Invasive Trends of Spartina alterniflora in the Southeastern Coast of China and Potential Distributional Impacts on Mangrove Forests
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
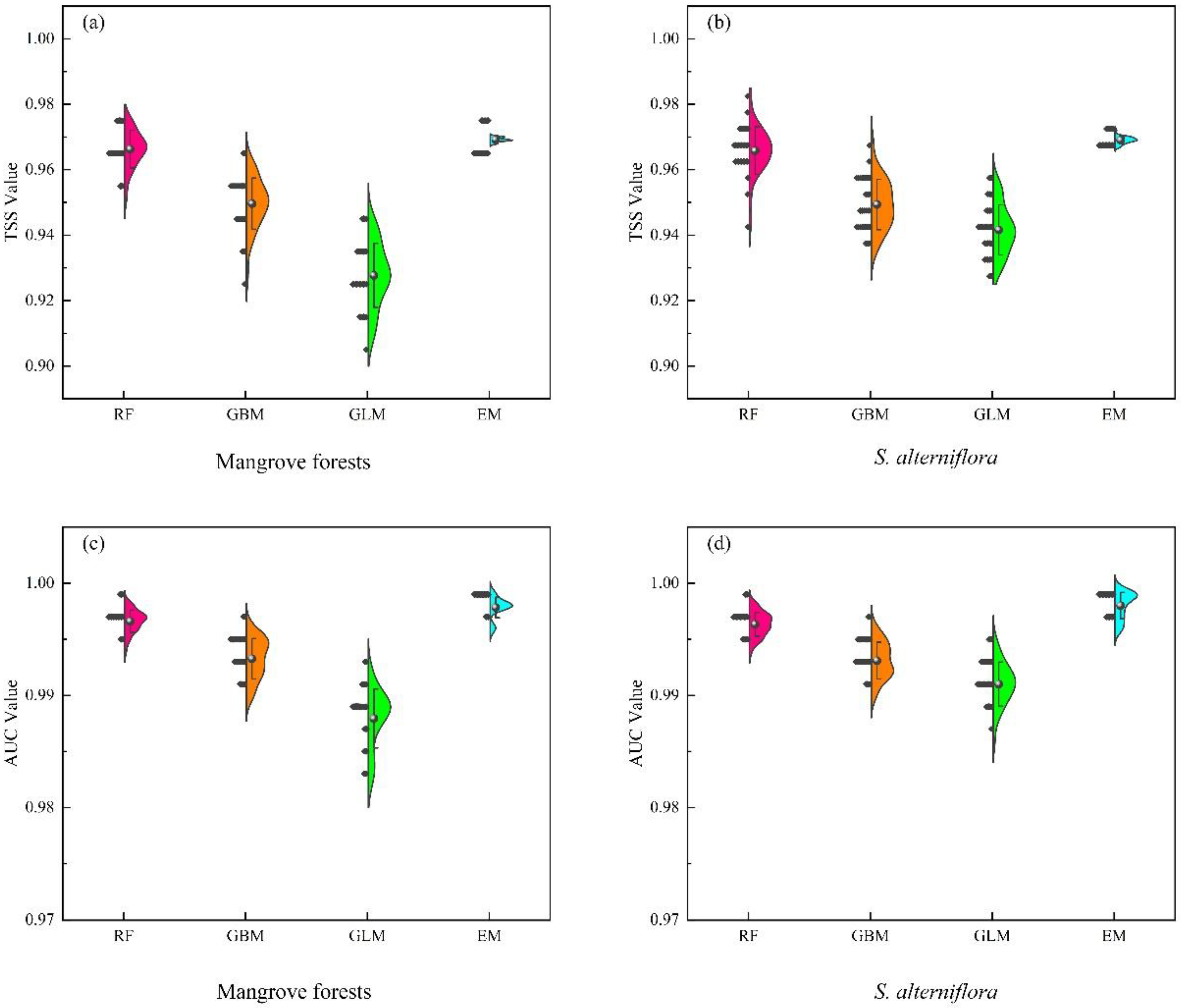
2.1. Model Evaluation
2.2. Analysis of Environmental Variables
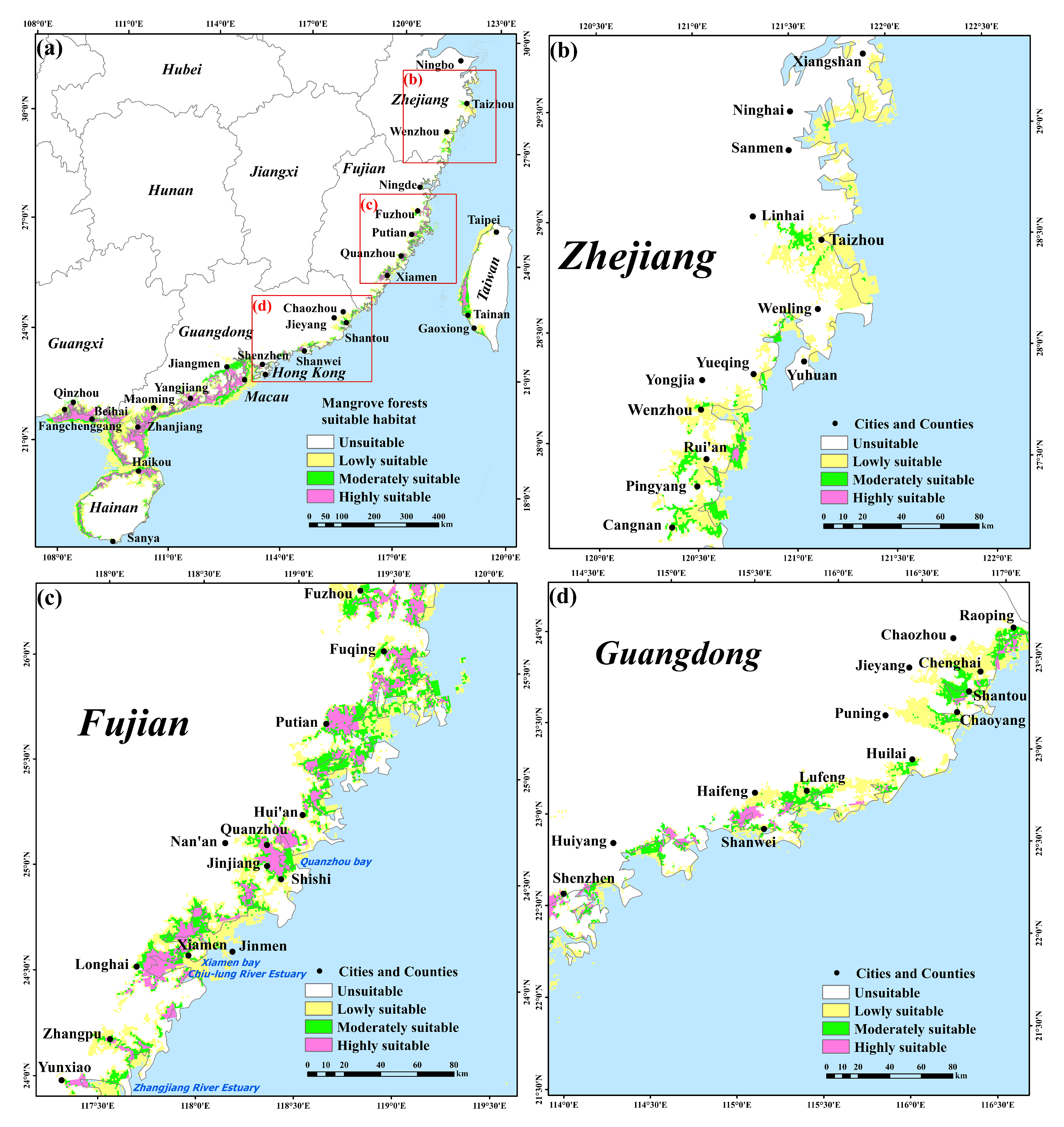
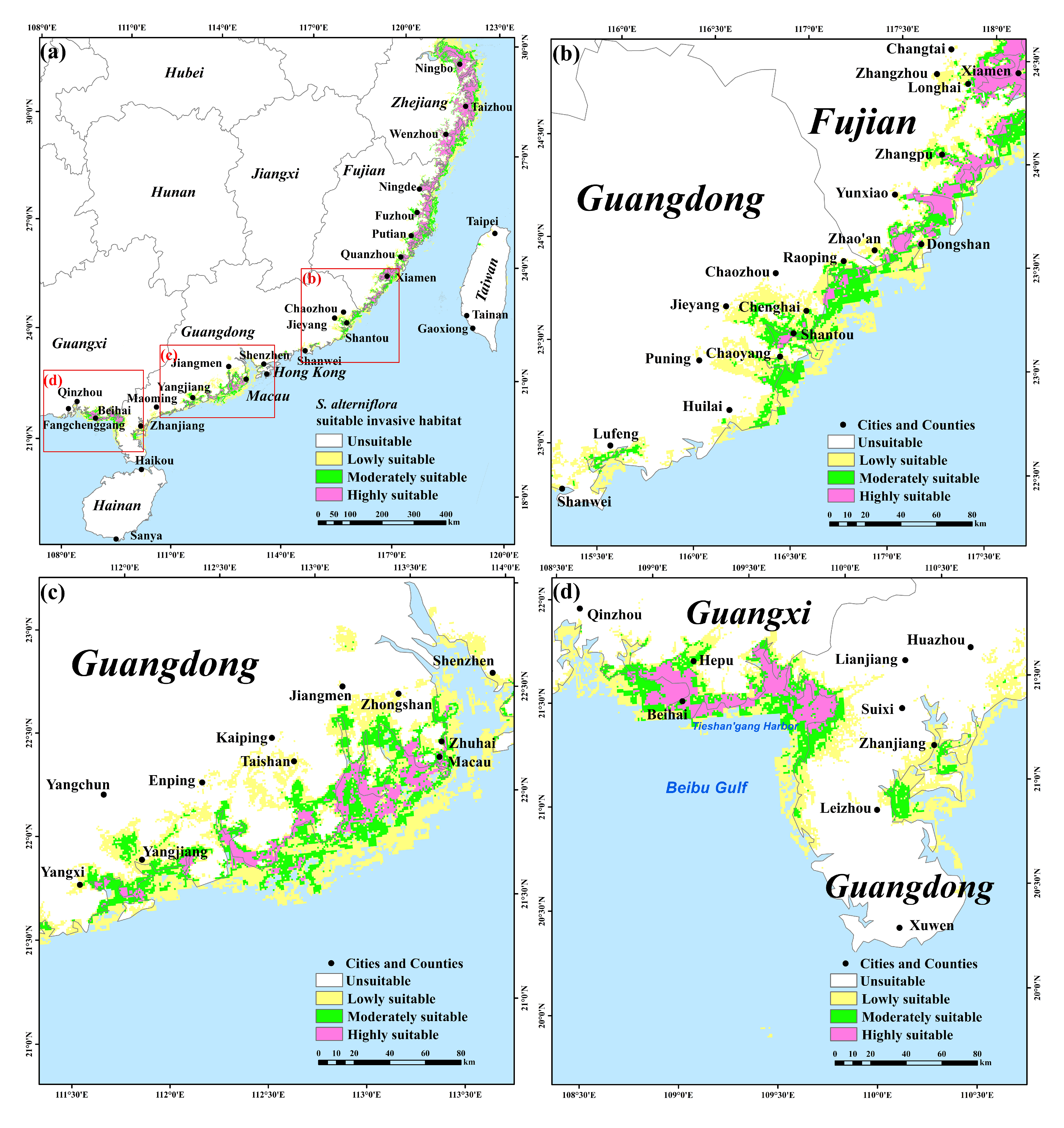
2.3. Simulation Analysis of Potential Distribution for Mangrove Forests and S. alterniflora
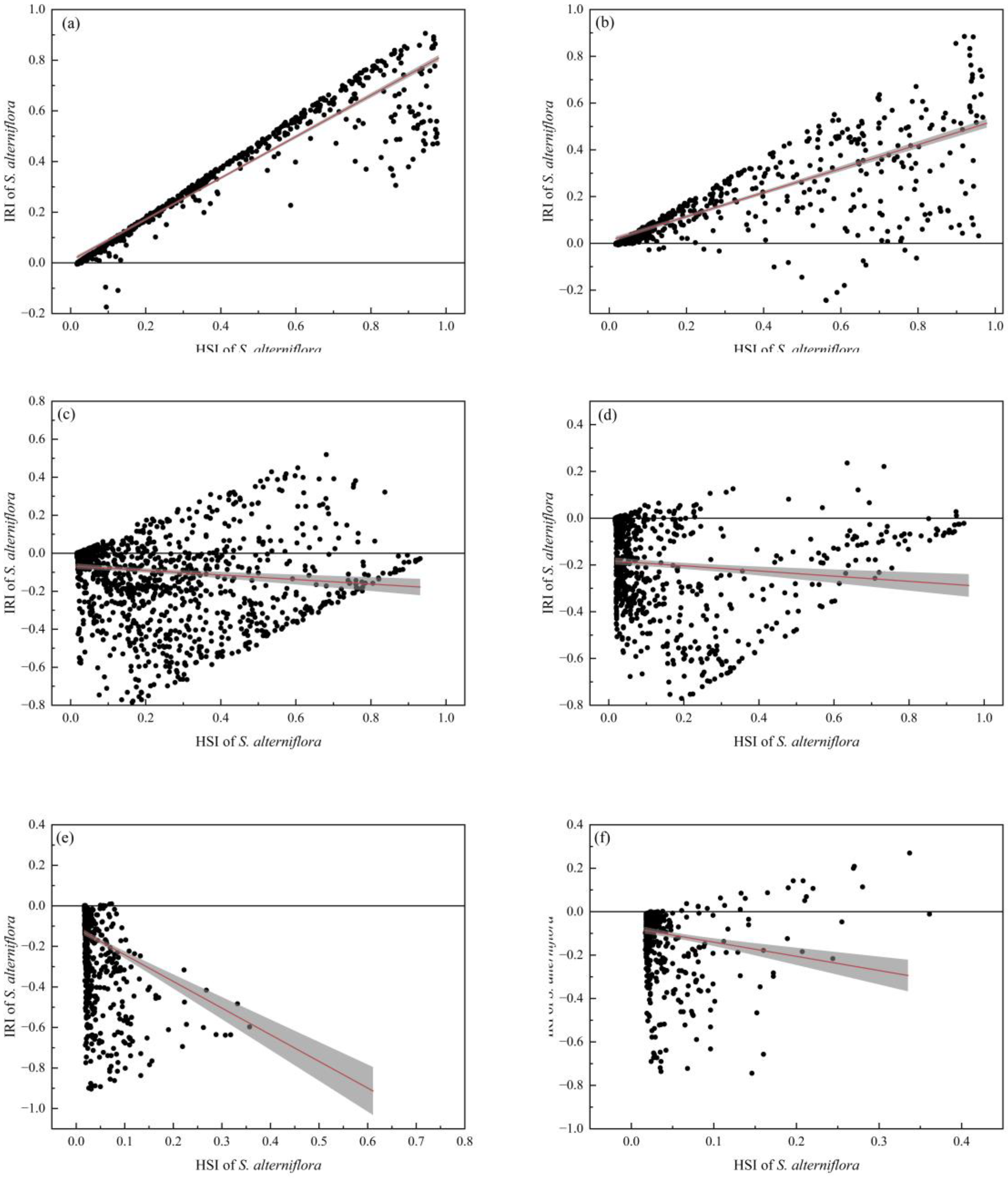
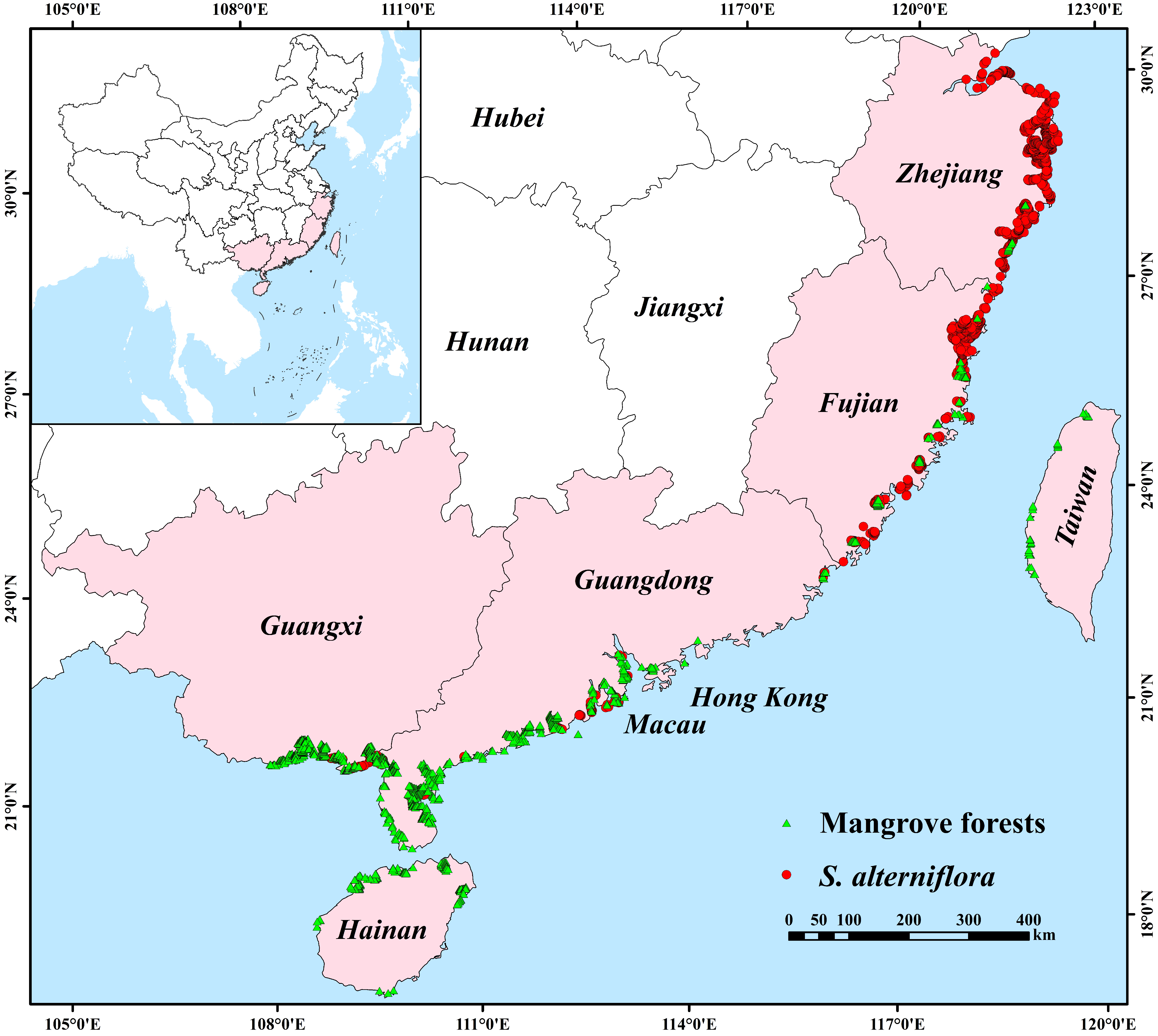
2.4. Risk Analysis of S. alterniflora Invades Mangrove Forests along the Southeastern Coast of China
3. Discussion
3.1. Applicability of SDMs
3.2. Ensemble Model Simulation Accuracy
3.3. Selection of Environmental Factors
3.4. Uncertainty in Species Distribution Model Simulations
3.5. Important Variables Affecting Mangrove Forests and S. alterniflora
3.6. Potential Distribution of Mangrove Forests and S. alterniflora
3.7. S. alterniflora Invades Mangrove Forests along the Southeastern Coast of China
3.8. Conservation of Mangrove Forests and Control of S. alterniflora
3.8.1. Rationalize Mangrove Forest Protection Actions
3.8.2. Control S. alterniflora According to Local Conditions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Occurrence Data
4.2. Environment Data
4.3. Model Construction and Evaluation
4.4. Risk Assessment of S. alterniflora Invading Mangrove Forests
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Ding, J.; Mark, R.N.; Lu, P.; Ren, M.; Huang, H. China’s booming economy is sparking and accelerating biological invasions. Bioscience 2008, 58, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; López-Pujol, J.; Meyerson, L.A.; Qiu, J.; Wang, X.; Ouyang, Z. Biological invasions in rapidly urbanizing areas: A case study of Beijing, China. Biodivers. Conserv. 2011, 20, 2483–2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Sun, Y.; Han, Z.; Huang, H.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, G.; Liu, W. Challenges in preventing and controlling invasive alien species in China. J. Biosaf. 2020, 29, 157–163. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Daehler, C.C.; Strong, D.R. Status, prediction and prevention of introduced cordgrass Spartina spp. invasions in Pacific estuaries, USA. Biol. Conserv. 1996, 78, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partridge, T.R. Spartina in New Zealand. N. Z. J. Bot. 1987, 25, 567–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, J.; van Wyk, E.; Riddin, T. First record of Spartina alterniflora in southern Africa indicates adaptive potential of this saline grass. Biol. Invasions 2016, 18, 2153–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumel, A.; Ainouche, M.L.; Misset, M.T.; Gourret, J.P.; Bayer, R.J. Genetic evidence for hybridization between the native Spartina maritima and the introduced Spartina alterniflora (Poaceae) in South-West France: Spartina × neyrautii re-examined. Plant Syst. Evol. 2003, 237, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, J.A.; Herrera, M.; Biurrun, I.; Loidi, J. The role of alien plants in the natural coastal vegetation in central-northern Spain. Biodivers. Conserv. 2004, 13, 2275–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.-H. Forty years of ecological engineering with Spartina plantations in China. Ecol. Eng. 2006, 27, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; An, S.; Zhi, Y.; Zhou, C.; Chen, L.; Zhao, C.; Fang, S.; Li, H. Preliminary studies on invasive model and outbreak mechanism of exotic species, Spartiona alterniflora Loisel. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2006, 26, 2678–2686. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zuo, P.; Zhao, S.; Liu, C.a.; Wang, C.; Liang, Y. Distribution of Spartina spp. along China’s coast. Ecol. Eng. 2012, 40, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; An, S.; Ma, Z.; Zhao, B.; Chen, J.; Li, B. Invasive Spartina alterniflora: Biology, ecology and management. Acta Phytotaxon. Sin. 2006, 44, 559–588. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesavan, S.; Xavier, K.A.M.; Deshmukhe, G.; Jaiswar, A.K.; Bhusan, S.; Sukla, S.P. Anthropogenic pressure on mangrove ecosystems: Quantification and source identification of surficial and trapped debris. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 794, 148677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romañach, S.S.; DeAngelis, D.L.; Koh, H.L.; Li, Y.; Teh, S.Y.; Raja Barizan, R.S.; Zhai, L. Conservation and restoration of mangroves: Global status, perspectives, and prognosis. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2018, 154, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charrua, A.B.; Bandeira, S.O.; Catarino, S.; Cabral, P.; Romeiras, M.M. Assessment of the vulnerability of coastal mangrove ecosystems in Mozambique. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2020, 189, 105145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carugati, L.; Gatto, B.; Rastelli, E.; Lo Martire, M.; Coral, C.; Greco, S.; Danovaro, R. Impact of mangrove forests degradation on biodiversity and ecosystem functioning. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gu, J. Ecological responses, adaptation and mechanisms of mangrove wetland ecosystem to global climate change and anthropogenic activities. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2021, 162, 105248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inyang, A.I.; Wang, Y. Phytoplankton diversity and community responses to physicochemical variables in mangrove zones of Guangzhou Province, China. Ecotoxicology 2020, 29, 650–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alongi, D.M. Mangrove forests: Resilience, protection from tsunamis, and responses to global climate change. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2008, 76, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, C.; Ochieng, E.; Tieszen, L.L.; Zhu, Z.; Singh, A.; Loveland, T.; Masek, J.; Duke, N. Status and distribution of mangrove forests of the world using earth observation satellite data. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2011, 20, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valiela, I.; Bowen, J.L.; York, J.K. Mangrove forests: One of the World’s threatened major tropical environments. Bioscience 2001, 51, 807–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polidoro, B.A.; Carpenter, K.E.; Collins, L.; Duke, N.C.; Ellison, A.M.; Ellison, J.C.; Farnsworth, E.J.; Fernando, E.S.; Kathiresan, K.; Koedam, N.E.; et al. The loss of species: Mangrove extinction risk and geographic areas of global concern. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellison, J.C.; Zouh, I. Vulnerability to climate change of mangroves: Assessment from cameroon, central Africa. Biology 2012, 1, 617–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Fu, H.; Lee, S.Y.; Fan, H.; Wang, M. Can strict protection stop the decline of mangrove ecosystems in China? From rapid destruction to rampant degradation. Forests 2020, 11, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, L.; Lagomasino, D.; Thomas, N.; Fatoyinbo, T. Global declines in human-driven mangrove loss. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2020, 26, 5844–5855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, J.; Huang, Q.; Qi, F.; Guo, J.; Lin, G. Utilization of exotic Spartina alterniflora by fish community in the mangrove ecosystem of Zhangjiang Estuary: Evidence from stable isotope analyses. Biol. Invasions 2015, 17, 2113–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Huang, G.; Wang, W.; Chen, L.; Lin, G. Interactions between mangroves and exotic Spartina in an anthropogenically disturbed estuary in southern China. Ecology 2012, 93, 588–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Yang, J.; Yu, X.; Liu, L.; Tian, Y. Aboveground vegetation influences belowground microeukaryotic community in a mangrove nature reserve. Wetlands 2013, 34, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Y. Recruitment and herbivory affect spread of invasive Spartina alterniflora in China. Ecology 2014, 95, 1972–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, K.; Ramanathan, A.L.; Raju, N.J. Assessment of blue carbon stock of Coringa mangroves: Climate change perspective. J. Clim. Chang. 2022, 8, 41–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Feng, X.; Chen, Q.; Li, L.; Li, S.; Han, K.; Guo, Z.; Wang, J.; Liu, M.; Shi, C.; et al. Evolution of coastal forests based on a full set of mangrove genomes. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 6, 738–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamprogno, G.C.; Tognella, M.M.P.; Costa, M.B.d.; Otegui, M.B.P.; Menezes, K.M. Spatio-temporal distribution of benthic fauna in mangrove areas in the Bay of Vitória estuary, Brazil. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2023, 62, 102939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Gasparatos, A. Perceptions about mangrove restoration and ecosystem services to inform ecosystem-based restoration in Large Xiamen Bay, China. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2023, 235, 104763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granse, D.; Suchrow, S.; Jensen, K. Long-term invasion dynamics of Spartina increase vegetation diversity and geomorphological resistance of salt marshes against sea level rise. Biol. Invasions 2021, 23, 871–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Han, S.; Wang, J. Impacts of Spartina alterniflora expansion on landscape pattern and habitat quality: A case study in Yancheng coastal wetland, China. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2020, 18, 4669–4683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Yang, F. Impacts of Spartina alterniflora invasion on soil inorganic carbon in coastal wetlands in China. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2020, 84, 844–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macy, A.; Osland, M.J.; Cherry, J.A.; Cebrian, J. Changes in ecosystem Nitrogen and Carbon allocation with black mangrove (Avicennia germinans) encroachment into Spartina alterniflora salt marsh. Ecosystems 2021, 24, 1007–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Pang, M.; Xi, M.; Kong, F. Responses of contents and structure of DOM to Spartina alterniflora invasion in Yanghe estuary wetland of Jiaozhou Bay, China. Wetlands 2019, 39, 729–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Maung-Douglass, K.; Strong, D.R.; Pennings, S.C.; Zhang, Y. Geographical variation in vegetative growth and sexual reproduction of the invasive Spartina alterniflora in China. J. Ecol. 2016, 104, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Hu, Y.; Liu, M.; Chang, Y.; Sun, L. Geographical variation and influencing factors of Spartina alterniflora expansion rate in coastal China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2020, 30, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, B.; Jiang, S.; Yang, L.; Zhang, H.; Tang, B. Succession of macrofaunal communities and environmental properties along a gradient of smooth cordgrass Spartina alterniflora invasion stages. Mar. Environ. Res. 2020, 156, 104862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noto, A.E.; Hughes, A.R. Genotypic diversity weakens competition within, but not between, plant species. J. Ecol. 2020, 108, 2212–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Lin, X. Exotic Spartina alterniflora invasion enhances sediment N-loss while reducing N retention in mangrove wetland. Geoderma 2023, 431, 116362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhou, C.; He, Q.; Qiu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, J.; Li, B.; Nie, M. Phenotypic plasticity of light use favors a plant invader in nitrogen-enriched ecosystems. Ecology 2022, 103, e3665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, S.; Mo, S.; Gao, T.; Yan, B.; Shen, P.; Kashif, M.; Zhang, Z.; Li, J.; Jiang, C. Coupling effects of nitrate reduction and sulfur oxidation in a subtropical marine mangrove ecosystem with Spartina alterniflora invasion. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 862, 160930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Yu, W.; Chen, G.; Xie, T.; Liu, Z.; Ma, Z.; Du, J.; Chao, B.; et al. Mapping the potential of mangrove forest restoration based on species distribution models: A case study in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 748, 142321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Qi, X.; Gong, H.; Li, L.; Zhang, M.; Li, Y.; Lin, Z. Combined effects of global climate suitability and regional environmental variables on the distribution of an invasive marsh species Spartina Alterniflora. Estuaries Coast. 2018, 42, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, C.D.; Cameron, A.; Green, R.E.; Bakkenes, M.; Beaumont, L.J.; Collingham, Y.C.; Erasmus, B.F.; De Siqueira, M.F.; Grainger, A.; Hannah, L.; et al. Extinction risk from climate change. Nature 2004, 427, 145–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Lv, J.; Ai, L. The impacts of climate change on the biodiversity:vulnerability and adaptation. Energy Environ. Sci. 2009, 18, 693–703. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. In Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Masson-Delmotte, V., Zhai, P., Pirani, A., Connors, S.L., Péan, C., Berger, S., Caud, N., Chen, Y., Goldfarb, L., Gomis, M.I., et al., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ning, H.; Ling, L.; Sun, X.; Kang, X.; Chen, H. Predicting the future redistribution of Chinese white pine Pinus armandii Franch. Under climate change scenarios in China using species distribution models. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2021, 25, e01420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wei, H.; Wang, D.; Chen, R.; Wang, L.; Gu, W. Predicting the invasive trend of exotic plants in China based on the ensemble model under climate change: A case for three invasive plants of Asteraceae. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 756, 143841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Li, X.; Zhao, Z.; Nawaz, Z. Predicting the impacts of climate change, soils and vegetation types on the geographic distribution of Polyporus umbellatus in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 648, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wei, H.; Zhang, X.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Gu, W. Non-pessimistic predictions of the distributions and suitability of Metasequoia glyptostroboides under climate change using a Random Forest model. Forests 2020, 11, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wei, H.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Gu, W. The global potential distribution of invasive plants: Anredera cordifolia under climate change and human activity based on Random Forest models. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Wei, H.; Zhang, X.; Fang, Y.; Gu, W. Habitat suitability modeling based on remote sensing to realize time synchronization of species and environmental variables. J. Plant Ecol. 2021, 14, 241–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayathilake, D.R.M.; Costello, M.J. A modelled global distribution of the seagrass biome. Biol. Conserv. 2018, 226, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Li, X.; Zhao, Z.; Wei, H.; Gao, B.; Gu, W. Prediction of the potential geographic distribution of the ectomycorrhizal mushroom Tricholoma matsutake under multiple climate change scenarios. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 46221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Liu, C.; Liu, Y.; Yang, J.; Zhang, X.; Guo, K. Advances in theoretical issues of species distribution models. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2013, 33, 4827–4835. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Elith, J.; Phillips, S.J.; Hastie, T.; Dudík, M.; Chee, Y.E.; Yates, C.J. A statistical explanation of MaxEnt for ecologists. Divers. Distrib. 2011, 17, 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, S.J.; Anderson, R.P.; Schapire, R.E. Maximum entropy modeling of species geographic distributions. Ecol. Model. 2006, 190, 231–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guisan, A.; Edwards, T.C.; Hastie, T. Generalized linear and generalized additive models in studies of species distributions: Setting the scene. Ecol. Model. 2002, 157, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yee, T.W.; Mitchell, N.D. Generalized Additive Models in Plant Ecology. J. Veg. Sci. 1991, 2, 587–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuiller, W.; Araújo, M.B.; Lavorel, S. Generalized models vs. classification tree analysis: Predicting spatial distributions of plant species at different scales. J. Veg. Sci. 2003, 14, 669–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özesmi, S.L.; Özesmi, U. An artificial neural network approach to spatial habitat modelling with interspecific interaction. Ecol. Model. 1999, 116, 15–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R.; Buja, A. Flexible discriminant analysis by optimal scoring. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1994, 89, 1255–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moisen, G.G.; Freeman, E.A.; Blackard, J.A.; Frescino, T.S.; Zimmermann, N.E.; Edwards, T.C. Predicting tree species presence and basal area in Utah: A comparison of stochastic gradient boosting, generalized additive models, and tree-based methods. Ecol. Model. 2006, 199, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, E.A.; Moisen, G.G.; Frescino, T.S. Evaluating effectiveness of down-sampling for stratified designs and unbalanced prevalence in Random Forest models of tree species distributions in Nevada. Ecol. Model. 2012, 233, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booth, T.H.; Nix, H.A.; Busby, J.R.; Hutchinson, M.F.; Franklin, J. bioclim: The first species distribution modelling package, its early applications and relevance to most current MaxEnt studies. Divers. Distrib. 2014, 20, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verburg, P.H.; Overmars, K.P. Combining top-down and bottom-up dynamics in land use modeling: Exploring the future of abandoned farmlands in Europe with the Dyna-CLUE model. Landsc. Ecol. 2009, 24, 1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, J.H. Multivariate adaptive regression splines. Ann. Statist. 1991, 19, 1–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouteau, R.; Meyer, J.-Y.; Stoll, B. A SVM-based model for predicting distribution of the invasive tree Miconia calvescens in tropical rainforests. Ecol. Model. 2011, 222, 2631–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hefley, T.J.; Hooten, M.B.; Warton, D. On the existence of maximum likelihood estimates for presence-only data. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2015, 6, 648–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietterich, T.G. Ensemble methods in machine learning. In Multiple Classifier Systems. MCS 2000.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2000; Volume 1857. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.; Wei, H.; Guo, Y.; Gu, W. Potential distribution of Panax ginseng and its predicted responses to climate change. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2016, 27, 3607–3615. [Google Scholar]
- Thuiller, W.; Georges, D.; Gueguen, M.; Engler, R.; Breiner, F. Biomod2: Ensemble Platform for Species Distribution Modeling. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/biomod2/index.html (accessed on 8 August 2022).
- Dyderski, M.K.; Paź, S.; Frelich, L.E.; Jagodziński, A.M. How much does climate change threaten European forest tree species distributions? Glob. Chang. Biol. 2018, 24, 1150–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranc, N.; Santini, L.; Rondinini, C.; Boitani, L.; Poitevin, F.; Angerbjörn, A.; Maiorano, L. Performance tradeoffs in target-group bias correction for species distribution models. Ecography 2017, 40, 1076–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez-Villegas, J.; Cuesta, F.; Devenish, C.; Peralvo, M.; Jarvis, A.; Arnillas, C.A. Using species distributions models for designing conservation strategies of Tropical Andean biodiversity under climate change. J. Nat. Conserv. 2014, 22, 391–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, J.; Liu, J.; Wei, H.; Fang, Y.; Wang, D.; Chen, R.; Gu, W. Revealing the long-term trend of the global-scale Ginkgo biloba distribution and the impact of future climate change based on the ensemble modeling. Biodivers. Conserv. 2023, 32, 2077–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grenouillet, G.; Buisson, L.; Casajus, N.; Lek, S. Ensemble modelling of species distribution: The effects of geographical and environmental ranges. Ecography 2011, 34, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mtengwana, B.; Dube, T.; Mudereri, B.T.; Shoko, C. Modeling the geographic spread and proliferation of invasive alien plants (IAPs) into new ecosystems using multi-source data and multiple predictive models in the Heuningnes catchment, South Africa. Gisci. Remote Sens. 2021, 58, 483–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marmion, M.; Parviainen, M.; Luoto, M.; Heikkinen, R.K.; Thuiller, W. Evaluation of consensus methods in predictive species distribution modelling. Divers. Distrib. 2009, 15, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, T.; Elith, J.; Guillera-Arroita, G.; Lahoz-Monfort, J.J. A review of evidence about use and performance of species distribution modelling ensembles like BIOMOD. Divers. Distrib. 2019, 25, 839–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardestani, E.G.; Ghahfarrokhi, Z.H. Ensembpecies distribution modeling of Salvia hydrangea under future climate change scenarios in Central Zagros Mountains, Iran. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2021, 26, e01488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valavi, R.; Shafizadeh-Moghadam, H.; Matkan, A.; Shakiba, A.; Mirbagheri, B.; Kia, S.H. Modelling climate change effects on Zagros forests in Iran using individual and ensemble forecasting approaches. Theor. Appl. Clim. 2018, 137, 1015–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, B.; Zhang, Q. Area, distribution and species composition of mangroves in China. Wetl. Sci. 2014, 12, 435–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, S.; Yu, F. Quality of presence data determines species distribution model performance: A novel index to evaluate data quality. Landsc. Ecol. 2016, 31, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, W.; He, J.; Yang, R.; Wu, H.; Wang, X.; Jiao, L.; Tang, Z.; Yao, Y. Range shifts in response to climate change of Ophiocordyceps sinensis, a fungus endemic to the Tibetan Plateau. Biol. Conserv. 2017, 206, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoar, A.; Allouche, O.; Steinitz, O.; Rotem, D.; Kadmon, R. A comparative evaluation of presence-only methods for modelling species distribution. Divers. Distrib. 2007, 13, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thibaud, E.; Petitpierre, B.; Broennimann, O.; Davison, A.C.; Guisan, A. Measuring the relative effect of factors affecting species distribution model predictions. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2014, 5, 947–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P. Ecological notes on mangroves in southeast coast of China including Taiwan Province and Hainan Island. Acta Ecol. Sin. 1981, 3, 283–290. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y. Impacts, challenges and opportunities of global climate change on mangrove ecosystems. J. Trop. Oceanogr. 2021, 40, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Lin, P. Responses and roles of mangroves in China to global climate changes. Trans. Oceanol. Limnol. 1999, 2, 11–17. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Gao, H.; Zhou, H.Y.; Guo, W.D. Preliminary study on the chlorophyll-a and nutrients in seawater of the mangrove area of Qi’ao Island in Zhujiang River estuary. J. Oceanogr. Taiwan Strait 2005, 4, 502–507. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Wei, M.; Fan, H.; Pan, L.; Cao, Q. Spatio-temporal change of inorganic nitrogen content and the evaluation of eutrophication in the surface seawaters of mangrove area in Guangxi bays. J. Appl. Oceanogr. 2014, 33, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snedaker, S.C. Mangroves and climate change in the Florida and Caribbean region: Scenarios and hypotheses. Hydrobiologia 1995, 295, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, A.K.; Das, M.; Philip, P.; Bhadury, P. An assessment of the implications of seasonal precipitation and anthropogenic influences on a mangrove ecosystem using phytoplankton as proxies. Estuar. Coast. 2014, 38, 854–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, A.; Johnson, R.; Wigand, C.; Oczkowski, A.; Davey, E.; Markham, E. Responses of Spartina alterniflora to multiple stressors: Changing precipitation patterns, accelerated sea level rise, and nutrient enrichment. Estuaries Coasts 2016, 39, 1376–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, J.M.; Stephen Brewer, J.; Bertness, M.D. Nutrients, competition and plant zonation in a New England salt marsh. J. Ecol. 1998, 86, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matzke, S.; Elsey-Quirk, T. Spartina patens productivity and soil organic matter response to sedimentation and nutrient enrichment. Wetlands 2018, 38, 1233–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donnell, J.P.R.; Schalles, J.F. Examination of abiotic drivers and their influence on Spartina alterniflora biomass over a Twenty-Eight Year period using Landsat 5 TM satellite imagery of the central Georgia coast. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zhao, C.; Liu, X.; Gong, L.; Deng, Z.; Li, J. Growth characteristic and adaptability of Spartina alterniflora in different latitudes areas along China coast. Ecol. Sci. 2015, 34, 119–128. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Wang, W. Some thematic issues for mangrove conservation in China. J. Xiamen Univ. Nat. Sci. 2017, 56, 323–330. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Ren, G.; Wu, P.; Liu, A.; Pan, L.; Ma, Y.; Ma, Y.; Wang, J. Analysis on the remote sensing monitoring and landscape pattern change of mangrove in China from 1990 to 2019. J. Ocean Technol. 2020, 39, 1–12. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Fang, B.; Dan, X. On the mangrove resources and its conservation in China. Contral S. For. Inv. Plan. 2001, 3, 20–30. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lu, J.; Zhang, Y. Spatial distribution of an invasive plant Spartina alterniflora and its potential as biofuels in China. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 52, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Sardans, J.; Wang, C.; Zeng, C.; Tong, C.; Chen, G.; Huang, J.; Pan, H.; Peguero, G.; Vallicrosa, H.; et al. The response of stocks of C, N, and P to plant invasion in the coastal wetlands of China. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2019, 25, 733–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Ma, K. Research overview and trend on biological invasion in mangrove forests. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2015, 39, 283–299. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Pan, W.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, W.; He, T.; Liu, Y.; Liu, W.; Zhang, Y. Invasion of Spartina alterniflora and protection of mangroves in Guangdong Zhanjiang Mangrove National Nature Reserve and adjacent coastal area. For. Environ. Sci. 2018, 34, 58–63. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Xie, T.; Pennings, S.C.; Wang, Y.; Craft, C.; Hu, M. A comparison of coastal habitat restoration projects in China and the United States. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Forestry and Grassland Administration. Special Action Plan for Mangrove Forests Protection and Restoration (2020–2025). 2020. Available online: http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/zhengceku/2020-08/29/content_5538354.htm (accessed on 20 December 2022).
- Li, H.; Peng, X.; Wu, Z.; Li, J. Investigation on the invasion status of Spartina alterniflora to mangrove wetlands. J. Guangdong Univ. Edu. 2014, 34, 55–60. [Google Scholar]
- Hedge, P.; Kriwoken, L.K.; Patten, K. A Review of Spartina Management in Washington State, US. J. Aquat. Plant Manag. 2003, 41, 82–90. [Google Scholar]
- Grevstad, F.S.; Strong, D.R.; Garcia-Rossi, D.; Switzer, R.W.; Wecker, M.S. Biological control of Spartina alterniflora in Willapa Bay, Washington using the planthopper Prokelisia marginata: Agent specificity and early results. Biol. Control 2003, 27, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Hacker, S.; Ayres, D.; Strong, D.R. Potential of Prokelisia spp. as biological control agents of English cordgrass, Spartina anglica. Biol. Control 1999, 16, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhuang, Z.; Cai, X.; Xu, Y.; Lu, H. Studies on the influence of Micaojing on the plankton in coastal waters. China Environ. Sci. 2004, 6, 83–85. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Liu, S.; Feng, Z.; Liu, G.; Gan, Q.; Peng, S. Use of exotic plants to control Spartina alterniflora invasion and promote mangrove restoration. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Li, J.; Liu, X.; Gong, L.; Zhao, C. Combined effects of mowing and shading on growth and survival of Spartina alterniflora. Guihaia 2017, 37, 303–307. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Liao, B.; Zhu, N.; Guan, W. Effect of sun-shade on the growth of Spartina alterniflora. For. Pest Dis. 2010, 29, 34–36. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Pan, X.; Ma, Z.; Chen, J.; Li, B. Effects of winter burning and cutting on aboveground growth and reproduction of Spartina alterniflora: A field experiment at Chongming Dongtan, Shanghai. Biodivers. Sci. 2006, 14, 275–283. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, G.; Liu, J.; Xu, W.; Ren, L. Effects of waterlogging regulation on growth of Spartina Alterniflora. Res. Environ. Sci. 2011, 24, 1003–1007. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Zhao, F. Advances in remote sensing monitoring of lake eutrophication. Guizhou Sci. 2017, 35, 39–45. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Zhao, C. Application and development of Lidar to detect the vertical distribution of marine materials. Infrared Laser Eng. 2020, 49, 24–32. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, H.; Liao, X.; He, X.; Yue, H. Remote sensing monitoring and variation analysis of marine ecological environment in coastal waters of SriLanka. J. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2020, 22, 1463–1475. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fielding, A.H.; Bell, J.F. A review of methods for the assessment of prediction errors in conservation presence/absence models. Environ. Conserv. 1997, 24, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manel, S.; Williams, H.C.; Ormerod, S.J. Evaluating presence-absence models in ecology: The need to account for prevalence. J. Appl. Ecol. 2001, 38, 921–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allouche, O.; Tsoar, A.; Kadmon, R. Assessing the accuracy of species distribution models: Prevalence, kappa and the true skill statistic (TSS). J. Appl. Ecol. 2006, 43, 1223–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Mangrove Forests | S. alterniflora | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | Contribution Rate (%) | Cumulative Contribution Rate (%) | Best Suitable Range (Unit) | Variables | Contribution Rate (%) | Cumulative Contribution Rate (%) | Best Suitable Range (Unit) |
| Bio1 | 25.07 | 25.07 | 18.7–25.7 °C | CHL | 22.34 | 22.34 | 3.04–13.85 µg/L |
| Ele | 17.86 | 42.93 | −140–16 m | Bio16 | 21.27 | 43.61 | 438–1226 mm |
| CHL | 17.84 | 60.77 | 1.17–13.14 µg/L | Ele | 8.29 | 51.90 | −149–165 m |
| Bio16 | 7.63 | 68.40 | 438–1642.76 mm | Bio19 | 7.05 | 58.95 | 69–332 mm |
| Bio12 | 7.30 | 75.70 | 949–2669 mm | Bio3 | 6.34 | 65.29 | 116–276 |
| SST2 | 5.14 | 80.84 | 25.41–38.4 °C | Bio12 | 6.08 | 71.37 | 932–2491.4 mm |
| Bio19 | 3.19 | 84.03 | 23.6–566 mm | Bio2 | 6.06 | 77.43 | 25–70 |
| PAR | 3.18 | 87.21 | 28.13–39.56 E/m2day | PAR | 5.92 | 83.35 | 26.25–35.48 E/m2day |
| Bio15 | 2.63 | 89.84 | 20–100 mm | Bio18 | 3.68 | 87.03 | 302–1137 mm |
| Bio2 | 2.54 | 92.38 | 20–62 | Bio15 | 2.61 | 89.64 | 32–87 mm |
| Bio18 | 1.83 | 94.21 | 302–1586.94 mm | SST1 | 2.31 | 91.95 | 8.8–35.4 °C |
| SSS | 1.65 | 95.86 | 30.9–33.9% | Bio5 | 1.91 | 93.86 | 28.4–33.3 |
| Bio5 | 1.31 | 97.17 | 29.7–32.5 | Bio1 | 1.75 | 95.61 | 16.9–23.8 °C |
| Bio3 | 1.08 | 98.25 | 150–297 | SST2 | 1.16 | 96.77 | 22.1–37.3 °C |
| SST4 | 0.89 | 99.14 | 13.29–32.03 °C | SSS | 1.04 | 97.81 | 21.4–33.1% |
| SST3 | 0.31 | 99.45 | 19.82–36.87 °C | Slop | 0.75 | 98.56 | 0–90° |
| SST1 | 0.29 | 99.74 | 16.6–36.5 °C | SST3 | 0.75 | 99.31 | 15.9–36.1 °C |
| SST5 | 0.14 | 99.88 | 22.39–34.9 °C | SST4 | 0.56 | 99.87 | 8.8–31.1 °C |
| Slop | 0.10 | 99.98 | 0–90° | SST5 | 0.10 | 99.97 | 15.88–34.42 °C |
| Aspe | 0.02 | 100.00 | −1–359.82° | Aspe | 0.03 | 100.00 | −1–359.82° |
| Factors | Variables | Description | Unit | Data Sources |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BioClimate | Bio1 | Annual mean temperature | °C | CHELSA (https://chelsa-climate.org/ (accessed on 12 March 2023)) |
| Bio2 | Mean diurnal range | °C | ||
| Bio3 | Isothermality | - | ||
| Bio5 | Max temperature of warmest month | - | ||
| Bio12 | Annual precipitation | mm | ||
| Bio15 | Precipitation seasonality | mm | ||
| Bio16 | Precipitation of wettest quarter | mm | ||
| Bio18 | Precipitation of warmest | mm | ||
| Bio19 | Precipitation of coldest quarter | mm | ||
| Sea–land topography | Ele | Elevation | m | National Marine Data Center (http://mds.nmdis.org.cn/ (accessed on 12 March 2023)), Slop and Aspe are extracted from the sea–land topography by ArcGIS. |
| Slop | Slope | ° | ||
| Aspe | Aspect | ° | ||
| Marine environment | CHL | Chlorophyll concentration | µg/L | NASA MODIS-Aqua Level-3 (http://oceancolor.gsfc.nasa.gov (accessed on 12 March 2023)) |
| PAR | Photosynthetically available radiation | E/m2day | ||
| SSS | Annual mean sea surface salinity | % | National Marine Data Center (http://mds.nmdis.org.cn/ (accessed on 12 March 2023)) | |
| SST1 | Annual mean sea surface temperature | °C | NASA MODIS-Aqua Level-3 (http://oceancolor.gsfc.nasa.gov (accessed on 12 March 2023)) | |
| SST2 | Sea surface temperature of warmest quarter | °C | ||
| SST3 | Sea surface temperature of wettest quarter | °C | ||
| SST4 | Sea surface temperature of coldest quarter | °C | ||
| SST5 | Sea surface temperature of driest quarter | °C |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, J.; Wei, H.; Chen, R.; Liu, J.; Wang, L.; Gu, W. Invasive Trends of Spartina alterniflora in the Southeastern Coast of China and Potential Distributional Impacts on Mangrove Forests. Plants 2023, 12, 1923. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12101923
Zheng J, Wei H, Chen R, Liu J, Wang L, Gu W. Invasive Trends of Spartina alterniflora in the Southeastern Coast of China and Potential Distributional Impacts on Mangrove Forests. Plants. 2023; 12(10):1923. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12101923
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Jiaying, Haiyan Wei, Ruidun Chen, Jiamin Liu, Lukun Wang, and Wei Gu. 2023. "Invasive Trends of Spartina alterniflora in the Southeastern Coast of China and Potential Distributional Impacts on Mangrove Forests" Plants 12, no. 10: 1923. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12101923
APA StyleZheng, J., Wei, H., Chen, R., Liu, J., Wang, L., & Gu, W. (2023). Invasive Trends of Spartina alterniflora in the Southeastern Coast of China and Potential Distributional Impacts on Mangrove Forests. Plants, 12(10), 1923. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12101923







