Mapping of a Quantitative Trait Locus for Stay-Green Trait in Common Wheat
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials and Experimental Conditions
2.2. Phenotyping of SG
2.3. Genotyping and QTL Mapping
2.4. Diagnostic Marker Developing
2.5. Expression Pattern of Annotated Genes Within QTL
2.6. Association Analysis Between SG-QTL and Agronomic Traits
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
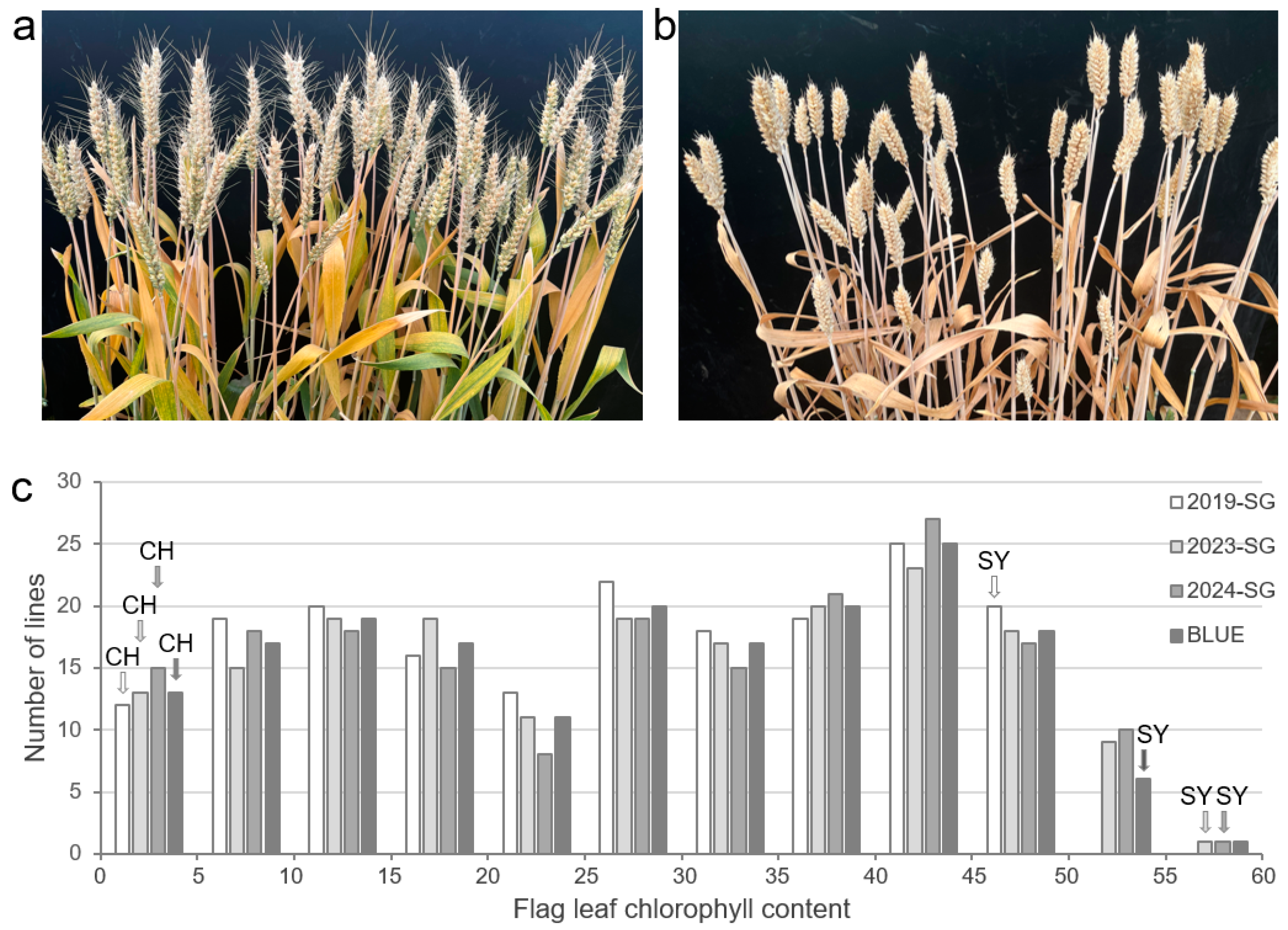
3.1. Assessment of SG for CH and SY
3.2. Phenotypic Variance of SG in the CH × SY RILs
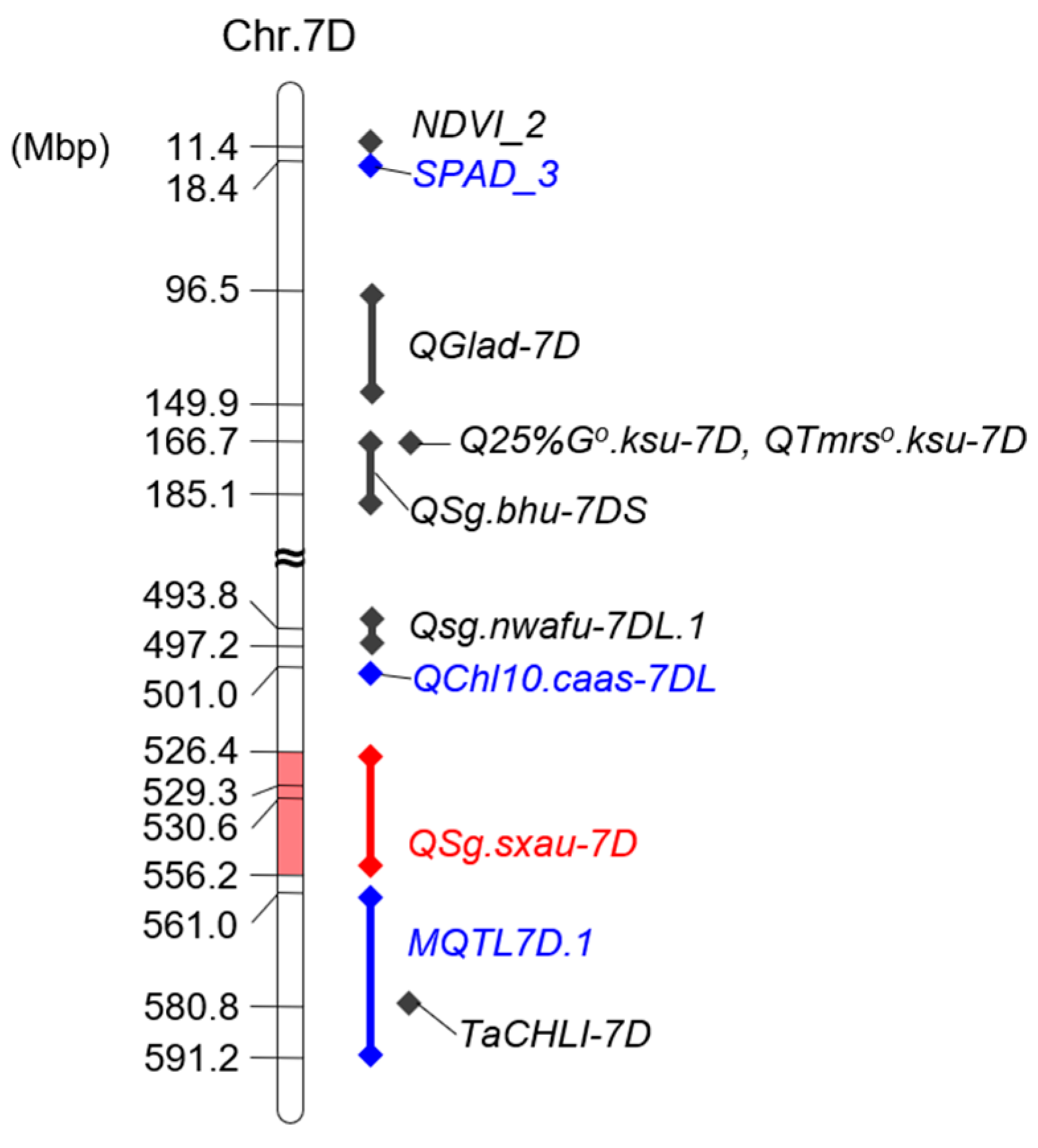
3.3. Genetic Mapping of SG
3.4. Verification of QSg.sxau-7D
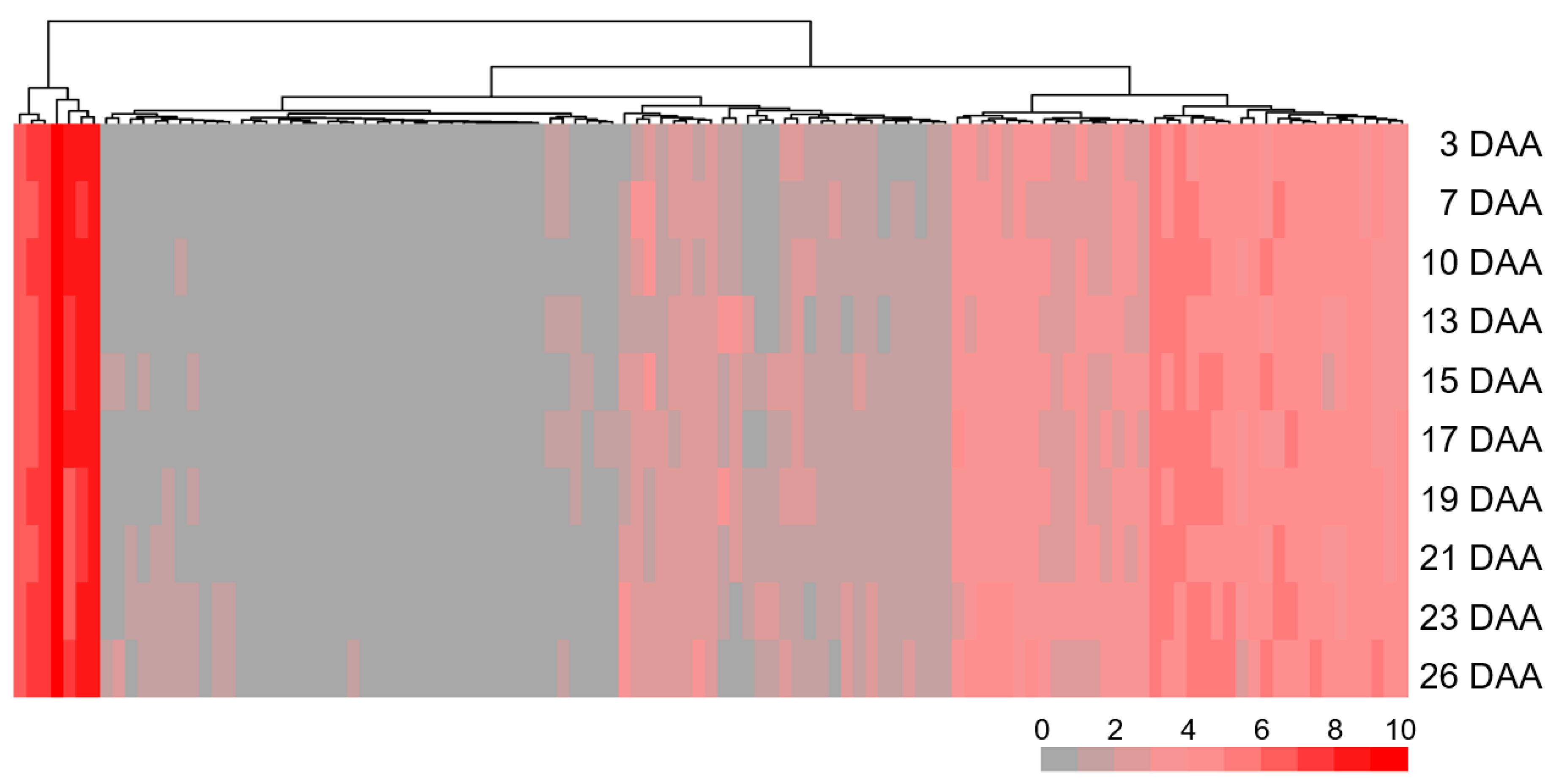
3.5. Annotated Genes Within QSg.sxau-7D
3.6. The Correlation Between QSg.sxau-7D and Agronomic Traits
4. Discussion
4.1. QSg.sxau-7D Is a Novel SG Locus
4.2. Prediction of Candidate Genes for QSg.sxau-7D
4.3. CH7034 Can Be Used for Wheat Breeding
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- van Dijk, M.; Morley, T.; Rau, M.L.; Saghai, Y. A meta-analysis of projected global food demand and population at risk of hunger for the period 2010–2050. Nat. Food 2021, 2, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guarin, J.R.; Martre, P.; Ewert, F.; Webber, H.; Dueri, S.; Calderini, D.; Asseng, S. Evidence for increasing global wheat yield potential. Environ. Res. Lett. 2022, 17, 124045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiferaw, B.; Smale, M.; Braun, H.-J.; Duveiller, E.; Reynolds, M.; Muricho, G. Crops that feed the world 10. past successes and future challenges to the role played by wheat in global food security. Food Secur. 2013, 5, 291–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Singh, R.; Grover, M.; Singh, A.K. Terminal heat-an emerging problem for wheat production. Biotech. Today 2012, 2, 7–9. [Google Scholar]
- Saini, D.K.; Chopra, Y.; Singh, J.; Sandhu, K.S.; Kumar, A.; Bazzer, S.; Srivastava, P. Comprehensive evaluation of mapping complex traits in wheat using genome-wide association studies. Mol. Breed. 2022, 42, 1–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, H.; Ougham, H. The stay-green trait. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 3889–3900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjödin, J. Induced morphological variation in Vicia faba L. Hereditas 1971, 67, 155–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djanaguiraman, M.; Gowsiga, S.; Govindaraj, M.; Habyarimana, E.; Senthil, A.; Thavaprakaash, N.; Jeyakumar, P.; Kokilavani, J.; Chellammal, C. Impact of root architecture and transpiration rate on drought tolerance in stay-green sorghum. Crop Sci. 2024, 64, 2612–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chibane, N.; Caicedo, M.; Martinez, S.; Marcet, P.; Revilla, P.; Ordás, B. Relationship between delayed leaf senescence (stay-green) and agronomic and physiological characters in maize (Zea mays L.). Agronomy 2021, 11, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Masclaux-Daubresse, C. Current understanding of leaf senescence in rice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, J.L.; Sherman, J.D.; Lamb, P.; Cook, J.; Lachowiec, J.A.; Bourgault, M. Relationships between roots, the stay-green phenotype, and agronomic performance in barley and wheat grown in semi-arid conditions. Plant Phenome J. 2022, 5, e220050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liang, Y.; Hu, X.; Wang, X.; Tan, F.; Zhang, H.; Ren, Z.; Luo, P. Physiological characterization of ‘stay green’wheat cultivars during the grain filling stage under field growing conditions. Acta Physiol. Plantarum 2010, 32, 875–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luche, H.D.S.; Silva, J.A.G.D.; Nornberg, R.; Hawerroth, M.C.; Silveira, S.F.D.S.; Caetano, V.D.R.; Santos, R.L.; Figueiredo, R.G.; Maia, L.C.D.; Oliveira, A.C.D. Stay-green character and its contribution in Brazilian wheats. Ciência Rural 2017, 47, e20160583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jocković, B.; Mirosavljević, M.; Momčilović, V.; Dražić, T.; Mikić, S.; Aćin, V.; Ilin, S.; Živančev, D. The contribution of stay green traits to the breeding progress of the pannonian wheat. Field Crops Res. 2022, 287, 108649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christopher, J.T.; Christopher, M.J.; Borrell, A.K.; Fletcher, S.; Chenu, K. Stay-green traits to improve wheat adaptation in well-watered and water-limited environments. J. Exp. Bot. 2016, 67, 5159–5172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderegg, J.; Aasen, H.; Perich, G.; Roth, L.; Walter, A.; Hund, A. Temporal trends in canopy temperature and greenness are potential indicators of late-season drought avoidance and functional stay-green in wheat. Field Crops Res. 2021, 274, 108311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Krishna Jagadish, S.V.; Bowden, R.L. Effects of post-flowering heat stress on chlorophyll content and yield components of a spring wheat diversity panel. Crop Sci. 2022, 62, 1926–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Ullah, Z.; Sher, H.; Abbas, Z.; Rasheed, A. Water stress effects on stay green and chlorophyll fluorescence with focus on yield characteristics of diverse bread wheats. Planta 2023, 257, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Ren, G.; Zhang, K.; Li, Z.; Miao, Y.; Guo, H. Leaf senescence: Progression, regulation, and application. Mol. Hortic. 2021, 1, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Cao, T.; Guo, Y.; Grimm, B.; Li, X.; Duanmu, D.; Lin, R. Regulatory and retrograde signaling networks in the chlorophyll biosynthetic pathway. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2025, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, R.; Tanaka, A. Tetrapyrrole biosynthesis in higher plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2007, 58, 321–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y.; Ali Buttar, Z.; Wang, N.; Xie, Y. Single nucleotide mutagenesis of the TaCHLI gene suppressed chlorophyll and fatty acid biosynthesis in common wheat seedlings. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Xu, H.; Wang, F.; Sun, L.; Meng, X.; Li, Z.; Xie, C.; Jiang, H.; Ding, G.; Hu, X.; et al. EMS-induced missense mutation in TaCHLI-7D affects leaf color and yield-related traits in wheat. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2024, 137, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.P.; Charng, Y.Y. Chlorophyll dephytylation in chlorophyll metabolism: A simple reaction catalyzed by various enzymes. Plant Sci. 2021, 302, 110682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gedam, P.A.; Krishna, G.K.; Ramakrishnan, R.S.; Sharma, R.; Chaturvedi, A.K.; Singh, V.P. Ethylene induced stay-green gene expression regulates drought stress in wheat. Indian J. Exp. Biol. 2021, 59, 761–769. [Google Scholar]
- Kamal, N.M.; Gorafi, Y.S.A.; Abdelrahman, M.; Abdellatef, E.; Tsujimoto, H. Stay-green trait: A prospective approach for yield potential, and drought and heat stress adaptation in globally important cereals. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hairat, S.; Agisho, H.A.; Zaki, M. Challenges and management of wheat under global climate change. Plant Cell Biotech. Mol. Biol. 2021, 22, 136–151. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, D.; Kumari, A.; Sharma, P.; Singh, A.; Sharma, A.; Mir, Z.A.; Kumar, U.; Jan, S.; Parthiban, M.; Mir, R.R.; et al. Meta-QTL analysis in wheat: Progress, challenges and opportunities. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2023, 136, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, K.; Chen, T.; Zhang, P.; Liu, Y.; Che, Z.; Shahinnia, F.; Yang, D. Meta-QTL analysis and in-silico transcriptome assessment for controlling chlorophyll traits in common wheat. Plant Genome 2023, 16, e20294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christopher, M.; Chenu, K.; Jennings, R.; Fletcher, S.; Butler, D.; Borrell, A.; Christopher, J. QTL for stay-green traits in wheat in well-watered and water-limited environments. Field Crops Res. 2018, 217, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, J.P.; Acharya, R.K.; Martin, J.M.; Blake, N.K.; Khan, I.J.; Heo, H.Y.; Kephart, K.D.; Eckhoff, J.; Talbert, L.E.; Sherman, J.D. Genetic analysis of stay-green, yield, and agronomic traits in spring wheat. Crop Sci. 2021, 61, 383–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Q.; Li, C.; Li, H.; Zheng, Q.; Li, B.; Li, Z. An analysis of the genetic relation between photosynthesis and yield-related traits in wheat. Agriculture 2022, 12, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.K.C.; Bellundagi, A.; Krishna, H.; Mallikarjuna, M.G.; Thimmappa, R.K.; Rai, N.; Shashikumara, P.; Sinha, N.; Jain, N.; Singh, P.K.; et al. Development of bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) variety HD3411 following marker-assisted backcross breeding for drought tolerance. Front. Genet. 2023, 14, 1046624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahranavard, N.; Jorjani, E.; Sabouri, H.; Alegh, S.M.; Katouzi, M. Detecting QTLs controlling chlorophyll fluorescence parameters in Iranian wheat recombinant inbred lines. Plant Gene 2024, 37, 100437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Gao, X.; Cheng, Y.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, R.; Cao, J.; Geng, H. QTL mapping of leaf area index and chlorophyll content based on UAV remote sensing in wheat. Agriculture 2022, 12, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Wen, X.; Wen, H.; Feng, Y.; Zhao, J.; Wu, B.; Zheng, X.; Yang, C.; Yang, S.; Qiao, L.; et al. Identification of genetic loci affecting flag leaf chlorophyll in wheat grown under different water regimes. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 832898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Chen, N.; Dang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wen, H.; Zheng, J.; Zheng, X.; Zhao, J.; Lu, J.; Qiao, L. Identification and validation of quantitative trait loci for chlorophyll content of flag leaf in wheat under different phosphorus treatments. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1019012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Azam, F.I.; Li, H.; Chang, X.; Li, B.; Jing, R. Mapping QTL for stay-green and agronomic traits in wheat under diverse water regimes. Euphytica 2017, 213, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, L.; Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Yang, Z.; Li, R.; Jia, J.; Yan, L.; Chang, Z. Genetic incorporation of genes for the optimal plant architecture in common wheat. Mol. Breed. 2022, 42, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, L.; Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, J.; Chang, Z. Development of NBS-related microsatellite (NRM) markers in hexaploid wheat. Euphytica 2017, 213, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrill, P.; Harrington, S.A.; Simmonds, J.; Uauy, C. Identification of transcription factors regulating senescence in wheat through gene regulatory network modelling. Plant Physiol. 2019, 180, 1740–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Y.; Shen, X.; Guo, Y.; Ma, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Cheng, T.; Wen, H.; et al. RNA-Seq-based WGCNA and association analysis reveal the key regulatory module and genes responding to salt stress in wheat roots. Plants 2024, 13, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, L.; Chang, L.; Kai, M.; Zhang, X.; Kang, T.; Wu, L.; Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, Z.; et al. Exploring drought resistance genes from the roots of the wheat cultivar Yunhan1818. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 13458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malakondaiah, A.C.; Arora, A.; Krishna, H.; Taria, S.; Kumar, S.; Devate, N.B.; Padaria, J.C.; Kousalya, S.; Patil, S.P.; Singh, P.K. Genome-wide association mapping for stay-green and stem reserve mobilization traits in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) under combined heat and drought stress. Protoplasma 2025, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.G.; Lian, Y.; Shi, H.W.; Wang, S.G.; Fan, H.; Sun, D.Z.; Jing, R.L. Dynamic analysis of QTLs for green leaf area duration and green leaf number of main stem in wheat. Cereal Res. Commun. 2019, 47, 250–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayalakshmi, K.; Fritz, A.K.; Paulsen, G.M.; Bai, G.; Pandravada, S.; Gill, B.S. Modeling and mapping QTL for senescence-related traits in winter wheat under high temperature. Mol. Breed. 2010, 26, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, U.; Joshi, A.K.; Kumari, M.; Paliwal, R.; Kumar, S.; Röder, M.S. Identification of QTLs for stay green trait in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) in the ‘Chirya 3’ × ‘Sonalika’ population. Euphytica 2010, 174, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.; Cao, X.; Liu, J.; Nie, R.; Zhang, C.; Yuan, M.; Huang, Y.; Liu, X.; Zheng, W.; Wang, C.; et al. Using UAV-based temporal spectral indices to dissect changes in the stay-green trait in wheat. Plant Phenomics 2024, 6, a0171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Wen, W.; Liu, J.; Zhai, S.; Cao, X.; Liu, C.; Cheng, D.G.; Guo, J.; Zi, Y.; Han, R.; et al. Genome-wide linkage mapping for canopy activity related traits using three RIL populations in bread wheat. Euphytica 2021, 217, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallam, A.; Eltaher, S.; Alqudah, A.M.; Belamkar, V.; Baenziger, P.S. Combined GWAS and QTL mapping revealed candidate genes and SNP network controlling recovery and tolerance traits associated with drought tolerance in seedling winter wheat. Genomics 2022, 114, 110358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, L.; Li, H.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, X. Towards a better understanding of auxin response factors for improving cereal crops. J. Integr. Agric. 2024, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liu, H.; Hao, C.; Li, T.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Yang, Y.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, X. The auxin response factor TaARF15-A1 negatively regulates senescence in common wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Plant Physiol. 2023, 191, 1254–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, L.Y.; Zhang, W.P.; Li, X.Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, X.J.; Li, X.; Guo, H.J.; Ren, Y.; Zheng, J.; Chang, Z.J. Characterization and expression patterns of auxin response factors in wheat. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Z.; Yu, G.; Lei, S.; Wang, H.; Xu, B. STRONG STAYGREEN inhibits DNA binding of PvNAP transcription factors during leaf senescence in switchgrass. Plant Physiol. 2022, 190, 2045–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, D.Y.; Shim, Y.; Gi, E.; Lee, B.D.; An, G.; Kang, K.; Paek, N.C. The MYB-related transcription factor RADIALIS-LIKE3 (OsRL3) functions in ABA-induced leaf senescence and salt sensitivity in rice. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2018, 156, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Yang, Y.Y.; Lakshmanan, P.; Kuang, J.F.; Lu, W.J.; Pang, X.Q.; Chen, J.Y.; Shan, W. Proteasomal degradation of MaMYB60 mediated by the E3 ligase MaBAH1 causes high temperature-induced repression of chlorophyll catabolism and green ripening in banana. Plant Cell 2023, 35, 1408–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Qiao, L.; Li, X.; Yang, Z.; Liu, C.; Guo, H.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, S.; Chang, L.; Chen, F.; et al. Genetic incorporation of the favorable alleles for three genes associated with spikelet development in wheat. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 892642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, L.; Li, Y.; Wang, L.; Gu, C.; Luo, S.; Li, X.; Yan, J.; Lu, C.; Chang, Z.; Gao, W.; et al. Identification of salt-stress-responding genes by weighted gene correlation network analysis and association analysis in wheat leaves. Plants 2024, 13, 2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Marker | Position | Forward Primer Sequence (5′–3′) | Reverse Primer Sequence (5′–3′) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 7D-1 | 7D:520269556 | ATAGATTTGACTTTGGGGTAGTAG | TCTCAGAGAGCAACTTGGG |
| 7D-31 | 7D:522918576 | TAGCTCCCTCCAGTGAAAC | CCTGCTCCAAACCCAATCT |
| 7D-32 | 7D:523485210 | ATGCTTCCACGCCGGTGT | AGACATCAACCTTTCCCAGATC |
| 7D-36 | 7D:524917078 | ACTGCTCTCTCTATTATAGCAG | GCTTTGACATGGTCTAAATCTG |
| 7D-16 | 7D:535195126 | GGACTCGGACGCCAAAGT | CCAGTTTCGAGTCTCGTTTTTTA |
| 7D-19 | 7D:536464127 | CAAAACATGGGCTAGATCCC | CTAGATCTACAGGCCAACAC |
| Trait | Parents | RIL Population | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CH | SY | Min | Max | Mean | CV | |
| 2019-SG | 44.17 | 4.12 **** | 2.33 | 49.43 | 29.11 | 0.32 |
| 2023-SG | 50.39 | 3.84 **** | 2.69 | 55.74 | 30.04 | 0.47 |
| 2024-SG | 42.27 | 3.43 **** | 1.66 | 57.28 | 28.01 | 0.56 |
| BLUE | 45.61 | 3.80 **** | 3.05 | 52.86 | 31.37 | 0.44 |
| Trait | Chromosome | Position (cM) | Left Marker | Right Marker | LOD | PVE (%) | ADD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019-SG | 5A | 198.5 | 2260698 | 1234116 | 2.84 | 5.77 | 5.39 |
| 7D | 213.9 | 1004225 | 1090372 | 5.27 | 11.46 | 12.54 | |
| 2023-SG | 2B | 170.2 | 5411126 | 1863181 | 2.63 | 5.24 | 2.47 |
| 7D | 211.2 | 1004225 | 2242097 | 5.06 | 10.62 | 12.24 | |
| 2024-SG | 7D | 213.9 | 1004225 | 1090372 | 3.50 | 8.81 | 4.81 |
| BLUE | 7D | 213.9 | 1004225 | 1090372 | 5.57 | 10.33 | 9.26 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Bai, X.; Wu, L.; Wang, C.; Liu, X.; Li, Q.; Zhang, X.; Chen, F.; Lu, C.; Gao, W.; et al. Mapping of a Quantitative Trait Locus for Stay-Green Trait in Common Wheat. Plants 2025, 14, 727. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14050727
Li X, Bai X, Wu L, Wang C, Liu X, Li Q, Zhang X, Chen F, Lu C, Gao W, et al. Mapping of a Quantitative Trait Locus for Stay-Green Trait in Common Wheat. Plants. 2025; 14(5):727. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14050727
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xin, Xin Bai, Lijuan Wu, Congya Wang, Xinghui Liu, Qiqi Li, Xiaojun Zhang, Fang Chen, Chengda Lu, Wei Gao, and et al. 2025. "Mapping of a Quantitative Trait Locus for Stay-Green Trait in Common Wheat" Plants 14, no. 5: 727. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14050727
APA StyleLi, X., Bai, X., Wu, L., Wang, C., Liu, X., Li, Q., Zhang, X., Chen, F., Lu, C., Gao, W., & Cheng, T. (2025). Mapping of a Quantitative Trait Locus for Stay-Green Trait in Common Wheat. Plants, 14(5), 727. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14050727





