Transcriptome and Metabolome Analysis of Rice Cultivar CBB23 after Inoculation by Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae Strains AH28 and PXO99A
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Resistance Reaction of Rice Inoculated with AH28 and PXO99A
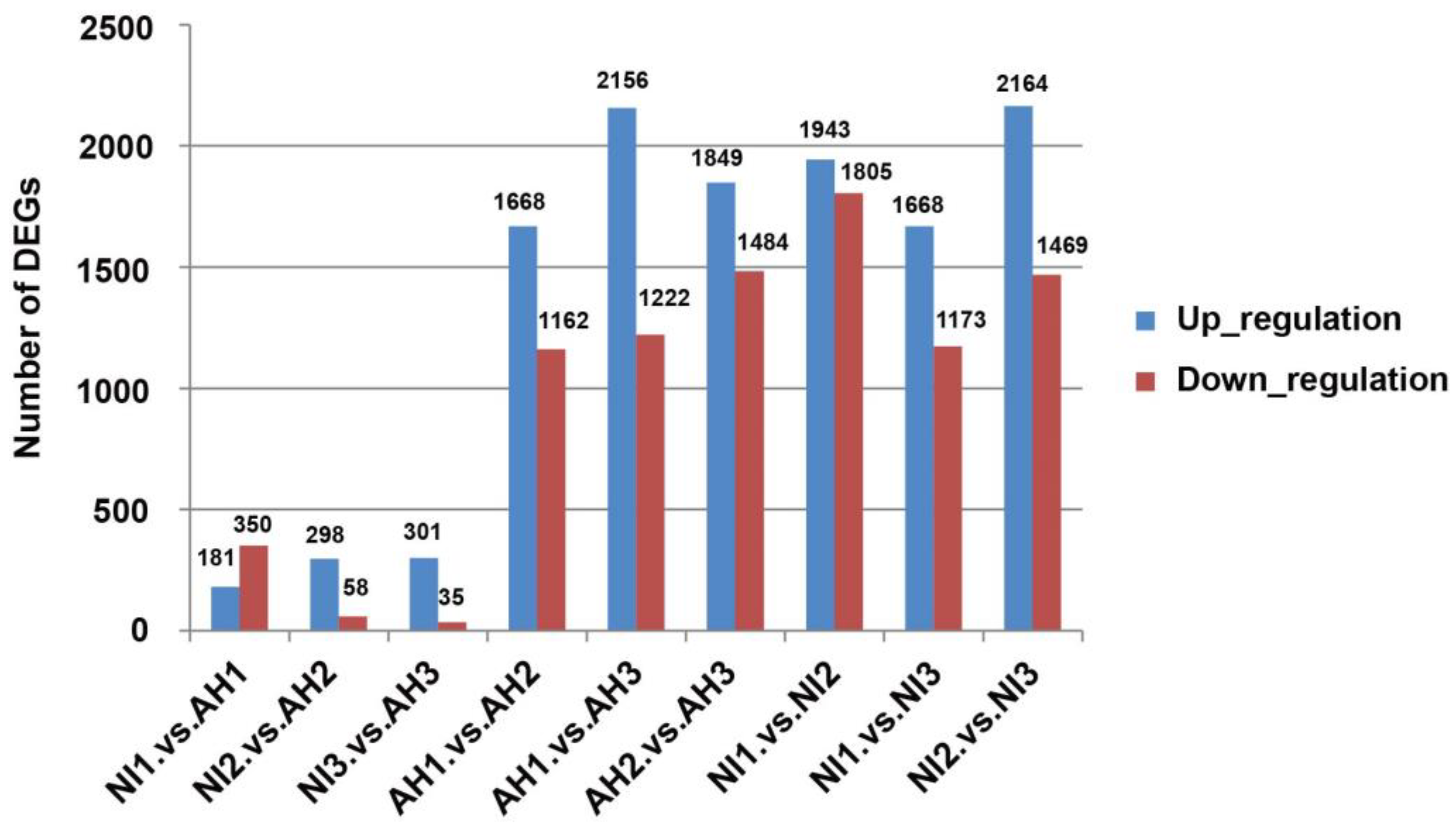
2.2. DEG Analysis
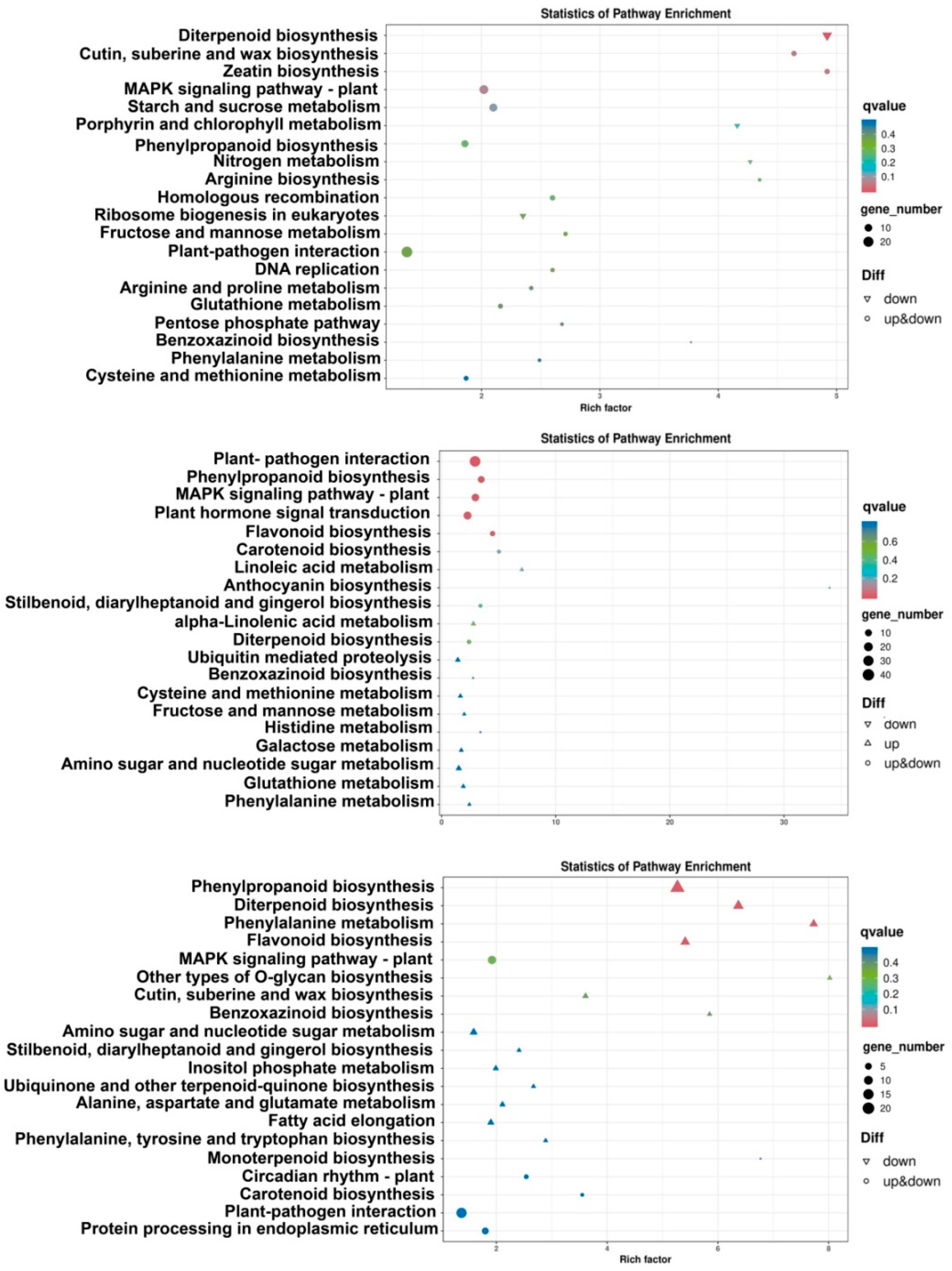
2.3. DEGs in Different Pathways Analysis
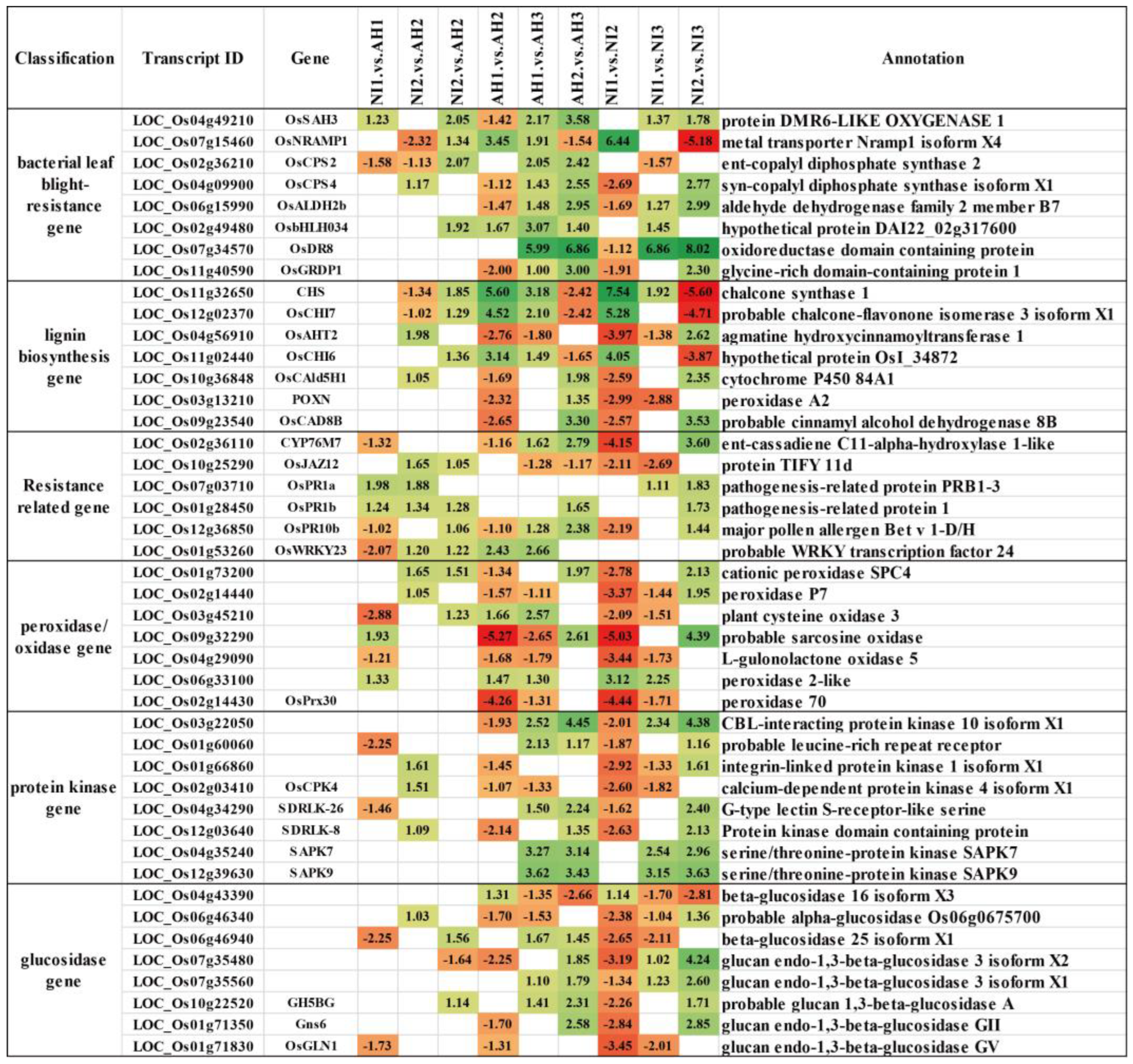
2.4. DEGs Are Closely Related to Disease Resistance
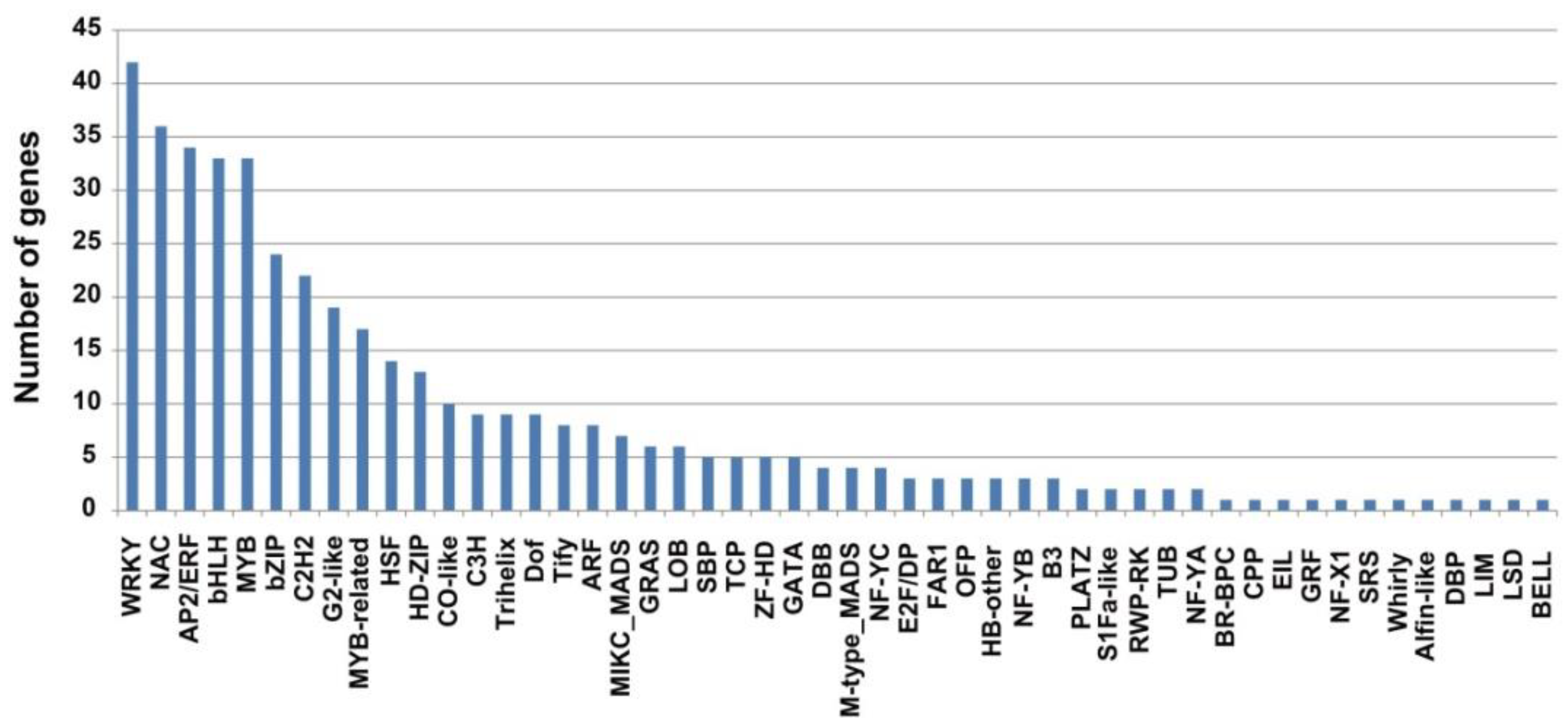
2.5. Transcription Factor (TF) Analysis
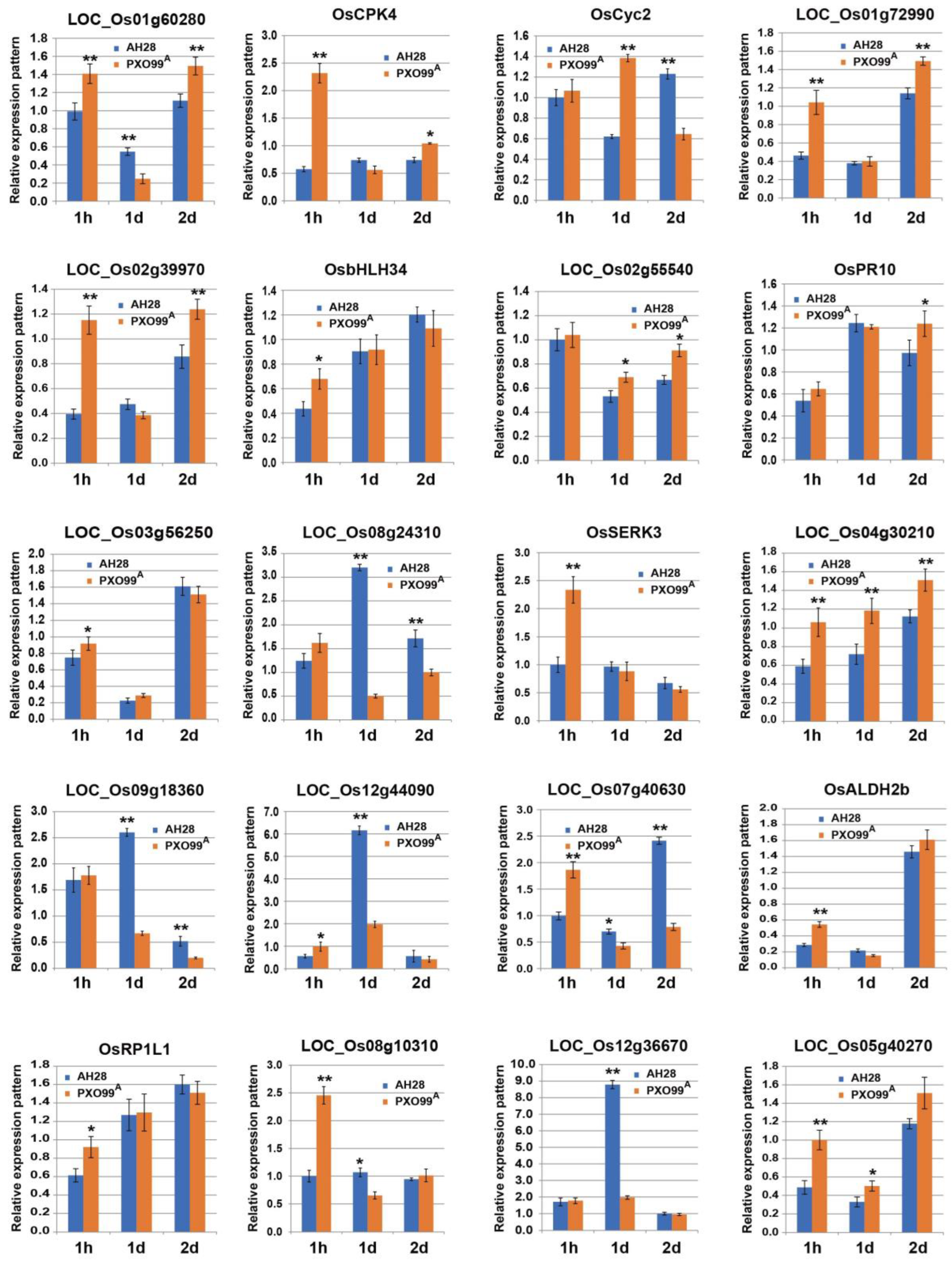
2.6. qPCR Verification and Analysis of DEGs in the Transcriptome
2.7. Metabolome Analysis of CBB23 in Response to Disease Resistance
3. Discussion
3.1. The Exploration of New Genes Plays an Important Role in the Prevention and Control of Virulent Bacterial Strains
3.2. Possible Genes Involved in the Resistance Response of Plants Containing xa23 to Xoo Strains
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Rice and Bacterial Strains
4.2. Inoculation and Investigation of BLB
4.3. Sample Preparation, Sequencing, and Analysis of RNA-seq
4.4. Analysis of DEGs and Their Functional Enrichment
4.5. RNA Extraction and qRT-PCR Detection
4.6. Metabolome Sample Preparation and Metabolomics Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, Z.; Xu, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, L.; Li, Y.; Yang, Y.; Liu, L.; Zou, L.; Chen, G. A varied AvrXa23-like TALE enables the bacterial blight pathogen to avoid being trapped by Xa23 resistance gene in rice. J. Adv. Res. 2022, 42, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, N.; Yan, J.; Liang, Y.; Shi, Y.; Peng, J. Resistance Genes and their Interactions with Bacterial Blight/Leaf Streak Pathogens (Xanthomonas oryzae) in Rice (Oryza sativa L.)—An Updated Review. Rice 2020, 13, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Quintero, A.L.; Szurek, B. A Decade Decoded: Spies and Hackers in the History of TAL Effectors Research. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2019, 57, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliva, R.; Ji, C.; Atienza-Grande, G.; Huguet-Tapia, J.C.; Perez-Quintero, A.; Li, T.; Eom, J.S.; Li, C.; Nguyen, H.; Liu, B.; et al. Broad-spectrum resistance to bacterial blight in rice using genome editing. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 1344–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Xu, X.; Gong, Q.; Li, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, S.; Yang, Y.; Ma, W.; Liu, L.; Zhu, B.; et al. Engineering Broad-Spectrum Bacterial Blight Resistance by Simultaneously Disrupting Variable TALE-Binding Elements of Multiple Susceptibility Genes in Rice. Mol. Plant 2019, 12, 1434–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, W.-Y.; Wang, G.-L.; Chen, L.-L.; Kim, H.-S.; Pi, L.-Y.; Holsten, T.; Gardner, J.; Wang, B.; Zhai, W.-X.; Zhu, L.-H.; et al. A receptor kinase-like protein encoded by the rice disease resistance gene, Xa21. Science 1995, 270, 1804–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Wang, C.; Yang, J.; Chen, B.; Wang, W.; Su, J.; Feng, A.; Zeng, L.; Zhu, X. Identification of the novel bacterial blight resistance gene Xa46(t) by mapping and expression analysis of the rice mutant H120. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 12642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, C.; Ji, Z.; Liu, B.; Cheng, H.; Chen, G. Xa1 allelic R genes activate rice blight resistance suppressed by interfering TAL effectors. Plant Commun. 2020, 1, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Liu, P.; Mei, L.; He, X.; Chen, L.; Liu, H.; Shen, S.; Ji, Z.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, Y. Xa7, a new executorRgene that confers durable and broad-spectrum resistance to bacterial blight disease in rice. Plant Commun. 2021, 2, 100143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Gao, C. Generation of Stable Transgenic Rice (Oryza sativa L.) by Agrobacterium-Mediated Transformation. Curr. Protoc. Plant Biol. 2016, 1, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Sangha, J.S.; Wang, S.; Li, Z.; Yang, J.; Yin, Z. Marker-assisted breeding of Xa4, Xa21 and Xa27 in the restorer lines of hybrid rice for broad-spectrum and enhanced disease resistance to bacterial blight. Mol. Breed. 2012, 30, 1601–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, X.; Fan, Y.; Gao, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Zheng, C.; Qin, T.; Li, Y.; Che, J.; Zhang, M.; et al. XA23 is an executor R protein and confers broad-spectrum disease resistance in rice. Mol. Plant 2015, 8, 290–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer-Pascuzzi, A.S.; Jiang, H.; Huang, L.; McCouch, S.R. Genetic and Functional Characterization of the Rice Bacterial Blight Disease Resistance Gene xa5. Phytopathology 2008, 98, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding-Qin, L.I.; Chen, L.; Wei-Jiao, L.I.; Xue, K.E.; Cheng, Z.Q. Identification of Bacterial Blight Resistance Gene in Yunnan Wild Rice. Acta Agron. Sin. 2015, 41, 386. [Google Scholar]
- Antony, G.; Zhou, J.; Huang, S.; Li, T.; Liu, B.; White, F.; Yang, B. Rice xa13 recessive resistance to bacterial blight is defeated by induction of the disease susceptibility gene Os-11N3. Plant Cell 2010, 22, 3864–3876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, J.; Liu, H.; Li, Y.; Yu, H.; Li, X.; Xiao, J.; Wang, S. Manipulating broad-spectrum disease resistance by suppressing pathogen-induced auxin accumulation in rice. Plant Physiol. 2011, 155, 589–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Z.; Liu, H.; Qiu, D.; Zhou, Y.; Li, X.; Xu, C.; Wang, S. A Pair of Allelic WRKY Genes Play Opposite Role in Rice-Bacteria Interactions1. Plant Physiol. 2009, 151, 936–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.L.; Qin, T.F.; Yu, H.M.; Zhang, X.P.; Che, J.Y.; Gao, Y.; Zheng, C.K.; Yang, B.; Zhao, K.J. The broad bacterial blight resistance of rice line CBB23 is triggered by a novel transcription activator-like (TAL) effector of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2014, 15, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liu, W.; Lu, D.; Lu, Z.; He, X. Distribution of Bacterial Blight Resistance Genes in the Main Cultivars and Application of Xa23 in Rice Breeding. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 555228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Xu, J.Y.; Hou, M.S.; Ali, J.; Mou, T.M. Introgression of bacterial blight resistance genes Xa7, Xa21, Xa22 and Xa23 into hybrid rice restorer lines by molecular marker-assisted selection. Euphytica 2012, 187, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Yang, D.; Ali, J.; Mou, T. Molecular marker-assisted pyramiding of broad-spectrum disease resistance genes, Pi2 and Xa23, into GZ63-4S, an elite thermo-sensitive genic male-sterile line in rice. Mol. Breed. 2015, 35, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezwan, T.; Chunlian, W.; Tengfei, Q.; Feifei, X.; Yongchao, T.; Ying, G.; Zhiyuan, J.; Kaijun, Z. Comparative Transcriptome Profiling of Rice Near-Isogenic Line Carrying Xa23 under Infection of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. Int. J. Mol. Ences 2018, 19, 717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, K.; Yang, B.; Tian, D.; Wu, L.; Wang, D.; Sreekala, C.; Yang, F.; Chu, Z.; Wang, G.; White, F. R gene expression induced by a type-III effector triggers disease resistance in rice. Nature 2005, 435, 1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Tariq, R.; Ji, Z.; Wei, Z.; Zheng, K.; Mishra, R.; Zhao, K. Transcriptome analysis of a rice cultivar reveals the differentially expressed genes in response to wild and mutant strains of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tariq, R.; Ji, Z.; Wang, C.; Tang, Y.; Zou, L.; Sun, H.; Chen, G.; Zhao, K. RNA-Seq analysis of gene expression changes triggered by Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae in a susceptible rice genotype. Rice 2019, 12, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, C.J.; Peng, Y.; Chen, X.; Dardick, C.; Ronald, P.C. Rice XB15, a Protein Phosphatase 2C, Negatively Regulates Cell Death and XA21-Mediated Innate Immunity. PLoS Biol. 2008, 6, e231–e282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.J.; Wei, T.; Sharma, R.; Ronald, P.C. Overexpression of Rice Auxilin-Like Protein, XB21, Induces Necrotic Lesions, up-Regulates Endocytosis-Related Genes, and Confers Enhanced Resistance to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. Rice 2017, 10, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, S.; Yoshimura, A.; Iwata, N.; Mccouch, S.R.; Nelson, R.J. Tagging and combining bacterial blight resistance genes in rice using RAPD and RFLP markers. Mol. Breed. 1995, 1, 375–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, Y.C.; Chiu, C.H.; Yap, R.; Tseng, Y.C.; Wu, Y.P. Pyramiding Bacterial Blight Resistance Genes in Tainung82 for Broad-Spectrum Resistance Using Marker-Assisted Selection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yugander, A.; Sundaram, R.M.; Singh, K.; Senguttuvel, P.; Ladhalakshmi, D.; Kemparaju, K.B.; Madhav, M.S.; Prasad, M.S.; Hariprasad, A.S.; Laha, G.S. Improved versions of rice maintainer line, APMS 6B, possessing two resistance genes, Xa21 and Xa38, exhibit high level of resistance to bacterial blight disease. Mol. Breed. 2018, 38, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keyu, G.U.; Tian, D.; Qiu, C.; Yin, Z. Transcription activator-like type III effector AvrXa27 depends on OsTFIIAgamma5 for the activation of Xa27 transcription in rice that triggers disease resistance to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2010, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, M.; Ke, Y.; Huang, R.; Ma, L.; Yang, Z.; Chu, Z.; Xiao, J.; Li, X.; Wang, S. A host basal transcription factor is a key component for infection of rice by TALE-carrying bacteria. eLife 2016, 5, e19605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Goh, M.L.; Sreekala, C.; Yin, Z. XA27 Depends on an Amino-Terminal Signal-Anchor-Like Sequence to Localize to the Apoplast for Resistance to Xanthomonas oryzae pv oryzae. Plant Physiol. 2008, 148, 1497–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Chen, J.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Qiu, Y.; Yu, C.; Cheng, Y.; Yan, C.; Chen, J. Characterization of a Novel NBS-LRR Gene Involved in Bacterial Blight Resistance in Rice. Plant Mol. Biol. Report. 2013, 31, 649–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Streubel, J.; Pesce, C.; Hutin, M.; Koebnik, R.; Boch, J.; Szurek, B. Five phylogenetically close rice SWEET genes confer TAL effector-mediated susceptibility to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. New Phytol. 2013, 200, 808–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, D.; Duan, M.; Liu, Y.; Shen, Z.; Yang, C.; Qiu, Z.; Liu, D.; Wen, P. An R2R3 MYB transcription factor confers brown planthopper resistance by regulating the phenylalanine ammonia-lyase pathway in rice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonnessen, B.W.; Manosalva, P.; Lang, J.M.; Baraoidan, M.; Bordeos, A.; Mauleon, R.; Oard, J.; Hulbert, S.; Leung, H.; Leach, J.E. Rice phenylalanine ammonia-lyase gene OsPAL4 is associated with broad spectrum disease resistance. Plant Mol. Biol. 2015, 87, 273–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Xue, C.; Liu, J.; He, Y.; Mei, Q.; Wei, S.; Xuan, Y. Sheath blight resistance in rice is negatively regulated by WRKY53 via SWEET2a activation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2021, 585, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathan, J.; Singh, A.; Ranjan, A. Sucrose transport in response to drought and salt stress involves ABA-mediated induction of OsSWEET13 and OsSWEET15 in rice. Physiol. Plant. 2021, 171, 620–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, P.; Wang, Y.; Tan, Z.; Liu, W.; Miao, W. Antibacterial activity and rice-induced resistance, mediated by C15surfactin A, in controlling rice disease caused by Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2020, 169, 104669. [Google Scholar]
- Ramaroson, M.L.; Koutouan, C.; Helesbeux, J.J.; Le Clerc, V.; Hamama, L.; Geoffriau, E.; Briard, M. Role of Phenylpropanoids and Flavonoids in Plant Resistance to Pests and Diseases. Molecules 2022, 27, 8371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Ning, Y.; Gentzel, I.N.; Wang, G.L. Achieving broad-spectrum resistance against rice bacterial blight through targeted promoter editing and pathogen population monitoring. aBIOTECH 2020, 1, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, M.; Wang, S. Rice MtN3/Saliva/SWEET Family Genes and Their Homologs in Cellular Organisms. Mol. Plant 2013, 6, 665–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, Z.; Fu, B.; Yang, H.; Xu, C.; Li, Z.; Sanchez, A.; Park, Y.J.; Bennetzen, J.L.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, S. Targeting xa13, a recessive gene for bacterial blight resistance in rice. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2006, 112, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Yuan, M.; Zhou, Y.; Li, X.; Xiao, J.; Wang, S. A paralog of the MtN3/saliva family recessively confers race-specific resistance to Xanthomonas oryzae in rice. Plant Cell Environ. 2011, 34, 1958–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutin, M.; Sabot, F.; Ghesquière, A.; Koebnik, R.; Szurek, B. A knowledge-based molecular screen uncovers a broad-spectrum OsSWEET14 resistance allele to bacterial blight from wild rice. Plant J. Cell Mol. Biol. 2015, 84, 694–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Xia, Y.; Lin, S.; Wang, Y.; Guo, B.; Song, X.; Ding, S.; Zheng, L.; Feng, R.; Chen, S.; et al. Osa-miR164a targets OsNAC60 and negatively regulates rice immunity against the blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae. Plant J. Cell Mol. Biol. 2018, 95, 584–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wang, K.; Chern, M.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhu, X.; Yin, J.; Ran, L.; Xiong, J.; et al. Sclerenchyma cell thickening through enhanced lignification induced by OsMYB30 prevents fungal penetration of rice leaves. New Phytol. 2020, 226, 1850–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, H.; Hayashi, N.; Matsushita, A.; Xinqiong, L.; Nakayama, A.; Sugano, S.; Jiang, C.J.; Takatsuji, H. Blast resistance of CC-NB-LRR protein Pb1 is mediated by WRKY45 through protein-protein interaction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 9577–9582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, K.T.X.; Kim, C.Y.; Hoang, T.V.; Lee, S.K.; Shirsekar, G.; Seo, Y.S.; Lee, S.W.; Wang, G.L.; Jeon, J.S. OsWRKY67 Plays a Positive Role in Basal and XA21-Mediated Resistance in Rice. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.Q.; Bai, X.Q.; Qian, Q.; Wang, X.J.; Chen, M.S.; Chu, C.C. OsWRKY03, a rice transcriptional activator that functions in defense signaling pathway upstream of OsNPR1. Cell Res. 2005, 15, 593–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, D.; Xiao, J.; Ding, X.; Xiong, M.; Cai, M.; Cao, Y.; Li, X.; Xu, C.; Wang, S. OsWRKY13 mediates rice disease resistance by regulating defense-related genes in salicylate- and jasmonate-dependent signaling. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. MPMI 2007, 20, 492–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Bartley, L.E.; Chen, X.; Dardick, C.; Chern, M.; Ruan, R.; Canlas, P.E.; Ronald, P.C. OsWRKY62 is a Negative Regulator of Basal and Xa21-Mediated Defense against Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae in Rice. Mol. Plant 2008, 1, 446–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, J.; Song, C. Comparative metabolomics of the interaction between rice and the brown planthopper. Metabolomics 2016, 12, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sana, T.R.; Fischer, S.; Wohlgemuth, G.; Katrekar, A.; Jung, K.; Ronald, P.; Fiehn, O. Metabolomic and transcriptomic analysis of the rice response to the bacterial blight pathogen Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. Metabolomics 2010, 6, 451–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuc, J. Phytoalexins, stress metabolism, and disease resistance in plant. Webster R. K. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 1995, 33, 275–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Zuo, R.F.; Zhu, Q.; Sun, Y.; Li, M.Y.; Dong, Y.H.; Ru, Y.Y.; Zhang, H.F.; Zheng, X.B.; Zhang, Z.G. MoLys2 is necessary for growth, conidiogenesis, lysine biosynthesis, and pathogenicity in Magnaporthe oryzae. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2014, 67, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akira, M.; Tsukada, M.; Wada, Y.; Ohsumi, Y. Apg1p, a novel protein kinase required for the autophagic process in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Gene 1997, 192, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaynab, M.; Fatima, M.; Abbas, S.; Sharif, Y.; Umair, M.; Zafar, H.; Bahadar, K. Role of secondary metabolites in plant defense against pathogens. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 124, 198–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauffman, H.E.; Reddy, A.; Hsieh, S.P.Y.; Merca, S.D. An improved technique for evaluating resistance of rice varieties to Xanthomonas oryzae. Plant Dis. Report. 1973, 57, 537–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amante-Bordeos, A.; Sitch, L.A.; Nelson, R.; Dalmacio, R.D.; Oliva, N.P.; Aswidinnoor, H.; Leung, H. Transfer of bacterial blight and blast resistance from the tetraploid wild riceOryza minutato cultivated rice, Oryza sativa. Theor. Appl. Genet. Int. J. Breed. Res. Cell Genet. 1992, 84, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Gong, L.; Guo, Z.; Wang, W.; Zhang, H.; Liu, X.; Yu, S. A Novel Integrated Method for Large-Scale Detection, Identification, and Quantification of Widely Targeted Metabolites: Application in the Study of Rice Metabolomics. Mol. Plant 2013, 6, 1769–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
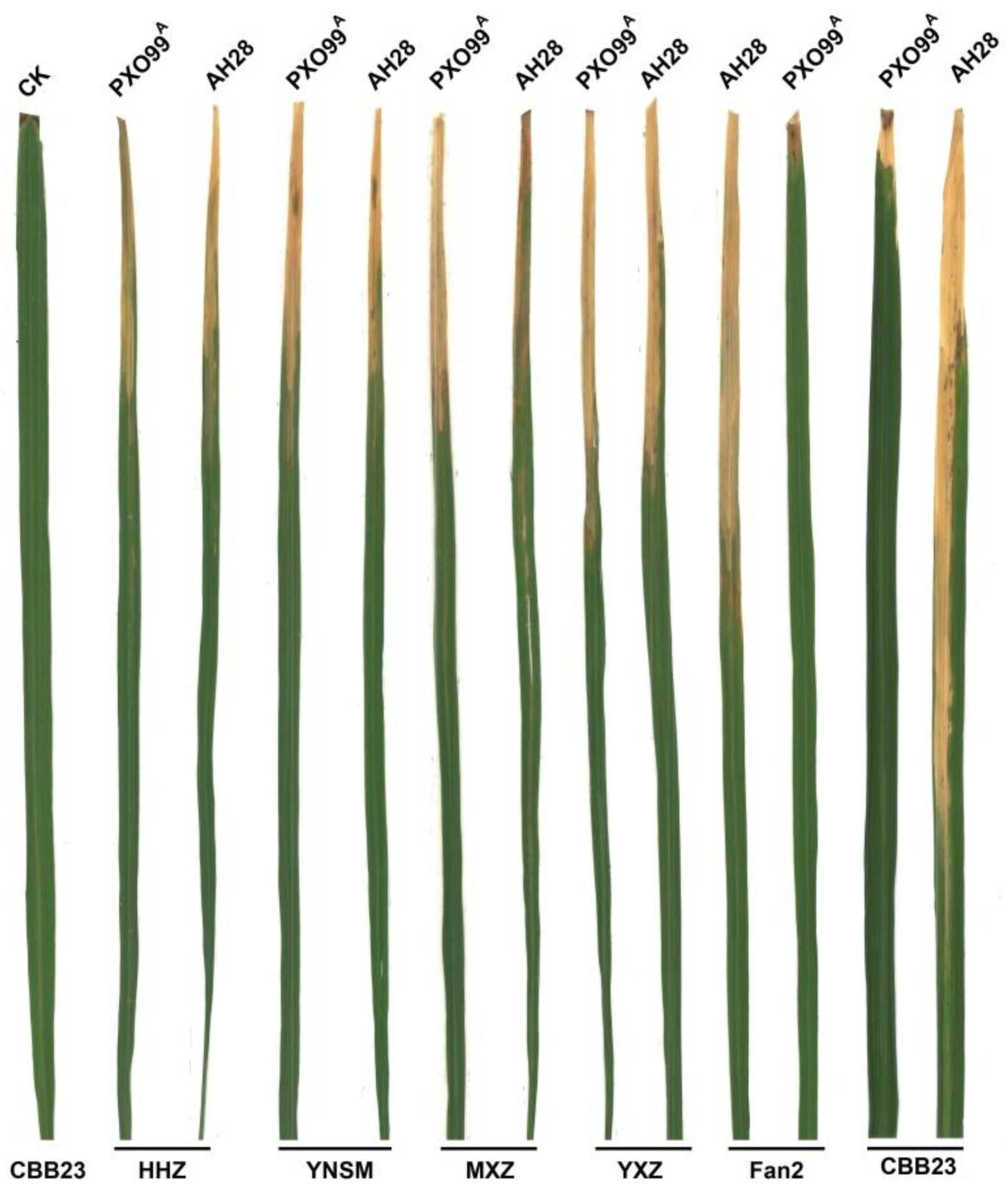



| Variety | PXO99A | AH28 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lesion Length (cm) | SD (cm) | Phenotypes | Lesion Length (cm) | SD (cm) | Phenotypes | |
| CBB23 | 2.12 | 0.67 | R | 25.65 | 5.87 | S |
| HHZ | 9.50 | 3.39 | MS | 9.33 | 3.42 | MS |
| YNSM | 10.73 | 1.54 | S | 10.41 | 2.22 | S |
| MXZ | 15.53 | 2.16 | S | 17.98 | 3.67 | S |
| YXZ | 14.78 | 2.28 | S | 13.70 | 3.67 | S |
| Fan2 | 2.08 | 0.53 | R | 19.38 | 3.94 | S |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, P.; Wang, J.; Liu, Q.; Liu, J.; Mo, Q.; Sun, B.; Mao, X.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, J.; Lv, S.; et al. Transcriptome and Metabolome Analysis of Rice Cultivar CBB23 after Inoculation by Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae Strains AH28 and PXO99A. Plants 2024, 13, 1411. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13101411
Chen P, Wang J, Liu Q, Liu J, Mo Q, Sun B, Mao X, Jiang L, Zhang J, Lv S, et al. Transcriptome and Metabolome Analysis of Rice Cultivar CBB23 after Inoculation by Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae Strains AH28 and PXO99A. Plants. 2024; 13(10):1411. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13101411
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Pingli, Junjie Wang, Qing Liu, Junjie Liu, Qiaoping Mo, Bingrui Sun, Xingxue Mao, Liqun Jiang, Jing Zhang, Shuwei Lv, and et al. 2024. "Transcriptome and Metabolome Analysis of Rice Cultivar CBB23 after Inoculation by Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae Strains AH28 and PXO99A" Plants 13, no. 10: 1411. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13101411
APA StyleChen, P., Wang, J., Liu, Q., Liu, J., Mo, Q., Sun, B., Mao, X., Jiang, L., Zhang, J., Lv, S., Yu, H., Chen, W., Liu, W., & Li, C. (2024). Transcriptome and Metabolome Analysis of Rice Cultivar CBB23 after Inoculation by Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae Strains AH28 and PXO99A. Plants, 13(10), 1411. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13101411





