Thermal Comfort Performance in Buildings: Challenges and Innovative Solutions
A special issue of Buildings (ISSN 2075-5309). This special issue belongs to the section "Building Energy, Physics, Environment, and Systems".
Deadline for manuscript submissions: closed (15 February 2023) | Viewed by 3449
Special Issue Editor
Special Issue Information
Dear Colleagues,
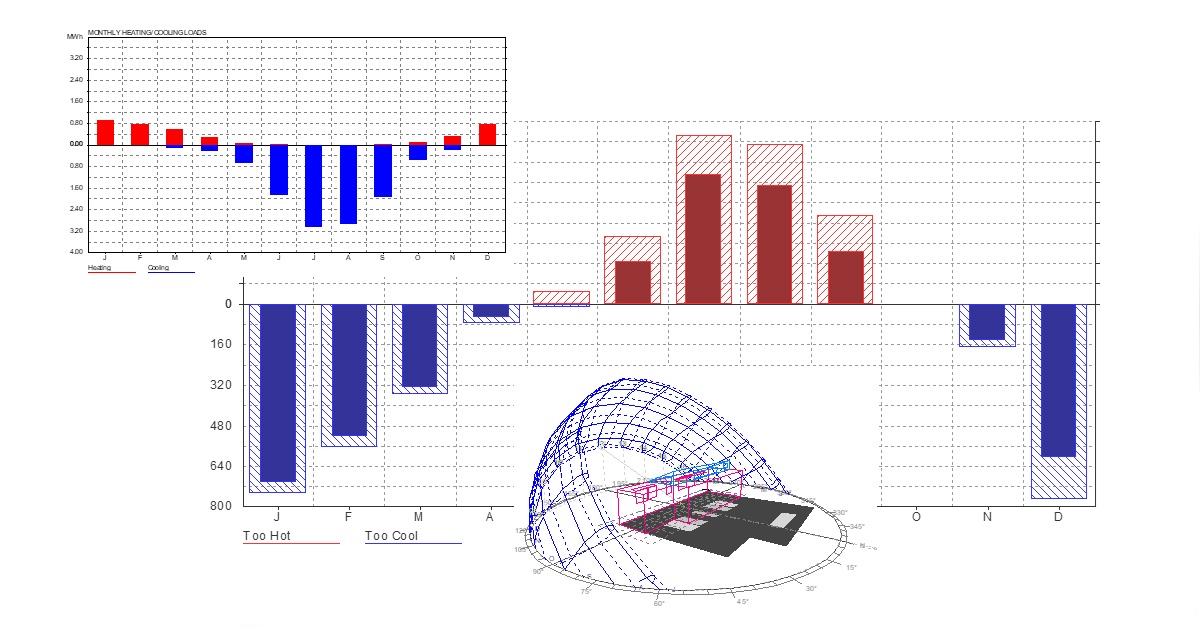
Sustainability of resources including energy is a main global concern today, as reflected in the development plans of different countries and organizations. This includes the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), specifically Goal 11. This goal aims to “make cities and human settlements inclusive, safe, resilient and sustainable”. One key determinant here is to create buildings that are sustainable and healthy. Thermal comfort in this context is a main important issue to designers, researchers, and policy makers. It is an ultimate design goal that improves people’s physical and mental health and contributes to energy savings in green buildings. There are several architectural design strategies that could be innovatively explored in this regard, considering the recent technological developments and the post-pandemic design requirements. Thus, the goal of this Special Issue of Buildings titled “Thermal Comfort Performance in Buildings: Challenges and Innovative Solutions” is to address the urban and architectural strategies that could be implemented to improve thermal comfort conditions in our built environment. Papers that critically address these strategies are particularly welcome to this Special Issue.
Dr. Omar S. Asfour
Guest Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the special issue website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Buildings is an international peer-reviewed open access monthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2600 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- green buildings
- sustainable architecture
- solar architecture
- thermal comfort
- energy efficient design
- passive urban design
- low energy buildings





