S.; Suzuki, K.; et al. Decreased dopamine D2 receptor binding in the anterior cingulate cortex in schizophrenia. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2002, 59, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martorana, A.; Koch, G. Is dopamine involved in Alzheimer’s disease? Front. Aging Neurosci. 2014, 6, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, A.S.; Vale, N. Antidepressants in Alzheimer’s disease: A focus on the role of mirtazapine. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, L.; Xu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Huang, J.; Zhu, J.; Wang, W.; Li, W.; Sun, A.; Li, X.; et al. Discovery of novel dual RAGE/SERT inhibitors for the potential treatment of the comorbidity of Alzheimer’s disease and depression. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 236, 114347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, M.J.; Okun, M.S. Diagnosis and treatment of Parkinson disease. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2020, 323, 548–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suescun, J.; Chandra, S.; Schiess, M.C. Chapter 13. The role of neuroinflammation in neurodegenerative disorders. In Translational Inflammation; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 241–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, P.; Chaney, A.M.; Carlson, M.L.; Jackson, I.M.; Rao, A.; James, M.L. Neuroinflammation PET imaging: Current opinion and future directions. J. Nucl. Med. 2020, 61, 1107–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

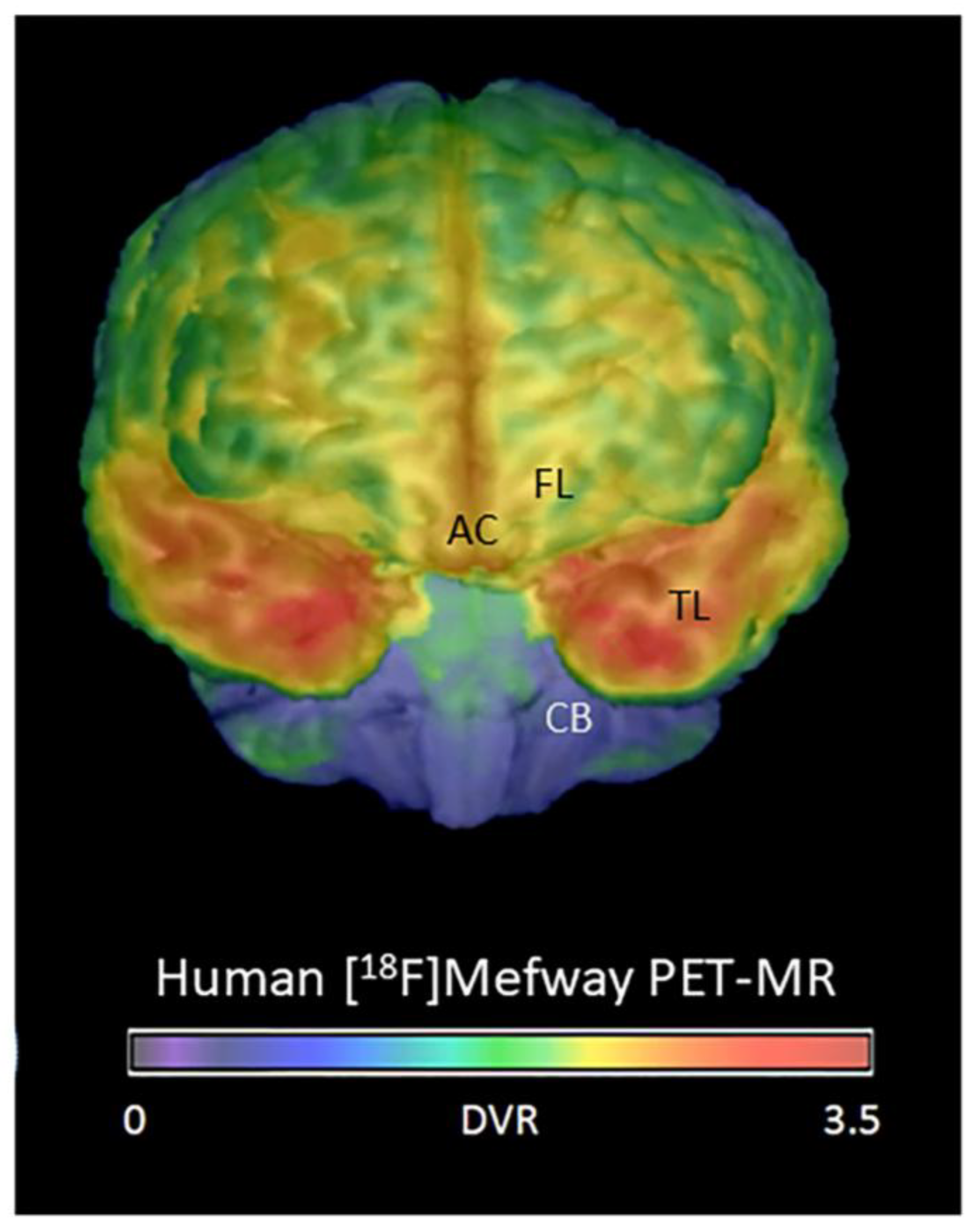
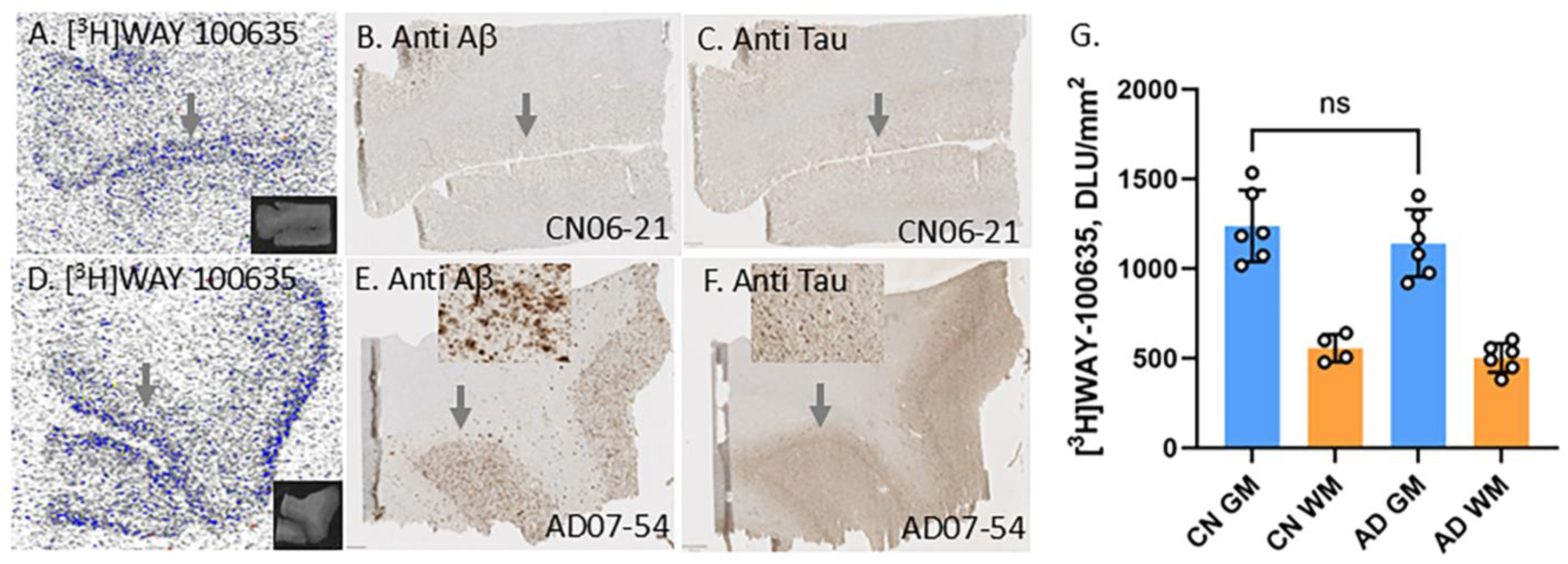
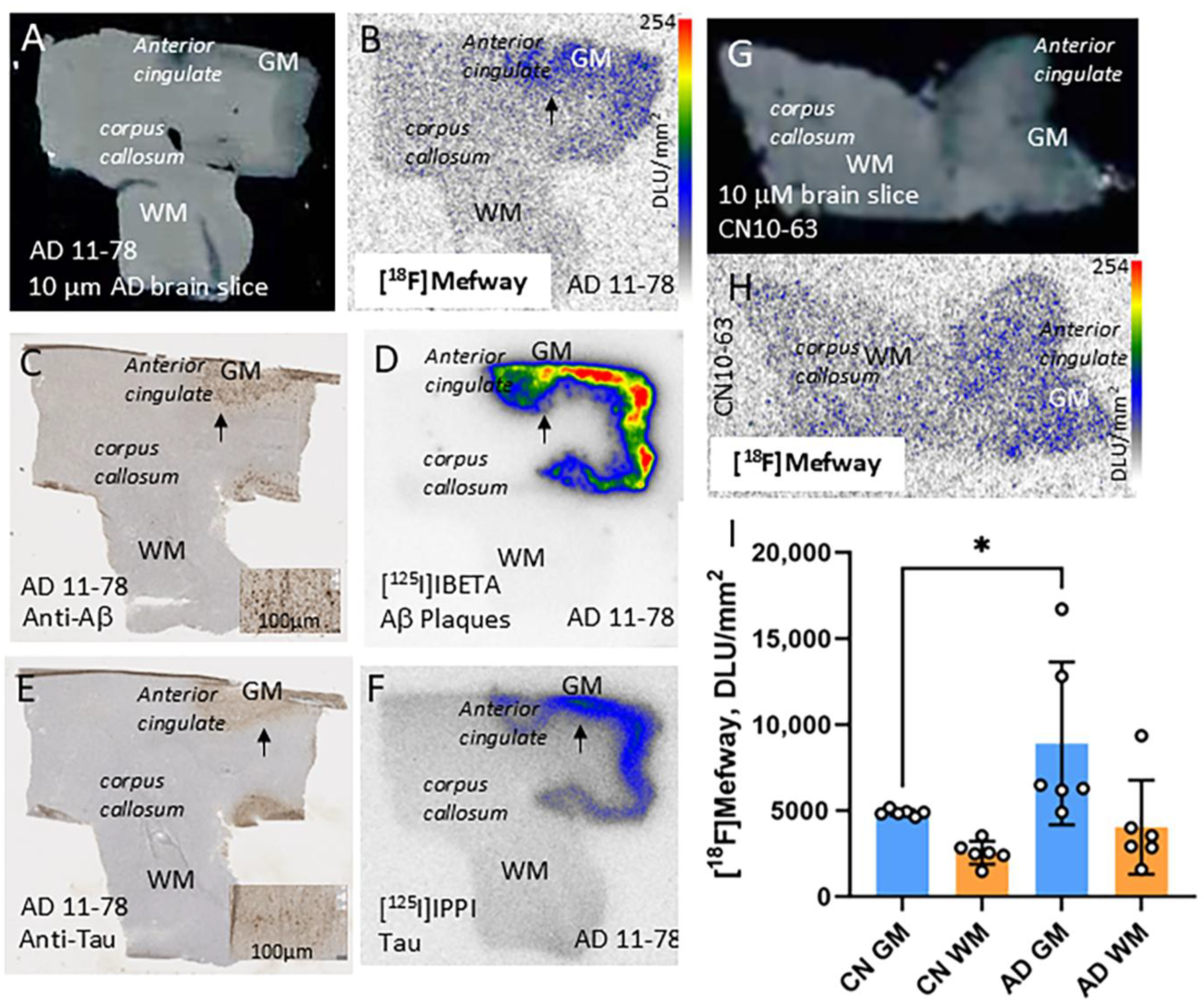
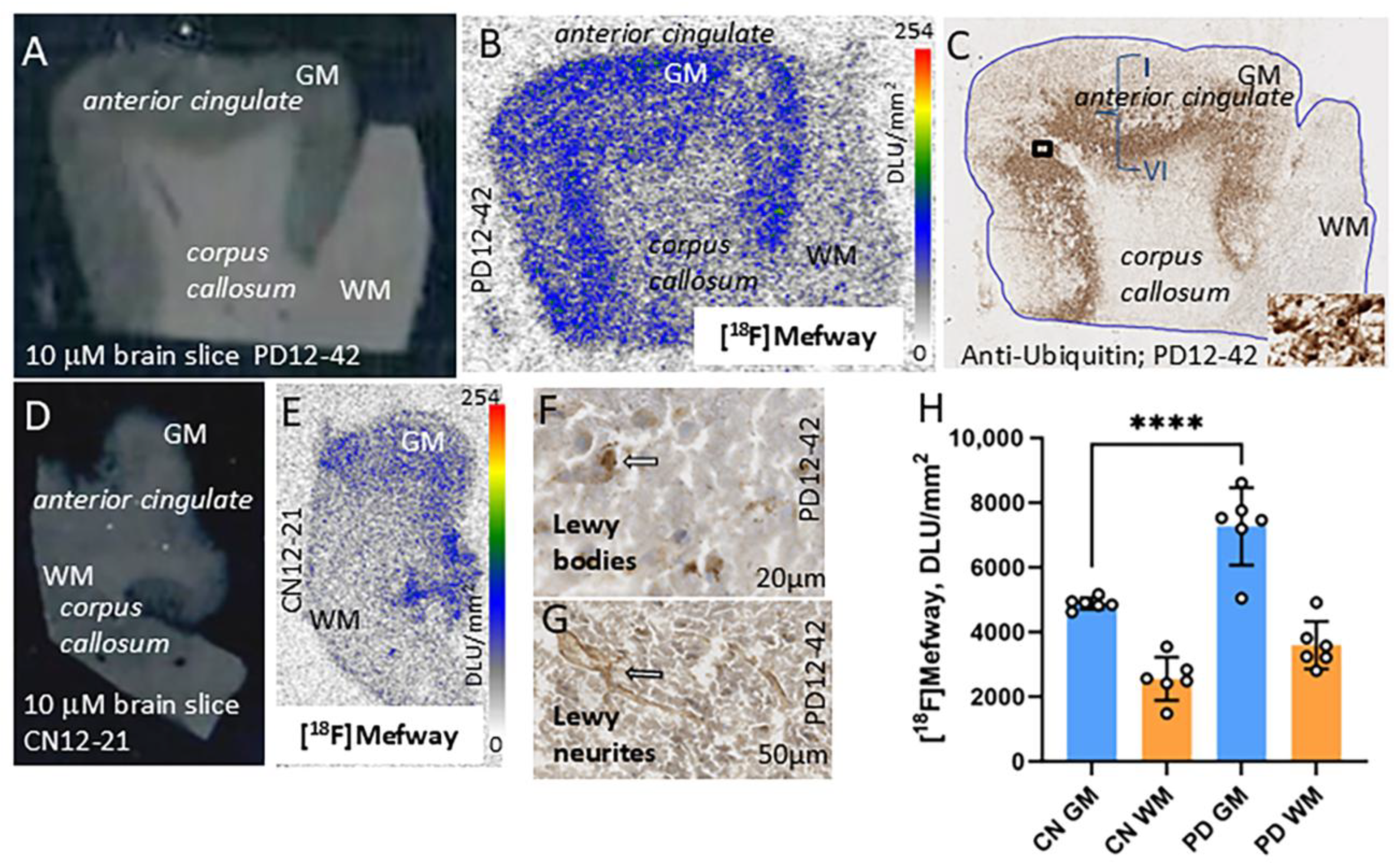

| Subjects, N | CERAD Pathology | Gender | Age Range, Mean ± SD | PMI, hrs | Brain Region 1 | Plaque Total | Tangle Total | LB | Braak Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 | CN | 5 Male 1 Female | 73–92 (85.2 ± 7.03) | 2–5.4 | FC | 0–5.5 | 0–6 | 0 | II-III |
| 6 | AD | 3 Male 3 Female | 75–90 (81.3 ± 6.12) | 1.8–5 | FC | 10–15 | 12–15 | 0 | V-VI |
| 6 | CN | 4 Male 2 Female | 71–97 (79.9 ± 8.55) | 2–5.4 | AC | 0–5.5 | 0–6 | 0 | I-III |
| 6 | AD | 5 Male 1 Female | 70–91 (80.4 ± 5.98) | 2.3–4.8 | AC | 14–15 | 10–15 | 0 | V-VI |
| 6 | PD | 4 Male 2 Female | 53–95 (80.4 ± 13.1) | 2.1–4.8 | AC | 0–10 | 0.5–6.5 | 0 | I-III |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gonzaga, N.L.; Karim, F.; Liang, C.; Mukherjee, J. [18F]Mefway: Imaging Serotonin 5HT1A Receptors in Human Postmortem Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Disease Anterior Cingulate. Potential Applications to Human Positron Emission Tomography Studies. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 592. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15040592
Gonzaga NL, Karim F, Liang C, Mukherjee J. [18F]Mefway: Imaging Serotonin 5HT1A Receptors in Human Postmortem Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Disease Anterior Cingulate. Potential Applications to Human Positron Emission Tomography Studies. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(4):592. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15040592
Chicago/Turabian StyleGonzaga, Noresa L., Fariha Karim, Christopher Liang, and Jogeshwar Mukherjee. 2025. "[18F]Mefway: Imaging Serotonin 5HT1A Receptors in Human Postmortem Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Disease Anterior Cingulate. Potential Applications to Human Positron Emission Tomography Studies" Biomolecules 15, no. 4: 592. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15040592
APA StyleGonzaga, N. L., Karim, F., Liang, C., & Mukherjee, J. (2025). [18F]Mefway: Imaging Serotonin 5HT1A Receptors in Human Postmortem Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Disease Anterior Cingulate. Potential Applications to Human Positron Emission Tomography Studies. Biomolecules, 15(4), 592. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15040592








