Industrial Symbiosis and Sustainability
A topical collection in Sustainability (ISSN 2071-1050). This collection belongs to the section "Social Ecology and Sustainability".
Viewed by 104167Editors
Interests: supply chain; sustainability; circular economy; industrial symbiosis; eco-innovation
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
2. Department of Management, Economics and Industrial Engineering, Politecnico di Milano, Piazza L. Da Vinci 32, 20133 Milano, Italy
Interests: environment; sustainability; environmental impact assessment; sustainable development; environmental analysis; climate change; environmental management; energy; renewable energy; environmental studies; biofuel production; life cycle assessment; biofuels; sustainable consumption and production; life cycle thinking; waste; LCA; bioenergy; biogas; biodiesel; industrial ecology; cleaner production; ethanol; industrial symbiosis; sustainable development goals
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: industrial engineering; industrial symbiosis; energy management; sustainability; circular economy; additive manufacturing; lean manufacturing; quality management systems; sustainable energy systems
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
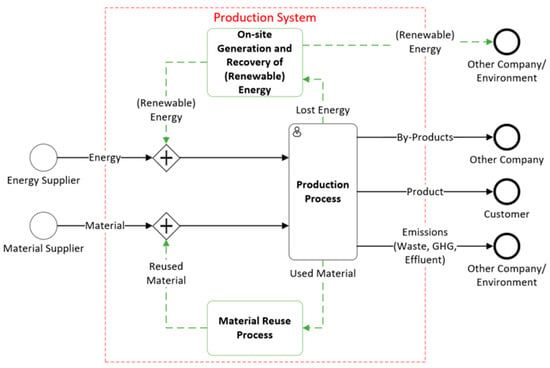
In the current economic and political environment, proper waste management systems are an unconditional priority, and challenge, for both private and public sectors. The research topic of industrial symbiosis seeks to address these concerns by improving the exchanges of resources between industries, where the waste of one company may be useful for others. When it comes to facing these challenges, industrial symbiosis allows for the reuse of materials that otherwise could have been wasted, and it prevents them from being misused or discarded altogether.
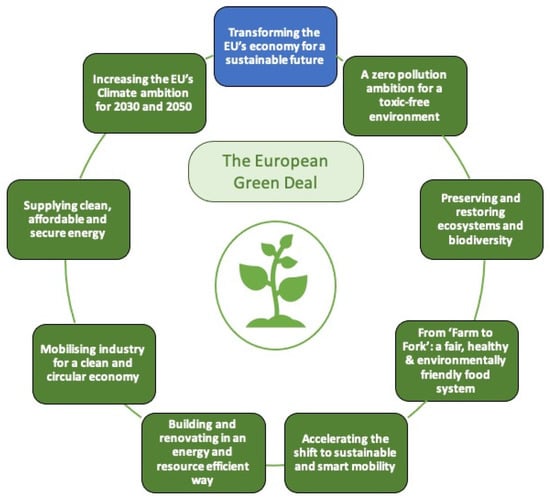
Industrial symbiosis has generally been associated with primarily industries. However, other types of sectors, such as research and academia, governments, and municipal and associated systems (agriculture, forestry, etc.) can also become involved in symbiotic exchanges of material, energy, and knowledge. These exchanges can result in numerous environmental and economic benefits among different entities to bring collective benefits. Interwoven with the concept of circular economy, industrial ecology, and eco-industrial parks, industrial symbiosis is considered to be a groundbreaking method that could decrease resource waste and is a key element for circular economy realization.
This Special Issue intends to deepen the knowledge of industrial symbiosis and its implications for sustainability, one of the main concepts in the circular economy and industrial ecology. The potential benefits that industrial symbiosis can bring are diverse; therefore, contributions from different research areas are welcome. Researchers are encouraged to submit contributions that touch on several aspects of industrial symbiosis and its relationship to several contiguous topics.
Dr. Helena Carvalho
Dr. Michael Martin
Dr. Radu Godina
Guest Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 250 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for assessment.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Sustainability is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2400 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- Industrial symbiosis
- Eco-industrial parks
- Urban industrial symbiosis
- Industrial ecology
- Management of industrial waste and materials
- Industrial symbiosis policies
- Recycling, reuse, regeneration, and recovery of waste in industry
- Resource sharing
- Eco-industrial development
- Inter-firm cooperation
- Sustainable production.