Tetracera loureiri Extract Regulates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammatory Response Via Nuclear Factor-κB and Mitogen Activated Protein Kinase Signaling Pathways
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
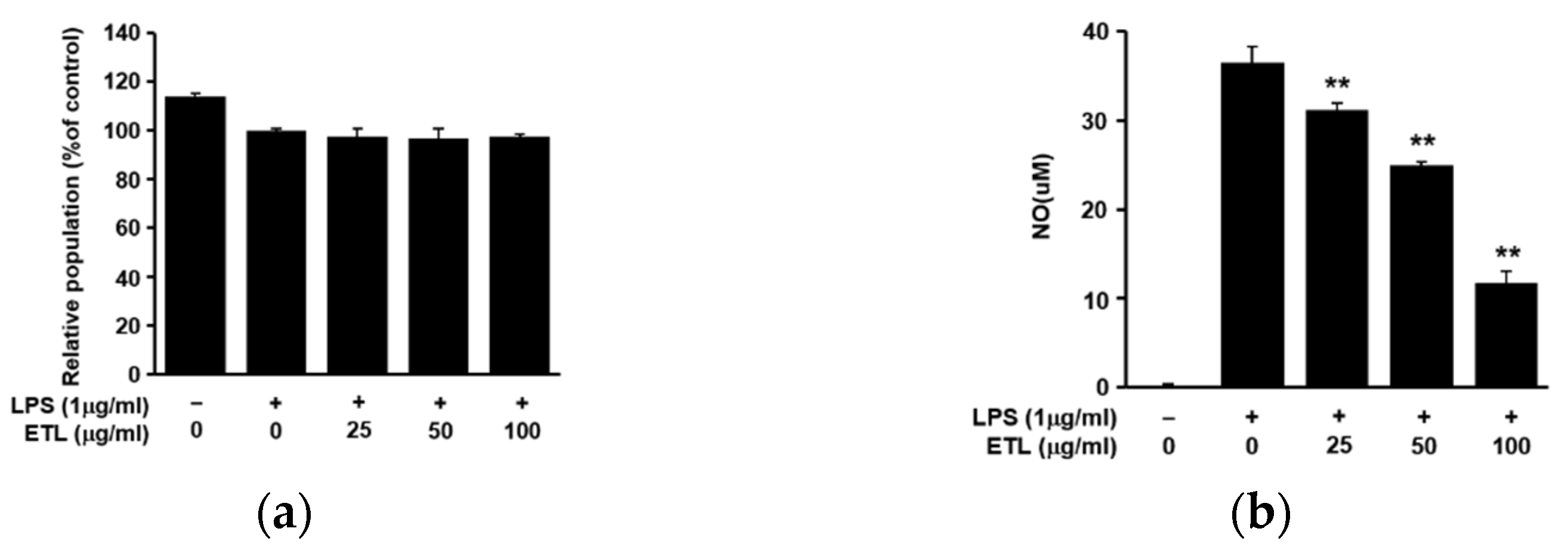
2.1. Effect of ETL on Cell Viability and NO Production in LPS-Stimulated RAW264.7 Cells
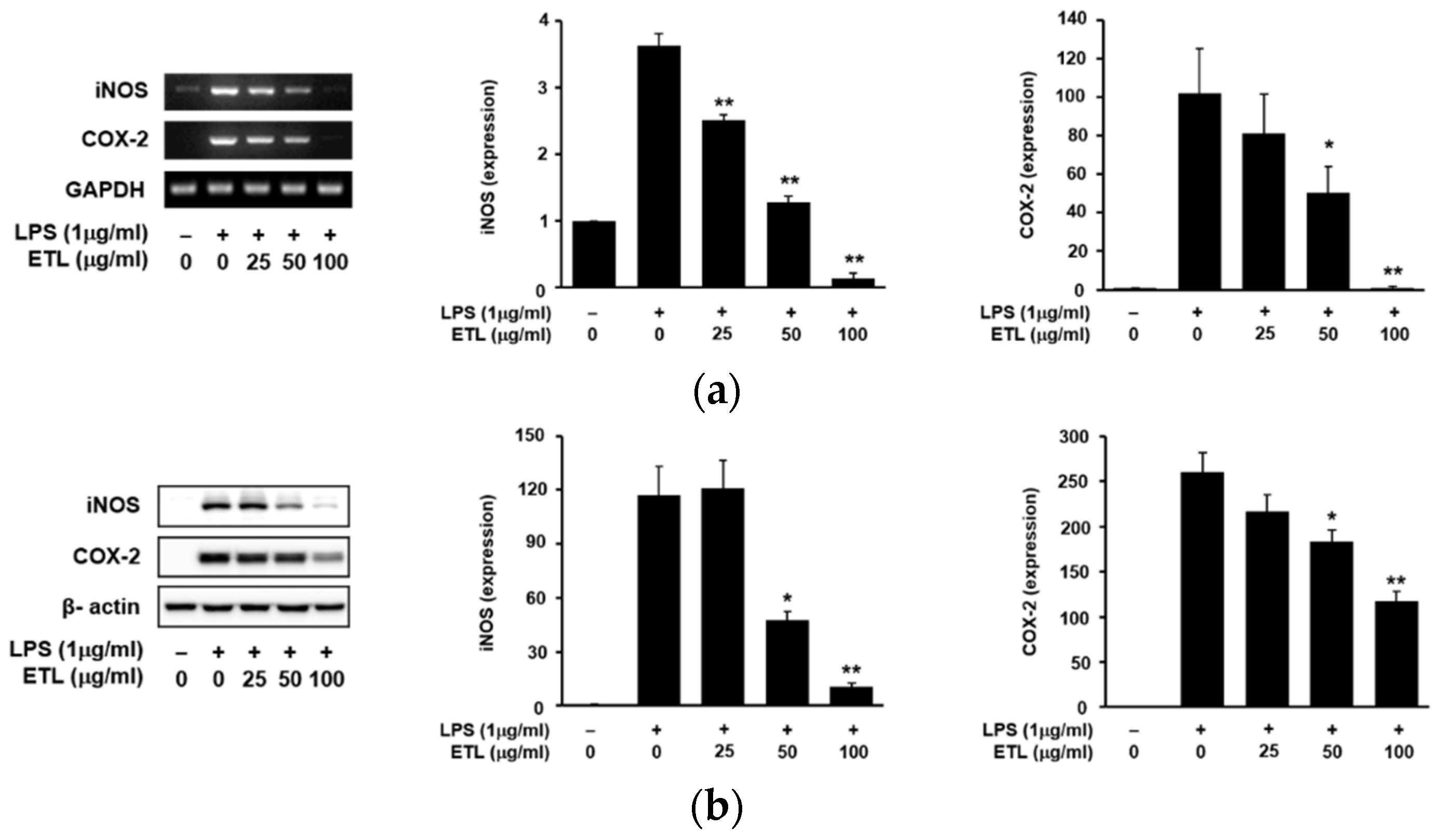
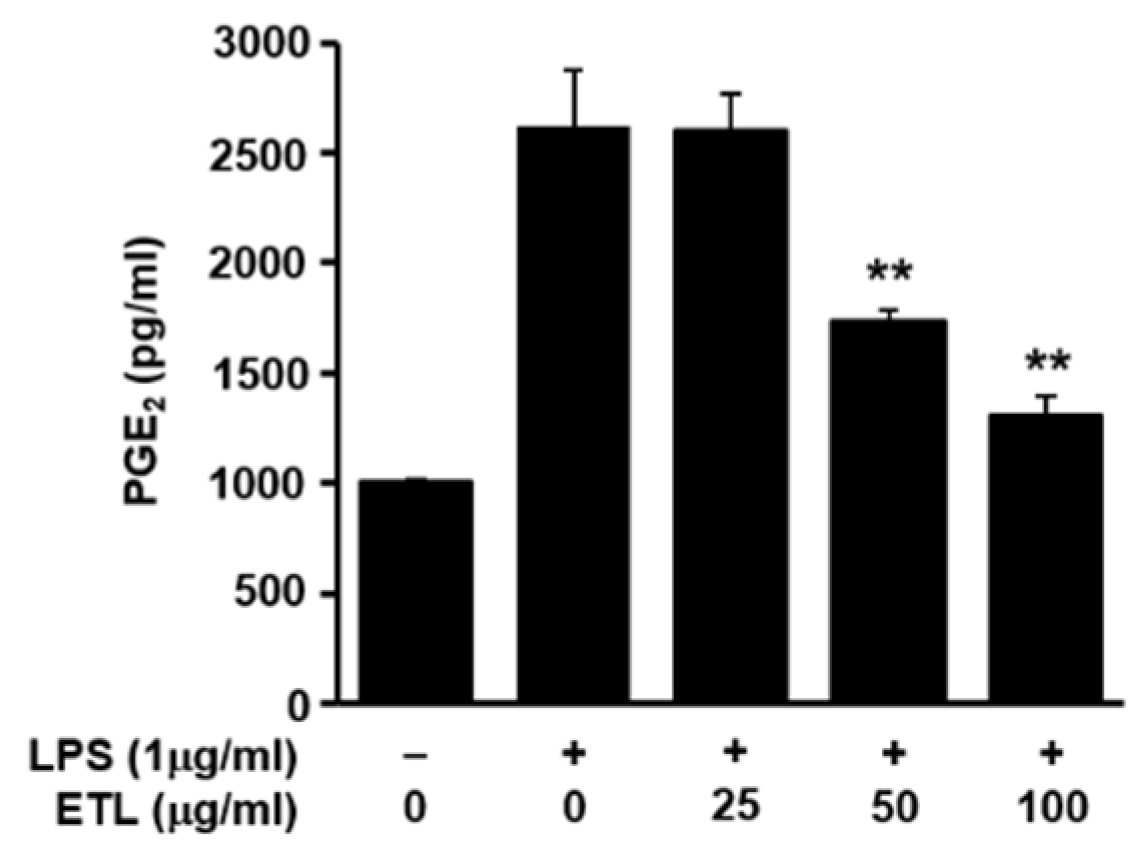
2.2. Effect of ETL on the Expression of iNOS, COX-2 and PGE2 Production
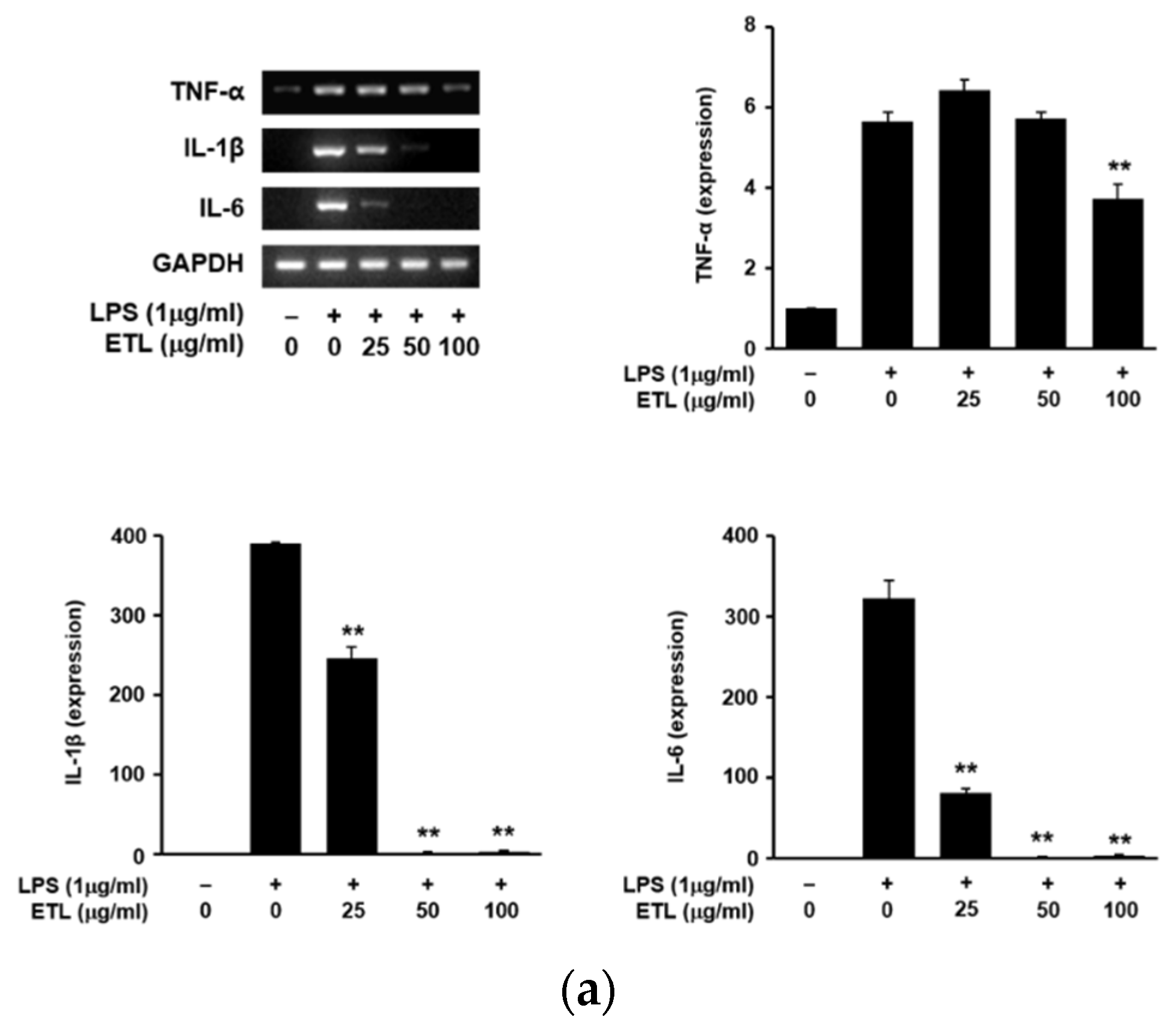
2.3. Effect of ETL on the Production of Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines in LPS-Stimulated RAW264.7 Cells
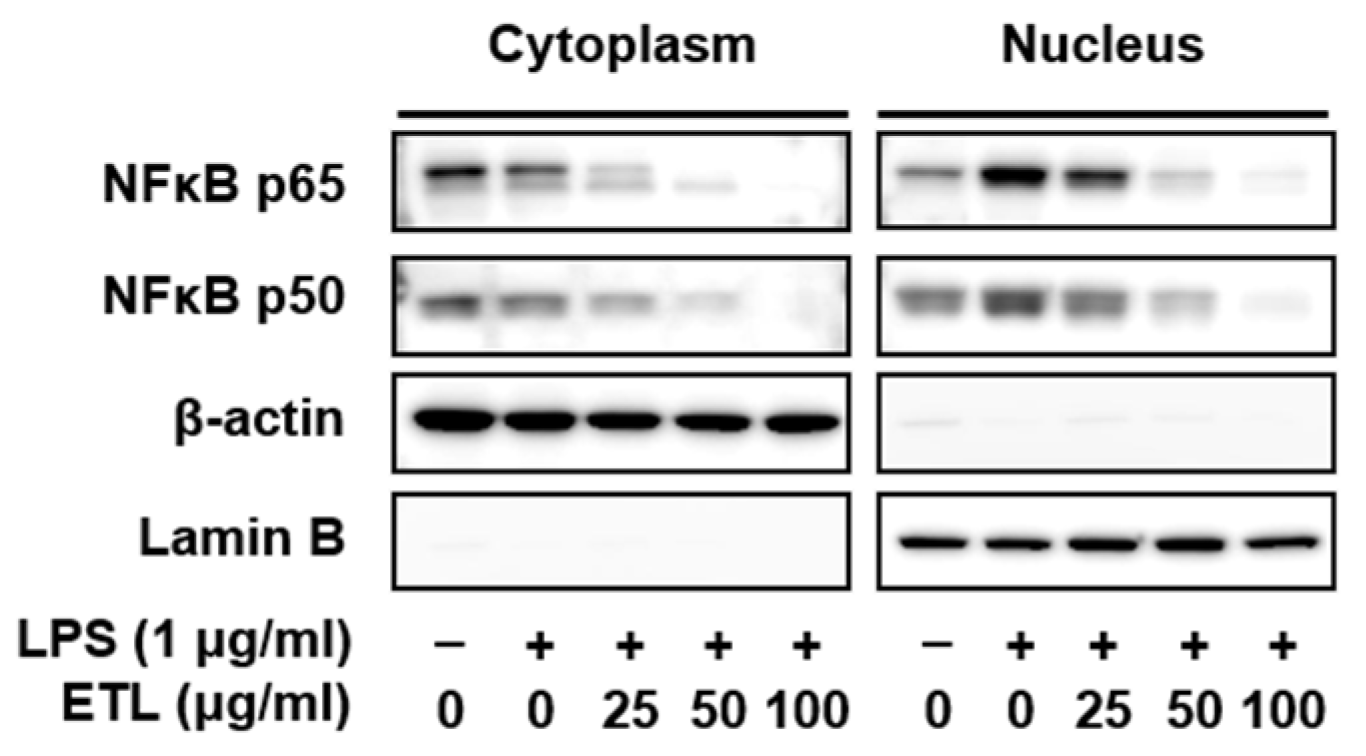
2.4. Effect of ETL on the Nuclear Translocation of NF-κB in LPS-Stimulated RAW264.7 Cells
2.5. Effect of ETL on LPS-Stimulated MAPK Phosphorylation
2.6. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Quercetin and Rhamnocitrin Isolated from ETL on RAW264.7 Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials
4.2. Preparation of T. loureiri Extract
4.3. Apparatus and Chromatography Conditions
4.4. Cell Culture
4.5. Cell Viability Assay
4.6. Measurement of NO Production
4.7. ELISA
4.8. Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR)
4.9. Preparation of Nuclear Extract
4.10. Western Blot Analysis
4.11. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lima, C.C.; Lemos, R.P.L.; Conserva, L.M. Dilleniaceae family: An overview of its ethnomedicinal uses, biological and phytochemical profile. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. 2014, 3, 181–204. [Google Scholar]
- Seo, C.; Lee, J.E.; Lee, J.A.; Ahn, E.K.; Kang, J.S.; Hyun, C.W.; Hong, S.S. Acylated triterpenoids, flavonoids, and lignans isolated from, the stems of Tetracera loureiri. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2019, 55, 386–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.L.; Chuang, T.H.; He, C.X.; Wu, T.S. Cytotoxicity of phenylpropanoid esters from the stems of Hibiscus taiwanensis. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2004, 12, 2193–2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Luo, P.; Zhao, Y.; Hong, J.; Morris-Natschke, S.L.; Xu, J.; Chen, C.H.; Lee, K.H.; Gu, Q. Carolignans from the aerial parts of Euphorbia sikkimensis and their anti-HIV activity. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 578–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, J.F.; Garo, E.; Goering, M.G.; Pasmore, M.; Yoo, H.D.; Esser, T.; Sestrich, J.; Cremin, P.A.; Hough, G.W.; Perrone, P.; et al. Bacterial biofilm inhibitors from Diospyros dendo. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 118–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukongviriyapan, V.; Janyacharoen, T.; Kukongviriyapan, U.; Laupattarakasaem, P.; Kanokmedhakul, S.; Chantaranothai, P. Hepatoprotective and antioxidant activities of Tetracera loureiri. Phytother. Res. 2003, 17, 717–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittiwisut, S.; Amnuoypol, S.; Pathompak, P.; Setharaksa, S. α-Glucosidase and α-amylase inhibitory effects with anti-oxidative activity of Tetracera loureiri (Finet & Gagnep.) Pierre ex Craib leaf extracts. Pharm. Sci. Asia 2021, 48, 175–184. [Google Scholar]
- Willeaume, V.; Kruys, V.; Mijatovic, T.; Huez, G. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha production induced by viruses and by lipopolysaccharides in macrophages: Similarities and differences. J. Inflamm. 1995, 46, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Deng, H.; Cui, H.; Fang, J.; Zuo, Z.; Deng, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhao, L. Inflammatory responses and inflammationassociated diseases in organs. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 7204–7218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Berenbaum, F. Proinflammatory cytokines, prostaglandins, and the chondrocyte: Mechanisms of intracellular activation. Jt. Bone Sprine 2000, 67, 561–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpurapu, M.; Wang, X.; Deng, J.; Park, H.; Xiao, L.; Sadikot, R.T.; Frey, R.S.; Maus, U.A.; Park, G.Y.; Scott, E.W.; et al. Functional PU.1 in macrophage has a pivotal role in NF-κB activation and neutrophilic lung inflammation during endotoxemia. Blood 2011, 118, 5255–5266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, K.S.; Lee, D.S.; Kim, D.C.; Yoon, C.S.; Ko, W.; Oh, H.; Kim, Y.C. Anti-inflammatory effects and mechanisms of action of coussaric and betulinic acids isolated from diospyros kaki in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages. Molecules 2016, 21, 1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, M.S.; Ahn, E.K.; Hong, S.S.; Oh, J.S. 2,8-Decadiene-1,10-Diol inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses through inactivation of mitogen-activated protein kinase and nuclear factor-κB signaling pathway. Inflammation 2016, 39, 583–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, J.Y.; Kang, J.S.; Byun, H.W.; Ahn, E.K. Regulatory effects and molecular mechanism of Trigonostemon reidioides on lipopolysaccharide induced inflammatory responses in RAW264.7 cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 5137–5142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.J.; Lee, H.J.; Choi, M.S.; Son, D.J.; Song, H.S.; Song, M.J.; Lee, J.M.; Han, S.B.; Kim, Y.; Hong, J.T. JNK pathway is involved in the inhibition of inflammatory target gene expression and NF-kappaB activation by melittin. J. Inflamm. 2008, 29, 5–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, S.H.; Le, B.; Androutsopoulos, V.P.; Tsukamoto, C.; Shin, T.S.; Tsatsakis, A.M.; Chung, G. Anti-inflammatory effects of soyasapogenol I-αa via downregulation of the MAPK signaling pathway in LPS-induced RAW 264.7 macrophages. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 113, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koundouras, S.; Marinos, V.; Gkoulioti, A.; Kotseridis, T.; van Leeuwen, C. Influence of Vineyard Location and Vine Water Status on Fruit Maturation of Nonirrigated Cv. Agiorgitiko (Vitis vinifera L.). Effects on Wine Phenolic and Aroma Components. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 5077–5086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Sakulnarmrat, K.; Konczak, I. Anti-inflammatory potential of native Australian herbs polyphenols. Toxicol. Rep. 2014, 1, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guzik, T.J.; Korbut, R.; Adamek-Guzik, T. Nitric oxide and superoxide in inflammation and immune regulation. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2003, 54, 469–487. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, S.S.; Lee, J.E.; Jung, Y.W.; Park, J.H.; Lee, J.A.; Jeong, W.; Ahn, E.K.; Choi, C.W.; Oh, J.S. Monoterpenoids from the fruits of Amomum tsao-ko have inhibitory effects on nitric oxide production. Plants 2021, 10, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.S.; Lee, D.S.; Bae, G.S.; Park, S.J.; Kang, D.G.; Lee, H.S.; Oh, H.; Kim, Y.C. The inhibition of JNK MAPK and NF-κB signaling by tenuifoliside A isolated from Polygala tenuifolia in lipopolysaccharide-induced macrophages is associated with its anti-inflammatory effect. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 721, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Ghosh, S. Molecular mechanisms of NF-κB activation induced by bacterial lipopolysaccharide through Toll-like receptors. J. Endotoxin Res. 2000, 6, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Hayden, M.S. New regulators of NF-kB in inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 837–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Miao, J.; Wang, H.; Zhao, F.; Hu, J.; Gao, P.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yan, M. The anti-inflammatory activities of Ainsliaea fragrans Champ. extract and its components in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW264.7 macrophages through inhibition of NF-κB pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 170, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, M.J.; Cobb, M.H. Mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 1997, 9, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.H.; Jung, M.; Bang, M.H.; Chung, D.K.; Kim, J. Inhibitory effects of a spinasterol glycoside on lipopolysaccharide-induced production of nitric oxide and proinflammatory cytokines via down-regulating MAP kinase pathways and NF-κB activation in RAW264.7 macrophage cells. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2012, 13, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujiwawa, N.; Kobayashi, K. Macrophage in inflammation. Curr. Drug. Targets Inflammat. Allergy 2005, 4, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.Y.; Jung, H.W.; Kang, S.Y.; Kim, K.H.; Park, Y.K. Anti-inflammatory effect of Lycii radices in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophage. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2014, 42, 891–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCartney-Francis, N.; Allen, J.B.; Mizel, D.E.; Albina, J.E.; Xie, Q.W.; Nathan, C.F.; Wahl, S.M. Suppression of arthritis by an inhibitor of nitric oxide synthase. J. Exp. Med. 1993, 178, 749–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Masferrer, J.L.; Zweifel, B.S.; Manning, P.T.; Hauser, S.D.; Leahy, K.M.; Smith, W.G.; Isakson, P.C.; Seibert, K. Selective inhibition of inducible cyclooxygenase 2 in vivo is antiinflammatory and nonulcerogenic. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 3228–3232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nathan, C. Nitric oxide as a secretory product of mammalian cells. FASEB. J. 1992, 6, 3051–3064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, L.J.; Trinchieri, G.; Waldorf, H.A.; Whitaker, D.; Murphy, G.F. Human dermal mast cells contain and release tumor necrosis factor alpha, which induces endothelial leukocyte adhesion molecule 1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 4220–4224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dinarello, C.A. Proinflammatory cytokines. Chest 2000, 118, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, B.P.; Lin, C.H.; Chen, Y.C.; Kao, S.H. Anti-inflammatory effects of Perilla frutescens leaf extract on lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW264.7 cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2014, 10, 1077–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, D.H.; Chung, J.H.; Yoon, J.S.; Ha, Y.M.; Bae, S.; Lee, E.K.; Jung, K.J.; Kim, M.S.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, M.K.; et al. Ginsenoside Rd inhibits the expressions of iNOS and COX-2 by suppressing NF-κB in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 cells and mouse liver. J. Ginseng Res. 2013, 37, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bahuguna, A.; Khan, A.; Bajpai, V.K.; Kang, S.C. MTT assay to evaluate the cytotoxic potential of a drug. Bangladesh J. Pharmacol. 2017, 12, 115–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.; Park, H.J.; Jung, H.A.; Choi, J.S. Estragole exhibits anti-inflammatory activity with the regulation of NF-κB and Nrf-2 signaling pathways in LPS-induced RAW 264.7 cells. Nat. Prod. Sci. 2018, 24, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ryu, S.J.; Choi, J.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, J.S.; Choi, H.S.; Yoon, K.Y.; Hwang, J.H.; Kim, K.J.; Lee, B.Y. Compound K inhibits the lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses in Raw 264.7 cell line and Zebrafish. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muniandy, K.; Gothai, S.; Badran, K.M.H.; Kumar, S.S.; Esa, N.M.; Arulselvan, P. Suppression of proinflammatory cytokines and mediators in LPS-induced RAW 264.7 macrophages by stem extract of Alternanthera sessilis via the inhibition of the NF-κB pathway. J. Immunol. Res. 2018, 2018, 3430684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




| Gene | Primer Sequences | Accession No. | |
|---|---|---|---|
| TNF-α | forward reverse | 5′-AGCCTGTAGCCCACGTCGTA-3′ 5′-TCTTTGAGATCCATGCCGTTG-3′ | NM_013693 |
| IL-1β | forward reverse | 5′-CTTTGAAGAAGAGCCCATCC-3′ 5′-TTTGTCGTTGCTTGGTTCTC-3′ | NM_008361 |
| IL-6 | forward reverse | 5′-CACTTCACAAGTCGGAGGCTT-3′ 5′-GCAAGTGCATCATCGTTGTTC-3′ | NM_031168 |
| iNOS | forward reverse | 5′-GAGTTCGAGACTTCTGTGA-3′ 5′-GGCGATCTGGTAGTAGTG-3′ | NM_010927 |
| COX-2 | forward reverse | 5′-GGAGAGACTATCAAGATAGTGATC-3′ 5′-ATGGTCAT AGACTTTTACAGCTC-3′ | NM_011198 |
| GAPDH | forward reverse | 5′-GTATGACTCCACTCACGGCAAA-3′ 5′-GGTCTCGCTCCTGGAGAGATG-3′ | NM_008084 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, J.A.; Shin, J.Y.; Hong, S.S.; Cho, Y.-R.; Park, J.-H.; Seo, D.-W.; Oh, J.S.; Kang, J.-S.; Lee, J.H.; Ahn, E.-K. Tetracera loureiri Extract Regulates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammatory Response Via Nuclear Factor-κB and Mitogen Activated Protein Kinase Signaling Pathways. Plants 2022, 11, 284. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11030284
Lee JA, Shin JY, Hong SS, Cho Y-R, Park J-H, Seo D-W, Oh JS, Kang J-S, Lee JH, Ahn E-K. Tetracera loureiri Extract Regulates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammatory Response Via Nuclear Factor-κB and Mitogen Activated Protein Kinase Signaling Pathways. Plants. 2022; 11(3):284. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11030284
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Jung A, Ju Young Shin, Seong Su Hong, Young-Rak Cho, Ju-Hyoung Park, Dong-Wan Seo, Joa Sub Oh, Jae-Shin Kang, Jae Ho Lee, and Eun-Kyung Ahn. 2022. "Tetracera loureiri Extract Regulates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammatory Response Via Nuclear Factor-κB and Mitogen Activated Protein Kinase Signaling Pathways" Plants 11, no. 3: 284. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11030284
APA StyleLee, J. A., Shin, J. Y., Hong, S. S., Cho, Y.-R., Park, J.-H., Seo, D.-W., Oh, J. S., Kang, J.-S., Lee, J. H., & Ahn, E.-K. (2022). Tetracera loureiri Extract Regulates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammatory Response Via Nuclear Factor-κB and Mitogen Activated Protein Kinase Signaling Pathways. Plants, 11(3), 284. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11030284






