Identification of Novel Loci and Candidate Genes for Cucumber Downy Mildew Resistance Using GWAS
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
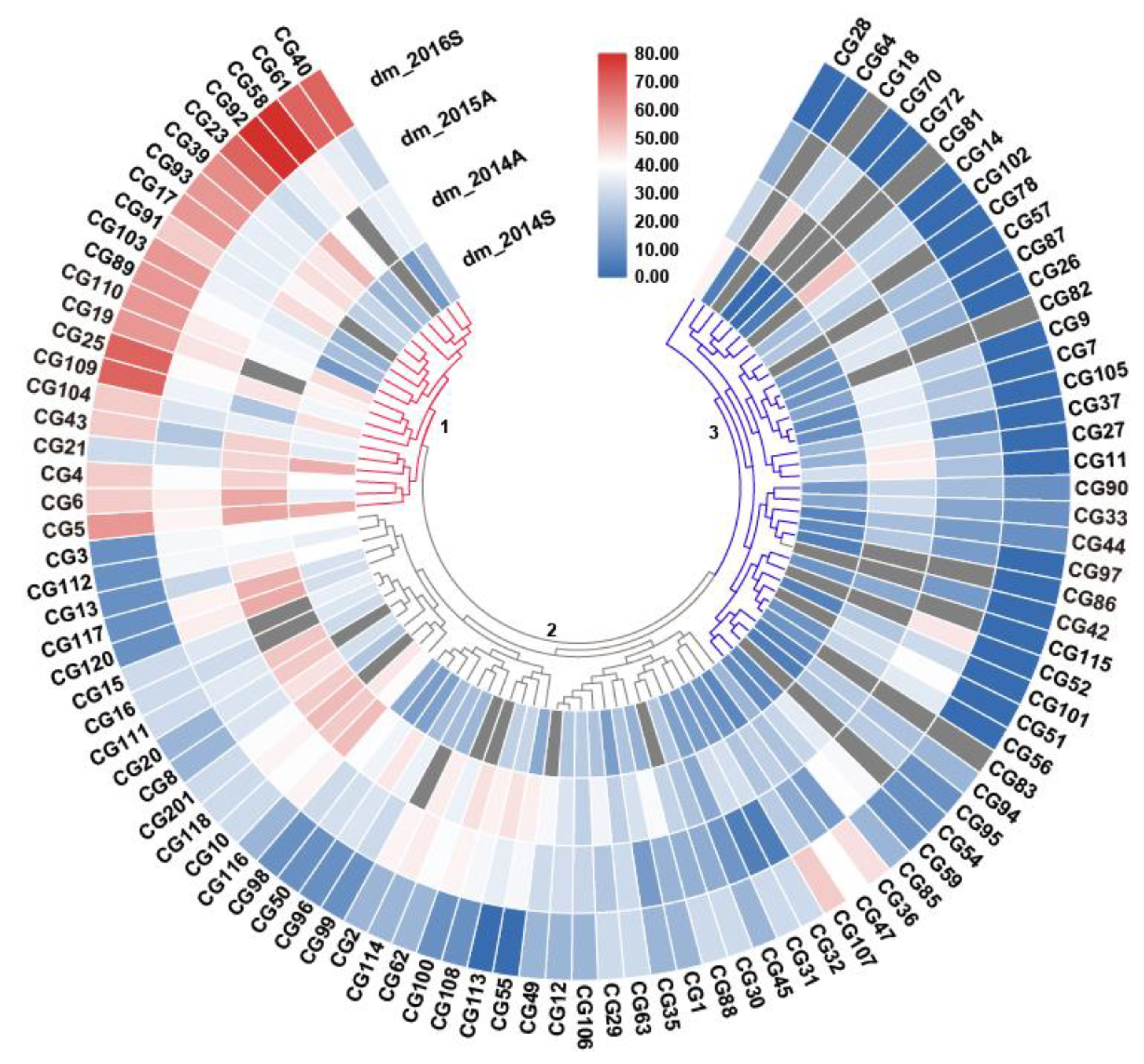
2.1. Genetic Diversity of DM Resistance in the CG Germplasm
2.2. Genome-Associated Analysis of DM Resistance
2.3. Candidate Gene Analysis for the Novel and Stable Loci
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials
4.2. Investigation of Disease Index of the Core Germplasm Resistance
4.3. Genetic Diversity of DM Resistance in Germplasm
4.4. Genome-Wide Association Analyses of DM Resistance
4.5. Linkage Disequilibrium Analysis
4.6. Candidate Gene Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lebeda, A.; Urban, J. Distribution, harmfulness and pathogenic variability of cucurbit downy mildew in the Czech Republic. Acta Fytotech. Zootech. 2004, 7, 170–173. [Google Scholar]
- Colucci, S.J.; Wehner, T.C.; Holmes, G.J. The downy mildew epidemic of 2004 and 2005 in the eastern United States. In Proceedings of the Cucurbitaceae, Asheville, NC, USA, 17–21 September 2006; pp. 403–410. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.L. The Vegetables of Ancient China. Econ. Bot. 1969, 23, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Pu, H.; Liu, P.; Walters, T.W. Preliminary studies on Cucumis sativus var. xishuangbannanesis. Cucurbit Genet. Coop. Rep. 1991, 14, 29–31. [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins, J.M., Jr. Studies on the inheritance of downy mildew resistance and of other characters in cucumbers. J. Hered. 1946, 37, 267–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Criswell, A.D.; Call, A.D.; Wehner, T.C. Genetic control of downy mildew resistance in cucumber—A review. Cucurbit Genet. Coop. Rep. 2010, 33, 13–16. [Google Scholar]
- Epps, W.; Barnes, W. The increased susceptibility of the Palmetto cucumber to downy mildew in South Carolina. Plant. Dis. Rep. 1952, 36, 14–15. [Google Scholar]
- Barnes, W.; Epps, W. An unreported type of resistance to cucumber downy mildew. Plant. Dis. Rep. 1954, 38, 620. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Tan, J.; Wu, Z.; VandenLangenberg, K.; Wehner, T.C.; Wen, C.; Zheng, X.; Owens, K.; Thornton, A.; Bang, H.H. STAYGREEN, STAY HEALTHY: A loss-of-susceptibility mutation in the STAYGREEN gene provides durable, broad-spectrum disease resistances for over 50 years of US cucumber production. New Phytol. 2019, 221, 415–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, Y.; Van den Langenberg, K.M.; Wehner, T.C.; Ojiambo, P.S.; Hausbeck, M.; Quesada-Ocampo, L.M.; Lebeda, A.; Sierotzki, H.; Gisi, U. Resurgence of Pseudoperonospora cubensis: The Causal Agent of Cucurbit Downy Mildew. Phytopathology 2015, 105, 998–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, J.A.; Hermans, F.W.; Beenders, F.; Lou, L.; Vriezen, W.H.; Visser, R.G.; Bai, Y.; Schouten, H.J. Analysis of QTL DM4. 1 for downy mildew resistance in cucumber reveals multiple subQTL: A novel RLK as candidate gene for the most important subQTL. Front. Plant. Sci. 2020, 11, 1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, J.A. Cucumber Mildew Resistance: Identification of Cucumber Genes Involved in Susceptibility and Resistance to Powdery and Downy Mildew. Ph.D. Thesis, Wageningen University & Research, Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, J.; Liu, X.; Shen, D.; Miao, H.; Xie, B.; Li, X.; Zeng, P.; Wang, S.; Shang, Y.; Gu, X. A genomic variation map provides insights into the genetic basis of cucumber domestication and diversity. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Call, A.D.; Criswell, A.D.; Wehner, T.C.; Klosinska, U.; Kozik, E.U. Screening Cucumber for Resistance to Downy Mildew Caused by Pseudoperonospora cubensis (Berk. and Curt.) Rostov. Crop Sci. 2012, 52, 577–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, M.; Miao, H.; Zhang, S.; Yang, Y.; Xie, B.; Wehner, T.; Gu, X. Chromosomal mapping and QTL analysis of resistance to downy mildew in Cucumis sativus. Plant. Dis. 2013, 97, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Z.; Yuan, X.; Cai, R.; Liu, L.; He, H.; Zhou, H.; Pan, J. QTL analysis of downy mildew resistance in cucumber. Prog. Nat. Sci. 2008, 18, 706–710. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, X.; Zhou, X.; Wan, H.; Chen, J. QTL mapping of downy mildew resistance in an introgression line derived from interspecific hybridization between cucumber and Cucumis hystrix. J. Phytopathol. 2013, 161, 536–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Wang, X.; Zhu, W.; Qin, X.; Xu, J.; Cheng, C.; Lou, Q.; Li, J.; Chen, J. Complete resistance to powdery mildew and partial resistance to downy mildew in a Cucumis hystrix introgression line of cucumber were controlled by a co-localized locus. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2018, 131, 2229–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; VandenLangenberg, K.; Wehner, T.C.; Kraan, P.A.; Suelmann, J.; Zheng, X.; Owens, K.; Weng, Y. QTL mapping for downy mildew resistance in cucumber inbred line WI7120 (PI 330628). Theor. Appl. Genet. 2016, 129, 1493–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Win, K.T.; Vegas, J.; Zhang, C.; Song, K.; Lee, S. QTL mapping for downy mildew resistance in cucumber via bulked segregant analysis using next-generation sequencing and conventional methods. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2017, 130, 199–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshioka, Y.; Sakata, Y.; Sugiyama, M.; Fukino, N. Identification of quantitative trait loci for downy mildew resistance in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). Euphytica 2014, 198, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; VandenLangenberg, K.; Wen, C.; Wehner, T.C.; Weng, Y. QTL mapping of downy and powdery mildew resistances in PI 197088 cucumber with genotyping-by-sequencing in RIL population. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2018, 131, 597–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; He, H.; Zou, Z.; Li, Y. QTL analysis for downy mildew resistance in cucumber inbred line PI 197088. Plant Dis. 2018, 102, 1240–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burkhardt, A.; Day, B. Transcriptome and small RNAome dynamics during a resistant and susceptible interaction between cucumber and downy mildew. Plant Genome 2016, 9, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Vliet, G.; Meysing, W. Inheritance of resistance to Pseudoperonospora cubensis Rost. in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). Euphytica 1974, 23, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelov, D. Inheritance of resistance to downy mildew, Pseudoperonospora cubensis (Berk. & Curt.) Rostow. In Proceedings of the Report of the 2nd National Symposium of Plant Immunity, Plovdiv, Bulgaria; 1994; Volume 3, pp. 99–105. [Google Scholar]
- El-Hafez, A.; Shehata, S.; El-Din, S.; El-Doweny, H.; Awad, M. Inheritance of downy mildew disease and its nature of resistance in cucumber. Ann. Agric. Sci. Moshtohor 1990, 28, 1681–1697. [Google Scholar]
- Badr, L.; Mohamed, F. Inheritance and nature of resistance to downy mildew disease in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). Ann. Agric. Sci. Moshtohor 1998, 36, 2517–2544. [Google Scholar]
- Szczechura, W.; Staniaszek, M.; Klosinska, U.; Kozik, E. Molecular analysis of new sources of resistance to Pseudoperonospora cubensis (Berk. et Curt.) Rostovzev in cucumber. Russ. J. Genet. 2015, 51, 1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VandenLangenberg, K.M. Studies on Downy Mildew Resistance in Cucumber. (Cucumis sativus L.). Ph.D. Thesis, North Carolina State University, Raleigh, NC, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Bao, K.; Reddy, U.K.; Bai, Y.; Hammar, S.A.; Jiao, C.; Wehner, T.C.; Ramírez-Madera, A.O.; Weng, Y.; Grumet, R. The USDA cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) collection: Genetic diversity, population structure, genome-wide association studies, and core collection development. Hortic. Res. 2018, 5, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, G.; Qin, Z.; Zhou, X.; Fan, J. RAPD and SCAR markers linked to downy mildew resistance genes in cucumber. Acta Bot. Boreali-Occident. Sin. 2007, 27, 1747–1751. [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell, D.; Chan, E.; De Vries, J.; Joobeur, T.; King, J.; Reina, A.; Shetty, N. Methods and Compositions for Identifying Downy Mildew Resistant Cucumber Plants. U.S. Patent WO2011050296A1, 28 April 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.; Katz, D.; Ben Naim, Y.; Hammer, R.; Ben Daniel, B.H.; Rubin, A.E.; Cohen, Y. Isolate-Dependent Inheritance of Resistance Against Pseudoperonospora cubensis in Cucumber. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, R.; Sinha, R.; Chattopadhyay, S. Changes in leaf proteome profile of Arabidopsis thaliana in response to salicylic acid. J. Biosci. 2013, 38, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhar, N.; Caruana, J.; Erdem, I.; Subbarao, K.V.; Klosterman, S.J.; Raina, R. The Arabidopsis SENESCENCE-ASSOCIATED GENE 13 Regulates Dark-Induced Senescence and Plays Contrasting Roles in Defense Against Bacterial and Fungal Pathogens. Mol. Plant. Microbe Interact. 2020, 33, 754–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuda, F.; Hirai, M.Y.; Sasaki, E.; Akiyama, K.; Yonekura-Sakakibara, K.; Provart, N.J.; Sakurai, T.; Shimada, Y.; Saito, K. AtMetExpress development: A phytochemical atlas of Arabidopsis development. Plant. Physiol. 2010, 152, 566–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, J.Y.; Choi, G.J.; Son, S.W.; Jang, K.S.; Lim, H.K.; Lee, S.O.; Sung, N.D.; Cho, K.Y.; Kim, J.C. Isolation and antifungal activity of lignans from Myristica fragrans against various plant pathogenic fungi. Pest. Manag. Sci. 2007, 63, 935–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SAS Institute. SAS/OR 9.3 User’s Guide: Mathematical Programming Examples; SAS Institute: Cary, NC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, L. CMplot: Circle Manhattan Plot; GitHub, Inc.: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Purcell, S.; Neale, B.; Todd-Brown, K.; Thomas, L.; Ferreira, M.A.; Bender, D.; Maller, J.; Sklar, P.; De Bakker, P.I.; Daly, M.J. PLINK: A tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 81, 559–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broman, K.W.; Wu, H.; Sen, Ś.; Churchill, G.A. R/qtl: QTL mapping in experimental crosses. Bioinformatics 2003, 19, 889–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arends, D.; Prins, P.; Jansen, R.C.; Broman, K.W. R/qtl: High-throughput multiple QTL mapping. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2990–2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








| Resistance Donor | Mapping Population | Gene/QTL | Chromo- Some | Causal Gene | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PR40 | - | - | - | - | Jenkins J.M., (1946) [5] |
| Indian accession PI 605996 | - | - | - | - | Call et al., (2012) [14] |
| Indian accession PI 197087 | RILs of Gy14 (R, derived from PI 197087) × 9930 and F2:3 families of WTF23 (R, derived from PI 197087) × True Lemon | dm-1 | 5 | Sgr | Wang et al., (2019) [9] |
| Chinese long cucumber hybrid, Yuanfeng | F2 and F2:3 families of Inbred line K8 (R) × K18 (S) | dm1.1, dm5.1, dm5.2, dm5.3, dm6.1 | 1, 5, 6 | - | Zhang et al., (2013) [15]; Bai et al., (2008) [16] |
| Cucumis hystrix | F2 population of IL52 (R) × Changcunmici (S) | DM_5.1, DM_5.2 | 5 | - | Pang et al., (2013) [17]; Zhang et al., (2018) [18] |
| Pakistan accession PI 330628 | F2:3 families of WI7120 (derived from PI 330628 (R)) × Chinses cultivar 9930 (S) | dm2.1, dm4.1, dm5.1, dm6.1 | 2, 4, 5, 6 | - | Wang et al., (2016) [19] |
| Hybrid Malini | F2:3 families of TH118FLM (derived from Malini (R)) × WMEJ (S) | dm2.2, dm4.1, dm5.1, dm5.2, dm6.1 | 2, 4, 5, 6 | - | Win et al., (2017) [20] |
| Indian accession PI 197088 & Japanese cultivar Santou | RILs of CS-PMR1 (derived from PI 197088, R) × Santou (intermediate S) | 7 QTLs from CS-PMR1 3 QTLs from Santou | 1, 3, 5 1, 6, 7 | - | Yoshioka et al., (2014) [21] |
| Indian accession PI 197088 | F2:3 families of PI 197088 (R) × Coolgree (S) | 11 QTLs of which dm5.1, dm5.2, and dm5.3 are major QTLs | All chromosomes except 7 | - | Wang et al., (2018) [22] |
| Indian accession PI 197088 | F2 and F2:3 families of PI 197088 × Changcunmici (S) | dm1.1, dm3.1, dm4.1, dm5.1, dm5.2 | 1, 3, 4, 5 | - | Li et al., (2018) [23] |
| Indian accession PI 197088 | NILs and F2:3 families of PI 197088 (R) × HS279 (S) | DM4.1 and its derived subQTLs, DM4.1.2 and DM4.1.3 | 4 | CsLRK10L2 & CsAAP2A | Berg J., (2020) [11] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, X.; Lu, H.; Liu, P.; Miao, H.; Bai, Y.; Gu, X.; Zhang, S. Identification of Novel Loci and Candidate Genes for Cucumber Downy Mildew Resistance Using GWAS. Plants 2020, 9, 1659. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9121659
Liu X, Lu H, Liu P, Miao H, Bai Y, Gu X, Zhang S. Identification of Novel Loci and Candidate Genes for Cucumber Downy Mildew Resistance Using GWAS. Plants. 2020; 9(12):1659. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9121659
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xiaoping, Hongwei Lu, Panna Liu, Han Miao, Yuling Bai, Xingfang Gu, and Shengping Zhang. 2020. "Identification of Novel Loci and Candidate Genes for Cucumber Downy Mildew Resistance Using GWAS" Plants 9, no. 12: 1659. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9121659
APA StyleLiu, X., Lu, H., Liu, P., Miao, H., Bai, Y., Gu, X., & Zhang, S. (2020). Identification of Novel Loci and Candidate Genes for Cucumber Downy Mildew Resistance Using GWAS. Plants, 9(12), 1659. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9121659




