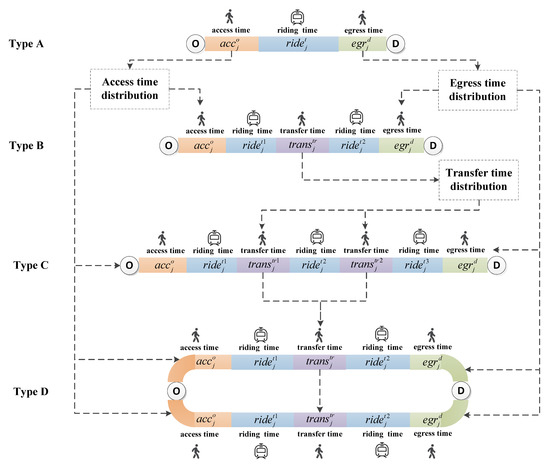
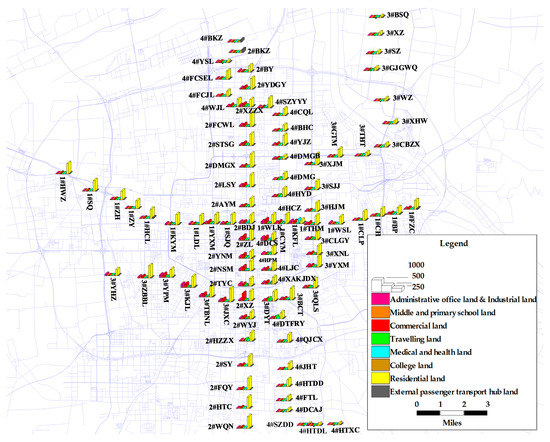
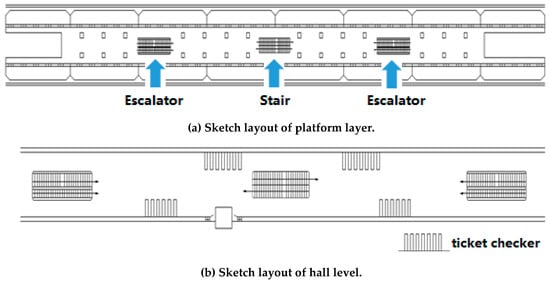
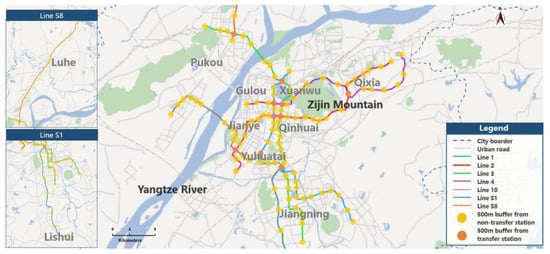
Sustainable Rail and Metro Systems (Closed)
A topical collection in Sustainability (ISSN 2071-1050). This collection belongs to the section "Sustainable Transportation".
Viewed by 110928Editors
Interests: transportation planning; transportation network design; simulation of transport systems; mass transit systems; rail transportation; energy-saving strategies; pricing policy analysis
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: transport system analysis and management; smart and sustainable mobility; cooperative driving; rail and metro systems; energy-saving applications; travel demand estimation; passenger behavior simulation
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
According to the recent data released by the European Commission, in 2016, the transport sector contributed 27% of the total greenhouse gas emissions, and road transport accounted for 72% of that. Likewise, in terms of energy consumption, the transport sector covers a share of 33%, within which road transport demand represents 73%. In this scenario, the adoption of measures to promote sustainable transportation systems and, jointly, reduce vehicular (cars and trucks) flows on the road system could significantly abate the sector’s externalities. Hence, the implementation of policies to improve the use of rail and metro systems could help to increase the sustainability features of the transport sector.
In light of the above, this Special Issue calls for reviews and original research articles related to the main aspects concerning, but not limited to, the promotion, analysis, and optimization of rail and metro systems in a sustainable perspective by investigating theoretical, methodological, energetical, operational, implemental, and technological aspects.
Prof. Dr. Luca D’Acierno
Dr. Marilisa Botte
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. All papers will be peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Sustainability is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 1800 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- Public transport planning and management
- Network hierarchization of local public transport systems
- Sustainable rail-based mobility
- Freight rail-based transport
- Footprint analysis of rail and metro systems
- Advanced simulation models and methods for rail and metro systems
- Railway traffic optimization, control, and management
- Energy-saving, energy-recovery, and energy-efficient strategies and technologies
- Artificial neural network adoption
- Data-driven approaches
- Advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) in the rail and metro contexts
- Advanced traveler information systems (ATIS) in the rail and metro contexts
- Mobility as a service (MaaS) and related implications on rail and metro systems
- Innovative propulsion systems for rail and metro systems
- Sustainable improvements of tractive power systems based on fossil fuels
- Effects of pantograph–catenary dynamics on rail system performance
- Effects of wheel–rail contact on rail system performance