Prolonged Diuretic, Natriuretic, and Potassium- and Calcium-Sparing Effect of Hesperidin in Hypertensive Rats
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Prolonged Diuretic Effect of Hesperidin in Hypertensive Male Rats
2.2. Prolonged Natriuretic and Potassium- and Calcium-Sparing Effects of Hesperidin
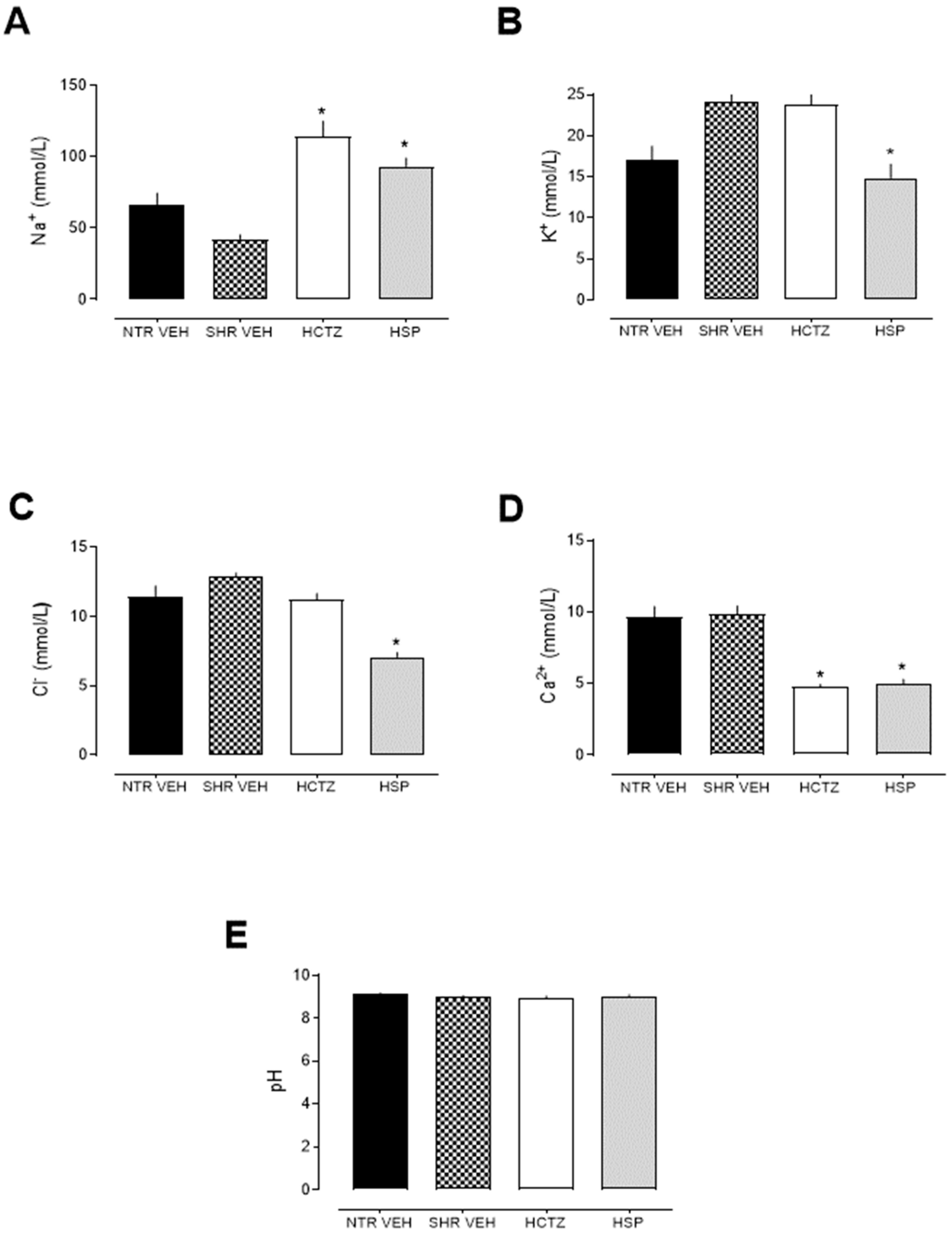
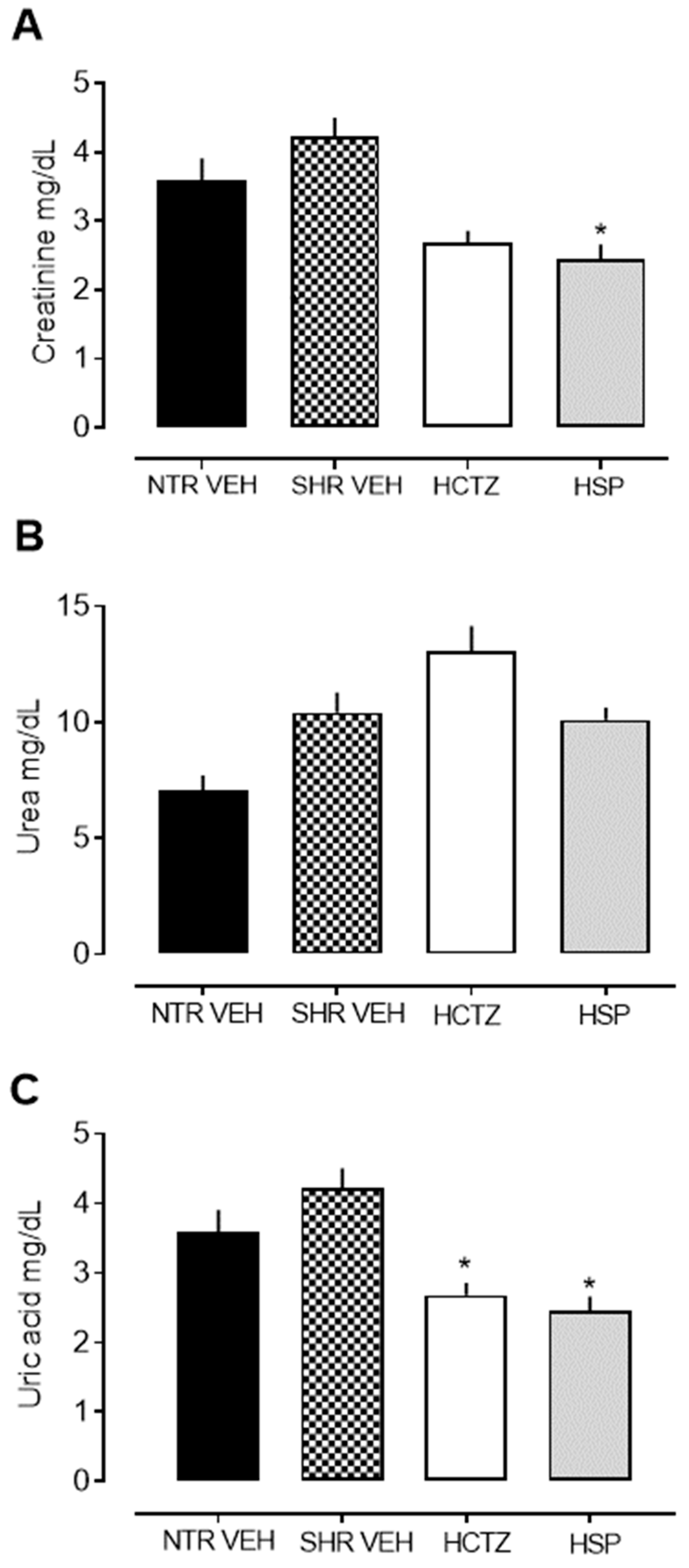
2.3. Analysis of Urinary Biochemical Parameters
2.4. Analysis of Plasmatic Parameters
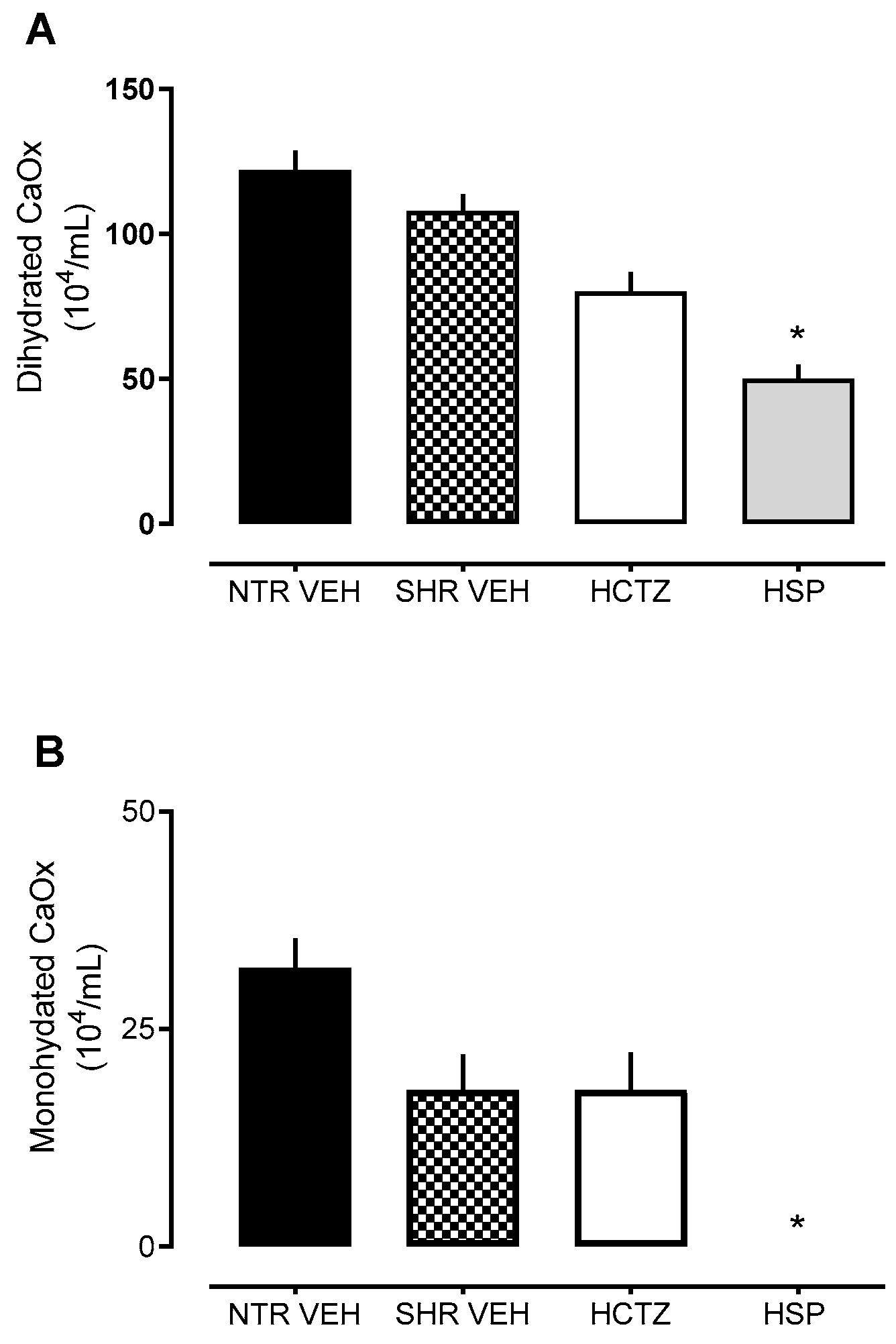
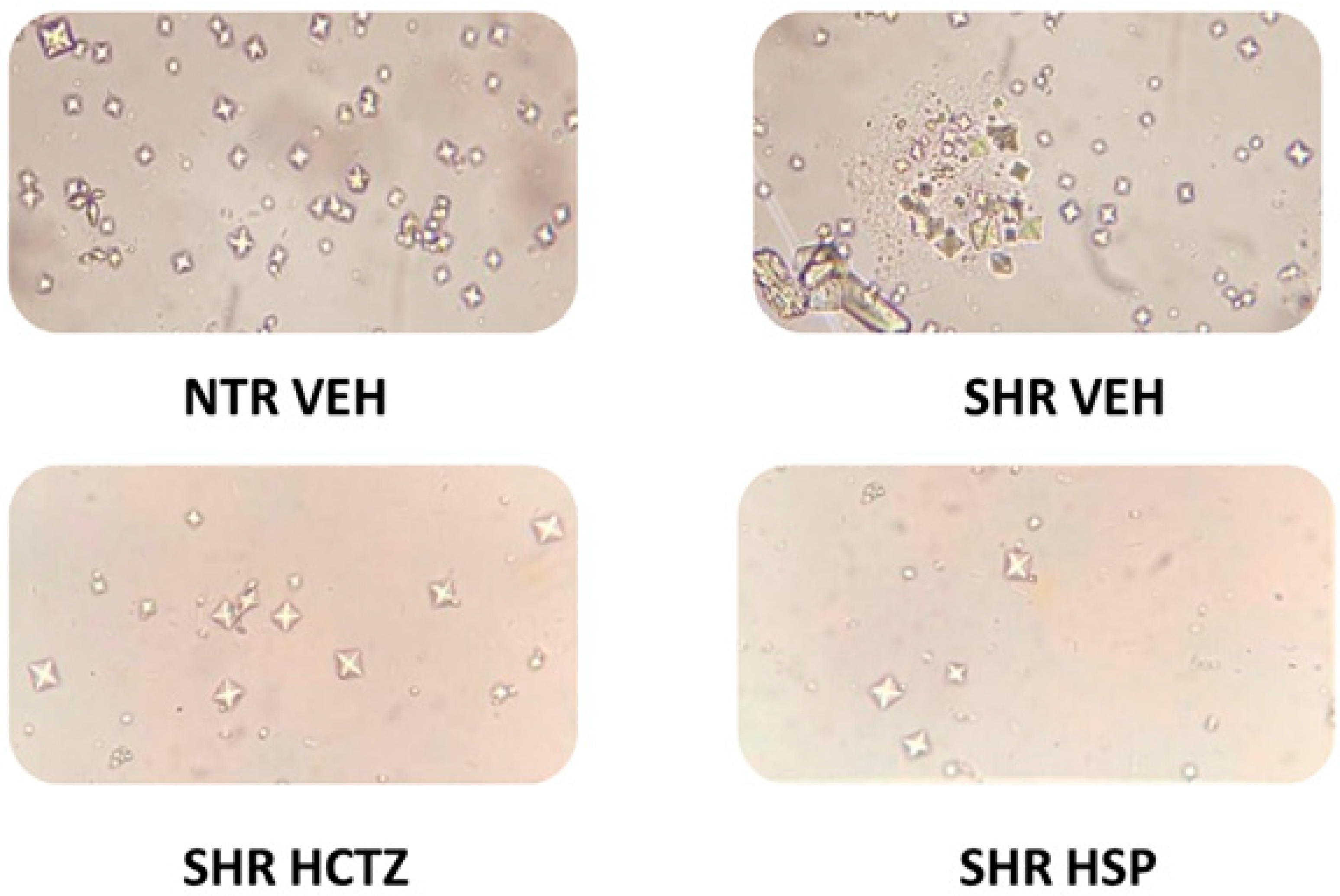
2.5. Assessment of Crystal Formation in Urine
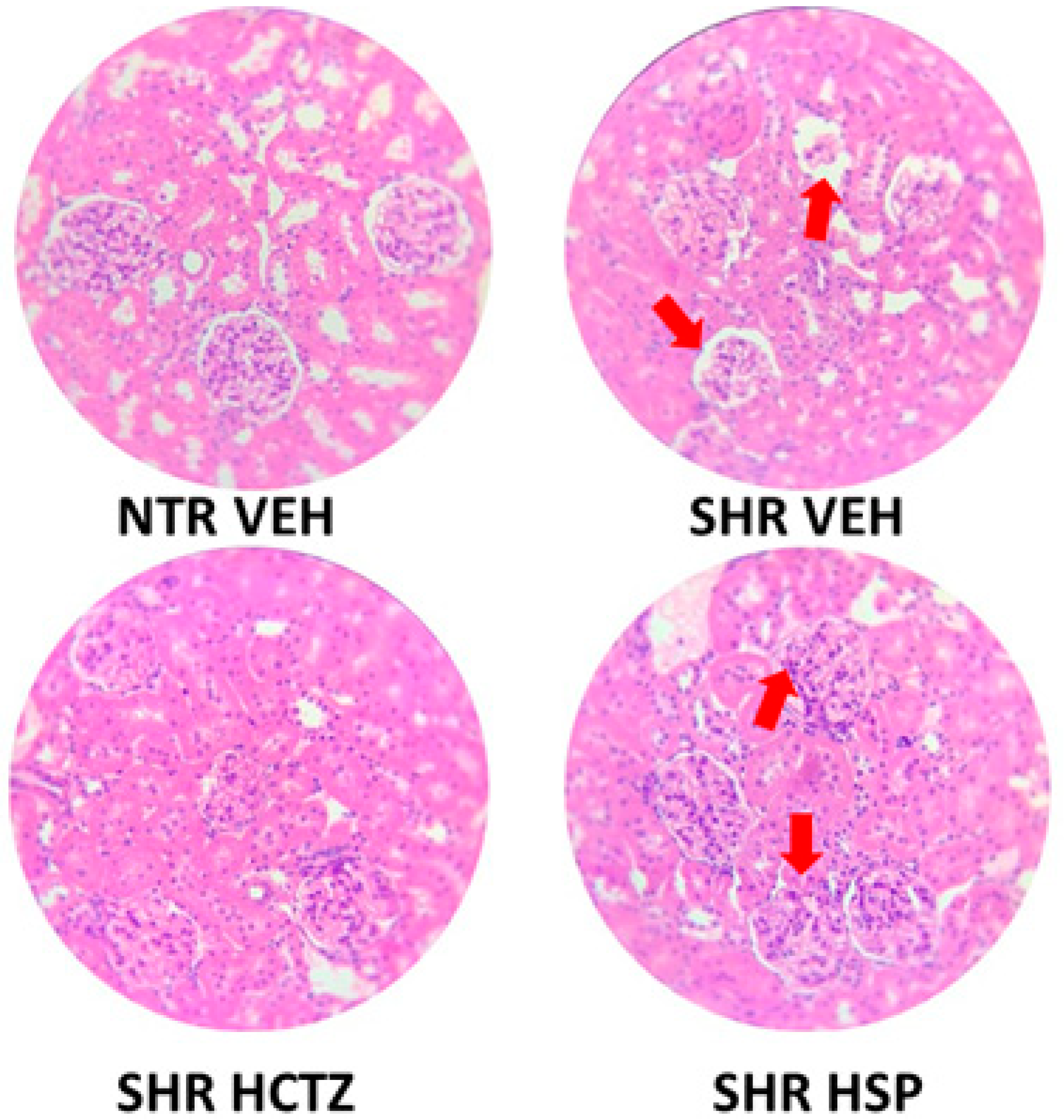
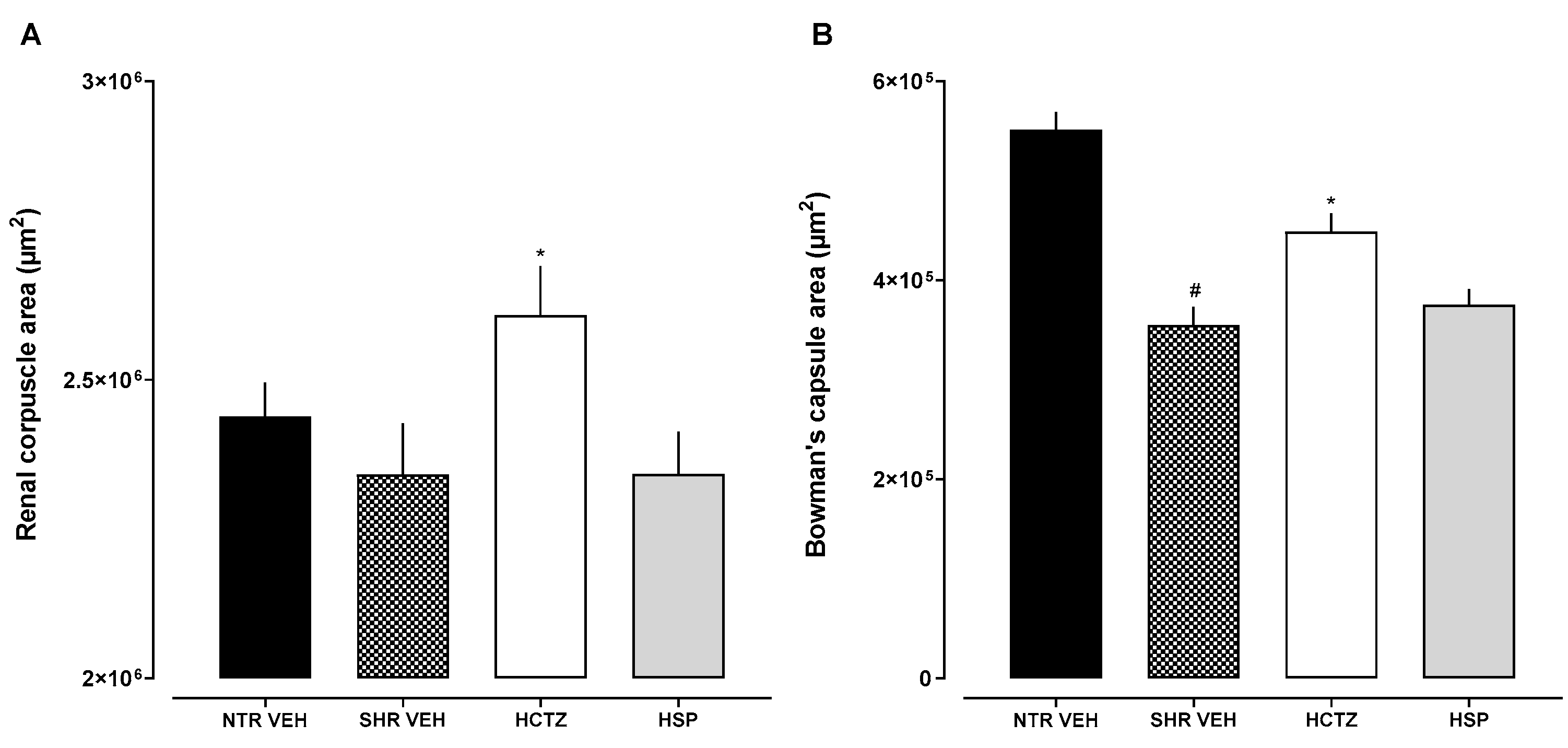
2.6. Histological Evaluation
2.7. Molecular Docking
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Drugs and Reagents
4.2. Animals
4.3. Assessment of Prolonged Diuresis
4.4. Statistical Analysis
4.5. Molecular Docking
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mills, K.T.; Stefanescu, A.; He, J. The global epidemiology of hypertension. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2020, 16, 223–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu, H.; Aboumatar, H.; Carson, K.A.; Goldberg, R.; Cooper, L.A. Hypertension knowledge, heart healthy lifestyle practices and medication adherence among adults with hypertension. Eur. J. Pers. Cent. Healthc. 2018, 6, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomopoulos, C.; Parati, G.; Zanchetti, A. Effects of blood-pressure-lowering treatment on outcome incidence. 12. Effects in individuals with high-normal and normal blood pressure: Overview and meta-analyses of randomized trials. J. Hypertens. 2017, 35, 2150–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsioufis, C.; Thomopoulos, C. Combination drug treatment in hypertension. Pharmacol. Res. 2017, 125, 266–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blowey, D.L. Diuretics in the treatment of hypertension. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2016, 31, 2223–2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sica, D.A. Diuretic-related side effects: Development and treatment. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2004, 6, 532–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M. Natural products as sources of new drugs over the nearly four decades from 01/1981 to 09/2019. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 770–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miler, M.; Živanović, J.; Ajdžanović, V.; Oreščanin-Dušić, Z.; Milenković, D.; Konić-Ristić, A.; Blagojević, D.; Milošević, V.; Šošić-Jurjević, B. Citrus flavanones naringenin and hesperetin improve antioxidant status and membrane lipid compositions in the liver of old-aged Wistar rats. Exp. Gerontol. 2016, 84, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantin, R.P.; Constantin, R.P.; Bracht, A.; Yamamoto, N.S.; Ishii-Iwamoto, E.L.; Constantin, J. Molecular mechanisms of citrus flavanones on hepatic gluconeogenesis. Fitoterapia 2014, 92, 148–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyrzynska, K. Hesperidin: A Review on Extraction Methods, Stability and Biological Activities. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.L.; Chen, S.C.; Senthil Kumar, K.J.; Yu, K.N.; Lee Chao, P.D.; Tsai, S.Y.; Hou, Y.C.; Hseu, Y.C. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory potential of hesperetin metabolites obtained from hesperetin-administered rat serum: An ex vivo approach. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 522–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, V.; Tuli, H.S.; Thakral, F.; Singhal, P.; Aggarwal, D.; Srivastava, S.; Pandey, A.; Sak, K.; Varol, M.; Khan, M.A.; et al. Molecular mechanisms of action of hesperidin in cancer: Recent trends and advancements. Exp. Biol. Med. 2020, 245, 486–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roohbakhsh, A.; Parhiz, H.; Soltani, F.; Rezaee, R.; Iranshahi, M. Molecular mechanisms behind the biological effects of hesperidin and hesperetin for the prevention of cancer and cardiovascular diseases. Life Sci. 2015, 124, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maneesai, P.; Bunbupha, S.; Potue, P.; Berkban, T.; Kukongviriyapan, U.; Kukongviriyapan, V.; Prachaney, P.; Pakdeechote, P. Hesperidin Prevents Nitric Oxide Deficiency-Induced Cardiovascular Remodeling in Rats via Suppressing TGF-β1 and MMPs Protein Expression. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Souza, P.; da Silva, R.C.V.; Mariano, L.N.B.; Dick, S.L.; Ventura, G.C.; Cechinel-Filho, V. Diuretic and Natriuretic Effects of Hesperidin, a Flavanone Glycoside, in Female and Male Hypertensive Rats. Plants 2022, 12, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera, N.; Cuesta, S.A.; Mora, J.R.; Paz, J.L.; Márquez, E.A.; Espinoza-Montero, P.J.; Marrero-Ponce, Y.; Pérez, N.; Contreras-Torres, E. Searching glycolate oxidase inhibitors based on QSAR, molecular docking, and molecular dynamic simulation approaches. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 19969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, K.P.; Tandon, S.; Naik, P.K.; Singh, S.K.; Tandon, C. Peeping into Human Renal Calcium Oxalate Stone Matrix: Characterization of Novel Proteins Involved in the Intricate Mechanism of Urolithiasis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e69916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chattaraj, B.; Nandi, A.; Das, A.; Sharma, A.; Dey, Y.N.; Kumar, D. Inhibitory activity of Enhydra fluctuans Lour. on calcium oxalate crystallisation through in silico and in vitro studies. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 13, 982419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannan, F.M.; Kallay, E.; Chang, W.; Brandi, M.L.; Thakker, R.V. The calcium-sensing receptor in physiology and in calcitropic and noncalcitropic diseases. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2019, 15, 33–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, T.; Wang, Z.; Chen, X.; Ren, Y.; Lu, X.; Xing, Y.; Lu, J.; Chang, S.; Zhang, X.; Shen, Y.; et al. Structural basis for activation and allosteric modulation of full-length calcium-sensing receptor. Sci Adv. 2021, 7, eabg1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, T.; Zou, J.; Miller, C.L.; Gorkhali, R.; Yang, J.-Y.; Schilmiller, A.; Wang, S.; Huang, K.; Brown, E.M.; et al. Structural basis for regulation of human calcium-sensing receptor by magnesium ions and an unexpected tryptophan derivative co-agonist. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1600241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diao, J.; DeBono, A.; Josephs, T.M.; Bourke, J.E.; Capuano, B.; Gregory, K.J.; Leach, K. Therapeutic opportunities of targeting allosteric binding sites on the calcium-sensing receptor. ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci. 2021, 4, 666–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kehrenberg, M.C.A.; Bachmann, H.S. Diuretics: A contemporary pharmacological classification? Naunyn-Schmiedeberg Arch. Pharmacol. 2022, 395, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, P.; Mariano, L.N.B.; Cechinel-Zanchett, C.C.; Cechinel-Filho, V. Promising Medicinal Plants with Diuretic Potential Used in Brazil: State of the Art, Challenges, and Prospects. Planta Med. 2021, 87, 24–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariano, L.N.B.; Boeing, T.; da Silva, R.C.V.; da Silva, L.M.; Gasparotto-Júnior, A.; Cechinel-Filho, V.; de Souza, P. Exotic Medicinal Plants Used in Brazil with Diuretic Properties: A Review. Chem. Biodivers. 2022, 19, e202200258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Morales, N.; Baranda-Alonso, E.M.; Martínez-Salgado, C.; López-Hernández, F.J. Renal sympathetic activity: A key modulator of pressure natriuresis in hypertension. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2023, 208, 115386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pravenec, M.; Křen, V.; Landa, V.; Mlejnek, P.; Musilová, A.; Šilhavý, J.; Šimáková, M.; Zídek, V. Recent progress in the genetics of spontaneously hypertensive rats. Physiol. Res. 2014, 63 (Suppl. S1), S1–S8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Beze, J.; Mazeaud, C.; Daul, C.; Ochoa-Ruiz, G.; Daudon, M.; Eschwège, P.; Hubert, J. Evaluation and understanding of automated urinary stone recognition methods. BJU Int. 2022, 130, 786–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratkalkar, V.N.; Kleinman, J.G. Mechanisms of Stone Formation. Clin. Rev. Bone Miner. Metab. 2011, 9, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorensen, M.D. Calcium intake and urinary stone disease. Transl. Androl. Urol. 2014, 3, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, Z.; Taleuzzaman, M.; Jamal, R.; Al-Qahtani, N.H.; Haque, A. Targeting protein receptors and enzymes for precision management of urolithiasis: A comprehensive review. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2024, 981, 176904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macarini, A.F.; Mariano, L.N.B.; Zanovello, M.; da Silva, R.C.V.; Corrêa, R.; de Souza, P. Protective Role of Rosmarinic Acid in Experimental Urolithiasis: Understanding Its Impact on Renal Parameters. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirfule, A.L.; Sangamwar, A.T.; Khobragade, C.N. Exploring glycolate oxidase (GOX) as an antiurolithic drug target: Molecular modeling and in vitro inhibitor study. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2011, 49, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, B.B.; Yuan, W.; Li, S.; Gupta, S.C. Curcumin-free turmeric exhibits anti-inflammatory and anticancer activities: Identification of novel components of turmeric. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2013, 57, 1529–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hultström, M. Development of structural kidney damage in spontaneously hypertensive rats. J. Hypertens. 2012, 30, 1087–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kandhwal, M.; Grewal, A.K.; Singh, M.; Singh, V.; Singh, T.G. Neuroprotective effects of hesperidin: In-Vitro and in silico evaluation of its antioxidant and enzyme inhibitory activities. Carpath. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 16, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, H.M.; Westbrook, J.; Feng, Z.; Gilliland, G.; Bhat, T.N.; Weissig, H.; Shindyalov, I.N.; Bourne, P.E. The Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, V.T.; de Franco, É.P.D.; de Araújo, M.E.M.B.; Messias, M.C.F.; Priviero, F.B.M.; Frankland Sawaya, A.C.; de Oliveira Carvalho, P. Characterization of the antioxidant activity of aglycone and glycosylated derivatives of hesperetin: An in vitro and in vivo study. J. Mol. Recognit. 2016, 29, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock Vina: Improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| VEH NTR | VEH SHR | HCTZ SHR | HSP SHR | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Na+ (mmol/L) | 137.50 ± 1.23 | 139.50 ± 0.54 | 137.00 ± 0.76 | 138.30 ± 0.15 |
| K+ (mmol/L) | 5.90 ± 0.34 | 5.58 ± 0.18 | 5.45 ± 0.04 | 5.51 ± 0.12 |
| Cl− (mmol/L) | 97.14 ± 0.46 | 98.52 ± 0.18 | 98.66 ± 0.48 | 98.52 ± 0.41 |
| Ca2+ (mmol/L) | 1.42 ± 0.03 | 1.37 ± 0.01 | 1.36 ± 0.01 | 1.35 ± 0.01 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.25 ± 0.03 | 0.23 ± 0.01 | 0.24 ± 0.01 | 0.22 ± 0.01 |
| Urea (mg/dL) | 59.64 ± 1.31 | 52.35 ± 0.91 | 54.35 ± 0.48 | 54.48 ± 0.99 |
| Uric acid (mg/dL) | 1.24 ± 0.09 | 1.03 ± 0.09 | 1.03 ± 0.09 | 1.16 ± 0.08 |
| Binding Affinity (kcal/mol) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Enzyme | PDB ID | Hesperetin | Hesperidin |
| Glycolate Oxidase | 2RDT | −7.5 | −8.5 |
| Calcium-sensing receptor VFT | 5FBK | −9.2 | −8.5 |
| Calcium-sensing receptor 7TM | 7DD7 | −8.5 | −9.6 |
| Phosphoethanolamine Cytidylyltransferase | 3ELB | −8.4 | −8.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Orengo, S.L.D.; Vilhena da Silva, R.d.C.; Macarini, A.F.; Cechinel Filho, V.; de Souza, P. Prolonged Diuretic, Natriuretic, and Potassium- and Calcium-Sparing Effect of Hesperidin in Hypertensive Rats. Plants 2025, 14, 1324. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14091324
Orengo SLD, Vilhena da Silva RdC, Macarini AF, Cechinel Filho V, de Souza P. Prolonged Diuretic, Natriuretic, and Potassium- and Calcium-Sparing Effect of Hesperidin in Hypertensive Rats. Plants. 2025; 14(9):1324. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14091324
Chicago/Turabian StyleOrengo, Sabrina Lucietti Dick, Rita de Cássia Vilhena da Silva, Anelise Felício Macarini, Valdir Cechinel Filho, and Priscila de Souza. 2025. "Prolonged Diuretic, Natriuretic, and Potassium- and Calcium-Sparing Effect of Hesperidin in Hypertensive Rats" Plants 14, no. 9: 1324. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14091324
APA StyleOrengo, S. L. D., Vilhena da Silva, R. d. C., Macarini, A. F., Cechinel Filho, V., & de Souza, P. (2025). Prolonged Diuretic, Natriuretic, and Potassium- and Calcium-Sparing Effect of Hesperidin in Hypertensive Rats. Plants, 14(9), 1324. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14091324









