Quillaja lancifolia Immunoadjuvant Saponins Show Toxicity to Herbivores and Pathogenic Fungi
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
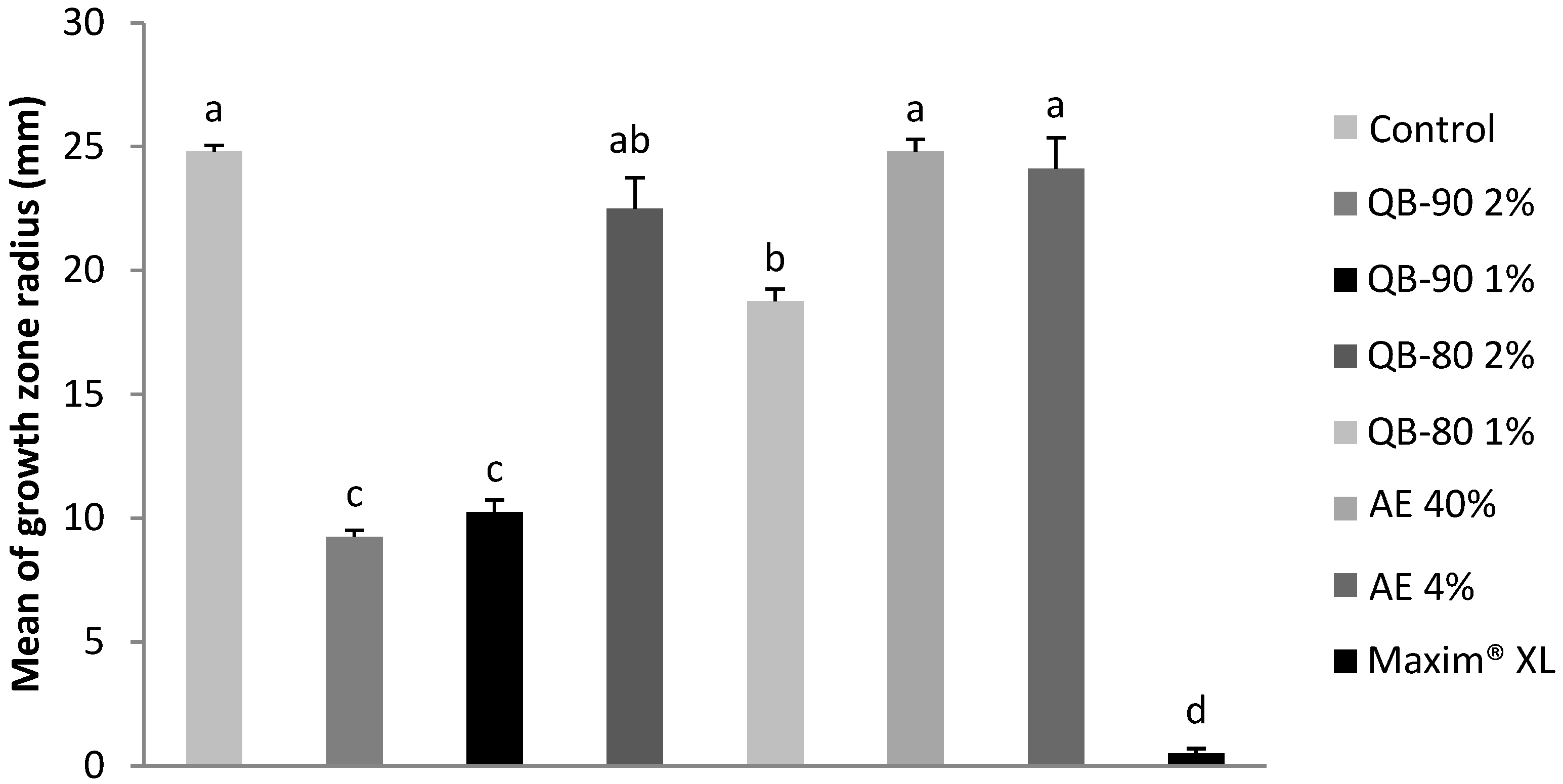
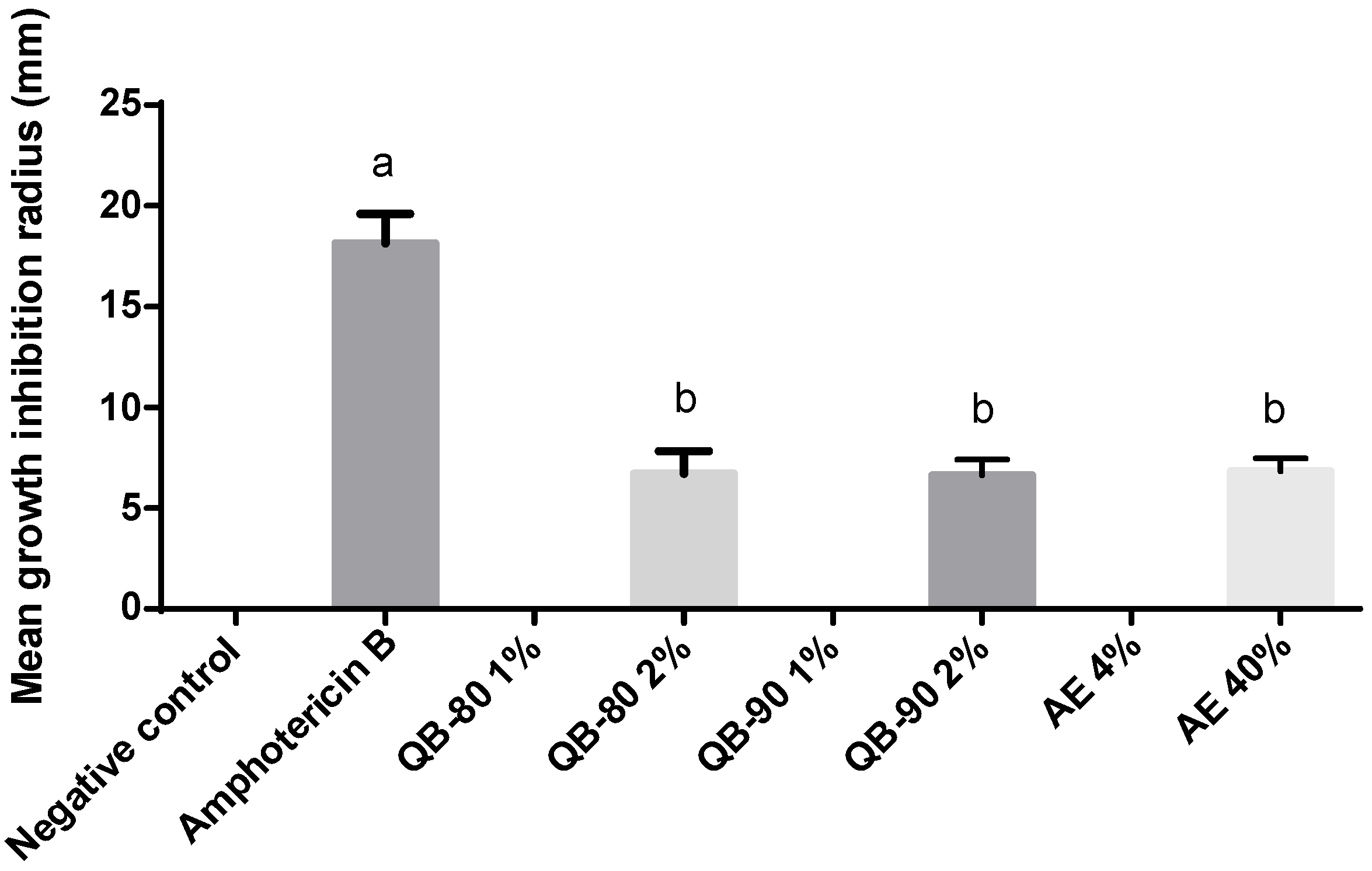
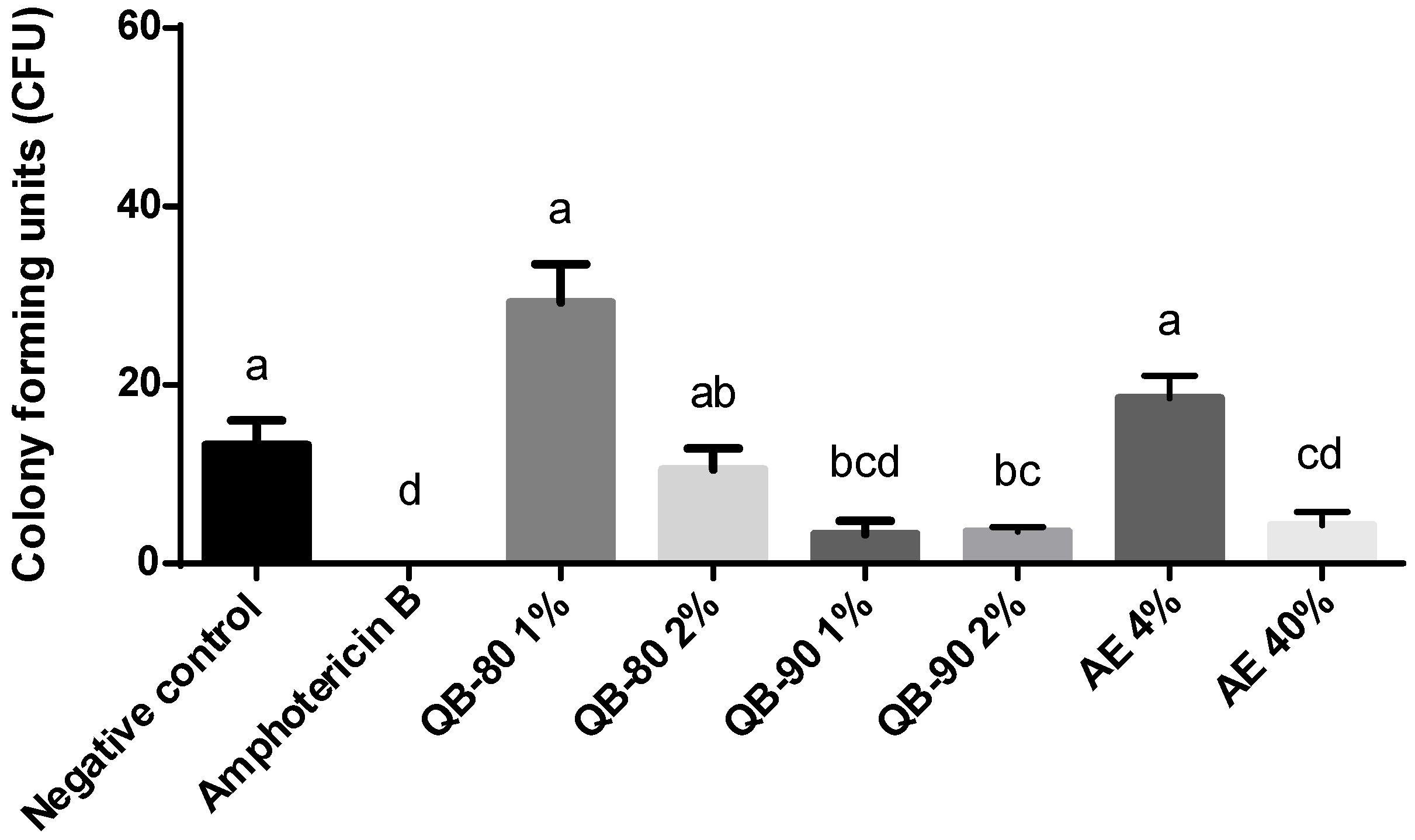
2.1. Antifungal Assays
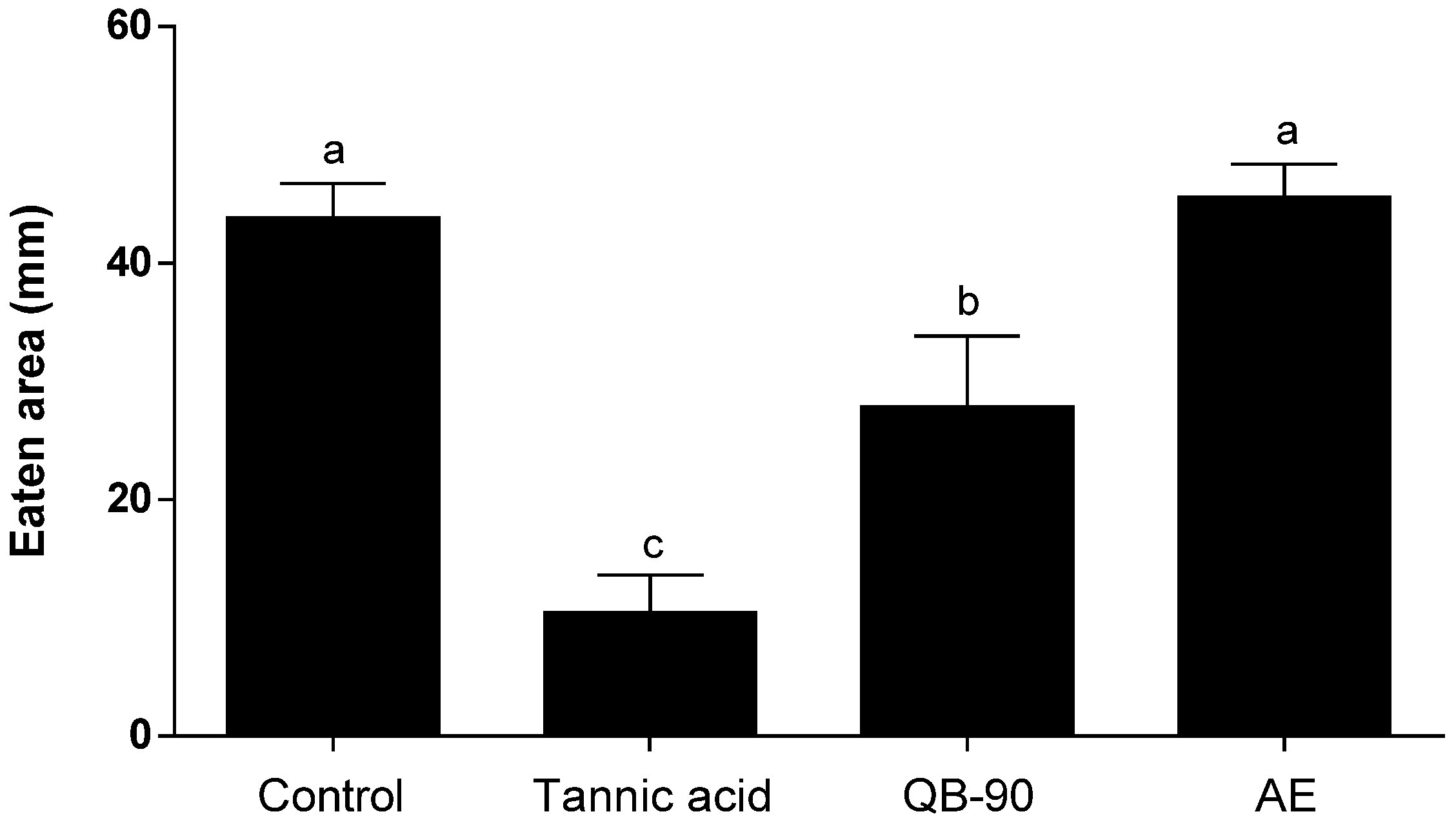
2.2. Generalist Herbivore Assays
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Material and Preparation of Aqueous Extract and Saponin-Enriched Fractions QB-80 and QB-90
4.2. Antifungal Assays
4.2.1. Fungi Cultures
4.2.2. Fungal Bioassays
4.3. Herbivore Assays
4.3.1. Helix aspersa Assay
4.3.2. Spodoptera frugiperda Assay
4.4. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Junaid, M.D.; Gokce, A.F.; Bostani, R. Global agricultural losses and their causes. Bull. Biol. All. Sci. Res. 2024, 9, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oerke, E.C. Crop losses to pests. J. Agr. Sci. 2006, 144, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, L.; Rebetez, M.; Rasmann, S. The effect of climate change on invasive crop pests across biomes. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2022, 50, 100895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, A.M. Resistance to herbivores and fungal pathogens: Variations on a common theme? A review comparing the effect of secondary metabolites, induced and constitutive, on herbivores and fungal pathogens. Isr. J. Plant Sci. 2004, 52, 279–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincken, J.P.; Heng, L.; De Groot, A.; Gruppen, H. Saponins, classification and occurrence in the plant kingdom. Phytochemistry 2007, 68, 275–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Costa, F.; Yendo, A.C.A.; Fleck, J.D.; Gosmann, G.; Fett-Neto, A.G. Immunoadjuvant and anti-inflammatory plant saponins: Characteristics and biotechnological approaches towards sustainable production. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2011, 11, 857–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yendo, A.C.A.; De Costa, F.; Gosmann, G.; Fett-Neto, A.G. Production of plant bioactive triterpenoid saponins: Elicitation strategies and target genes to improve yields. Mol. Biotechnol. 2010, 46, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Geyter, E.; Lambert, E.; Geelen, D.; Smagghe, G. Novel advances with plant saponins as natural insecticides to control pest insects. Pest. Technol. 2007, 2, 96–105. [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi, H.; Huang, P.; Inoue, K. Up-regulation of soyasaponin biosynthesis by methyl jasmonate in cultured cells of Glycyrrhiza glabra. Plant Cell Physiol. 2003, 44, 404–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangas, S.; Bonfill, M.; Osuna, L.; Moyano, E.; Tortoriello, J.; Cusido, R.M.; Piñol, M.T.; Palazón, J. The effect of methyl jasmonate on triterpene and sterol metabolisms of Centella asiatica, Ruscus aculeatus and Galphimia glauca cultured plants. Phytochemistry 2006, 67, 2041–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reitz, R.; Reis, A.; Klein, R.M. Flora Ilustrada Catarinense—Rosáceas (Illustrated Flora of the State of Santa Catarina—Rosaceae); Herbário Barbosa Rodrigues: Itajaí, Brazil, 1996; pp. 113–116. [Google Scholar]
- Magedans, Y.V.S.; Yendo, A.C.A.; De Costa, F.; Gosmann, G.; Fett-Neto, A.G. Foamy matters: An update on Quillaja saponins and their use as immunoadjuvants. Future Med. Chem. 2019, 11, 1485–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Costa, F.; Yendo, A.C.A.; Fleck, J.D.; Gosmann, G.; Fett-Neto, A.G. Accumulation of a bioactive triterpene saponin fraction of Quillaja brasiliensis leaves is associated with abiotic and biotic stresses. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2013, 66, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, M.E.M.; de Carvalho, A.C.; Yendo, A.C.A.; Magedans, Y.V.S.; Zachert, E.; Fett-Neto, A.G. Phytotoxicity of Quillaja lancifolia leaf saponins and their bioherbicide potential. Plants. 2023, 12, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleck, J.D.; Betti, A.H.; Da Silva, F.P.; Troian, E.A.; Olivaro, C.; Ferreira, F.; Verza, S.G. Saponins from Quillaja saponaria and Quillaja brasiliensis: Particular chemical characteristics and biological activities. Molecules 2019, 24, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cibulski, S.; Teixeira, T.F.; Varela, A.P.M.; De Lima, M.F.; Casanova, G.; Nascimento, Y.M.; Tavares, J.F.; Da Silva, M.S.; Sesterheim, P.; Souza, D.O.; et al. IMXQB-80: A Quillaja brasiliensis saponin-based nanoadjuvant enhances Zika virus specific immune responses in mice. Vaccine 2021, 39, 571–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaynab, M.; Sharif, Y.; Abbas, S.; Afzal, M.Z.; Qasim, M.; Khalofah, A.; Ansari, M.J.; Khan, K.A.; Tao, L.; Li, S. Saponin toxicity as key player in plant defense against pathogens. Toxicon 2021, 193, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapagain, B.P.; Wiesman, Z.; Tsror, L. In vitro study of the antifungal activity of saponin-rich extracts against prevalent phytopathogenic fungi. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2007, 26, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Guo, H.; Zhang, L.; Yang, L.; Wei, Z.; Zhang, X.; Niu, Y. Crude saponins from Chenopodium quinoa Willd. reduce Fusarium wilt infection in tomato seedlings. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trdá, L.; Janda, M.; Macková, D.; Pospíchalová, R.; Dobrev, P.; Burketová, L.; Matušinsky, P. Dual mode of the saponin aescin in plant protection: Antifungal agent and plant defense elicitor. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparg, S.G.; Light, M.E.; Van Staden, J. Biological activities and distribution of plant saponins. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2004, 94, 219–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Liu, X.; Zhuang, X.; Feng, X.; Zhong, L.; Ma, T. Antifungal effects of saponin extract from rhizomes of Dioscorea panthaica Prain et Burk against Candida albicans. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat Med. 2018, 2018, 6095307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cota, B.B.; De Oliveira, D.B.B.; Borges, T.C.; Catto, A.C.; Serafim, C.V.; Rodrigues, A.R.A.; Kohlhoff, M.; Zani, C.L.; Andrade, A.A. Antifungal activity of extracts and purified saponins from the rhizomes of Chamaecostus cuspidatus against Candida and Trichophyton species. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 130, 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaki, A.A.; Kaddah, M.M.Y.; Abulkhair, H.S.; Ashour, A. Unravelling the antifungal and antiprotozoal activities and LC-MS/MS quantification of steroidal saponins isolated from Panicum turgidum. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 2980–2991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Gao, Y.; Yuan, M.; Zheng, Z.; Yin, J. Anti-Candida albicans effects and mechanisms of theasaponin E1 and assamsaponin A. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Yan, Q.; Ji, Y.; Bai, X.; Li, D.; Mu, R.; Guo, K.; Yang, M.; Tao, Y.; Gershenzon, J.; et al. Unraveling the serial glycosylation in the biosynthesis of steroidal saponins in the medicinal plant Paris. polyphylla and their antifungal action. Acta Pharm. Sin. B. 2023, 11, 4638–4654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zheng, D.; Mu, Y.; Cao, B.; Yang, J.; Han, L.; Huang, X. Structure–activity relationship and biofilm formation-related gene targets of oleanolic acid-type saponins from Pulsatilla chinensis against Candida albicans. Biorg. Chem. 2024, 146, 107311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porsche, F.M.; Molitor, D.; Beyer, M.; Charton, S.; André, C.; Kollar, A. Antifungal activity of saponins from the fruit pericarp of Sapindus mukorossi against Venturia inaequalis and Botrytis cinerea. Plant Dis. 2018, 102, 991–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, M.T.; Han, J.W.; Yoon, S.; Bae, S.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, H.; Choi, G.J. discovery of new triterpenoid saponins isolated from Maesa japonica with antifungal activity against rice blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 7706–7715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heng, M.Y.; Thuerig, B.; Danton, O.; Ramseyer, J.; Gupta, M.P.; Tamm, L.; Hamburger, M.; Potterat, O. Ingadosides A-C, acacic acid-type saponins from Inga sapindoides with potent inhibitory activity against downy mildew. Phytochemistry 2022, 199, 113183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valencia-Mejía, E.; León-Wilchez, Y.Y.; Monribot-Villanueva, J.L.; Ramírez-Vázquez, M.; Bonilla-Landa, I.; Guerrero-Analco, J.A. Isolation and identification of pennogenin tetraglycoside from Cestrum nocturnum (Solanaceae) and its antifungal activity against Fusarium kuroshium, causal agent of fusarium dieback. Molecules 2022, 27, 1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.F.; Zhang, H.B.; Cai, Z.S.; Gao, H.; Wang, D.; Shang, S.B. Two new steroidal sapogenins from Rohdea chinensis (synonym Tupistra chinensis) rhizomes and their antifungal activity. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2022, 24, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.Y.; Sun, Q.; Ma, N.; Zhang, F.J.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Wang, X.F.; Sun, P.; You, C.X.; Zhang, Z. inhibitory effect of tea saponin on major apple-disease-inducing fungi. Phytopathology 2023, 113, 1853–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wise, C.; Falardeau, J.; Hagberg, I.; Avis, T.J. Cellular lipid composition affects sensitivity of plant pathogens to fengycin, an antifungal compound produced by Bacillus subtilis strain CU12. Phytopathology 2014, 104, 1036–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Groot, C.; Muller-Goymann, C.C. Saponin interactions with model membrane systems—Langmuir Monolayer Studies, hemolysis and formation of ISCOMs. Planta Med. 2016, 82, 1496–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrissey, J.P.; Osbourn, A.E. Fungal resistance to plant antibiotics as a mechanism of pathogenesis. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 1999, 63, 708–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrelli, J.; Oleszek, W.; Stochmal, A.; Olsen, M.; Anderson, P. Herbivore-induced responses in alfalfa (Medicago sativa). J. Chem. Ecol. 2003, 29, 303–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowd, P.F.; Berhow, M.A.; Johnson, E.T. Differential activity of multiple saponins against omnivorous insects with varying feeding preferences. J. Chem. Ecol. 2011, 37, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, G.D.; Santos, C.D.; Carvalho, G.A.; Alves, D.S.; Pereira, L.I.S.; Carvalho, G.A. Biochemical analysis of a castor bean leaf extract and its insecticidal effects against Spodoptera frugiperda (Smith) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Neotrop. Entomol. 2012, 41, 503–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazzam, K.E.; Mhada, M.; Bakrim, W.B.; Taourirte, M.; Yasri, A. Antinutritional and insecticidal potential of Chenopodium quinoa saponin rich extract against Tribolium castaneum (Herbst) and its action mechanism. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 6815–6829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wang, X.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, R.; Xiao, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L. Antifeedant and ovicidal activities of ginsenosides against Asian corn borer, Ostrinia furnacalis (Guenee). PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0211905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badalamenti, N.; Rosselli, S.; Zito, P.; Bruno, M. Phytochemical profile and insecticidal activity of Drimia pancration (Asparagaceae) against adults of Stegobium paniceum (Anobiidae). Nat. Prod. Res. 2021, 35, 4468–4478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelah, D.; Abramovich, Z.; Markus, A.; Wiesman, Z. The use of commercial saponin from Quillaja saponaria bark as a natural larvicidal agent against Aedes aegypti and Culex pipiens. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2002, 81, 407–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Geyter, E.; Smagghe, G.; Rahbé, Y.; Geelen, D. Triterpene saponins of Quillaja saponaria show strong aphicidal and deterrent activity against the pea aphid Acyrthosiphon pisum. Pest. Manag. Sci. 2012, 68, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirhaghparast, S.K.; Zibaee, A.; Hajizadeh, J.; Ramzi, J. Changes in immune responses, gene expression, and life table parameters of Helicoverpa armigera Hübner fed on a diet containing the saponin of tea plant, Camellia sinensis. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2022, 111, e21962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yendo, A.C.A.; De Costa, F.; Fleck, J.D.; Gosmann, G.; Fett-Neto, A.G. Irradiance-based treatments of Quillaja brasiliensis leaves (A. St.-Hil. & Tul.) Mart. as means to improve immunoadjuvant saponin yield. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2015, 74, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, L.T.; Alexandre, B.; Cacciatore, F.A.; Magedans, Y.V.S.; Fett-Neto, A.G.; Contri, R.V.; Malheiros, P.S. Carvacrol-loaded nanoemulsions produced with a natural emulsifier for lettuce sanitization. Food Res. Int. 2023, 168, 112748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Shraogi, N.; Verma, R.; Saji, J.; Kar, A.K.; Tehlan, S.; Ghosh, D.; Patnaik, S. Challenges in current pest management practices: Navigating problems and a way forward by integrating controlled release system approach. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 498, 154989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yendo, A.C.A.; De Costa, F.; Kauffmann, C.; Fleck, J.D.; Gosmann, G.; Fett-Neto, A.G. Purification of an immunoadjuvant saponin fraction from Quillaja brasiliensis leaves by reversed-phase silica gel chromatography. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1494, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Pizá, M.C.; Sautua, F.J.; Kocira, S.; Bohatá, A.; Bedrnicek, J.; Sozoniuk, M.; Carmona, M.A. Quick and effective evaluation methods for biocontrol agents and biostimulants against phytopathogenic fungi relevant for various cropping systems. Plant Pathol. 2025, 74, 641–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, S.R.; Utkalaja, B.G.; Patel, S.K.; Acharya, N. Spot assay and colony forming unit (CFU) analyses–based sensitivity test for Candida albicans and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Bio-protocol 2023, 13, e4872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.B.; Roddick, J.G.; Jones, J.L. Synergism between the potato alkaloids α-chaconine and α-solanine in inhibition of snail feeding. Phytochemistry 2001, 57, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greene, G.L.; Lepla, N.C.; Dickerson, W.A. Velvetbean caterpillar: A rearing procedure and artificial medium. J. Econ. Entomol. 1976, 69, 488–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, T.R.F.B.; Almeida, A.C.S.; Moura, T.L.; da Silva, A.R.; Freitas, S.S.; Jesus, F.G. Effect of the flavonoid rutin on the biology of Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Acta Sci. Agron. 2016, 38, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yendo, A.C.A.; Colling, L.C.; Matsuura, H.N.; Vargas, L.R.B.; Martinelli, J.A.; Chitolina, G.Z.; Vainstein, M.H.; Fett-Neto, A.G. Quillaja lancifolia Immunoadjuvant Saponins Show Toxicity to Herbivores and Pathogenic Fungi. Plants 2025, 14, 1252. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14081252
Yendo ACA, Colling LC, Matsuura HN, Vargas LRB, Martinelli JA, Chitolina GZ, Vainstein MH, Fett-Neto AG. Quillaja lancifolia Immunoadjuvant Saponins Show Toxicity to Herbivores and Pathogenic Fungi. Plants. 2025; 14(8):1252. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14081252
Chicago/Turabian StyleYendo, Anna C. A., Luana C. Colling, Hélio N. Matsuura, Lúcia R. B. Vargas, José A. Martinelli, Gabriela Z. Chitolina, Marilene H. Vainstein, and Arthur G. Fett-Neto. 2025. "Quillaja lancifolia Immunoadjuvant Saponins Show Toxicity to Herbivores and Pathogenic Fungi" Plants 14, no. 8: 1252. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14081252
APA StyleYendo, A. C. A., Colling, L. C., Matsuura, H. N., Vargas, L. R. B., Martinelli, J. A., Chitolina, G. Z., Vainstein, M. H., & Fett-Neto, A. G. (2025). Quillaja lancifolia Immunoadjuvant Saponins Show Toxicity to Herbivores and Pathogenic Fungi. Plants, 14(8), 1252. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14081252








