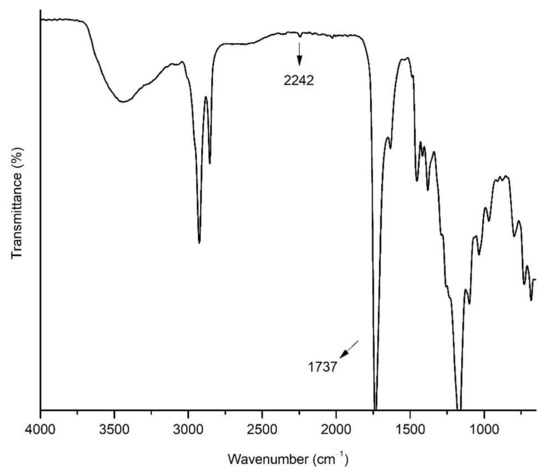
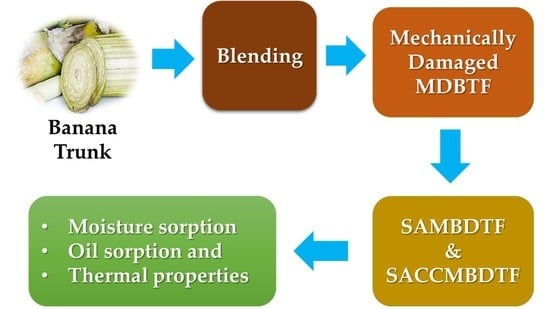
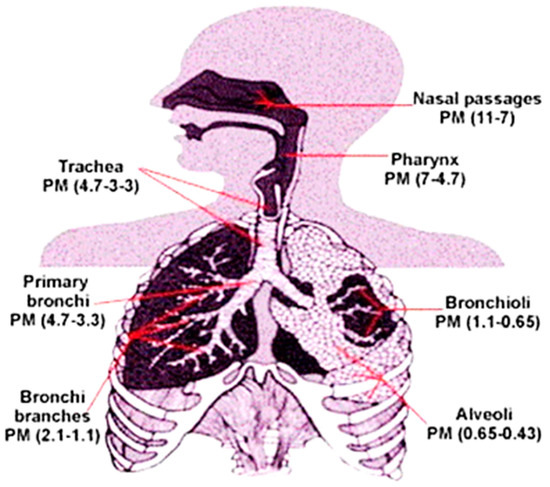
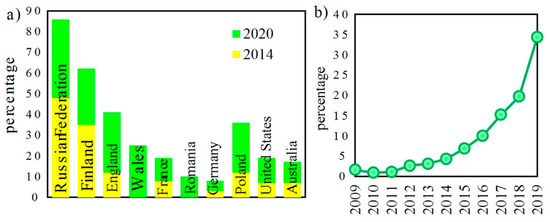
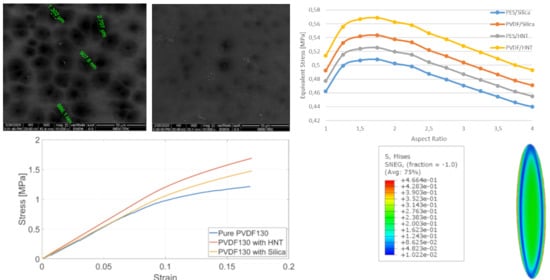
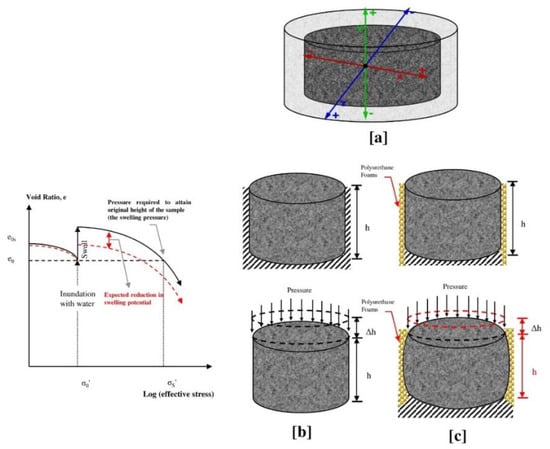
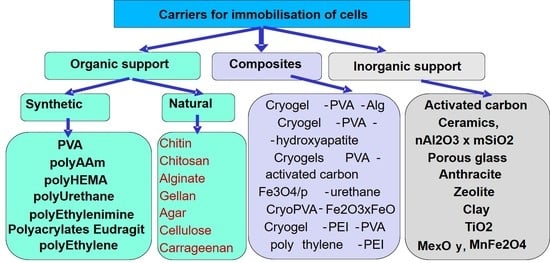
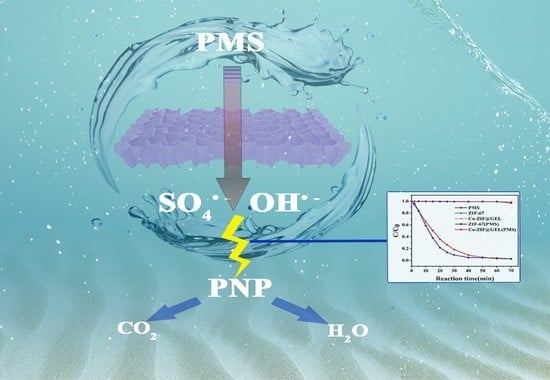
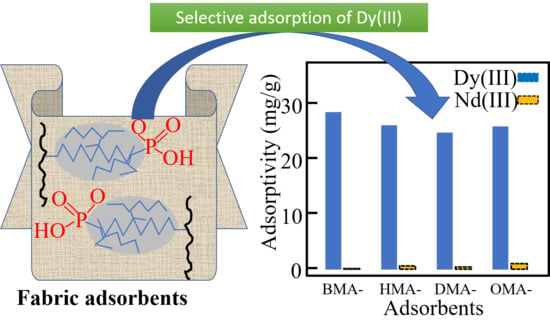
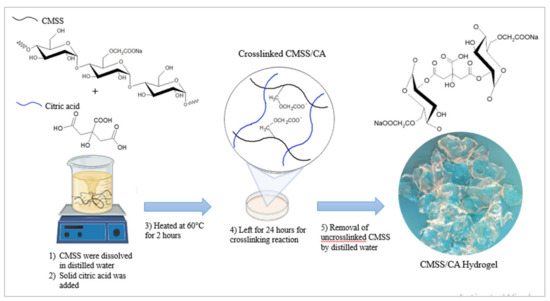
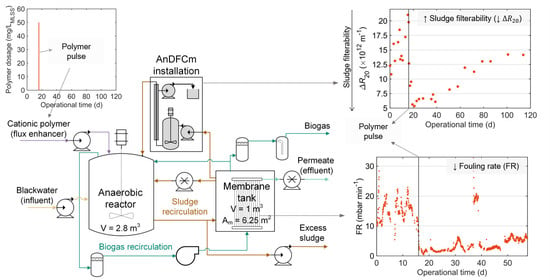
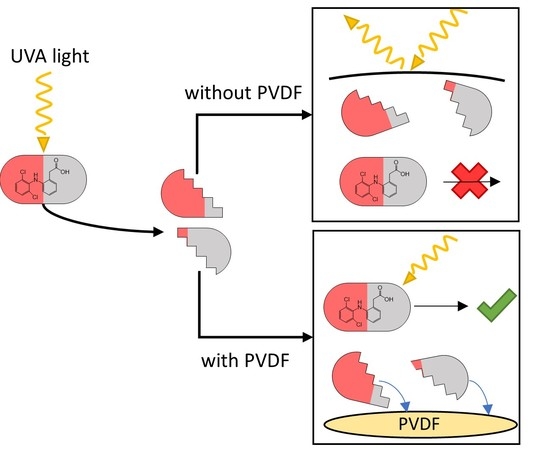
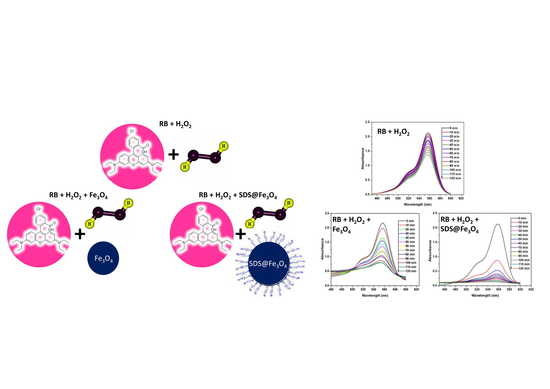
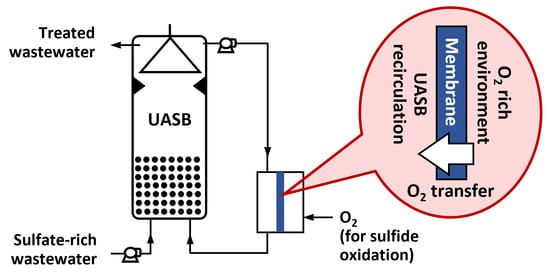
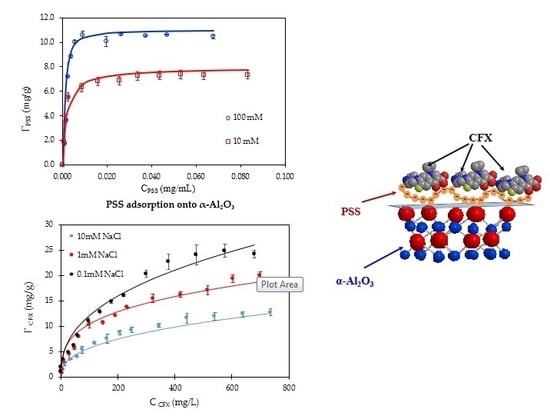
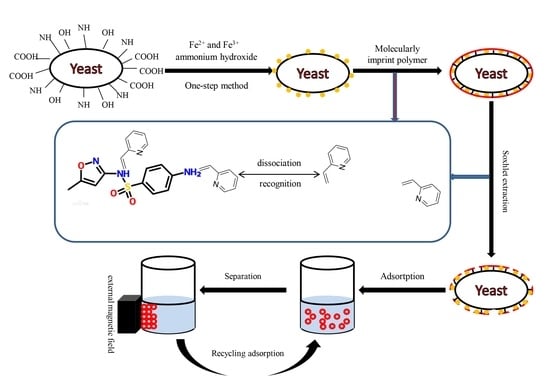
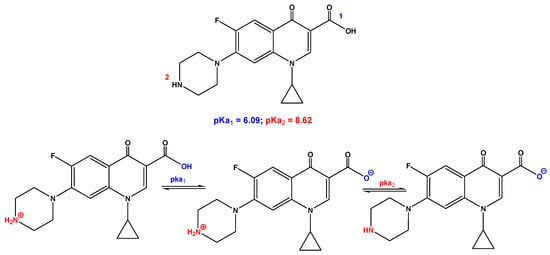
Polymer Applications in Environmental Science
A topical collection in Polymers (ISSN 2073-4360). This collection belongs to the section "Polymer Applications".
Viewed by 31744Editors
2. Department of Environment and Planning, University of Aveiro, Campus Universitário de Santiago, 3810-193 Aveiro, Portugal
Interests: water pollution and contamination; water and wastewater treatment: global treatment systems; sustainable treatment processes; clean and alternative technologies; waste management and valorization; alternative adsorbent materials; alternative photocatalysts
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: polymeric materials; polymer processing; polymer applications; water treatment; emerging contaminants
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
In the twentieth century, humanity was responsible for a host of huge environmental damages but also became aware of their adverse effects and the necessity of implementing measurements to avoid them. Now, in the twenty-first century, we have the responsibility to solve these issues and prevent new ones from manifesting. We are currently facing a vast variety of concerns regarding the climate, energy, and water necessities, among others. Approaching appropriate solutions is one of the biggest challenges of the present, and contributions from all areas of knowledge are valuable.
Progress in polymer science and engineering is revolutionary since polymeric materials can be designed to meet the ever more demanding needs of advanced technology. In the environmental field, there is a place for creating new polymeric materials, modifying existing polymers or even discovering green and novel applications of conventional polymers. Thus, polymer scientists and engineers have the capability of helping to make our planet a better place to live, and this Topic Collection aims to show the different ways in which they may do so.
The present Collection aims to represent an update on the current progress regarding “Polymer Applications in Environmental Science”. The Topic is intentionally interdisciplinary, and we hope it may serve to gather important advances from a wide range of subjects on polymer research. The main objective is to make evident the endless applications of polymers and their contribution to solve environmental problems, provide smart waste management strategies, fight contamination, amend and prevent ecosystems pollution, and help sustainability.
Dr. Marta Otero
Dr. Ricardo N. Coimbra
Guest Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Polymers is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2700 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- air purification
- soil remediation
- water treatment
- renewable energy
- circular economy
- life cycle assessment
- recycling and reutilization
- biodegradation and composting
- smart polymeric materials
- wastes management and valorization
- zero-waste approaches
Related Special Issues
- Polymer-Based Materials as Ecological Adsorbents for Environmental Protection II in Polymers (5 articles - displayed below)
- Polymer Materials in Environmental Chemistry II in Polymers (8 articles - displayed below)
- Current Trends and Perspectives in the Application of Polymeric Materials for Wastewater Treatment in Polymers (12 articles - displayed below)
- Advanced Polymeric Membranes for Wastewater Reclamation and Water Purification in Polymers (9 articles - displayed below)
- Polymeric Materials for Wastewater Purification in Polymers (6 articles - displayed below)
- Advances in Polymeric Electrospinning in Polymers (2 articles - displayed below)