Salinity Effect on Germination and Further Development of Parasitic Cuscuta spp. and Related Non-Parasitic Vines
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
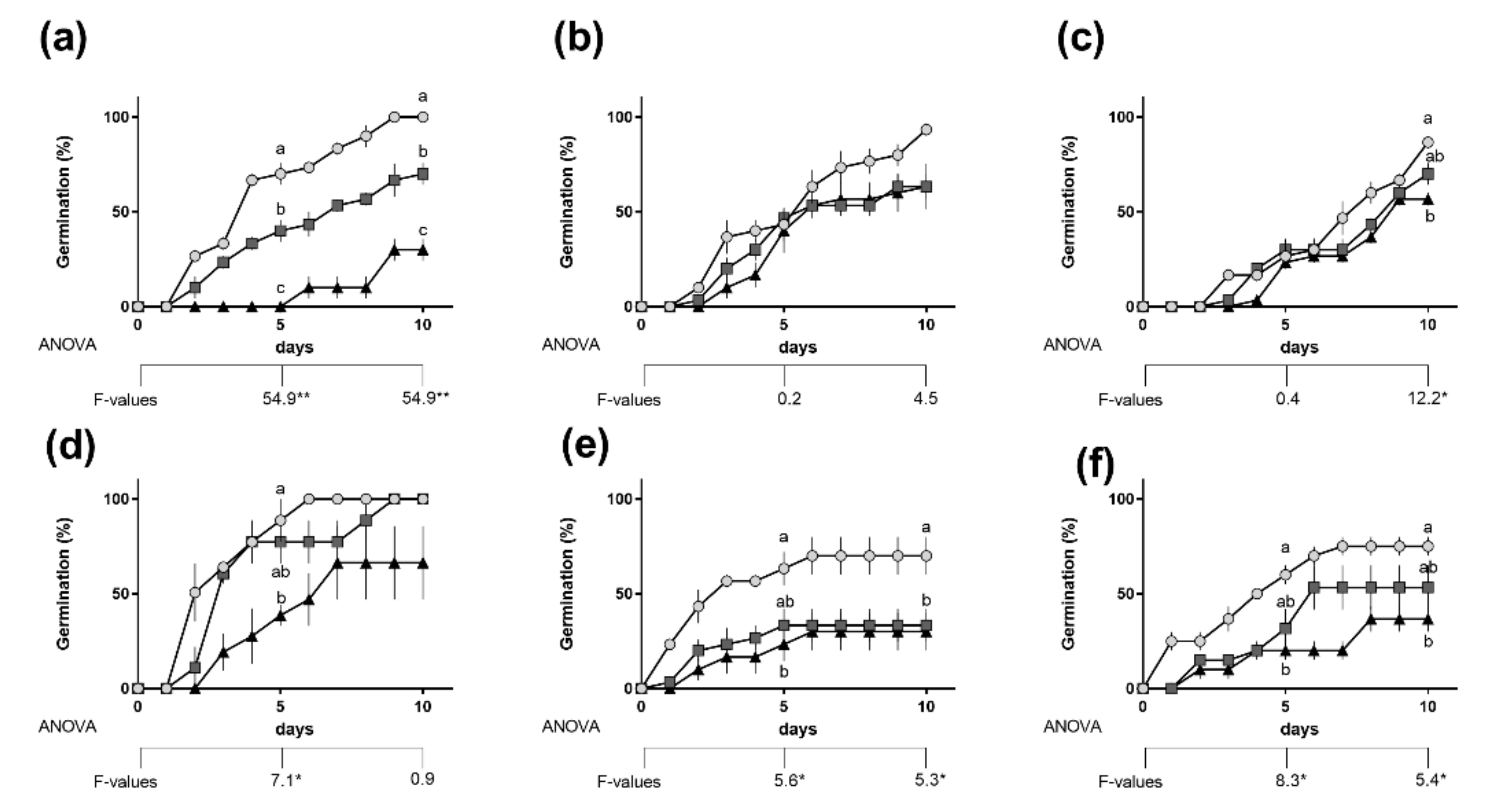
2.1. Effect of Salinity on Germination and Seedling Growth
2.2. Hydrolytic Enzymes in Seeds
2.3. Effect of Salinity on Subsequent Growth
3. Discussion
3.1. Seed Germination Differences Are Related to Parasitic Lifestyle
3.2. Salinity Negatively Affects but Does Not Obliterate Cuscuta campestris Parasitic Ability
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Material
4.2. Experimental Design
4.3. Protein Isolation and Zymographic Analysis
4.4. Software and Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Munns, R.; James, R.A.; Läuchli, A. Approaches to increasing the salt tolerance of wheat and other cereals. J. Exp. Bot. 2006, 57, 1025–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Flowers, T.J.; Colmer, T.D. Salinity tolerance in halophytes. New Phytol. 2008, 179, 945–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flowers, T.J. Improving crop salt tolerance. J. Exp. Bot. 2004, 55, 307–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallejo, A.J.; Yanovsky, M.J.; Botto, J.F. Germination variation in Arabidopsis thaliana accessions under moderate osmotic and salt stresses. Ann. Bot. 2010, 106, 833–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gul, B.; Ansari, R.; Flowers, T.J.; Khan, M.A. Germination strategies of halophyte seeds under salinity. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2013, 92, 4–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muscolo, A.; Sidari, M.; Anastasi, U.; Santonoceto, C.; Maggio, A. Effect of PEG-induced drought stress on seed germination of four lentil genotypes. J. Plant Interact. 2013, 9, 354–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.; Lan, H.; Zhang, F. Variation of seed heteromorphism in Chenopodium album and the effect of salinity stress on the descendants. Ann. Bot. 2010, 105, 1015–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jisha, K.C.; Vijayakumari, K.; Puthur, J.T. Seed priming for abiotic stress tolerance: An overview. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2013, 35, 1381–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-G.; Lee, A.-K.; Yoon, H.-K.; Park, C.-M. A membrane-bound NAC transcription factor NTL8 regulates gibberellic acid-mediated salt signaling in Arabidopsis seed germination. Plant J. 2008, 55, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Yamaguchi, S.; Khan, M.A.; Weiqiang, L.; Liu, X.; Tran, L.-S.P. Roles of Gibberellins and Abscisic Acid in Regulating Germination of Suaeda salsa Dimorphic Seeds Under Salt Stress. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 6, 1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, Y.; Yang, L.; Paul, M.; Zu, Y.; Tang, Z. Ethylene promotes germination of Arabidopsis seed under salinity by decreasing reactive oxygen species: Evidence for the involvement of nitric oxide simulated by sodium nitroprusside. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2013, 73, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munns, R.; Tester, M. Mechanisms of salinity tolerance. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2008, 59, 651–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Møller, I.S.; Gilliham, M.; Jha, D.; Mayo, G.M.; Roy, S.J.; Coates, J.C.; Haseloff, J.; Tester, M. Shoot Na+ Exclusion and Increased Salinity Tolerance Engineered by Cell Type–Specific Alteration of Na+ Transport in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2009, 21, 2163–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Z.; Cuin, T.A.; Zhou, M.; Twomey, A.; Naidu, B.P.; Shabala, S. Compatible solute accumulation and stress-mitigating effects in barley genotypes contrasting in their salt tolerance. J. Exp. Bot. 2007, 58, 4245–4255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bose, J.; Rodrigo-Moreno, A.; Shabala, S. ROS homeostasis in halophytes in the context of salinity stress tolerance. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 1241–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vera-Gargallo, B.; Chowdhury, T.R.; Brown, J.; Fansler, S.J.; Durán-Viseras, A.; Sánchez-Porro, C.; Bailey, V.L.; Jansson, J.K.; Ventosa, A. Spatial distribution of prokaryotic communities in hypersaline soils. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, J.; Terrones, A.; Juan, A.; Alonso, M. Ángeles Halophytic plant community patterns in Mediterranean saltmarshes: Shedding light on the connection between abiotic factors and the distribution of halophytes. Plant Soil 2018, 430, 185–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latef, A.A.H.A.; Hashem, A.; Rasool, S.; Abd_Allah, E.F.; Alqarawi, A.A.; Egamberdieva, D.; Jan, S.; Anjum, N.A.; Ahmad, P. Arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis and abiotic stress in plants: A review. J. Plant Biol. 2016, 59, 407–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asano, T.; Hayashi, N.; Kobayashi, M.; Aoki, N.; Miyao, A.; Mitsuhara, I.; Ichikawa, H.; Komatsu, S.; Hirochika, H.; Kikuchi, S.; et al. A rice calcium-dependent protein kinase OsCPK12 oppositely modulates salt-stress tolerance and blast disease resistance. Plant J. 2011, 69, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bostock, R.M. Signal Crosstalk and Induced Resistance: Straddling the Line Between Cost and Benefit. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2005, 43, 545–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veste, M.; Todt, H.; Breckle, S.-W. Influence of halophytic hosts on their parasites—the case of Plicosepalus acaciae. AoB Plants 2015, 7, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Callaway, R.M.; Pennings, S.C. Impact of a parasitic plant on the zonation of two salt marsh perennials. Oecologia 1998, 114, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grewell, B.J. Parasite facilitates plant species coexistence in a coastal wetland. Ecology 2008, 89, 1481–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zagorchev, L.; Albanova, I.; Tosheva, A.; Li, J.; Teofanova, D. Salinity effect on Cuscuta campestris Yunck. Parasitism on Arabidopsis thaliana L. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 132, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cochavi, A.; Ephrath, J.; Eizenberg, H.; Rachmilevitch, S. Phelipanche aegyptiaca parasitism impairs salinity tolerance in young leaves of tomato. Physiol. Plant. 2018, 164, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dawson, J.H.; Musselman, L.J.; Wolswinkel, P.; Dorr, I. Biology and control of Cuscuta. Rev. Weed Sci. 1994, 6, 265–317. [Google Scholar]
- Parker, C. Parasitic Weeds: A World Challenge. Weed Sci. 2012, 60, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costea, M.; Spence, I.; Stefanović, S. Systematics of Cuscuta chinensis species complex (subgenus Grammica, Convolvulaceae): Evidence for long-distance dispersal and one new species. Org. Divers. Evol. 2011, 11, 373–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrusa, G.F.; Kelch, D. Giant dodders 2004–2006. In Plant Pest Diagnostics Center; Kodira, U.C., Ed.; California Department of Food and Agriculture: Sacramento, CA, USA, 2006; pp. 9–19. [Google Scholar]
- Pfirter, H.A.; Ammon, H.-U.; Guntli, D.; Greaves, M.P.; Defago, G. Towards the management of field bindweed (Convolvulus arvensis) and hedge bindweed (Calystegia sepium) with fungal pathogens and cover crops. Integr. Pest Manag. Rev. 1997, 2, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherman, T.D.; Bowling, A.J.; Barger, T.W.; Vaughn, K.C. The Vestigial Root of Dodder (Cuscuta pentagona) Seedlings. Int. J. Plant Sci. 2008, 169, 998–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, S.; Xu, G.; Clements, D.R.; Jin, G.; Liu, S.; Yang, Y.; Chen, A.; Zhang, F.; Kato-Noguchi, H. Suppression of reproductive characteristics of the invasive plant Mikania micrantha by sweet potato competition. BMC Ecol. 2016, 16, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jayasuriya, K.M.G.G.; Baskin, J.M.; Geneve, R.L.; Baskin, C.C.; Chien, C.-T. Physical Dormancy in Seeds of the Holoparasitic Angiosperm Cuscuta australis (Convolvulaceae, Cuscuteae): Dormancy-breaking Requirements, Anatomy of the Water Gap and Sensitivity Cycling. Ann. Bot. 2008, 102, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNeal, J.R.; Arumugunathan, K.; Kuehl, J.V.; Boore, J.L.; Depamphilis, C.W. Systematics and plastid genome evolution of the cryptically photosynthetic parasitic plant genus Cuscuta(Convolvulaceae). BMC Biol. 2007, 5, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van Der Kooij, T.A.W.; Krause, K.; Dörr, I.; Krupinska, K. Molecular, functional and ultrastructural characterisation of plastids from six species of the parasitic flowering plant genus Cuscuta. Planta 2000, 210, 701–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, A.; Schwacke, R.; Denton, A.K.; Usadel, B.; Hollmann, J.; Fischer, K.; Bolger, A.; Schmidt, M.H.-W.; Bolger, M.E.; Gundlach, H.; et al. Footprints of parasitism in the genome of the parasitic flowering plant Cuscuta campestris. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoneyama, K.; Awad, A.A.; Xie, X.; Takeuchi, Y. Strigolactones as Germination Stimulants for Root Parasitic Plants. Plant Cell Physiol. 2010, 51, 1095–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Charles, D.J.; Singh, M.; Sanwal, G.G. Biochemical changes during germination and seedling growth in Cuscuta campestris. Physiol. Plant. 1982, 56, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tănase, M.; Stanciu, M.; Moise, C.; Gheorghe, M. Ecological and economic impact of dodder species (Cuscuta spp. Convolvulaceae) on pratological ecosystems. J. Hortic. For. Biotechnol. 2012, 16, 93–97. [Google Scholar]
- Yergin-Ozkan, R.; Tepe, I. Emergence characteristics and germination physiology of smoothseed alfalfa dodder (Cuscuta approximata Bab.). Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2018, 27, 104–109. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Hettenhausen, C.; Sun, G.; Zhuang, H.; Li, J.-H.; Wu, J. The Parasitic Plant Cuscuta australis Is Highly Insensitive to Abscisic Acid-Induced Suppression of Hypocotyl Elongation and Seed Germination. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0135197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manchenko, G.P. Handbook of Detection of Enzymes on Electrophoretic Gels; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Raccuia, S.A.; Cavallaro, V.; Melilli, M.G. Intraspecific variability in Cynara cardunculus L. var. sylvestris Lam. Sicilian populations: Seed germination under salt and moisture stresses. J. Arid. Environ. 2004, 56, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Source of Variation | df | Mean Square | F-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Species | 5 | 673.8 | 2.35 |
| Salinity | 2 | 9792.5 | 34.1 ** |
| Species × salinity | 10 | 418.1 | 1.46 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zagorchev, L.; Atanasova, A.; Pachedjieva, K.; Tosheva, A.; Li, J.; Teofanova, D. Salinity Effect on Germination and Further Development of Parasitic Cuscuta spp. and Related Non-Parasitic Vines. Plants 2021, 10, 438. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10030438
Zagorchev L, Atanasova A, Pachedjieva K, Tosheva A, Li J, Teofanova D. Salinity Effect on Germination and Further Development of Parasitic Cuscuta spp. and Related Non-Parasitic Vines. Plants. 2021; 10(3):438. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10030438
Chicago/Turabian StyleZagorchev, Lyuben, Alexandra Atanasova, Kalina Pachedjieva, Anita Tosheva, Junmin Li, and Denitsa Teofanova. 2021. "Salinity Effect on Germination and Further Development of Parasitic Cuscuta spp. and Related Non-Parasitic Vines" Plants 10, no. 3: 438. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10030438
APA StyleZagorchev, L., Atanasova, A., Pachedjieva, K., Tosheva, A., Li, J., & Teofanova, D. (2021). Salinity Effect on Germination and Further Development of Parasitic Cuscuta spp. and Related Non-Parasitic Vines. Plants, 10(3), 438. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10030438







