Combined Application of Organic Fertilizer with Microbial Inoculum Improved Aggregate Formation and Salt Leaching in a Secondary Salinized Soil
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Result
2.1. Soil Nutrients with Bio-Organic Fertilizer
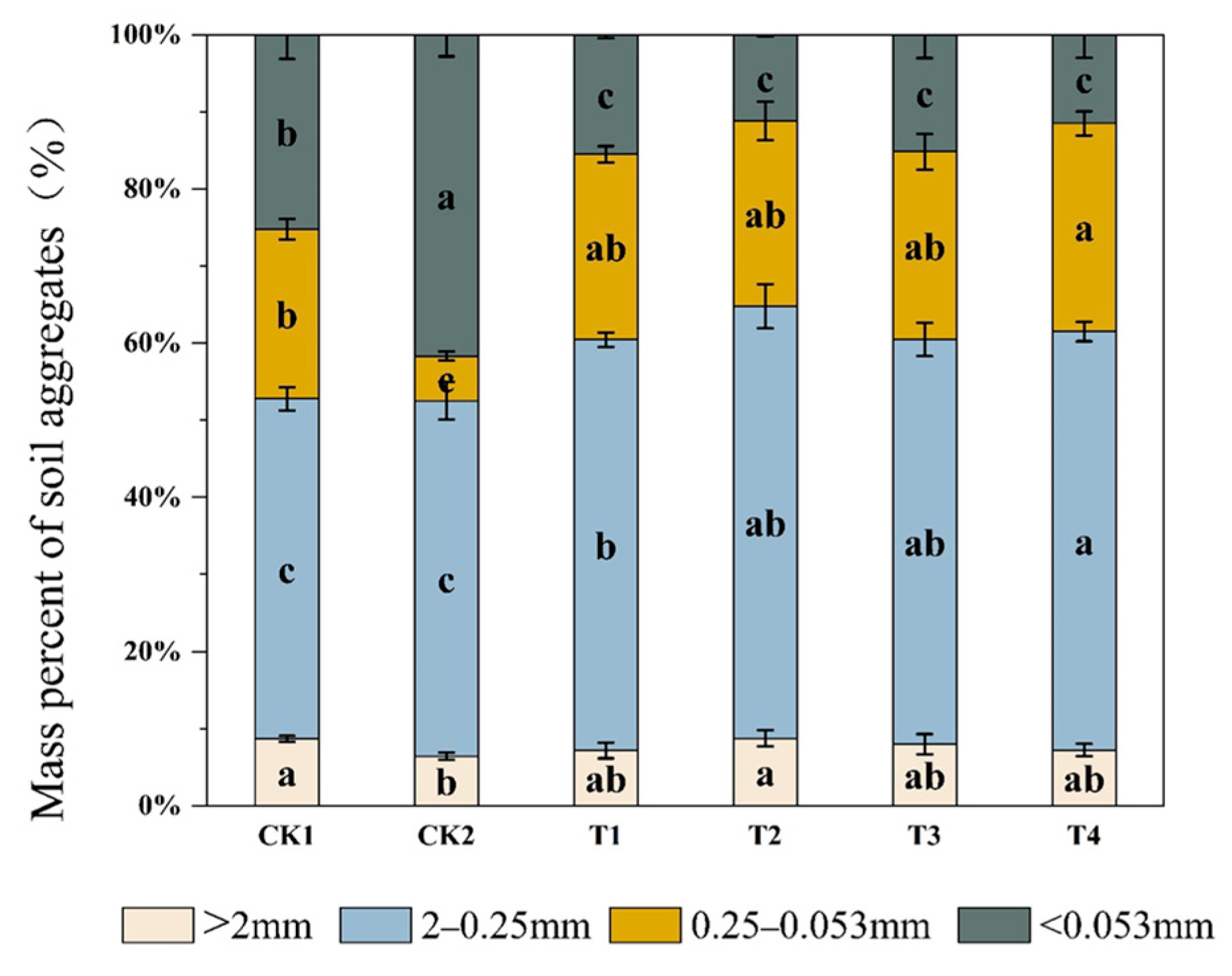
2.2. Effect of Bio-Organic Fertilizer on Soil Aggregate Formation
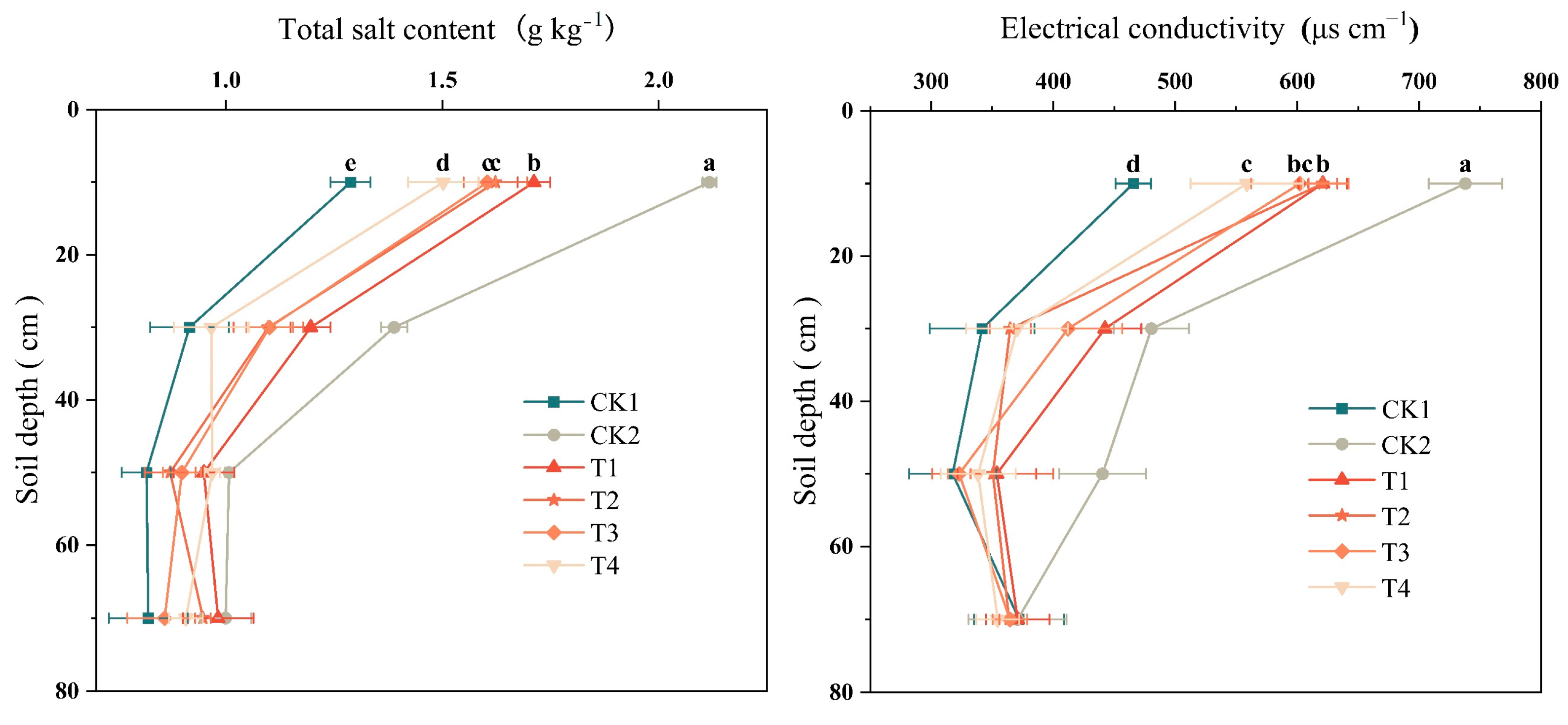
2.3. Effect of Bio-Organic Fertilizer on Soil EC and Total Salt Content
2.4. Effect of Bio-Organic Fertilizer on Anion and Cation Contents
2.4.1. Soil Anions
2.4.2. Soil Cations
2.5. Relationships between Soil Aggregates and Soil Salinity, Soil Nutrients
2.6. Effect of Bio-Organic Fertilizer on Cucumber Yield
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Site Description
4.2. Experimental Design and Management
4.3. Soil Sample Collection and Analysis
4.4. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aznar-Sánchez, J.A.; Piquer-Rodríguez, M.; Velasco-Muñoz, J.F.; Manzano-Agugliaro, F. Worldwide Research Trends on Sustainable Land Use in Agriculture. Land Use Policy 2019, 87, 104069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aznar-Sánchez, J.A.; Velasco-Muñoz, J.F.; López-Felices, B.; Román-Sánchez, I.M. An Analysis of Global Research Trends on Greenhouse Technology: Towards a Sustainable Agriculture. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 22, 664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Wan, X.; Liu, X.; Chen, Y.; Slaughter, L.C.; Weindorf, D.C.; Dong, Y. Changes in Soil Physical and Chemical Characteristics in Intensively Cultivated Greenhouse Vegetable Fields in North China. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 195, 104366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Sun, D.; Tang, Y.; Zhu, R.; Li, X.; Gruda, N.; Dong, J.; Duan, Z. Plastic Shed Soil Salinity in China: Current Status and next Steps. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 296, 126453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otlewska, A.; Migliore, M.; Dybka-Stępień, K.; Manfredini, A.; Struszczyk-Świta, K.; Napoli, R.; Białkowska, A.; Canfora, L.; Pinzari, F. When Salt Meddles Between Plant, Soil, and Microorganisms. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 553087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rath, K.M.; Rousk, J. Salt Effects on the Soil Microbial Decomposer Community and Their Role in Organic Carbon Cycling: A Review. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 81, 108–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Six, J.; Bossuyt, H.; Degryze, S.; Denef, K. A History of Research on the Link between (Micro)Aggregates, Soil Biota, and Soil Organic Matter Dynamics. Soil Tillage Res. 2004, 79, 7–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Six, J.; Elliott, E.T.; Paustian, K. Soil Macroaggregate Turnover and Microaggregate Formation: A Mechanism for C Sequestration under No-Tillage Agriculture. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2000, 32, 2099–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Zhang, S.; Liu, L.; Liu, J.; Ding, X. Organic Fertilization Increased Soil Organic Carbon Stability and Sequestration by Improving Aggregate Stability and Iron Oxide Transformation in Saline-Alkaline Soil. Plant Soil 2022, 474, 233–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.; Ma, X.; Zhang, J.; Yu, Z. The Long-Term Effects of Cattle Manure Application to Agricultural Soils as a Natural-Based Solution to Combat Salinization. CATENA 2019, 175, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wei, W.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Ding, X. Fertilization Effects on Microbial Community Composition and Aggregate Formation in Saline-alkaline Soil. Plant Soil 2021, 463, 523–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Orenes, F.; Guerrero, C.; Mataix-Solera, J.; Navarro-Pedreño, J.; Gómez, I.; Mataix-Beneyto, J. Factors Controlling the Aggregate Stability and Bulk Density in Two Different Degraded Soils Amended with Biosolids. Soil Tillage Res. 2005, 82, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Chen, Q.; Wu, L.; Yang, H.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Y. Coastal Saline Soil Aggregate Formation and Salt Distribution Are Affected by Straw and Nitrogen Application: A 4-Year Field Study. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 198, 104535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Yu, F.; Zhai, C.; Zhong, R.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Meng, Q. Long-Term Effects of Cattle Manure Application on the Soil Aggregate Stability of Salt-Affected Soil on the Songnen Plain of North-Eastern China. J. Soils Sediments 2023, 23, 344–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sądej, W.; Żołnowski, A.C. Comparison of the Effect of Various Long-Term Fertilization Systems on the Content and Fractional Composition of Humic Compounds in Lessive Soil. Plant Soil Environ. 2019, 65, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, P.; Li, Y.; Lai, D.; Geng, L.; Liu, C.; Zhang, J.; Shu, C.; Liu, R. Protaetia Brevitarsis Larvae Can Feed on and Convert Spent Mushroom Substrate from Auricularia Auricula and Lentinula Edodes Cultivation. Waste Manag. 2020, 114, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coban, O.; De Deyn, G.B.; van der Ploeg, M. Soil Microbiota as Game-Changers in Restoration of Degraded Lands. Science 2022, 375, abe0725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Cao, M.; Sang, C.; Li, T.; Zhang, Y.; Chang, Y.; Li, L. Trichoderma Bio-Fertilizer Decreased C Mineralization in Aggregates on the Southern North China Plain. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, P.; Ouyang, Z.; Hou, R.; Han, D. Effects of Application of Microbial Fertilizer on Aggregation and Aggregate-Associated Carbon in Saline Soils. Soil Tillage Res. 2017, 168, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Jia, X.; Li, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Hou, J.; Wang, X. Associative Effectiveness of Bio-Organic Fertilizer and Soil Conditioners Derived from the Fermentation of Food Waste Applied to Greenhouse Saline Soil in Shan Dong Province, China. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2021, 167, 104006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.-H.; Zheng, J.-H.; Shao, X.-H.; Shen, S.-S.; Yu, Z.-H.; Mao, X.-Y.; Chang, T.-T. Effects of Trichoderma Harzianum T83 on Suaeda Salsa L. in Coastal Saline Soil. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 91, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahin, U.; Eroğlu, S.; Sahin, F. Microbial Application with Gypsum Increases the Saturated Hydraulic Conductivity of Saline–Sodic Soils. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2011, 48, 247–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallenbach, C.M.; Frey, S.D.; Grandy, A.S. Direct Evidence for Microbial-Derived Soil Organic Matter Formation and Its Ecophysiological Controls. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, M.; Wang, C.; Liu, X.; Lu, Y.; Wang, Y. Saline-Alkali Soil Applied with Vermicompost and Humic Acid Fertilizer Improved Macroaggregate Microstructure to Enhance Salt Leaching and Inhibit Nitrogen Losses. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2020, 156, 103705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Wang, C.; Wang, F.; Xie, Y. Vermicompost and Humic Fertilizer Improve Coastal Saline Soil by Regulating Soil Aggregates and the Bacterial Community. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2019, 65, 281–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; La, S.; Zhang, X.; Gao, L.; Tian, Y. Salt-Induced Recruitment of Specific Root-Associated Bacterial Consortium Capable of Enhancing Plant Adaptability to Salt Stress. ISME J. 2021, 15, 2865–2882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, O.Y.A.; Raaijmakers, J.M.; Kuramae, E.E. Microbial Extracellular Polymeric Substances: Ecological Function and Impact on Soil Aggregation. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ritz, K.; Young, I.M. Interactions between Soil Structure and Fungi. Mycologist 2004, 18, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qurashi, A.W.; Sabri, A.N. Bacterial Exopolysaccharide and Biofilm Formation Stimulate Chickpea Growth and Soil Aggregation under Salt Stress. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2012, 43, 1183–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Daynes, C.N.; Field, D.J.; Saleeba, J.A.; Cole, M.A.; McGee, P.A. Development and Stabilisation of Soil Structure via Interactions between Organic Matter, Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi and Plant Roots. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 57, 683–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chenu, C.; Cosentino, D. Microbial Regulation of Soil Structural Dynamics. In The Architecture and Biology of Soils: Life in Inner Space; Ritz, K., Young, I., Eds.; CABI: London, UK, 2011; pp. 37–70. ISBN 978-1-84593-532-0. [Google Scholar]
- Nisha, R.; Kiran, B.; Kaushik, A.; Kaushik, C.P. Bioremediation of Salt Affected Soils Using Cyanobacteria in Terms of Physical Structure, Nutrient Status and Microbial Activity. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 15, 571–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.; Bainard, L.D.; Ma, B.; Liu, J. Bio-Fertilizer and Rotten Straw Amendments Alter the Rhizosphere Bacterial Community and Increase Oat Productivity in a Saline–Alkaline Environment. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 19896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, Y. A Sustainable Approach for Removing Nitrate: Studying the Nitrate Transformation and Metabolic Potential under Different Carbon Source by Microorganism. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 10, 131169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Gu, L.; Bao, L.; Zhang, S.; Wei, Y.; Bai, Z.; Zhuang, G.; Zhuang, X. Application of Biofertilizer Containing Bacillus Subtilis Reduced the Nitrogen Loss in Agricultural Soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 148, 107911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anees, M.; Qayyum, A.; Jamil, M.; Rehman, F.U.; Abid, M.; Malik, M.S.; Yunas, M.; Ullah, K. Role of Halotolerant and Chitinolytic Bacteria in Phytoremediation of Saline Soil Using Spinach Plant. Int. J. Phytorem. 2020, 22, 653–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrivastava, P.; Kumar, R. Soil Salinity: A Serious Environmental Issue and Plant Growth Promoting Bacteria as One of the Tools for Its Alleviation. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2015, 22, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sheldon, A.R.; Dalal, R.C.; Kirchhof, G.; Kopittke, P.M.; Menzies, N.W. The Effect of Salinity on Plant-Available Water. Plant Soil 2017, 418, 477–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.L.; Mylon, S.E.; Elimelech, M. Aggregation Kinetics of Alginate-Coated Hematite Nanoparticles in Monovalent and Divalent Electrolytes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 1516–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bremner, J.M. Determination of Nitrogen in Soil by the Kjeldahl Method. J. Agric. Sci. 1960, 55, 11–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, S.R. Estimation of Available Phosphorus in Soils by Extraction with Sodium Bicarbonate; Circular/United States Department of Agriculture; no. 939; U.S. Dept. of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1954.
- Storie, R.E. Methods of Chemical Analysis for Soil Survey Samples: By A. J. Metson, New Zealand Department of Scientific and Industrial Research, Soil Bureau, Bulletin 12, 208 Pp., 1956. 30s. Agron. J. 1957, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walkley, A. A Critical Examination of a Rapid Method for Determining Organic Carbon in SOILS—EFFECT of Variations in Digestion Conditions and of Inorganic Soil Constituents. Soil Sci. 1947, 63, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pribyl, D.W. A Critical Review of the Conventional SOC to SOM Conversion Factor. Geoderma 2010, 156, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cambardella, C.A.; Elliott, E.T. Carbon and Nitrogen Distribution in Aggregates from Cultivated and Native Grassland Soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1993, 57, 1071–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van Bavel, C.H.M. Mean Weight-Diameter of Soil Aggregates as a Statistical Index of Aggregation. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1950, 14, 20–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kemper, W.D.; Rosenau, R.C. Aggregate Stability and Size Distribution. In SSSA Book Series; Klute, A., Ed.; Soil Science Society of America, American Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA, 2018; pp. 425–442. ISBN 978-0-89118-864-3. [Google Scholar]




| Treatments | SOM | TN | AP | AK |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (g kg−1) | (g kg−1) | (mg kg−1) | (mg kg−1) | |
| CK1 | 57.32 ± 0.71 e | 3.04 ± 0.05 bc | 227.6 ± 17.15 d | 399.1 ± 28.43 c |
| CK2 | 59.36 ± 0.70 de | 3.03 ± 0.05 c | 264.4 ± 13.02 c | 472.0 ± 3.41 b |
| T1 | 66.32 ± 4.26 cd | 3.42 ± 0.87 abc | 267.3 ± 14.24 c | 522.6 ± 21.26 a |
| T2 | 70.74 ± 1.34 bc | 3.86 ± 0.30 a | 432.2 ± 18.91 a | 543.0 ± 7.88 a |
| T3 | 74.24 ± 3.16 ab | 3.79 ± 0.23 ab | 357.2 ± 15.06 b | 527.8 ± 20.52 a |
| T4 | 78.56 ± 0.55 a | 4.03 ± 0.43 a | 337.2 ± 16.46 b | 536.4 ± 18.63 a |
| Treatments | MWD (mm) | GWD (mm) | WR0.25 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK1 | 0.97 ± 0.03 b | 0.32 ± 0.03 c | 0.53 ± 0.02 c |
| CK2 | 0.86 ± 0.03 c | 0.23 ± 0.02 d | 0.52 ± 0.02 c |
| T1 | 0.99 ± 0.04 b | 0.43 ± 0.01 b | 0.60 ± 0.08 b |
| T2 | 1.11 ± 0.04 a | 0.52 ± 0.01 a | 0.65 ± 0.02 a |
| T3 | 1.03 ± 0.04 b | 0.44 ± 0.02 b | 0.60 ± 0.01 b |
| T4 | 1.01 ± 0.04 b | 0.47 ± 0.04 b | 0.61 ± 0.01 b |
| pH | SOM (g kg−1) | TN (g kg−1) | AP (mg kg−1) | AK (mg kg−1) | TSC (g kg−1) | EC (dS m−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7.26 | 62.5 | 3.23 | 289.9 | 137.5 | 4.63 | 1.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peng, Y.; Zhang, H.; Lian, J.; Zhang, W.; Li, G.; Zhang, J. Combined Application of Organic Fertilizer with Microbial Inoculum Improved Aggregate Formation and Salt Leaching in a Secondary Salinized Soil. Plants 2023, 12, 2945. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12162945
Peng Y, Zhang H, Lian J, Zhang W, Li G, Zhang J. Combined Application of Organic Fertilizer with Microbial Inoculum Improved Aggregate Formation and Salt Leaching in a Secondary Salinized Soil. Plants. 2023; 12(16):2945. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12162945
Chicago/Turabian StylePeng, Yuanyuan, He Zhang, Jinshan Lian, Wen Zhang, Guihua Li, and Jianfeng Zhang. 2023. "Combined Application of Organic Fertilizer with Microbial Inoculum Improved Aggregate Formation and Salt Leaching in a Secondary Salinized Soil" Plants 12, no. 16: 2945. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12162945
APA StylePeng, Y., Zhang, H., Lian, J., Zhang, W., Li, G., & Zhang, J. (2023). Combined Application of Organic Fertilizer with Microbial Inoculum Improved Aggregate Formation and Salt Leaching in a Secondary Salinized Soil. Plants, 12(16), 2945. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12162945






