A High-Resolution Linkage Map Construction and QTL Analysis for Morphological Traits in Anthurium (Anthurium andraeanum Linden)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Phenotypic Analysis
2.2. SLAF Sequencing Data Analysis and Genotyping
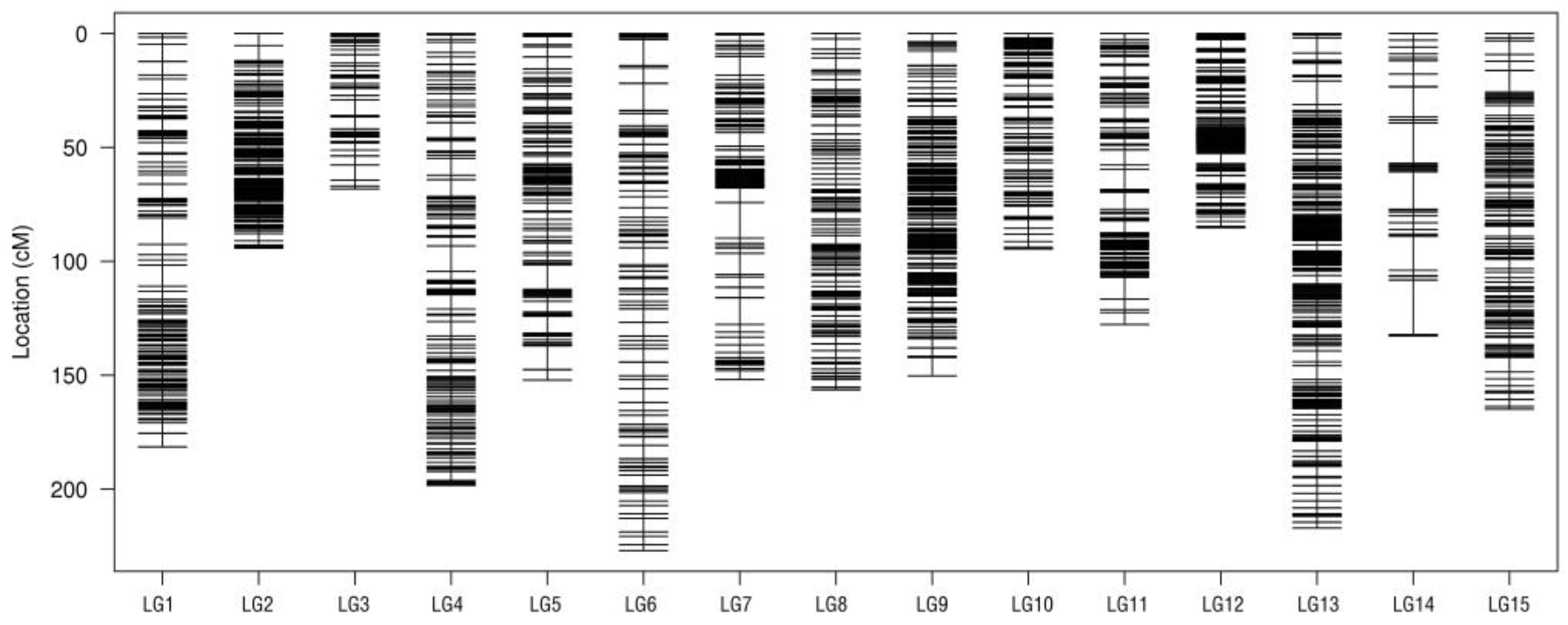
2.3. High-Density Genetic Map Construction
2.4. QTL Analysis of Morphological Traits
3. Discussion
3.1. Constructing Linkage Map in Anthurium
3.2. Segregation Distortion Markers
3.3. QTLs Related to Morphological Traits
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials and DNA Extraction
4.2. Phenotypic Measured and Statistical Analysis
4.3. SLAF library Construction and Sequencing
4.4. SNP Markers Detecting and Genotyping
4.5. Linkage Map Construction
4.6. QTL Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carlsen, M.M.; Croat, T.B. An analysis of the sectional classification of Anthurium (Araceae): Comparing infrageneric groupings and their diagnostic morphology with a molecular phylogeny of the genus. Ann. Mo. Bot. Gard. 2019, 104, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; McConnell, D.B.; Henny, R.J.; Everitt, K.C. Cultural guidelines for commercial production of interiorscape anthurium. IFAS Ext. 2021, 956, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, A.F.M.J.; Shahrin, S.; Roni, M.Z.K.; Mehraj, H.; Islam, M.S. Varietal study of Anthurium (Anthurium andraeanum) as a cut flower in Bangladesh. J. Bangladesh Acad. Sci. 2013, 37, 103–107. [Google Scholar]
- Elibox, W.; Umaharan, P. Inheritance of major spathe colors in Anthurium andraeanum Hort. is determined by three major genes. HortScience 2008, 43, 787–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avila-Rostant, O.; Lennon, A.M.; Umaharan, P. Spathe color variation in Anthurium andraeanum Hort. and its relationship to vacuolar pH. HortScience 2010, 45, 1768–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopaulchan, D.; Umaharan, P.; Lennon, A.M.A. Molecular assessment of the genetic model of spathe color inheritance in Anthurium andraeanum (Hort.). Planta 2014, 239, 695–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osorio-Guarin, J.A.; Gopaulchan, D.; Quackenbush, C.; Lennon, A.M.; Umaharan, P.; Cornejo, O.E. Comparative transcriptomic analysis reveals key components controlling spathe color in Anthurium andraeanum (Hort.). PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0261364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Zhang, F.; Shen, X.; Yu, Y.; Pan, X.; Liu, X.; Liu, J.; Pan, G.; Tian, D. Genetic variations within a collection of anthuriums unraveled by morphological traits and AFLP markers. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2012, 45, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croat, T.B. Araceae, a family with great potential. Ann. Mo. Bot. Gard. 2019, 104, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubo, N.; Saito, M.; Tsukazaki, H.; Kondo, T.; Matsumoto, S.; Hirai, M. Detection of quantitative trait loci controlling morphological traits in Brassica rapa L. Breeding Sci. 2010, 60, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Huang, L.; He, H.; Chen, W.; Ren, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, X.; Xia, Y.; Wang, X.; Jiang, X.; Liao, B.; et al. Quantitative trait locus analysis of agronomic and quality-related traits in cultivated peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 2015, 128, 1103–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulz, D.; Linde, M.; Debener, T. Detection of reproducible major effect QTL for petal traits in garden roses. Plants 2021, 10, 897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henz, A.; Debener, T.; Linde, M. Identification of major stable QTLs for flower color in roses. Mol. Breeding. 2015, 35, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagi, M.; Shirasawa, K.; Hirakawa, H.; Isobe, S.; Matsuno, J.; Uno, Y.; Tanase, K.; Onozaki, T.; Yamaguchi, H. QTL analysis for flowering time in carnation (Dianthus caryophyllus L.). Sci. Hortic. 2020, 262, 109053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Xu, Y.; Gao, K.; Fan, G.; Zhang, F.; Deng, C.; Dai, S.; Huang, H.; Xin, H.; Li, Y. High-density genetic map construction and identification of loci controlling flower-type traits in Chrysanthemum (Chrysanthemum x morifolium Ramat.). Hortic Res. 2020, 7, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pourbeyrami Hir, Y.; Yuan, S.; Torabi Giglou, M.; Jun, M. QTLs position of some important ornamental traits in recently developed OO lily population. Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plants. 2019, 25, 1419–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakano, M.; Nakatsuka, A.; Nakayama, M.; Koshioka, M.; Yamagishi, M. Mapping of quantitative trait loci for carotenoid pigmentation in flower tepals of Asiatic hybrid lily. Sci. Hortic. 2005, 104, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Guo, Y.; Yang, Q.; He, Y.; Fetouh, M.I.; Warner, R.M.; Deng, Z. Genome-wide identification of quantitative trait loci for important plant and flower traits in petunia using a high-density linkage map and an interspecific recombinant inbred population derived from Petunia integrifolia and P. axillaris. Hortic Res. 2019, 6, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Guo, L.L.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.X.; Ma, H.L.; Guo, D.L.; Hou, X.G. Construction of a genetic linkage map in tree peony (Paeonia Sect. Moutan) using simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers. Sci. Hortic. 2017, 219, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagi, M. Recent progress in whole genome sequencing, high-density linkage maps, and genomic databases of ornamental plants. Breed Sci. 2018, 68, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.Q.; Wang, L.Y.; Xu, L.Y.; Wu, L.Y.; Peng, M.; Zhang, C.C.; Wei, K.; Bai, P.X.; Li, H.L.; Cheng, H.; et al. SSR-based genetic mapping and QTL analysis for timing of spring bud flush, young shoot color, and mature leaf size in tea plant (Camellia sinensis). Tree Genet. Genomes 2016, 12, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Jia, J.; Wei, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, L.; Chen, H.; Fan, Y.; Sun, H.; Zhao, X.; Lei, T.; et al. A intervarietal genetic map and QTL analysis for yield traits in wheat. Mol. Breed. 2007, 20, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, T.H.; van Eck, H.J.; De Jeu, M.J.; Jacobsen, E. Mapping of quantitative trait loci involved in ornamental traits in Alstroemeria. HortScience 2002, 37, 585–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Liu, D.; Zhang, X.; Li, W.; Liu, H.; Hong, W.; Jiang, C.; Guan, N.; Ma, C.; Zeng, H.; et al. SLAF-seq: An efficient method of large-scale de novo SNP discovery and genotyping using high-throughput sequencing. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e58700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Q.; Wang, W.; Hu, T.; Hu, H.; Wang, J.; Bao, C. Construction of a SNP-based genetic map using SLAF-Seq and QTL analysis of morphological traits in eggplant. Front Genet 2020, 11, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Yang, L.; Shi, C.; Li, S.; Tang, H.; He, C.; Cai, N.; Duan, A.; Gong, H. QTL mapping for growth-related traits by constructing the first genetic linkage map in Simao pine. BMC Plant. Biol. 2022, 22, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, F.C.; Chen, Z.; Wang, X.H.; Wang, J.B.; Fan, H.Y.; Qin, Y.H.; Zhao, J.T.; Hu, G.B. Construction of high-density SNP genetic maps and QTL mapping for dwarf-related traits in Litchi chinensis Sonn. J. Integr. Agric. 2021, 20, 2900–2913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, F.; Gong, H.; Li, Z.; Zeng, S.; Yang, T.; Ai, P.; Pan, L.; Huang, H.; Wang, Y. Identification of fruit size associated quantitative trait loci featuring SLAF based high-density linkage map of goji berry (Lycium spp.). BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira da Silva, J.A.; Dobránszki, J.; Zeng, S.; Winarto, B.; Lennon, A.M.; Jaufeerally-Fakim, Y.; Christopher, D.A. Genetic transformation and molecular research in Anthurium: Progress and prospects. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. 2015, 123, 205–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkat, S.K.; Bommisetty, P.; Patil, M.S.; Reddy, L.; Chennareddy, A. The genetic linkage maps of Anthurium species based on RAPD, ISSR and SRAP markers. Sci. Hortic. 2014, 178, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.; Cheng, F.Y.; Wu, J.; Zhong, Y.; Liu, G. The first high-density genetic map construction in tree peony (Paeonia Sect. Moutan) using genotyping by specific-locus amplified fragment sequencing. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0128584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Ma, C.; Hong, W.; Huang, L.; Liu, M.; Liu, H.; Zeng, H.; Deng, D.; Xin, H.; Song, J.; et al. Construction and analysis of high-density linkage map using high-throughput sequencing data. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheffer, R.D.; Croat, T.B. Chromosome numbers in the genus Anthurium (Araceae) II. Am. J. Bot. 1983, 70, 858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyttle, T.W. Cheaters sometimes prosper: Distortion of Mendelian segregation by meiotic drive. Trends Genet. 1993, 9, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sibov, S.T.; Lopes De Souza, C., Jr.; Garcia, A.A.F.; Garcia, A.F.; Silva, A.R.; Mangolin, C.A.; Benchimol, L.A.; De Souza, A.P. Molecular mapping in tropical maize (Zea mays L.) using microsatellite markers. 1. Map construction and localization of loci showing distorted segregation. Hereditas 2003, 139, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Lashermes, P.; Combes, M.C.; Prakash, N.S.; Trouslot, P.; Lorieux, M.; Charrier, A. Genetic linkage map of Coffea canephora: Effect of segregation distortion and analysis of recombination rate in male and female meioses. Genome 2001, 44, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coulton, A.; Przewieslik-Allen, A.M.; Burridge, A.J.; Shaw, D.S.; Edwards, K.J.; Barker, G.L.A. Segregation distortion: Utilizing simulated genotyping data to evaluate statistical methods. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0228951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hackett, C.A.; Broadfoot, L.B. Effects of genotyping errors, missing values and segregation distortion in molecular marker data on the construction of linkage maps. Heredity 2003, 90, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, S.; Li, H.; Deng, Q.; Zheng, A.; Li, S.; Li, P.; Li, Z.; Wang, J. Effects of missing marker and segregation distortion on QTL mapping in F2 populations. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2010, 121, 1071–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, J.F.; Niu, Y.; Cheng, P.; Feng, J.Y.; Han, S.F.; Zhang, Y.H.; Shu, G.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.M. Effect of marker segregation distortion on high density linkage map construction and QTL mapping in Soybean (Glycine max L.). Heredity 2019, 123, 579–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaprada, N.V.T.; Geekiyanage, S. Analysis of morphological variation of anthurium from southern Sri Lank. Bangl. J. Bot. 2017, 46, 799–804. [Google Scholar]
- Roni, M.Z.K.; Ahmad, H.; Mirana, A.S.; Islam, M.S.; Uddin, A.J. Study on morpho-physiological characteristics of five anthurium varieties. Nternational J.Bus. Soc. Sci. Res. 2016, 4, 103–110. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, L.; Wang, Y.; Yan, X.; Cheng, T.; Ma, K.; Yang, W.; Pan, H.; Zheng, C.; Zhu, X.; Wang, J.; et al. Genetic control of juvenile growth and botanical architecture in an ornamental woody plant, Prunus mume Sieb. et Zucc. as revealed by a high-density linkage map. BMC Genet. 2014, 15, 1471–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Sang, M.; Wen, Z.; Meng, J.; Cheng, T.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, L. Mapping floral genetic architecture in Prunus mume, an ornamental woody plant. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 828579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, W.H.; Wang, P.; Chen, H.X.; Zhou, H.J.; Li, Q.P.; Wang, C.R.; Ding, Z.H.; Zhang, Y.S.; Yu, S.B.; Xing, Y.Z.; et al. A major QTL, Ghd8, plays pleiotropic roles in regulating grain productivity, plant height, and heading date in rice. Mol. Plant 2011, 4, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Cheng, X.; Chai, L.; Wang, Z.; Du, D.; Wang, Z.; Bian, R.; Zhao, A.; Xin, M.; Guo, W.; et al. Pleiotropic QTL influencing spikelet number and heading date in common wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 2020, 133, 1825–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, J.; Liu, D.; Qi, Y.; Ma, J.; Zhen, W. Major QTL for seven yield-related traits in common wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Front Genet. 2020, 11, 1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Zhou, R.; Dossou, S.S.K.; Song, S.; Wang, L. Fine mapping of a major pleiotropic QTL associated with sesamin and sesamolin variation in Sesame (Sesamum indicum L.). Plants 2021, 10, 1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.Q.; Sheng, X.G.; Yu, H.F.; Wang, J.S.; Shen, Y.S.; Gu, H.H. Identification of QTLs associated with curd architecture in cauliflower. BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moursi, Y.S.; Thabet, S.G.; Amro, A.; Dawood, M.F.A.; Baenziger, P.S.; Sallam, A. Detailed genetic analysis for identifying QTLs associated with drought tolerance at seed germination and seedling stages in barley. Plants 2020, 9, 1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elibox, W.; Umaharan, P. A study of morphophysiological descriptors of cultivated Anthurium andraeanum Hort. HortScience 2012, 47, 1234–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Xin, H.; Li, D.; Ma, C.; Ding, X.; Hong, W.; Zhang, X. Construction of a high-density genetic map for sesame based on large scale marker development by specific length amplified fragment (SLAF) sequencing. BMC Plant Biol. 2013, 13, 1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Meng, L.; Wu, W.; Wang, J. GACD: Integrated software for genetic analysis in clonal F1 and double cross populations. J. Hered. 2015, 106, 741–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

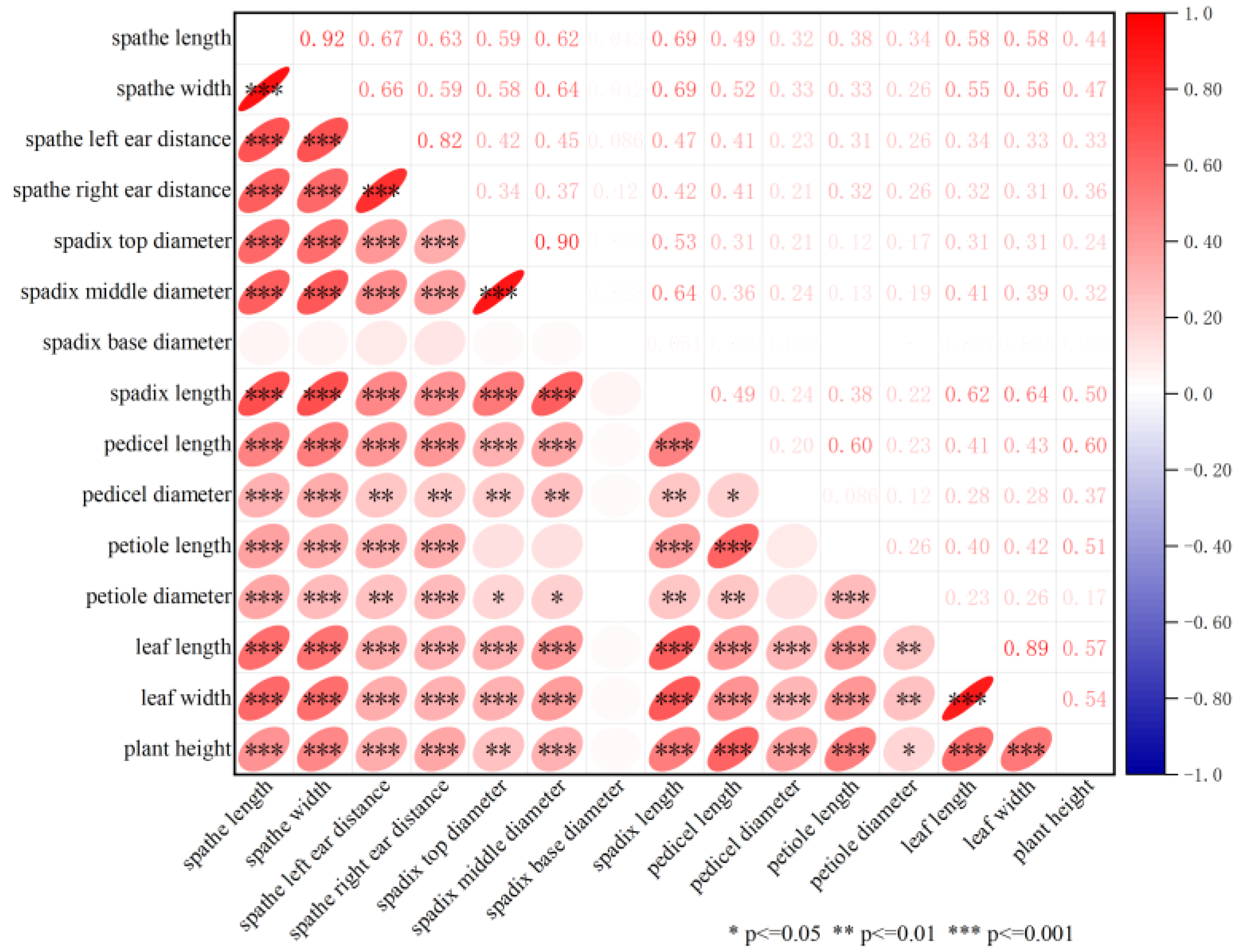

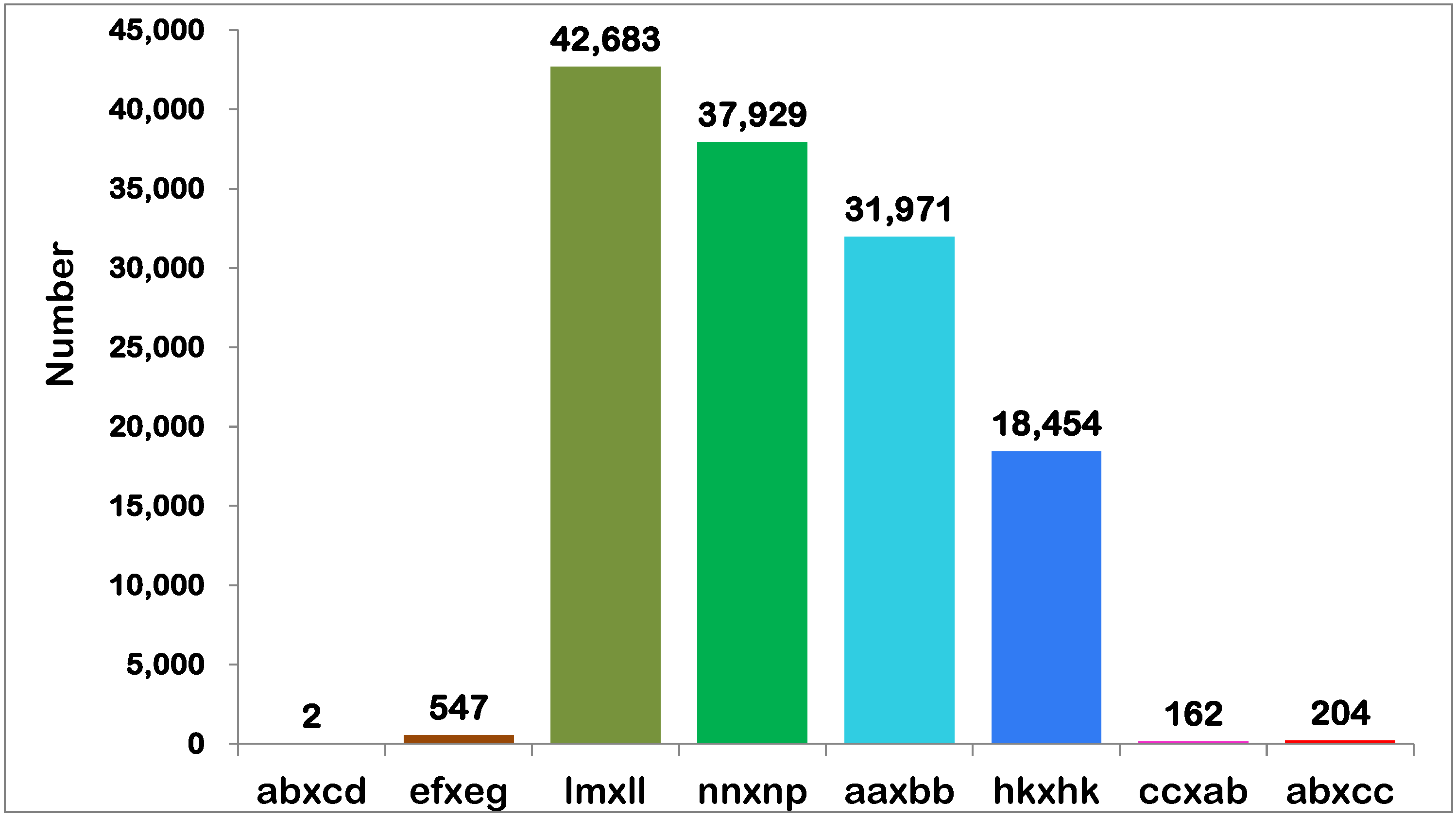
| Traits | Parents | MPs | F1 Population | CV (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ‘Pink Champion’ X ± σ Mean ± SD | ‘Acropolis’ X ± σ Mean ± SD | X ± σ Mean ± SD | Max | Min | Skewness | Kurtosis | |||
| spathe length | 4.76 ± 0.13 | 13.48 ± 0.27 | 9.12 | 10.37 ± 2.52 | 16.6 | 5.7 | 0.39 | −0.28 | 24.27 |
| spathe width | 3.88 ± 0.14 | 11.64 ± 0.18 | 7.76 | 8.81 ± 1.95 | 14.0 | 4.9 | 0.52 | 0.03 | 22.11 |
| spathe left ear distance | 0.58 ± 0.07 | 3.98 ± 0.17 | 2.28 | 2.54 ± 0.87 | 5.4 | 1.2 | 0.70 | −0.18 | 34.04 |
| spathe right ear distance | 0.42 ± 0.06 | 3.88 ± 0.33 | 2.15 | 2.48 ± 0.88 | 4.8 | 0.4 | 0.70 | −0.03 | 35.53 |
| spadix length | 2.72 ± 0.10 | 8.00 ± 0.08 | 5.36 | 5.57 ± 1.46 | 10.1 | 2.4 | 0.18 | −0.59 | 26.13 |
| spadix top diameter | 4.43 ± 0.17 | 5.69 ± 0.20 | 5.06 | 6.21 ± 0.88 | 8.28 | 4.32 | 0.10 | −0.59 | 14.18 |
| spadix middle diameter | 5.46 ± 0.19 | 7.84 ± 0.22 | 6.65 | 8.09 ± 1.36 | 11.45 | 5.1 | 0.39 | −0.18 | 16.80 |
| spadix base diameter | 5.77 ± 0.15 | 8.47 ± 0.14 | 7.12 | 8.67 ± 1.55 | 12.73 | 5.45 | 0.33 | −0.38 | 17.93 |
| pedicel length | 19.58 ± 0.86 | 36.00 ± 1.00 | 27.79 | 33.94 ± 7.40 | 56.4 | 9.4 | 0.09 | 0.62 | 21.82 |
| pedicel diameter | 3.17 ± 0.08 | 6.25 ± 0.12 | 20.74 | 6.47 ± 1.55 | 10.23 | 3.15 | 0.21 | −0.52 | 23.88 |
| petiole length | 15.04 ± 1.06 | 26.4 ± 1.87 | 20.74 | 24.44 ± 5.43 | 37.4 | 7.47 | −0.13 | 0.03 | 22.22 |
| petiole diameter | 3.62 ± 0.19 | 5.53 ± 0.28 | 4.58 | 6.03 ± 0.99 | 8.1 | 3.71 | −0.14 | −0.47 | 16.49 |
| leaf length | 13.28 ± 0.69 | 28.66 ± 0.80 | 20.97 | 25.33 ± 4.49 | 37.2 | 14.5 | 0.11 | −0.32 | 17.72 |
| leaf width | 6.96 ± 0.63 | 15.04 ± 0.54 | 11.00 | 14.76 ± 2.54 | 21.8 | 5.7 | −0.10 | 0.83 | 17.20 |
| plant height | 24.42 ± 0.73 | 44.74 ± 1.22 | 34.58 | 49.15 ± 7.78 | 67.8 | 29.7 | 0.22 | −0.36 | 15.82 |
| Sample | Total Reads | Total bases | Q30 Percentage (%) | GC Percentage (%) | Average Depth |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ‘Pink Champion’ | 9,869,344 | 1,973,515,426 | 96.38 | 39.40 | 80.65× |
| ‘Acropolis’ | 11,383,208 | 2,276,329,712 | 96.53 | 39.29 | 91.85× |
| F1 progeny | 5,790,723 | 1,157,976,894 | 95.80 | 40.53 | 31.68× |
| Oryza sativa subsp. japonica | 404,628 | 80,919,752 | 95.32 | 37.6 | |
| Total | 941,977,531 | 188,368,171,360 | 95.81 | 40.5 |
| Linkage Group ID | Total Distance (cM) | Total Marker | Average Distance (cM) | Gap < 5 cM (%) | Max Gap (cM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LG1 | 181.48 | 290 | 0.63 | 97.23 | 11.63 |
| LG2 | 94.19 | 509 | 0.19 | 99.61 | 6.68 |
| LG3 | 68.23 | 127 | 0.54 | 97.62 | 6.77 |
| LG4 | 198.39 | 230 | 0.87 | 97.38 | 11.16 |
| LG5 | 152.14 | 266 | 0.57 | 98.49 | 10.71 |
| LG6 | 226.98 | 1082 | 0.21 | 98.89 | 11.97 |
| LG7 | 151.14 | 573 | 0.27 | 98.95 | 15.63 |
| LG8 | 156.36 | 678 | 0.23 | 99.85 | 5.34 |
| LG9 | 150.31 | 615 | 0.24 | 99.67 | 8.1 |
| LG10 | 94.5 | 211 | 0.45 | 100.00 | 4.58 |
| LG11 | 127.73 | 338 | 0.38 | 97.63 | 9.57 |
| LG12 | 85.27 | 987 | 0.09 | 100.00 | 4.46 |
| LG13 | 217.11 | 973 | 0.22 | 99.59 | 10.38 |
| LG14 | 132.74 | 1.33 | 1.00 | 91.26 | 23.88 |
| LG15 | 164.93 | 1159 | 0.14 | 99.74 | 9.37 |
| Total | 2202.27 | 9341 | 0.24 | 98.40 | 23.88 |
| Phenotypic Traits | QTLs | LGs | Position (cM) | Left Marker | Right Marker | LOD Threshold | LOD | PVE(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spathe length | qSptL1 a | 1 | 169.22 | Marker125870 | Marker86061 | 4.00 | 4.52 | 6.21 |
| qSptL2 b | 6 | 7.34 | Marker29182 | Marker27771 | 7.61 | 12.08 | ||
| qSptL3 | 8 | 51.54 | Marker22818 | Marker25881 | 8.18 | 12.67 | ||
| qSptL4 c | 10 | 55.88 | Marker75159 | Marker9344 | 56.83 | 7.59 | ||
| Spathe width | qSptW1 a | 1 | 169.22 | Marker125870 | Marker86061 | 3.50 | 3.82 | 9.96 |
| qSptW2 b | 6 | 7.34 | Marker29182 | Marker27771 | 8.94 | 12.43 | ||
| qSptW3 | 6 | 16.06 | Marker129013 | Marker17981 | 3.9 | 8.84 | ||
| qSptW4 | 8 | 14.45 | Marker15415 | Marker18261 | 5.28 | 10.86 | ||
| qSptW5 c | 10 | 55.08 | Marker75159 | Marker9344 | 5.35 | 12.71 | ||
| qSptW6 | 10 | 63.80 | Marker124314 | Marker10075 | 6.55 | 8.31 | ||
| qSptW7 | 12 | 17.15 | Marker1346 | Marker4679 | 4.07 | 8.36 | ||
| Spathe left ear distance | qLED1 | 1 | 112.33 | Marker7131 | Marker130377 | 3.50 | 3.93 | 9.51 |
| qLED2 | 12 | 36.03 | Marker9051 | Marker3948 | 6.76 | 17.21 | ||
| Spathe right ear distance | qRED1 | 1 | 126.35 | Marker25500 | Marker1420 | 3.60 | 32.43 | 17.74 |
| qRED2 e | 1 | 130.34 | Marker17440 | Marker21610 | 25.26 | 11.82 | ||
| qRED3 | 8 | 22.25 | Marker131050 | Marker15414 | 3.6 | 12.79 | ||
| qRED4 d | 9 | 25.17 | Marker12185 | Marker30201 | 4.71 | 12.91 | ||
| Spadix length | qSpdL1 | 2 | 56.70 | Marker46740 | Marker63007 | 3.60 | 3.66 | 12.03 |
| qSpdL2 | 2 | 58.08 | Marker63007 | Marker38589 | 3.78 | 11.92 | ||
| qSpdL3 f | 6 | 3.44 | Marker68802 | Marker28040 | 4.36 | 9.74 | ||
| qSpdL4 | 6 | 12.24 | Marker36909 | Marker129577 | 3.74 | 9.38 | ||
| Spadix top diameter | qSpdTD1 | 1 | 122.98 | Marker5630 | Marker124889 | 3.00 | 5.81 | 10.58 |
| qSpdTD2 f | 6 | 3.44 | Marker68802 | Marker28040 | 6.04 | 9.1 | ||
| qSpdTD3 | 8 | 36.47 | Marker21492 | Marker98352 | 4.87 | 10.47 | ||
| qSpdTD4 | 12 | 75.26 | Marker29474 | Marker10355 | 5.46 | 9.62 | ||
| qSpdTD5 | 12 | 28.42 | Marker129430 | Marker5235 | 5.97 | 10.37 | ||
| Spadix middle diameter | qSpdMD1 | 1 | 125.56 | Marker124889 | Marker25500 | 2.50 | 4.08 | 11 |
| qSpdMD2 e | 1 | 130.34 | Marker17440 | Marker21610 | 4.61 | 9.47 | ||
| qSpdMD3 | 6 | 2.44 | Marker8889 | Marker28041 | 2.75 | 8.51 | ||
| Spadix base diameter | qSpdBD1 e | 1 | 130.44 | Marker17440 | Marker21610 | 2.50 | 4.09 | 11.28 |
| qSpdBD2 | 6 | 6.07 | Marker124707 | Marker32959 | 5.3 | 11.75 | ||
| Pedicel length | qPdL1 d | 9 | 25.17 | Marker12185 | Marker30201 | 3.50 | 3.52 | 11.84 |
| qPdL2 | 12 | 99.32 | Marker27459 | Marker28180 | 4.12 | 8.81 | ||
| qPdL3 | 12 | 29.62 | Marker44684 | Marker44683 | 8.31 | 13.85 | ||
| qPdL4 | 12 | 32.81 | Marker18483 | Marker125128 | 5.85 | 8.79 | ||
| Pedicel diameter | qPdD1 b | 6 | 7.34 | Marker29182 | Marker27771 | 3.50 | 4.03 | 11.16 |
| qPdD2 | 8 | 78.25 | Marker8125 | Marker49700 | 3.71 | 10.85 | ||
| qPdD3 | 10 | 61.33 | Marker9341 | Marker124314 | 26.96 | 8.3 | ||
| qPdD4 | 10 | 64.33 | Marker10075 | Marker7177 | 35.97 | 13.35 | ||
| Petiole length | qPtL1 | 4 | 26.29 | Marker127434 | Marker125835 | 4.10 | 4.17 | 14.01 |
| qPtL2 | 7 | 5.82 | Marker27651 | Marker48346 | 7.98 | 11.45 | ||
| qPtL3 | 12 | 64.64 | Marker1990 | Marker56730 | 6.58 | 9.06 | ||
| Petiole diameter | qPtD1 | 12 | 29.56 | Marker5470 | Marker22855 | 3.20 | 3.3 | 9.94 |
| qPtD2 | 15 | 12.91 | Marker26166 | Marker126412 | 3.23 | 9.83 | ||
| Plant height | qPH1 h | 9 | 127.45 | Marker12865 | Marker37220 | 3.00 | 3.11 | 9.32 |
| Leaf length | qLL1 | 1 | 110.17 | Marker77752 | Marker130680 | 3.00 | 4.2 | 8.96 |
| qLL2 | 4 | 44.40 | Marker22748 | Marker7385 | 4.54 | 13.23 | ||
| qLL3 | 4 | 99.04 | Marker20320 | Marker26418 | 4.64 | 8.47 | ||
| qLL4 | 5 | 100.48 | Marker129900 | Marker129902 | 4.23 | 10.78 | ||
| qLL5 | 7 | 60.07 | Marker124796 | Marker66308 | 4.4 | 11.59 | ||
| qLL6 g | 9 | 108.08 | Marker122327 | Marker7345 | 3.14 | 10.03 | ||
| Leaf width | qLW1 | 2 | 59.54 | Marker63007 | Marker38589 | 3.50 | 4.92 | 9.18 |
| qLW2 b | 6 | 7.34 | Marker29182 | Marker27771 | 4.42 | 11.49 | ||
| qLW3 h | 9 | 108.06 | Marker122327 | Marker7345 | 4.9 | 12.77 | ||
| qLW4 | 9 | 119.05 | Marker78056 | Marker18037 | 6.69 | 11.77 | ||
| qLW5 g | 9 | 127.45 | Marker12865 | Marker37220 | 4.77 | 8.55 | ||
| qLW6 | 12 | 29.97 | Marker44683 | Marker33277 | 4.75 | 12.45 | ||
| qLW7 | 12 | 36.91 | Marker124398 | Marker27267 | 3.57 | 8.68 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, L.; Chen, Y.; Leng, Q.; Lin, X.; Lu, J.; Xu, Y.; Li, H.; Xu, S.; Huang, S.; López Hernán, A.; et al. A High-Resolution Linkage Map Construction and QTL Analysis for Morphological Traits in Anthurium (Anthurium andraeanum Linden). Plants 2023, 12, 4185. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12244185
Zhang L, Chen Y, Leng Q, Lin X, Lu J, Xu Y, Li H, Xu S, Huang S, López Hernán A, et al. A High-Resolution Linkage Map Construction and QTL Analysis for Morphological Traits in Anthurium (Anthurium andraeanum Linden). Plants. 2023; 12(24):4185. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12244185
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Linbi, Yanyan Chen, Qingyun Leng, Xinge Lin, Jinping Lu, Yueting Xu, Haiyan Li, Shisong Xu, Shaohua Huang, Ariel López Hernán, and et al. 2023. "A High-Resolution Linkage Map Construction and QTL Analysis for Morphological Traits in Anthurium (Anthurium andraeanum Linden)" Plants 12, no. 24: 4185. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12244185
APA StyleZhang, L., Chen, Y., Leng, Q., Lin, X., Lu, J., Xu, Y., Li, H., Xu, S., Huang, S., López Hernán, A., Wang, Y., Yin, J., & Niu, J. (2023). A High-Resolution Linkage Map Construction and QTL Analysis for Morphological Traits in Anthurium (Anthurium andraeanum Linden). Plants, 12(24), 4185. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12244185





