Abstract
The basic leucine zipper (bZIP) transcription factors constitute the most widely distributed and conserved eukaryotic family. They play crucial roles in plant growth, development, and responses to both biotic and abiotic stresses, exerting strong regulatory control over the expression of downstream genes. In this study, a genome-wide characterization of the CebZIP transcription factor family was conducted using bioinformatic analysis. Various aspects, including physicochemical properties, phylogenetics, conserved structural domains, gene structures, chromosomal distribution, gene covariance relationships, promoter cis-acting elements, and gene expression patterns, were thoroughly analyzed. A total of 70 CebZIP genes were identified from the C. ensifolium genome, and they were randomly distributed across 18 chromosomes. The phylogenetic tree clustered them into 11 subfamilies, each exhibiting complex gene structures and conserved motifs arranged in a specific order. Nineteen pairs of duplicated genes were identified among the 70 CebZIP genes, with sixteen pairs affected by purifying selection. Cis-acting elements analysis revealed a plethora of regulatory elements associated with stress response, plant hormones, and plant growth and development. Transcriptome and qRT-PCR results demonstrated that the expression of CebZIP genes was universally up-regulated under low temperature conditions. However, the expression patterns varied among different members. This study provides theoretical references for identifying key bZIP genes in C. ensifolium that confer resistance to low-temperature stress, and lays the groundwork for further research into their broader biological functions.
1. Introduction
The basic leucine zipper (bZIP) transcription factors (TFs) are ubiquitously found in eukaryotes and are characterized by a highly conserved bZIP domain, which includes a region rich in basic amino acids and a leucine zipper [1,2,3]. Specifically, the basic region is located at the N-terminal end and exhibits a high degree of conservation, consisting of 16 amino acid residues that recognize and bind to specific sequences on the promoter through the N-X7-R/K motifs [3]. On the other hand, the leucine zipper region is relatively less conserved and is marked by a leucine or a repetitive region containing seven amino acid residues, including isoleucine, methionine, and other hydrophobic amino acids [4]. The leucine zipper can form an amphipathic α helix, mediating the formation of homodimers or heterodimers of bZIP proteins with transcriptional activation or repression functions [5,6]. In plants, bZIP proteins preferentially recognize cis-acting elements on promoters with ACGT core sequences, such as the G-box (CACGTG) and C-box (GACGTC) [7,8]. Notably, most of the promoter regions of bZIP genes induced by abscisic acid (ABA) contain these cis-acting elements.
bZIP TFs have been found to play a widespread role in regulating various plant life activities, including seed germination and maturation, flower development, root development, plant senescence, photomorphogenesis, and light signaling [3,9,10,11,12,13,14]. The co-expression of AtbZIP10/25 with ABI3 significantly enhances the activation of the At2S1 (2S storage protein) promoter, indicating their involvement in the composition of the regulatory complex associated with seed maturation-specific expression [15]. In addition, AtbZIP18 interacts with AtbZIP34, while AtbZIP52 interacts with AtbZIP61 in yeast to co-regulate pollen development [10]. Notably, the mutants AtbZIP18 and AtbZIP34 exhibit a failure in forming normal pollen walls, leading to a reduced amount of viable pollen [10]. In Zea mays, ZmbZIP4 binds to the promoters of root development-related genes, such as ZmLRP1 and ZmSCR, thereby activating the transcription of root development-related genes, consequently promoting root growth and development [12].
Furthermore, bZIP TFs are involved in abiotic stresses, including low-temperature stress, drought stress, and salinity stress, as well as in biotic stresses such as disease and pathogen defense, and they also contribute to the induction of various hormones [4,16,17,18,19,20,21]. For instance, the overexpression of TabZIP6 in Arabidopsis thaliana significantly reduced the expression of genes like CBF and CORs in plants, leading to decreased freezing resistance in transgenic A. thaliana seedlings [22]. In Camellia sinense, CsbZIP6 acts as a negative regulator of the low-temperature stress responses, reducing the expression of low-temperature-responsive genes and influencing ABA sensitivity [23]. Moreover, the overexpression of BnbZIP2 in Arabidopsis significantly increases the sensitivity of transgenic plants to drought and salinity stress [24]. Under drought stress, the down-regulation of ABA biosynthesis and signal transduction-related genes in tomato occurred when SlbZIP1 was silenced, indicating that SlbZIP1 plays a role in promoting drought resistance in tomato [25].
Cymbidium ensifolium thrives in warm and humid environments, displaying limited cold tolerance. Safe overwintering requires temperatures above 5 °C, and the plant becomes susceptible to frost damage when temperatures drop below 0 °C. Despite bZIP TFs having been identified in various species, including A. thaliana (78 genes) [7], Glycine max (160 genes) [18], Ipomoea batatas (87 genes) [26], Sorghum bicolor (92 genes) [27], Juglans regia (88 genes) [28], Populus trichocarpa (41 genes) [29], and Malus pumila (112 genes) [30], their presence is mainly concentrated in cash crops. The bZIP gene family has been rarely reported in C. ensifolium. This study is based on the genome-wide sequencing data of C. ensifolium, aiming to identify and characterize the members of the bZIP family in C. ensifolium (CebZIP). Bioinformatic methods were applied to comprehensively analyze the protein properties, phylogenetic relationships, conserved motifs, gene structure, and other information of the CebZIP family. The findings of this study can provide reference for enhancing the cold tolerance of C. ensifolium, and provide a theoretical foundation for the functional verification of CebZIP genes (CebZIPs) and the identification of key response genes in future research.
2. Results
2.1. Identification and Characterization Analysis of CebZIPs in C. ensifolium
Using HMM from the Pfam database for alignment on the C. ensifolium genome database, 78 matches were obtained as candidate CebZIP proteins [31]. By identifying the complete bZIP domains in both the Pfam and SMART databases, a total of 70 CebZIP protein sequences were finally selected [31,32,33]. These CebZIP proteins were designated CebZIP1–CebZIP70 in accordance with their chromosomal arrangement (Table S1). An analysis of the physicochemical properties revealed that the molecular weights (MW) of the 70 CebZIP proteins ranged from 9.04 kDa (CebZIP31) to 75.16 kDa (CebZIP67). The smallest CebZIP protein was CebZIP23 (77 aa and 234 bp), while the largest was CebZIP67 (697 aa and 2094 bp). The isoelectric point (PI) ranged from 4.99 (CebZIP10) to 11.55 (CebZIP45). The instability coefficients ranged from 29.74 (CebZIP3) to 86.21 (CebZIP45), and the aliphatic index coefficients ranged from 53.46 (CebZIP8) to 90.17 (CebZIP55). The grand average of hydropathicity (GRAVY) consistently remained below 0 for all CebZIP proteins, indicating their hydrophilic nature.
2.2. Phylogenetic Analysis of CebZIPs
A. thaliana is one of the earliest plants studied for the bZIP TF family, holds significant reference value, and is commonly employed as a model genetic plant for plant gene research [3,7]. To gain a deeper understanding of the evolutionary properties of CebZIP family members, a phylogenetic tree was constructed by combining 70 CebZIPs with 78 AtbZIPs (Figure 1) [7]. Following the classification method used for AtbZIP proteins in previous studies [7], the CebZIPs were clustered into 11 subfamilies (A–I, K, and S), along with four unclassified genes. In the AtbZIP family, the largest subfamily is subfamily S (17 members), and the smallest subfamilies are subfamilies K and J (each with 1 member). Similarly, in the CebZIP family, the number of members varies among the 11 subfamilies, with the largest number in subfamily S (18 members) and the smallest in subfamily K (1 member). The high amino acid sequence similarity observed among members of the same subfamily demonstrates substantial homology between CebZIPs and AtbZIPs.
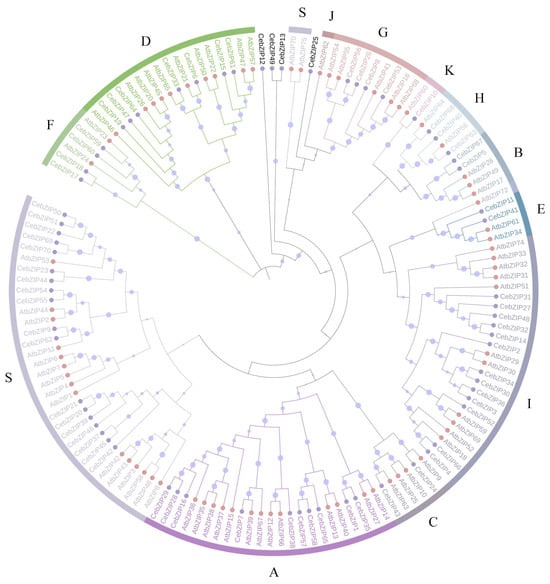
Figure 1.
Phylogenetic tree of bZIP proteins from C. ensifolium and A. thaliana. Different bZIP subfamilies are marked by different colors. Pink and purple circles represent CebZIP proteins and AtbZIP proteins, respectively. The size of the purple circle on the branch reflects the level of support.
2.3. Analysis of Conserved Domains, Conserved Motifs, and the Gene Structure of the CebZIPs
To further study and characterize the homologous conserved domains in CebZIP proteins, a multiple sequence alignment and a weblogo analysis of CebZIP proteins were performed by analyzing the characteristic amino acid sequences of the leucine zipper and basic domains within the bZIP gene family. Similar to other species, CebZIP proteins contain basic domains and leucine zipper, namely, [-N-X7-R/K-] and [-L-X6-L-X6-L-] (Figure 2).
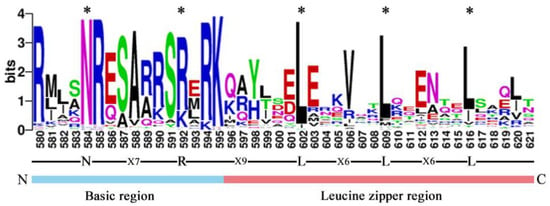
Figure 2.
The bZIP domain of CebZIP proteins, consisting of a basic region and a leucine zipper region. The * represent the conserved amino acids of bZIP domain.
Predictions of conserved motifs among the 70 CebZIP proteins revealed the presence of 10 motifs, strategically distributed at the N-terminal and C-terminal ends, and the middle part of the proteins. Motif 1 displayed universal presence across all CebZIP proteins, underscoring its high conservation within the CebZIP gene family. Moreover, certain motifs have significant specificity. For instance, motifs 2, 5, 7, and 8 were exclusive to subfamily D, while motif 4 was uniquely present in subfamily I. As expected, substantial differences in motif composition were observed between subfamilies. In contrast, motifs within the same subfamily demonstrated similarities, and the overall pattern of motif distribution within each subfamily remained essentially similar.
To further verify the structural characteristics of all CebZIPs, we analyzed the number and structure of intron/exon (Figure 3). The gene structure of CebZIPs displayed significant variability and diversity in terms of the relative position and number of introns and exons. The intron numbers among the 70 CebZIPs ranged from 0 and 18. Seventeen (24.3%) CebZIPs showed no intron structure, with the majority concentrated in the S subfamily. CebZIP53, belonging to the G subfamily, exhibited the highest number of introns (18), resembling the gene structure of AtbZIPs. The exon numbers varied from two to seven in subfamilies A, B, C, E, F, H, I, and K. Conversely, subfamilies D and G have the most complex gene structures, with exon numbers ranging from nine to nineteen.

Figure 3.
Conserved motif and gene structure analysis of CebZIPs. (a) Phylogenetic tree. (b) Conserved motifs are shown by colored boxes. (c) Exon/intron structure of CebZIPs are displayed by green bars and black lines, respectively.
2.4. Chromosomal Distribution and Covariance Analysis of CebZIP Family Members
A chromosomal distribution map of CebZIP gene family was generated using Tbtools [34]. The C. ensifolium genome comprises 20 chromosomes, and the 70 CebZIPs are randomly distributed across 18 of these chromosomes, with chromosomes 11 and 18 lacking bZIP genes (Figure 4). Chromosome 13 accommodates the highest number of CebZIP genes (eight), while chromosomes 9, 12, 15, 16, 17, and 19 each contain two genes.
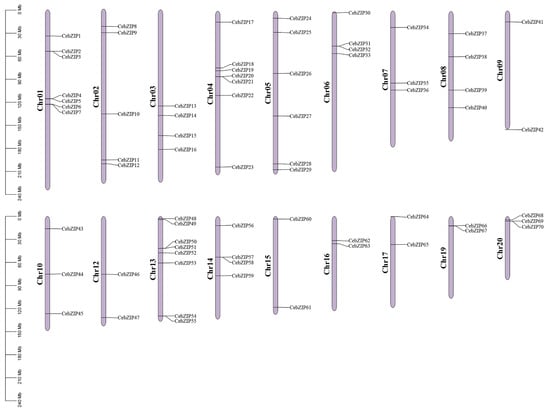
Figure 4.
Localization and distribution of the 70 CebZIP genes on the 18 chromosomes of C. ensifolium. Red boxes indicate tandem duplicated genes. The scale represents the chromosomal distances (Mbp).
Gene duplication is a major driver in the evolution of genomes and genetic systems. The analysis of the intraspecific collinearity in C. ensifolium revealed that the CebZIP family consists of 19 duplicated gene pairs, including 9 pairs of segmental duplicates and 10 pairs of tandem duplicates (Figure 5). Chromosomes 1 harbors the highest number of tandem duplicated gene pairs (three), followed by chromosomes 13, 4, 6, 14, and 19 (two each), while chromosomes 20 contained only one pair. To explore the evolutionary characteristics of the bZIP family in orchids, collinearity relationships were established by comparing C. ensifolium with two other orchids, Cymbidium goeringii and Dendrobium chrysotoxum (Figure 6). The number of homologous pairs between C. ensifolium and these two orchids was similar, with 56 and 54 pairs, respectively.
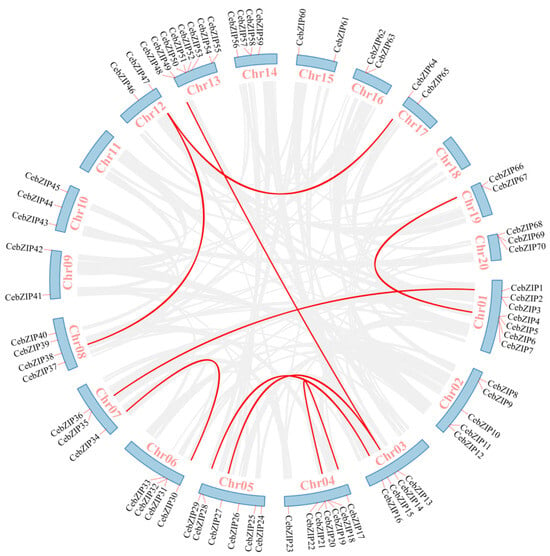
Figure 5.
Collinear distribution of CebZIP genes on chromosomes. The 18 chromosomes of C. ensifolium are arranged in a circular blue bar. Red lines connecting chromosomes represent segmentally duplicated genes.
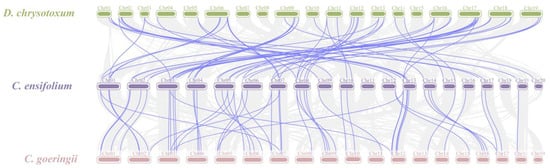
Figure 6.
Collinearity analysis of bZIP genes among three orchids. Gray lines indicate all syntenic blocks between C. ensifolium and the other two orchids. The blue lines delineate collinear pairs of bZIPs.
To investigate the environmental selection pressure experienced by these duplicated CebZIP genes, we calculated the non-synonymous site (Ka) and synonymous site (Ks) of each gene pair and analyzed their ratios (Ka/Ks) (Table S2). Three pairs of CebZIP genes yielded NaN (Not a Number), which might be attributed to potential genome sequencing errors. Among the remaining 16 duplicated gene pairs, 2 gene pairs displayed only synonymous without non-synonymous. The remaining 14 Ka/Ks values were all less than 1, with 75% of them being less than 0.5, suggesting that the majority of the CebZIPs evolved under strong purifying selection.
2.5. Prediction of Cis-Acting Elements in CebZIP Promoters
To predict the biological function of the CebZIPs, a cis-acting element analysis of the 2000 bp promoter region upstream of the CebZIPs start codons was performed using the PlantCARE database (Figure 7) [35]. Abundant cis-acting elements were identified, and 19 crucial elements, excluding general transcriptional regulatory and functionally unknown elements, were selected for analysis. These included light-responsive element (e.g., G-Box, GT1-motif, and Sp1), ABA-responsive element (ABRE), and low-temperature response element (LTR), among others. These elements were categorized into three groups: plant hormones, abiotic stress, and plant growth/development. Further analysis revealed that the cis-acting element number in the abiotic stress group was the largest, followed by the plant hormone group. Notably, 28 (40%) genes in the CebZIP gene family contained LTR. The presence of various cis-acting elements suggests a wide range of functional roles for CebZIP genes.
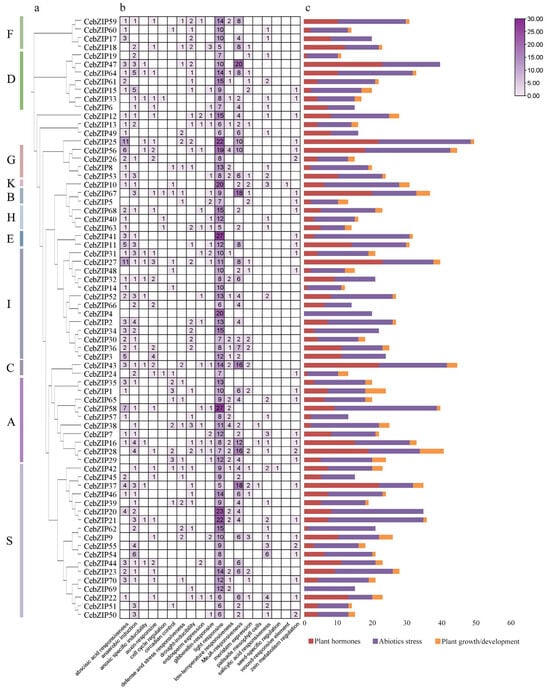
Figure 7.
The cis-acting elements of CebZIP gene promoters. (a) Phylogenetic tree. (b) The number of cis-acting elements is shown in boxes. (c) The different colors delineate the main categories of the functional components. The size of the box delineates the number of functional components.
2.6. Analysis of Expression Patterns of CebZIP Genes from Transcriptome Data
Gene expression patterns can unveil various biological functions in plants. To validate the role of CebZIPs in response to low-temperature stress, we used transcriptome data to examine the expression levels of CebZIPs at 0 h, 4 h, 12 h, and 24 h post treatment with low-temperature stress. Subsequently, we constructed a gene expression heat map (Figure 8). Following low-temperature stress, the expression level of most CebZIP genes changed significantly and exhibited diverse temporal expression patterns, suggesting their distinct regulatory roles in response to low-temperature stress.
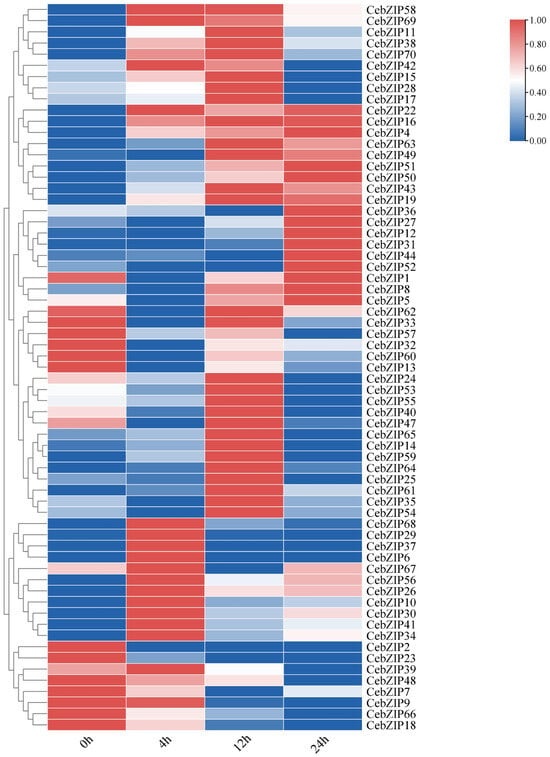
Figure 8.
Heat map of bZIPs expression under low-temperature stress in C. ensifolium, with 0 h, 4 h, 12 h, and 24 h delineating different times of low-temperature treatment.
After low-temperature treatment, CebZIP2, CebZIP23, CebZIP48, CebZIP9, CebZIP66, and CebZIP18 displayed lower expression than the control group (0 h). Seventeen genes were up-regulated after 4 h of low-temperature stress, while twenty-seven genes showed elevated expression after 12 h of low-temperature stress. Fourteen genes exhibited high expression after 24 h of low-temperature stress. These findings underscore the functional diversity of the CebZIP gene family in responding to adverse stress in C. ensifolium.
2.7. Analysis of CebZIP Gene Expression Patterns under Cold Stress
Combining the results of CebZIP gene promoter and transcriptome data analysis, nine genes were selected for qRT-PCR experiment. As shown in Figure 9, their expression levels were generally consistent with the transcriptome analysis results. Under low-temperature stress, the gene expression patterns changed significantly over time. CebZIP8 expression began to rise at 12 h, reaching its peak at 24 h. CebZIP24 showed its highest expression at 12 h, followed by a sharp decrease. CebZIP26 exhibited high expression at 4 h, followed by a decrease and then a slight increase at 24 h. The overall expression patterns of CebZIP28, CebZIP38, and CebZIP70 followed an increase and a decrease, reaching a peak at 12 h, followed by a sharp down-regulation. The highest expression of CebZIP37 and CebZIP56 occurred at 4 h. CebZIP43 demonstrated a slight increase at 4 h, reaching its peak at 24 h.
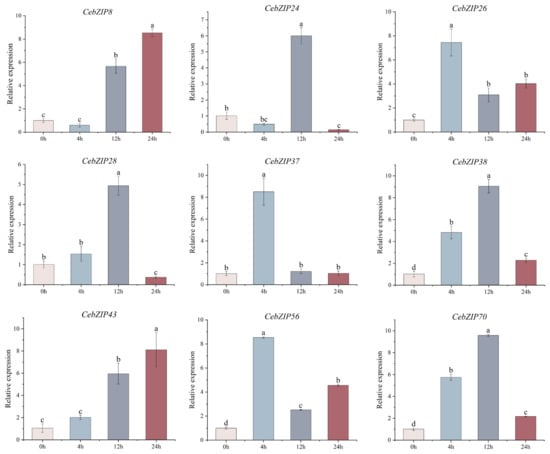
Figure 9.
qRT-PCR analysis of nine CebZIP genes in C. ensifolium under low-temperature treatment. Error bars indicate the SD of three biological replicates. Letters delineate significant differences among treatments (p < 0.05, Duncan).
3. Discussion
C. ensifolium is a shade-tolerant plant typically found in cool environments such as thickets and forests, displaying low tolerance to both cold and heat. The bZIP gene family plays an essential role in regulating growth and development throughout the entire life cycle of plant, and it also contributes significantly to enhance resistance to low temperatures [36,37]. Previous research has confirmed that bZIP TFs have a strong response to various abiotic stresses, and their high expression has been shown to enhance resistance in different species, including maize [38], cotton [39], rice [40], and other crops. The genome-wide characterization of the bZIP gene family has been conducted in many species. However, it has not yet been reported for C. ensifolium nor has the involvement of bZIP genes in responding to low temperatures in C. ensifolium been studied.
Based on the whole genome data, we used bioinformatic methods to identify and analyze the members of the bZIP gene family in C. ensifolium [41]. A total of 70 CebZIPs were identified after removing redundancy and were found to be randomly distributed on 18 chromosomes. Using these CebZIP genes, we constructed an evolutionary tree together with AtbZIP genes. The CebZIPs were clustered into 11 subfamilies (A–I, K, S), a pattern observed in other species, such as sweet potato [26], tobacco [42], and pineapple [43], suggesting that the bZIP gene family is conserved. No CebZIP family members were categorized into subfamily M and subfamily J, which is similar to poplar [29]. In addition, four CebZIP proteins were not clustered and may represent new members formed during the evolutionary process, which requires further investigation of their biological functions. These findings indicated the absence or increase of bZIP members during the evolution of C. ensifolium, potentially linked to the diverse functions of CebZIP proteins.
The multiple sequence alignment and weblogo analysis of CebZIP proteins revealed that all CebZIP proteins contain the basic domain [-N-X7-R/K-] and leucine zipper region [-L-(X6)-L-(X6)-L-], similar to A. thaliana, poplar, and other species [3,29]. These results indicate that the bZIP family is highly conserved during the evolutionary process. The motif composition of the CebZIP varied among subfamilies, but motifs were similar within the same subfamily. Moreover, the motifs encoding the bZIP domains were relatively conserved, suggesting inter-clade-specific functions of CebZIP proteins. There also appear to be potential functional similarities among proteins within the same subfamily of CebZIPs.
Conservative gene structure changes are likely to represent key events in evolution, and variations in exon-intron positions and numbers can lead to specific gene functions and evolutionary directions [44]. The gene structure of CebZIPs is significantly diverse in terms of the relative position and number of introns/exons. The intron numbers ranged from 0 to 18, and there were notable differences in gene length. Seventeen (24.3%) CebZIP genes had no intron structure, with most of them concentrated in subfamily S. The high degree of similarity in the structural features of the genes may be attributed to gene duplication events during the gene family expansion [37]. Differences in gene structure arise from mutations in introns such as base substitutions, insertions, and deletions, which alter the gene sequence and result in diversity in the number and arrangement of introns, contributing to the functional development of CebZIP proteins [45].
Tandem duplication and segmental duplication are primary mechanisms responsible for the expansion of gene families and the emergence of new functional genes during gene evolution [46]. In the CebZIP gene family, a total of 19 pairs of duplicated genes were identified, including 9 pairs of segmental duplicates and 10 pairs of tandem duplicates. This suggest that gene duplication events play an essential role in the evolutionary dynamics of bZIP. In comparison, poplar has 31 pairs of segmental duplicates [29], wheat has 14 pairs of segmental duplicates [47], and tobacco has 16 pairs of segmental duplicates [42], none of which involve tandem events. In tomato, 21 pairs of segmental duplicate genes and 8 pairs of tandem duplicate genes were identified [48]. These findings underscore the ongoing evolution of the bZIP gene family, generating genes with novel functions.
The analysis of the collinearity between C. ensifolium and two other orchids (D. chrysotoxum and C. goeringii) revealed strong homology and highly conserved evolutionary relationships among these three orchids. To assess selection pressure on protein-coding genes [49], a selection pressure analysis was performed. The segregation and selection processes were examined by calculating Ka/Ks values for 19 pairs of duplicate genes. The Ka/Ks values of 16 pairs of duplicate genes were all < 1, with 75% of them < 0.5. These findings suggest that these genes underwent strong selection for purification, and the bZIP genes exhibited a slow and highly conserved evolutionary process in C. ensifolium, demonstrating a certain level of stability in both structure and function.
The analysis of cis-acting elements situated in the CebZIP promoter region revealed the presence of various phytohormone response elements, in addition to abiotic stress response elements. This suggests that CebZIPs are involved in both phytohormone and abiotic stress response pathways, which is consistent with the results observed in wheat [47]. The data indicated that bZIP genes across different species contain response elements for low temperature, hormones, hypoxia, and trauma, showcasing their adaptability to diverse environment conditions.
The qRT-PCR results demonstrated substantial changes in gene expression upon low-temperature induction, aligning with the findings from the transcriptome data analysis. However, different expression patterns were observed among different members, with varying maximum values and time points to reach those maxima. Specifically, CebZIP26, CebZIP37, and CebZIP56 were highly expressed after 4 h of low-temperature stress, while CebZIP24, CebZIP28, CebZIP38, and CebZIP70 peaked after 12 h. On the other hand, CebZIP8 and CebZIP43 were most strongly expressed at 24 h. The expression of CebZIP26, CebZIP37, and CebZIP56 remained high after 4 h of low-temperature stress. These findings suggest that CebZIPs may play a significant role in the process of low-temperature resistance, demonstrating diverse low-temperature stress response modes and distinct functions in the physiological processes of C. ensifolium under low-temperature stress.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials
The study utilized plants from the Forest Orchid Garden at Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University, all of which were grown in the same conditions within the greenhouses. Prior to the experiment, these plants underwent pre-cultivation in an artificial climate chamber, followed by a seven-day period of cultivation under standard conditions. After pre-cultivation, the plant materials were exposed to a 4 °C artificial climate incubator for 0 h, 4 h, 12 h, and 24 h. Subsequently, the leaves were aseptically cut using enzyme-free scissors, with the midrib removed. Rapid freezing with liquid nitrogen and storage in a −80 °C refrigerator ensured the preservation of the samples. All samples were subjected to three biological replicates.
4.2. CebZIP Transcription Factor Identification and Sequence Retrieval
The whole genome data of C. ensifolium were acquired from the National Genomics Data Center (https://ngdc.cncb.ac.cn/, accessed on 2 March 2023), and Arabidopsis bZIP TF sequences were retrieved from the TAIR database (http://www.arabidopsis.org/, accessed on 2 March 2023). The conserved domain of the bZIP transcription factor (ID: PF00170, bZIP_1) was downloaded from the Pfam database (http://pfam.xfam.org/, accessed on 2 March 2023) [31]. This conserved domain was employed as a seed model for initial screening (E-value ≤ 10−5) using the Simple HMM Search of the TBtools v1.120 [34]. The candidate bZIP protein sequences of C. ensifolium underwent structural domain detection via the SMART (http://smart.embl.de, accessed on 2 March 2023), pfam, and NCBI CDD (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/cdd/wrpsb.cgi, accessed on 2 March 2023) databases. The removal of duplicate sequences yielded a final set of 70 putative genes [31,32,33]. The online website ExPASy was utilized to predict the molecular weight (MW), amino acid number (aa), isoelectric point (PI), aliphatic index, grand average of hydropathicity (GRAVY), and instability index of CebZIP proteins [50].
4.3. Phylogenetic Analysis of CebZIP Transcription Factors
The bZIP protein sequences from C. ensifolium and A. thaliana were subjected to ClustalW multiple alignment using MEGA11.0 software. The phylogenetic tree was constructed using the Neighbor-Joining (NJ) method [51]. The calibration parameter Bootstrap repetitions was set to 1000. The evolutionary tree was refined and polished using ITOL (https://itol.embl.de/itol.cgi, accessed on 11 March 2023) [52].
4.4. Analysis of Gene Conserved Structural Domains, Gene Structure, and Conserved Motifs
The 70 identified CebZIP family members were individually aligned using Clustal W, and the online software WebLogo 3 (http://weblogo.berkeley.edu/logo.cgi/, accessed on 31 March 2023) was utilized to map the conserved structural domains LOGO [53]. The gene structures (introns-exons) were analyzed and visualized using Tbtools v1.120 [34]. The online software MEME (http://meme-suite.org/tools/meme, accessed on 31 March 2023) was used to predict the conserved motifs of the CebZIP family [54]. The output value was set to 10, and the analysis results were visualized using Tbtools v1.120 [34]. The Ka/Ks ratio was calculated using Tbtools v1.120 to determine the evolutionary selection pressure of genes. Generally, if Ka > Ks or Ka/Ks > 1, the gene undergoes positive selection; if Ka = Ks or Ka/Ks = 1, the gene is subject to neutral evolution; and if Ka < Ks or Ka/Ks < 1, the gene undergoes purifying selection [34,49].
4.5. Chromosome Localization and Collinear Analysis of CebZIP
The chromosomal details of the 70 CebZIP genes were obtained from genome annotation files, and their chromosomal distribution was visualized using Tbtools v1.120 [34]. One Step MCScanX in TBtools v1.120 was used to analyze the intra-species collinear relationship of C. ensifolium, generating a Circos plot to represent the gene interactions [34]. The duplication events of bZIP genes among three species (C. ensifolium and D. chrysotoxum, and C. goeringii) were analyzed to obtain the collinear relationship among genes and plot the interspecies collinear map.
4.6. Examination of Cis-Acting Elements within the Promoter Region of CebZIP
Tbtools v1.120 was used to obtain 2000 base pair (bp) upstream of the coding sequence (CDS) of CebZIP genes from the genome sequence of C. ensifolium. The obtained sequence was submitted to the online website PlantCARE (http://bioinformatics.psb.ugent.be/webtools/plantcare/html/, accessed on 20 March 2023) for cis-acting element prediction [34,35]. General transcriptional regulatory elements and elements of unknown function were filtered out. The predictions were organized, classified, and visualized using EXCEL 2019.
4.7. Gene Expression Analysis under Low-Temperature Stress
The leaves, cultured for 0 h, 4 h, 12 h and 24 h in a 4 °C artificial climate chamber, were used for RNA extraction using a total RNA extraction kit (OMEGA, Norcross, GA, USA). Transcriptome data library construction was performed using Novozymes (Beijing, China) on the Illumina Hiseq 2500 platform. Gene expression levels are indicated by FPKM (Fragment Per Kilobase of exon model per Million mapped fragments) (Table S3). The heatmap of CebZIP genes expression under different low-temperature stress treatments was generated using the HeatMap tool in TBtools v1.120 [34]. The clustering method was set to cluster rows, and the normalization mode was selected as row scale. The scale method was set to zero to one, with other parameters using the default values.
cDNA was synthesized using a reverse transcription kit. Primers were designed using Primer 5 with GAPDH gene as the house-keeping gene (Table S4). Fluorescence quantification experiments were performed on an ABI 7500 real-time system (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA) using the Hieff® qPCR SYBR Green Master Mix (No Rox) (Next Sense Bio, Shanghai, China) kit. Three biological replicates and three technical replicates were performed. The 2−ΔΔCt formula was used for the calculation of relative gene expression [55]. The details of the 2−ΔΔCt formula and qRT-PCR data are provided in Supplemental Table S5.
5. Conclusions
In this study, 70 CebZIP genes were identified in the genome of C. ensifolium and their physicochemical properties were analyzed. CebZIP members exhibit diverse structures and have been classified into 11 subfamilies based on phylogenetic trees drawn from amino acid sequences. The conserved motifs vary among the subfamilies of the CebZIP family, while the motifs of bZIP domains encoded by the same subfamily are relatively conserved and similar. A total of 19 pairs of duplicated genes were identified in the CebZIP gene family, indicating that gene duplication events play a crucial role in driving bZIP evolution. Moreover, the expression profiling and qRT-PCR experiment showed that CebZIPs were subjected to low-temperature induction with varying degrees of changes in expression. These findings provide a certain theoretical foundation for identifying potential genetic resources for the molecular breeding of orchid stress resistance.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/plants13020219/s1, Table S1. The characteristics of 70 CebZIP in C. ensifolium; Table S2. Analysis of evolutionary pressure on the CebZIPs; Table S3. The FPKM values of CebZIPs under different low-temperature stress treatment times; Table S4. Primer sequence information; Table S5. Calculation of the 2−ΔΔCt formula and qRT-PCR data.
Author Contributions
Y.A. and Y.Z. conceived and designed the experiments. S.L. and D.P. directed the project. H.L. performed the bioinformatics analysis and wrote the manuscript. H.L., M.W. and L.Y. conducted the experiments. C.F., Y.T. and X.T. contributed reagents/materials/analysis tools. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by The Natural Science Foundation of Anhui Province (Grant no. 2108085QC128), The National Key Research and Development Program of China (no. 2019YFD1000400), and The Outstanding Young Scientific Research Talent Project of Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University (no. xjq201910).
Data Availability Statement
All supporting data of the current study are available within the paper and within the Supplementary Materials published online. The sequences of C. ensifolium used in this study are available at the National Genomics Data Center (NGDC). The RNA-Seq data have been deposited in NCBI under SRA accession codes: PRJNA1044247.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to the Key Laboratory of National Forestry and Grassland Administration for Orchid Conservation and Utilization, College of Landscape Architecture and Art, Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University, for the materials used for experiments and technical assistance. We also thank the Anhui Province Key Laboratory of Forest Resources and Silviculture, School of Forestry and Landscape Architecture, AnHui Agricultural University, for experiments and technical assistance.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Nijhawan, A.; Jain, M.; Tyagi, A.K.; Khurana, J.P. Genomic survey and gene expression analysis of the basic leucine zipper transcription factor family in rice. Plant Physiol. 2008, 146, 323–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landschulz, W.H.; Johnson, P.F.; Mcknight, S.L. The leucine zipper: A hypothetical structure common to a new class of DNA binding proteins. Science 1988, 240, 1759–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakoby, M.; Weisshaar, B.; Dröge-Laser, W.; Vicente-Carbajosa, J.; Tiedemann, J.; Kroj, T.; Parcy, F. bZIP transcription factors in Arabidopsis. Trends Plant Sci. 2002, 7, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, I.; Jung, H.J.; Park, J.I.; Yang, T.J.; Nou, I.S. Transcriptome analysis of newly classified bZIP transcription factors of Brassica rapa in cold stress response. Genomics 2014, 104, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, Z.; Sarwat, S.S.; Karim, I.; Faridi, R.; Jaskani, M.J.; Khan, A.A. Functions of plant’s bZIP transcription factors. Pak. J. Agric. Sci. 2016, 53, 303–314. [Google Scholar]
- Zg, E.; Zhang, Y.P.; Zhou, J.H.; Wang, L. Mini review roles of the bZIP gene family in rice. Genet Mol. Res. 2014, 13, 3025–3036. [Google Scholar]
- Dröge-Laser, W.; Snoek, B.L.; Snel, B.; Weiste, C. The Arabidopsis bZIP transcription factor family-an update. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2018, 45, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, W.; Cui, P.; Wei, W.; Lin, Y.; Luo, C. Genome-wide identification and analysis of the basic leucine zipper (bZIP) transcription factor gene family in Ustilaginoidea virens. Genome 2017, 60, 1051–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izawa, T.; Foster, R.; Nakajima, M.; Shimamoto, K.; Chua, N.H. The rice bZIP transcriptional activator RITA-1 is highly expressed during seed development. Plant Cell 1994, 6, 1277–1287. [Google Scholar]
- Gibalová, A.; Steinbachová, L.; Hafidh, S.; Bláhová, V.; Gadiou, Z.; Michailidis, C.; Műller, K.; Pleskot, R.; Dupľáková, N.; Honys, D. Characterization of pollen-expressed bZIP protein interactions and the role of ATbZIP18 in the male gametophyte. Plant Reprod. 2017, 30, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.S.; Liu, X.F.; Wang, D.H.; Chen, R.; Zhang, X.L.; Xu, Z.H.; Bai, S.N. Transcription factor OsTGA10 is a target of the MADS protein OsMADS8 and is required for tapetum development. Plant Physiol. 2018, 176, 819–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.Z.; Liu, C.; Li, Z.; Ran, Q.J.; Xie, G.N.; Wang, B.M.; Fang, S.; Chu, J.F.; Zhang, J.R. ZmbZIP4 contributes to stress resistance in maize by regulating ABA synthesis and root development. Plant Physiol. 2018, 178, 753–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Liang, T.; Zhang, L.B.; Shao, K.; Gu, X.X.; Shang, R.X.; Shi, N.; Li, X.; Zhang, P.; Liu, H.T. UVR8 interacts with WRKY36 to regulate HY5 transcription and hypocotyl elongation in Arabidopsis. Nat. Plants 2018, 4, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Ouyang, X.H.; Yang, P.Y.; Lau, O.S.; Li, G.; Li, J.G.; Chen, H.D.; Deng, X.W. Arabidopsis FHY3 and HY5 positively mediate induction of COP1 transcription in response to photomorphogenic UV-B light. Plant Cell 2012, 24, 4590–4606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lara, P.; Oñate-Sánchez, L.; Abraham, Z.; Ferrándiz, C.; Díaz, I.; Carbonero, P.; Vicente-Carbajosa, J. Synergistic activation of seed storage protein gene expression in Arabidopsis by ABI3 and two bZIPs related to OPAQUE2. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 21003–21011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Wu, Y.; Wang, X. bZIP transcription factor OsbZIP52/RISBZ5: A potential negative regulator of cold and drought stress response in rice. Planta 2012, 235, 1157–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, A.; Roychoudhury, A. Abscisic-acid-dependent basic leucine zipper (bZIP) transcription factors in plant abiotic stress. Protoplasma 2017, 254, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Liu, Y.; Shi, H.; Guo, M.; Chai, M.; He, Q.; Yan, M.H.; Cao, D.; Zhao, L.H.; Cai, H.Y.; et al. Evolutionary and expression analyses of soybean basic Leucine zipper transcription factor family. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakra, N.; Nutan, K.K.; Das, P.; Anwar, K.; Singla-Pareek, S.L.; Pareek, A. A nuclear-localized histone-gene binding protein from rice (OsHBP1b) functions in salinity and drought stress tolerance by maintaining chlorophyll content and improving the antioxidant machinery. Plant Physiol. 2015, 176, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorim, L.L.B.; da Fonseca Dos Santos, R.; Neto, J.P.B.; Guida-Santos, M.; Crovella, S.; Benko-Iseppon, A.M. Transcription factors involved in plant resistance to pathogens. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2017, 18, 335–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Fu, X.; Lv, Z.; Lu, X.; Shen, Q.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, M.; Wang, G.; Sun, X.; Liao, Z.; et al. A basic leucine zipper transcription factor, AabZIP1, connects abscisic acid signaling with artemisinin biosynthesis in Artemisia annua. Mol. Plant 2015, 8, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Yang, Y.; Wang, W.; Guo, G.; Liu, W.; Bi, C. Overexpression of a wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) bZIP transcription factor gene, TabZIP6, decreased the freezing tolerance of transgenic Arabidopsis seedlings by down-regulating the expression of CBFs. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 124, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Cao, H.; Qian, W.; Yao, L.; Hao, X.; Li, N.; Yang, Y.; Wang, X. Identification of a novel bZIP transcription factor in Camellia sinensis as a negative regulator of freezing tolerance in transgenic arabidopsis. Ann. Bot. 2017, 119, 1195–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Zhou, J.; Jie, Y.; Xing, H.; Zhong, Y.; Yu, W.; She, W.; Ma, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y. A ramie bZIP transcription factor BnbZIP2 is involved in drought, salt, and heavy metal stress response. DNA Cell Biol. 2016, 35, 776–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, M.K.; Meng, X.Q.; Cai, J.; Li, G.; Dong, T.T.; Li, Z.Y. Basic leucine zipper transcription factor SlbZIP1 mediates salt and drought stress tolerance in tomato. BMC Plant Biol. 2018, 18, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Zhang, C.; Zhu, Q.; Guo, F.; Chai, R.; Wang, M.; Deng, X.; Dong, T.; Meng, X.; Zhu, M. Genome- and transcriptome-wide systematic characterization of bZIP transcription factor family identifies promising members involved in abiotic stress response in sweetpotato. Sci. Hortic. 2022, 303, 111185–111196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, B.; Vanitha, J.; Ramachandran, S.; Jiang, S.Y. Genome-wide expansion and expression divergence of the basic leucine zipper transcription factors in higher plants with an emphasis on sorghum. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2011, 53, 212–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Quan, S.; Niu, J.; Guo, C.; Kang, C.; Liu, J.; Yuan, X. Genome-Wide identification, classification, expression and duplication analysis of bZIP family genes in Juglans regia L. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Chen, S.; Yao, W.; Cheng, Z.; Zhou, B.; Jiang, T. Genome-wide analysis and expression profile of the bZIP gene family in poplar. BMC Plant Biol. 2021, 21, 122–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Guo, R.; Guo, C.; Hou, H.; Wang, X.; Gao, H. Evolutionary and expression analyses of the apple basic leucine zipper transcription factor family. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Gebali, S.; Mistry, J.; Bateman, A.; Eddy, S.R.; Luciani, A.; Potter, S.C.; Qureshi, M.; Richardson, L.J.; Salazar, G.A.; Smart, A.; et al. The Pfam protein families database in 2019. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D427–D432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. 20 years of the SMART protein domain annotation resource. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D493–D496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Letunic, I.; Doerks, T.; Bork, P. SMART: Recent updates, new developments and status in 2015. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, D257–D260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.R.; Frank, M.H.; He, Y.; Xia, R. TBtools: An integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data. Mol. Plant. 2020, 13, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lescot, M.; Déhais, P.; Thijs, G.; Marchal, K.; Moreau, Y.; Van de Peer, Y.; Rouzé, P.; Rombauts, S. PlantCARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 325–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, F.; Maeta, E.; Terashima, A.; Takumi, S. Positive role of a wheat HvABI5 ortholog in abiotic stress response of seedlings. Physiol Plant. 2008, 34, 74–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yáñez, M.; Cáceres, S.; Orellana, S.; Bastías, A.; Verdugo, I.; Ruiz-Lara, S.; Casaretto, J.A. An abiotic stress-responsive bZIP transcription factor from wild and cultivated tomatoes regulates stress-related genes. Plant Cell Rep. 2009, 28, 1497–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, S.; Zhang, D.F.; Fu, J.; Shi, Y.S.; Song, Y.C.; Wang, T.Y.; Li, Y. Cloning and characterization of a maize bZIP transcription factor, ZmbZIP72, confers drought and salt tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis. Planta 2012, 235, 253–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Meng, Z.; Meng, Z.; Malik, W.; Yan, R.; Lwin, K.M.; Lin, F.; Wang, Y.; Sun, G.; Zhou, T.; et al. GhABF2, a bZIP transcription factor, confers drought and salinity tolerance in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Mao, B.; Ou, S.; Wang, W.; Liu, L.; Wu, Y.; Chu, C.; Wang, X. OsbZIP71, a bZIP transcription factor, confers salinity and drought tolerance in rice. Plant Mol. Biol. 2014, 84, 19–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, Y.; Li, Z.; Sun, W.H.; Chen, J.; Zhang, D.; Ma, L.; Zhang, Q.H.; Chen, M.K.; Zheng, Q.D.; Liu, J.F.; et al. The Cymbidium genome reveals the evolution of unique morphological traits. Hortic. Res. 2021, 8, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, L.; Mo, Z.; Fan, Y.; Li, K.; Yang, M.; Li, D.; Ke, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, F.; Fan, Y.; et al. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the bZIP transcription factor family genes in response to abiotic stress in Nicotiana tabacum L. BMC Genom. 2022, 23, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chai, M.; Zhang, M.; He, Q.; Su, Z.; Priyadarshani, S.V.G.N.; Liu, L.; Dong, G.; Qin, Y. Genome-Wide analysis, characterization, and expression profile of the basic leucine zipper transcription factor family in pineapple. Int. J. Genom. 2020, 2020, 3165958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Betts, M.J.; Guigó, R.; Agarwal, P.; Russell, R.B. Exon structure conservation despite low sequence similarity: A relic of dramatic events in evolution? Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 34, W369–W373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Tan, X.; Paterson, A.H. Different patterns of gene structure divergence following gene duplication in Arabidopsis. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, G.; Guo, C.; Shan, H.; Kong, H. Divergence of duplicate genes in exon–intron structure. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 1187–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Xia, J.Q.; Jiang, Y.S.; Bao, Y.Z.; Chen, H.C.; Wang, D.J.; Zhang, D.; Yu, J.; Cang, J. Genome-wide identification and analysis of bZIP gene family and resistance of TaABI5 (TabZIP96) under freezing stress in wheat (Triticum aestivum). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Fu, F.; Zhang, H.; Song, F. Genome-wide systematic characterization of the bZIP transcriptional factor family in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.). BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurst, L.D. The Ka/Ks ratio: Diagnosing the form of sequence evolution. Trends Genet. 2002, 18, 486–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duvaud, S.; Gabella, C.; Lisacek, F.; Stockinger, H.; Ioannidis, V.; Durinx, C. Expasy, the Swiss Bioinformatics Resource Portal, as designed by its users. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W216–W227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree Of Life (ITOL): An online tool for phylogenetic tree display and annotation. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 127–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crooks, G.E.; Hon, G.; Chandonia, J.M.; Brenner, S.E. WebLogo: A sequence logo generator. Genome Res. 2004, 14, 1188–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, T.L.; Williams, N.; Misleh, C.; Li, W.W. MEME: Discovering and analyzing DNA and protein sequence motifs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, W369–W373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).