Journal Description
Scientia Pharmaceutica
Scientia Pharmaceutica
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal related to the pharmaceutical sciences. The journal is owned by the Austrian Pharmaceutical Society (Österreichische Pharmazeutische Gesellschaft, ÖPhG) and is published quarterly online by MDPI (since Volume 73, Issue 1 - 2016) and in print by the Austrian Pharmacists' Publishing House (Österreichischer Apothekerverlag). ÖPhG members receive discounts on the APC.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, ESCI (Web of Science), Embase, CAPlus / SciFinder, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: CiteScore - Q2 (Pharmaceutical Science)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 26.1 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 5.3 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2024).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
Impact Factor:
2.3 (2023);
5-Year Impact Factor:
2.9 (2023)
Latest Articles
Comparative Analysis of Adverse Effects: Protein Kinase Inhibitors Versus Traditional Anticancer Therapies
Sci. Pharm. 2025, 93(2), 20; https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm93020020 - 21 Apr 2025
Abstract
►
Show Figures
The adverse effects of protein kinase inhibitors (PKIs) and other anticancer therapies were compared using FDA Adverse Events Reporting System (FAERS) data. The dataset included 159 FDA-approved anticancer drugs (71 PKIs, 88 nonPKIs) and analyzed 8216 unique adverse event (AE) terms. PKIs showed
[...] Read more.
The adverse effects of protein kinase inhibitors (PKIs) and other anticancer therapies were compared using FDA Adverse Events Reporting System (FAERS) data. The dataset included 159 FDA-approved anticancer drugs (71 PKIs, 88 nonPKIs) and analyzed 8216 unique adverse event (AE) terms. PKIs showed fewer systemic toxicities, with an average of 230.1 distinct AEs per drug, compared to 537.7 in nonPKIs. Hematologic AEs were significantly lower in PKIs (e.g., febrile neutropenia: 1.93% vs. 5.25%; thrombocytopenia: 2.18% vs. 3.87%), coupled with a lower incidence of infections (6.87% vs. 14.2%) and immunosuppressive effects. However, gastrointestinal and skin-related AEs were more common in PKIs (e.g., diarrhea: 13.95% vs. 8.36%). A higher proportion AEs in the PKI group (14.57%) were classified under “Investigations”, compared to the nonPKI group (9.87%). The frequency of “Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders” AEs was twice as high in the PKI group. Clustering analysis grouped drugs by AE profiles, showing that PKIs formed more homogeneous clusters, while nonPKIs had broader variability. Multi-kinase inhibitors with VEGFR activity were linked to dermatologic AEs, likely due to EGFR inhibition in basal keratinocytes. Despite PKIs’ targeted mechanisms, resistance remains a challenge, requiring biomarker-driven strategies. This study highlights PKIs’ improved tolerability but emphasizes using personalized treatment approaches to optimize efficacy and safety.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Study of the Influence of Pharmaceutical Excipients on the Solubility and Permeability of BCS Class II Drugs
by
Vivien Bárdos, Rita Szolláth, Petra Tőzsér, Arash Mirzahosseini, Bálint Sinkó, Réka Angi and Krisztina Takács-Novák
Sci. Pharm. 2025, 93(2), 19; https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm93020019 - 11 Apr 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Most novel active pharmaceutical ingredients have low water solubility; therefore, solubility-enhancing methods are applied. The aim of the present investigation is to study the impact of nine commonly used pharmaceutical excipients (fillers, surfactants, cyclodextrins, polymers) on solubility, permeability and their relationship. This is
[...] Read more.
Most novel active pharmaceutical ingredients have low water solubility; therefore, solubility-enhancing methods are applied. The aim of the present investigation is to study the impact of nine commonly used pharmaceutical excipients (fillers, surfactants, cyclodextrins, polymers) on solubility, permeability and their relationship. This is crucial for ensuring optimal bioavailability. Carbamazepine, naproxen and pimobendan were chosen as model compounds due to their different acid–base properties. Equilibrium solubility was measured by the traditional shake flask method. Effective permeability was determined by the PAMPA model. Measurements of ionizable compounds were carried out at three pH values. The pH-dependent change in the investigated parameters is maintained even in the presence of excipients. Fillers resulted in a slight or no effect, while the impact of other excipients showed a significant concentration dependence. The impact of excipients was influenced by the structure and ionization state of the molecules. The dominance of the ionized form moderates the impact of excipients. The changes in solubility were more pronounced than in the case of permeability. By examining the effect of the ionization state and interactions with excipients, this work supports the development of formulations that enhance solubility with minimal impacts on permeability. Additionally, it can serve as good basis for preformulation studies and design optimization.
Full article
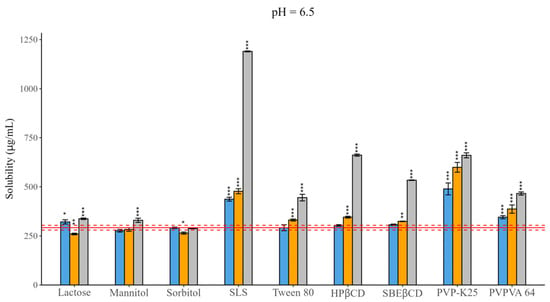
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Polygenic Risk Scores for Personalized Cardiovascular Pharmacogenomics―A Scoping Review
by
Aaryan Dwivedi, Jobanjit S. Phulka, Peyman Namdarimoghaddam and Zachary Laksman
Sci. Pharm. 2025, 93(2), 18; https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm93020018 - 8 Apr 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the leading cause of mortality worldwide, often involving a strong genetic background. Polygenic risk scores (PRSs) combine the cumulative effects of multiple genetic variants to quantify an individual’s susceptibility to CVD. Pharmacogenomics (PGx) can further personalize treatment by tailoring
[...] Read more.
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the leading cause of mortality worldwide, often involving a strong genetic background. Polygenic risk scores (PRSs) combine the cumulative effects of multiple genetic variants to quantify an individual’s susceptibility to CVD. Pharmacogenomics (PGx) can further personalize treatment by tailoring medication choices to an individual’s genetic profile. Even with these potential benefits, the extent to which PRS can be integrated into the PGx of CVD remains unclear. Our review provides an overview of current evidence on the application of PRS in the PGx of CVD, examining clinical utility and limitations and providing directions for future research. Following the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses extension for Scoping Reviews protocol, we conducted a comprehensive literature search in PubMed, EMBASE, and the Web of Science. Studies investigating the relationship between PRS in predicting the efficacy, adverse effects, or cost-effectiveness of cardiovascular medications were selected. Of the 1894 articles identified, 32 met the inclusion criteria. These studies predominantly examined lipid-lowering therapies, antihypertensives, and antiplatelets, although other medication classes (e.g., rate-control drugs, ibuprofen/acetaminophen, diuretics, and antiarrhythmics) were also included. Our findings showed that PRS is most robustly validated in lipid-lowering therapies, especially statins, where studies reported that individuals with higher PRSs derived the greatest reduction in lipids while on statins. Studies analyzing antihypertensives, antiplatelets, and antiarrhythmic medications demonstrated more variable outcomes, though certain PRSs did identify subgroups with significantly improved response rates or a higher risk of adverse events. Though PRS was a strong tool in many cases, we found some key limitations in its applicability in research, such as the under-representation of non-European-ancestry cohorts in the examined studies and a lack of standardized outcome reporting. In conclusion, though PRS offers promise in improving the efficacy of PGx of CVD by enhancing the personalization of medication on an individual level, several obstacles, such as the need for including a broader ancestral diversity and more robust cost-effectiveness data remain. Future research must (i) prioritize validating PRS in ethnically diverse populations, (ii) refine PRS derivation methods to tailor them for drug response phenotypes, and (iii) establish clear and attainable guidelines for standardizing the reporting of outcomes.
Full article
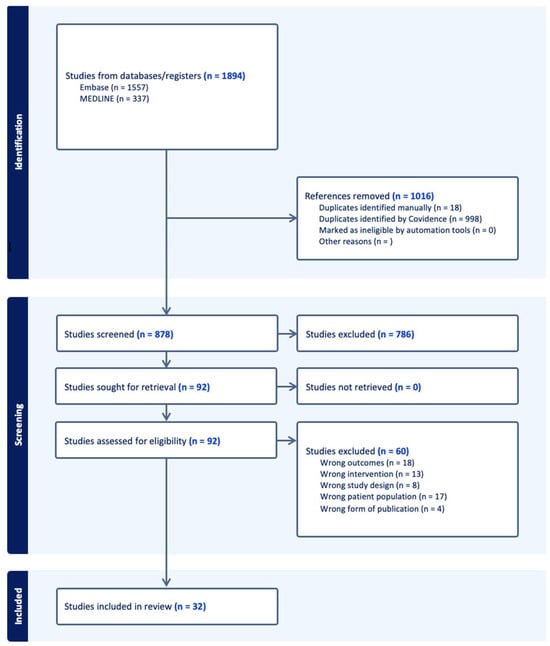
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Pregestational Stress Representing a Maternal Depression Model and Prenatally Applied Antidepressant Mirtazapine Modulate Hippocampal Excitability in Offspring
by
Lucia Dubiel-Hoppanova, Alzbeta Filipova, Stanislava Bukatova, Katarina Ondacova, Matus Tomko, Bohumila Jurkovicova-Tarabova, Michal Dubovicky, Eliyahu Dremencov and Lubica Lacinova
Sci. Pharm. 2025, 93(2), 17; https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm93020017 - 31 Mar 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Maternal depression negatively affects the neurodevelopment of offspring, but its pharmacological treatment during gestation remains controversial. This study reports the consequences of maternal depression and/or prenatal antidepressant treatment with mirtazapine on offspring early neurodevelopment via an animal model of maternal depression induced by
[...] Read more.
Maternal depression negatively affects the neurodevelopment of offspring, but its pharmacological treatment during gestation remains controversial. This study reports the consequences of maternal depression and/or prenatal antidepressant treatment with mirtazapine on offspring early neurodevelopment via an animal model of maternal depression induced by pregestational chronic unpredictable stress (CUS). Offspring from four groups were studied: nonstressed vehicle-treated dams, nonstressed mirtazapine-treated dams, stressed vehicle-treated dams, and stressed mirtazapine-treated dams. The hippocampal excitability of offspring was examined in primary hippocampal cultures established on the first postnatal day, reflecting mostly prenatal development, and in hippocampal slices prepared on postnatal days 11–13, reflecting an early postnatal development. The pregestational CUS modeling of maternal depression moderately suppressed offspring hippocampal excitability in primary cultures but facilitated it in slices. Mirtazapine administered to CUS-exposed dams partly rectified the changes observed in primary cultures of pups from untreated dams and, more prominently, in slices. Mirtazapine itself negatively affected the hippocampal excitability of nonstressed dam offspring in primary culture, and this effect was diminished in slices. Since altered hippocampal neurotransmission might be responsible, at least in part, for the neuropsychopathologies frequently observed in the offspring of depressed mothers, and mirtazapine was able to partly relieve such changes, this treatment may be also beneficial during the prenatal and perinatal periods.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Some Coumarin–Triazole Conjugates as Potential Anticancer Agents
by
Anarkul S. Kishkentayeva, Mohammad Saleh Hamad, Mikhail A. Pokrovsky, Zhanar R. Shaimerdenova, Aigerim S. Adekenova, Gulnara K. Mambeterzina, Victor A. Savelyev, Andrey G. Pokrovsky and Elvira E. Shults
Sci. Pharm. 2025, 93(2), 16; https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm93020016 - 31 Mar 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Despite the discovery of many chemotherapeutic drugs that prevent uncontrolled cell division processes, the development of compounds with higher anticancer efficacy and a lower level of side effects is an important task in modern pharmaceutical chemistry. Herein, a mild and convenient method for
[...] Read more.
Despite the discovery of many chemotherapeutic drugs that prevent uncontrolled cell division processes, the development of compounds with higher anticancer efficacy and a lower level of side effects is an important task in modern pharmaceutical chemistry. Herein, a mild and convenient method for the preparation of N1-substituted 3-(1,2,3-triazolyl-methoxycarbonyl)coumarins or bis(coumarine-3-carboxylate)bis(triazole)alkandiyl by the copper(I)-catalyzed Huisgen cycloaddition reaction of readily available coumarin-3-carboxylic acid propynyl ester with azides or diazides has been presented. The synthesized compounds have been tested for their cytotoxicity on various cancer and noncancerous cell lines using the MTT assay. All new compounds were nontoxic on normal epithelial VERO cells. Two derivatives exhibited selectivity towards HPV-negative human cervical cancer cells, C33 A, with excellent activities in low concentrations (GI50 4.4–7.0 µM). In vitro mechanistic studies showed that bis(coumarine)bis(triazolylester) conjugate 3 induced time-dependent apoptosis in cervical cancer cell lines C33 A and CaSki, at the GI50 concentration, as measured by Annexin V-FITC/PI staining. The most active coumarin–triazolyl ester conjugate 2g possessed anticancer activities, as indicated by its ability to induce S/G2 phase cell cycle arrest at a low concentration and early apoptosis in CaSki cells. The obtained results revealed the potential of new compounds as anticancer agents, particularly against cervical cancer.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Wild Harvesting vs. Cultivation: Total Petasin Content in Petasites hybridus Rhizome Extracts Determines Spasmolytic Effects
by
Christiane Halbsguth, Verena M. Merk, Jürgen Drewe, Georg Boonen and Veronika Butterweck
Sci. Pharm. 2025, 93(2), 15; https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm93020015 - 21 Mar 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The use of herbal medicines containing Petasites hybridus extracts has a long history in the treatment of various ailments. The observed effects are primarily due to pharmacologically active compounds such as petasin, isopetasin, and neopetasin. In evidence-based phytotherapy, extracts from leaves and rhizomes
[...] Read more.
The use of herbal medicines containing Petasites hybridus extracts has a long history in the treatment of various ailments. The observed effects are primarily due to pharmacologically active compounds such as petasin, isopetasin, and neopetasin. In evidence-based phytotherapy, extracts from leaves and rhizomes are applied for different indications. While leaf extracts are administered to treat allergic rhinitis symptoms, rhizome extracts are utilized among others in the management of gastrointestinal spasms and migraines. The quality and source of plants are critical for producing authorized herbal medicinal products. Although the preparation of P. hybridus leaf extracts from cultivated plant material is already established, the rhizomes used for preparing extracts are still derived from commercial wild collections. However, switching to cultivation is desirable to ensure consistent quality and availability. For regulatory purposes, comparative pharmacological studies are needed to assess the bioactivity of plant material from different sources. Therefore, this study analyzed rhizome extracts from wild harvesting and cultivation for their petasin composition (i.e., isopetasin, neopetasin, petasin) and spasmolytic effects on Ca2+-dependent precontracted guinea pig ileum ex vivo. The results confirm petasins as active compounds of P. hybridus rhizome extracts. Moreover, they demonstrate that the total content of petasins determines the spasmolytic effects, regardless of the individual composition of the different petasins. No significant differences in efficacy were found between cultivated and wild-collected rhizomes, demonstrating that cultivated material is a reliable, consistent, and sustainable alternative for P. hybridus rhizome extract production.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Formulations with Boric Acid or Aryl-Organoboron Compounds for Treating Diabetic Foot Ulcers
by
Marvin A. Soriano-Ursúa, Marlet Martínez-Archundia, Ahmet Kilic, Teresa Pérez-Capistran, Miriam A. Hernández-Zamora, Juan E. López-Ramos and Eunice D. Farfán-García
Sci. Pharm. 2025, 93(1), 14; https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm93010014 - 19 Mar 2025
Abstract
Boron-containing compounds (BCCs) have been proposed for the treatment of diabetes and its complications. Recent studies have reported an improvement in the design and development of pharmaceutical formulations (often gels) containing boric acid applied to the foot ulcers of humans diagnosed with diabetes.
[...] Read more.
Boron-containing compounds (BCCs) have been proposed for the treatment of diabetes and its complications. Recent studies have reported an improvement in the design and development of pharmaceutical formulations (often gels) containing boric acid applied to the foot ulcers of humans diagnosed with diabetes. The proposed mechanisms of action of boric acid include antimicrobial effects, the modulation of inflammation and metabolism, and the induction of cell differentiation. On the other hand, recent studies have suggested that boronic acids are potent antibacterial and antifungal compounds, effective modulators of inflammation, and inducers of vascular regeneration as well as inducers of healing, and they confer attractive properties such as adhesion, interaction, and the formation of complexes in formulations. Moreover, only a handful of studies conducted in animals have suggested the effective role of some BCCs as potent enhancers of wound healing, including their actions on induced and/or infected wounds in animals with disrupted metabolism. Also, it should be mentioned that no strong interactions between boric acid and the boronic acids present in formulations have been described. The developed combination could act as an additive and complementary therapy in the treatment of diabetic ulcers in humans. Further studies are required to support the hypothesis that this combination acts through diverse mechanisms to improve healing while avoiding or limiting a local or disseminated infection. Furthermore, the safety of BCCs used for foot ulcers should be established, as should the role of these formulations as a complementary therapy in current protocols for treating patients with diabetic foot ulcers.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic New Compounds Discovery and Development in Medicine — Advances in Research on Potential Therapeutic Agents and Drug Candidates, 2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures
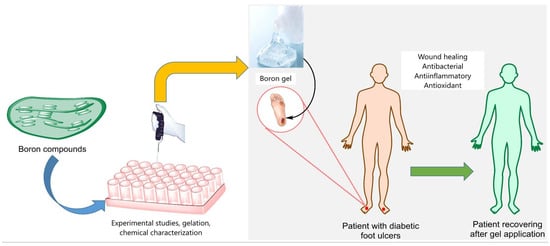
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Physicochemical Characteristics of Cardiological Drugs and Practical Recommendations for Intravenous Administration: A Systematic Review
by
Massimiliano Quici, Elena Martini, Davide Giustivi, Maria Calloni, Chiara Cogliati, Alba Taino, Antonella Foschi, Andrea Gori, Paolo Zappa, Francesco Casella, Arianna Bartoli, Leyla La Cava, Alessia Meschia, Rosita Celano, Francesco Urso, Dario Cattaneo and Antonio Gidaro
Sci. Pharm. 2025, 93(1), 13; https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm93010013 - 12 Mar 2025
Abstract
Most cardiological drugs need intravenous administration to have a fast effect in an emergency. Intravenous administration is linked to complications, such as tissue infiltration and thrombophlebitis. Aiming to supply an effective tool for the development of appropriate policies, this systematic review provides practical
[...] Read more.
Most cardiological drugs need intravenous administration to have a fast effect in an emergency. Intravenous administration is linked to complications, such as tissue infiltration and thrombophlebitis. Aiming to supply an effective tool for the development of appropriate policies, this systematic review provides practical recommendations about the diluent, pH, osmolarity, dosage, vesicant properties, and phlebitis rate of the most commonly used cardiological drugs evaluated in randomized controlled trials (RCTs) till 31 August 2024. The authors searched for available IV cardiological drugs in RCTs in PUBMED EMBASE®, EBSCO-CINAHL®, and Cochrane Controlled Clinical trials. Drugs’ chemical features were obtained online, in drug data sheets, and in scientific papers, establishing that the drugs with a pH of <5 or >9, an osmolarity > 600 mOsm/L, and a high incidence of phlebitis reported in the literature, as well as vesicant drugs, require utmost caution during administration. A total of 857 papers were evaluated and 316 studies were included. A total of 84 cardiological drugs were identified, of which only 31 (37%) can be safely infused via a peripheral route. Thrombolytics and anticoagulants are considered the safest classes of drugs, with only one drug flagged as a “red flag” medication. However, a higher percentage of drugs in other categories meet the “red flag” criteria, including antiarrhythmics (52%), antiplatelet agents (67%), diuretics (67%), antihypertensives (70%), other drugs (77%), and vasoconstrictors and inotropics (89%). Understanding the physicochemical properties of cardiological drugs is essential for significantly improving patient safety and preventing administration errors and local side effects.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Challenges and Opportunities in Drug Delivery Research)
►▼
Show Figures
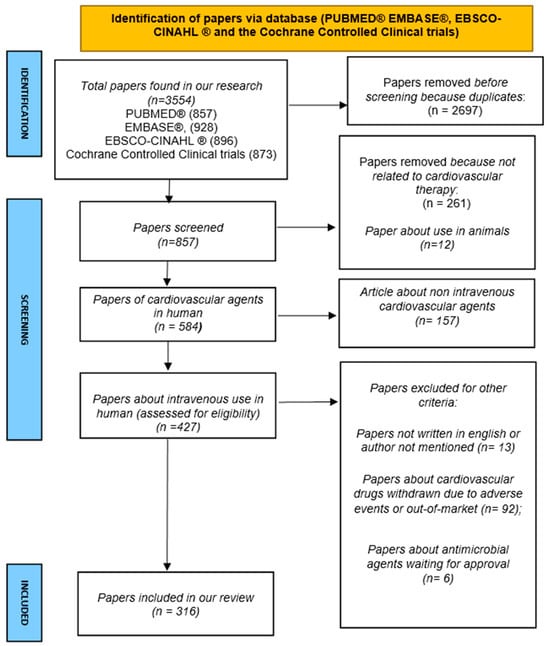
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Exploring Cannabidiol’s Therapeutic Role in Colorectal Cancer: Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking Insights
by
Juan Manuel Guzmán-Flores, Fernando Martínez-Esquivias, Antistio Alviz-Amador, Guadalupe Thonanzyn Avilés-Rodríguez and Michel Fabricio García-Azuela
Sci. Pharm. 2025, 93(1), 12; https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm93010012 - 28 Feb 2025
Abstract
Background: Colorectal cancer (CRC) is one of the most prevalent cancers worldwide, and current treatments have significant side effects. Cannabidiol (CBD), a compound derived from Cannabis sativa, has demonstrated promising anticancer properties. However, further investigation is required to elucidate its underlying molecular
[...] Read more.
Background: Colorectal cancer (CRC) is one of the most prevalent cancers worldwide, and current treatments have significant side effects. Cannabidiol (CBD), a compound derived from Cannabis sativa, has demonstrated promising anticancer properties. However, further investigation is required to elucidate its underlying molecular mechanisms. Methods: Network pharmacology and molecular docking analysis approaches were utilized. Molecular targets of CBD and CRC-associated genes were identified using the Swiss Target Prediction, Malacards, and DisGeNet databases. Protein–protein interactions were analyzed using the STRING and Cytoscape. Ontology enrichment was conducted using ShinyGO, and gene expression and immune infiltration were evaluated with UALCAN and TISIDB. Results: We found 95 common genes between CRC and CBD targets. Six major genes (ANXA5, IGF1R, JAK2, MAPK8, MDM2, and PARP1) were particularly interesting due to their high connectivity and role in relevant metabolic pathways. The results of the molecular docking analysis indicated that CBD interacts favorably with these genes, modulating critical pathways such as RAS/MAPK and PI3K-AKT/FoxO, which are involved in cell proliferation, apoptosis, and cell cycle regulation. ANXA5 and JAK2 were identified as particularly relevant, as they correlated significantly with immune cell infiltration, suggesting a role in the immunoregulation of the tumor microenvironment. Conclusions: CBD has the potential to modulate key molecular processes in CRC through specific pathways and core genes, presenting itself as a possible complementary therapy to improve efficacy and reduce the adverse effects of conventional treatments.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Bioinformatics in Drug Design and Discovery—2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Analysis of Functional Compounds in Matcha by Quantitative Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy
by
Kengo Hori, Yuki Kurauchi, Shunsuke Kotani and Hari Prasad Devkota
Sci. Pharm. 2025, 93(1), 11; https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm93010011 - 14 Feb 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Matcha is reported to have high content of some bioactive components such as catechins, theanine, and caffeine, and its consumption is increasing worldwide. Several analytical methods have been established for matcha powder and bioactive compounds, but most of them are based on HPLC
[...] Read more.
Matcha is reported to have high content of some bioactive components such as catechins, theanine, and caffeine, and its consumption is increasing worldwide. Several analytical methods have been established for matcha powder and bioactive compounds, but most of them are based on HPLC methods. This study focused on NMR as an analytical method for simple quantitative analysis of the functional components of matcha. The analytical conditions were established by preparing extract and solvent fractions, evaluating hygroscopicity, and examining quantitative NMR parameters. The analytical performance was evaluated, and the developed analytical condition was also applied to matcha powder by directly mixing in NMR solvent without pre-extraction. Caffeine, epicatechin, epicatechin-3-O-gallate, epigallocatechin-3-O-gallate, epigallocatechin, gallocatechin-3-O-gallate, and gallocatechin were quantified. Analysis of matcha and normal green tea powder suggested the possibility of distinguishing between matcha and green tea powder by the ratio of caffeine content and total catechins content. The qNMR method can be adopted for the simple analysis of the amount of caffeine and catechin compounds in the powders and extracts.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Phytochemical Profile and Antioxidant and Gastroprotective Effects of Three Varieties of Chenopodium quinoa Willd. Sprouts Cultivated in Peru
by
Edwin Carlos Enciso-Roca, Jorge Luis Arroyo-Acevedo, Pablo Williams Común-Ventura, Johnny Aldo Tinco-Jayo, Enrique Javier Aguilar-Felices, Mahomi Bertha Ramos-Meneses, Rosa Elizabeth Carrera-Palao and Oscar Herrera-Calderon
Sci. Pharm. 2025, 93(1), 10; https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm93010010 - 13 Feb 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Chenopodium quinoa sprouts possess a superior nutritional profile relative to conventional quinoa seeds, which is mainly attributable to their germination process. Sprouting quinoa is able to preserve its substantial nutritional value while enhancing its bioavailability and digestibility. The aim of this study was
[...] Read more.
Chenopodium quinoa sprouts possess a superior nutritional profile relative to conventional quinoa seeds, which is mainly attributable to their germination process. Sprouting quinoa is able to preserve its substantial nutritional value while enhancing its bioavailability and digestibility. The aim of this study was to evaluate the gastroprotective effects of hydroalcoholic extracts of three varieties of quinoa sprouts (pasankalla, yellow maranganí, and black coito). The chemical compounds were determined using LC-MS (Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry). Antioxidant activity was determined using two analytical methods, 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) and 2,2′-azino-bis (3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) (ABTS). To evaluate the gastroprotective effects of these hydroalcoholic extracts in Holtzman male rats, a gastric lesion was induced with 96% ethanol after the administration of the hydroalcoholic extract of the three varieties of C. quinoa sprouts. Our phytochemical analysis results reveal the presence of amino acids (valine, leucine, isoleucine, phenylalanine, tryptophane, proline, tyrosine, and arginine, among others) and their derivatives, organic acids, monosaccharides, lipids, nucleobases/nucleosides, steroids, triterpene saponins, and coumarins. The pasankalla, yellow maranganí, and black coito varieties exhibited antioxidant capacities of 36.70, 32.32, and 34.63 µmol Trolox equivalent (TE)/mg of extract for the DPPH radical and 56.61, 41.56, and 52.09 µmol TE/mg of extract for the ABTS radical, respectively. The percentage of antisecretory efficiency at a dose of 500 mg/kg for the pasankalla, yellow maranganí, and black coito varieties was 34.13%, 30.67%, and 26.67%, respectively, and the anti-ulcer effect, expressed as a percentage of inhibition of ulcer formation, was 74.7%, 67.4%, and 69.5%, respectively. In contrast, the groups treated with ranitidine and sucralfate exhibited percentages of 59.0% and 67.4%, respectively. The pasankalla quinoa exhibits more significant antioxidant activity and a stronger gastroprotective effect compared to the other varieties examined in this study. In conclusion, the hydroalcoholic extracts of the three varieties of C. quinoa sprouts exhibited a gastroprotective effect, and the pasankalla variety at a dose of 500 mg/kg exhibited a stronger protective effect on the gastric mucosa of the rats.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Chemical Composition and Anticancer Activity of Essential Oils from Cyperaceae Species: A Comprehensive Review
by
José Jailson Lima Bezerra, Anderson Angel Vieira Pinheiro and Antônio Fernando Morais de Oliveira
Sci. Pharm. 2025, 93(1), 9; https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm93010009 - 5 Feb 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Cancer is one of the leading causes of mortality worldwide, and the currently available therapies are often associated with severe side effects, including nephrotoxicity, hepatotoxicity, and cardiotoxicity. In this context, essential oils (EOs) have stood out as a less toxic natural alternative, with
[...] Read more.
Cancer is one of the leading causes of mortality worldwide, and the currently available therapies are often associated with severe side effects, including nephrotoxicity, hepatotoxicity, and cardiotoxicity. In this context, essential oils (EOs) have stood out as a less toxic natural alternative, with their anticancer potential widely investigated in in vitro and in vivo studies. The present study aimed to review, for the first time, the chemical composition, anticancer potential, and biological safety of EOs extracted from species of the Cyperaceae family. Research was conducted in different databases, covering publications from the first report on the topic in 1989 to November 2024. This review highlights 33 Cyperaceae species known to produce essential oils, with sesquiterpenes (67%) identified as the predominant compounds. The notable compounds across multiple species include cyperene, cyperotundone, caryophyllene oxide, and mustakone. Regarding the pharmacological potential, the EOs of Cyperus rotundus, Cyperus kyllingia, and Cyperus longus exhibited high cytotoxic activity against the HCT-116, HepG2, MCF-7, HeLa, and NCI-H187 cell lines. The mechanisms of action associated with the anticancer effect of EOs include DNA fragmentation, cell cycle arrest, and induction of apoptosis. Acute toxicity reports indicate that only the EOs of Cyperus articulatus have been evaluated in rodents and deemed biologically safe.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Assessing Safety Concerns in Omeprazole Use: An Observational Study of Potentially Inappropriate Prescriptions and Patient Adherence in a Spanish Community Pharmacy
by
Franc Capdevila Finestres, Daida Alberto Armas, Antoni Miró Manzano, Verónica Hernández García, Yeray Sosa Alonso, Arturo Hardisson de la Torre and Carmen Rubio Armendáriz
Sci. Pharm. 2025, 93(1), 8; https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm93010008 - 4 Feb 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Introduction: Omeprazole is commonly prescribed for conditions associated with excess gastric acid, including gastroesophageal reflux and Helicobacter pylori infection. Spain ranks highest among Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) countries in omeprazole consumption (measured in doses per 1000 inhabitants per day, DHD),
[...] Read more.
Introduction: Omeprazole is commonly prescribed for conditions associated with excess gastric acid, including gastroesophageal reflux and Helicobacter pylori infection. Spain ranks highest among Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) countries in omeprazole consumption (measured in doses per 1000 inhabitants per day, DHD), indicating potential overuse and misuse. Community pharmacists are pivotal in collaborating with healthcare professionals to address safety risks and improve patient outcomes. Objective: This study aims to profile omeprazole users to inform pharmaceutical care (PC) strategies that address patient-specific needs and improve treatment safety. Methods: We conducted an observational, cross-sectional study (CEIm Code FCF-OME-2023-01) involving 100 omeprazole users at a community pharmacy in Barcelona from November 2023 to May 2024. Data were collected via clinical interviews using a Data Collection Questionnaire. Results: Among the omeprazole users, 49% were male, 51% female, and 56% were over the age of 65. A significant proportion (71%) exhibited long-term omeprazole use, and 30% were polymedicated (taking five or more medications). Notably, 52% of patients reported no history of gastric symptoms. Additionally, 22% reported using omeprazole occasionally, following short-term, on-demand treatment regimens, while 78% adhered to a chronic daily dosing schedule. Among these patients, 29.5% demonstrated poor treatment adherence. The analysis of medication-related problems (MRPs) among the 78 patients using omeprazole daily and chronically revealed that the most prevalent MRPs were “unnecessary medication”, “lack of adherence”, “wrong administration”, “drug interactions”, and “lack of knowledge regarding medication use”. Based on STOPP criteria, 45% of users were candidates for deprescribing or dose adjustment. Conclusions: The high incidence of MRPs among omeprazole users highlights the need for enhanced pharmaceutical care (PC). Proactive pharmacist interventions, including deprescribing, dose adjustments, and prescriber collaboration, can reduce adverse medication outcomes and promote safer omeprazole use.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Purified Clinoptilolite-Tuff as a Trap for Amines Associated with Chronic Wounds: Binding of Cadaverine, Putrescine, Histamines and Polyamines
by
Ali El-Kasaby, Christian Nanoff, Stephane Nizet, Cornelius Tschegg and Michael Freissmuth
Sci. Pharm. 2025, 93(1), 7; https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm93010007 - 23 Jan 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Ulcerous lesions can arise in primary skin cancers and upon infiltration of the skin by malignant cells originating from other organs. These malignant fungating wounds are difficult to treat, and they cause pain, itching and malodor. Distressing malodor imposes a major burden on
[...] Read more.
Ulcerous lesions can arise in primary skin cancers and upon infiltration of the skin by malignant cells originating from other organs. These malignant fungating wounds are difficult to treat, and they cause pain, itching and malodor. Distressing malodor imposes a major burden on patients. The carrion odor of decaying tissue is—at least in part—due to the bacterial breakdown products cadaverine and putrescine. Here, we examined the binding of cadaverine, histamine, putrescine, spermidine and spermine to the preparation of micronized purified clinoptilolite-tuff (PCT) by relying on three radiolabeled tracers ([3H]cadaverine, [3H]histamine and [3H]spermidine). Binding was rapid, stable and of high capacity. The binding affinities were in the low µM range. Displacement experiments indicated that the binding sites were non-equivalent. These three properties combined to support effective binding for any given ligand in the presence of the expected, submillimolar concentrations of competing ligands. This was further verified by measuring the binding of [3H]cadaverine in the presence of wound drainage fluids. [3H]Cadaverine was effectively adsorbed by a wound dressing, into which purified clinoptilolite-tuff had been incorporated: the observed binding capacity of this wound dressing was consistent with its content of purified clinoptilolite-tuff. Based on these findings, we propose that purified clinoptilolite-tuff be further investigated as a means to control malodor emanating from chronic wounds.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Targeting c-MYC G-Quadruplexes for Cancer Treatment with Small Molecules
by
Prasanth Thumpati, Sachchida Nand Rai, Chandrabhan Prajapati, Kakarla Ramakrishna and Santosh Kumar Singh
Sci. Pharm. 2025, 93(1), 6; https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm93010006 - 22 Jan 2025
Cited by 4
Abstract
Novel therapies are required due to the rising cancer burden. Conventional chemotherapeutics tend to be particularly toxic, but there is a promising alternative for oncogenes, such as c-MYC. Often overexpressed in many cancer types, the potential c-MYC oncogene seems essential to the development
[...] Read more.
Novel therapies are required due to the rising cancer burden. Conventional chemotherapeutics tend to be particularly toxic, but there is a promising alternative for oncogenes, such as c-MYC. Often overexpressed in many cancer types, the potential c-MYC oncogene seems essential to the development of cancer. Targeting c-MYC protein directly was limited, but these DNA structures composed of guanine-rich sequences suppress c-MYC transcription. This review discusses recent advances in developing small compounds that selectively bind to and stabilize c-MYC G-quadruplexes (G4). These molecules have also shown promise for the inhibition of c-MYC signaling and inhibition of tumor growth, suggesting that G-quadruplex targeting could be a promising therapeutic for cancer.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Recent Advances in Anticancer Strategies, 2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Safety of Oral Administration of 5-Aminolevulinic Acid Phosphate Combined with Ferrous Iron in Healthy Subjects: An Open-Label Trial
by
Fumiko Higashikawa, Hidenori Ito and Tohru Tanaka
Sci. Pharm. 2025, 93(1), 5; https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm93010005 - 20 Jan 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The combination of 5-aminolevulinic acid (5-ALA) phosphate and sodium ferrous citrate (SFC) has been approved as an ingredient in dietary supplements in several countries, owing to its broad applicability in healthcare. This study aimed to assess the safety of oral administration of 5-ALA
[...] Read more.
The combination of 5-aminolevulinic acid (5-ALA) phosphate and sodium ferrous citrate (SFC) has been approved as an ingredient in dietary supplements in several countries, owing to its broad applicability in healthcare. This study aimed to assess the safety of oral administration of 5-ALA and SFC in healthy adults at doses several times higher than those commercially available. This study included 22 healthy subjects (11 males and 11 females) aged 21–59. Doses of 250 mg 5-ALA phosphate and 143.4 mg SFC (15 mg Fe) per day were administered orally for 28 days. Blood tests, urinalysis, and medical interviews were performed to assess safety. No test compound-related adverse events or abnormal changes were observed, except for elevated serum Fe levels, which were mild-to-moderate and transient. In conclusion, the combined oral administration of 5-ALA phosphate and SFC in healthy adults was safe and well-tolerated at the dose and duration investigated in this study.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Anti-Migratory Activity of Brazilin Chemodiversification on Breast Cancer Cells
by
Alberto Hernández-Moreno, Dania A. Nava-Tapia, Miriam D. Zuñiga-Eulogio, Jorge Bello-Martínez, Monserrat Olea-Flores, Tadeo Hernández-Moreno, Mario Ordoñez, Ana E. Zacapala-Gómez, Miguel A. Mendoza-Catalán and Napoleón Navarro-Tito
Sci. Pharm. 2025, 93(1), 4; https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm93010004 - 11 Jan 2025
Abstract
Breast cancer is the most common and the leading cause of cancer death in women worldwide; treating invasive breast carcinomas is challenging due to the side effects of chemotherapeutics. Compounds isolated from natural sources have been proposed as potential molecules for cancer therapy;
[...] Read more.
Breast cancer is the most common and the leading cause of cancer death in women worldwide; treating invasive breast carcinomas is challenging due to the side effects of chemotherapeutics. Compounds isolated from natural sources have been proposed as potential molecules for cancer therapy; for instance, the homoisoflavonoid brazilin has shown pharmacological properties, including anti-tumoral and anti-inflammatory activities. In this study, we isolated brazilin from the heartwood of Haematoxylum brasiletto; then, we performed a semi-synthesis by adding three methyl or acetyl groups to the core structure of brazilin. We confirmed the identity of brazilin and its derivatives by spectroscopic data (1H NMR and 13C NMR) and measured their purity by optical rotation. Then, we analyzed the effects of brazilin and its derivatives in three mammary gland-derived cell lines: the TNBC MDA-MB-231, the ERα(+) MCF7, and the non-tumorigenic MCF10A. We evaluated the cell viability by MTT assays, cell migration by wound-healing assays, and focal adhesion kinase (FAK) activation by Western blot. Regarding biological assays, the MTT assay showed that these compounds showed cytotoxic effects on the MCF7 and MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells at 20 µM but was not toxic in non-tumorigenic MCF10A mammary epithelial cells. Specifically, the greatest effects found from treatment with the compounds were in the MDA-MB-231 cell line, where the IC50 of brazilin was 49.92 μM, and for MCF7, the brazilin-(OAc)3 was 49.97 μM. These effects were dose- and time-dependent, as well as being associated with a decrease in the levels of cell migration and FAK activation.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Antitumor Activity of Natural Products and Related Compounds—2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Development of a Comprehensive Approach to Quality Control of Dermorphin Derivative—Representative of Synthetic Opioid Peptides with Non-Narcotic Type of Analgesia
by
Vasilisa A. Sukhanova, Elena V. Uspenskaya, Safdari Ainaz, Hoang Thi Ngoc Quynh and Aleksey A. Timofeev
Sci. Pharm. 2025, 93(1), 3; https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm93010003 - 31 Dec 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Peptides occupy a significant share of the pharmaceutical market and are among the top-200 selling drugs in the group of non-insulin drugs with analgesic, antibacterial and cardiovascular effects. The aim of this work is to develop a comprehensive analytical approach for quality control
[...] Read more.
Peptides occupy a significant share of the pharmaceutical market and are among the top-200 selling drugs in the group of non-insulin drugs with analgesic, antibacterial and cardiovascular effects. The aim of this work is to develop a comprehensive analytical approach for quality control of novel synthetic peptides with non-narcotic types of analgesia and to provide docking simulations of dermorphin complex formation at the μ-opioid receptor (MOR) binding site. The materials and methods used include the pharmaceutical substance dermorphin tetrapeptide (DMTP) (tyrosyl-D-arginyl-phenylalanyl-glycinamide); Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR); static and dynamic laser light scattering (DLS, LALLS); scanning optical microscopy (SEM); X-ray fluorescence elements analysis; polarimetry for optical activity determining; and Spirotox method for sample biotesting. FT-IR-Spectra indicated specific amino acid chemical groups in the tetrapeptide sequence at 3300–2700 cm−1, 1670 cm−1. UV-absorption spectra of aqueous solutions of dermorphin tetrapeptide showed an absorption maximum at 275 nm, which is in good agreement with the presented spectrum of the bovine serum albumin (BSA) standard; the Pearson’s r of calibration line “A-C%” in 0.0125% to 0.0500% concentration range is 0.999; and the calculated specific extinction value

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Marine Origin vs. Synthesized Compounds: In Silico Screening for a Potential Drug Against SARS-CoV-2
by
Amar Osmanović, Mirsada Salihović, Elma Veljović, Lamija Hindija, Mirha Pazalja, Maja Malenica, Aida Selmanagić and Selma Špirtović-Halilović
Sci. Pharm. 2025, 93(1), 2; https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm93010002 - 26 Dec 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Although COVID-19 is not a pandemic anymore, the virus frequently mutates, resulting in new strains and presenting global public health challenges. The lack of oral antiviral drugs makes it difficult to treat him, which makes the creation of broadly acting antivirals necessary to
[...] Read more.
Although COVID-19 is not a pandemic anymore, the virus frequently mutates, resulting in new strains and presenting global public health challenges. The lack of oral antiviral drugs makes it difficult to treat him, which makes the creation of broadly acting antivirals necessary to fight current and next epidemics of viruses. Using the molecular docking approach, 118 compounds derived from marine organisms and 92 previously synthesized compounds were screened to assess their binding affinity for the main protease and papain-like protease enzymes of SARS-CoV-2. The best candidates from the xanthene, benzoxazole, and coumarin classes were identified. Marine-derived compounds showed slightly better potential as enzyme inhibitors, though the binding affinities of synthesized compounds were similar, with the best candidates displaying affinity values between 0.2 and 0.4 mM. Xanthenes, among both marine origin and synthesized compounds, emerged as the most promising scaffolds for further research as inhibitors. The papain-like protease was found to be more druggable than the main protease. Additionally, all top candidates met the criteria for various drug-likeness properties, indicating good oral bioavailability and low risk of adverse effects. This research provides valuable insights into the comparative affinities of marine origin and synthesized compounds from the xanthene, coumarin, and benzoxazole classes, highlighting promising candidates for further in vitro and in vivo studies.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Colon Cancer: Overview on Improved Therapeutic Potential of Plant-Based Compounds Using Nanotechnology
by
Manuel López-Cabanillas Lomelí, Alexandra Tijerina-Sáenz, David Gilberto García-Hernández, Marcelo Hernández-Salazar, Rogelio Salas García, José Luis González-Llerena, María Julia Verde-Star, Anthonny Cordero-Díaz and Michel Stéphane Heya
Sci. Pharm. 2025, 93(1), 1; https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm93010001 - 24 Dec 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Colon cancer (CC) is the third most frequent neoplasm, with a considerably high mortality rate. Due to the side effects of conventional forms of CC treatment (surgery, chemotherapy, and radiotherapy), several studies have focused on the use of medicinal plant derivatives to provide
[...] Read more.
Colon cancer (CC) is the third most frequent neoplasm, with a considerably high mortality rate. Due to the side effects of conventional forms of CC treatment (surgery, chemotherapy, and radiotherapy), several studies have focused on the use of medicinal plant derivatives to provide a green therapy for CC; although phytochemicals have shown promising results against CC, translating the results obtained in vitro and in vivo to the clinical setting remains a challenge. Indeed, like other orally applied medicines, medicinal plant derivatives have to cross different physiological barriers to reach the CC microenvironment, which considerably limits their dose-dependent therapeutic efficacy. On the other hand, phytocompounds are not free from biopharmaceutical drawbacks, so novel strategies using nanoparticles (NPs) have been proposed to overcome the physiological barriers of the body and provide controlled release of actives of interest. Accordingly, the current review provides an overview and discussion on the predisposing factors to CC and conventional treatment, the use of medicinal plants in CC treatment, and the advantages provided by NPs in the treatment of CC.
Full article

Figure 1

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal MenuJournal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
CIMB, Foods, IJMS, Sci. Pharm., Antioxidants, Nutrients
Nutrients, Food Bioactives, and Functional Foods in Gastrointestinal and Metabolic Disorders
Topic Editors: Samuel Fernández-Tomé, Ortega Moreno LorenaDeadline: 31 May 2025
Topic in
Biomolecules, CIMB, Sci. Pharm., Cancers, Current Oncology, Cells
The Role of Extracellular Vesicles as Modulators of the Tumor Microenvironment
Topic Editors: Nils Ludwig, Miroslaw J SzczepanskiDeadline: 30 June 2025
Topic in
Biomolecules, IJMS, Molecules, Sci. Pharm., Marine Drugs, Plants
Antioxidant Activity of Natural Products—2nd Edition
Topic Editors: José Virgílio Santulhão Pinela, Maria Inês Moreira Figueiredo Dias, Carla Susana Correia Pereira, Alexandra PlácidoDeadline: 30 September 2025
Topic in
Biomedicines, JCM, Molecules, Pharmaceutics, Sci. Pharm., IJMS
Cannabis, Cannabinoids and Its Derivatives
Topic Editors: Melanie Kelly, Christian LehmannDeadline: 31 October 2025

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Sci. Pharm.
Monoclonal Antibodies in the Treatment of Diseases: Focus on Stability, Storage, and Administration
Guest Editor: Stefano RugaDeadline: 31 August 2025







