Genome-Wide Identification of the Soybean AlkB Homologue Gene Family and Functional Characterization of GmALKBH10Bs as RNA m6A Demethylases and Expression Patterns under Abiotic Stress
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Genome-Wide Identification of the GmALKBH Genes in Soybean
2.2. Chromosomal Localization and Duplication Analysis of Soybean ALKBH Family Genes
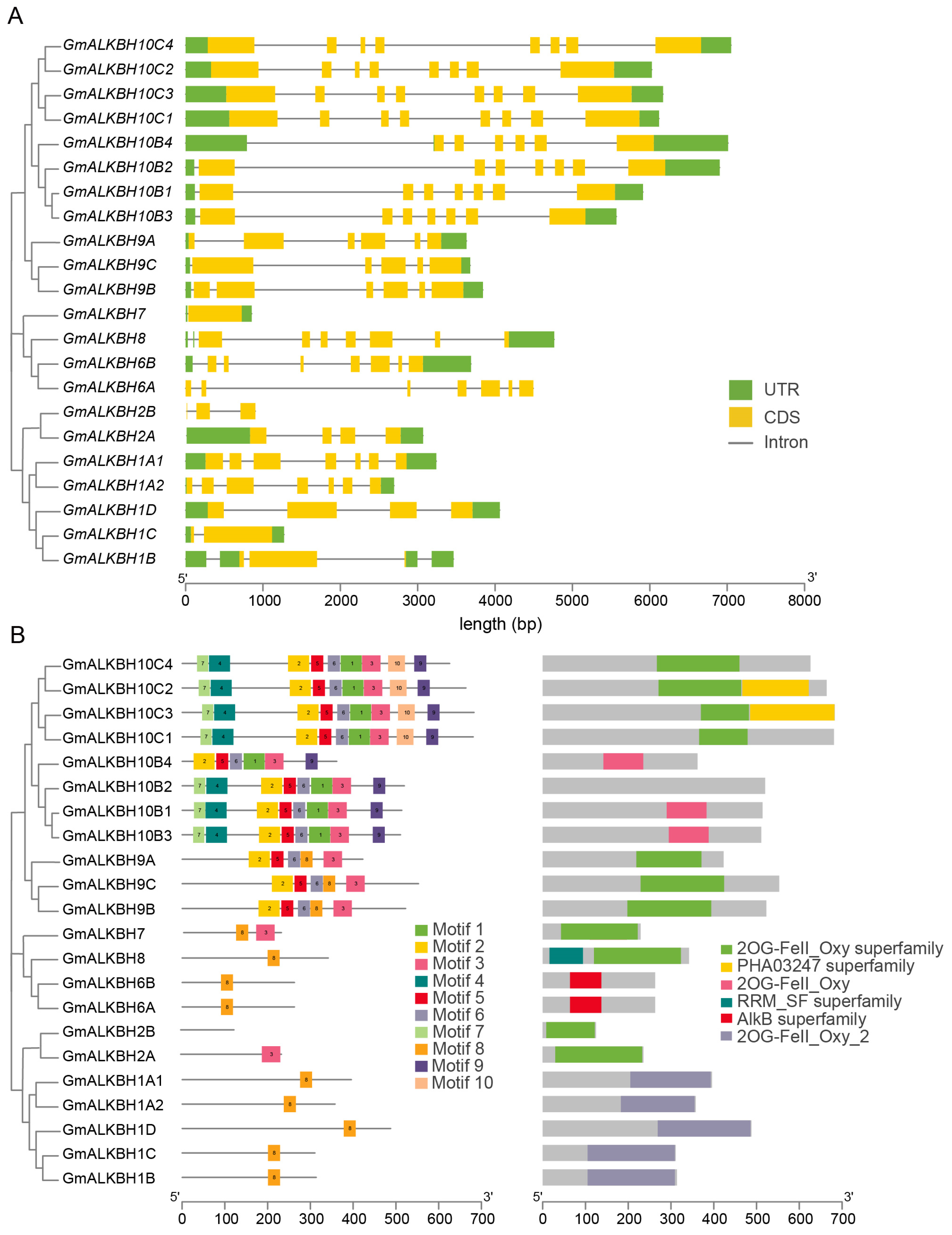
2.3. Gene Structure and Conserved Motifs of the GmALKBH Family of Genes
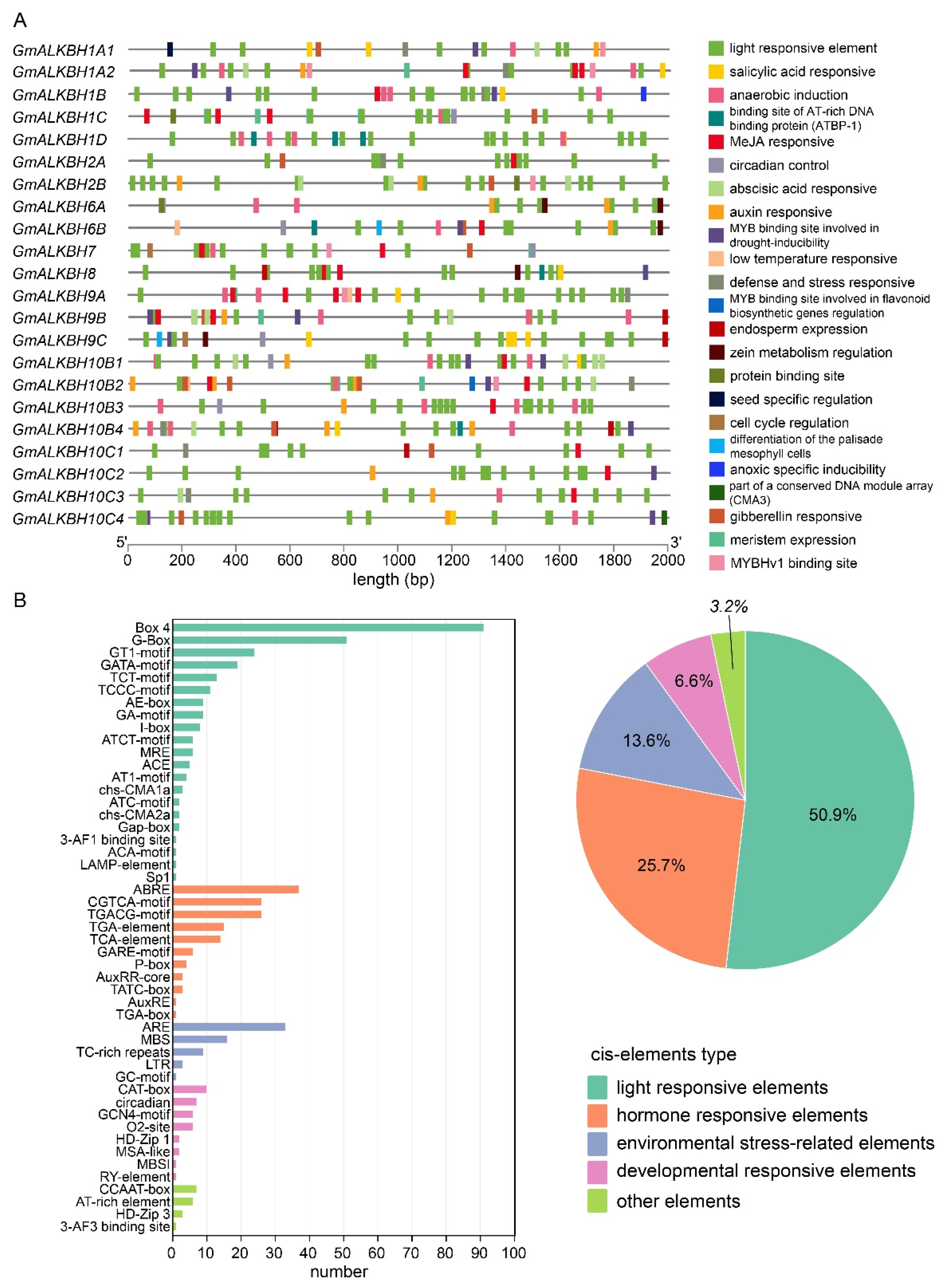
2.4. Cis-Element Analysis of the GmALKBH Family of Genes
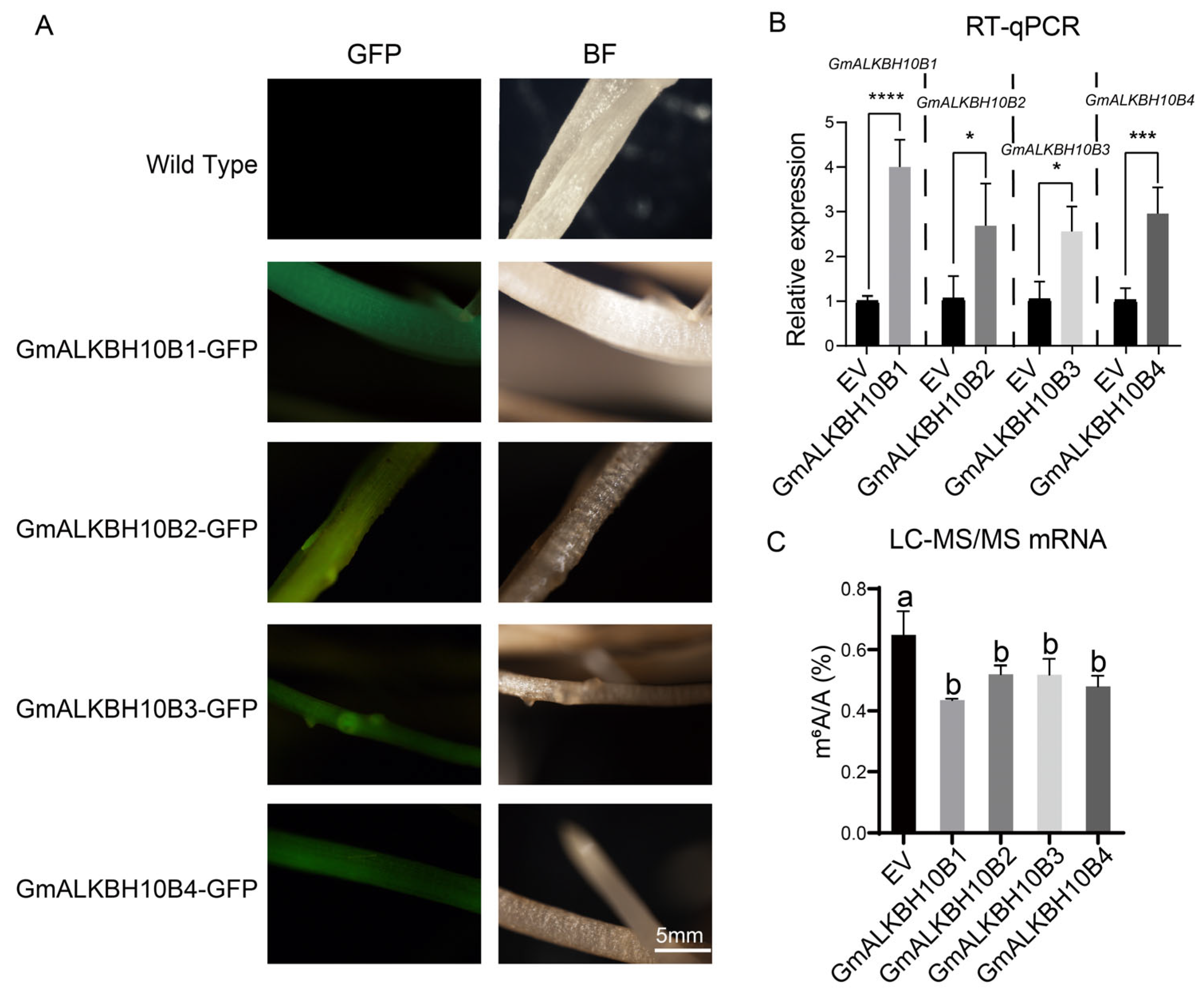
2.5. GmALKBH10Bs Are RNA N6-Methyladenosine Demethylases in Soybean
2.6. Spatiotemporal Expression and Subcellular Localization of GmALKBH10B Subfamily Members
2.7. Expression Patterns of GmALKBH10B Genes in Response to Abiotic Stress
3. Discussion
4. Method
4.1. Plant Materials and Abiotic Treatment
4.2. Identification of GmALKBH Gene Family Members and Construction of the Phylogenetic Tree of the ALKBH Family
4.3. Chromosomal Location and Duplication Analysis of the GmALKBH Gene Family
4.4. Gene Structure, Conserved Domain, Motif Analysis, and Cis-Element Analysis of GmALKBH Genes in Soybean
4.5. RNA Isolation, cDNA Synthesis and Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT–PCR)
4.6. Cloning and Vector Construction
4.7. Soybean Hairy Root Transformation
4.8. Subcellular Localization and Tissue-Specific Expression of GmALKBH10B Genes
4.9. Quantitative Analysis with LC–MS/MS
4.10. Statistics
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ries, R.J.; Zaccara, S.; Klein, P.; Olarerin-George, A.; Namkoong, S.; Pickering, B.F.; Patil, D.P.; Kwak, H.; Lee, J.H.; Jaffrey, S.R. m6A Enhances the Phase Separation Potential of mRNA. Nature 2019, 571, 424–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Urs, M.J.; Sánchez-González, I.; Olayioye, M.A.; Herde, M.; Witte, C.-P. m6A RNA Degradation Products Are Catabolized by an Evolutionarily Conserved N6-Methyl-AMP Deaminase in Plant and Mammalian Cells. Plant Cell 2018, 30, 1511–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataoka, H.; Yamamoto, Y.; Sekiguchi, M. A New Gene (alkB) of Escherichia coli That Controls Sensitivity to Methyl Methane Sulfonate. J. Bacteriol. 1983, 153, 1301–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, G.; Fu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Dai, Q.; Zheng, G.; Yang, Y.; Yi, C.; Lindahl, T.; Pan, T.; Yang, Y.-G.; et al. N6-Methyladenosine in Nuclear RNA Is a Major Substrate of the Obesity-Associated FTO. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2011, 7, 885–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.; Dahl, J.A.; Niu, Y.; Fedorcsak, P.; Huang, C.-M.; Li, C.J.; Vågbø, C.B.; Shi, Y.; Wang, W.-L.; Song, S.-H.; et al. ALKBH5 Is a Mammalian RNA Demethylase That Impacts RNA Metabolism and Mouse Fertility. Mol. Cell 2013, 49, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Pérez, M.; Aparicio, F.; López-Gresa, M.P.; Bellés, J.M.; Sánchez-Navarro, J.A.; Pallás, V. Arabidopsis m6A Demethylase Activity Modulates Viral Infection of a Plant Virus and the m6A Abundance in Its Genomic RNAs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 10755–10760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.-C.; Wei, L.-H.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Y.; Chen, L.; Lu, Z.; Chen, P.R.; He, C.; Jia, G. ALKBH10B Is an RNA N6-Methyladenosine Demethylase Affecting Arabidopsis Floral Transition. Plant Cell 2017, 29, 2995–3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Tian, S.; Qin, G. RNA Methylomes Reveal the m6A-Mediated Regulation of DNA Demethylase Gene SlDML2 in Tomato Fruit Ripening. Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox, J.R. World Distribution and Trade of Soybean. In Agronomy Monographs; Shibles, R.M., Harper, J.E., Wilson, R.F., Shoemaker, R.C., Eds.; American Society of Agronomy, Crop Science Society of America, and Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 2016; pp. 1–14. ISBN 978-0-89118-266-5. [Google Scholar]
- Koberg, M.; Abu-Much, R.; Gedanken, A. Optimization of Bio-Diesel Production from Soybean and Wastes of Cooked Oil: Combining Dielectric Microwave Irradiation and a SrO Catalyst. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 1073–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riechmann, J.L.; Heard, J.; Martin, G.; Reuber, L.; Jiang, C.; Keddie, J.; Adam, L.; Pineda, O.; Ratcliffe, O.J.; Samaha, R.R.; et al. Arabidopsis Transcription Factors: Genome-Wide Comparative Analysis among Eukaryotes. Science 2000, 290, 2105–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.-K. Abiotic Stress Signaling and Responses in Plants. Cell 2016, 167, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Tian, J.; Zhou, M.; Tian, J.; Liang, C. Research Progress on the Physiological and Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Soybean Aluminum Resistance. New Crops 2025, 2, 100034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Chen, Y.; Hu, Q.; Yang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Lin, Y.; Yuan, J.; Gu, J.; Li, Y.; He, J.; et al. PSEUDO-RESPONSE REGULATOR 3b and Transcription Factor ABF3 Modulate Abscisic Acid-Dependent Drought Stress Response in Soybean. Plant Physiol. 2024, 195, 3053–3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, M.; Li, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, W.; Niu, L.; Hu, T. Unraveling Antibiotic Resistomes Associated with Bacterial and Viral Communities in Intertidal Mudflat Aquaculture Area. J. Hazard. Mater 2023, 459, 132087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Han, X.; Su, D.; Liu, C.; Chen, Q.; Qi, Z. An Analysis of Differentially Expressed and Differentially m6A-Modified Transcripts in Soybean Roots Treated with Lead. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 453, 131370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, H.; Liu, B.; Zhao, T. N6-Methyladenosine mRNA Methylation Is Important for the Light Response in Soybean. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1153840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Liu, H.; Zhao, J.; Yang, T.; Guo, S.; Chang, L.; Xiao, T.; Xu, A.; Liu, X.; Zhu, C.; et al. Genome-Wide Identification and Functional Analysis of mRNA m6A Writers in Soybean under Abiotic Stress. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1446591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Yang, J.; Lu, Q.; Tang, Q.; Chen, S.; Jia, G. The RNA N6 -Methyladenosine Demethylase ALKBH9B Modulates ABA Responses in Arabidopsis. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2022, 64, 2361–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Riaz, A.; Chachar, S.; Ding, Y.; Du, H.; Gu, X. Epigenetic Modifications of mRNA and DNA in Plants. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 14–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Zhang, W.; Fu, R.; Zhang, Y. Genome-Wide Characterization of 2-Oxoglutarate and Fe(II)-Dependent Dioxygenase Family Genes in Tomato during Growth Cycle and Their Roles in Metabolism. BMC Genom. 2021, 22, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannon, S.B.; Mitra, A.; Baumgarten, A.; Young, N.D.; May, G. The Roles of Segmental and Tandem Gene Duplication in the Evolution of Large Gene Families in Arabidopsis Thaliana. BMC Plant Biol. 2004, 4, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Hu, X.; Ren, Y.; Song, M.; Ma, C.; Miao, Z. IPOP: An Integrative Plant Multi-Omics Platform for Cross-Species Comparison and Evolutionary Study. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2023, 40, msad248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Wang, X.; Cao, L.; Ji, J.; Liu, T.; Duan, K. Highly Efficient Agrobacterium Rhizogenes-Mediated Hairy Root Transformation for Gene Functional and Gene Editing Analysis in Soybean. Plant Methods 2021, 17, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Guo, J.; Peng, Y.; Lyu, X.; Liu, B.; Sun, S.; Wang, X. Light-Induced Mobile Factors from Shoots Regulate Rhizobium-Triggered Soybean Root Nodulation. Science 2021, 374, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kereszt, A.; Li, D.; Indrasumunar, A.; Nguyen, C.D.; Nontachaiyapoom, S.; Kinkema, M.; Gresshoff, P.M. Agrobacterium Rhizogenes-Mediated Transformation of Soybean to Study Root Biology. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 948–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhong, L.; Wang, X.; Jin, L.; Lyu, S. One-Step Generation of Composite Soybean Plants with Transgenic Roots by Agrobacterium rhizogenes-Mediated Transformation. BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Guo, Q.; Cao, S.; Tian, Y.; Han, K.; Sun, Y.; Li, J.; Yang, Q.; Ji, Q.; Sederoff, R.; et al. Genome-Wide Identification of the AlkB Homologs Gene Family, PagALKBH9B and PagALKBH10B Regulated Salt Stress Response in Populus. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 994154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, R.; Shoaib, Y.; Cai, J.; Kang, H. ALKBH10B-Mediated m6A Demethylation Is Crucial for Drought Tolerance by Affecting mRNA Stability in Arabidopsis. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2023, 209, 105306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Yang, J.; Duan, H.; Jia, G. ALKBH10B, an mRNA m6A Demethylase, Modulates ABA Response During Seed Germination in Arabidopsis. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 712713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Luo, B.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Hu, Z.; Xie, Q.; Wu, T.; Chen, G. Genome-Wide Identification, Classification and Expression Analysis of m6A Gene Family in Solanum Lycopersicum. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.; Xing, F.; Xu, C.; Zhang, Q.; Che, J.; Wang, X.; Song, J.; Li, X.; Xiao, J.; Chen, L.-L.; et al. Patterns of Genome-Wide Allele-Specific Expression in Hybrid Rice and the Implications on the Genetic Basis of Heterosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 5653–5658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.; Li, G.-J.; Bressan, R.A.; Song, C.-P.; Zhu, J.-K.; Zhao, Y. Abscisic Acid Dynamics, Signaling, and Functions in Plants. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2020, 62, 25–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Wang, H.; Xu, Z.; Jiang, S.; Shi, Y.; Xie, H.; Wang, S.; Hua, J.; Wu, Y. m6A mRNA Modification Promotes Chilling Tolerance and Modulates Gene Translation Efficiency in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2023, 192, 1466–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Fu, L.; Su, T.; Xiong, J.; Chen, Y.; Shen, Q.; Kuang, L.; Wu, D. N6-Methyladenosine Methylation Analysis Reveals Transcriptome-Wide Expression Response to Salt Stress in Rice Roots. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2022, 201, 104945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, N.; Li, C.; He, J.; Liu, Y.; Yu, S.; Malnoy, M.; Mobeen Tahir, M.; Xu, L.; Ma, F.; Guan, Q. MdMTA-mediated m6A Modification Enhances Drought Tolerance by Promoting mRNA Stability and Translation Efficiency of Genes Involved in Lignin Deposition and Oxidative Stress. New Phytol. 2022, 234, 1294–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Chen, S.; Jia, G. Detection, Regulation, and Functions of RNA N6-Methyladenosine Modification in Plants. Plant Commun. 2023, 4, 100546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Zhou, Y.; Liao, C.; Xie, Q.; Chen, G.; Hu, Z.; Wu, T. The AlkB Homolog SlALKBH10B Negatively Affects Drought and Salt Tolerance in Solanum Lycopersicum. IJMS 2023, 25, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Chen, Y.; Cai, G.; Cai, R.; Hu, Z.; Wang, H. Tree Visualization By One Table (tvBOT): A Web Application for Visualizing, Modifying and Annotating Phylogenetic Trees. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, W587–W592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wu, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Zeng, Z.; Xu, J.; Liu, Y.; Feng, J.; Chen, H.; He, Y.; et al. TBtools-II: A “One for All, All for One” Bioinformatics Platform for Biological Big-Data Mining. Mol. Plant 2023, 16, 1733–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, S.J.; Kramer, M.C.; Gosai, S.J.; Yu, X.; Vandivier, L.E.; Nelson, A.D.L.; Anderson, Z.D.; Beilstein, M.A.; Fray, R.G.; Lyons, E.; et al. N6-Methyladenosine Inhibits Local Ribonucleolytic Cleavage to Stabilize mRNAs in Arabidopsis. Cell Rep. 2018, 25, 1146–1157.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Liu, H.; Wang, F.; Liu, X.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhu, C.; Gan, L.; Yu, J.; Witte, C.-P.; et al. N4-Acetylation of Cytidine in mRNA Plays Essential Roles in Plants. Plant Cell 2023, 35, 3739–3756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.; Sun, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhu, C.; Liu, X.; Wang, W.; Gan, L.; Lu, Y.; Schaarschmidt, F.; Herde, M.; et al. Pyrimidine Catabolism Is Required to Prevent the Accumulation of 5-Methyluridine in RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, 7451–7464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real-Time Quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Witte, C.-P. A Kinase and a Glycosylase Catabolize Pseudouridine in the Peroxisome to Prevent Toxic Pseudouridine Monophosphate Accumulation. Plant Cell 2020, 32, 722–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, K.; Kopperud, K.; Chakrabarty, R.; Banerjee, R.; Brooks, R.; Goodin, M.M. Transient Expression in Nicotiana Benthamiana Fluorescent Marker Lines Provides Enhanced Definition of Protein Localization, Movement and Interactions in Planta. Plant J. 2009, 59, 150–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Tan, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Liu, H.; Liu, P.; Meng, W.; Ding, A.; Xiang, Z.; Chen, M. Dissecting the Roles of Increased mRNA m6A Methylation in Autotetraploidization in Stevia Rebaudiana. Plant Growth Regul. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Liu, X.; Wang, W.; Chen, X.; Gao, S.; Qian, M.; Yang, N.; Xu, Y.; Chen, M. Plant Sample Preparation for Nucleoside/Nucleotide Content Measurement with An HPLC-MS/MS. J. Vis. Exp. 2021, 168, e61956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Gene Name | Gene ID (Phytozome) | Amino Acid Length | Isoelectric Point | Molecular Weight (kDa) | Subcellular Localization Prediction |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GmALKBH1A1 | Glyma.11G250800 | 396 | 7.13 | 45.05 | chloroplast |
| GmALKBH1A2 | Glyma.18G006200 | 358 | 5.89 | 40.53 | nucleus |
| GmALKBH1B | Glyma.19G263000 | 314 | 9.33 | 34.62 | nucleus |
| GmALKBH1C | Glyma.20G056000 | 311 | 8.72 | 34.37 | nucleus |
| GmALKBH1D | Glyma.01G129600 | 488 | 8.94 | 54.13 | mitochondrion |
| GmALKBH2A | Glyma.09G014800 | 236 | 9.14 | 27.12 | nucleus |
| GmALKBH2B | Glyma.15G120500 | 125 | 9.86 | 14.32 | extracellular space |
| GmALKBH6A | Glyma.09G156400 | 263 | 6.26 | 30.03 | nucleus |
| GmALKBH6B | Glyma.16G207100 | 263 | 6.20 | 29.79 | nucleus |
| GmALKBH7 | Glyma.14G026500 | 229 | 5.91 | 25.75 | nucleus |
| GmALKBH8 | Glyma.09G217100 | 342 | 6.83 | 38.34 | nucleus |
| GmALKBH9A | Glyma.08G186500 | 423 | 6.29 | 48.00 | nucleus |
| GmALKBH9B | Glyma.14G106000 | 523 | 6.22 | 58.58 | nucleus |
| GmALKBH9C | Glyma.17G220300 | 553 | 7.60 | 62.19 | nucleus |
| GmALKBH10B1 | Glyma.02G149900 | 514 | 5.95 | 56.37 | nucleus |
| GmALKBH10B2 | Glyma.03G149900 | 520 | 5.88 | 57.46 | nucleus |
| GmALKBH10B3 | Glyma.10G023900 | 511 | 5.71 | 56.08 | nucleus |
| GmALKBH10B4 | Glyma.19G152900 | 362 | 8.66 | 40.24 | nucleus |
| GmALKBH10C1 | Glyma.05G138600 | 681 | 6.79 | 73.69 | nucleus |
| GmALKBH10C2 | Glyma.07G175300 | 664 | 6.61 | 71.74 | nucleus |
| GmALKBH10C3 | Glyma.08G093800 | 683 | 7.12 | 73.46 | nucleus |
| GmALKBH10C4 | Glyma.20G012100 | 626 | 6.73 | 68.04 | nucleus |
| Duplicated 1 | Duplication 2 | Duplication Event |
|---|---|---|
| GmALKBH1A1 | GmALKBH1A2 | whole genome duplication |
| GmALKBH1B | GmALKBH1D | transposed duplication |
| GmALKBH1C | GmALKBH1D | transposed duplication |
| GmALKBH2A | GmALKBH2B | whole genome duplication |
| GmALKBH6A | GmALKBH6B | whole genome duplication |
| GmALKBH9A | GmALKBH9B | transposed duplication |
| GmALKBH9B | GmALKBH9C | whole genome duplication |
| GmALKBH10B1 | GmALKBH10B2 | whole genome duplication |
| GmALKBH10B1 | GmALKBH10B3 | whole genome duplication |
| GmALKBH10B2 | GmALKBH10B3 | whole genome duplication |
| GmALKBH10B2 | GmALKBH10B4 | whole genome duplication |
| GmALKBH10C1 | GmALKBH10C2 | whole genome duplication |
| GmALKBH10C1 | GmALKBH10C3 | whole genome duplication |
| GmALKBH10C1 | GmALKBH10C4 | whole genome duplication |
| GmALKBH10C2 | GmALKBH10C3 | whole genome duplication |
| GmALKBH10C2 | GmALKBH10C4 | whole genome duplication |
| GmALKBH10C3 | GmALKBH10C4 | whole genome duplication |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, J.; Yang, T.; Liu, P.; Liu, H.; Zhang, H.; Guo, S.; Liu, X.; Chen, X.; Chen, M. Genome-Wide Identification of the Soybean AlkB Homologue Gene Family and Functional Characterization of GmALKBH10Bs as RNA m6A Demethylases and Expression Patterns under Abiotic Stress. Plants 2024, 13, 2491. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13172491
Zhao J, Yang T, Liu P, Liu H, Zhang H, Guo S, Liu X, Chen X, Chen M. Genome-Wide Identification of the Soybean AlkB Homologue Gene Family and Functional Characterization of GmALKBH10Bs as RNA m6A Demethylases and Expression Patterns under Abiotic Stress. Plants. 2024; 13(17):2491. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13172491
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Jie, Tengfeng Yang, Peng Liu, Huijie Liu, Hui Zhang, Sichao Guo, Xiaoye Liu, Xiaoguang Chen, and Mingjia Chen. 2024. "Genome-Wide Identification of the Soybean AlkB Homologue Gene Family and Functional Characterization of GmALKBH10Bs as RNA m6A Demethylases and Expression Patterns under Abiotic Stress" Plants 13, no. 17: 2491. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13172491
APA StyleZhao, J., Yang, T., Liu, P., Liu, H., Zhang, H., Guo, S., Liu, X., Chen, X., & Chen, M. (2024). Genome-Wide Identification of the Soybean AlkB Homologue Gene Family and Functional Characterization of GmALKBH10Bs as RNA m6A Demethylases and Expression Patterns under Abiotic Stress. Plants, 13(17), 2491. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13172491







