Journal Description
Regional Science and Environmental Economics
Regional Science and Environmental Economics
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on regional studies and environmental economics issues published quarterly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- Rapid Publication: first decisions in 19 days; acceptance to publication in 4 days (median values for MDPI journals in the first half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
Latest Articles
Evaluating the Sustainable Development of Red Cultural Tourism in Yunnan, China, Using GIS and Machine Learning Methods
Reg. Sci. Environ. Econ. 2025, 2(4), 32; https://doi.org/10.3390/rsee2040032 - 13 Oct 2025
Abstract
Against the backdrop of the accelerated integration of culture and tourism in China, red cultural tourism, as an important component of China’s cultural tourism system, urgently requires a systematic assessment of its development status and synergistic impact mechanisms. This study takes the Long
[...] Read more.
Against the backdrop of the accelerated integration of culture and tourism in China, red cultural tourism, as an important component of China’s cultural tourism system, urgently requires a systematic assessment of its development status and synergistic impact mechanisms. This study takes the Long March tourism resources in Yunnan as the research object and constructs a comprehensive evaluation system integrating social influence and ecological carrying capacity. By applying GIS spatial analysis, as well as K-means and XGBoost machine learning models, the development level of red cultural tourism in Yunnan is quantitatively assessed. Furthermore, the interpretable SHAP model is employed to identify the contribution of each evaluation indicator and to analyze the relationships among development levels under three different indicator models. The results reveal that (1) the development level of red cultural tourism in Yunnan generally exhibits a spatial pattern of being lower in the northwest and higher in the southeast; (2) transportation accessibility (TA), average annual precipitation (AAP), and average annual temperature (AAT) are the dominant indicators influencing the development level; (3) there are significant disparities in development levels among cities, indicating that future development needs to comprehensively consider both the social influence and ecological carrying capacity of red cultural tourism resources and adhere to a “social–ecological” synergistic development mechanism. This study not only uncovers the synergistic impacts of social and ecological dimensions on the development of red cultural tourism in Yunnan but also provides theoretical and data support for the optimization and sustainable development of Yunnan’s red cultural tourism resources.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Sustainability and Regional Development: Foundations and Challenges for This Symbiotic Relationship)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Regionalization of Input–Output Matrices with Limited Information: Application to the State of Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil
by
Eduardo Rodrigues Sanguinet, Adelar Fochezatto and Cristian Gonzalez Santander
Reg. Sci. Environ. Econ. 2025, 2(4), 31; https://doi.org/10.3390/rsee2040031 - 11 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The regionalization of input–output tables enables a granular understanding of economic systems, allowing for interregional and interindustry analysis for goods and services in a local economy. This paper details the construction of an intermunicipal IO matrix for the state of Rio Grande do
[...] Read more.
The regionalization of input–output tables enables a granular understanding of economic systems, allowing for interregional and interindustry analysis for goods and services in a local economy. This paper details the construction of an intermunicipal IO matrix for the state of Rio Grande do Sul (Brazil), a region marked by both economic diversification and significant territorial disparities. Using the 16-sector state IO matrix (base year 2019) provided by the state-level treasury (SEFAZ-RS) as a starting point, we adapt the Interregional Input–Output Adjustment System (IIOAS), integrating gravity-based trade modelling and RAS balancing, to produce a disaggregated structure for 497 municipalities. The regionalization follows three main steps: (i) generation of an initial matrix assuming proportional municipal shares in sectoral supply and demand; (ii) iterative RAS-based adjustments to align with municipal and state-level constraints; and (iii) incorporation of complementary municipal data—including employment, GDP, household consumption, and exports—to refine final demand and value-added allocations. The results demonstrate the feasibility of deriving spatially intermunicipal IO structures from limited data. The results show that, while industrial and service activities are concentrated around the Porto Alegre metropolitan area, rural subregions remain specialized in low value-added primary sectors.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Between Regulation and Global Influence: Can the EU Compete in the Digital Economy?
by
Fernando Pacheco and Maria João Velez
Reg. Sci. Environ. Econ. 2025, 2(4), 30; https://doi.org/10.3390/rsee2040030 - 1 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The European Union (EU) has positioned itself as a global leader in digital regulation, with landmark frameworks such as the Digital Services Act (DSA), the Digital Markets Act (DMA), and relevant AI Act. These initiatives reflect the EU’s ambition to balance technological innovation
[...] Read more.
The European Union (EU) has positioned itself as a global leader in digital regulation, with landmark frameworks such as the Digital Services Act (DSA), the Digital Markets Act (DMA), and relevant AI Act. These initiatives reflect the EU’s ambition to balance technological innovation with consumer protection, market fairness, and digital sovereignty. Yet, a growing body of research suggests that the EU may be lagging its global competitors—namely the United States and China—when it comes to scaling high-growth digital enterprises and attracting investment in frontier technologies. This study investigates the paradox of regulation versus innovation in the EU by comparing key performance indicators such as R&D investment, venture capital availability, and digital innovation output with those of the U.S. and China. Drawing on datasets from WIPO, the OECD, IMF, and the World Bank, the paper incorporates both cross-sectional and longitudinal analysis to assess the EU’s digital trajectory. Findings suggest that while the EU excels in institutional frameworks and research output, structural barriers—such as regulatory fragmentation and underdeveloped capital markets—limit its global competitiveness. The article concludes by discussing policy implications and the need for adaptive governance to maintain Europe’s digital leadership.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Relationship Between Green Patents, Green FDI, Economic Growth and Sustainable Tourism Development in ASEAN Countries: A Spatial Econometrics Approach
by
Ha Van Trung
Reg. Sci. Environ. Econ. 2025, 2(4), 29; https://doi.org/10.3390/rsee2040029 - 25 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Sustainable tourism development has emerged as a strategic priority across ASEAN countries, yet the role of green innovation and environmentally responsible investment in shaping tourism outcomes remains underexplored. Existing studies often overlook the spatial interdependencies that characterize regional integration and cross-border environmental dynamics.
[...] Read more.
Sustainable tourism development has emerged as a strategic priority across ASEAN countries, yet the role of green innovation and environmentally responsible investment in shaping tourism outcomes remains underexplored. Existing studies often overlook the spatial interdependencies that characterize regional integration and cross-border environmental dynamics. This study investigates how green patents and green foreign direct investment (FDI) influence sustainable tourism development, both within and across ASEAN nations. Drawing on endogenous growth theory, ecological modernization, and FDI spillover frameworks, the analysis employs a Spatial Durbin Model (SDM) using panel data from 2000 to 2023. The findings reveal that green innovation and green FDI significantly enhance tourism development, with notable spatial spillover effects that benefit neighboring countries. These effects are most pronounced in leading ASEAN economies, where institutional capacity and absorptive readiness amplify the impact of green practices. The relationship is further shaped by economic growth, human capital, and political stability, while environmental degradation and inflation pose constraints. The study underscores the nonlinear and regionally heterogeneous nature of green tourism development, offering policy insights for fostering inclusive, resilient, and environmentally sustainable tourism strategies across ASEAN.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessSystematic Review
Parcelas de Agrado in Chile: A Systematic Review of Scientific and Grey Literature
by
Gerardo Francisco Ubilla-Bravo and Julián Valdés-Figueroa
Reg. Sci. Environ. Econ. 2025, 2(3), 28; https://doi.org/10.3390/rsee2030028 - 12 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Since 1980, a land use type known as parcelas de agrado has developed in Chile, generating a series of social, economic, and environmental impacts. In recent years, its use has increased further and has become a subject of public debate. To address this,
[...] Read more.
Since 1980, a land use type known as parcelas de agrado has developed in Chile, generating a series of social, economic, and environmental impacts. In recent years, its use has increased further and has become a subject of public debate. To address this, it is necessary to have evidence that documents its evolution. Within this context, the aim of the article is to analyze the state of the literature on parcelas de agrado in Chile. The method is based on three stages: the application of the PRISMA model for the identification and selection of documents, the establishment of areas and categories for quantitative analysis, and content analysis based on five dimensions. The results show a diversity of types of studies conducted in different years, territories, and scales in Chile, with a greater concentration of scientific articles and studies in areas of the central macrozone of Chile. The discussion highlights the diversity and proliferation of studies, facilitating elements and the spread of parcelas de agrado, the consequences on the territory, as well as the contribution of spatial planning. It is concluded that parcelas de agrado in Chile require greater attention from the State in relation to the territorial planning of rural, peri-urban, and suburban areas.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Promoting Urban Community Gardens as “Third Places”: Lessons from Toronto and São Paulo
by
Ashley Brito Valentim, Guiomar Freitas Guimarães, Carla Soraya Costa Maia and Fatih Sekercioglu
Reg. Sci. Environ. Econ. 2025, 2(3), 27; https://doi.org/10.3390/rsee2030027 - 25 Aug 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Urban community gardens (UCGs) have been expanding globally. Initially created to provide fresh, organic produce for low-income populations, UCGs have evolved into models of sustainable agriculture with increasing economic significance. Beyond their economic role, UCGs serve as vital social spaces and may be
[...] Read more.
Urban community gardens (UCGs) have been expanding globally. Initially created to provide fresh, organic produce for low-income populations, UCGs have evolved into models of sustainable agriculture with increasing economic significance. Beyond their economic role, UCGs serve as vital social spaces and may be categorized as third places—informal gathering spaces that foster social connections and promote well-being. This study analyzes and compares the impact of UCGs as third places in Toronto and São Paulo, focusing on their contributions to social cohesion, financial resilience, environmental sustainability, cultural transmission, and mental well-being. It is a review-based study utilizing publicly available data from policy documents, the academic literature, and official websites. Although the practice of community gardening has a long-standing history, the concept of gardens as third places is relatively recent, emerging in the late 1980s. In recent decades, there has been growing interest in their association not only with aesthetic and functional benefits but also with health, well-being, and social connection. UCGs are valuable not only for food production but also for fostering social interaction, preserving cultural practices, and promoting overall well-being. Cities must develop policies that strengthen community resilience by recognizing and supporting UCGs as essential third places.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Assessing the Perception and Value of Marine Biodiversity and Taxonomy Research by the Recreational Diving Tourism Industry in Thailand
by
Wan Chantavilasvong, Pin Udomcharoenchaikit and Rahul Mehrotra
Reg. Sci. Environ. Econ. 2025, 2(3), 26; https://doi.org/10.3390/rsee2030026 - 25 Aug 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The 21st century has seen marine tourism in Southeast Asia transform in response to the rapid growth of SCUBA diving and snorkeling activities in the natural environment. However, despite this level of integration between recreation and the natural environment, few assessments have ever
[...] Read more.
The 21st century has seen marine tourism in Southeast Asia transform in response to the rapid growth of SCUBA diving and snorkeling activities in the natural environment. However, despite this level of integration between recreation and the natural environment, few assessments have ever been conducted on the biodiversity or ecosystem values and experiences of the SCUBA diving community. Therefore, we explored the awareness, preferences and priorities of this community, with a particular emphasis on investigating the role of biodiversity documentation and species discoveries in motivating recreational diving. By conducting surveys of 366 recreational divers from Thailand, we were able to identify proportional priorities, finding greater valuation towards overall ecosystem esthetics than megafauna, with species-specific dive experiences being a niche but present interest. We also investigated diver priorities based on recently described or discovered marine fauna in Thai waters, focusing on five species of hard and soft coral, seven species of sea slug, and two species of shark. Of these, sea slug species were the most recognized and garnered the greatest potential economic value, likely due to their popularity with photographers. The results of this multidisciplinary investigation highlight the economic value of taxonomy and biodiversity research to the recreational SCUBA community.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Research on the Mechanism of the Impact of Population Aging in the Yangtze River Delta Urban Agglomeration on Economic Growth
by
Chen Li and Xing Li
Reg. Sci. Environ. Econ. 2025, 2(3), 25; https://doi.org/10.3390/rsee2030025 - 18 Aug 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
In the context of the deep transformation of population structure and the coordinated advancement of high-quality development, exploring the mechanism of the impact of aging on economic growth has become a major issue related to the sustainable development of China. This study takes
[...] Read more.
In the context of the deep transformation of population structure and the coordinated advancement of high-quality development, exploring the mechanism of the impact of aging on economic growth has become a major issue related to the sustainable development of China. This study takes the 41 cities of the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration as a sample, using the population and economic census data from 2000 to 2020. It comprehensively applies an improved Solow model, GIS spatial analysis, spatial econometric models, and mediation effect tests to arrive at the following findings: (1) There is a significant asynchrony between economic growth and population aging in the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration. Economic growth has shifted from high-speed to high-quality development, while the aging process is accelerating and becoming more aged. (2) Population aging in the Yangtze River Delta has a nonlinear positive impact on economic growth. The intensity of this impact shows a characteristic of “strong-weak-strong,” with the first aging rate threshold being 11.63% and the second being 17.53%. (3) There is significant spatial autocorrelation between population aging and economic growth in the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration. The overall direction of the effect shows a spatial distribution pattern of “positive in the south and negative in the north.” The deepening of population aging in neighboring areas promotes local economic growth. (4) Labor productivity and optimization of the living environment constitute the core transmission pathways. Together, they account for more than 80% of the contribution and serve as the key mechanism for transforming aging pressures into growth momentum. This research provides practical guidance for solving the “rich” and “aging” contradictions in the Yangtze River Delta. It also offers a universal theoretical framework and a Chinese solution for aging economies worldwide to address the risk of growth stagnation.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
B Impact Assessment as a Driving Force for Sustainable Development: A Case Study in the Pulp and Paper Industry
by
Yago de Zabala, Gerusa Giménez, Elsa Diez and Rodolfo de Castro
Reg. Sci. Environ. Econ. 2025, 2(3), 24; https://doi.org/10.3390/rsee2030024 - 6 Aug 2025
Abstract
This study evaluates the effectiveness of the B Impact Assessment (BIA) as a catalyst for integrating sustainability into industrial firms through a qualitative case study of LC Paper, the first B Corp-certified tissue manufacturer globally and a pioneer in applying BIA in the
[...] Read more.
This study evaluates the effectiveness of the B Impact Assessment (BIA) as a catalyst for integrating sustainability into industrial firms through a qualitative case study of LC Paper, the first B Corp-certified tissue manufacturer globally and a pioneer in applying BIA in the pulp and paper sector. Based on semi-structured interviews, organizational documents, and direct observation, this study examines how BIA influences corporate governance, environmental practices, and stakeholder engagement. The findings show that BIA fosters structured goal setting and the implementation of measurable actions aligned with environmental stewardship, social responsibility, and economic resilience. Tangible outcomes include improved stakeholder trust, internal transparency, and employee development, while implementation challenges such as resource allocation and procedural complexity are also reported. Although the single-case design limits generalizability, this study identifies mechanisms transferable to other firms, particularly those in environmentally intensive sectors. The case studied also illustrates how leadership commitment, participatory governance, and data-driven tools facilitate the operationalization of sustainability. By integrating stakeholder and institutional theory, this study contributes conceptually to understanding certification frameworks as tools for embedding sustainability. This research offers both theoretical and practical insights into how firms can align strategy and impact, expanding the application of BIA beyond early adopters and into traditional industrial contexts.
Full article
Open AccessReview
Exploring the Potential of Biochar in Enhancing U.S. Agriculture
by
Saman Janaranjana Herath Bandara
Reg. Sci. Environ. Econ. 2025, 2(3), 23; https://doi.org/10.3390/rsee2030023 - 1 Aug 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Biochar, a carbon-rich material derived from biomass, presents a sustainable solution to several pressing challenges in U.S. agriculture, including soil degradation, carbon emissions, and waste management. Despite global advancements, the U.S. biochar market remains underexplored in terms of economic viability, adoption potential, and
[...] Read more.
Biochar, a carbon-rich material derived from biomass, presents a sustainable solution to several pressing challenges in U.S. agriculture, including soil degradation, carbon emissions, and waste management. Despite global advancements, the U.S. biochar market remains underexplored in terms of economic viability, adoption potential, and sector-specific applications. This narrative review synthesizes two decades of literature to examine biochar’s applications, production methods, and market dynamics, with a focus on its economic and environmental role within the United States. The review identifies biochar’s multifunctional benefits: enhancing soil fertility and crop productivity, sequestering carbon, reducing greenhouse gas emissions, and improving water quality. Recent empirical studies also highlight biochar’s economic feasibility across global contexts, with yield increases of up to 294% and net returns exceeding USD 5000 per hectare in optimized systems. Economically, the global biochar market grew from USD 156.4 million in 2021 to USD 610.3 million in 2023, with U.S. production reaching ~50,000 metric tons annually and a market value of USD 203.4 million in 2022. Forecasts project U.S. market growth at a CAGR of 11.3%, reaching USD 478.5 million by 2030. California leads domestic adoption due to favorable policy and biomass availability. However, barriers such as inconsistent quality standards, limited awareness, high costs, and policy gaps constrain growth. This study goes beyond the existing literature by integrating market analysis, SWOT assessment, cost–benefit findings, and production technologies to highlight strategies for scaling biochar adoption. It concludes that with supportive legislation, investment in research, and enhanced supply chain transparency, biochar could become a pivotal tool for sustainable development in the U.S. agricultural and environmental sectors.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessPerspective
Integrating Community Well-Being into Natural Climate Solutions: A Framework for Enhanced Verification Standards and Project Permanence
by
Beth Allgood, John Waugh, Craig A. Talmage, Dehara Weeraman and Laura Musikanski
Reg. Sci. Environ. Econ. 2025, 2(3), 22; https://doi.org/10.3390/rsee2030022 - 25 Jul 2025
Abstract
Natural Climate Solutions (NCSs) represent a critical tool for addressing climate change, yet their long-term success is threatened by inadequate consideration of community impacts in current verification standards. While Article 6 of the Paris Agreement establishes rigorous requirements for carbon sequestration and emission
[...] Read more.
Natural Climate Solutions (NCSs) represent a critical tool for addressing climate change, yet their long-term success is threatened by inadequate consideration of community impacts in current verification standards. While Article 6 of the Paris Agreement establishes rigorous requirements for carbon sequestration and emission avoidance verification, existing standards lack comprehensive frameworks for assessing and ensuring community well-being, undermining project permanence and market confidence. We developed an integrated framework combining community well-being assessment with verification requirements through analysis of Article 6 implementation requirements, existing voluntary carbon offset credit standards, emerging national standards, and community engagement mechanisms. Our analysis yielded a framework establishing five core tenets for community engagement (inclusion, engagement, contribution, ownership, and well-being) and nine essential well-being assessment domains, each with specific measurable indicators. The framework provides clear verification alignment protocols that integrate with existing standards while maintaining rigorous requirements and offering practical implementation guidance. Integration of community well-being assessment into NCS verification standards strengthens project permanence while meeting verification requirements, providing practical tools for standards bodies, project developers, and market participants to ensure both environmental and social benefits. As Article 6 mechanisms mature, this integration becomes increasingly crucial for project success.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Perception of Climate Change and Adoption of Cottonseed Cake in Pastoral Systems in the Hauts-Bassins Region of Burkina Faso
by
Yacouba Kagambega and Patrice Rélouendé Zidouemba
Reg. Sci. Environ. Econ. 2025, 2(3), 21; https://doi.org/10.3390/rsee2030021 - 25 Jul 2025
Abstract
In the Sahelian context characterized by the increasing scarcity of forage resources, this study investigated how climate change perceptions influence the adoption of cottonseed cake in pastoral and agro-pastoral systems in the Hauts-Bassins region of Burkina Faso. Drawing on the Subjective Expected Utility
[...] Read more.
In the Sahelian context characterized by the increasing scarcity of forage resources, this study investigated how climate change perceptions influence the adoption of cottonseed cake in pastoral and agro-pastoral systems in the Hauts-Bassins region of Burkina Faso. Drawing on the Subjective Expected Utility (SEU) theory and using a logit model estimated from survey data collected from 366 livestock farms, the analysis reveals that the perceived degradation of rangelands due to climate change is a key determinant of adoption. Over 40% of surveyed herders believed that climate change is negatively affecting the availability of natural forage. This heightened awareness is significantly associated with a greater likelihood of adopting cottonseed cake as a feed supplementation strategy. This study highlights the crucial role of cognitive factors in shaping adaptation decisions, beyond traditional economic and structural determinants. It underscores the importance of incorporating environmental perceptions into public policies supporting livestock systems and technological innovations in pastoral.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Beyond the Cowboy Economy: Proposing Teaching and Research Agendas for Ecological Economics
by
Daniel Caixeta Andrade, Debora Nayar Hoff and Junior Ruiz Garcia
Reg. Sci. Environ. Econ. 2025, 2(3), 20; https://doi.org/10.3390/rsee2030020 - 24 Jul 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This article presents an initial effort to systematize two interrelated research fronts within ecological economics (EE): ecological microeconomics and ecological macroeconomics. In response to the field’s transdisciplinary and plural nature—attributes that, while enriching, may limit its political influence—the article proposes a conceptual delineation
[...] Read more.
This article presents an initial effort to systematize two interrelated research fronts within ecological economics (EE): ecological microeconomics and ecological macroeconomics. In response to the field’s transdisciplinary and plural nature—attributes that, while enriching, may limit its political influence—the article proposes a conceptual delineation of these two domains as a means to strengthen EE’s analytical identity and facilitate dialogue with other economic approaches. Ecological microeconomics focuses on the material and energy intensity of economic activity, the complementarity of natural capital in production processes, and the redesign of consumption and firm behavior under ecological constraints. Ecological macroeconomics, in turn, centers on the biophysical limits to growth, the concept of sustainable and optimal scale, and the integration of environmental variables into macroeconomic indicators and policy frameworks. The article argues that both fronts, despite their distinct emphases, are united by the need for long-term structural change and a normative commitment to sustainability. Together, they offer a coherent basis for rethinking prosperity within the ecological boundaries of the Earth system.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Sustainable Economic Security for Building Disaster-Resilient Communities in Vulnerable Coastal Areas of Bangladesh
by
Md. Rasheduzzaman, Md. Shamsuzzoha, Abu Saleh Md. Ifat Istiak, Md. Jashim Uddin, Kamrunnahar Ishana, Mohammad Kabirul Islam, Rajib Shaw and Kentaka Aruga
Reg. Sci. Environ. Econ. 2025, 2(3), 19; https://doi.org/10.3390/rsee2030019 - 18 Jul 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The present study was conducted in Dacope Upazila, a sub-district located within the Khulna District of the coastal region in Bangladesh. The research methods employed included the implementation of 350 household questionnaire surveys (HQSs), 12 focus group discussions (FGDs), and 20 key informant
[...] Read more.
The present study was conducted in Dacope Upazila, a sub-district located within the Khulna District of the coastal region in Bangladesh. The research methods employed included the implementation of 350 household questionnaire surveys (HQSs), 12 focus group discussions (FGDs), and 20 key informant interviews (KIIs) to assess economic security status in disaster-vulnerable areas. The findings indicate that the economic well-being of the region is precarious due to a paucity of revenue sources and the occurrence of various calamitous events, induced risks, and vulnerabilities. To achieve long-term economic security for households, a considerable proportion of the population (approximately 22%) in the study areas is dependent on agricultural activities for their livelihoods. The study also revealed that approximately 22% of households in the study areas reported experiencing salinity intrusion. Furthermore, most of the households, around 68%, reported cyclones as their primary obstacle to building disaster-resilient communities. Consequently, the prevailing local and institutional strategies to ensure economic security were found to be inadequate and unsustainable in the study upazila. Therefore, the study resulted in the formulation of a conceptual framework intended to measure the contribution of economic security to the adaptability and sustainability of disaster-resilient communities in vulnerable coastal areas of Bangladesh.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Women’s Land Ownership and Decision-Making Power in West Sumatra
by
Betrin Natasya and Atsushi Matsuoka
Reg. Sci. Environ. Econ. 2025, 2(3), 18; https://doi.org/10.3390/rsee2030018 - 2 Jul 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
In the socio-institutional framework of the Minangkabau society in West Sumatra, Indonesia—where women are typically assumed to have full power over land due to the matrilineal system of land ownership—this study asks: To what extent do women actually exercise power over land ownership
[...] Read more.
In the socio-institutional framework of the Minangkabau society in West Sumatra, Indonesia—where women are typically assumed to have full power over land due to the matrilineal system of land ownership—this study asks: To what extent do women actually exercise power over land ownership and decision-making, and what factors influence this power? Comprising 212 households, a methodical household survey carried out in 2024 across the regencies of Lima Puluh Kota and Padang Pariaman employed quantitative approaches and comparative analysis across rural and peri-urban areas. The survey results confirm the initial hypothesis, showing high rates of land ownership among women in West Sumatra, largely attributed to the matrilineal system. Land ownership by itself, though, does not significantly increase women’s influence in households. Rather, women’s decision-making in Lima Puluh Kota is strongly influenced by other assets such as ownership of cattle, poultry, and electronic items; in Padang Pariaman, time allocated to farming and social events has more influence. These findings underline the complex reality behind nominal land rights and practical empowerment, thereby stressing the need to consider broader socioeconomic factors. The report advises more research on how religious interpretations and modernization are altering West Sumatra’s customary matrilineal customs and women’s empowerment.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Tropical Peatlands in Indonesia and Global Environmental Change: A Multi-Dimensional System-Based Analysis and Policy Implications
by
Yee Keong Choy and Ayumi Onuma
Reg. Sci. Environ. Econ. 2025, 2(3), 17; https://doi.org/10.3390/rsee2030017 - 1 Jul 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Tropical peatlands store approximately 105 gigatons of carbon (GtC), serving as vital long-term carbon sinks, yet remain critically underrepresented in climate policy. Indonesia peatlands contain 57GtC—the largest tropical peatland carbon stock in the Asia–Pacific. However, decades of drainage, fires, and lax enforcement practices
[...] Read more.
Tropical peatlands store approximately 105 gigatons of carbon (GtC), serving as vital long-term carbon sinks, yet remain critically underrepresented in climate policy. Indonesia peatlands contain 57GtC—the largest tropical peatland carbon stock in the Asia–Pacific. However, decades of drainage, fires, and lax enforcement practices have degraded vast peatland areas, turning them from carbon sinks into emission sources—as evidenced by the 1997 and 2015 peatland fires which emitted 2.57 Gt CO2eq and 1.75 Gt CO2eq, respectively. Using system theory validated against historical data (1997–2023), we develop a causal loop model revealing three interconnected feedback loops driving irreversible collapse: (1) drainage–desiccation–oxidation, where water table below −40 cm triggers peat oxidation (2–5 cm subsistence) and fires; (2) fire–climate–permafrost, wherein emissions intensify radiative forcing, destabilizing monsoons and accelerating Arctic permafrost thaw (+15% since 2000); and (2) economy–governance failure, perpetuated by palm oil’s economic dominance and slack regulatory oversight. To break these vicious cycles, we propose a precautionary framework featuring IoT-enforced water table (≤40 cm), reducing emissions by 34%, legally protected “Global Climate Stabilization Zones” for peat domes (>3 m depth), safeguarding 57 GtC, and ASEAN transboundary enforcement funded by a 1–3% palm oil levy. Without intervention, annual emissions may reach 2.869 GtCO2e by 2030 (Nationally Determined Contribution’s business-as-usual scenario). Conversely, rewetting 590 km2/year aligns with Indonesia’s FOLU Net Sink 2030 target (−140 Mt CO2e) and mitigates 1.4–1.6 MtCO2 annually. We conclude that integrating peatlands as irreplaceable climate infrastructure into global policy is essential for achieving Paris Agreement goals and SDGs 13–15.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Reshaping Urban Innovation Landscapes for Green Growth: The Role of Smart City Policies in Digital Transformation
by
Dayu Zhu and Shengyong Zhang
Reg. Sci. Environ. Econ. 2025, 2(3), 16; https://doi.org/10.3390/rsee2030016 - 27 Jun 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Under the impetus of the global urbanization, the synergistic relationship between smart city policies and green innovation capabilities has emerged as a critical agenda for achieving sustainable development goals. While existing studies have explored the techno-economic effects of smart cities, systematic evidence remains
[...] Read more.
Under the impetus of the global urbanization, the synergistic relationship between smart city policies and green innovation capabilities has emerged as a critical agenda for achieving sustainable development goals. While existing studies have explored the techno-economic effects of smart cities, systematic evidence remains scarce regarding their pathways and heterogeneous impacts on green growth. This study investigates the influence of smart city pilot policies on urban green growth trajectories and their heterogeneous characteristics. Leveraging panel data from 293 Chinese prefecture-level cities, we employ a multi-period difference-in-differences (DID) model with two-way fixed effects to control for unobserved city-specific and time-specific factors, complemented by robustness checks including parallel trend tests, placebo tests, and alternative dependent variable specifications. Data sources encompass the China City Statistical Yearbook, CNRDS, and CSMAR databases, covering core metrics such as green patent applications and grants, industrial upgrading indices, and environmental regulation intensity, with missing values being addressed via mean imputation. The findings demonstrate that smart city pilot policies significantly enhance green innovation levels in treated cities, with effects exhibiting pronounced spatial and resource-based heterogeneity; there are notably stronger impacts in non-resource-dependent cities and eastern regions. Mechanism analysis shows that policies are driven by a dual effect of industrial upgrading and environmental regulation. The former is manifested by the high substitution elasticity of the digital economy for traditional manufacturing, while the latter is reflected in the rising compliance costs of polluting enterprises. This research advances a cross-nationally comparable theoretical framework for understanding green transition mechanisms in smart city development while providing empirical benchmarks for policy design in emerging economies.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Sustainability in Civil Construction: Study of Companies in Mossoró, Rio Grande do Norte, Brazil
by
Ingrid Eduarda Alves Paiva and Jorge Luís de Oliveira Pinto Filho
Reg. Sci. Environ. Econ. 2025, 2(2), 15; https://doi.org/10.3390/rsee2020015 - 12 Jun 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The growing relevance of sustainable practices has driven organizations from various sectors to adapt their activities to current socio-environmental demands. In the construction sector, this demand is even more pronounced due to the high consumption of natural resources and the significant generation of
[...] Read more.
The growing relevance of sustainable practices has driven organizations from various sectors to adapt their activities to current socio-environmental demands. In the construction sector, this demand is even more pronounced due to the high consumption of natural resources and the significant generation of solid waste. However, questions remain about the extent to which companies in this sector understand and incorporate sustainable practices into their routines. This study investigates the level of knowledge and the adoption of sustainable practices by residential building construction companies registered with the Civil Construction Industry Union of Mossoró/RN. A qualitative-quantitative approach was adopted, using questionnaires and photographic records collected during on-site visits. The data reveal an incipient adoption of Environmental Management Systems (EMSs) and limited knowledge about ESG principles, highlighting structural and cultural barriers to sustainability in the sector. Nevertheless, isolated initiatives related to waste reduction and the adoption of more efficient practices were observed. The study concludes that strengthening technical training, promoting management systems, and aligning with contemporary demands are relevant strategies to foster sustainability and competitiveness in the construction sector.
Full article
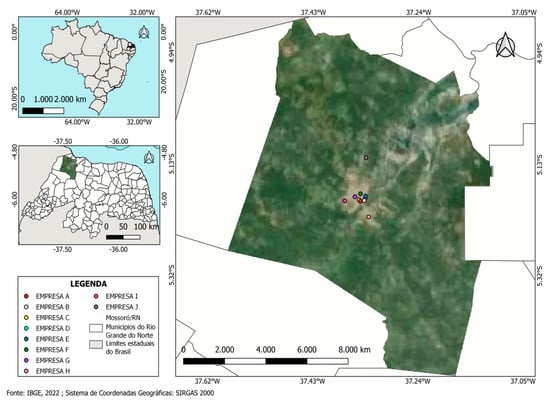
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
District-Level Spatial Distribution of Carbon Emissions Derived from Nighttime Light Data: A Case Study of Xi’an City, China
by
Fangmiao Chen, Qiang Chen, Kai Yin and Liping Li
Reg. Sci. Environ. Econ. 2025, 2(2), 14; https://doi.org/10.3390/rsee2020014 - 4 Jun 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide (CO2), released from excessive fossil fuel consumption, are major contributors to global warming. Understanding the spatial distribution of CO2 emissions on a refined scale is crucial for promoting green economic development. Xi’an, a key
[...] Read more.
Greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide (CO2), released from excessive fossil fuel consumption, are major contributors to global warming. Understanding the spatial distribution of CO2 emissions on a refined scale is crucial for promoting green economic development. Xi’an, a key central city in China, serves as the case study for this research. Using nighttime light data from Black Marble, combined with energy statistics and socio-economic information, this study employed spatial analysis to simulate CO2 emissions on the district and county levels in Xi’an for the years 2012 and 2022. The results indicated that nighttime light data were significantly correlated with CO2 emissions (linear function; coefficients of determination: 0.7838 and 0.7941 for 2012 and 2022, respectively). The spatial distribution analysis revealed a clear pattern in CO2 emissions, with higher emissions concentrated in central urban areas and lower emissions in peripheral regions. Additionally, a comparative analysis of carbon emissions and carbon emission intensity across districts and counties between 2012 and 2022 showed that CO2 emissions in central urban areas had continued to grow and expand, while emission intensity had declined. These findings suggest that the socio-economic development, policy interventions, and industrial structure in Xi’an influence the spatial distribution of CO2 emissions.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Regional Research on Ecological Environment in China: A Literature Review
by
Song Wang, Chaoquan Wang, Yuyao Cao and Xin Li
Reg. Sci. Environ. Econ. 2025, 2(2), 13; https://doi.org/10.3390/rsee2020013 - 21 May 2025
Abstract
With the rapid development of China’s economy, resource consumption and environmental pollution have become challenges faced by China in its development process. In order to effectively achieve a balance between economic development and ecological and environmental protection, the Chinese government has successively introduced
[...] Read more.
With the rapid development of China’s economy, resource consumption and environmental pollution have become challenges faced by China in its development process. In order to effectively achieve a balance between economic development and ecological and environmental protection, the Chinese government has successively introduced development strategies for ecological environment construction. However, how to scientifically evaluate the quality of regional ecological environments, analyze related impacts, and promote national ecological and environmental governance has always been difficult to reach consensus and continues to receive attention from the academic community. This paper sorts through research in recent years about regional ecological environment assessments in China in order to summarize the current assessment methods and dimensions of regional ecological environment research in China, as well as the impact of regional ecological environment construction. In terms of evaluation methods, this paper analyzes the applicability and limitations of current mainstream methods. In terms of evaluation dimensions, this paper summarizes the research results from different regional dimensions. In terms of the impact of regional ecological and environmental construction, this paper elaborates on the three aspects of influencing factors, influencing effects and research method analysis. Based on the above analysis, this paper finally proposes that the focus of future research should be on digital analysis and the evaluation of regional ecological and environmental quality, so as to provide more scientific and accurate support for regional ecological and environmental governance.
Full article
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Real Estate, RSEE, Sustainability, Urban Science
Sustainability and Regional Development: Foundations and Challenges for This Symbiotic Relationship
Topic Editors: Dimitrios Tsiotas, Serafeim PolyzosDeadline: 10 April 2027







