Effects of Paddy Rain-Flood Storage on Rice Growth Physiological Indices and Nitrogen Leaching under Organic Planting in Erhai Lake Basin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
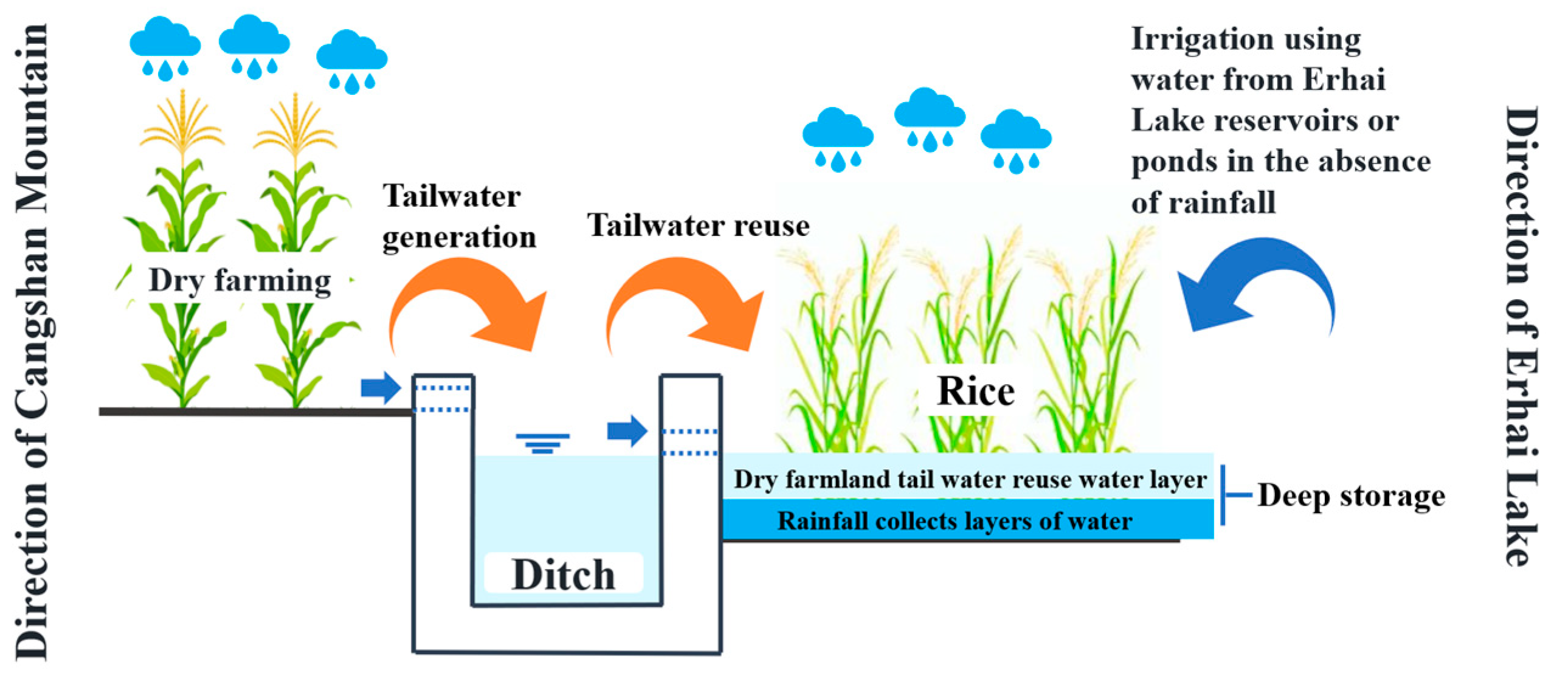
2.1. Description of Experiment Area
2.2. Experimental Materials
2.3. Experimental Design
2.4. Observation Index and Methods
- (1)
- Soil physicochemical indicators:
- (2)
- Daily climate data:
- (3)
- Leaf Area Index (LAI):
- (4)
- The root-to-shoot ratio (R/S):
- (5)
- Yields:
- (6)
- Physiological indicators [42]:
- (7)
- Nitrogen concentration [43]:
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Growth Indicator
3.1.1. Plant Length and Weight of Dry Matter Accumulation on the Ground
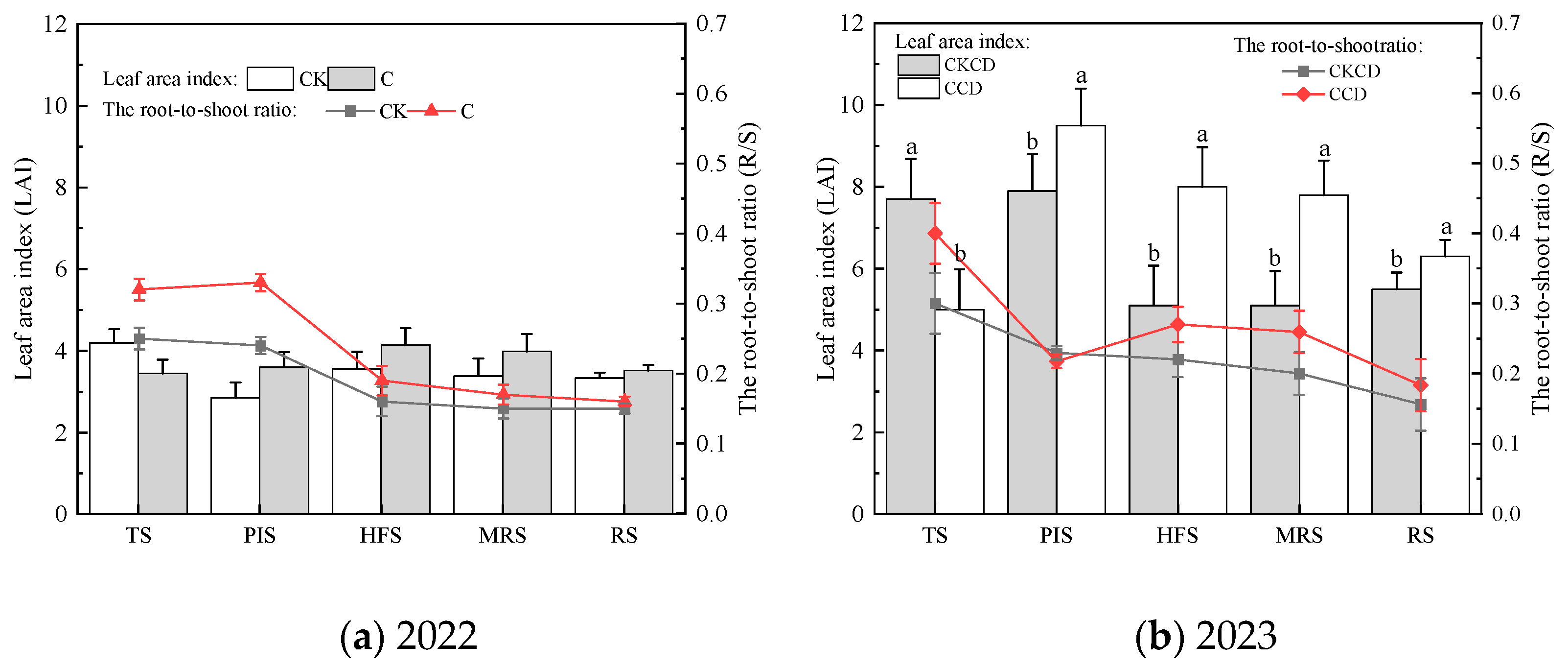
3.1.2. The Root-to-Shoot Ratio (R/S) and Leaf Area Index (LAI)
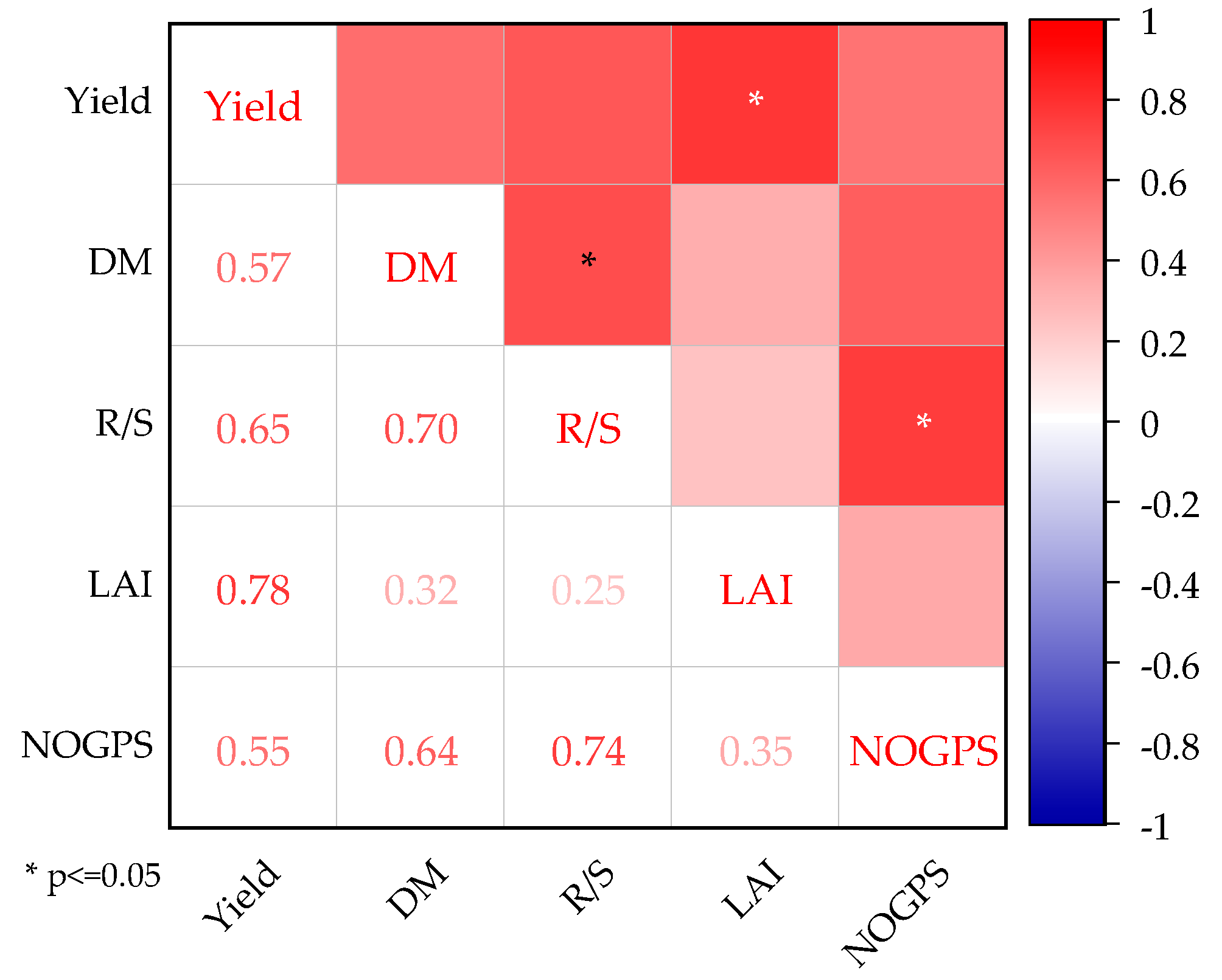
3.1.3. Yields and Their Constituent Factors
3.2. Physiological Indicators
3.2.1. Net Photosynthetic Rate (A)
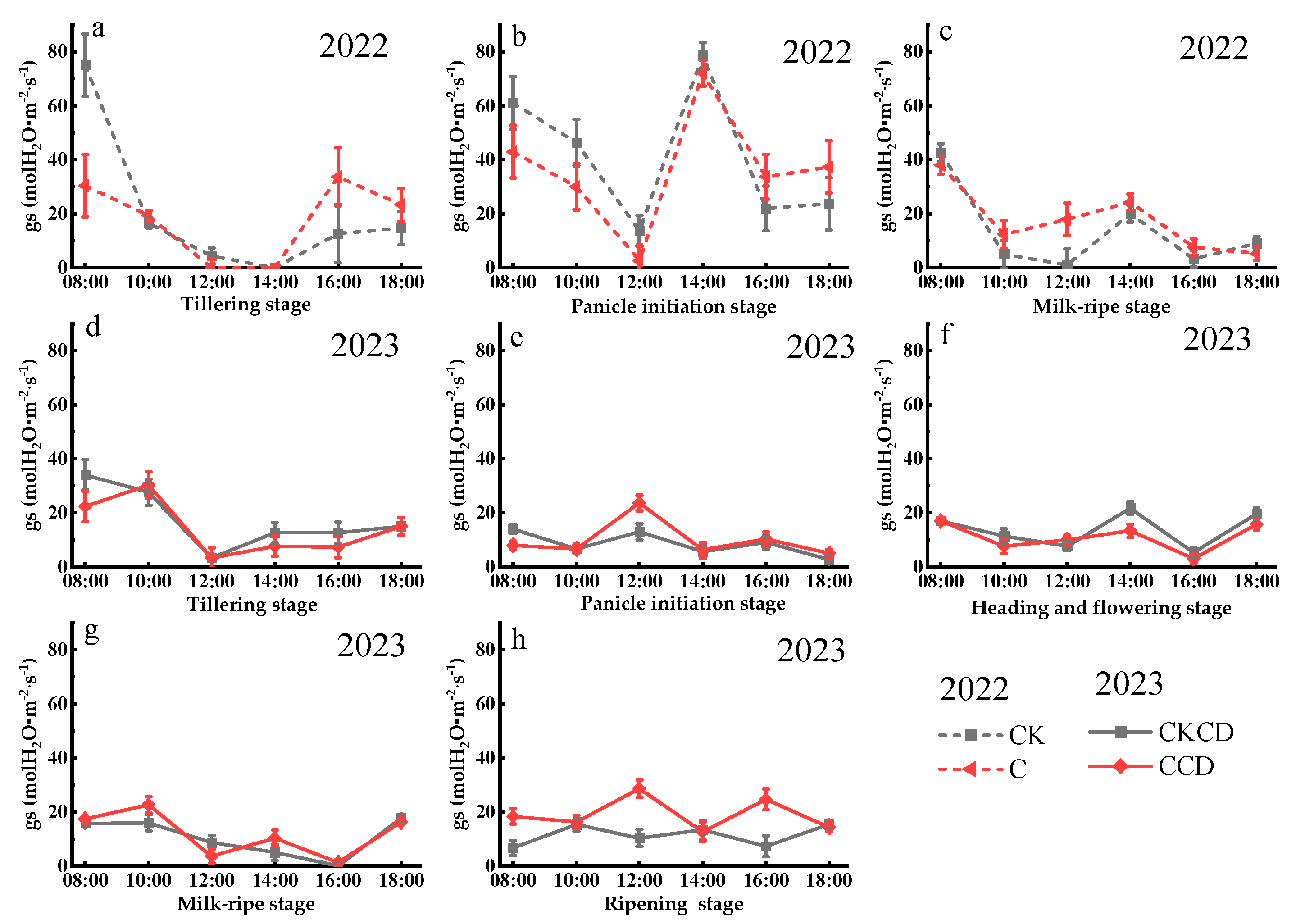
3.2.2. Stomatal Conductance (gs)
3.2.3. Transpiration Rate (E)

3.3. Nitrogen Leaching
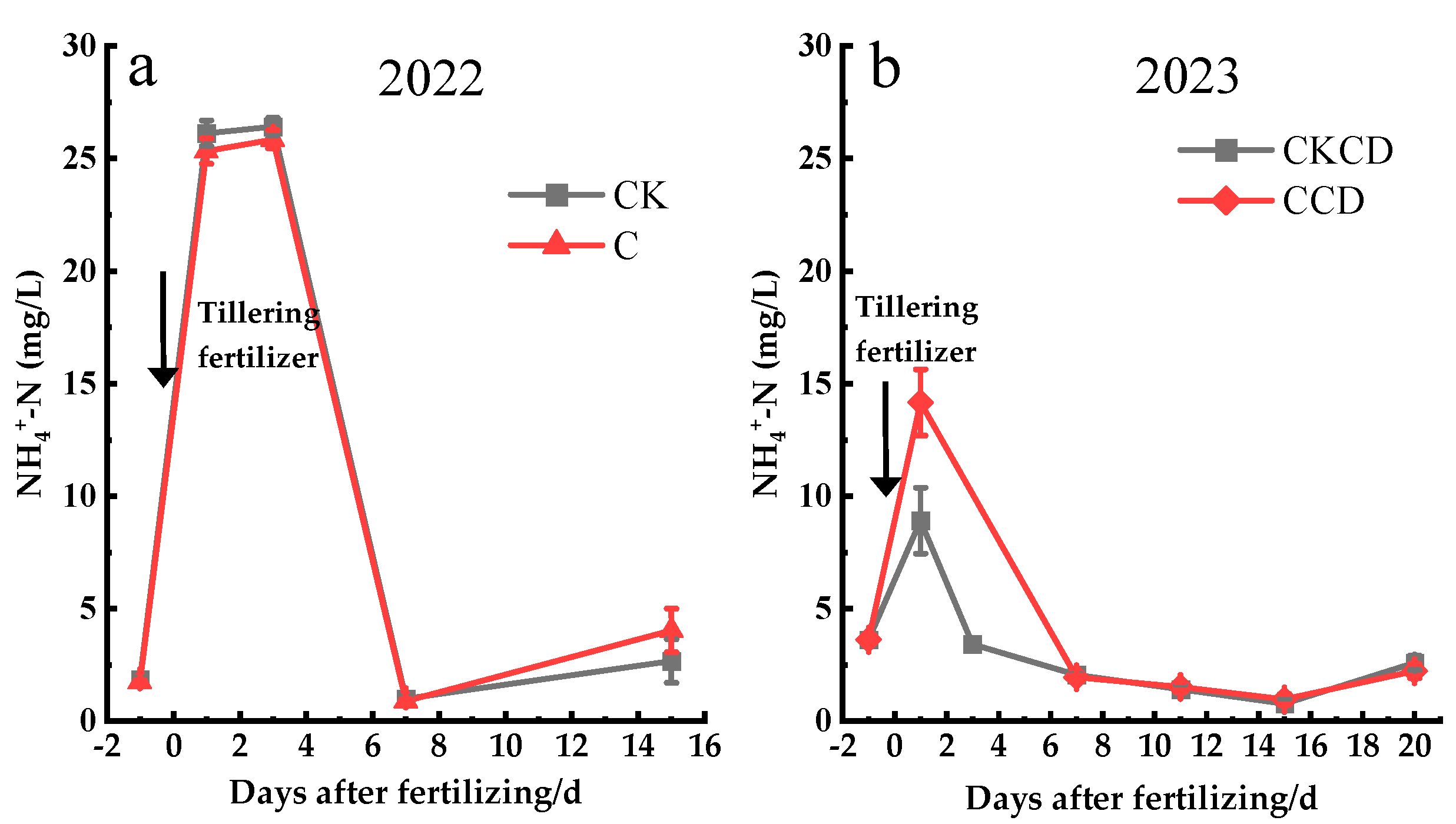
3.3.1. Surface Water Nitrogen Leaching
3.3.2. Soil Water Nitrogen Leaching
3.3.3. Groundwater Nitrogen Leaching
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Organic Planting Patterns on Rice Growth and Emission Reduction
4.2. Effects of Rain-Flood Storage Pattern on Rice Growth, Water Saving, and Emission Reduction
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, K.; Dong, X.; Yang, X.; Kattel, G.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, R. Ecological shift and resilience in China’s lake systems during the last two centuries. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2018, 165, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Janssen, A.B.; Strokal, M.; Kroeze, C.; Ma, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, Y. Assessing nitrogen sources in Lake Erhai: A spatially explicit modelling approach. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 289, 108549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; An, Z.; Chen, X.; Liu, H. Changes in Water Environment in Erhai Lake and Its Influencing Factors. Water 2021, 13, 1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, K.; Luo, Y.; Feng, Y.Y. Water quality evaluation of Erhai drainage ditch based on improved grey-mode identification model. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2019, 35, 234–241. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Shen, J.; Feng, J.; Sun, Z.; Sun, T.; Liu, D.; Xi, M.; Li, R.; Wang, X. The Estimation of Chemical Oxygen Demand of Erhai Lake Basin and Its Links with DOM Fluorescent Components Using Machine Learning. Water 2021, 13, 3629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.-S.; Shen, S.-L.; Zhou, A.; Lyu, H.-M. Assessment and management of lake eutrophication: A case study in Lake Erhai, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 751, 141618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, H.-M.; Sun, W.-J.; Shen, S.-L.; Zhou, A.-N. Risk Assessment Using a New Consulting Process in Fuzzy AHP. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2020, 146, 04019112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Gao, R.; Huang, Y.; Cui, Y.L.; Zhang, L. An Analysis of Water-saving and Pollution Reduction of Reclaimed Water Irrigation for the Paddy in Lake Erhai Watershed. China Rural. Water Hydropower 2017, 12, 13–16+21. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hou, X.; Xu, Z.; Tang, C.; Zhang, S. Spatial distributions of nitrogen and phosphorus losses in a basin and responses to best management practices—Jialing River Basin case study. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 255, 107048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Uddin, S.; Jahangir, M.M.R.; Solaiman, Z.M.; Alamri, S.; Siddiqui, M.H.; Islam, M.R. Integrated Nutrient Management Enhances Productivity and Nitrogen Use Efficiency of Crops in Acidic and Charland Soils. Plants 2021, 10, 2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.Q.; Fan, D.J.; Zhang, X.X.; Chen, J.; Li, C.F.; Cao, C.G. Deep placement of nitrogen fertilizers reduces ammonia volatilization and increases nitrogen utilization efficiency in no-tillage paddy fields in central China. Field Crops Res. 2015, 184, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhang, X.; Shao, L.; Sun, H.; Niu, J.; Liu, X. Effects of straw and manure management on soil and crop performance in North China Plain. Catena 2020, 187, 104359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayatu, N.G.; Liu, Y.R.; Han, T.F.; Daba, N.A.; Zhang, L.; Zhe, S.H.E.N.; Li, J.W.; Muazu, H.; Lamlom, S.F.; Zhang, H.M. Carbon sequestration rate, nitrogen use efficiency and rice yield responses to long-term substitution of chemical fertilizer by organic manure in a rice-rice cropping system. J. Integr. Agric. 2023, 22, 2848–2864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.B.; Zhang, K.Q.; Zou, H.T.; Ma, Y.J.; Qu, Q.B.; Gu, Y.R.; Shen, S.Z. Effects of Different Fertilization Patterns on Nitrogen Leaching Loss from Paddy Fields under Reduced Nitrogen. Environ. Sci. 2021, 42, 5405–5413. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.L.; Dong, W.Y.; Liu, Q.; Wang, H.Y.; Yan, C.R.; Liu, H.B.; Chen, B.Q.; Liu, E.K. Effects of Organic Fertilizer Substituting Chemical Nitrogen Fertilizer on Nitrogen Content in the Surface Water and Soil of Paddy Field in the Erhai Lake Basin. Chin. J. Agrometeorol. 2018, 39, 256. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Wang, X.; Ma, L.; Chadwick, D.; Chen, X. Combined applications of organic and synthetic nitrogen fertilizers for improving crop yield and reducing reactive nitrogen losses from China’s vegetable systems: A meta-analysis. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 269, 116143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Adhya, T.K. Effect of combine application of organic manure and inorganic fertilizer on methane and nitrous oxide emissions from a tropical flooded soil planted to rice. Geoderma 2014, 213, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.B.; Zhang, K.Q.; Shen, S.Z.; Ma, Y.J.; Qu, Q.B.; Zou, H.T. Rice yield and nitrogen and phosphorus changes in soil profile under different fertilization strategies in Erhai Lake Basin, Yunnan. J. Plant Nutr. Fertil. 2022, 28, 23–32. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Jin, X.; Cai, J.; Yang, S.; Li, S.; Shao, X.; Fu, C.; Li, C.; Deng, Y.; Huang, J.; Ruan, Y.; et al. Partial substitution of chemical fertilizer with organic fertilizer and slow-release fertilizer benefits soil microbial diversity and pineapple fruit yield in the tropics. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2023, 189, 104974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, B.; Liao, P.; Hu, R.; Cai, T.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, Q.; Zhang, B.; Shu, Y.; Wang, J.; Luo, Y.; et al. Mitigating ammonia volatilization in rice cultivation: The impact of partial organic fertilizer substitution. Chemosphere 2023, 344, 140326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, L.; Zhang, Z.X.; Qi, Z.J.; Han, Y.; Xu, D.; Zhang, Z.H.; Zhou, X. Effects of Straw Returning on N2O Emission and Yield under Water-saving Irrigation in Black Soil Paddy Field. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2024, 55, 280–289. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Xia, G.; Zheng, J.; Wang, Y.; Chen, T.; Chi, D.; Bolan, N.S.; Chang, S.X.; Wang, T.; Ok, Y.S. Mulched drip irrigation and biochar application reduce gaseous nitrogen emissions, but increase nitrogen uptake and peanut yield. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 830, 154753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, N.M.; Brandt, K.K.; Sørensen, J.; Hung, N.N.; Van Hach, C.; Tan, P.S.; Dalsgaard, T. Effects of alternating wetting and drying versus continuous flooding on fertilizer nitrogen fate in rice fields in the Mekong Delta, Vietnam. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2012, 47, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Li, S.; Xu, G.; Wu, Z. New water consumption pattern of rice under water-saving irrigation. Irrig. Drain. Syst. 1994, 8, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belder, P.; Bouman, B.; Cabangon, R.; Guoan, L.; Quilang, E.; Yuanhua, L.; Spiertz, J.; Tuong, T. Effect of water-saving irrigation on rice yield and water use in typical lowland conditions in Asia. Agric. Water Manag. 2004, 65, 193–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.Q.; Chen, Y.X.; Nie, Z.Y.; Ye, Y.S.; Liu, J.; Tian, G.M.; Wang, G.H.; Tuong, T.P. Mitigation of nutrient losses via surface runoff from rice cropping systems with alternate wetting and drying irrigation and site-specific nutrient management practices. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 6980–6991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, S.F.-U.; Sander, B.O.; Quilty, J.R.; de Neergaard, A.; van Groenigen, J.W.; Jensen, L.S. Mitigation of greenhouse gas emissions and reduced irrigation water use in rice production through water-saving irrigation scheduling, reduced tillage and fertiliser application strategies. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 739, 140215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Peng, S.; Xu, J.; Hou, H.; Gao, X. Nitrogen Loss from Paddy Field with Different Water and Nitrogen Managements in Taihu Lake Region of China. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2013, 44, 2393–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, Y.; Wan, Y.; Wang, B.; Cai, W.; Qin, X.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, X.; Yuan, J.; Deng, Q. Annual greenhouse gas emissions from a rice paddy with different water-nitrogen management strategies in Central China. Soil Tillage Res. 2024, 235, 105906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriphirom, P.; Rossopa, B. Assessment of greenhouse gas mitigation from rice cultivation using alternate wetting and drying and rice straw biochar in Thailand. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 290, 108586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.X.; Chen, P.; Nie, T.Z.; Jiang, H.; Meng, X.Y.; Yang, J.M. Effects of Different Water and Nitrogen Regulation Models on Nitrogen Distribution and Availability in Paddy Soils. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2018, 49, 210–219. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Fengle, Y.; Xianzhi, Z.; Jinhua, L.; Hongfeng, Z.; Fangming, J.; Zhou, B. Analysis and evaluation of the treatment and reuse of tailwater: A case study in Erhai Lake. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 327, 129435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.; Hu, T.; Wu, F.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, S.; Wang, Y. Photosynthetic and hydraulic changes caused by water deficit and flooding stress increase rice’s intrinsic water-use efficiency. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 289, 108527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Ghannam, M.K.; Wassar, F.; Morsy, S.; Hafez, M.; Parihar, C.M.; Burkey, K.O.; Abdallah, A.M. Controlled drainage in the Nile River delta of Egypt: A promising approach for decreasing drainage off-site effects and enhancing yield and water use efficiency of wheat. J. Arid. Land 2023, 15, 460–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kima, A.S.; Chung, W.G.; Wang, Y.-M.; Traoré, S. Evaluating water depths for high water productivity in irrigated lowland rice field by employing alternate wetting and drying technique under tropical climate conditions, Southern Taiwan. Paddy Water Environ. 2015, 13, 379–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natuhara, Y. Ecosystem services by paddy fields as substitutes of natural wetlands in Japan. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 56, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, G.L.; Xu, Y.H.; Yang, B.; Zhang, H.; Wang, P.L.; Liang, M.Z.; Lu, L.X.; Tian, Y.C. Effects of Water Management in Different Water Storage Depth on Nutrient Loss Potential of Rice Field. Acta Agric. Univ. Jiangxiensis 2017, 39, 871–876. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yu, S.E.; Li, S.; Gao, S.K.; Wang, M.; Meng, J.J.; Tang, S.H. Effect of controlled irrigation and drainage on water saving, nitrogen and phosphorus loss reduction with high yield in paddy field. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2018, 34, 128–136. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, M.; Hu, X.; Chu, L. Experimental study on water-saving and emission-reduction effects of controlled drainage technology. Water Sci. Eng. 2015, 8, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Yuan, X.J.; Cao, X.Q.; Gao, Z.L.; Jiang, S.M.; Yang, J.W.; Wang, Y.F. Variation in Paddy Soil Nitrogen as Impacted by Combination of Deep Rainfall Storage and Controlled Drainage. J. Irrig. Drain. 2022, 41, 40–48. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xianfa, M. Soil Science Experiments; China Forestry Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2020. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Guibin, P.; Lizhi, Z.; Xin, C.; Weiyan, P.; Zhenghe, X.; Junzeng, X. Leaf Photosynthesis and Light Response Curve Simulation of Winter Wheat under Brackish Water Irrigation. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2021, 52, 333–342. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Administration, S. Water and Wastewater Monitoring and Analysis Methods, 4th ed.; China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2002. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.G.; Chen, Y.; Wu, X.; Yu, Q.A.; Pan, S.B.; Yang, X.W.; Wang, J.; Wang, L.H. Growth Characteristics of Rice, Water—fertilizer Utilization and Nitrogen and Phosphorus Loss Law under Different Water—fertilizer Control Patterns. China Rural. Water Hydropower 2020, 000, 67–72+76. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Rativa, A.G.S.; de Araújo Junior, A.T.; da Silva Friedrich, D.; Gastmann, R.; Lamb, T.I.; dos Santos Silva, A.; Adamski, J.M.; Fett, J.P.; Ricachenevsky, F.K.; Sperotto, R.A. Root responses of contrasting rice genotypes to low temperature stress. J. Plant Physiol. 2020, 255, 153307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, B.; Liu, X.; Tan, J.; Shao, X.; Cheng, J. Effect of Plant Buffer Zone–Antifouling Curtain Wall on Reducing Non-Point Source Pollution in Paddy Fields, China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 6044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Ni, T.; Li, J.; Lu, Q.; Fang, Z.; Huang, Q.; Zhang, R.; Li, R.; Shen, B.; Shen, Q. Effects of organic–inorganic compound fertilizer with reduced chemical fertilizer application on crop yields, soil biological activity and bacterial community structure in a rice–wheat cropping system. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2016, 99, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.-W.; Lu, D.-K.; Wang, H.-Z.; Li, Y. Morphological and physiological traits of rice roots and their relationships to yield and nitrogen utilization as influenced by irrigation regime and nitrogen rate. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 203, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, R.; Okada, S.; Miura, H.; Kamichika, M. Relationships among the leaf area index, moisture availability, and spectral reflectance in an upland rice field. Agric. Water Manag. 2004, 69, 83–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.L.; Liu, W.G.; Wang, F.; Liu, D.L.; Kong, L.; Li, J.H.; Fu, C.Y.; Zen, X.Q.; Zhu, M.S.; Ma, X.Z.; et al. Dynamic changes of LAI, SPAD and LTR of late-season indica hybrid rice and their effects on grain yield traits. J. South China Agric. Univ. 2023, 44, 936–948. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Shao, G.-C.; Deng, S.; Liu, N.; Yu, S.-E.; Wang, M.-H.; She, D.-L. Effects of controlled irrigation and drainage on growth, grain yield and water use in paddy rice. Eur. J. Agron. 2014, 53, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, Q. Effects of Different Irrigation Patterns on Growth, Water and Radiation Use Efficiency of Rice. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2019, 50, 285–292. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Q.; Ma, X.; Lv, T.; Bai, M.; Wang, Z.; Niu, J. Effects of Water Stress on Fluorescence Parameters and Photosynthetic Characteristics of Drip Irrigation in Rice. Water 2020, 12, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-F.; Li, F.-S. Effect of irrigation method and fertilization dose on photosynthetic physiology of super rice. Acta Autom. Sin. 2013, 21, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, C.; Chaves, M.M. Photosynthesis and drought: Can we make metabolic connections from available data? J. Exp. Bot. 2011, 62, 869–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.S.; Liang, J.W.; Zhang, J.S.; Tong, T.Y.; Huang, S.H.; Mo, Z.W.; Tian, H.; Pan, S.G.; Duan, M.Y.; Tang, X.R. Effects of Different Irrigation Methods on Yield, Quality and Water Use Efficiency of Fragrant Rice. Acta Agric. Boreali-Sin. 2020, 35, 129–136. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, S.; Yang, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Z. Postanthesis Moderate Wetting Drying Improves Both Quality and Quantity of Rice Yield. Agron. J. 2008, 100, 726–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Peng, S.Z.; Xu, J.Z.; Ding, J.L. Photosynthetic Comparison Research on Rice under Different Irrigations Methods. J. Irrig. Drain. 2008, 31–34. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.H.; Yu, S.E.; Yu, Z.H.; Fu, C.X. Experimental study on variation rules of diurnal net photosynthetic rate of paddy rice under water level control in farmland. J. Hohai Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2011, 39, 104–108. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lei, S.; Wang, C.C.; Huang, Y.; Huang, S.H.; Fu, R.Z.; Tang, X.R. Effect of Control Irrigation on Soil Temperature and Dry Matter Accumulation of Rice During Tillering Stage. Acta Agric. Boreali-Sin. 2016, 31, 153–158. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, T.T.N.; Wallace, H.M.; Xu, C.-Y.; Xu, Z.; Farrar, M.B.; Joseph, S.; Van Zwieten, L.; Bai, S.H. Short-term effects of organo-mineral biochar and organic fertilisers on nitrogen cycling, plant photosynthesis, and nitrogen use efficiency. J. Soils Sediments 2017, 17, 2763–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.X.; Guo, C.C.; Sun, Y.J.; Liu, F.; Yang, Z.; Sun, Y.; Ma, M.; Ma, J. Relationship between Canopy Microclimate at Grain Filling Stage and Rice Quality of Directly Seeded Rice under Water and Nitrogen Interaction. Chin. J. Rice Sci. 2021, 35, 269–278. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Liu, X.; Tian, Y.; Yao, X.; Cao, W.; Zhu, Y. Effects of different soil water treatments on photosynthetic characteristics and grain yield in rice. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2012, 32, 7053–7060. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.Q.; Xia, H.P.; Peng, C.L. The Effects of Submergence on the Photosynthetic Characteristics of Five Grasses. J. For. Environ. 2004, 24, 374–378. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, W.; Li, S.; Zhu, K.; Hua, X.; Harrison, M.T.; Liu, K.; Yang, J.; Liu, L.; Chen, Y. Integrated management approaches enabling sustainable rice production under alternate wetting and drying irrigation. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 281, 108265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Peng, S.Z.; Jiao, J.; Kong, W.L. Research on Nitrogen Dynamics in Paddy Field under Different Levels of Water and Fertilizer during Whole Growing Period. Water Sav. Irrig. 2009, 9, 12–16. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.L.; Wu, M.Q.; Xia, Y.; Zhai, L.M.; Duan, X.L.; Fan, X.P.; Xiong, G.Y.; Liu, D.B.; Gao, L. Changes in Nitrogen and Phosphorus in Surface Water of Paddy Field in Jianghan Plain. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2019, 56, 1190–1200. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Miao, J.J.; Liu, Y.F.; Hu, H.X.; Tu, R.F.; Zhan, L.C.; Xue, Z.J.; Xu, Q.R. Effects of Different Fertilization Modes on Nitrogen and Phosphorus Loss Yield in Paddy Fields. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2020, 34, 86–93. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hua, K.J.; He, J.; Zhang, Y.H.; He, T.Z.; Shao, Q.; Zhao, S.J.; Zhang, L. Migration of Nitrogen and Phosphorus in Paddy Soil as Affected by Irrigation and Fertilization. J. Irrig. Drain. 2022, 41, 35–43. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Howden, N.J.; Burt, T.P.; Worrall, F.; Mathias, S.A.; Whelan, M.J. Farming for Water Quality: Balancing Food Security and Nitrate Pollution in UK River Basins. Ann. Assoc. Am. Geogr. 2013, 103, 397–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, S.H.; Wu, Q.F.; Zhu, X.X.; Wu, J.J. Effects of Different Fertilization Treatments on Runoff and Leaching Losses of Nitrogen in Paddy Field. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2016, 30, 23–28+33. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xia, H.X.; Zhu, Q.H.; Li, Q.; Wang, S.M.; Ding, W.Q.; Yang, Z.M.; Xhen, Y.C. Analysis on Characteristics of Nitrogen Losses of Typical Organic Fertilizers in Leaching Experiments. Southwest China J. Agric. Sci. 2018, 31, 1870–1874. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Du, X.Q.; Fang, M.; Ye, X.Y. Research Progress on the Sources of Inorganic Nitrogen Pollution in Groundwater and Identification Methods. Environ. Sci. 2018, 39, 5266–5275. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Feng, J.; He, H.Z.; Du, X.Q. Influencing factors of nitrogen concentration in groundwater based on weights of evidence method. China Environ. Sci. 2022, 43, 153–163. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.P.; Zhang, Z.U.; Xu, J.Z.; Yang, S.H.; Hong, D.L. Reducing nitrogen leaching losses from paddy field under water-saving irrigation by water table control. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2014, 30, 121–127. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.J. Soil Microbial Community Analysis of Garlic Season Farmland in Erhai Basin under Different Fertilization Modes; Northeast Agricultural University: Harbin, China, 2022; Volume 56. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Aguilera, E.; Guzmán, G.; Alonso, A. Greenhouse gas emissions from conventional and organic cropping systems in Spain. I. Herbaceous crops. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2015, 35, 713–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Liang, X.Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y.X.; Zhu, W.K.; Tian, G.M. Impact of Organic Fertilization on Dynamics of Phosphorus Forms in Floodwater and P Runoff from Paddy Field. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2015, 29, 42–47. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, H.B.; Shen, S.Z.; Gu, Y.R.; Yu, S.; Zou, H.T.; Arif, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, K.Q. Effects of different fertilization treatments on runoff losses of nitrogen and phosphorus in paddy fields in Erhai Lake basin, China. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2021, 40, 1305–1313. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ma, F.F.; Xing, S.L.; Gan, M.Q.; Liu, P.S.; Huang, Y.; Gan, X.Y.; Ma, Y.H. Effects of Organic Fertilizer Substituting for Chemical Fertilizer on Rice Yield, Soil Fertility and Nitrogen and Phosphorus Loss in Farmland. Crops 2019, 5, 89–96. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cai, J.P.; Zhu, J.; Peng, H.; Li, C.J.; Xiong, L.P.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Ji, X.H. Effects of Organic Fertilizer on the Risk of Nitrogen and Phosphorus Loss in Soil Surface Water. Res. Environ. Sci. 2019, 33, 210–217. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Rejesus, R.M.; Palis, F.G.; Rodriguez DG, P.; Lampayan, R.M.; Bouman, B.A. Impact of the alternate wetting and drying (AWD) water-saving irrigation technique: Evidence from rice producers in the Philippines. Food Policy 2011, 36, 280–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Ge, J.; Tian, S.; Li, S.; Nguy-Robertson, A.L.; Zhan, M.; Cao, C. Effects of water-saving irrigation practices and drought resistant rice variety on greenhouse gas emissions from a no-till paddy in the central lowlands of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 505, 1043–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sojka, M.; Kozłowski, M.; Stasik, R.; Napierała, M.; Kęsicka, B.; Wróżyński, R.; Jaskuła, J.; Liberacki, D.; Bykowski, J. Sustainable Water Management in Agriculture—The Impact of Drainage Water Management on Groundwater Table Dynamics and Subsurface Outflow. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crézé, C.M.; Madramootoo, C.A. Water table management and fertilizer application impacts on CO2, N2O and CH4 fluxes in a corn agro-ecosystem. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, V.M.; de Borja Reis, A.F.; de Melo ML, A.; Reichardt, K.; Santos, D.; van Lier QD, J. Sustainable irrigation management in tropical lowland rice in Brazil. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 284, 108345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.R. Effects of Different Water-Saving Irrigation Methods at Tillering Stage on Photosynthetic Characteristics and Yield Formation of Japonica Rice in Cold Region; Northeast Agricultural University: Harbin, China, 2022; Volume 66. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yin, C.Y.; Wang, S.Y.; Liu, H.M.; Sun, J.Q.; Hu, X.M.; Wang, H.L.; Tian, F.H.; Ma, C.Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, D.P.; et al. Effects on Leaf Physiological Characteristics, Yield and Quality of Dry Seeding Rice: Water-saving Irrigation and Conventional Irrigation. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2020, 36, 1–9. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]






| 2022 | 2023 | |
|---|---|---|
| Base fertilizer | Yunye organic fertilizer (N-P2O5-K2O = 2.74%-1.1%-1.78%), 1500 kg/ha; Yunye biological bacterial fertilizer (N-P2O5-K2O = 3.46%-3.48%-3.77%), 1200 kg/ha | Green source organic fertilizer (N-P2O5-K2O = 2.84%-4.96%-2.02%), 1200 kg/hm2; Jiuyuan Organic Bio-fertilizer (N-P2O5-K2O = 3%-1%-1.7%), 1500 kg/ha; green intelligent rice special fertilizer (compound fertilizer N-P2O5-K2O = 15%-11%-14%), 525 kg/ha |
| Tillering fertilizer | Green all over organic water-soluble fertilizer in small barrels (N-P2O5-K2O = 149 g/L-60.1 g/L-151.2 g/L), 495 L/ha | Urea (TN ≥ 46.5%), 225 kg/ha |
| Panicle fertilizer | Gallium and magnesium (K2O: 22%, Mg: 11%), 90 kg/ha | Potassium chloride (K2O ≥ 60%), 45 kg/ha |
| Total nutrient inputs (N-P2O5-K2O) | 156-88-169 kg/ha | 262-132-150 kg/ha |
| Year | Treatment | Depth of Water (mm) | Rice Growth Stages | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Recovery Stage | Pre-Tillering Stage | Mid-Tillering Stage | Post-Tillering Stage | Panicle Initiation Stage | Heading and Flowering Stage | Milk-Ripe Stage | Ripening Stage | |||
| 2022 | CK | Upper limit | 25 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | Natural drying |
| Lower limit | 5 | 100%θs | 100%θs | 100%θs | 100%θs | 100%θs | 100%θs | |||
| C | Upper limit | 25 | 100%θs | 100%θs | 100%θs | 100%θs | 100%θs | 100%θs | ||
| Lower limit | 5 | 80%θs | 70%θs | 65%θs | 80%θs | 85%θs | 75%θs | |||
| Root observation depth | 0–200 | 0–200 | 0–200 | 0–300 | 0–400 | 0–400 | ||||
| 2023 | CKCD | Upper limit | 25 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | Natural drying |
| Lower limit | 5 | 100%θs | 100%θs | 100%θs | 100%θs | 100%θs | 100%θs | |||
| Storage depth | 25 | 1/3H | 50 | 1/4H | ||||||
| CCD | Upper limit | 25 | 100%θs | 100%θs | 100%θs | 100%θs | 100%θs | 100%θs | ||
| Lower limit | 5 | 80%θs | 70%θs | 65%θs | 80%θs | 85%θs | 75%θs | |||
| Storage depth | 25 | 1/3H | 50 | 1/3H | ||||||
| Storage duration/d | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | ||||
| Root observation depth | 0–200 | 0–200 | 0–200 | 0–300 | 0–400 | 0–400 | ||||
| Year | Treatment | Effective Number of Spikes (Panicles/Hole) | Number of Grains per Spike (Grains/Panicle) | 1000-Grain Weight (g) | Yield (kg/hm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2022 | CK | 13 * | 78.9 * | 26.4 ** | 9805.5 * |
| C | 17 * | 82.2 * | 27.8 ** | 10,279.5 * | |
| 2023 | CKCD | 15 | 105.9 | 26.2 ** | 11,574.2 * |
| CCD | 16 | 111.8 | 27.2 ** | 12,322.7 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Q.; Lu, Q.; Zhang, L.; Wang, S.; Zou, A.; Su, Y.; Sha, J.; Wang, Y.; Chen, L. Effects of Paddy Rain-Flood Storage on Rice Growth Physiological Indices and Nitrogen Leaching under Organic Planting in Erhai Lake Basin. Plants 2024, 13, 2381. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13172381
Liu Q, Lu Q, Zhang L, Wang S, Zou A, Su Y, Sha J, Wang Y, Chen L. Effects of Paddy Rain-Flood Storage on Rice Growth Physiological Indices and Nitrogen Leaching under Organic Planting in Erhai Lake Basin. Plants. 2024; 13(17):2381. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13172381
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Qingsheng, Qiling Lu, Liudong Zhang, Shufang Wang, Aiqing Zou, Yong Su, Jun Sha, Ying Wang, and Lihong Chen. 2024. "Effects of Paddy Rain-Flood Storage on Rice Growth Physiological Indices and Nitrogen Leaching under Organic Planting in Erhai Lake Basin" Plants 13, no. 17: 2381. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13172381
APA StyleLiu, Q., Lu, Q., Zhang, L., Wang, S., Zou, A., Su, Y., Sha, J., Wang, Y., & Chen, L. (2024). Effects of Paddy Rain-Flood Storage on Rice Growth Physiological Indices and Nitrogen Leaching under Organic Planting in Erhai Lake Basin. Plants, 13(17), 2381. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13172381





