Policies for Sustainable Agricultural Productivity and Efficiency
Share This Topical Collection
Editor
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
Recent times have witnessed an increased frequency and severity of droughts and floods, and increased agricultural and industrial greenhouse gas emissions. These outcomes pose a threat to agriculture production and food security, and the livelihoods of farmers in terms of food security and income. In addition to facing extreme weather and greenhouse gases, farmers have to practice sustainable farming methods to prevent soil degradation. In the face of these challenges, farmers therefore have to be efficient and productive in their farming practices while minimising their impact on ecosystems through sustainable practices. This Special Issue therefore seeks to gain new insights into agricultural efficiency and productivity, and the impact on the environment via sustainable practices with focus on policy implications. Papers selected for this Special Issue shall be subject to a rigorous peer review procedure with the aim of rapid and wide dissemination of research results and applications.
Assoc. Prof. Dr. Boon Lee
Guest Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Sustainability is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript.
The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2400 CHF (Swiss Francs).
Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's
English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- productivity
- efficiency
- sustainability
- food security
- agriculture
Published Papers (15 papers)
Open AccessArticle
Agricultural Service Trade and Green Development: A Perspective Based on China’s Agricultural Total Factor Productivity
by
Xiaocheng Wang, Chenxi Yang and Cuixia Qiao
Cited by 6 | Viewed by 2020
Abstract
Agricultural service trade is closely related to the promotion of the sustainable development of China’s agriculture and is necessary for comprehensive rural revitalization. To clarify the relationship between trade in agricultural services and agricultural green total factor productivity (AGTFP) from a macroscopic perspective
[...] Read more.
Agricultural service trade is closely related to the promotion of the sustainable development of China’s agriculture and is necessary for comprehensive rural revitalization. To clarify the relationship between trade in agricultural services and agricultural green total factor productivity (AGTFP) from a macroscopic perspective and then analyze the acting path and threshold effect, can provide an important reference for improving agriculture’s green level and realizing the sustainable development of agriculture. This paper uses the provincial panel data of China from 2007 to 2022 to measure agricultural green total factor productivity (AGTFP) using the SBM-GML model and explores the impact of agricultural service trade on AGTFP with the help of the fixed effect model, the mediation effect model, and the threshold model. According to this study: (1) Trade in agricultural services can significantly increase AGTFP. (2) Mechanism analysis shows that trade in agricultural services can promote AGTFP through promoting industrial agglomeration, enhancing technological innovation, and improving factor allocation. (3) Heterogeneity analysis shows that trade in agricultural services has a more obvious role in promoting AGTFP in the eastern region and the main grain marketing area. (4) The threshold effect finds that the promotion of agricultural services trade on AGTFP will gradually increase as the level of government support rises. Therefore, China should actively promote the development of agricultural service trade, implement the concept of sustainable development, improve the level of government support, and promote the improvement in agricultural total factor productivity and sustainable development.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Research on Coupling Coordination of Agricultural Carbon Emission Efficiency and Food Security in Hebei Province, China
by
Yongqiang Cao, Xinhui Ji, Jiaqi Yao, Nan Xu, Min Chen, Xueting Yang, Zihua Liu, Zhonghong Li and Fan Mo
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 1768
Abstract
The delineation and measurement of carbon emissions in agricultural production systems constitute a complex issue involving multiple factors. Previous research in this area has been limited in terms of comprehensive carbon emission assessment throughout the agricultural production process and systematic measurement. This study
[...] Read more.
The delineation and measurement of carbon emissions in agricultural production systems constitute a complex issue involving multiple factors. Previous research in this area has been limited in terms of comprehensive carbon emission assessment throughout the agricultural production process and systematic measurement. This study focuses on both dynamic and static aspects, systematically analyzing the agricultural carbon emissions and emission efficiency in Hebei Province from 2000 to 2020. It comprehensively explores the influencing factors of carbon emissions and delves into the relationship between agricultural carbon emission efficiency and food security. The experimental results revealed the following: (1) From 2000 to 2020, the agricultural carbon emissions in Hebei Province exhibited a fluctuating downward trend, with a spatial distribution pattern where they were high in the south and low in the north. And the carbon emissions caused by chemical fertilizers and plowed land accounted for 42.6% of the total. (2) The efficiency of agricultural carbon emissions in the static dimension fluctuated at a rate of 0.0265, whereas the ML index fluctuated less in the dynamic dimension, and the agricultural industrial structure had the most significant impact. (3) The coupling coordination degree of food security and agricultural carbon emission efficiency increases with time, and “coordination” gradually dominates in spatial change. The conclusions of this study are of great significance in stabilizing grain production and achieving low-carbon production in the Hebei Province.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Ecological–Economical and Ethno-Cultural Determinants of the Development of Organic Farming in Kazakhstan
by
Sergey V. Pashkov, Eduard Z. Imashev, Gaukhar K. Baubekova, Kulyash D. Kaimuldinova, Yerkin A. Tokpanov, Gulshat Z. Nurgaliyeva, Gaini K. Baimukasheva, Rabiga N. Kenzhebay, Soltanbek K. Kassenov and Pavel A. Ukrainskiy
Cited by 4 | Viewed by 4771
Abstract
In the context of the transition to sustainable agriculture in Kazakhstan, the article considers one of its forms—organic farming. The adopted laws and by-laws not only have not contributed to but have also significantly hindered the development of organic farming due to the
[...] Read more.
In the context of the transition to sustainable agriculture in Kazakhstan, the article considers one of its forms—organic farming. The adopted laws and by-laws not only have not contributed to but have also significantly hindered the development of organic farming due to the complexity of their implementation in the Kazakh legal field. The activities of Kazakhstani public organizations, deprived of any state support, are symbolic in nature. The absolute instability of organic production, the multidirectional long-term dynamics of the area of organic land and the cost yield of the products are demonstrated. The lack of demand for organic farming products among the population of Kazakhstan is due to socio-economic determinants, the dominance of livestock products in the nutrition structure of the indigenous population, only a small part of the inhabitants of megacities being the main consumers of any organic products, the exorbitant share of food costs and the high premium of organic products. The reasons for the ecological and economic instability of organic farming are the extensive development model, the lack of subsidiary obligations of the state and the zero-marginal cost of the export product. Conservative, utilitarian and innovative ways of developing organic farming are proposed.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
The Impact of Technological Innovation on Agricultural Green Total Factor Productivity: The Mediating Role of Environmental Regulation in China
by
Lihuan Huang and Ying Ping
Cited by 8 | Viewed by 2594
Abstract
This study delves into the effects of agricultural technological innovation on agricultural green total factor productivity (AGTFP) and the intermediating role of environmental regulation (ER) in 30 Chinese provinces from 2010 to 2021. Employing mediation analysis methods such as the three-step approach, Sobel–Goodman
[...] Read more.
This study delves into the effects of agricultural technological innovation on agricultural green total factor productivity (AGTFP) and the intermediating role of environmental regulation (ER) in 30 Chinese provinces from 2010 to 2021. Employing mediation analysis methods such as the three-step approach, Sobel–Goodman test, and Bootstrap methods, the findings are robust: technological innovation significantly enhances AGTFP, as evidenced by a 1% level significant coefficient of 0.030. Additionally, ER acts as a potent mediator, where its inclusion as an independent variable alongside agricultural technological innovation (AST) boosts the coefficient to 0.031, further confirming its synergistic effect on AGTFP. These data points underline the importance of innovation in agricultural sustainability and the reinforcing role of environmental regulation. Consequently, this study advocates for intensified agricultural innovation support, tailored environmental regulation policies, augmented environmental education, and a meticulous evaluation system for environmental legislation to foster sustainable agricultural practices.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Perception of Public Policies and Sustainability among Agricultural Producers in the Municipality of Guasave
by
Aldo Alan Cuadras-Berrelleza, Héctor José Peinado-Guevara, Esteban Otoniel Moreno-López, Lizbeth Beltrán-Lúgo and Víctor Manuel Peinado-Guevara
Cited by 1 | Viewed by 1838
Abstract
The agricultural sector of Sinaloa is one of the most representative in Mexico. Its economic and social contributions are of great magnitude, as is its scale of production and the social impacts it generates. The objective was to study the perception of maize
[...] Read more.
The agricultural sector of Sinaloa is one of the most representative in Mexico. Its economic and social contributions are of great magnitude, as is its scale of production and the social impacts it generates. The objective was to study the perception of maize farmers in the municipality of Guasave on agricultural public policies and their impact on sustainable results in the sector. The methodology was quantitative-descriptive and cross-sectional. A sample of 260 farmers was analysed out of a study population of 18,650, to whom a survey was applied using the Likert scale. The internal consistency of the instrument was validated using the McDonald omega test, giving a (ω) of 0.868, considered reliable. Kendall’s Tau-c was used to find the relationship between the category and its respective subcategories. The results showed statistically significant correlations (Sig < 5%) that were greater than 0.7, so it was considered that the category “Public policies and sustainable development” showed a strong correlation with the subcategories “Governance and agricultural sustainability” and “Public policies in agriculture”. The results indicate that there is a need for greater attention to public policies, from their design to implementation. Agricultural activity has had a negative impact on a sustainable environment due to the current production methods. It is considered that to achieve significant progress in this sector, studies are needed to help detect and correct these problems and encourage greater participation of the actors in the sector in their work through training and the dissemination of sustainable practices.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Research on Spatial-Temporal Characteristics and Affecting Factors of Agricultural Green Total Factor Productivity in Jiangxi Province
by
Zhen Wang, Jiayi Zhu, Xieqihua Liu, Dongdong Ge and Bin Liu
Cited by 9 | Viewed by 2162
Abstract
Increasing green total factor productivity is the key to achieving green development in agriculture. This study measured the green total factor productivity of Jiangxi’s agriculture, and its regional and temporal evolution characteristics were examined. The fixed-effects model was then used to investigate the
[...] Read more.
Increasing green total factor productivity is the key to achieving green development in agriculture. This study measured the green total factor productivity of Jiangxi’s agriculture, and its regional and temporal evolution characteristics were examined. The fixed-effects model was then used to investigate the model’s fundamental components empirically. The study’s findings reveal the following: During the period under review, technical change was the primary element driving the rise in the green total factor productivity of agriculture. A rising “U”-shaped trend with notable regional variances characterizes the spatial and temporal evolution. The primary factors that affect changes in green total factor productivity in agriculture include the ease of transportation, the per capita disposable income of rural residents, the level of agricultural mechanization, the degree of urbanization, the level of financial support for agriculture, and the percentage of workers in secondary industries, with the impact effect values of 0.581, 0.647, −0.126, −0.729, −0.326, and −0.559, respectively. As a result, it is suggested that in order to substantially increase agricultural green total factor productivity, agricultural green technological support should be strengthened, more fully developed, and promoted in a multi-pronged approach.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Rural Population Aging, Capital Deepening, and Agricultural Labor Productivity
by
Danhong Shen, Haimeng Liang and Wangfang Shi
Cited by 17 | Viewed by 3436
Abstract
Whether the aging of rural population will affect the high-quality development of China’s agriculture is an important issue facing the construction of China’s characteristic modern agriculture. Using panel data from 30 provinces in China from 1999 to 2020, this paper used fixed effects
[...] Read more.
Whether the aging of rural population will affect the high-quality development of China’s agriculture is an important issue facing the construction of China’s characteristic modern agriculture. Using panel data from 30 provinces in China from 1999 to 2020, this paper used fixed effects models and mediation models for econometric regressions to explore the relationship between rural population aging and agricultural development, as well as the intermediate mechanisms involved. The study found that there was a positive relationship between rural population aging and agricultural labor productivity, and aging can stimulate agricultural development. Mechanism analysis revealed that rural population aging can promote the adjustment of the structure of agricultural factors, drive the deepening accumulation of capital and other factors, promote the modernization of agricultural production methods, and ultimately achieve an increase in agricultural labor productivity. Further examination showed that the positive relationship between rural population aging and agricultural productivity gradually weakened as the degree of rural population aging deepened. The study provides empirical evidence for sustainable agricultural development in the context of population aging.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
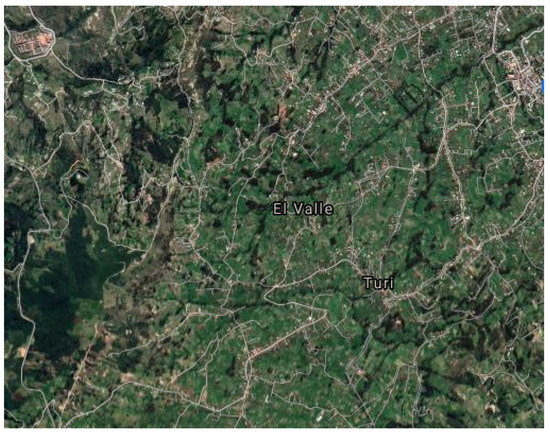
Popular and Solidarity Economy: Policies and Realities in the Local Context—The Case of the Agricultural Productive Associations of El Valle, Ecuador
by
Gliceria Gómez-Ceballos, Juan Pablo Vázquez-Loaiza, Dora Priscilla Herrera-Torres and Ana Julia Vega-Luna
Cited by 6 | Viewed by 4390
Abstract
The popular and solidarity economy (EPS) emerges as an alternative approach to poverty aligned with the principles of sustainable development; in this sense, some countries in the region have adopted policies for its growth and development, among them Ecuador. The experience of a
[...] Read more.
The popular and solidarity economy (EPS) emerges as an alternative approach to poverty aligned with the principles of sustainable development; in this sense, some countries in the region have adopted policies for its growth and development, among them Ecuador. The experience of a rural community was shown; the objective of the study was to identify the factors that hinder the achievement of better efficiency indexes, regarding the implementation of policies at the local level, with respect to rural productive associations. The case of the agricultural productive associations located in the parish of El Valle, Cuenca, Ecuador, was studied. The type of research was mixed: quantitative to support the information extracted from the instruments applied and derive the pertinent analysis and qualitative to collect primary information from the actors involved in the study. We used the action research model through the use of surveys, interviews and focus groups. The key contribution of this work was to making visible and understanding the needs of the rural communities of the sector from their development perspectives, respecting their ancestral knowledge and articulating from the academy the private–public action for the generation of policies for governance, effective application of democracy and promotion of the technical and associative potential of the agroecological productive units. The results show regularities in terms of their socioeconomic situation, their mode of action and the impact caused on their productive dynamics by the atomized decisions of local actors in the exercise of governance. These fail to articulate the implementation of policies at the territorial level to the detriment of their effectiveness and efficiency and, therefore, do not bring about substantial changes in their levels of dependence and dynamics of productive activity—diagnostic components that will be used for the formulation of joint multilevel policies.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
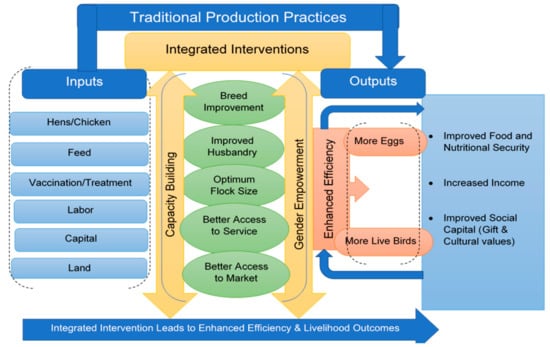
Technical Efficiency of Traditional Village Chicken Production in Africa: Entry Points for Sustainable Transformation and Improved Livelihood
by
Mulugeta Y. Birhanu, Tesfahun Alemayehu, Jasmine E. Bruno, Fasil Getachew Kebede, Emmanuel Babafunso Sonaiya, Ezekiel H. Goromela, Oladeji Bamidele and Tadelle Dessie
Cited by 25 | Viewed by 5193
Abstract
Increasing poultry product consumption trends have attracted researchers and development practitioners to look for interventions that transform the low-input low-output-based village chicken production to a high yielding production system. However, due to the intricate nature of the production system, there is a dearth
[...] Read more.
Increasing poultry product consumption trends have attracted researchers and development practitioners to look for interventions that transform the low-input low-output-based village chicken production to a high yielding production system. However, due to the intricate nature of the production system, there is a dearth of evidence that helps design comprehensive interventions at the smallholder level. Using national-level representative data collected from 3555 village chicken producers in Ethiopia, Nigeria, and Tanzania, this study examines the technical efficiency of village chicken production and investigates the main factors that explain the level of inefficiency. We applied a stochastic frontier analysis to simultaneously quantify the level of technical efficiency and identify factors associated with heterogeneity in inefficiency. We found that the level of technical efficiency is extremely low in the three countries, suggesting enormous opportunities to enhance productivity using available resources. The heterogeneity in technical efficiency is strongly associated with producers’ experience in breed improvements and flock management, limited technical knowledge and skills, limited access to institutions and markets, smaller flock size, gender disparities, and household livelihood orientation. We argue the need to adopt an integrated approach to enhance village producers’ productivity and transform the traditional subsistence-based production system into a commercially oriented semi-intensive production system.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
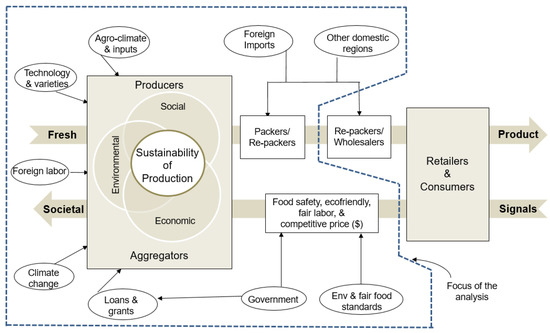
Technology, Policy, and Market Adaptation Mechanisms for Sustainable Fresh Produce Industry: The Case of Tomato Production in Florida, USA
by
Saoli Chanda, Mahadev Bhat, Kateel G. Shetty and Krishnaswamy Jayachandran
Cited by 21 | Viewed by 8204
Abstract
Tomato (
Solanum lycopersicum L.) is an important vegetable crop in Florida, a state located in the south-eastern region of the United States. The state is the second largest producer of tomatoes in the country and contributes to almost 90% of the domestic
[...] Read more.
Tomato (
Solanum lycopersicum L.) is an important vegetable crop in Florida, a state located in the south-eastern region of the United States. The state is the second largest producer of tomatoes in the country and contributes to almost 90% of the domestic winter tomato supplies. However, tomato farmers in Florida have come under increasing pressure due to climate changes, foreign imports, and rising production costs. The purpose of this paper is to analyze whether Florida tomato growers will continue to sustain their production given the seasonal and geographic production advantage, yet against various internal and external threats emerging throughout the fresh produce supply chain. We developed our study on a multi-disciplinary conceptual model of network (supply chain) relationship and primary and secondary data gathered from various stakeholders and the literature. We found that Florida farmers have done remarkably well by adapting to warming temperatures and changing consumer expectations about environmental sustainability and responsible labor practices. However, foreign competition, labor shortage, the rising costs of inputs, extreme weather events (hurricanes), and pests and diseases due to humid climate continue to affect the sustainability of the Florida tomato production. Our paper suggests various farm-, market-, and institution-level adaptation mechanisms for preventing the regional production advantage of the Florida tomato industry from eroding. Newer immigration laws are necessary for easing the labor situation. In order to have a level playing field with respect to the use of protected agriculture technology such as in Mexico and Canada, U.S. farmers in general and Florida farmers in particular need government support. Florida farmers need to diversify their fresh produce market strategies, finding new product streams. There is also a need for reforming the product certification landscape, which some growers find cumbersome and cost prohibitive. Growers may gain from being better able to convey to consumers the information regarding their effort put into environmental sustainability, workers welfare, and safe food.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
The Role of Technical Efficiency Achieving Sustainable Development: A Dynamic Analysis of Norwegian Dairy Farms
by
Habtamu Alem
Cited by 19 | Viewed by 3681
Abstract
Growing environmental concerns have prompted governments to make sustainable choices in agricultural resource use. Evaluating the sustainability of agricultural systems is a key issue for the implementation of policies and practices aimed at revealing sustainability. This study aimed to evaluate the performance of
[...] Read more.
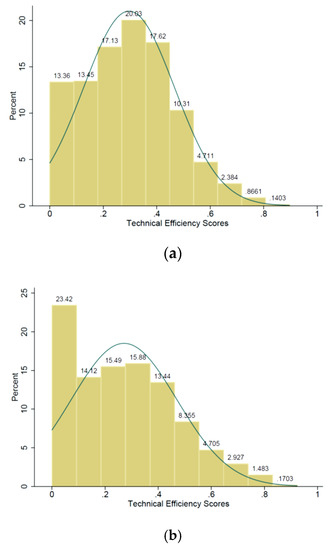
Growing environmental concerns have prompted governments to make sustainable choices in agricultural resource use. Evaluating the sustainability of agricultural systems is a key issue for the implementation of policies and practices aimed at revealing sustainability. This study aimed to evaluate the performance of Norwegian dairy farms, accounting for marginal effects of environmental (exogenous) variables. We adopted the dynamic parametric approach within the input distance function framework to estimate the performance of Norwegian dairy farms, focusing on the technical efficiency and determinates. For comparison, we also estimated the static parametric model, which was used by previous studies. We used unbalanced farm-level panel data for the period 2000–2018. The result shows a mean technical efficiency score of 0.92 for the dynamic model and 0.87 for the static models. The empirical result shows that the previous studies that focused on the static model reported a biased result on the performance of dairy farms. The dynamic efficiency score suggests that Norwegian dairy farms can reduce the input requirement of producing the average output by 8% if the operation becomes technically efficient. The environmental variables have a different effect on the performance of the farmers; thus, policymakers need to place special focus on these variables for the sustainable development of the dairy sector.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Irrigation, Technical Efficiency, and Farm Size: The Case of Brazil
by
Gabriel A. Sampaio Morais, Felipe F. Silva, Carlos Otávio de Freitas and Marcelo José Braga
Cited by 21 | Viewed by 5183
Abstract
In developing countries, irrigation can help to decrease poverty in rural areas through increased employment in the agricultural sector. Evidence shows that irrigation may increase farm productivity and technical efficiency. In this paper, we estimate the effect of irrigation on farm technical efficiency
[...] Read more.
In developing countries, irrigation can help to decrease poverty in rural areas through increased employment in the agricultural sector. Evidence shows that irrigation may increase farm productivity and technical efficiency. In this paper, we estimate the effect of irrigation on farm technical efficiency in Brazil using the 2006 Agricultural Census dataset on more than 4 million farms. We estimate a stochastic production frontier at farm level, considering potential selection bias in irrigation adoption. We find that farms using irrigation are on average 2.51% more technically efficient compared to rain-fed farms. Our findings also suggest that while small farms are more efficient than medium and large farms, the largest difference in technical efficiency between rain-fed and irrigated farms is among large farms. Our results indicate that policies that seek to support expansion of irrigation adoption has also the potential to achieve greater rural development given the estimated effects estimated in this paper among very small and small farms, which are more than 70% of the farms in Brazil.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Sustainability of Agricultural Crop Policies in Rwanda: An Integrated Cost–Benefit Analysis
by
Mikhail Miklyaev, Glenn Jenkins and David Shobowale
Cited by 14 | Viewed by 5756
Abstract
Rwanda has aimed to achieve food self-sufficiency but faces binding land and budgetary constraints. A set of government policies have been in force for 20 years that have controlled the major cropping decisions of farmers. A cost–benefit analysis methodology is employed to evaluate
[...] Read more.
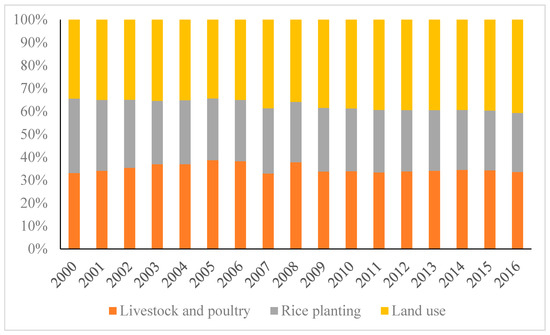
Rwanda has aimed to achieve food self-sufficiency but faces binding land and budgetary constraints. A set of government policies have been in force for 20 years that have controlled the major cropping decisions of farmers. A cost–benefit analysis methodology is employed to evaluate the financial and resource flow statements of the key stakeholders. The object of the analysis is to determine the sustainability of the prevailing agricultural policies from the perspectives of the farmers, the economy, and the government budget. A total of seven crops were evaluated. In all provinces, one or more of the crops were either not sustainable from the financial perspective of the farmers or are economically inefficient in the use of Rwanda’s scarce resources. The annual fiscal cost to the government of supporting the sector is substantial but overall viewed to be sustainable. A major refocusing is needed of agricultural policies, away from a monocropping strategy to one that allows the farmers to adapt to local circumstances. A more market-oriented approach is needed if the government wishes to achieve its economic development goal of having a sustainable agricultural sector that supports the policy goal of achieving food self-sufficiency.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Analysis of Environmental Policy and the Performance of Sustainable Agricultural Development in China
by
Guofeng Wang, Ziyu Qian and Xiangzheng Deng
Cited by 7 | Viewed by 3207
Abstract
A community with a shared future for mankind embodies the concept of sustainable development. This is also China’s contribution to global governance. Some of the Sustainable Development Goals (such as the elimination of hunger and malnutrition) require countries to implement people-centered overall agricultural
[...] Read more.
A community with a shared future for mankind embodies the concept of sustainable development. This is also China’s contribution to global governance. Some of the Sustainable Development Goals (such as the elimination of hunger and malnutrition) require countries to implement people-centered overall agricultural transformations, and achieving such agricultural transformations is key to ensuring sustainable agricultural development and shifting agriculture toward a greener and more ecological direction. This paper uses the SBM Directional Distance Function and Malmquist Productivity Index with calculated data from 2000 to 2016. The results show that, since 2000, China’s environmental performance index growth has been slow, with an average annual growth rate of only 0.80%. This growth has gone through three phases: a stable up and down phase, a volatility decrease phase, and a volatility increase phase. In general, agricultural technological advances have played a more visible role in promoting a strong performance in reducing carbon emissions. Agriculture in China is also on the way to becoming more sustainable and green.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Effects of Agricultural Cooperative Society on Farmers’ Technical Efficiency: Evidence from Stochastic Frontier Analysis
by
Ruopin Qu, Yongchang Wu, Jing Chen, Glyn D. Jones, Wenjing Li, Shan Jin, Qian Chang, Yiying Cao, Guijun Yang, Zhenhong Li and Lynn J. Frewer
Cited by 28 | Viewed by 7865
Abstract
The impact of agricultural cooperatives on apple farmers’ technical efficiency (TE) in China was examined. The cooperatives were divided into two groups: a collective marketing group for farmers and an equivalent non-marketing group that did not provide a marketing service, although other functions
[...] Read more.
The impact of agricultural cooperatives on apple farmers’ technical efficiency (TE) in China was examined. The cooperatives were divided into two groups: a collective marketing group for farmers and an equivalent non-marketing group that did not provide a marketing service, although other functions remained the same. Using the propensity score matching (PSM) procedure and stochastic production frontier (SPF) modelling, cooperatives’ key functions that potentially increase farmers’ TE can be identified. The results indicate that membership of either group is positively related to yield. However, cooperatives that were not engaged in marketing achieved higher TE than non-members. This suggests that policy makers should encourage cooperatives to focus on activities that do not include direct marketing to increase TE in apple production in China.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures