Detecting Cotton Leaf Curl Virus Resistance Quantitative Trait Loci in Gossypium hirsutum and iCottonQTL a New R/Shiny App to Streamline Genetic Mapping
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
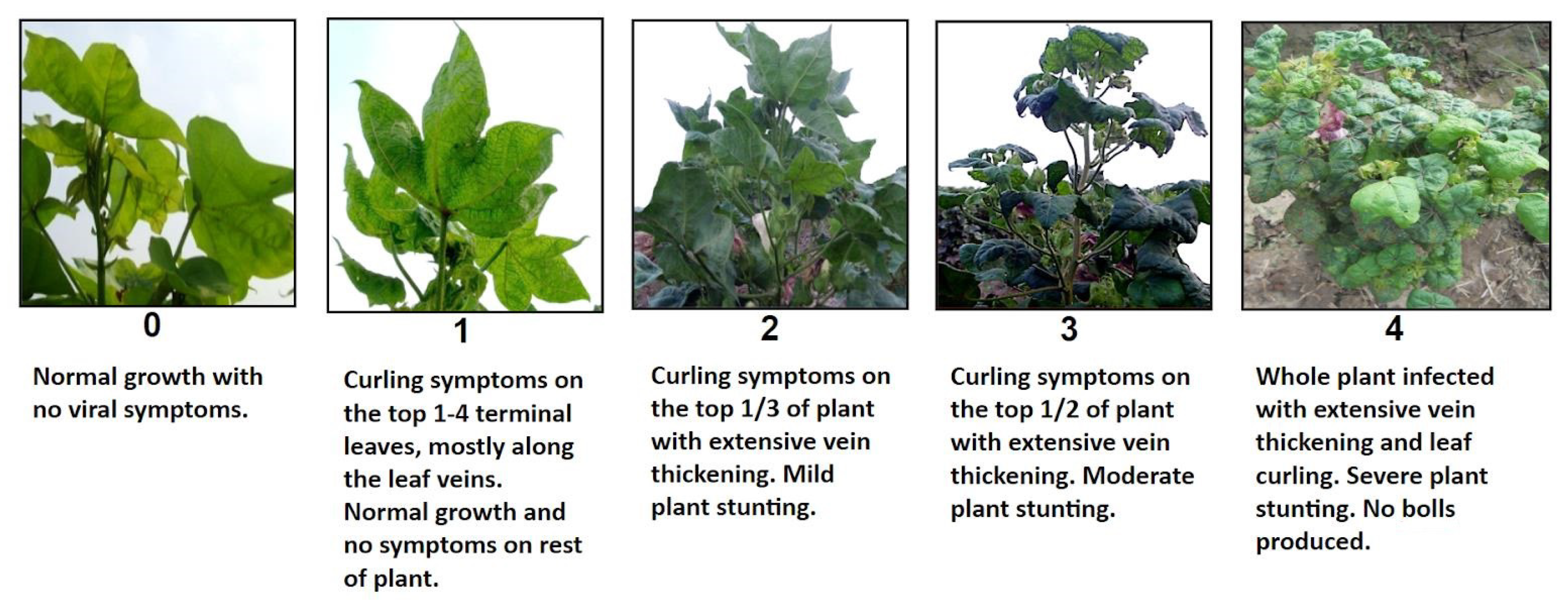
2.1. Phenotyping
2.2. Genetic Mapping
2.3. Marker Assay Development and Validation
2.4. R/Shiny App iCottonQTL
3. Discussion
3.1. Genetic Mapping Was Able to Identify Regions Associated with Disease Resistance
3.2. Multiple Independent Sources of Resistance Indicated
3.3. App for Streamlining Cotton Genetic Mapping
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Material and Phenotyping
4.2. DNA Extraction and Genotyping
4.3. Data Quality-Control and Filtering
4.4. Map Construction
4.5. Quantitative Trait Loci (QTL) Analysis
4.6. Marker Assay Development and Validation
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sattar, M.N.; Kvarnheden, A.; Saeed, M.; Briddon, R.W. Cotton leaf curl disease—An emerging threat to cotton production worldwide. J. Gen. Virol. 2013, 94, 695–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santhanam, K.; Sekaran, S.; Vaikundam, S.; Kumarasamy, A.M. Counterfeit Currency Detection Technique Using Image Processing, Polarization Principle and Holographic Technique. In Proceedings of the 2013 Fifth International Conference on Computational Intelligence, Modelling and Simulation, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 24–26 September 2013; pp. 231–235. [Google Scholar]
- Cororaton, C.B.; Orden, D. Pakistan’s Cotton and Textile Economy: Intersectoral Linkages and Effects on Rural and Urban Poverty; International Food Policy Research Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 2008; Volume 158. [Google Scholar]
- Mansoor, S.; Amin, I.; Iram, S.; Hussain, M.; Zafar, Y.; Malik, K.A.; Briddon, R.W. Breakdown of resistance in cotton to cotton leaf curl disease in Pakistan. Plant Pathol. 2003, 52, 784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansoor, S.; Khan, S.H.; Bashir, A.; Saeed, M.; Zafar, Y.; Malik, K.A.; Briddon, R.; Stanley, J.; Markham, P.G. Identification of a novel circular single-stranded DNA associated with cotton leaf curl disease in Pakistan. Virology 1999, 259, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briddon, R.W.; Markham, P.G. Cotton leaf curl virus disease. Virus Res. 2000, 71, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briddon, R.W.; Mansoor, S.; Bedford, I.D.; Pinner, M.S.; Saunders, K.; Stanley, J.; Zafar, Y.; Malik, K.A.; Markham, P.G. Identification of DNA components required for induction of cotton leaf curl disease. Virology 2001, 285, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.; Khan, A.Q.; Rahmat, Z.; Iqbal, M.A.; Zafar, Y. Genetics and Genomics of Cotton Leaf Curl Disease, Its Viral Causal Agents and Whitefly Vector: A Way Forward to Sustain Cotton Fiber Security. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amrao, L.; Amin, I.; Shahid, M.S.; Briddon, R.W.; Mansoor, S. Cotton leaf curl disease in resistant cotton is associated with a single begomovirus that lacks an intact transcriptional activator protein. Virus Res. 2010, 152, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.H.; Xie, K.; Lin, L.; Qin, B.X.; Chen, B.S.; Meng, J.R.; Liu, Y.L. Cotton leaf curl Multan virus newly reported to be associated with cotton leaf curl disease in China. Plant Pathol. 2010, 59, 794–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulse-Kemp, A.M.; Lemm, J.; Plieske, J.; Ashrafi, H.; Buyyarapu, R.; Fang, D.D.; Frelichowski, J.; Giband, M.; Hague, S.; Hinze, L.L.; et al. Development of a 63K SNP Array for Cotton and High-Density Mapping of Intraspecific and Interspecific Populations of Gossypium spp. G3 Genes Genomes Genet. 2015, 5, 1187–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulse-Kemp, A.M.; Ashrafi, H.; Stoffel, K.; Zheng, X.; Saski, C.A.; Scheffler, B.E.; Fang, D.D.; Chen, Z.J.; Van Deynze, A.; Stelly, D.M. BAC-end sequence-based SNP mining in allotetraploid cotton (Gossypium) utilizing resequencing data, phylogenetic inferences, and perspectives for genetic mapping. G3 Genes Genomes Genet. 2015, 5, 1095–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, R.; Akhtar, K.P.; Moffett, P.; Shah, T.A.; Hussain, M.; Khan, M.K.R.; Mansoor, S.; Saeed, M. Analysis of the resistance of Gossypium herbaceum to cotton leaf curl kokhran virus strain burewala and cotton leaf curl multan betasatellite. J. Plant Pathol. 2018, 100, 313–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naqvi, R.; Zaidi, S.; Akhtar, K.P.; Strickler, S.; Woldemariam, M.; Mishra, B.; Mukhtar, M.; Scheffler, B.E.; Scheffler, J.A.; Jander, G.; et al. Transcriptomics reveals multiple resistance mechanisms against cotton leaf curl disease in a naturally immune cotton species, Gossypium arboreum. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidi, S.S.; Naqvi, R.Z.; Asif, M.; Strickler, S.; Shakir, S.; Shafi, M.; Khan, A.M.; Amin, I.; Mishra, B.; Mukhtar, M.S.; et al. Molecular insight into cotton leaf curl geminivirus disease resistance in cultivated cotton (Gossypium hirsutum). Plant. Biotechnol. J. 2020, 18, 691–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vij, S.; Pathak, D.; Rathore, P.; Kumar, H.; Sekhon, D.B.; Chhuneja, P. Molecular mapping of CLCuD resistance introgressed from synthetic cotton polyploid in upland cotton. J. Genet. 2022, 101, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, S.; Neale, B.; Todd-Brown, K.; Thomas, L.; Ferreira, M.A.; Bender, D.; Maller, J.; Sklar, P.; de Bakker, P.I.W.; Daly, M.J.; et al. PLINK: A Tool Set for Whole-Genome Association and Population-Based Linkage Analyses. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 81, 559–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.C.; Chow, C.C.; Tellier, L.C.; Vattikuti, S.; Purcell, S.M.; Lee, J.J. Second-generation PLINK: Rising to the challenge of larger and richer datasets. GigaScience 2015, 4, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagtap, A.B.; Vikal, Y.; Johal, G.S. Genome-Wide Development and Validation of Cost-Effective KASP Marker Assays for Genetic Dissection of Heat Stress Tolerance in Maize. IJMS 2020, 21, 7386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowda, S.A.; Shrestha, N.; Harris, T.M.; Phillips, A.Z.; Fang, H.; Sood, S.; Zhang, K.; Bourland, F.; Bart, R.; Kuraparthy, V. Identification and genomic characterization of major effect bacterial blight resistance locus (BB-13) in Upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 2022, 135, 4421–4436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.; Zhu, G.; Zhang, T.; Guo, W. High-density 80 K SNP array is a powerful tool for genotyping G. hirsutum accessions and genome analysis. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarty, J.C., Jr.; Hedin, P.A.; Stipanovic, R.D. Cotton Gossypium Spp. Plant Gossypol Contents of Selected GL2 and GL3 Alleles. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1996, 44, 613–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youngblood, R. Seed sterilization and tissue disruption for optimal DNA extractions for short read sequencing. Protocols.io. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Oijen, J.W. JoinMap 5; Software for the Calculation of Genetic Linkage ma kps in Experimental Populations; Kyazma BV: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Voorrips, R. MapChart: Software for the graphical presentation of linkage maps and QTLs. J. Hered. 2002, 93, 77–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Ooijen, J.W. MapQTL® 6; Software for the Mapping of Quantitative Trait Loci in Experimental Populations of Diploid Species; Kyazma BV: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2009. [Google Scholar]




| Population | Cross a | Size of F2 Population b | Number of Polymorphic Markers c |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | MD26ne × TX1214 | 36 | 7969 |
| 2 | Mac7-1238 × TX1145 | 39 | 8600 |
| 3 | 48 | ||
| 4 | MD26ne × TX1145 | 35 | 8307 |
| 5 | 30 | ||
| 6 | MD26ne × Mac7-0238 | 66 | 5369 |
| Population a | Cross | Chromosome | Number of Markers | % Explained | Effect Parent |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | MD26ne × TX1214 | 8 | 2 | 33–51.5 | TX1214 |
| 2 & 3 | Mac7-1238 × TX1145 | 9 | 2 | 30.4 & 17.2 | TX1145 |
| 10 | 7 | 17–18 | |||
| 15 | 1 | 18.5 | |||
| 21 | 1 | 18.4 | |||
| 4 | MD26ne × TX1145 | 0 | 0 | 0 | N/A |
| 4 & 5 | MD26ne × TX1145 | 0 | 0 | 0 | N/A |
| 5 | MD26ne × TX1145 | 16 | 6 | 53–55.4 | TX1145 |
| 6 | MD26ne × Mac7-0238 | 3 | 6 | 41.3–50.6 | Mac7-0238 |
| 5 | 3 | 39.3–40.5 | |||
| 16 | 2 | 39.3 |
| Marker | Cross | QTL a | Linkage Group | Position (cM) | Good/Bad b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| i04503Gh | MD26ne × TX1214 | Yes | 36 | 0 | GOOD |
| i60979Gt | MD26ne × TX1214 | Yes | 36 | 1.502 | GOOD |
| i64854Gm | MD26ne × TX1214 | No | 36 | 32.553 | GOOD |
| i01747Gh | MD26ne × TX1145 | No | 27 | 70.891 | BAD |
| i01975Gh | MD26ne × TX1145 | Yes | 27 | 104.098 | GOOD |
| i20534Gh | MD26ne × TX1145 | Yes | 27 | 105.866 | GOOD |
| i38904Gh | MD26ne × TX1145 | No | 27 | 132.962 | GOOD |
| i38317Gh | MD26ne × TX1145 | No | 27 | 132.962 | BAD |
| i35622Gh | MD26ne × TX1145 | Yes | 27 | 134.712 | GOOD * |
| i41454Gh | MD26ne × TX1145 | Yes | 27 | 134.712 | BAD |
| i01767Gh | MD26ne × TX1145 | No | 27 | 147.669 | GOOD |
| Sample Class | Entries b | Biological Reps/Sample (#) | Technical Reps/Sample (#) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Parents | MD26ne, TX1145, TX1214, TX2425, TX2452, Mac7-1238 | 3,4,4,2,2,3 | 2,2,2,2,2,2 |
| a Synthetic F1s | MD26ne × TX1145, Mac7-1238 × MD26ne, MD26ne × TX1214, Mac7-1238 × TX1145 | 3,3,3,3 | 0,0,0,0 |
| F2s | MD26ne × TX1145, MD26ne × TX1214, Mac7-1238 × TX1145 | 10,10,10 | 0,0,0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schoonmaker, A.N.; Hulse-Kemp, A.M.; Youngblood, R.C.; Rahmat, Z.; Atif Iqbal, M.; Rahman, M.-u.; Kochan, K.J.; Scheffler, B.E.; Scheffler, J.A. Detecting Cotton Leaf Curl Virus Resistance Quantitative Trait Loci in Gossypium hirsutum and iCottonQTL a New R/Shiny App to Streamline Genetic Mapping. Plants 2023, 12, 1153. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12051153
Schoonmaker AN, Hulse-Kemp AM, Youngblood RC, Rahmat Z, Atif Iqbal M, Rahman M-u, Kochan KJ, Scheffler BE, Scheffler JA. Detecting Cotton Leaf Curl Virus Resistance Quantitative Trait Loci in Gossypium hirsutum and iCottonQTL a New R/Shiny App to Streamline Genetic Mapping. Plants. 2023; 12(5):1153. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12051153
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchoonmaker, Ashley N., Amanda M. Hulse-Kemp, Ramey C. Youngblood, Zainab Rahmat, Muhammad Atif Iqbal, Mehboob-ur Rahman, Kelli J. Kochan, Brian E. Scheffler, and Jodi A. Scheffler. 2023. "Detecting Cotton Leaf Curl Virus Resistance Quantitative Trait Loci in Gossypium hirsutum and iCottonQTL a New R/Shiny App to Streamline Genetic Mapping" Plants 12, no. 5: 1153. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12051153
APA StyleSchoonmaker, A. N., Hulse-Kemp, A. M., Youngblood, R. C., Rahmat, Z., Atif Iqbal, M., Rahman, M.-u., Kochan, K. J., Scheffler, B. E., & Scheffler, J. A. (2023). Detecting Cotton Leaf Curl Virus Resistance Quantitative Trait Loci in Gossypium hirsutum and iCottonQTL a New R/Shiny App to Streamline Genetic Mapping. Plants, 12(5), 1153. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12051153






