Integrated Approaches to Biomass Sustainability
A special issue of Sustainability (ISSN 2071-1050). This special issue belongs to the section "Resources and Sustainable Utilization".
Deadline for manuscript submissions: 31 March 2025 | Viewed by 1378
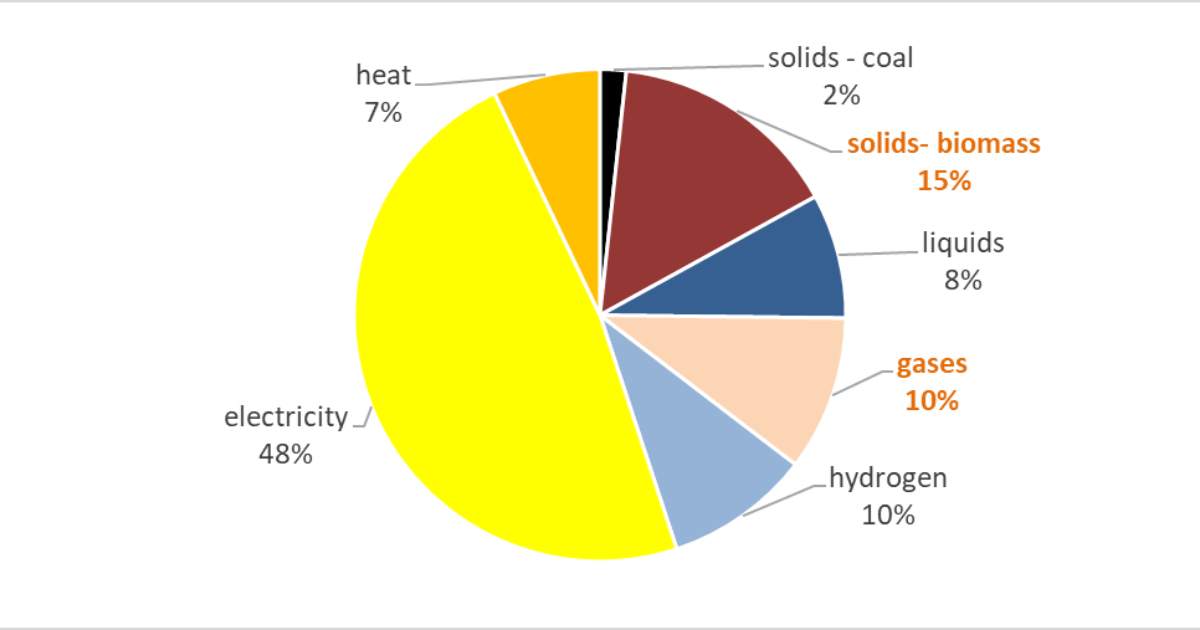
Image courtesy of Source: Based on EU28 Eurostat/LTS 1.5LIFE/TECH scenarios
Special Issue Editor
Interests: biomass; bioeconomy; bioenergy; sustainability; decarbonization; defossilization energy policy; renewables; advanced biofuels; low carbon fuels; gasification; international cooperation
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Special Issue Information
Dear Colleagues,
Global efforts to defossilize the economy are gaining momentum in view of fighting climate change and, in all strategies and policies of OECD countries and the IEA, biomass is considered as one of the main sources to replace fossil fuels up to a certain extent. In the EU, the new policies encompassing the Fit-for-55[1] foresee a significant increase in biomass by 2050 from 6% in 2018 to 15% in 2050.
This implies that new crops have to be developed, marginal and abandoned lands must be put into production, new land management systems such as double cropping must be improved, and more intense forestry operations must be fostered while ensuring the sustainability aspects of biomass production and use in a circular economy.
Traditionally, at the European Biomass and Exhibition Conference, all the above issues are usually addressed in several presentations. At the EUBCE 2023, 5‒8 June in Bologna, several presentations and poster articles are going to be presented on the topic.
The scope of the Special Issue is to provide a solid basis for a clear understanding of the above biomass issues with a special focus on innovative biomass production and use in all type of applications and markets. The Special Issue aims to become a global reference on the state of the art on innovative intergraded approaches to biomass sustainability.
The Guest Editor hopes that this Special Issue will set the foundations of a new chapter on biomass sustainability, laying the fundamentals for increased biomass production in the EU and globally.
[1] https://ec.europa.eu/commission/presscorner/detail/en/IP_21_3541
Dr. Kyriakos Maniatis
Guest Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the special issue website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Sustainability is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2400 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- sustainability
- biomass
- biomass cultivation
- biomass applications
- biomaterials
- biochemicals
- circular economy
- integrated approaches
- life cycle analysis
Benefits of Publishing in a Special Issue
- Ease of navigation: Grouping papers by topic helps scholars navigate broad scope journals more efficiently.
- Greater discoverability: Special Issues support the reach and impact of scientific research. Articles in Special Issues are more discoverable and cited more frequently.
- Expansion of research network: Special Issues facilitate connections among authors, fostering scientific collaborations.
- External promotion: Articles in Special Issues are often promoted through the journal's social media, increasing their visibility.
- e-Book format: Special Issues with more than 10 articles can be published as dedicated e-books, ensuring wide and rapid dissemination.
Further information on MDPI's Special Issue polices can be found here.





