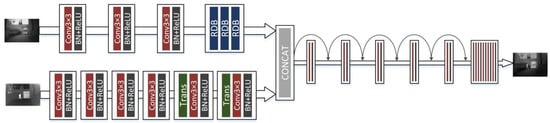
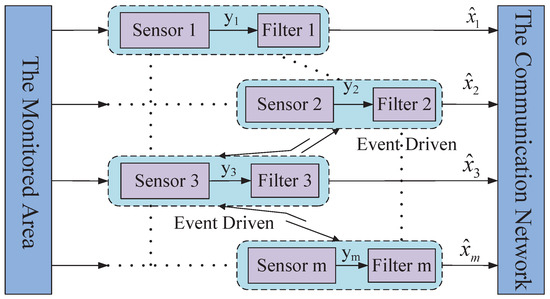
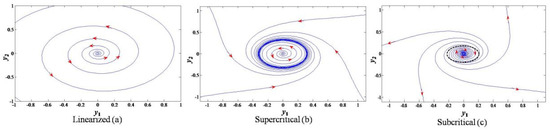
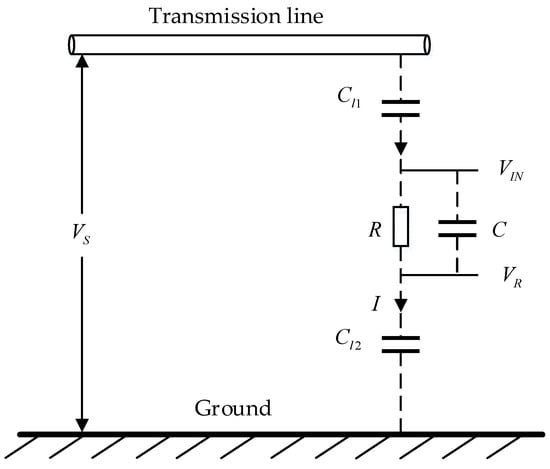
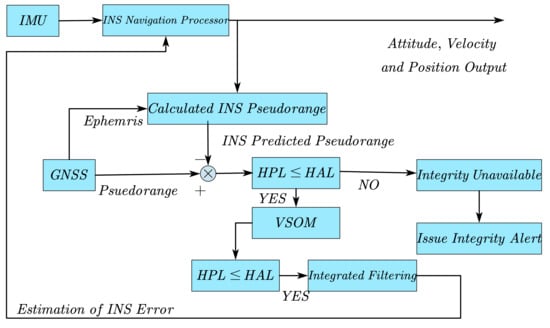
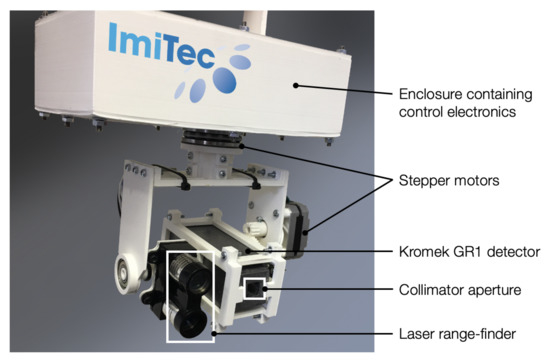
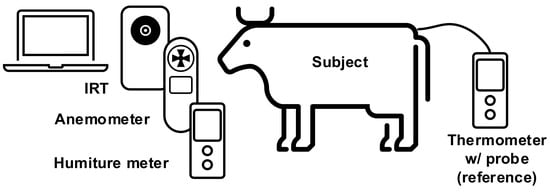
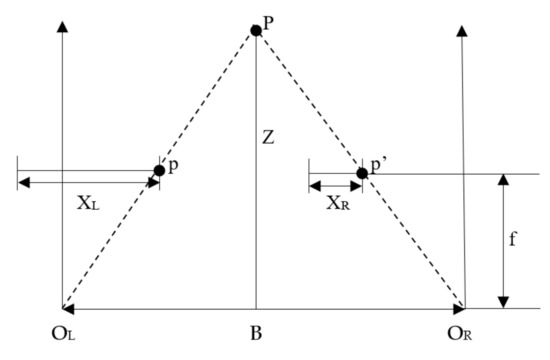
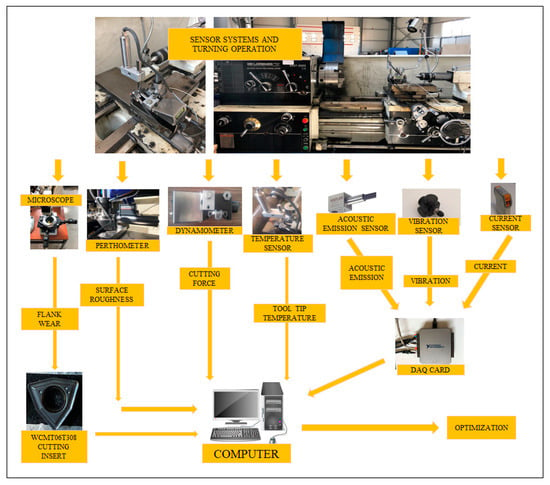
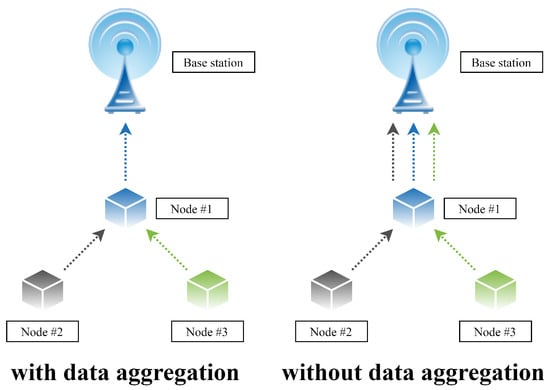
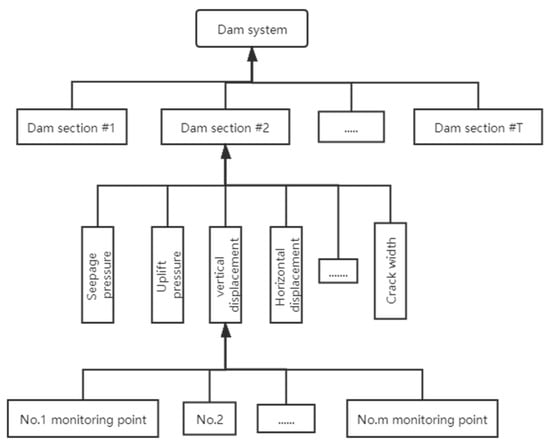
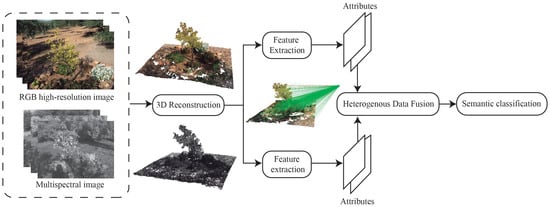
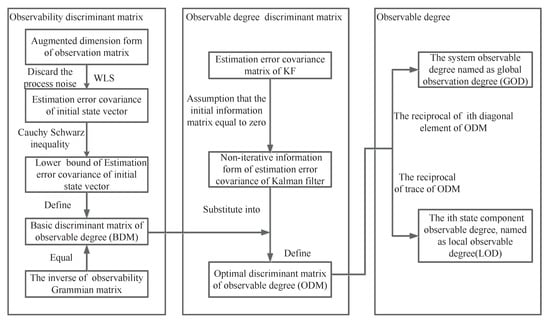
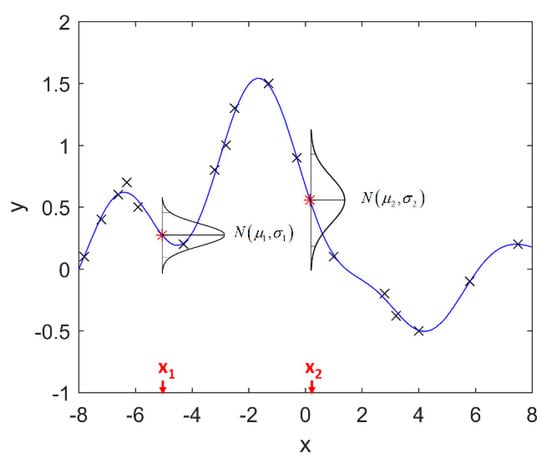
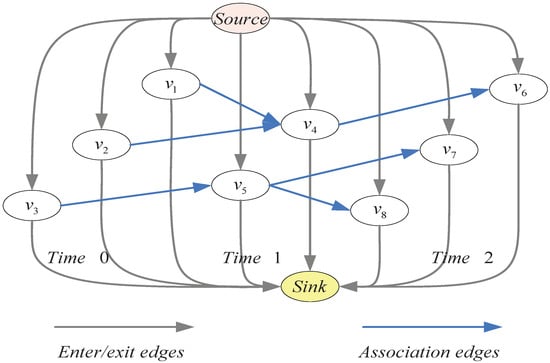
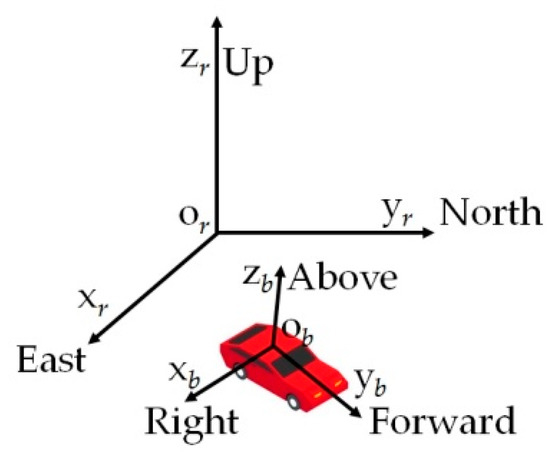
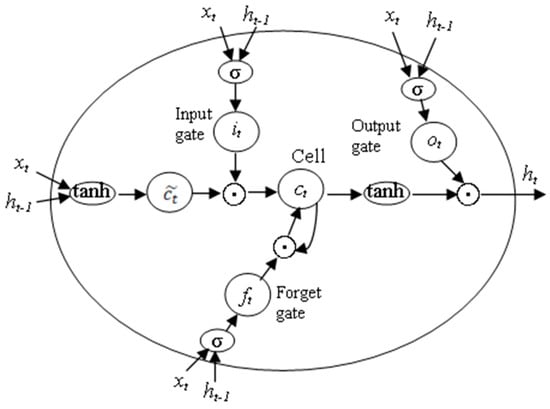
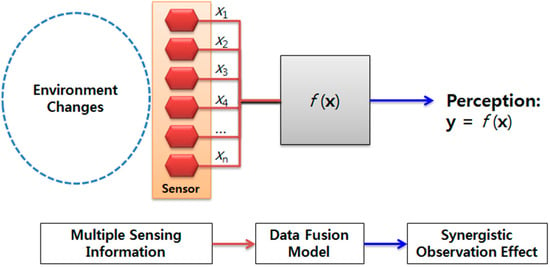
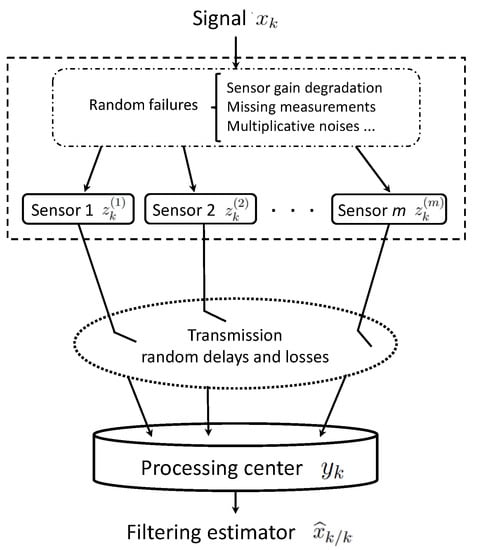
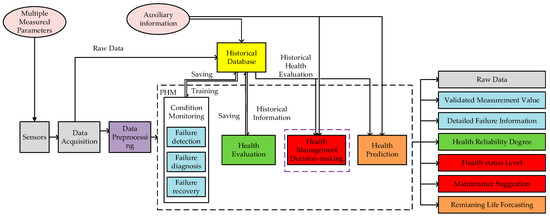
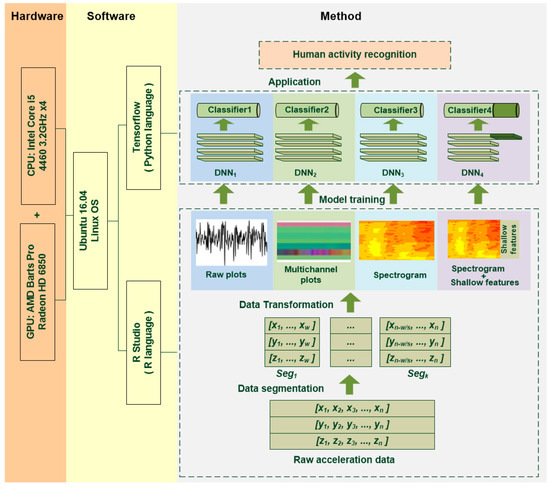
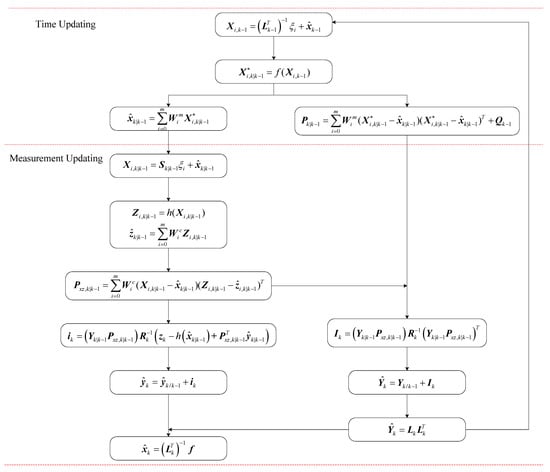
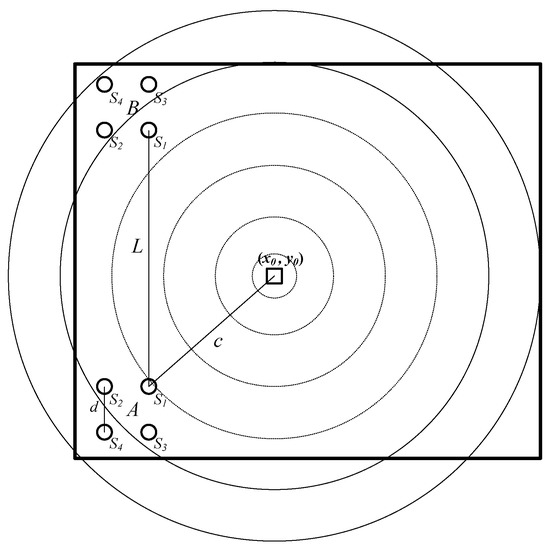
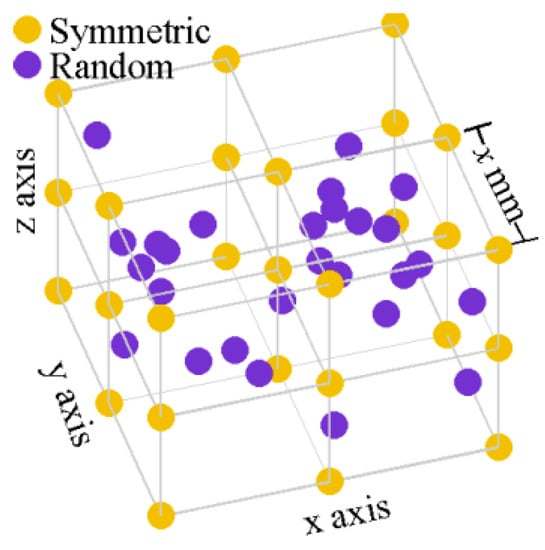
Multi-Sensor Information Fusion
A topical collection in Sensors (ISSN 1424-8220).
Viewed by 333031Editors
Interests: multisensor fusion; statistical signal processing; video/image processing; Bayesian theory; time series analysis; artificial intelligence; target tracking and dynamic analysis
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: information fusion; state estimation; modern time series analysis; system identification
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
Information fusion techniques can integrate a large amount of data and knowledge, representing the same real-world object, and obtain a consistent, accurate and useful representation of that object. These data may be independent or redundant and can be obtained by different sensors at the same time, or at different times. A suitable combination of investigative methods can substantially increase the profit of information in comparison with that from a single sensor.
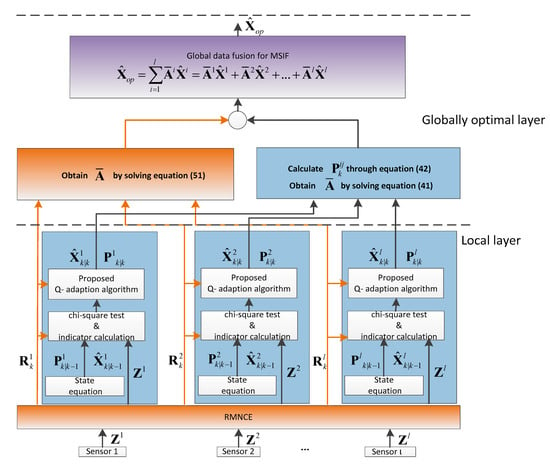
Multi-sensor information fusion has been a key issue in sensor research and has been applied in many fields, such as geospatial information systems, business intelligence, oceanography, discovery science, intelligent transport systems, and wireless sensor networks, etc. Recently, thanks to the vast developments in senor and computer memory technologies, more and more sensors are being used in practical systems and a large amount of measurement data is recorded and restored, which may actually be "time series big data". For example, sensors in machines and process control industries can generate a lot of data, which have real, actionable business value. The fusion of these data can greatly improve productivity through digitization.
The classical multi-sensor information fusion technique can effectively deal with a limited amount of sensor data, and can even obtain optimal results in real time. However, regarding "big series time data", we have to consider how to deal with the mass of sensor data in real-time processes, and how to model the multi-sensor system based on the huge amount of data, etc. The development of sensor systems has created many new challenges in multi-sensor information fusion theory and its application. Therefore, the innovations of information fusion still need to be studiously pursued in future research works.
The goal of this Special Issue is to report on innovative ideas and solutions for the methods of multi-sensor information fusion in the emerging applications era, focusing on development, adoption and applications.
Prof. Xue-Bo JinDr. Yuan Gao
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Sensors is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2600 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- Tracking by the big data from multi-sensor system
- Information (speech or image, etc.) fusion processing
- Knowledge cognitive based on multi-sensor system
- Fusion decision theory
- Fusion estimation and control algorithms
- Modeling by the big data from multi-sensor system
- The structure and/or levels of multi-sensor fusion system
- Uncertain information integration
- Possibility theory and other reasoning methods
- Remote sensing data processing
- The basic theory of the information fusion
- Artificial intelligence (AI) technology for multi-sensor fusion system