Journal Description
Immuno
Immuno
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on immunological research and clinical applications published quarterly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within ESCI (Web of Science), Scopus, EBSCO, and other databases.
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 26.8 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 2.2 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2024).
- Journal Rank: CiteScore - Q2 (Medicine (miscellaneous))
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
Impact Factor:
2.1 (2023);
5-Year Impact Factor:
2.1 (2023)
Latest Articles
Preliminary Evidence of Enhanced Immunogenicity of Hepatitis B Virus Vaccines When Co-Administered with Calcium Phosphate, Aluminum Hydroxide, and Cytosine Phospho-Guanine Oligodeoxynucleotides Combined Adjuvant in BALB/c Mice
Immuno 2025, 5(1), 12; https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno5010012 - 14 Mar 2025
Abstract
►
Show Figures
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection is a major public health risk. Despite the introduction of successful vaccines, which are normally single adjuvanted, there are still some drawbacks, including non-responsiveness in certain groups, short durability of immunity, inadequate protection, and the need for additional
[...] Read more.
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection is a major public health risk. Despite the introduction of successful vaccines, which are normally single adjuvanted, there are still some drawbacks, including non-responsiveness in certain groups, short durability of immunity, inadequate protection, and the need for additional doses to be addressed. This study aimed to develop an optimized combination of Cytosine-phosphate-Guanine Oligonucleotides (CPG-ODN2395, CPG-ODN-18281-2 23 mer) and calcium phosphate, and to assess its immunogenicity and toxicity when co-administrated with the commercial HBV vaccine (BEVAC, containing aluminum hydroxide) and an in-house aluminum hydroxide-adjuvanted HBs purified antigen in Balb/c mice. Tail blood was collected from vaccinated Balb/c mice on days 14 and 28 post-immunization to determine the antibody secretion level using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). The Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF-a) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) cytokine expression levels were assessed through real-time PCR, and the safety profile was checked through biochemical and hematological analysis. Our results showed that the combination of CPG-ODN2395, CPG-ODN 18281-2 23 mer, and CAP significantly enhanced the IgG antibody secretion level (p < 0.0001), which also showed a significant increase in IL-6 expression (p < 0.0001). The safety evaluations revealed no adverse impact on liver and kidney function, with normal ALT, AST, urea, and creatinine levels (p < 0.55). Hematological assessments revealed stable parameters across all groups. This study concludes that combining CpG ODNs and calcium phosphate adjuvants with hepatitis B vaccinations has the potential to enhance a stronger immunological response to hepatitis B infection than single adjuvants. These results highlight the promise of this innovative adjuvant system, necessitating more research in clinical environments to increase vaccine effectiveness and sustained protection against HBV.
Full article
Open AccessReview
Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Oxidative Effects of GLP1-RAs and SGLT2i: The Guiding Star Towards Cardiovascular Protection in Type 2 Diabetes
by
Livia M. R. Marcon and Alessio Mazzieri
Immuno 2025, 5(1), 11; https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno5010011 - 14 Mar 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is a chronic and progressive dysmetabolic condition related to several complications, including cardiovascular disease, whose incidence is increasing worldwide. Sodium–glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors (SGLT2i) and glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP1-RAs) are two new molecules recently made available
[...] Read more.
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is a chronic and progressive dysmetabolic condition related to several complications, including cardiovascular disease, whose incidence is increasing worldwide. Sodium–glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors (SGLT2i) and glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP1-RAs) are two new molecules recently made available for T2DM treatment, with the aim of reducing hyperglycemia. Recent evidence has also highlighted that in addition to the glucose-lowering action, both SGLT2i and GLP1-RAs ensure significant beneficial effects in reducing cardiovascular damage in T2DM patients. Interestingly, these benefits cannot be exclusively attributed to the improved glycemic control. Indeed, experimental and clinical studies have shed light on the protective role of SGLT2i and GLP-1RAs against inflammation and oxidative stress, especially in the heart and vasculature. In our review we elucidate the potential cardiovascular benefits provided by SGLT2i and GLP1-RAs to T2DM subjects by exploring the molecular pathways involved in the process of cardiovascular protection.
Full article
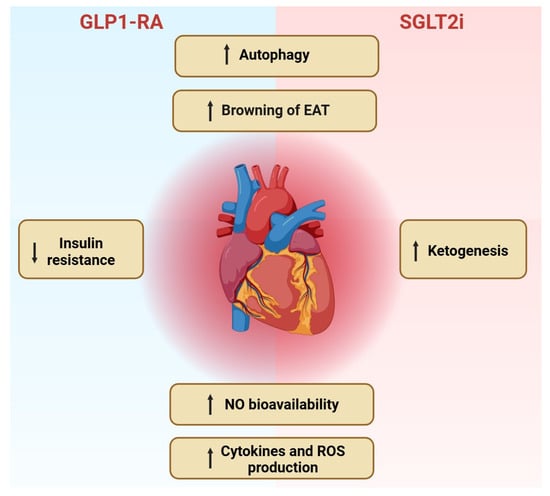
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
The Microbiome, Inflammation, and GVHD Axis: The Balance Between the “Gut” and the Bad
by
Paula Pinzon-Leal, Hernando Gutierrez-Barbosa, Sandra Medina-Moreno and Juan C. Zapata
Immuno 2025, 5(1), 10; https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno5010010 - 7 Mar 2025
Abstract
Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation is one of the most intricate immune therapies used for patients with hematological diseases or immune disorders. In addition to the inherent immunosuppression from their primary condition, many of these patients usually receive cytotoxic chemotherapy, radiation therapy, broad-spectrum antibiotics,
[...] Read more.
Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation is one of the most intricate immune therapies used for patients with hematological diseases or immune disorders. In addition to the inherent immunosuppression from their primary condition, many of these patients usually receive cytotoxic chemotherapy, radiation therapy, broad-spectrum antibiotics, or experience extended nutritional perturbations. These factors collectively lead to inflammation and the disruption of gut microbiota. Additionally, about 40–60% of patients undergoing fully HLA-matched allogeneic transplantation are expected to develop acute graft-versus-host disease (aGVHD), even with prophylactic measures such as calcineurin inhibitors, methotrexate/mycophenolate, or post-transplant cyclophosphamide treatment. Recent research has elucidated the complex interplay between immune effectors in the gastrointestinal tract and microbial populations within a proinflammatory peri-transplant environment, revealing its significant effect on survival and post-transplant complications such as aGVHD. This review will explore the relationship between dysbiosis during allogeneic transplantation and mechanisms that can help clarify the link between gut microbiota and the risk of GVHD, along with emerging therapeutic strategies aimed at addressing dysbiosis during hematopoietic stem cell transplantation.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Transplantation Immunology)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
A Concise Review of the Role of the NKG2D Receptor and Its Ligands in Cancer
by
Elitsa Boneva, Velizar Shivarov and Milena Ivanova
Immuno 2025, 5(1), 9; https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno5010009 - 2 Mar 2025
Abstract
The immune system’s ability to detect and eliminate transformed cells is a critical factor in suppressing cancer development. However, immune surveillance in tumors is often disrupted by various immune escape mechanisms, many of which remain poorly understood. The Natural Killer Group 2D (NKG2D)
[...] Read more.
The immune system’s ability to detect and eliminate transformed cells is a critical factor in suppressing cancer development. However, immune surveillance in tumors is often disrupted by various immune escape mechanisms, many of which remain poorly understood. The Natural Killer Group 2D (NKG2D) receptor is an activating receptor expressed on natural killer (NK) cells and cytotoxic T lymphocytes. It can recognize and bind with varying affinities to a wide range of structurally diverse ligands, including MHC class I chain-related proteins A and B (MICA and MICB) and members of the ULBP family (ULBP1-6). The expression of these ligands plays a crucial role in immune antitumor responses and cancer immunoevasion mechanisms. Some evidence suggests that functional polymorphisms in the NKG2D receptor and the genes encoding its ligands significantly influence HLA-independent cancer immunosurveillance. Consequently, the NKG2D-NKG2D ligands (NKG2DLs) axis represents a promising target for developing novel therapeutic strategies. This review aims to provide a general overview of the role of NKG2D and its ligands in various malignancies and explore their potential in advancing personalized cancer treatment protocols.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Cancer Immunology and Immunotherapy)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Super-Charged Natural Killer Cells: A Promising Immunotherapeutic Strategy for Oral Cancer
by
Kawaljit Kaur and Anahid Jewett
Immuno 2025, 5(1), 8; https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno5010008 - 25 Feb 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
NK cells have traditionally been classified as effectors of innate immunity, even though they also exhibit some features of adaptive immunity such as memory. NK cells contribute to the lysis and growth inhibition of cancer, mediating direct cytotoxicity and antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC)
[...] Read more.
NK cells have traditionally been classified as effectors of innate immunity, even though they also exhibit some features of adaptive immunity such as memory. NK cells contribute to the lysis and growth inhibition of cancer, mediating direct cytotoxicity and antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) and regulating the functions of other immune cells, respectively. NK cells regulate the function of other immune cells via the release of inflammatory cytokines and chemokines. Currently, NK cell therapeutics in oral cancer have been less efficient due to several limitations, as follows: (a) lower percentages of NK cells in peripheral blood immune cells; (b) limited survival and decreased function of NK cells, especially in the tumor microenvironment; and (c) a lack of tools or methodologies to expand and activate NK cells to the levels that are required for the effective targeting of oral cancer. To overcome these limitations, we established and demonstrated a novel technology for activating and expanding highly functional NK cells coined as supercharged NK (sNK) cells. This review summarizes the characteristics of sNK cells and highlights their superior anti-cancer activity when compared to primary activated NK cells.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Applications of Multiplex Immunohistochemistry in Evaluating Spatiotemporal Heterogeneity of T Cells
by
Mercedes Machuca-Ostos, Tim de Martines, Kanako Yoshimura, Junichi Mitsuda, Sumiyo Saburi, Alisa Kimura, Hiroki Morimoto, Koichi Yoshizawa, Nana Sakurai, Nanako Murakami, Kayo Kitamoto, Makoto Yasuda, Yoichiro Sugiyama, Hiroshi Ogi, Saya Shibata, Aya Miyagawa-Hayashino, Eiichi Konishi, Kyoko Itoh, Takahiro Tsujikawa and Shigeru Hirano
Immuno 2025, 5(1), 7; https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno5010007 - 17 Feb 2025
Abstract
T cell phenotypes and kinetics are emerging as crucial factors associated with immunotherapeutic responses in a wide range of solid cancer types. However, challenges remain in understanding the spatial and temporal profiles of T cells with differential phenotypes due to difficulties in single-cell
[...] Read more.
T cell phenotypes and kinetics are emerging as crucial factors associated with immunotherapeutic responses in a wide range of solid cancer types. However, challenges remain in understanding the spatial and temporal profiles of T cells with differential phenotypes due to difficulties in single-cell analysis with preserved tissue structures. Here, we provide an optimized 12-marker multiplex immunohistochemical (IHC) panel and single-cell-based quantitative assessment to identify the spatial distributions of T cell phenotypes in formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded sections. This panel revealed differential T cell populations with spatial localizations in human tonsil tissue, where the percentages of CD8+ T cell-expressing programmed death receptor-1 (PD-1), T cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain 3 (TIM3), and other T cell phenotypic markers vary by tonsillar tissue components such as follicles, parenchyma, and epithelium. A specimen from salivary gland adenocarcinoma during hyper-progression, followed by anti-PD-1 treatment, exhibited the exclusion of CD8+ T cells from the intratumoral regions. Although the vast majority of peritumoral CD8+ T cells exhibited proliferative effector T cell phenotypes with PD-1−TIM3−Ki67+CD45RA+, intratumoral CD8+ T cells showed exhausted phenotypes with PD-1+TIM3− and increased Eomes expression, which might be related to poor therapeutic response in this case. To verify these findings in the context of temporal changes, we analyzed six longitudinal samples from a single patient with maxillary sinus cancer, observing increased T cell exhaustion along with metastasis and progression. Together, highly multiplexed IHC can be applied to analyze the spatiotemporal phenotypes of T cells, potentially contributing to the understanding of the mechanisms of resistance to immunotherapy.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Next-Generation Cancer Immunotherapy)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Advances in Synthetic Immunology for Targeted Treatment of Systemic Autoimmune Diseases: Opportunities, Challenges, and Future Directions
by
Galih Januar Adytia, Henry Sutanto, Laras Pratiwi and Deasy Fetarayani
Immuno 2025, 5(1), 6; https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno5010006 - 25 Jan 2025
Cited by 1
Abstract
Systemic autoimmune diseases (SAIDs) affect millions worldwide, presenting significant clinical challenges due to their complex pathogenesis and limited treatment options. Traditional immunosuppressive therapies, while effective, often lack precision, leading to significant side effects and inadequate disease control. Recent advances in synthetic immunology offer
[...] Read more.
Systemic autoimmune diseases (SAIDs) affect millions worldwide, presenting significant clinical challenges due to their complex pathogenesis and limited treatment options. Traditional immunosuppressive therapies, while effective, often lack precision, leading to significant side effects and inadequate disease control. Recent advances in synthetic immunology offer promising avenues for precise, targeted interventions in SAIDs. This review examines the latest innovations in synthetic immunology for treating autoimmune diseases, focusing on engineered immune cells, synthetic biologics, and gene-editing technologies. It explores the therapeutic potential of these approaches to modulate immune tolerance, reduce systemic inflammation, and enhance patient-specific treatment efficacy. However, despite these promising developments, challenges remain, including immune system complexity, safety concerns, and regulatory hurdles that may hinder clinical translation. This review aims to consolidate current advancements, address existing barriers, and outline potential future directions for synthetic immunology in autoimmune disease management, highlighting synthetic immunology’s role in transforming the therapeutic landscape for SAIDs.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Synthetic Immunity and Immune Engineering)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Verification of Immune Debts in Children Caused by the COVID-19 Pandemic from an Epidemiological and Clinical Perspective
by
Masayuki Nagasawa
Immuno 2025, 5(1), 5; https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno5010005 - 25 Jan 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Social behavior restrictions, social distancing, and promotion of non-pharmaceutical interventions (NPIs) during the COVID-19 pandemic have significantly reduced the incidence of many epidemic infections in the world, especially in children. Resurges of infectious diseases vary depending on the biological characteristics of each infectious
[...] Read more.
Social behavior restrictions, social distancing, and promotion of non-pharmaceutical interventions (NPIs) during the COVID-19 pandemic have significantly reduced the incidence of many epidemic infections in the world, especially in children. Resurges of infectious diseases vary depending on the biological characteristics of each infectious pathogen and differences in culture, lifestyle, and infection control mitigation policies by country or region. Although the gapping of infectious disease outbreaks can cause children who were uninfected during that period to become more susceptible to infection after the pandemic, resulting in a slightly older age of infected children, there are no conclusive reports that suggest a definite impact on the development of children’s immune maturation or its balance. Insufficient immune challenges in early life may influence the risk of developing immune-mediated conditions such as allergies or autoimmune diseases later in life, though evidence for this is still emerging. Future observational studies are needed to determine the long-term impact of the epidemic gap caused by the COVID-19 pandemic as well as the long-term impact of COVID-19 infection itself on the immune function or balance of children.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Turning the Tables: Loss of Adaptive Immunity Reverses Sex Differences in Tuberculosis
by
David Hertz, Lars Eggers, Linda von Borstel, Torsten Goldmann, Hanna Lotter and Bianca E. Schneider
Immuno 2025, 5(1), 4; https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno5010004 - 4 Jan 2025
Abstract
Sex-based differences in innate immunity may play a crucial role in susceptibility to and progression of tuberculosis (TB), a disease that disproportionately affects men. This study aimed to examine whether early host–pathogen interactions contribute to the heightened vulnerability of males to Mycobacterium tuberculosis
[...] Read more.
Sex-based differences in innate immunity may play a crucial role in susceptibility to and progression of tuberculosis (TB), a disease that disproportionately affects men. This study aimed to examine whether early host–pathogen interactions contribute to the heightened vulnerability of males to Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) infection. Using recombination activating gene 2 knockout (RAG2 KO) mice, which lack adaptive immunity, we were able to isolate and analyze innate immune responses to Mtb without the influence of T and B cells. Surprisingly, and in stark contrast to wild-type mice that reflect the male bias as observed in humans, female RAG2 KO mice were more susceptible to Mtb than their male counterparts. Increased lung CFU in females was accompanied by a significant rise in inflammation, indicated by elevated levels of inflammatory cytokines and chemokines, as well as a massive influx of neutrophils into the lungs. In contrast, male mice exhibited higher levels of IFN-γ and CCL5, along with a greater presence of NK cells in their lungs, suggesting that, in the absence of adaptive immunity, males benefit from a more robust NK cell response, potentially offering greater protection by better controlling inflammation and slowing disease progression.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Innate Immunity and Inflammation)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Changes in Analytes Related to Immunity in the Saliva of Pigs After Vaccination Against Lawsonia intracellularis
by
Andrea Martínez-Martínez, Manuel Toledo, Emilio Ruiz, Simón García, Anabel Fernández, José Joaquín Cerón, Rut Menjon, María Teresa Tejedor, Elena Goyena and Alberto Muñoz-Prieto
Immuno 2025, 5(1), 3; https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno5010003 - 2 Jan 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Lawsonia intracellularis is a Gram-negative, intracellular bacterium that can infect several animal species. In pigs, the bacteria cause porcine proliferative enteropathy, or ileitis. The wide spread of the pathogen produces a large impact on pig production worldwide. Saliva is a source of biomarkers
[...] Read more.
Lawsonia intracellularis is a Gram-negative, intracellular bacterium that can infect several animal species. In pigs, the bacteria cause porcine proliferative enteropathy, or ileitis. The wide spread of the pathogen produces a large impact on pig production worldwide. Saliva is a source of biomarkers that can help to monitor changes in the immune system after vaccination. The purpose of this study was to study the changes in haptoglobin (Hp), immunoglobulin G (IgG), and adenosine deaminase (ADA) in saliva after vaccination against Lawsonia intracellularis. In addition, productivity parameters were analysed to evaluate if vaccination and changes in salivary analytes could be associated with changes in these parameters. The pigs vaccinated against Lawsonia showed an improvement in the productive parameters and a reduction in food conversion and frequency of diseases. In addition, they showed lower values of Hp (p = 0.011), IgG (p < 0.01), and ADA (p < 0.003) in saliva during the first two months of the fattening period compared to non-vaccinated pigs. It could be concluded that in our experimental conditions, the vaccination against Lawsonia intracellularis produced a significant decrease in biomarkers of the immune response in saliva compared with the non-vaccinated pigs. This would indicate a reduction in the activation of the immune system, which could be postulated to be due to the increased defence ability of the organism against pathogens. This reduced activation of the immune system can lead to better food conversion and an increase in the productive parameters of these pigs. Overall, this report opens a new window for the possible use of saliva for non-invasive evaluation of the immune system after vaccination in pigs.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Impact of Sofosbuvir Plus Daclatasvir Therapy on the Frequency of CD200R+ Dendritic Cells in Chronic Hepatitis C Virus Infection
by
Helal F. Hetta, Mohamed A. Mekky, Hani I. Sayed, Ahmed AbdElkader Soliman Mahran, Eman H. Salama, Douaa Sayed, Mariam E. Abdallah, Doaa Safwat Mohamed, Omnia El-Badawy and Mohamed A. El-Mokhtar
Immuno 2025, 5(1), 2; https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno5010002 - 28 Dec 2024
Abstract
Dendritic cells (DCs) play a crucial role in controlling viral infections. Little is known about the changes in frequencies of the DC subsets in patients with chronic hepatitis C (CHC), particularly in the era of interferon-free regimens. We aimed to evaluate the impact
[...] Read more.
Dendritic cells (DCs) play a crucial role in controlling viral infections. Little is known about the changes in frequencies of the DC subsets in patients with chronic hepatitis C (CHC), particularly in the era of interferon-free regimens. We aimed to evaluate the impact of sofosbuvir/daclatasvir on the frequency of different peripheral DC subsets, the expression of the inhibitory CD200R and its ligand CD200 on DC, and their relation to the treatment outcome. A total of 1000 patients with CHC were enrolled and treated with a fixed oral dose of 400 mg of sofosbuvir and 60 mg of daclatasvir for 12 weeks. A total of 940 patients achieved sustained virologic response (SVR), and only 60 patients were non-responders (NRs). The frequencies of the peripheral plasmacytoid (pDC) and myeloid (mDCs) subsets and their surface expressions of CD200R and CD200 molecules were analyzed using flow cytometry. This analysis included 60 non-responders (NR group), 60 randomly selected sustained virologic responders (SVR group) at baseline, and at the end of treatment, and 60 healthy controls. HCV infection was associated with a down-regulation in the frequency of mDC, compared to healthy controls. In addition, mDC in HCV-infected patients showed lower levels of CD200R. However, neither the pDC frequency nor their CD200R expression was significantly altered. Interestingly, by the end of therapy, the frequencies of circulating mDCs and CD200R+mDC increased significantly in the SVR group and were even comparable to healthy controls. The levels of these cells were not normalized in the NR group. Percentages of mDCs and CD200R+mDC subsets showed good prognostic accuracy for predicting virologic response to therapy. Our results showed that HCV infection was associated with modulation of the mDC frequency and their surface expression of CD200R. Successful daclatasvir and sofosbuvir combined therapy was associated with the normalization of the percentages of mDC and CD200R+mDC.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Infectious Immunology and Vaccines)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
EXT1 as an Independent Prognostic Biomarker in Breast Cancer: Its Correlation with Immune Infiltration and Clinicopathological Parameters
by
Amira Hossny, Hatem A. F. M. Hassan, Sherif Ashraf Fahmy, Hazem Abdelazim, Mahmoud Mohamed Kamel, Ahmed H. Osman and Sherif Abdelaziz Ibrahim
Immuno 2025, 5(1), 1; https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno5010001 - 26 Dec 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Exostosin 1 (EXT1) encodes a type II transmembrane glycosyltransferase residing in the endoplasmic reticulum and plays an essential role in the elongation of heparan sulfate chain biosynthesis. Additionally, EXT1 may act as an oncogene that could promote cell proliferation as well as cancer
[...] Read more.
Exostosin 1 (EXT1) encodes a type II transmembrane glycosyltransferase residing in the endoplasmic reticulum and plays an essential role in the elongation of heparan sulfate chain biosynthesis. Additionally, EXT1 may act as an oncogene that could promote cell proliferation as well as cancer cell metastasis. Herein, we investigated EXT1’s expression pattern and prognostic value in breast cancer, along with its immunological implications. Immunohistochemical staining of EXT1 was assessed in 85 breast cancer patients. Patients were categorized into molecular subtypes, namely luminal A, luminal B, and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2), along with triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC). Correlations of EXT1 immunostaining with clinicopathological parameters were evaluated. Furthermore, the correlations of EXT1 expression with tumor immune infiltration and immune cell surface markers were assessed using TIMER. Moreover, survival analysis was conducted to reveal EXT1’s prognostic value. EXT1 expression was markedly associated with the status of the estrogen receptor (ER), molecular subtypes, and recurrence status. In addition, high levels of EXT1 expression were associated with worse overall survival (OS) and relapse-free survival (RFS). Analysis of immune infiltration indicated that EXT1 expression was positively correlated with dendritic cells (DCs), macrophages, neutrophils, CD4+ T cells, and CD8+ T cells, although it showed a negative correlation with the tumor purity. Overall, this study suggests that the elevated EXT1 expression, particularly in TNBC, has a positive correlation with poor prognosis and with immune-infiltrated cells in breast cancer. Therefore, it may emerge as an independent prognostic biomarker, immunological marker, and potential future therapeutic target for the most aggressive TNBC subtype.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
ADGRB3-High and POSTN-High Fibroblasts Are Markers of Endotypic Traits in Chronic Rhinosinusitis
by
Hideyuki Takahashi, Toshiyuki Matsuyama, Reika Kawabata-Iwakawa, Yohei Morishita, Takayuki Kawamoto and Kazuaki Chikamatsu
Immuno 2024, 4(4), 646-656; https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno4040038 - 14 Dec 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS) is a disease characterized by persistent sinonasal mucosal inflammation. Fibroblasts play a crucial role in extracellular matrix production and inflammation. We investigated the heterogeneity of fibroblasts in patients with CRS. Methods: Fibroblasts were isolated from nasal polyp tissues. RNA
[...] Read more.
Background: Chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS) is a disease characterized by persistent sinonasal mucosal inflammation. Fibroblasts play a crucial role in extracellular matrix production and inflammation. We investigated the heterogeneity of fibroblasts in patients with CRS. Methods: Fibroblasts were isolated from nasal polyp tissues. RNA sequencing was then performed. We also analyzed the GSE136825 dataset obtained from the Gene Expression Omnibus database. Alternatively, fibroblasts were stimulated in vitro. Results: Hierarchical clustering of samples indicated ADGRB3-high and POSTN-high fibroblasts. A Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA) revealed that cytotoxic immune responses were enriched in ADGRB3-high fibroblasts, while cell cycle pathways were enriched in POSTN-high fibroblasts. Similar GSEA results were observed in the GSE136825 dataset. Additionally, type 1 and type 3 inflammation-related genes were highly expressed in ADGRB3-high samples, whereas type 2-related genes were highly expressed in POSTN-high samples. In vitro, ADGRB3 expression increased in fibroblasts stimulated with IFN-γ, while POSTN increased in those stimulated with IL-4 and IL-13. Conclusions: Our study demonstrates that type 1 inflammation induces ADGRB3-high fibroblasts, associated with the cytotoxic immune response, while type 2 inflammation induces POSTN-high fibroblasts, linked to CRS progression via an elevated cell cycle. The further characterization of fibroblasts could provide insights into the stromal networks in the CRS microenvironment.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Protective Mechanisms of Carica papaya Leaf Extract and Its Bioactive Compounds Against Dengue: Insights and Prospects
by
Tanvir Zaman Shoyshob, Irin Amin Heya, Nusrat Afrin, Mansura Akter Enni, Israt Jahan Asha, Akhi Moni, Md. Abdul Hannan and Md. Jamal Uddin
Immuno 2024, 4(4), 629-645; https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno4040037 - 12 Dec 2024
Abstract
Dengue fever is currently a major global issue, especially in tropical and subtropical countries. The absence of specific antiviral medications supports alternative dengue treatment strategies. South Asian countries have been using Carica papaya leaves as a traditional remedy for dengue for many years.
[...] Read more.
Dengue fever is currently a major global issue, especially in tropical and subtropical countries. The absence of specific antiviral medications supports alternative dengue treatment strategies. South Asian countries have been using Carica papaya leaves as a traditional remedy for dengue for many years. Carica papaya possesses several biological features, including anti-inflammatory, antiviral, cancer-fighting, anti-diabetic, and antioxidant qualities. Additionally, numerous studies have demonstrated that bioactive compounds found in papaya leaf extracts, including carpaine, dehydrocarpaine I and II, chymopapain, and papain, significantly influence platelet counts, while phenolic compounds, such as chlorogenic acid, kaemferol, protocatechuic acid, quercetin, and 5,7-dimethoxycoumarin significantly inhibit viral replication in dengue patients, with negligible side effects. Carica papaya may be considered a viable pharmacological candidate with several targets for treating dengue. It has been shown to prevent infections, reduce oxidative stress, control cytokine storms and the immune system, lessen thrombocytopenia, and increase the body’s protein and hemoglobin levels. This literature review highlights the pathophysiological mechanism of dengue, as well as the pharmacological action of Carica papaya, both of which combat this debilitating disease. Despite these findings, additional investigation, including clinical studies, is necessary to confirm the effectiveness and safety of papaya-based treatments. It is necessary to address issues like standardizing papaya extracts, figuring out the best dosages, and assessing any drug interactions.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Effects of Malnutrition of Immune Response)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Antithrombotic Treatment in Antiphospholipid Syndrome: A Review
by
Carmine Siniscalchi, Francesca Futura Bernardi, Pierpaolo Di Micco, Alessandro Perrella, Tiziana Meschi and Ugo Trama
Immuno 2024, 4(4), 620-628; https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno4040036 - 11 Dec 2024
Abstract
Antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) is a thrombo-inflammatory disease propelled by circulating autoantibodies that recognize cell surface phospholipids and phospholipid-binding proteins. APS is an autoimmune disorder associated with recurrent thrombosis of arterial or venous vessels and/or recurrent obstetric complications as miscarriages. APS can be divided
[...] Read more.
Antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) is a thrombo-inflammatory disease propelled by circulating autoantibodies that recognize cell surface phospholipids and phospholipid-binding proteins. APS is an autoimmune disorder associated with recurrent thrombosis of arterial or venous vessels and/or recurrent obstetric complications as miscarriages. APS can be divided into primary or secondary clinical syndrome because of the possible association with other autoimmune systemic diseases as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Vitamin K antagonists remain the mainstay of treatment for most patients with APS and, based on current data, appear superior to the more targeted direct oral anticoagulants. However, the choice of the type of antithrombotic drug is based on the anamnesis of affected patients: patients with previous arterial or venous thrombosis may benefit from anticoagulants, while patients with previous obstetric diseases may benefit from aspirin, but several clinical exceptions may be evaluated. This short review is dedicated to underlining the main clinical evidence for patients affected by APS or CAPS (catastrophic antiphospholipid syndrome) in order to prevent recurrent thrombosis.
Full article
Open AccessReview
Health Promoting Properties of Vitamins C and D Against HIV Disease Progression, a Narrative Review
by
Garyfallos Markou, Ellie Panoutsopoulou, Evangelia Stavrakoudi, Charalampos Mylonas, Sofia Ioannou, Maria Chini and Alexandros Tsoupras
Immuno 2024, 4(4), 601-619; https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno4040035 - 7 Dec 2024
Abstract
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) has troubled humankind for many years. The rate of new HIV cases is decreasing steadily, mostly because of safer sexual practices and scientific advances in medicine. However, the number of HIV-related trials has significantly increased, as the search for
[...] Read more.
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) has troubled humankind for many years. The rate of new HIV cases is decreasing steadily, mostly because of safer sexual practices and scientific advances in medicine. However, the number of HIV-related trials has significantly increased, as the search for a definite cure for HIV is still fruitless. Our current treatment options involve antiretroviral therapy (ART) with various drug combinations that lower the patients’ viral load in order for the immune system to reconstitute itself. This way, adherent patients achieve a life expectancy similar to the general population. Besides the established treatment protocols, the focus has currently shifted towards secondary pharmaceutical regimen programs that enhance a patient’s immune system and response to opportunistic infections. Vitamins C and D are easily obtainable even in the developing world and are known to improve an individual’s daily life, with vitamin D enhancing the human immune response and vitamin C having an assisting role in both the immune response and as an important antioxidant. Recently, many studies assessing the effect of these vitamins on the progression of HIV have been performed. We aimed to collect and review these studies in order to determine the necessity of the supplementation of these vitamins in HIV-infected patients, which might complement the existing ART. To this day, the scientific community is conflicted, and more studies must be conducted before a definite conclusion about these vitamins’ effects on HIV patients can be reached.
Full article
Open AccessReview
Mpox Virus Infection and Vaccination: Immunopathogenesis and Exploring the Link to Neuropsychiatric Manifestations
by
Helal F. Hetta, Ahmad A. Alharbi, Shumukh M. Alsharif, Tala T. Alkindy, Alanoud Alkhamali, Abdullah S. Albalawi, Hager Hamdy Sayed, Moaiad Eldin Ahmed Mohamed, Yasmine Adel Mohammed, Yasmin N. Ramadan and Reem Sayad
Immuno 2024, 4(4), 578-600; https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno4040034 - 2 Dec 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background and Aim: Monkeypox (Mpox) is a viral disease mainly found in central and western Africa, with symptoms similar to variola virus (smallpox) but distinguished by the early lymph node swelling specific to Mpox. This review summarizes the neuropsychiatric manifestations of Mpox infection
[...] Read more.
Background and Aim: Monkeypox (Mpox) is a viral disease mainly found in central and western Africa, with symptoms similar to variola virus (smallpox) but distinguished by the early lymph node swelling specific to Mpox. This review summarizes the neuropsychiatric manifestations of Mpox infection and vaccination, along with management approaches. Method: We searched different databases such as PubMed, Scopus, WoS, and Google Scholar about the neuropsychiatric manifestations of Mpox disease and the associated strategies of management. Results and conclusions: Mpox can cause a wide range of neurological symptoms. These range from mild symptoms like headaches, muscle aches, fatigue, and pain to severe symptoms, including seizures, blindness, photophobia, delirium, coma, encephalitis, and transverse myelitis. It is essential to distinguish Mpox from smallpox and other orthopox viruses. Psychiatric issues, such as stigma, disfigurement, isolation, and physical pain, are common in Mpox patients. To address these, healthcare providers should provide accurate information, counseling, and virtual support. Neurological side effects were associated with the previous smallpox vaccine, which offered cross-protection against Mpox. This vaccine has since been replaced by JYNNEOS, which does not pose any neurological risks. Mpox-related neurological symptoms are generally managed with supportive care, including NSAIDs, antibiotics, antiepileptics, and sedatives for seizures. Antivirals like acyclovir are also used. Severe cases may require hospitalization or intubation. So, we recommend early diagnosis, isolation, and prompt treatment, as Mpox spreading to the central nervous system can lead to serious and potentially fatal complications.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Host Immune Response to Dengue Virus Infection: Friend or Foe?
by
Priya Dhole, Amir Zaidi, Hardik K. Nariya, Shruti Sinha, Sandhya Jinesh and Shivani Srivastava
Immuno 2024, 4(4), 549-577; https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno4040033 - 21 Nov 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
DENV belongs to the Flaviviridae family and possesses a single-stranded RNA genome of positive polarity. DENV infection manifests in mild subclinical forms or severe forms that may be dengue hemorrhagic fever (DHF) or dengue shock syndrome (DSS). Despite a lot of effort worldwide,
[...] Read more.
DENV belongs to the Flaviviridae family and possesses a single-stranded RNA genome of positive polarity. DENV infection manifests in mild subclinical forms or severe forms that may be dengue hemorrhagic fever (DHF) or dengue shock syndrome (DSS). Despite a lot of effort worldwide, the exact mechanism underlying the pathogenesis of severe DENV infection remains elusive. It is believed that both host and viral factors contribute to the outcome of dengue disease. The host factors are age at the time of infection, sex, nutrition, and immune status, including the presence of pre-existing antibodies or reactive T cells. Viral factors include the serotype, genotype, and mutation(s) due to error-prone RNA-dependent polymerase leading to the development of quasispecies. Accumulating bodies of literature have depicted that DENV has many ways to invade and escape the immune system of the host. These invading strategies are directed to overcome innate and adaptive immune responses. Like other viruses, once the infection is established, the host also mounts a series of antiviral responses to combat and eliminate the virus replication. Nevertheless, DENV has evolved a variety of mechanisms to evade the immune system. In this review, we have emphasized the strategies that DENV employs to hijack the host innate (interferon, IFN; toll-like receptors, TLR; major histocompatibility complex, MHC; autophagy; complement; apoptosis; RNAi) and adaptive (antibody-dependent enhancement, ADE; T cell immunity) immune responses, which contribute to the severity of DENV disease.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Neglected Issues in T Lymphocyte Metabolism: Purine Metabolism and Control of Nuclear Envelope Regulatory Processes. New Insights into Triggering Potential Metabolic Fragilities
by
Naomi Torchia, Carolina Brescia, Emanuela Chiarella, Salvatore Audia, Francesco Trapasso and Rosario Amato
Immuno 2024, 4(4), 521-548; https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno4040032 - 19 Nov 2024
Cited by 1
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The metabolism of T-lymphocytes has recently emerged as a pivotal area of investigation, offering insights into the supra-genic modulations that can influence the genetic mechanisms underlying lymphocyte clustering processes. Furthermore, it has become a crucial aspect in understanding lymphocyte plasticity within the immune
[...] Read more.
The metabolism of T-lymphocytes has recently emerged as a pivotal area of investigation, offering insights into the supra-genic modulations that can influence the genetic mechanisms underlying lymphocyte clustering processes. Furthermore, it has become a crucial aspect in understanding lymphocyte plasticity within the immune microenvironment, both in physiological and pathological contexts. T-lymphocyte metabolism has recently emerged as a pivotal factor in both targeted therapy and the genetic signature of the T-lymphocyte, as a result of its influence on gatekeeper processes. From this perspective, the interconnections between the metabolic processes traditionally associated with energy production and the capacity to influence the genetic fate of the T lymphocyte have identified purine metabolism and nuclear/cytoplasmic signaling as pivotal elements in comprehending the intricacies of these molecular phenomena. The two aspects of purine metabolism and metabolic/molecular control of the nuclear envelope have been the subject of a number of significant studies published in recent years. However, from a certain perspective, the existing evidence remains sparse and inconclusive, hindering a comprehensive understanding of the subject matter. In this review, we endeavor to establish a connection between these aspects for the first time and to present a review of the molecular, immunological and genetic events that determine how these aspects, which have hitherto received insufficient attention, may represent a new avenue for lymphocyte reprogramming in the therapeutic field. This will be achieved by understanding the connections between nuclear control and purine flux within and outside the cell.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Anti-Inflammatory Effects of SGLT1 Synthetic Ligand in In Vitro and In Vivo Models of Lung Diseases
by
Cristiano Rumio, Giuseppina Dusio, Diego Cardani, Barbara La Ferla and Giuseppe D’Orazio
Immuno 2024, 4(4), 502-520; https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno4040031 - 8 Nov 2024
Cited by 2
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background. Several research findings suggest that sodium–glucose co-transporter 1 (SGLT1) is implicated in the progression and control of infections and inflammation processes at the pulmonary level. Moreover, our previous works indicate an engagement of SGLT1 in inhibiting the inflammatory response induced in intestinal
[...] Read more.
Background. Several research findings suggest that sodium–glucose co-transporter 1 (SGLT1) is implicated in the progression and control of infections and inflammation processes at the pulmonary level. Moreover, our previous works indicate an engagement of SGLT1 in inhibiting the inflammatory response induced in intestinal epithelial cells by TLR agonists. In this study, we report the anti-inflammatory effects observed in the lung upon engagement of the transporter, and upon the use of glucose and BLF501, a synthetic SGLT1 ligand, for the treatment of animal models of lung inflammation, including a model of allergic asthma. Methods. In vitro experiments were carried out on human pneumocytes stimulated with LPS from Pseudomonas aeruginosa and co-treated with glucose or BLF501, and the production of IL-8 was determined. The anti-inflammatory effect associated with SGLT1 engagement was then assessed in in vivo models of LPS-induced lung injury, as well as in a murine model of ovalbumin (OVA)-induced asthma, treating mice with aerosolized LPS and the synthetic ligand. After the treatments, lung samples were collected and analyzed for morphological alterations by histological examination and immunohistochemical analysis; serum and BALF samples were collected for the determination of several pro- and anti-inflammatory markers. Results. In vitro experiments on human pneumocytes treated with LPS showed significant inhibition of IL-8 production. The results of two in vivo experimental models, mice exposed to aerosolized LPS and OVA-induced asthma, revealed that the engagement of glucose transport protein 1 (SGLT1) induced a significant anti-inflammatory effect in the lungs. In the first model, the acute respiratory distress induced in mice was abrogated by co-treatment with the ligand, with almost complete recovery of the lung morphology and physiology. Similar results were observed in the OVA-induced model of allergic asthma, both with aerosolized and oral BLF501, suggesting an engagement of SGLT1 expressed both in intestinal and alveolar cells. Conclusions. Our results confirmed the engagement of SGLT1 in lung inflammation processes and suggested that BLF501, a non-metabolizable synthetic ligand of the co-transporter, might represent a drug candidate for therapeutic intervention against lung inflammation states.
Full article

Figure 1
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Biomedicines, Cancers, Immuno, IJMS
New Advancements in Innate Immunity and Cancer Immunotherapy
Topic Editors: Jeonghyun Ahn, Zhiwei HuDeadline: 30 November 2025
Topic in
Cells, Immuno, IJMS, JCM, Allergies, Dermato
Skin Barrier Function and Immune Mediators as Key Therapeutic Targets of Main Inflammatory Diseases
Topic Editors: Marco Manfredini, Carlo PincelliDeadline: 31 August 2026

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Immuno
Recent Advances in Antiphospholipid Syndrome
Guest Editor: Pierpaolo Di MiccoDeadline: 30 June 2025
Special Issue in
Immuno
The Role of Cytokines and Autoantibodies Against Cytokines in Health and Disease
Guest Editor: Juan Bautista De SanctisDeadline: 30 August 2025
Special Issue in
Immuno
Nano-Pharmacology: Nanotechnology Based Therapeutics for Targeting Neuroinflammation
Guest Editor: Supriya MahajanDeadline: 31 August 2025
Special Issue in
Immuno
New Insights of Anti-cancer Immunity and Cancer Immune Evasion
Guest Editor: Vadim SumbayevDeadline: 31 October 2025








